A Placement Planning Scheme of Intelligent-Reflecting-Surface for In-door Deployment
-
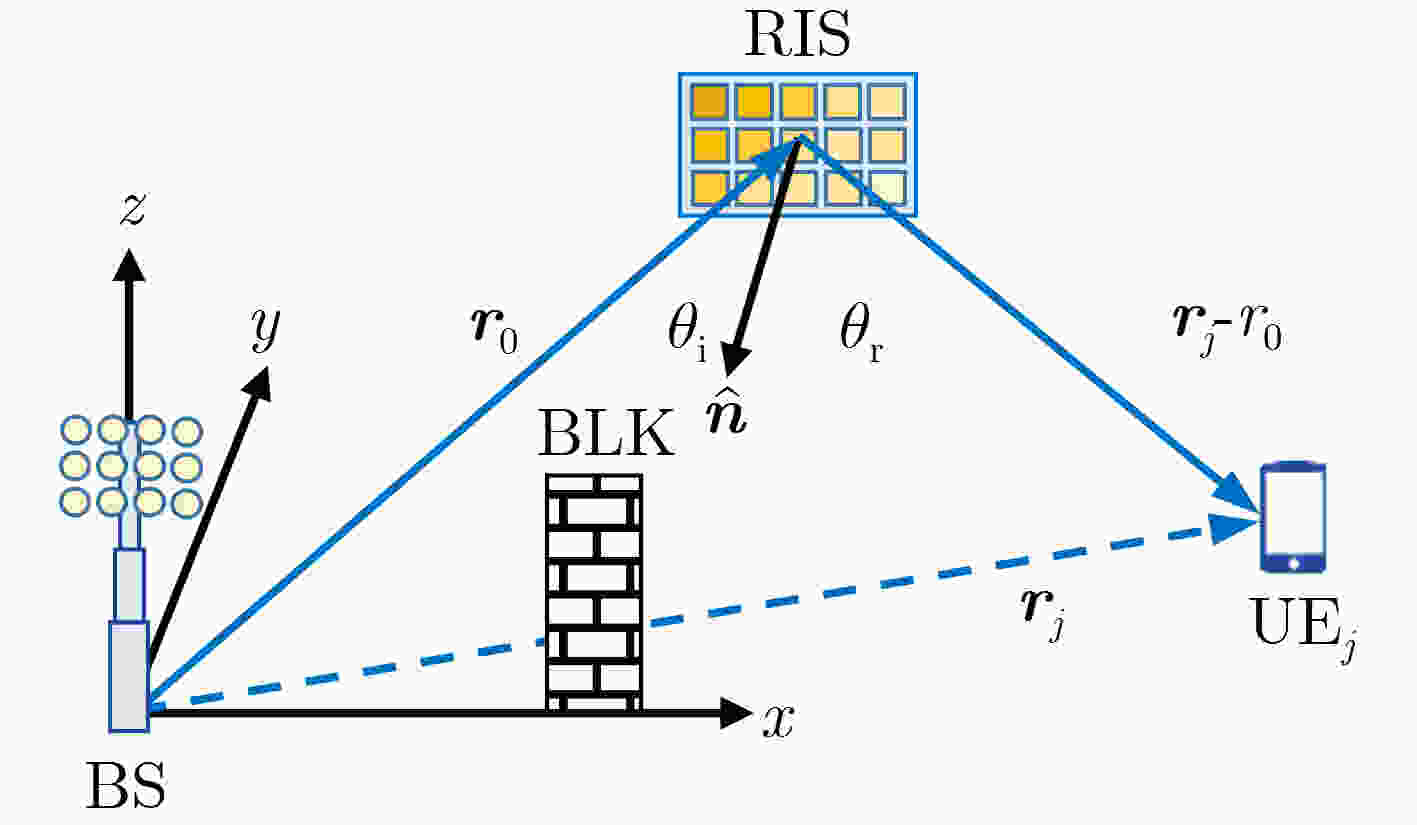
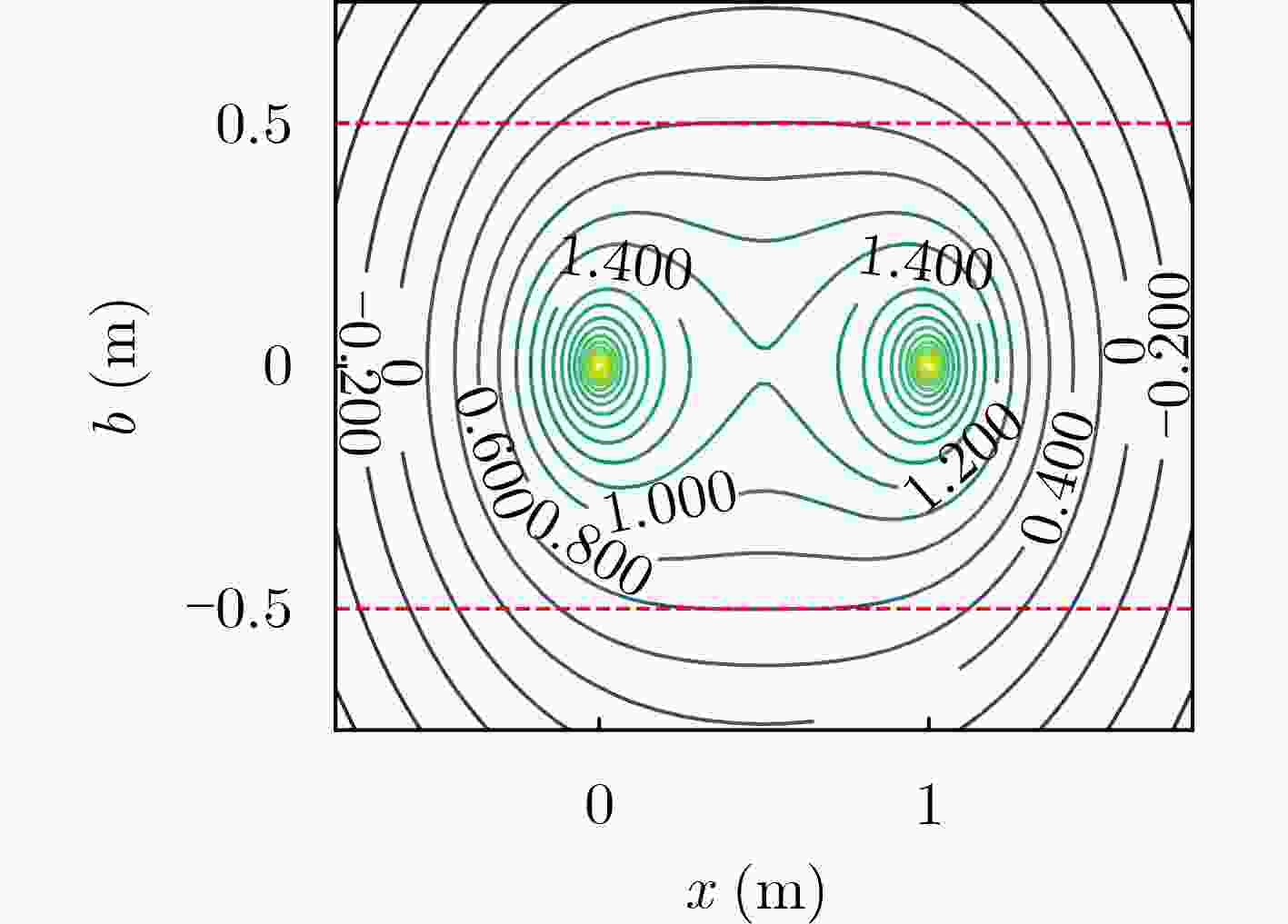
摘要: 智能反射面(IRS/RIS)应用于实际无线通信系统时,如何优选布放位置及面板取向,是提升技术实效所面临的主要问题之一。RIS布放的数学规划问题,不仅有优化目标的设计,还要考虑通信环境的建筑物分布和可选部署面的有效散射截面。相比于室外较为开放的空间,RIS的室内部署存在更多限制性条件。针对室内既有墙面的RIS布放,该文设计了多终端接入选址规划模型和等价问题。为约化其非线性计算,通过单终端退化分析,给出目标函数的卡西尼卵形线分布特征,证明RIS布放范围限于各终端及基站在部署面投影的重叠区,提出基于对半搜索法的高效启发式算法。数值仿真了2种复杂室内结构的多终端接入场景,结果表明所提算法不仅有显著加速效益,还可扩展用于多RIS网络规划。Abstract: The Intelligent-Reflecting-Surface (IRS) / Reconfigurable-Intelligent-Surface (RIS) is challenged by the placement and direction of its adhering panel when it is used to assist an actual wireless communication system to improve performance. As a mathematic programming problem, RIS placement not only depends on objective design but also is subjective to the distribution of buildings surrounded and the effective reflection area of walls to be hung with the RIS. The in-door deployment of a planar RIS is much more complex than the out-door counterpart in free and open space. The focus of this paper is on the in-door deployment of RIS adhering to environmental walls. A multi-terminal access optimization is modelled by site planning and a simplified equivalent expression is presented. A degenerated case for a single terminal is analyzed in order to transform the non-linear problem to be tractable. The function of Cassini oval is deduced from the objective and feasible solutions are narrowed to the common projection area of terminals and base-state. A heuristic and efficient algorithm is then developed based on a binary searching scheme. Numerical simulations by two in-door cases with complex constructions have verified that the proposed algorithm is benefit to speed-up computing, and extensible for multiple-RIS network planning.
-
1 RPP启发式搜索算法(RPP-HS)伪代码
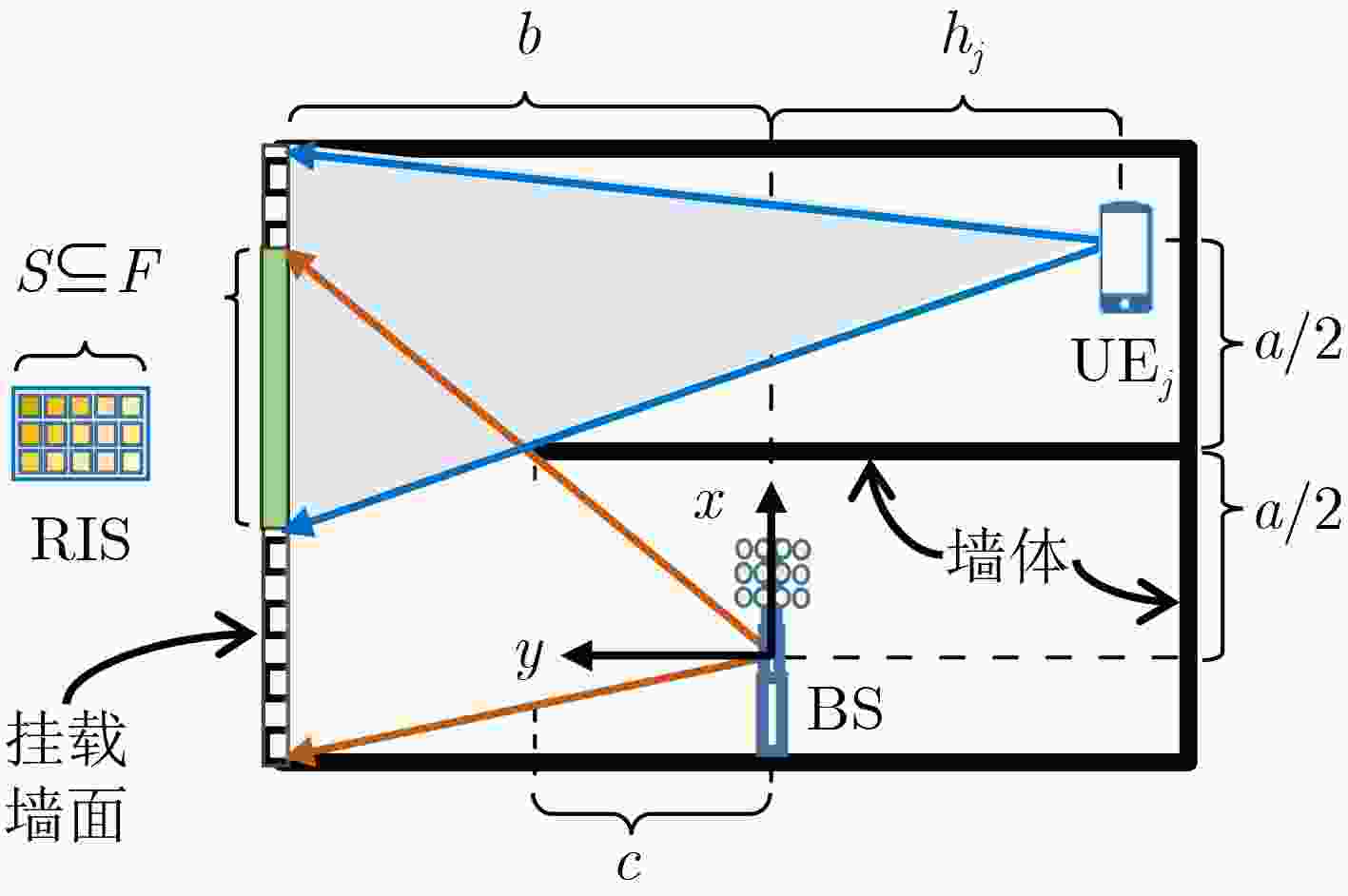
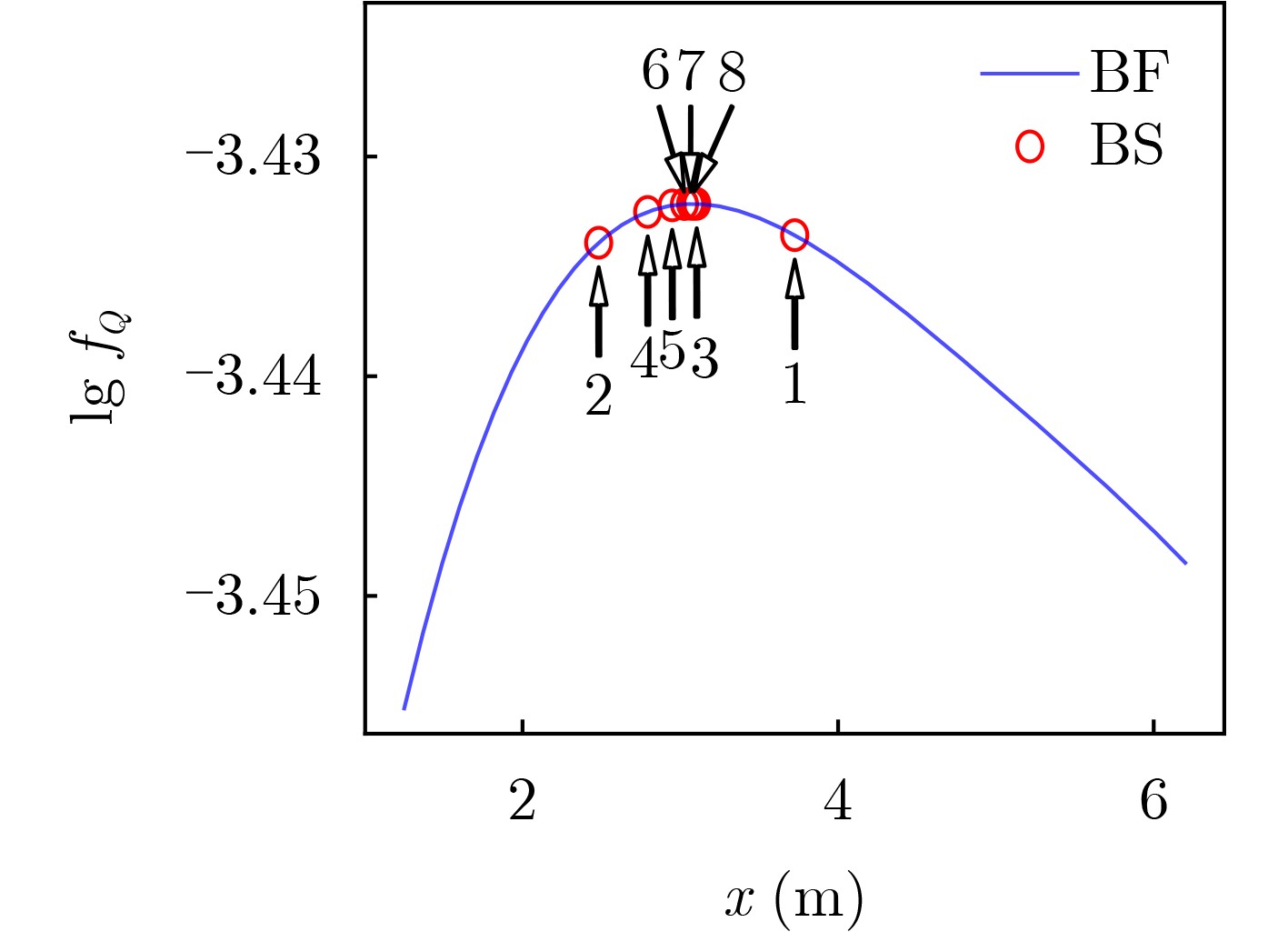
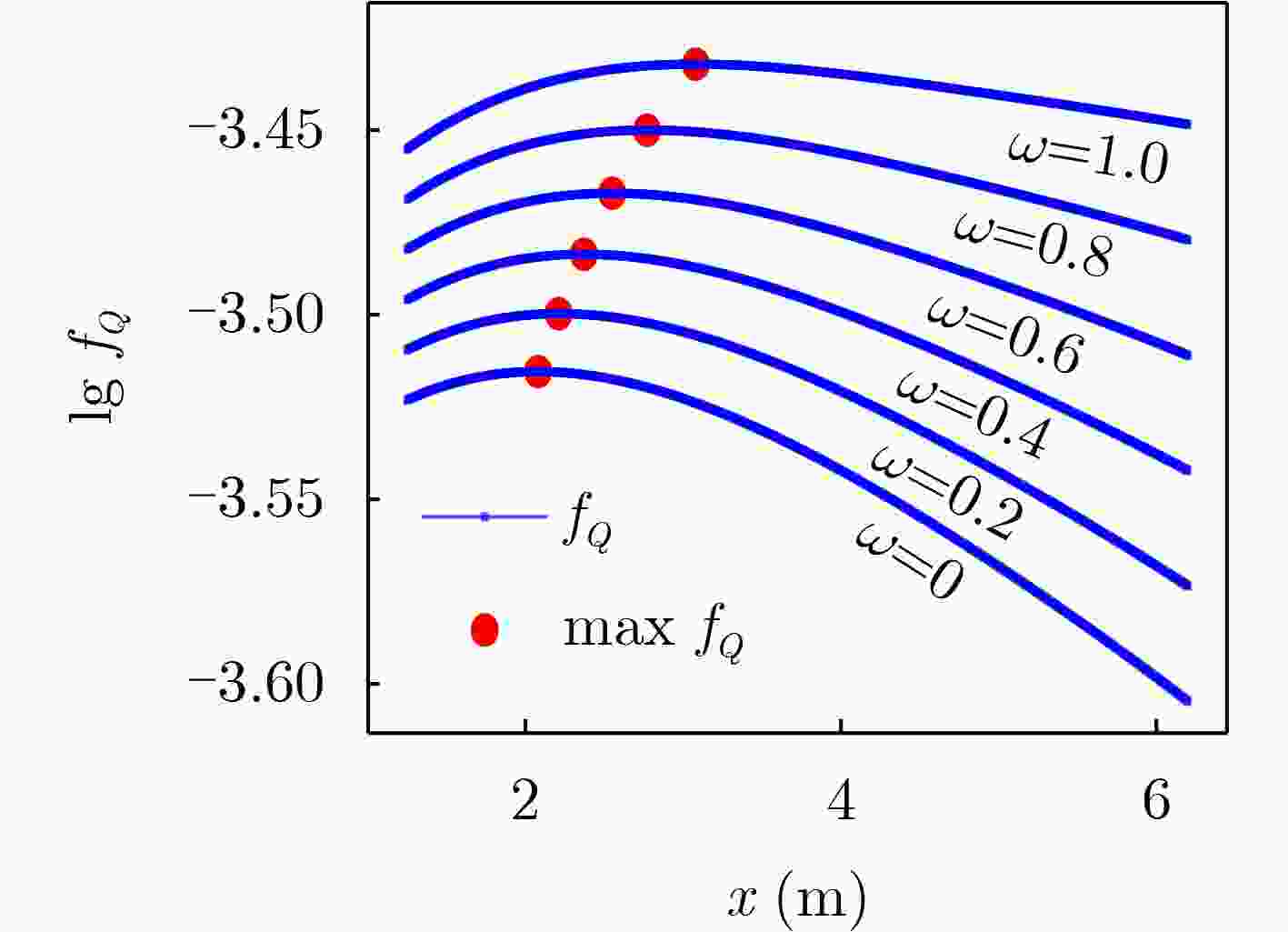
- 输入:R[j], j∈[1,N] //UE位置坐标 F //RIS部署可行区 N //UE总数 EPS //计算精度 输出:R[0] //RIS最优位置 0 RPP-HS (R,F,N,EPS) { 1 dm = 0; S = F; R[0] = vec3d(0); //初始化 2 p[0],c[0],d[0] = proj(R[0]); //BS投影计算 3 for (j = 1 to N) { 4 p[j],c[j],d[j] = proj(R[j]); //UE投影计算 5 if (d[0] < d[j]) { //如果远离RIS 6 p[j] = p[0]; //选BS投影点 7 } 8 S = S ∩ rect(c[j], p[j]); //UE附近可行区 9 if (dm < dist(c[j], p[0])) { //中心投影点计算 10 dm = dist(c[j], p[0]); 11 c[0] = c[j]; //最远中心 12 } 13 }//end-of-for 14 S = S ∪ rect(c[0], p[0]); //BS附近可行区 15 R[0] = p[0]; //初始搜索点 16 MAX = argmax{|p-p[0]|,p∈S}; //最远搜索点 17 while (dist(R[0], MAX) > EPS) { //收敛判定 18 MID = mid(R[0], MAX); //对半 19 if (slopeFQ(MID)>0) { //式(12) 20 R[0]= MID; //前推 21 } else { 22 MAX = MID; //后退 23 } 24 }//end-of-while 25 return R[0]; 26 } 表 1 测例A的主要计算参数
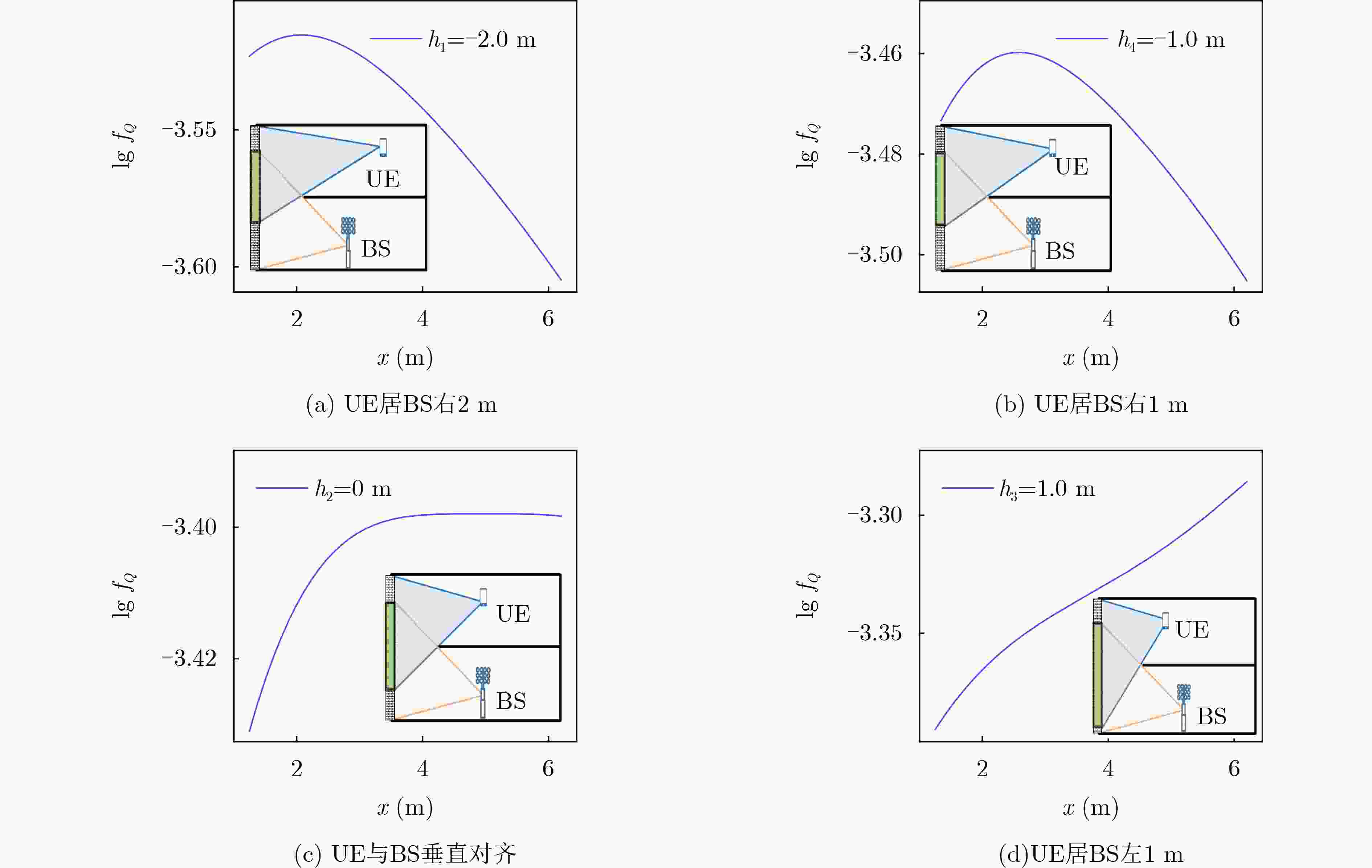
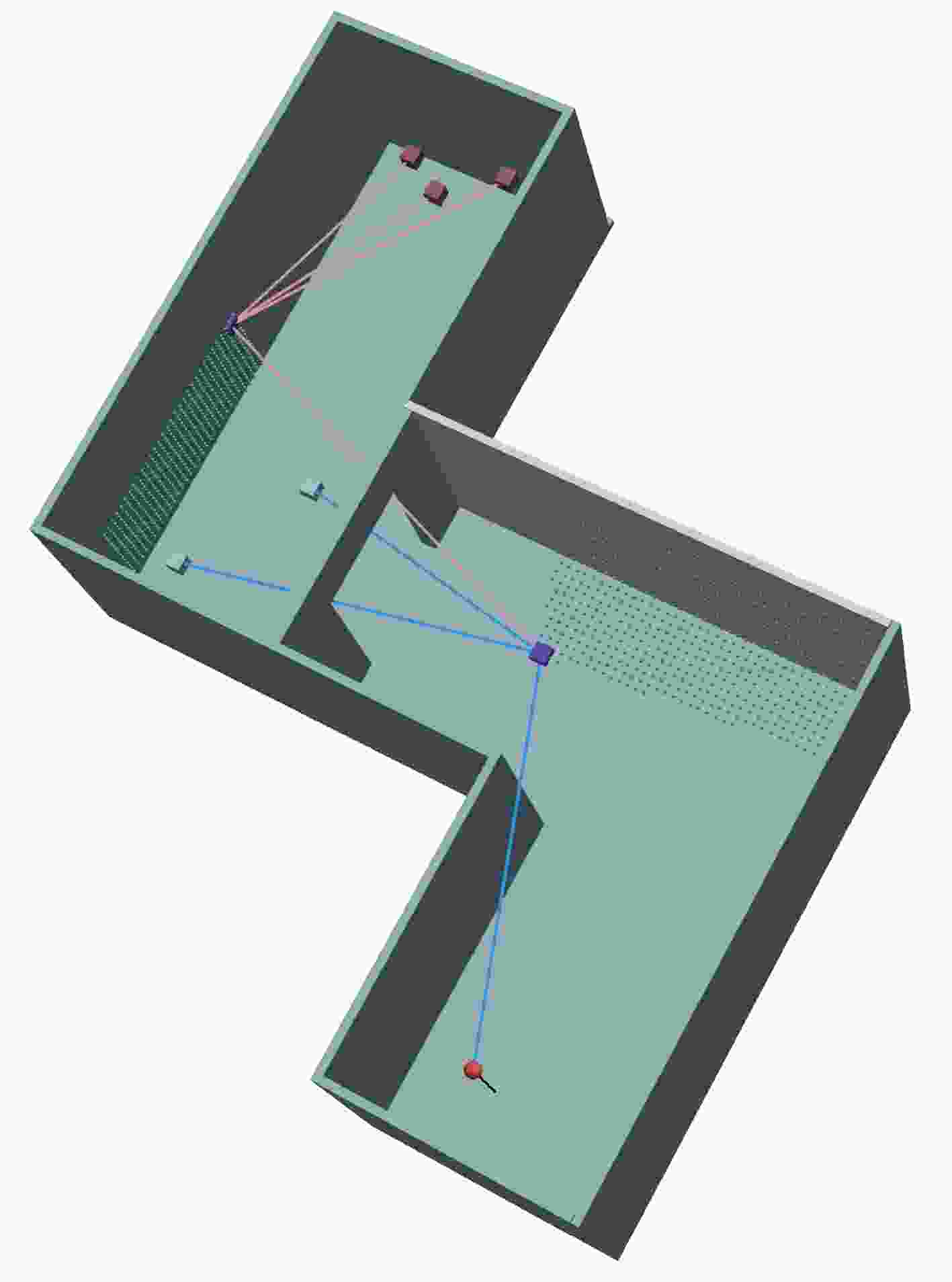
类别 参数名 值 空间结
构参数a 10.0 m b 5.0 m c 2.0 m N 4 h1 –2.0 m h2 0.0 m h3 1.0 m h4 –1.0 m 计算精度 EPS 0.1 m -
[1] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: Intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(1): 106–112. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900107. [2] PAN Cunhua, ZHOU Gui, ZHI Kangda, et al. An overview of signal processing techniques for RIS/IRS-aided wireless systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2022, 16(5): 883–917. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2022.3195671. [3] 陈新颖, 盛敏, 李博, 等. 面向6G的无人机通信综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(3): 781–789. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210789.CHEN Xinying, SHENG Min, LI Bo, et al. Survey on unmanned aerial vehicle communications for 6G[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(3): 781–789. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210789. [4] CHEN Zhen, CHEN Gaojie, TANG Jie, et al. Reconfigurable-intelligent-surface-assisted B5G/6G wireless communications: Challenges, solution, and future opportunities[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2023, 61(1): 16–22. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.002.2200047. [5] BOYER C. ETSI launches a new group on reconfigurable intelligent surfaces[EB/OL]. https://www.etsi.org/technologies/reconfigurable-intelligent-surfaces, 2021. [6] 马红兵, 张平, 杨帆, 等. 智能超表面技术展望与思考[J]. 中兴通讯技术, 2022, 28(3): 70–77. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202203012.MA Hongbing, ZHANG Ping, YANG Fan, et al. Reflections on reconfigurable intelligent surface technology[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2022, 28(3): 70–77. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202203012. [7] NEMATI M, PARK J, and CHOI J. RIS-assisted coverage enhancement in millimeter-wave cellular networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 188171–188185. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3031392. [8] TISHCHENKO A, ALI A, BOTHAM P, et al. Reflective metasurface for 5G mmWave coverage enhancement[C]. 2022 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Sydney, Australia, 2022: 507–508. doi: 10.1109/ISAP53582.2022.9998700. [9] NTONTIN K, BOULOGEORGOS A A A, SELIMIS D G, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface optimal placement in millimeter-wave networks[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2021, 2: 704–718. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2021.3068790. [10] AMALDI E, CAPONE A, CESANA M, et al. WLAN coverage planning: Optimization models and algorithms[C]. IEEE 59th Vehicular Technology Conference. VTC 2004-Spring, Milan, Italy, 2004: 2219–2223. doi: 10.1109/VETECS.2004.1390668. [11] FORTUNE S J, GAY D M, KERNIGHAN B W, et al. WISE design of indoor wireless systems: Practical computation and optimization[J]. IEEE Computational Science and Engineering, 1995, 2(1): 58–68. doi: 10.1109/99.372944. [12] LING Bifeng, LÜ Jiangbin, and FU Liqun. Placement optimization and power control in intelligent reflecting surface aided multiuser system[C]. 2021 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Madrid, Spain, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM46510.2021.9686030. [13] YOU Changsheng, ZHENG Beixiong, MEI Weidong, et al. How to deploy intelligent reflecting surfaces in Wireless Network: BS-Side, user-side, or both sides?[J]. Journal of Communications and Information Networks, 2022, 7(1): 1–10. doi: 10.23919/JCIN.2022.9745477. [14] KAYRAKLIK S, YILDIRIM I, GEVEZ Y, et al. Indoor coverage enhancement for RIS-assisted communication systems: Practical measurements and efficient grouping[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Rome, Italy, 2023: 485–490. doi: 10.1109/ICC45041.2023.10278759. [15] TOHIDI E, HAESLOOP S, THIELE L, et al. Near-optimal LOS and orientation aware intelligent reflecting surface placement[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Rome, Italy, 2023: 498–504. doi: 10.1109/ICC45041.2023.10279027. [16] KHEYFITS A. The theorem of cosines for pyramids[J]. The College Mathematics Journal, 2004, 35(5): 385–388. doi: 10.2307/4146849. [17] KARATAŞ M. A multi foci closed curve: Cassini Oval, its properties and applications[J]. Doğuş Üniversitesi Dergisi, 2013, 2(14): 231–248. doi: 10.31671/dogus.2018.108. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
