A Cross-modal Person Re-identification Method Based on Hybrid Channel Augmentation with Structured Dual Attention
-
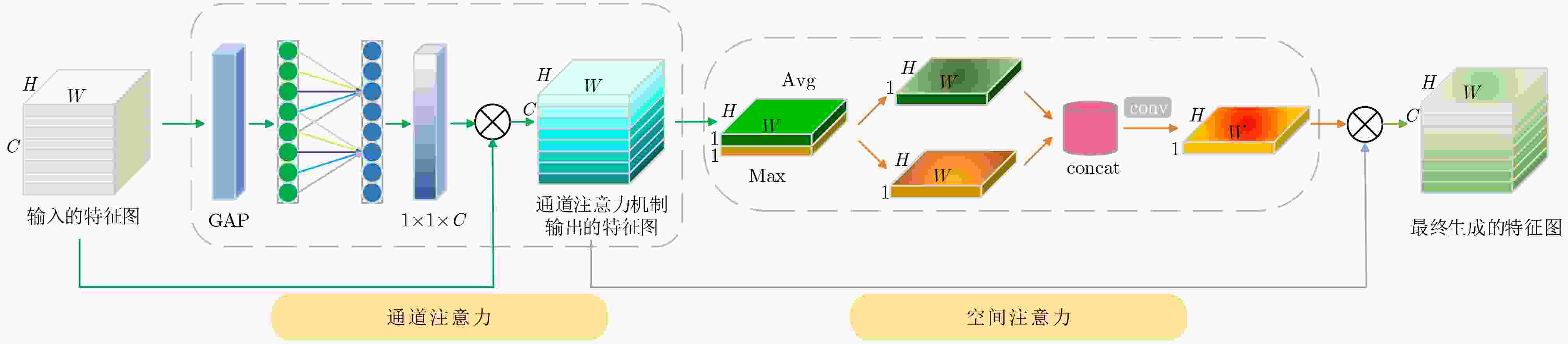
摘要: 在目前跨模态行人重识别技术的研究中,大部分现有的方法会通过单模态原始可见光图像或者对抗生成图像的局部共享特征来降低跨模态差异,导致在红外图像判别中由于底层特征信息丢失而缺乏稳定的识别准确率。为了解决该问题,该文提出一种结构化双注意力可交换混合随机通道增强的特征融合跨模态行人重识别方法,利用通道增强后的可视图像作为第三模态,通过图像通道可交换随机混合增强(I-CSA)模块对可见光图像进行单通道和三通道随机混合增强抽取,从而突出行人的姿态结构细节,在学习中减少模态间差异。结构化联合注意力特征融合 (SAFF)模块在注重模态间行人姿态结构关系的前提下,为跨模态表征学习提供更丰富的监督,增强了模态变化中共享特征的鲁棒性。在SYSU-MM01数据集全搜索模式单摄设置下Rank-1和mAP分别达到71.2%和68.1%,优于同类前沿方法。Abstract: In the current research on cross-modal person re-identification technology, most existing methods reduce cross-modal differences by using single modal original visible light images or locally shared features of adversarially generated images, resulting in a lack of stable recognition accuracy in infrared image discrimination due to the loss of feature information. In order to solve this problem, A cross-modal person re-identification method based on swappable hybrid random channel augmentation with structured dual attention is proposed. The visual image after channel enhancement is used as the third mode, and the single channel and three channels random hybrid enhancement extraction of visible image is performed through the Image Channel Swappable random mix Augmentation (I-CSA) module, so as to highlight the structural details of pedestrian posture, Reduce modal differences in learning. The Structured joint Attention Feature Fusion (SAFF) module provides richer supervision for cross-modal Feature learning, and enhances the robustness of shared features in modal changes, under the premise of focusing on the structural relationship of pedestrian attitudes between modes. Under the single shot setting of full search mode in the SYSU-MM01 dataset, Rank-1 and mAP reached 71.2% and 68.1%, respectively, surpassing similar cutting-edge methods.
-
Key words:
- Person Re-identification /
- Cross-modal /
- Hybrid channel enhancement /
- Joint attention /
- Feature fusion
-
表 1 SYSU-MM01数据集在单摄设置下的实验对比结果(%)
方法 全搜索 室内搜索 单摄 单摄 Method Rank-1 Rank-10 Rank-20 mAP Rank-1 Rank-10 Rank-20 mAP AlignGAN[5] 42.4 85.0 93.7 40.7 35.9 87.6 94.4 54.3 AGW[20] 47.5 84.4 92.1 47.7 54.2 91.1 96.0 63.0 DDAG[12] 54.8 90.4 95.8 53.0 61.0 94.1 98.4 68.0 MID[21] 60.3 92.9 – 59.4 64.9 96.1 – 70.1 SFANET[19] 60.5 91.8 95.2 53.9 64.8 94.7 98.1 75.2 cm-SSFT[6] 61.6 89.2 93.9 63.2 70.5 94.9 97.7 72.6 SPOT[22] 65.3 92.7 97.0 62.3 69.4 96.2 99.1 74.6 MCLNet[26] 65.4 93.3 97.1 62.0 72.6 97.0 99.2 76.6 FMCNet[23] 66.3 – – 62.5 68.2 – – 74.1 本文方法 71.2 96.3 98.9 68.1 77.4 98.0 99.6 81.1 表 2 RegDB数据集上的实验对比结果(%)
方法 可见光图像查询红外图像 红外图像查询可见光图像 Rank-1 Rank-10 Rank-20 mAP Rank-1 Rank-10 Rank-20 mAP MAC[24] 36.4 62.4 71.6 37.0 – – – – AlignGAN[5] 57.9 – – 53.6 56.3 – – 53.4 DDAG[12] 69.3 86.2 91.5 63.5 68.1 85.2 90.3 61.8 LbA[25] 74.2 – – 67.6 72.4 – – 65.5 MCLNet[26] 80.3 92.7 96.0 73.1 75.9 90.9 94.6 69.5 DCLNet[27] 81.2 – – 74.3 78.0 – – 70.6 本文方法 86.3 97.2 98.7 79.8 85.5 97.0 98.3 78.1 表 3 SYSU-MM01数据集上的消融实验(%)
RHCA TRE-DA SAFF EJ-Loss SYSU-MM01 Rank-1 mAP – – – – 48.8 46.6 √ – – – 57.4 55.1 √ √ – – 60.6 57.3 √ √ √ – 64.2 60.9 √ √ – √ 68.2 64.3 √ √ √ √ 71.2 68.1 表 4 SAFF模块嵌入位置研究结果(%)
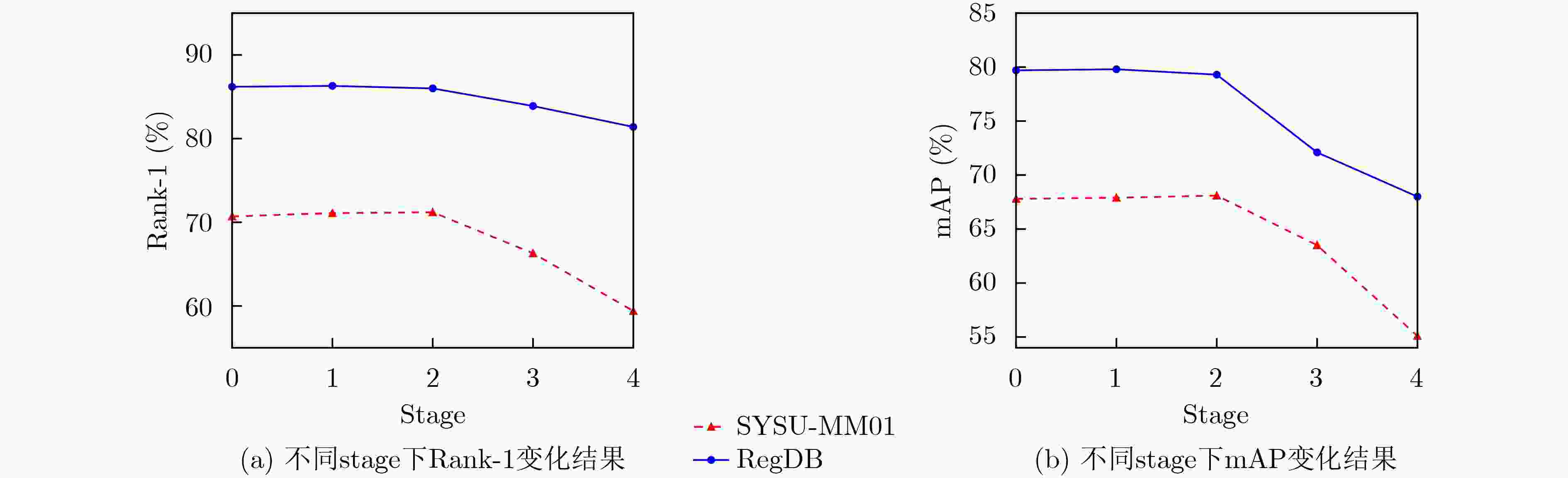
SAFF SYSU-MM01 RegDB Rank-1 mAP Rank-1 mAP stage0 70.7 67.8 86.2 79.7 stage1 71.1 67.9 86.3 79.8 stage2 71.2 68.1 86.0 79.3 stage3 66.3 63.5 83.9 72.1 stage4 59.4 55.1 81.4 68.0 表 5 $ \gamma $参数不同取值下的训练实验结果(%)
$ \gamma $ SYSU-MM01 Rank-1 Rank-10 Rank-20 mAP 0 66.7 94.6 97.1 64.7 0.1 68.4 95.2 97.8 65.9 0.3 69.9 95.8 98.5 67.3 0.5 70.8 96.2 98.7 67.9 0.7 59.3 91.1 95.4 57.7 0.9 55.4 89.0 94.2 53.1 0.47 71.2 96.3 98.9 68.1 -
[1] HUANG Yukun, FU Xueyang, LI Liang, et al. Learning degradation-invariant representation for robust real-world person Re-identification[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2022, 130(11): 2770–2796. doi: 10.1007/s11263-022-01666-w. [2] YANG Lei. Continuous epoch distance integration for unsupervised person Re-identification[C]. The 5th International Conference on Communications, Information System and Computer Engineering, Guangzhou, China, 2023: 464–469. doi: 10.1109/cisce58541.2023.10142496. [3] XUAN Shiyu and ZHANG Shiliang. Intra-inter domain similarity for unsupervised person Re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022: 1. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2022.3163451. [4] DAI Pingyang, JI Rongrong, WANG Haibin, et al. Cross-modality person Re-identification with generative adversarial training[C]. Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 677–683. doi: 10.24963/ijcai.2018/94. [5] WANG Guan’an, ZHANG Tianzhu, CHENG Jian, et al. RGB-infrared cross-modality person Re-identification via joint pixel and feature alignment[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 3622–3631. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00372. [6] LU Yan, WU Yue, LIU Bin, et al. Cross-modality person Re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 13376–13386. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01339. [7] LI Xulin, LU Yan, LIU Bin, et al. Counterfactual intervention feature transfer for visible-infrared person Re-identification[C]. 17th European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2022: 381–398. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-19809-0_22. [8] 王凤随, 闫涛, 刘芙蓉, 等. 融合子空间共享特征的多尺度跨模态行人重识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(1): 325–334. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211212.WANG Fengsui, YAN Tao, LIU Furong, et al. Multi-scale cross-modality person Re-identification method based on shared subspace features[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(1): 325–334. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211212. [9] LIANG Tengfei, JIN Yi, LIU Wu, et al. Cross-modality transformer with modality mining for visible-infrared person Re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2023: 1–13. doi: 10.1109/tmm.2023.3237155. [10] 徐胜军, 刘求缘, 史亚, 等. 基于多样化局部注意力网络的行人重识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 211–220. doi: 10.11999/ JEIT201003.XU Shengjun, LIU Qiuyuan, SHI Ya, et al. Person Re-identification based on diversified local attention network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 211–220. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201003. [11] JIA Mengxi, SUN Yifan, ZHAI Yunpeng, et al. Semi-attention partition for occluded person Re-identification[C]. The 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, USA, 2023: 998–1006. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v37i1.25180. [12] YE Mang, SHEN Jianbing, CRANDALL D J, et al. Dynamic dual-attentive aggregation learning for visible-infrared person Re-identification[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 229–247. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58520-4_14. [13] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [14] WANG Qilong, WU Banggu, ZHU Pengfei, et al. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 11531–11539. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01155. [15] WU Ancong, ZHENG Weishi, YU Hongxing, et al. RGB-infrared cross-modality person Re-identification[C]. The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5390–5399. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.575. [16] NGUYEN D T, HONG H G, KIM K W, et al. Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(3): 605. doi: 10.3390/s17030605. [17] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84–90. doi: 10.1145/3065386. [18] SONG Shuang, CHAUDHURI K, and SARWATE A D. Stochastic gradient descent with differentially private updates[C]. Global Conference on Signal & Information Processing, Austin, USA, 2014: 245–248. doi: 10.1109/globalsip.2013.6736861. [19] LIU Haojie, MA Shun, XIA Daoxun, et al. SFANet: A spectrum-aware feature augmentation network for visible-infrared person reidentification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(4): 1958–1971. doi: 10.1109/tnnls.2021.3105702. [20] YE Mang, SHEN Jianbing, LIN Gaojie, et al. Deep learning for person Re-identification: A survey and outlook[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(6): 2872–2893. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3054775. [21] HUANG Zhipeng, LIU Jiawei, LI Liang, et al. Modality-adaptive mixup and invariant decomposition for RGB-infrared person Re-identification[C/OL]. The 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2022: 1034–1042. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v36i1.19987. [22] CHEN Cuiqun, YE Mang, QI Meibin, et al. Structure-aware positional transformer for visible-infrared person Re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 2352–2364. doi: 10.1109/tip.2022.3141868. [23] ZHANG Qiang, LAI Changzhou, LIU Jianan, et al. FMCNet: Feature-level modality compensation for visible-infrared person Re-identification[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 7339–7348. doi: 10.1109/cvpr52688.2022.00720. [24] YE Mang, LAN Xiangyuan, and LENG Qingming. Modality-aware collaborative learning for visible thermal person Re-identification[C]. The 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 2019: 347–355. doi: 10.1145/3343031.3351043. [25] PARK H, LEE S, LEE J, et al. Learning by aligning: Visible-infrared person Re-identification using cross-modal correspondences[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 12026–12035. doi: 10.1109/iccv48922.2021.01183. [26] HAO Xin, ZHAO Sanyuan, YE Mang, et al. Cross-modality person Re-identification via modality confusion and center aggregation[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 16383–16392. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.01609. [27] SUN Hanzhe, LIU Jun, ZHANG Zhizhong, et al. Not all pixels are matched: Dense contrastive learning for cross-modality person Re-identification[C]. The 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisbon, Portugal, 2022: 5333–5341. doi: 10.1145/3503161.3547970. -





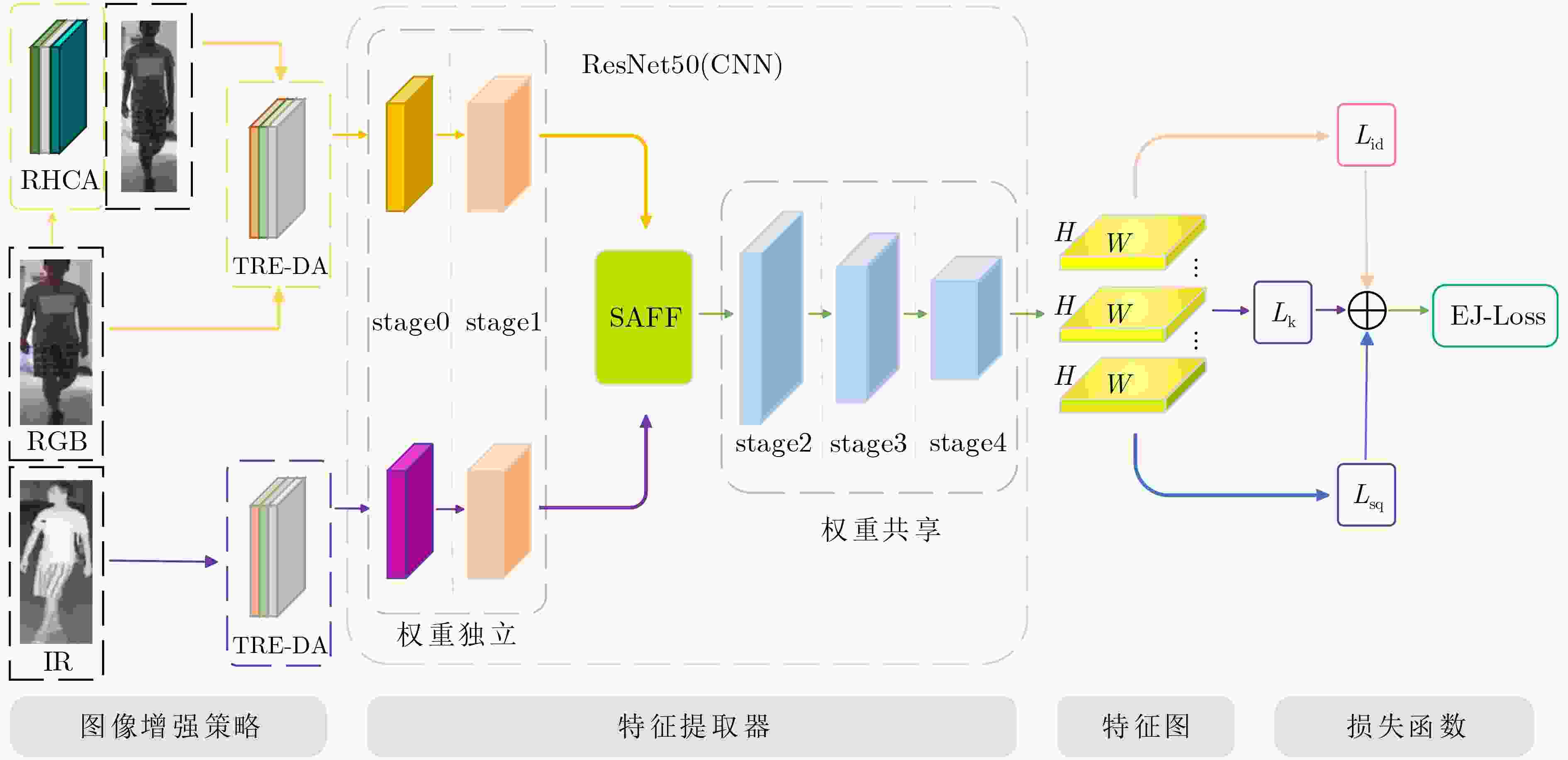
 下载:
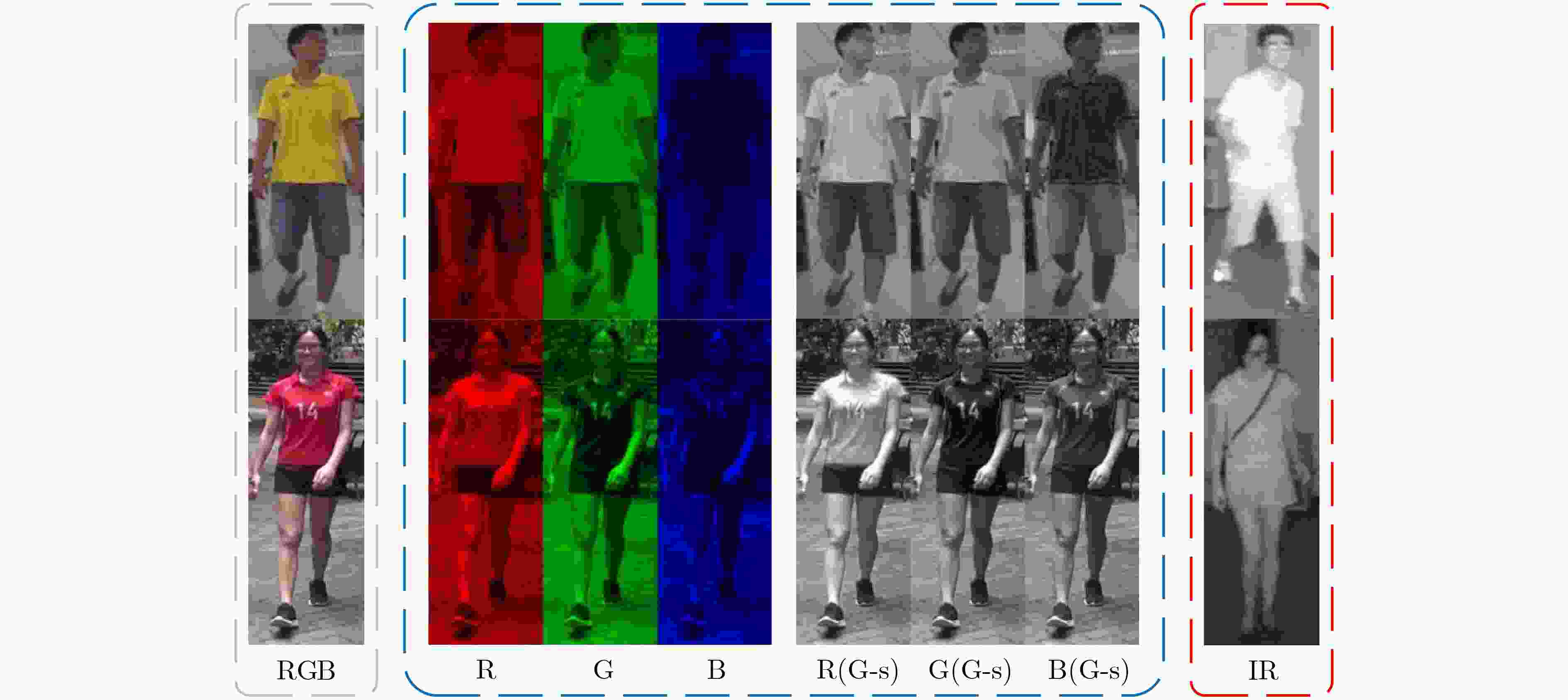
下载:
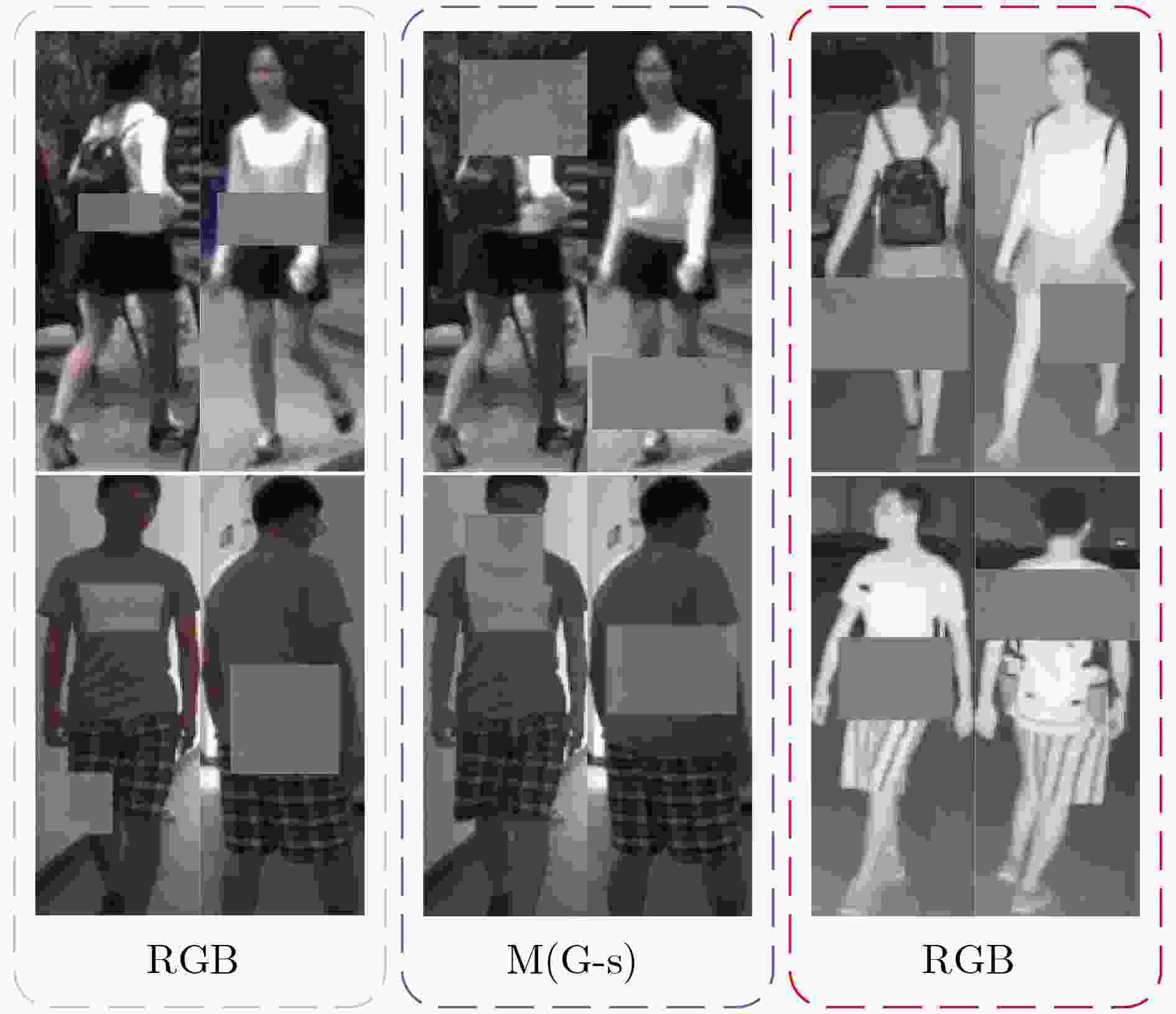
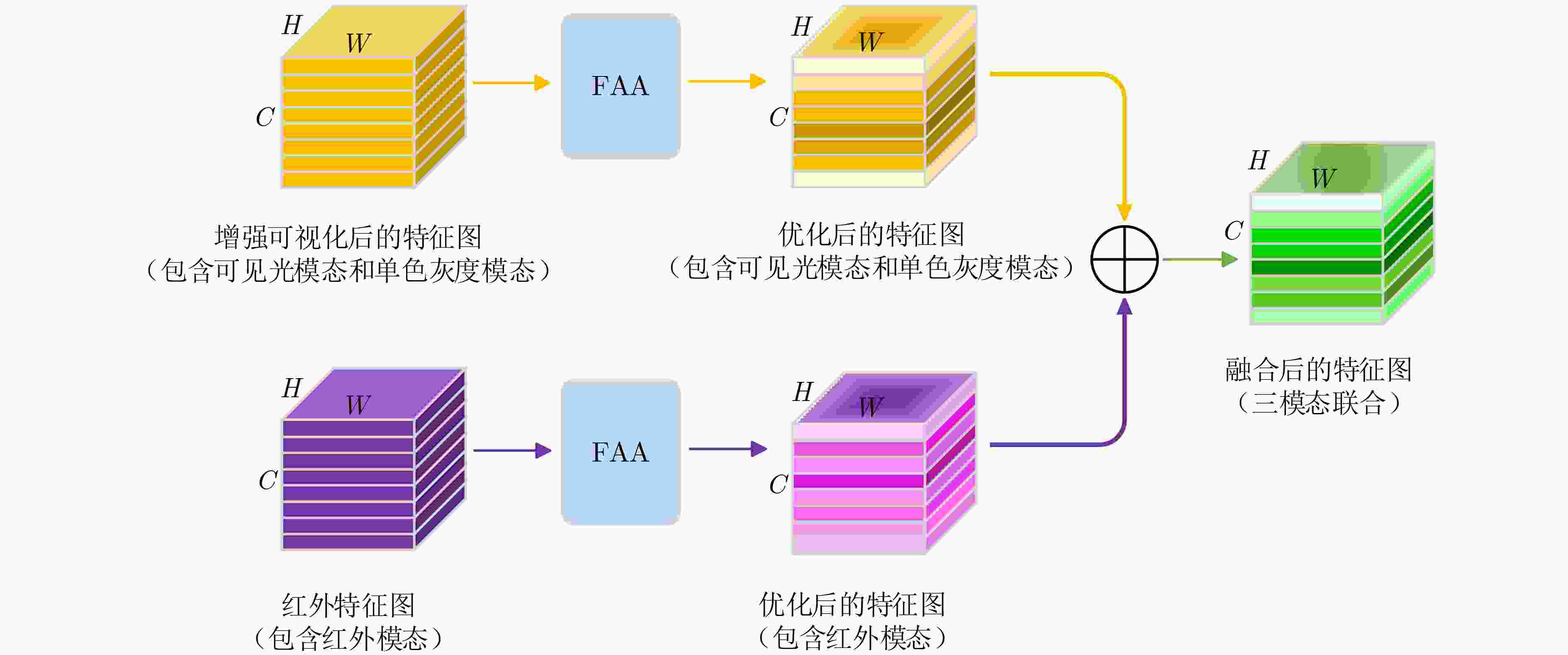


 下载:
下载:
