Underwater Image Enhancement Network Based on Multi-channel Hybrid Attention Mechanism
-
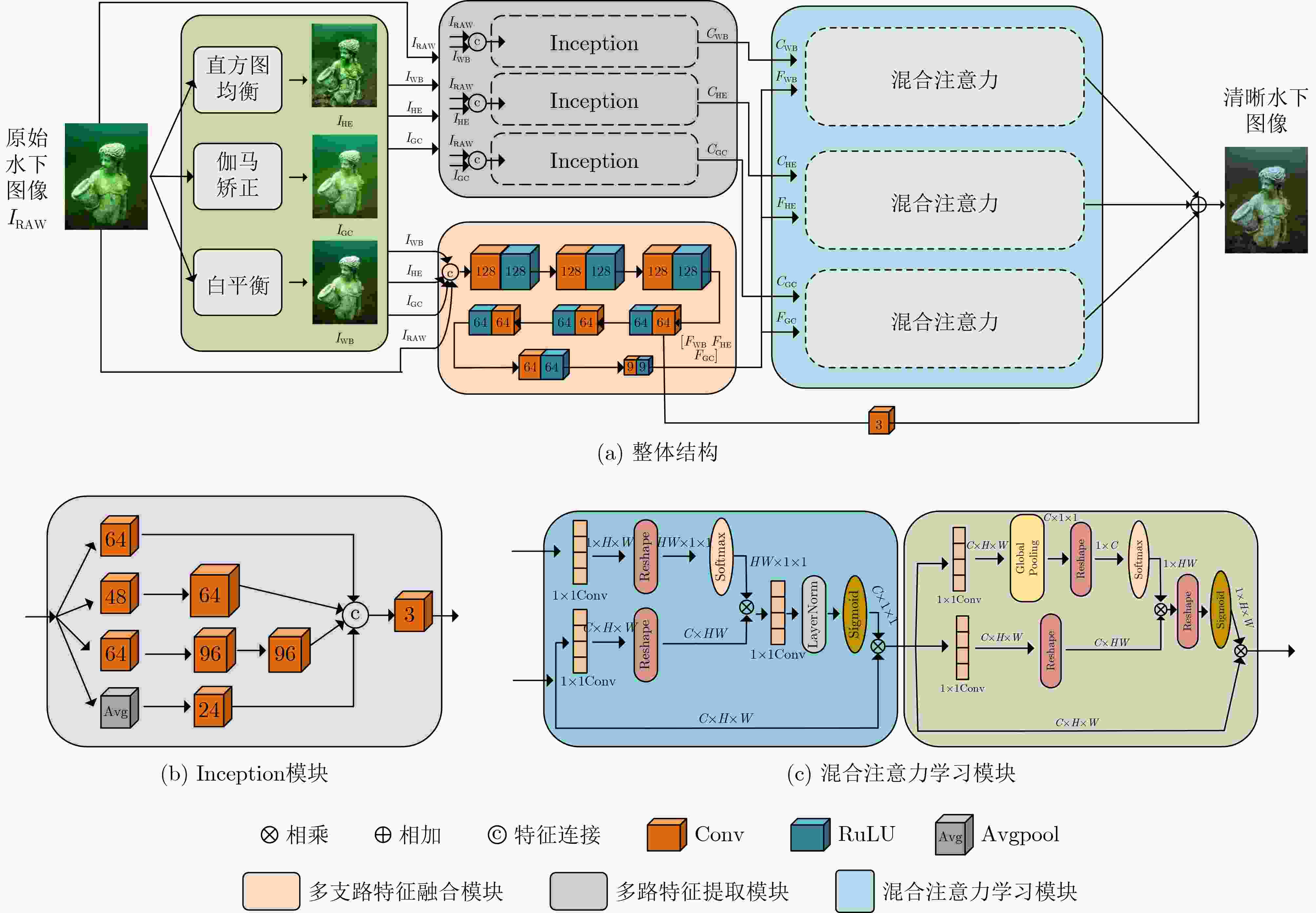
摘要: 光线在水下被吸收或者散射使得水下图像成像出现色偏、模糊遮挡等问题,影响水下视觉任务。传统的图像增强方法分别采用直方图均衡、伽马矫正和白平衡方法较好地增强水下图像。然而,3种方法融合增强水下图像的互补性和相关性方面的研究较少。因此,该文提出一种基于多路混合注意力机制的水下图像增强网络。首先,提出多路特征提取模块,对图像进行直方图均衡支路、伽马矫正支路和白平衡支路的多路特征提取,提取图像的对比度、亮度和颜色特征;然后,融合直方图均衡、伽马矫正和白平衡3支路特征,增强3支路特征融合的互补性;最后,设计混合注意力学习模块,深度挖掘3支路在对比度、亮度和颜色的相关性矩阵,并引入跳跃连接增强图像输出。在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法能够有效恢复水下图像色偏、模糊遮挡和提高图像明亮度。Abstract: The absorption or scattering of light under water causes problems such as color cast, blur and occlusion in underwater image imaging, which affects underwater vision tasks. Traditional image enhancement methods use histogram equalization, gamma correction and white balance methods to enhance underwater images well. However, there are few studies on the complementarity and correlation of the three methods fused to enhance underwater images. Therefore, an underwater image enhancement network based on multi-channel hybrid attention mechanism is proposed. Firstly, a multi-channel feature extraction module is proposed to extract the contrast, brightness and color features of the image by multi-channel feature extraction of histogram equalization branch, gamma correction branch and white balance branch. Then, the three branch features of histogram equalization, gamma correction and white balance are fused to enhance the complementarity of three branch feature fusion. Finally, a hybrid attention learning module is designed to deeply mine the correlation matrix of the three branches in contrast, brightness and color, and skip connections are introduced to enhance the image output. Experimental results on multiple datasets show that the proposed method can effectively recover the color cast, blur occlusion and improve the brightness of underwater images.
-
Key words:
- Underwater image enhancement /
- Deep learning /
- Attention mechanism /
- Skip connection
-
表 1 4种不同水下数据集的划分
UIEB EUVP1 EUVP2 LSUI 总图像 890 3700 2185 4279 训练集 790 3330 1966 3879 测试集 100 370 219 400 表 2 网络结构消融实验数值结果
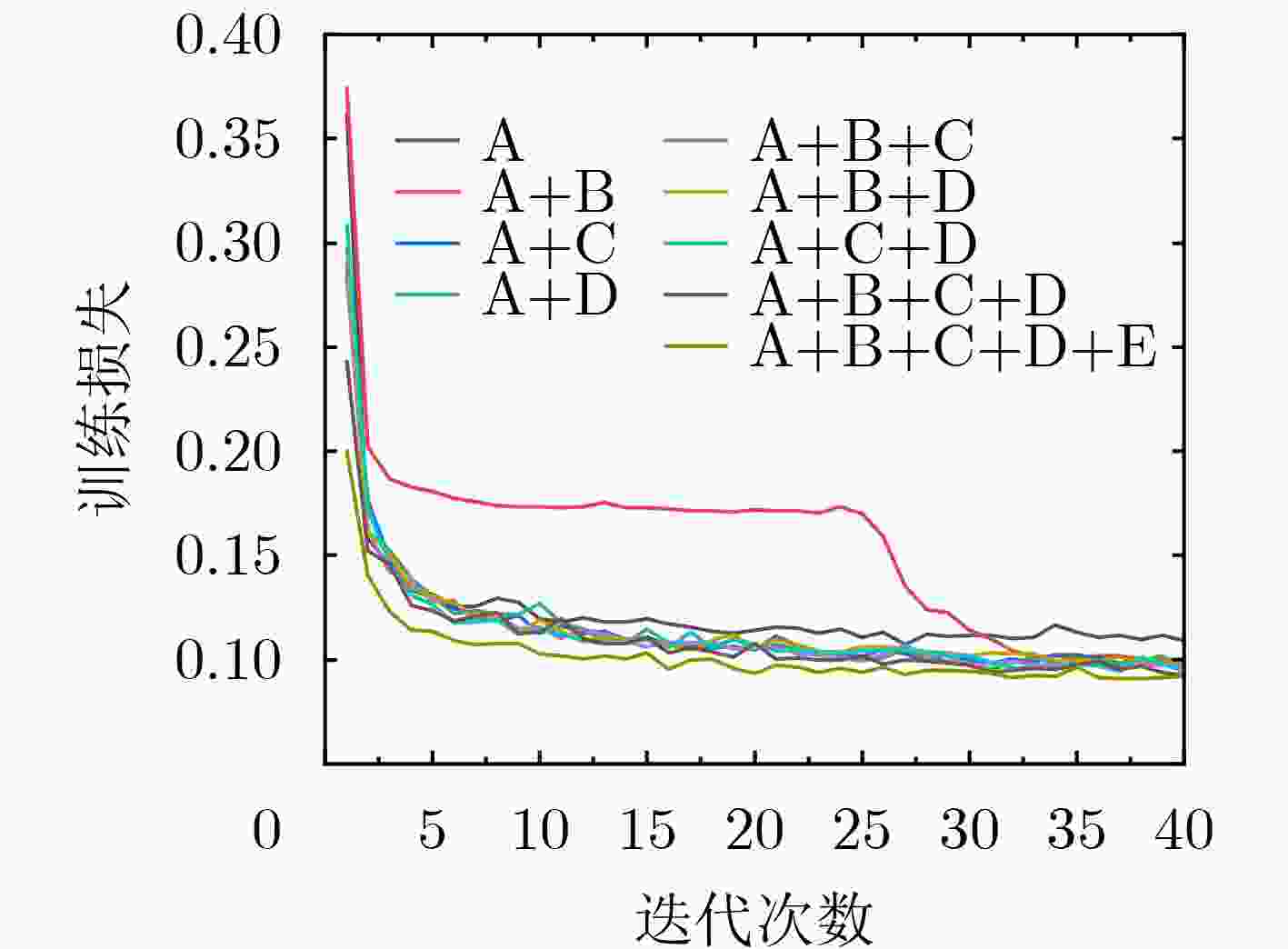
MSE(×103) PSNR SSIM A 0.9329 19.5549 0.8759 A+B 4.6547 11.8424 0.6027 A+C 1.0886 18.6155 0.8698 A+D 11.6075 7.6427 0.1967 A+B+C 0.9096 19.7709 0.8864 A+B+D 0.7690 20.2661 0.8901 A+C+D 0.8062 20.3661 0.8925 A+B+C+D 0.7671 20.3885 0.8798 A+B+C+D+E 0.7193 20.7678 0.8958 表 3 UIEB数据集上不同方法的定量评价
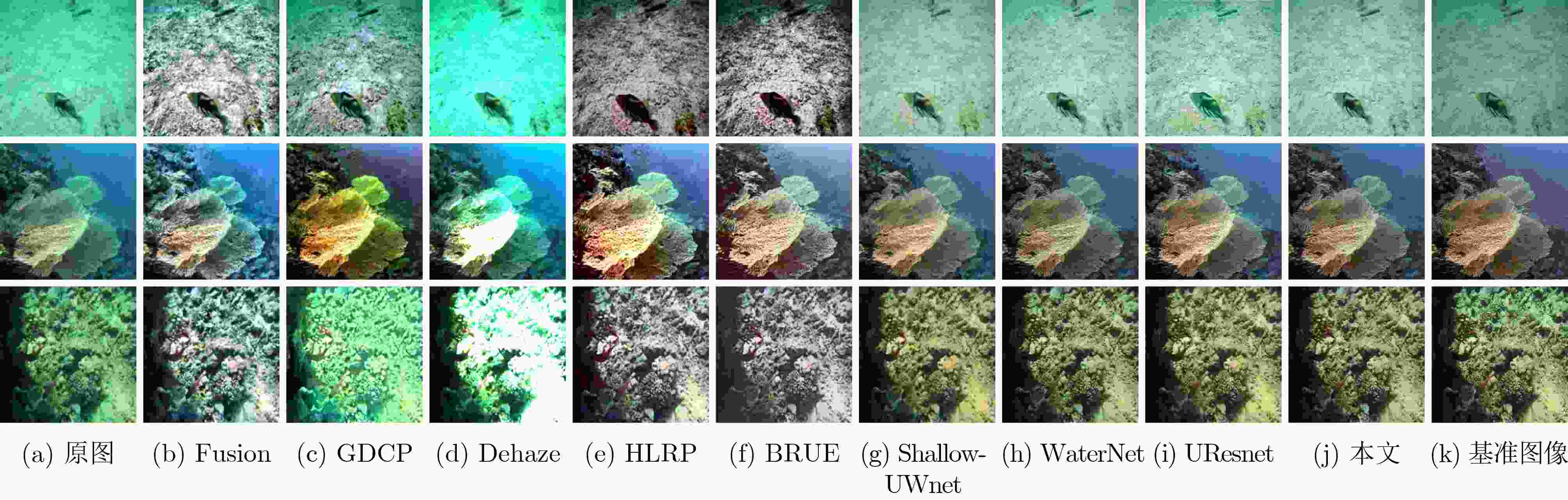
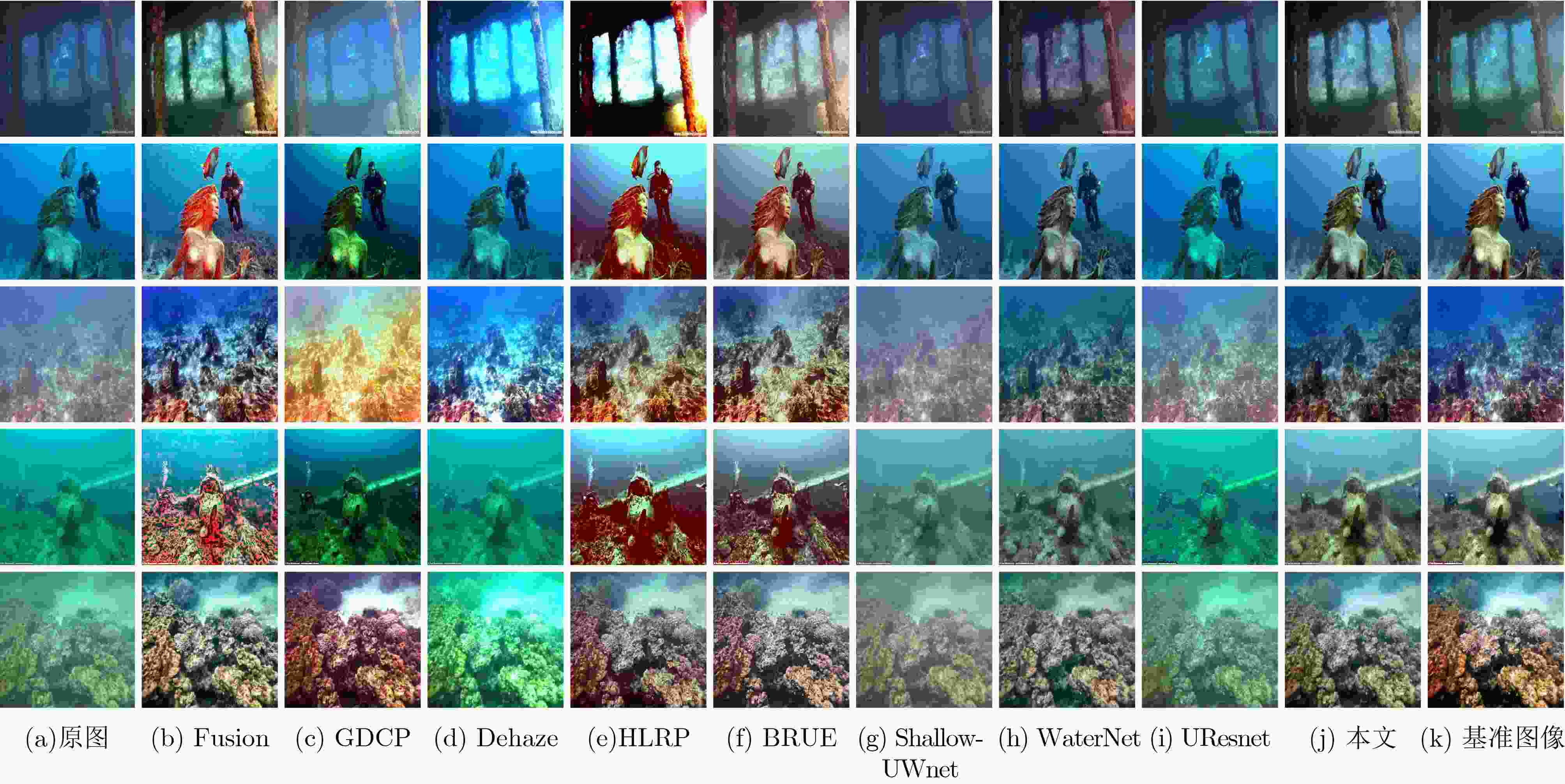
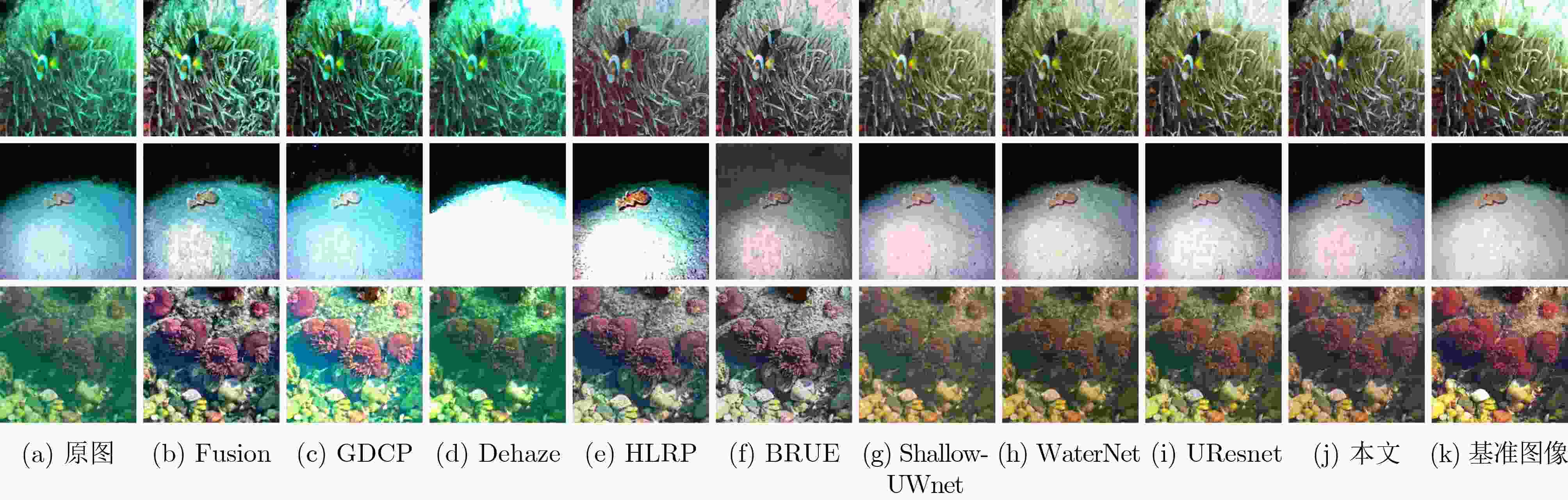
MSE(×103) PSNR SSIM UCIQE 运行时间(s) 原图 1.5160 18.3782 0.7763 0.3934 – Fusion 0.9764 28.1235 0.8428 0.4832 67.85 GDCP 3.6173 13.5613 0.7365 0.4560 579.41 Dehaze 2.3981 15.7978 0.7544 0.4624 12.74 HLRP 4.6692 12.1880 0.2309 0.4673 300.11 BRUE 2.6633 15.0887 0.6555 0.4257 249.12 Shallow-UWnet 1.2263 18.4789 0.8041 0.3566 30.48 WaterNet 1.0258 18.7704 0.8777 0.4165 64.85 UResnet 1.4343 17.9562 0.7615 0.4065 34.74 本文 0.7193 20.7678 0.8958 0.4076 57.85 表 4 EUVP1数据集上不同方法的定量评价
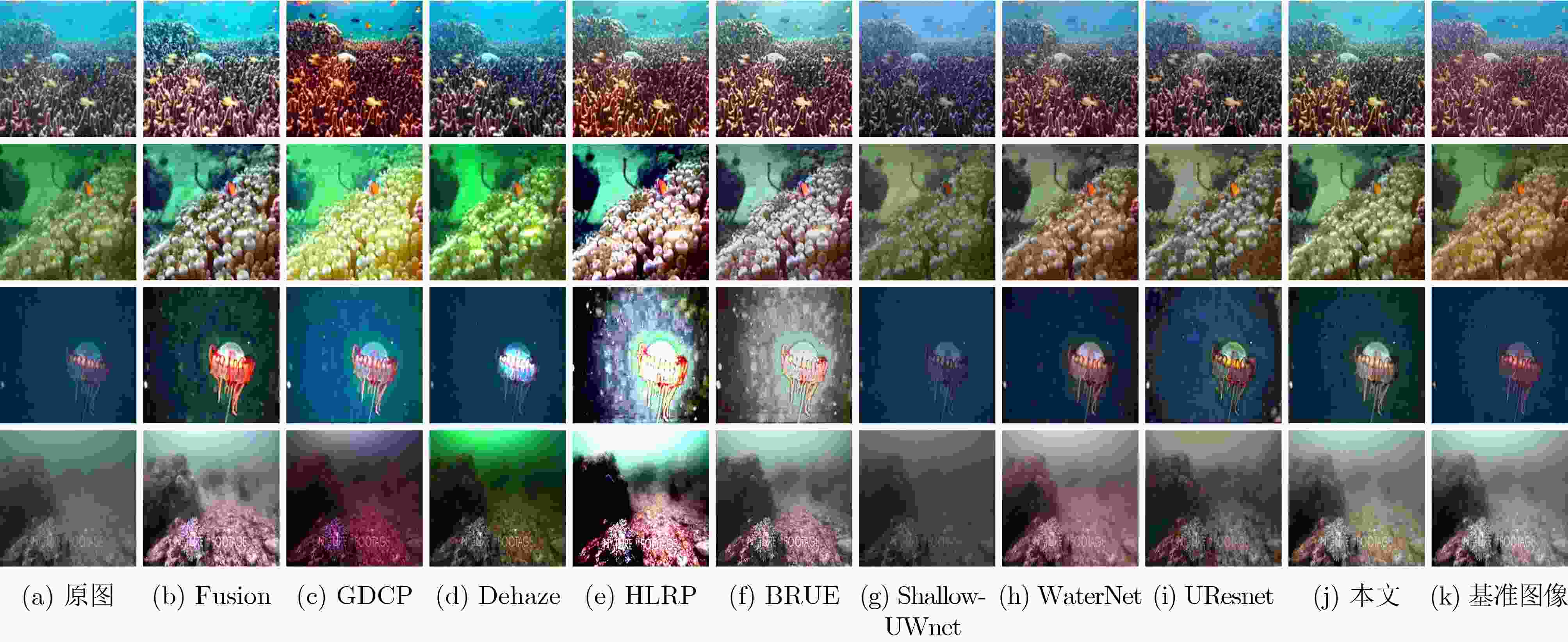
MSE(×103) PSNR SSIM UCIQE 运行时间(s) 原图 1.5162 16.9408 0.7282 0.4244 – Fusion 1.5543 16.5457 0.6606 0.4711 30.87 GDCP 4.3538 12.4384 0.5922 0.4735 223.98 Dehaze 2.9950 14.0605 0.6422 0.4575 7.87 HLRP 4.1953 12.2690 0.1295 0.4607 144.62 BRUE 1.9737 16.3921 0.6504 0.4281 85.99 Shallow-UWnet 0.3945 22.7718 0.8085 0.3938 5.28 WaterNet 0.4133 22.8706 0.8339 0.4128 6.90 UResnet 0.3237 23.7804 0.8296 0.4370 8.81 本文 0.3651 23.3899 0.8309 0.4378 7.49 表 5 EUVP2数据集上不同方法的定量评价
MSE(×103) PSNR SSIM UCIQE 运行时间(s) 原图 0.7644 19.8464 0.7361 0.4274 – Fusion 1.5287 16.8524 0.6682 0.4822 19.44 GDCP 3.2112 13.7086 0.6227 0.4794 149.14 Dehaze 2.0752 16.2689 0.6705 0.4646 5.25 HLRP 4.0604 12.3013 0.1669 0.4718 95.323 BRUE 2.0339 15.9520 0.6626 0.4324 58.81 Shallow-UWnet 0.3234 23.5612 0.7780 0.4128 4.71 WaterNet 0.4649 22.3487 0.7997 0.4207 10.00 UResnet 0.2982 24.0810 0.8034 0.4314 10.11 本文 0.3732 23.1460 0.8055 0.4063 5.40 表 6 LSUI数据集上不同方法的定量评价
MSE(×103) PSNR SSIM UCIQE 运行时间(s) 原图 1.0684 18.8053 0.7977 0.4194 – Fusion 1.3242 17.6604 0.7277 0.4825 34.72 GDCP 3.5459 13.4069 0.6766 0.4796 363.02 Dehaze 2.3828 15.4675 0.7192 0.4674 9.64 HLRP 3.8949 12.5132 0.1918 0.4915 240.86 BRUE 1.7558 16.6739 0.7074 0.4301 162.92 Shallow-UWnet 0.8527 19.6673 0.8046 0.3709 9.24 WaterNet 0.4931 22.1336 0.8628 0.4370 13.18 UResnet 0.5831 21.1576 0.8124 0.4243 13.13 本文 0.5576 21.5563 0.8552 0.4004 15.50 表 7 不同方法的运行时间和FPS
Fusion GDCP Dehaze HLRP BRUE Shallow-UWnet WaterNet UResnet 本文 时间(s) 67.85 579.41 12.74 300.11 249.12 30.48 64.85 34.74 57.85 Fps 1.47 0.17 7.85 0.33 0.40 3.28 1.54 2.88 1.73 -
[1] 侯冬, 任军委, 郭广坤, 等. 高精度水下激光频率传递研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(2): 220149. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220149HOU Dong, REN Junwei, GUO Guangkun, et al. Progress on high-precision laser-based underwater frequency transfer[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2023, 50(2): 220149. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220149 [2] PIZER S M, AMBURN E P, AUSTIN J D, et al. Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations[J]. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, 1987, 39(3): 355–368. doi: 10.1016/S0734-189X(87)80186-X [3] PIZER S M, JOHNSTON R E, ERICKSEN J P, et al. Contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization: Speed and effectiveness[C]. The First Conference on Visualization in Biomedical Computing, Atlanta, USA, 1990: 337–345. [4] ANCUTI C, ANCUTI C O, HABER T, et al. Enhancing underwater images and videos by fusion[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 81–88. [5] RIZZI A, GATTA C, and MARINI D. Color correction between gray world and white patch[C]. The SPIE 4662, Human Vision and Electronic Imaging VII, San Jose, USA, 2002: 1–10. [6] SINGH G, JAGGI N, VASAMSETTI S, et al. Underwater image/video enhancement using wavelet based color correction (WBCC) method[C]. 2015 IEEE Underwater Technology, Chennai, India, 2015: 1–5. [7] MUNIRAJ M and DHANDAPANI V. Underwater image enhancement by combining color constancy and dehazing based on depth estimation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 460: 211–230. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.07.003 [8] BERMAN D, LEVY D, AVIDAN S, et al. Underwater single image color restoration using haze-lines and a new quantitative dataset[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(8): 2822–2837. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2977624 [9] WANG Yi, LIU Hui, and CHAU L P. Single underwater image restoration using adaptive attenuation-curve prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2018, 65(3): 992–1002. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2017.2751671 [10] PENG Y T, CAO Keming, and COSMAN P C. Generalization of the dark channel prior for single image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(6): 2856–2868. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2813092 [11] LI Chongyi, ANWAR S, HOU Junhui, et al. Underwater image enhancement via medium transmission-guided multi-color space embedding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 4985–5000. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3076367 [12] 李钰, 杨道勇, 刘玲亚, 等. 利用生成对抗网络实现水下图像增强[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2022, 56(2): 134–142. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2021.075LI Yu, YANG Daoyong, LIU Lingya, et al. Underwater image enhancement based on generative adversarial networks[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2022, 56(2): 134–142. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2021.075 [13] MARQUES T P and ALBU A B. L2UWE: A framework for the efficient enhancement of low-light underwater images using local contrast and multi-scale fusion[C]. The 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020: 2286–2295. [14] LI Chongyi, GUO Chunle, REN Wenqi, et al. An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 4376–4389. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2955241 [15] SUN Xin, LIU Lipeng, LI Qiong, et al. Deep pixel-to-pixel network for underwater image enhancement and restoration[J]. IET Image Processing, 2018, 13(3): 469–474. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2018.5237 [16] 方明, 刘小晗, 付飞蚺. 基于注意力的多尺度水下图像增强网络[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(12): 3513–3521. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200836FANG Ming, LIU Xiaohan, and FU Feiran. Multi-scale underwater image enhancement network based on attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(12): 3513–3521. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200836 [17] 米泽田, 晋洁, 李圆圆, 等. 基于多尺度级联网络的水下图像增强方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3353–3362. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220375MI Zetian, JIN Jie, LI Yuanyuan, et al. Underwater image enhancement method based on multi-scale cascade network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3353–3362. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220375 [18] ZHUANG Peixian, WU Jiamin, PORIKLI F, et al. Underwater image enhancement with hyper-laplacian reflectance priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 5442–5455. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3196546 [19] ZHUANG Peixian, LI Chongyi, and WU Jiamin. Bayesian retinex underwater image enhancement[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 101: 104171. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104171 [20] SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2818–2826. [21] BAHDANAU D, CHO K, and BENGIO Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2014. [22] WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [23] ISLAM M J, XIA Youya, and SATTAR J. Fast underwater image enhancement for improved visual perception[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(2): 3227–3234. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.2974710 [24] PENG Lintao, ZHU Chunli, and BIAN Liheng. U-shape transformer for underwater image enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 3066–3079. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2023.3276332 [25] YANG Miao and SOWMYA A. An underwater color image quality evaluation metric[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 6062–6071. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2491020 [26] HE Kaiming, SUN Jian, and TANG Xiaoou. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341–2353. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168 [27] LIU Peng, WANG Guoyu, QI Hao, et al. Underwater image enhancement with a deep residual framework[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 94614–94629. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2928976 [28] NAIK A, SWARNAKAR A, and MITTAL K. Shallow-UWnet: Compressed model for underwater image enhancement (student abstract)[C]. The 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021: 15853–15854. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
