An RIS assisted Wideband Millimeter Wave SISO-Based Positioning Method
-
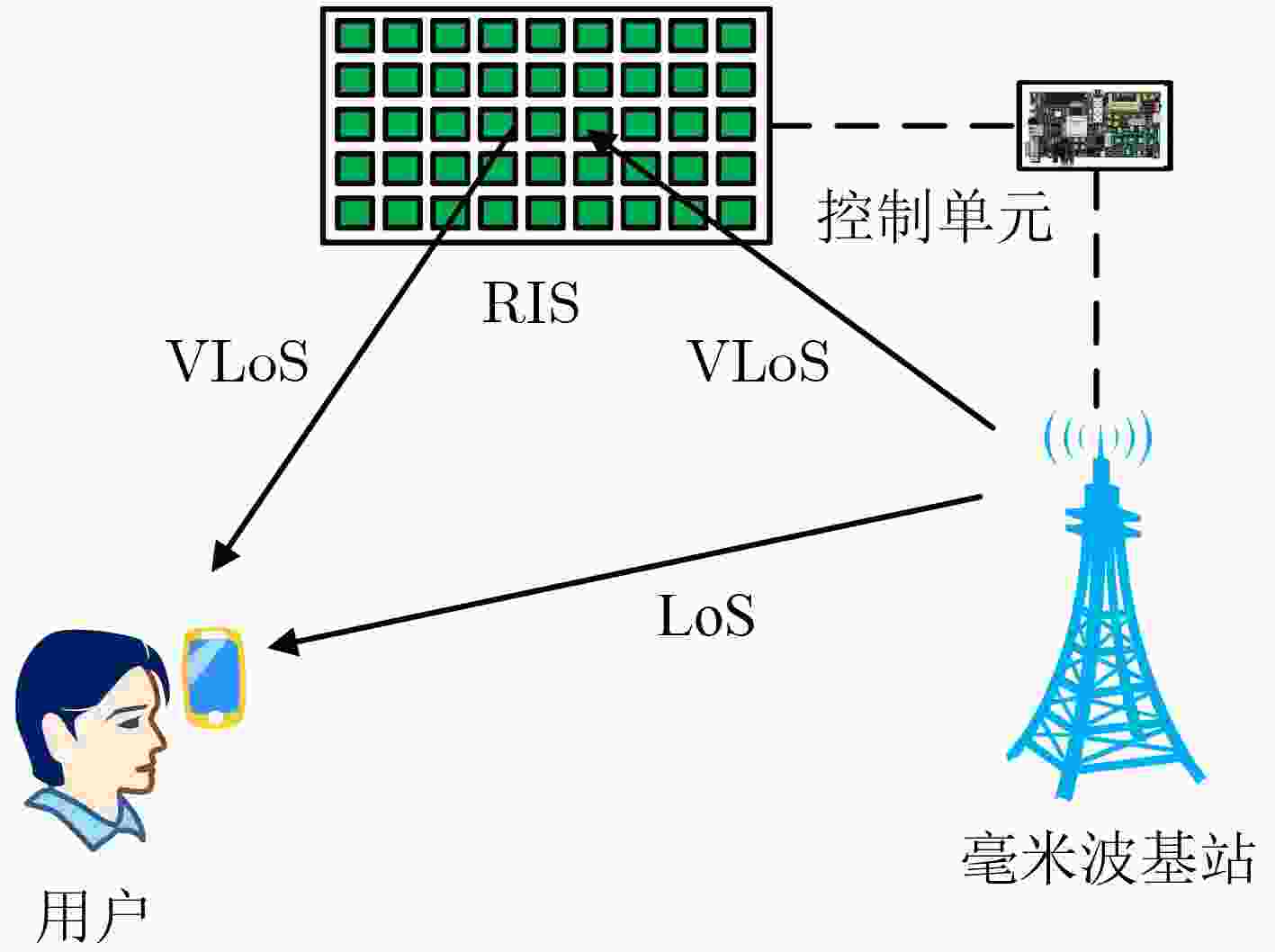
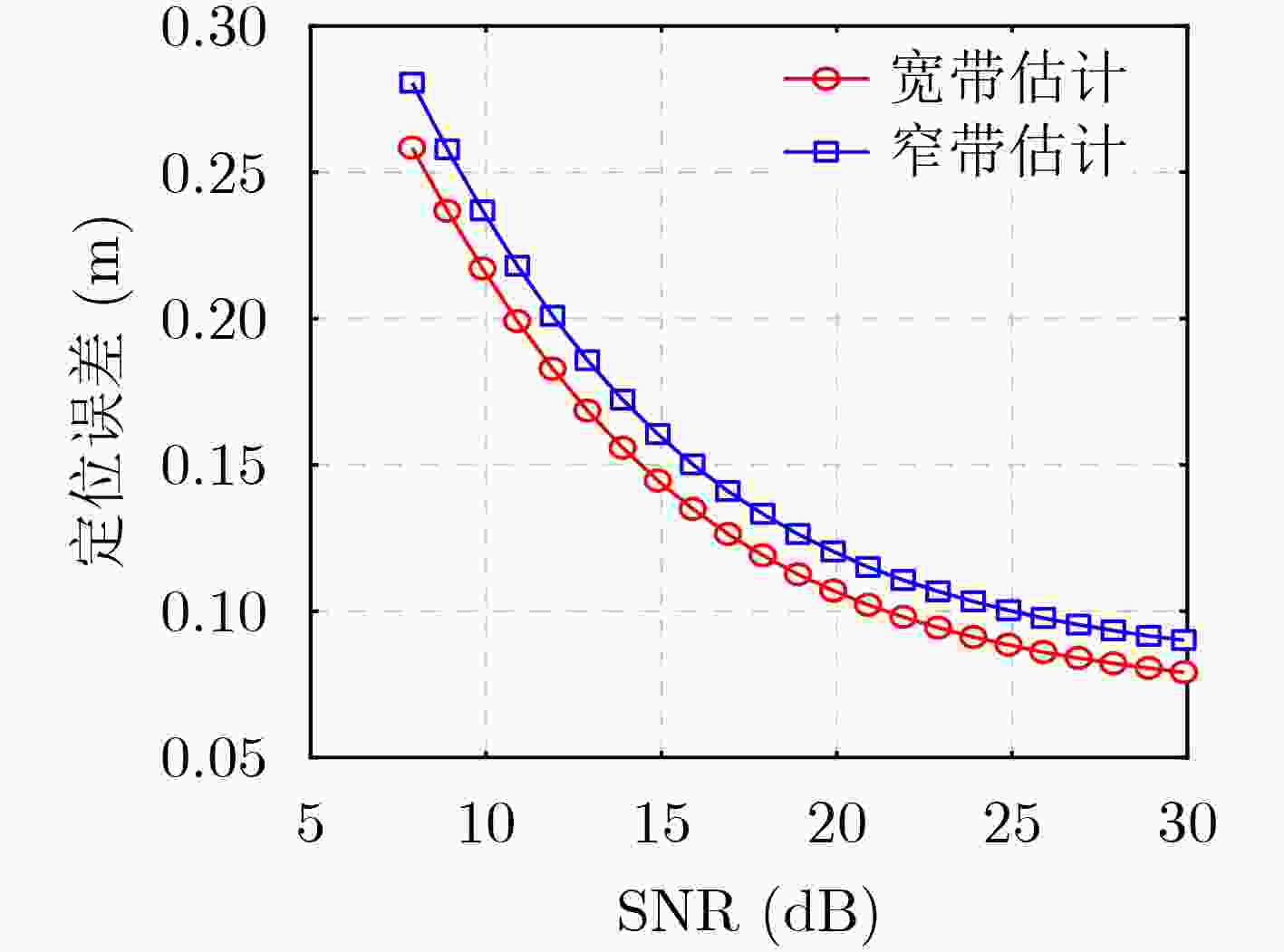
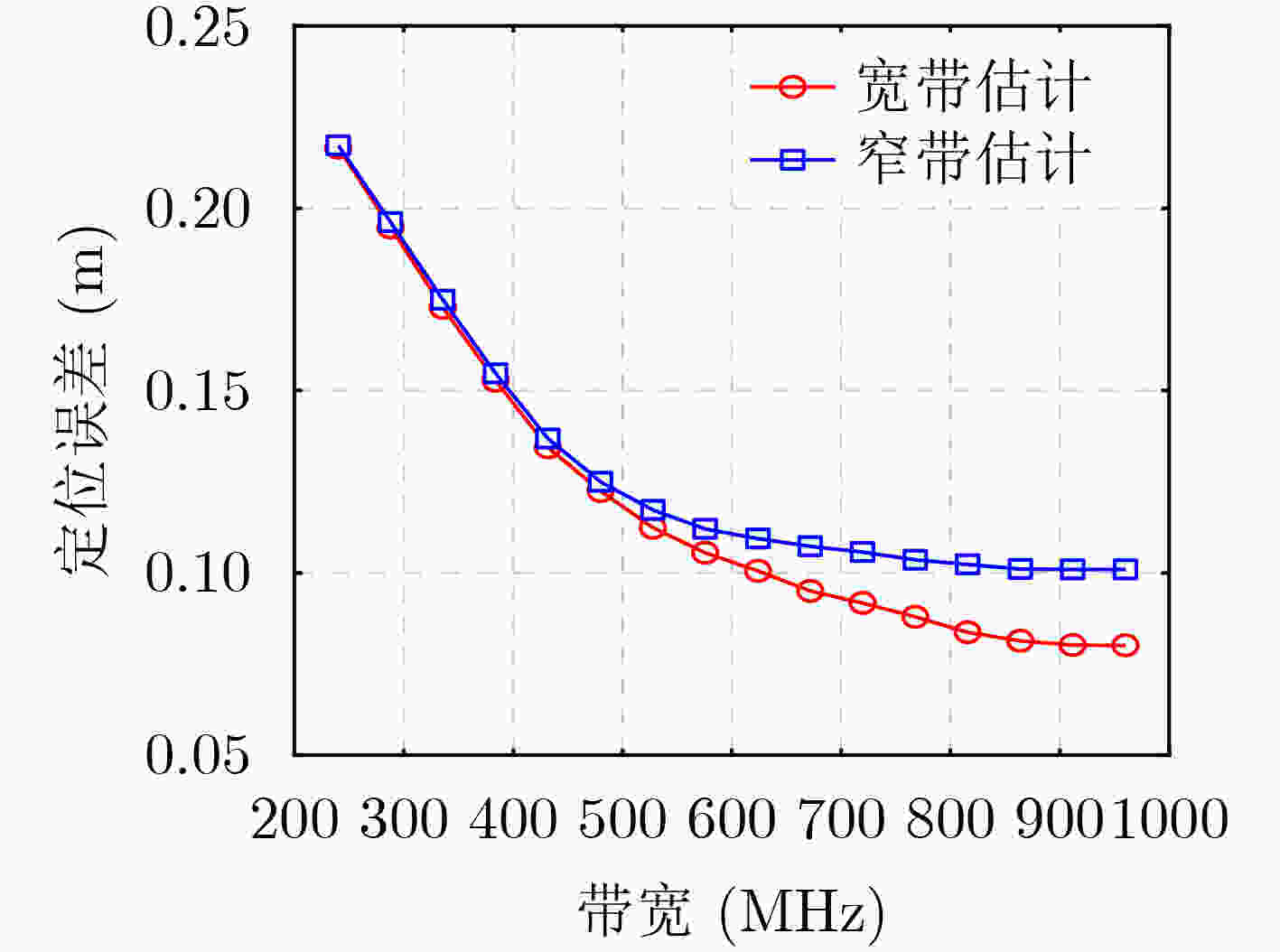
摘要: 针对毫米波定位过程中空间宽带效应产生的影响,该文基于可重构智能超表面(RIS)和单输入单输出(SISO)毫米波系统提出一种新颖的3维(3D)定位估计方法。首先,通过设计RIS相位,利用快速傅里叶逆变换(IFFT)粗略地估计直射路径的视距(LoS)时延、RIS路径的虚拟视距(VLoS)时延以及RIS与用户之间的出发角(AoD)等信道参数。然后,利用拟牛顿法修正上述参数进而估计用户的位置坐标。通过仿真模拟对比了所提宽带估计方法和传统的窄带估计方法的定位性能,结果表明,通过考虑空间宽带效应,带宽为240 MHz时定位精度大约可提高10%,随着带宽增大超过800 MHz时定位性能可提高超过20%。Abstract: For the effects of spatial-wideband effects during millimeter wave positioning, a novel 3-Dimensional (3D) positioning estimation method based on Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) and Single Input Single Output (SISO) millimeter wave system is proposed. First, by designing the RIS phase profiles, the channel parameters of the direct Line-of-Sight (LoS) delay, the RIS-aided Virtual Line-of-Sight (VLoS) delay, and the Angle-of-Departure (AoD) between the RIS and the user are coarsely estimated based on the Inverse Fast Fourier Transform (IFFT). Then, the quasi-Newton method is used to refine these parameters and to estimate the location of the user. Simulations are conducted to compare the positioning performance of the proposed spatial-wideband estimation method with that of the traditional narrowband estimation method. The results show that by taking into account the spatial-wideband effects, the positioning accuracy can be improved by approximately 10% for a bandwidth of 480 MHz and by more than 20% as the bandwidth increases beyond 800 MHz.
-
算法1 基于RIS的毫米波SISO系统定位算法 输入:接收信号${\mathbf{Y}}$ 输出:用户估计位置${\mathbf{\hat u}}$ 1:定义矩阵$ {{\mathbf{Z}}_{\text{b}}} $并利用IFFT估计${\hat k_{\text{b}}}$ 2:粗估计LoS时延${\tilde \tau _{\text{b}}}$ 3:利用拟牛顿法准确估计LoS时延${\hat \tau _{\text{b}}}$ 4:估计LoS复信道增益$ {\hat \rho _{\text{b}}} $ 5:定义矩阵$ {{\mathbf{Z}}_{\text{r}}} $并利用IFFT估计${\hat k_{\text{r}}}$ 6:粗估计VLoS时延$ {\tilde \tau _{\text{r}}} $ 7:利用拟牛顿法准确估计VLoS时延${\hat \tau _{\text{r}}}$ 8:粗估计RIS和用户之间的AoD$ {\tilde {\boldsymbol{\phi}} } $ 9:利用拟牛顿法准确估计AoD$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{\phi}} } $ 10:估计RIS和用户之间的距离$ \hat d $ 11:估计用户位置${\mathbf{\hat u}}$ 表 1 仿真参数设置
参数 值 频率${f_{\text{c}}}$ 30 GHz RIS尺寸大小$L$ $64 \times 64$ 子载波间距${\varDelta _f}$ 240 kHz 符号数目$T$ 120 RIS相位束数目$K$ 12 噪声PSD${N_0}$ $ - 174{\text{ dBm/Hz}}$ 噪声因子 8 dB IFFT维度${N_{\text{F}}}$ 4096 基站位置$ {\boldsymbol{p}} $ $\left( {2,2, - 7} \right)$ RIS位置${\boldsymbol{r}}$ $\left( {0,0,0} \right)$ 用户位置$ {\boldsymbol{u}} $ $\left( { - {\text{5/}}\sqrt {\text{2}} ,{\text{5/}}\sqrt {\text{2}} , - 10} \right)$ -
[1] 王丹阳, 薛秀珍, 魏伟, 等. 基于多天线信号合成的优化到达时间差定位算法[J]. 光学技术, 2022, 48(5): 536–540. doi: 10.13741/j.cnki.11-1879/o4.2022.05.004.WANG Danyang, XUE Xiuzhen, WEI Wei, et al. Optimal the time difference of arrival location algorithm localization algorithm based on multi-antenna signal combining[J]. Optical Technique, 2022, 48(5): 536–540. doi: 10.13741/j.cnki.11-1879/o4.2022.05.004. [2] 郭文飞, 齐书峰, 邓玥, 等. 融合TOA/AOD的5G/SINS紧组合导航定位算法分析[J]. 测绘学报, 2023, 52(3): 367–374. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2023.20210555.GUO Wenfei, QI Shufeng, DENG Yue, et al. Analysis of 5G/SINS tightly coupled navigation algorithm with TOA/AOD[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2023, 52(3): 367–374. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2023.20210555. [3] PALACIOS J, BIELSA G, CASARI P, et al. Single- and multiple-access point indoor localization for millimeter-wave networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(3): 1927–1942. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2899313. [4] TALVITIE J, KOIVISTO M, LEVANEN T, et al. High-accuracy joint position and orientation estimation in sparse 5G mmWave channel[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Shanghai, China, 2019: 1–7. [5] SHAHMANSOORI A, UGUEN B, DESTINO G, et al. Tracking position and orientation through millimeter wave lens MIMO in 5G systems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(8): 1222–1226. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2925969. [6] SHAHMANSOORI A, GARCIA G E, DESTINO G, et al. Position and orientation estimation through millimeter-wave MIMO in 5G systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(3): 1822–1835. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2785788. [7] MENDRZIK R, WYMEERSCH H, BAUCH G, et al. Harnessing NLOS components for position and orientation estimation in 5G millimeter wave MIMO[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(1): 93–107. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2877615. [8] FASCISTA A, COLUCCIA A, WYMEERSCH H, et al. Millimeter-wave downlink positioning with a single-antenna receiver[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(9): 4479–4490. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2925618. [9] LIN Zhipeng, LV Tiejun, and MATHIOPOULOS P T. 3-D indoor positioning for millimeter-wave massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(6): 2472–2486. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2797993. [10] GARCIA N, WYMEERSCH H, LARSSON E G, et al. Direct localization for massive MIMO[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(10): 2475–2487. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2666779. [11] GUO Shisheng, ZHAO Qingsong, CUI Guolong, et al. Behind corner targets location using small aperture millimeter wave radar in NLOS urban environment[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 460–470. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2963924. [12] 崔铁军. 电磁超材料—从等效媒质到现场可编程系统[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2020, 50(10): 1427–1461. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2020-0123.CUI Tiejun. Electromagnetic metamaterials-from effective media to field programmable systems[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2020, 50(10): 1427–1461. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2020-0123. [13] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network via joint active and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(11): 5394–5409. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2936025. [14] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: Intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(1): 106–112. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900107. [15] 刘海霞, 易浩, 马向进, 等. 基于无源可重构智能超表面的室内无线信号覆盖增强[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(12): 32–44. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022229.LIU Haixia, YI Hao, MA Xiangjin, et al. Indoor wireless signal coverage and enhancement based on passive reconfigurable intelligent metasurface[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(12): 32–44. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022229. [16] LIU Penglu, LI Yong, CHENG Wei, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface aided NOMA for millimeter-wave massive MIMO with lens antenna array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(5): 4419–4434. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3067938. [17] LIU Yang, SHI Qingjiang, WU Qingqing, et al. Joint node activation, beamforming and phase-shifting control in IoT sensor network assisted by reconfigurable intelligent surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(11): 9325–9340. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3175740. [18] ZHANG Jingwen, ZHENG Zhong, FEI Zesong, et al. Positioning with dual reconfigurable intelligent surfaces in millimeter-wave MIMO systems[C]. 2020 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China, Chongqing, China, 2020: 800–805. [19] ZHANG Haobo, ZHANG Hongliang, DI Boya, et al. Towards ubiquitous positioning by leveraging reconfigurable intelligent surface[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(1): 284–288. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3023130. [20] ABU-SHABAN Z, KEYKHOSRAVI K, KESKIN M F, et al. Near-field localization with a reconfigurable intelligent surface acting as lens[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2021: 1–6. [21] KEYKHOSRAVI K, KESKIN M F, SECO-GRANADOS G, et al. SISO RIS-enabled joint 3D downlink localization and synchronization[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 1–6. [22] RAHAL M, DENIS B, KEYKHOSRAVI K, et al. RIS-enabled localization continuity under near-field conditions[C]. 2021 IEEE 22nd International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications, Lucca, Italy, 2021: 436–440. [23] RINCHI O, ELZANATY A, and ALOUINI M S. Compressive near-field localization for multipath RIS-aided environments[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(6): 1268–1272. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3151036. [24] WANG Wei and ZHANG Wei. Joint beam training and positioning for intelligent reflecting surfaces assisted millimeter wave communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(10): 6282–6297. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3073140. [25] KEYKHOSRAVI K, KESKIN M F, SECO-GRANADOS G, et al. RIS-enabled SISO localization under user mobility and spatial-wideband effects[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2022, 16(5): 1125–1140. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2022.3175036. [26] WANG Bolei, GAO Feifei, JIN Shi, et al. Spatial- and frequency-wideband effects in millimeter-wave massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(13): 3393–3406. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2831628. [27] CAI Mingming, GAO Kang, NIE Ding, et al. Effect of wideband beam squint on codebook design in phased-array wireless systems[C]. 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Washington, D.C., USA, 2016: 1–6. [28] MYERS N J and HEATH R W. InFocus: A spatial coding technique to mitigate misfocus in near-field LoS beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(4): 2193–2209. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3110011. [29] MA Siqi, SHEN Wenqian, AN Jianping, et al. Wideband channel estimation for IRS-aided systems in the face of beam squint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(10): 6240–6253. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3072694. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
