Wireless Spectrum Status Sensing Driven by Few-Shot Learning
-
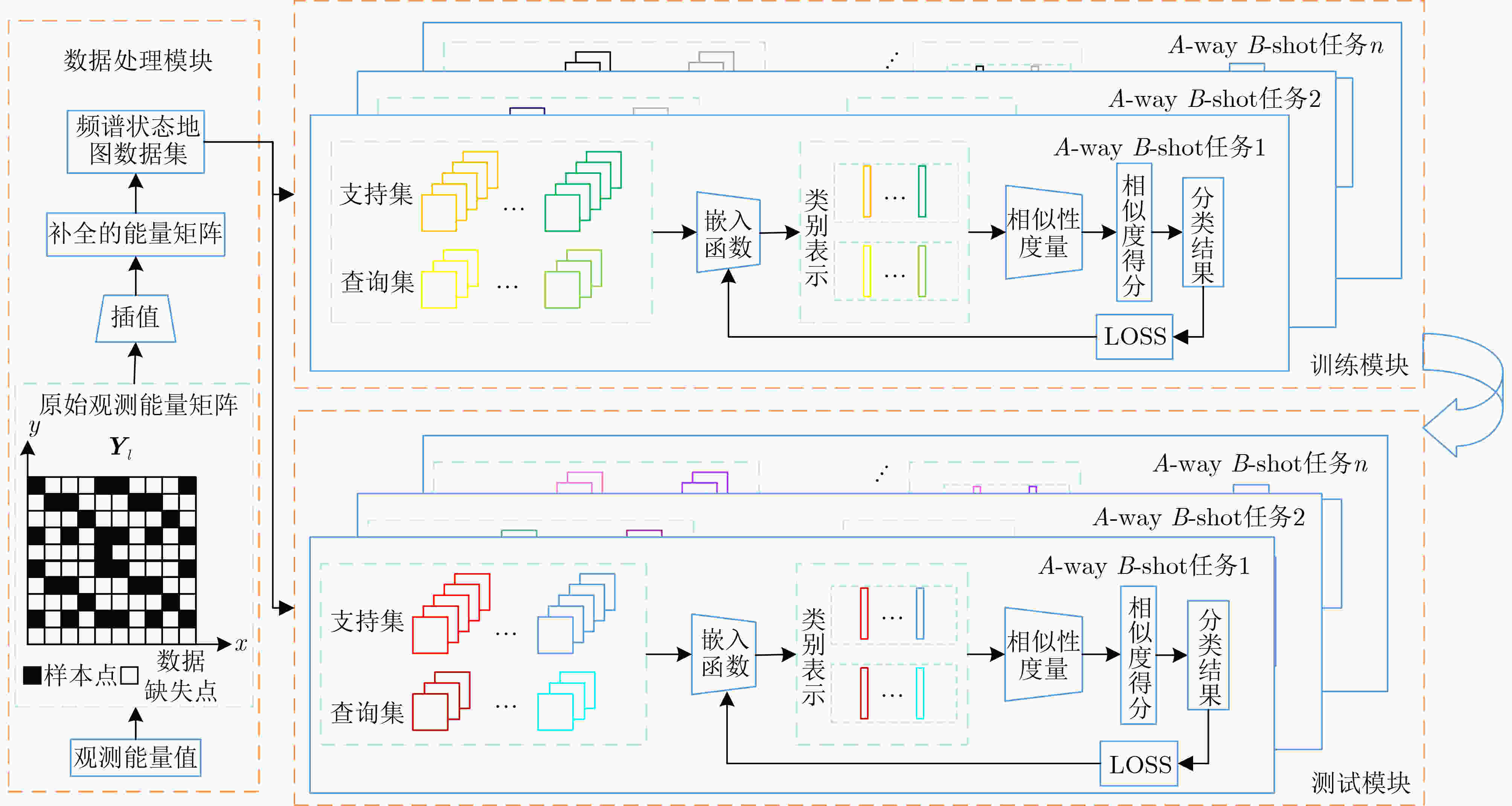
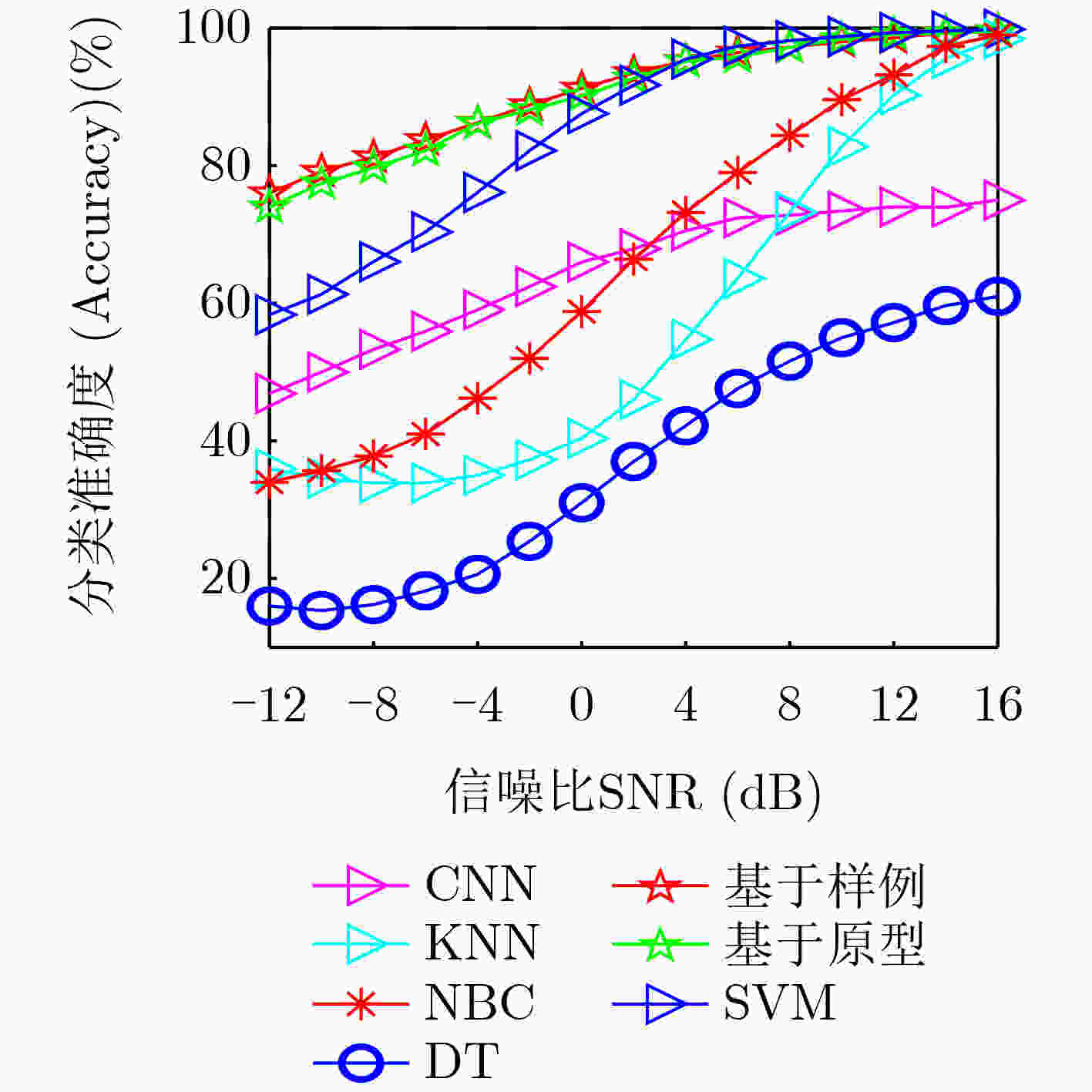
摘要: 无线频谱状态感知是实现无线频谱资源高效利用及各种用频系统和谐共存的先决条件之一。针对复杂无线传播环境下获取的频谱观测往往存在数据稀疏性、数据类别分布不稳定、标记数据严重不足的情况,该文提出基于插值和小样本学习(FSL)分类的无线频谱状态感知方法。首先,对捕获的稀疏频谱观测数据插值,构建频谱状态地图,作为频谱状态分类器的输入数据。其次,针对频谱数据类别分布不稳定、数据量严重不足的问题,基于小样本学习方法,利用嵌入模块和度量模块协同工作,以实现快速精确的频谱状态分类。具体地,利用嵌入模块将频谱数据映射到嵌入空间,提取频谱数据中的隐含特征;在度量模块的设计中,分别提出基于原型和基于样例的两种类别表示方式,通过计算待分类样本与类别之间的相似度判断待分类样本类别。最后,为了确保分类模型克服测试样本数量少导致过拟合问题,设置A-way B-shot任务训练模型。仿真结果表明,与传统机器学习方法相比,本文模型可以在低信噪比条件下进行精准分类;同时,在测试集样本数很少的情况下,或者在测试集中出现在训练集从未见到的新类时,所训练的模型也可以精准快速判别无线频谱的场景类别。Abstract: Wireless spectrum status sensing is one of the prerequisites for achieving efficient utilization of spectrum resources and harmonious coexistence among systems. A spectrum sensing scheme based on interpolation and Few-Shot Learning(FSL) classification is proposed to address the sparsity of spectrum data, unstable distribution of data categories, and severe shortage of labeled data in complex wireless propagation environments. Firstly, the sparsely distributed observation data is interpolated and a spectral status map is constructed as the input data to the spectral status classifier. Then, for the cases where the distributions of data categories are unstable and the amount of data is severely insufficient, a few-shot learning-based classification algorithm is proposed, incorporating the embedding modules and measurement modules to realize fast and accurate spectrum status classification. Specifically, the embedding module is used to map spectral data to the embedding space and extract hidden image features from the spectral data. In the measurement module, two category representation methods, prototype-based and sample-based, are proposed to determine the category of the samples by calculating the similarity between the samples and the categories. Finally, an A-way B-shot task training model is set to ensure that the classification model will not cause overfitting problems due to the small number of test samples. Simulation results show that compared with traditional machine learning methods, the proposed model can achieve accurate classification under low signal-to-noise ratio conditions. In addition, it can quickly distinguish the categories of radiation source activity scenarios even when the number of samples in the test set is small or when new classes that have never been seen in the training set appear in the test set.
-
Key words:
- Spectrum status sensing /
- Spectrum status map /
- Interpolation /
- Few Shot Learning(FSL)
-
1 基于原型的度量学习训练集损失计算
输入:$ {S_{{\mathrm{tr}}}} $, $ {Q_{{\mathrm{tr}}}} $,$ \varphi $ 输出:随机生成的训练episode的损失$ J $ (1) $ {u_i} \in {\mathrm{Random}}\left( {\left[ {0,1, \cdots ,{2^N} - 1} \right],{N_{{\mathrm{tr}}}}} \right) $ (2) For i in $ \left\{ {1,2, \cdots ,{N_{{\mathrm{tr}}}}} \right\} $ do (3) $ {c_{{N_{{\mathrm{tr}}}}}} \leftarrow \dfrac{1}{{\left| {{S_{{\mathrm{tr}}}}} \right|}}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{\left( {{{\boldsymbol{Y}}_i},{u_i}} \right) \in {S_{\rm{tr}}}} {{f_\varphi }} \left( {{{\boldsymbol{Y}}_i}} \right) $ (4) End for (5) $ J \leftarrow 0 $ (6) For i in $ \left\{ {1,2, \cdots ,{N_{{\mathrm{tr}}}}} \right\} $ do (7) For $ \left( {{{\boldsymbol{Y}}^ * },u} \right) $ in $ {Q_{{\mathrm{tr}}}} $ do $ (8) \;\;{p_\varphi }\left( {u = {u_{{N_{{\mathrm{tr}}}}}}\mid {{\boldsymbol{Y}}^ * }} \right) = \dfrac{{{\text{exp}}\left( { - d\left( {{f_\varphi }\left( {{{\boldsymbol{Y}}^ * }} \right),{c_{{N_{\rm{tr}}}}}} \right)} \right)}}{{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{{{N'}_{{\mathrm{tr}}}}} {{\text{exp}}\left( { - d\left( {{f_\varphi }\left( {{{\boldsymbol{Y}}^ * }} \right),{{c}'_{{N_{{\mathrm{tr}}}}}}} \right)} \right)} }} $ (9) $ J\left( \varphi \right) = - {\text{ln}}\:{p_\varphi }\left( {u = {u_{{N_{{\mathrm{tr}}}}}}\mid {{\boldsymbol{Y}}^ * }} \right) $ (10) $ J \leftarrow J + \dfrac{1}{{{N_{\mathrm{s}}}{N_{\mathrm{q}}}}}J\left( \varphi \right) $ (11) End for (12) End for 2 基于样例的度量学习训练集损失计算
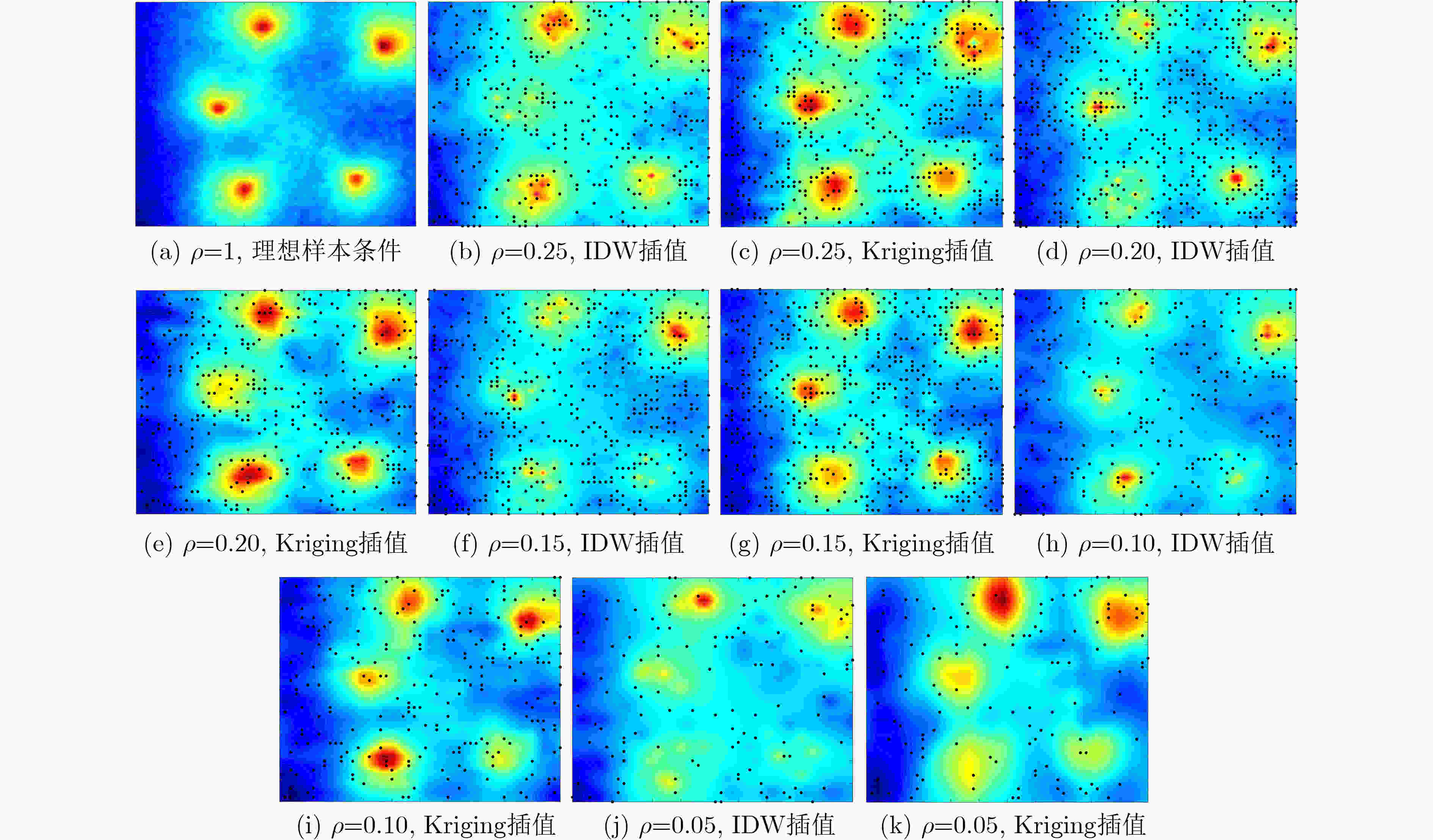
输入:$ {S_{{\mathrm{tr}}}} $, $ {Q_{{\mathrm{tr}}}} $, $ \varphi $, $ \psi $ 输出:随机生成的训练episode的损失$ J $ (1) $ {\mathcal{Y}^*} \leftarrow {g_\psi }({{\boldsymbol{Y}}^*}) $,$ {{\boldsymbol{Y}}^ * } $ in $ {Q_{{\mathrm{tr}}}} $ (2) $ \mathcal{Y} \leftarrow {g_\psi }({\boldsymbol{Y}}) $,$ {\boldsymbol{Y}} $ in $ {S_{{\mathrm{tr}}}} $ (3) $ J \leftarrow 0 $ (4) For i in $ \left\{ {1,2, \cdots ,{N_{{\mathrm{tr}}}}} \right\} $ do (5) For $ \left( {{{\boldsymbol{Y}}^ * },u} \right) $ in $ {Q_{{\mathrm{tr}}}} $ do (6) $ {p_\varphi }\left( {u = {u_{{N_{{\mathrm{tr}}}}}}\mid {{\boldsymbol{Y}}^ * }} \right) = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^{{N_d}} {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 1}^{{N_k}} } \cos\left( {\mathcal{Y}_i^*,\mathcal{Y}_i^j} \right) $ (7) $ J\left( \varphi \right) = - {\text{ln}}\:{p_\varphi }\left( {u = {u_{{N_{{\mathrm{tr}}}}}}\mid {{\boldsymbol{Y}}^ * }} \right) $ (8) $ J \leftarrow J + \dfrac{1}{{{N_{\mathrm{s}}}{N_{\mathrm{q}}}}}J\left( \varphi \right) $ (9) End for (10) End for 表 1 IDW插值法与Kriging插值法RMSE性能比较
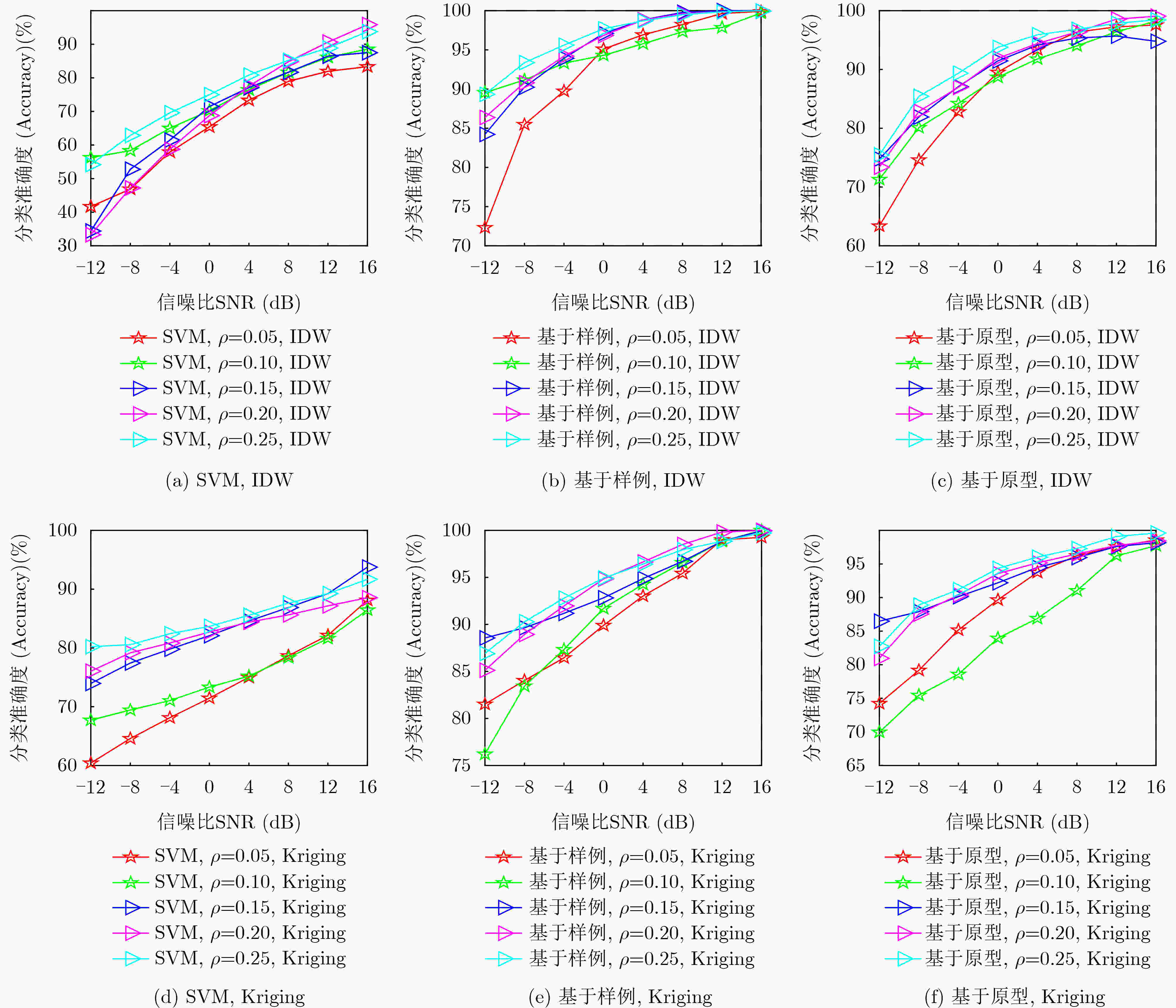
$ \rho $ RMSE IDW Kriging 0.25 0.052 2 0.066 5 0.20 0.060 2 0.080 5 0.15 0.060 5 0.082 5 0.10 0.081 2 0.106 5 0.05 0.092 3 0.125 5 表 2 SVM算法与FSL算法在5-way B-shot条件下的准确度比较
算法名称 5-way 1-shot 5-way 3-shot 5-way 5-shot SVM 0.200 0 0.220 0 0.240 0 基于原型 0.866 4 0.898 5 0.901 4 基于样例 0.956 4 0.975 84 0.997 8 -
[1] KHALEK N A and HAMOUDA W. Unsupervised two-stage learning framework for cooperative spectrum sensing[C]. ICC 2021 - IEEE International Conference on Communications. Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC42927.2021.9500681. [2] KRISHNAKUMAR V, SAVARINATHAN P, KARUPPASAMY T, et al. Machine learning based spectrum sensing and distribution in a cognitive radio network[C]. 2022 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI). Coimbatore, India: IEEE, 2022: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICCCI54379.2022.9740824. [3] LU Yingqi, ZHU Pai, WANG Donglin, et al. Machine learning techniques with probability vector for cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks[C]. 2016 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference. Doha, Qatar: IEEE, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WCNC.2016.7564840. [4] CHEN Siji, SHEN Bin, WANG Xin, et al. SVM and decision stumps based hybrid AdaBoost classification algorithm for cognitive radios[C]. 2019 21st International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT). PyeongChang, Korea (South): IEEE, 2019: 492–497. doi: 10.23919/ICACT.2019.8702007. [5] LIU Chang, WANG Jie, LIU Xuemeng, et al. Deep cm-cnn for spectrum sensing in cognitive radio[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37(10): 2306–2321. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2933892. [6] 盖建新, 薛宪峰, 吴静谊, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络的协作频谱感知方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(10): 2911–2919. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201005.GAI Jianxin, XUE Xianfeng, WU Jingyi, et al. Cooperative spectrum sensing method based on deep convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(10): 2911–2919. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201005. [7] 申滨, 王欣, 陈思吉, 等. 基于机器学习主用户发射模式分类的蜂窝认知无线电网络频谱感知 [J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 92–100. doi: 10.11999/JEIT191012.SHEN Bin, WANG Xin, CHEN Siji, et al. Machine learning based primary user transmit mode classification for spectrum sensing in cellular cognitive radio network[J] Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 92–100. doi: 10.11999/JEIT191012. [8] WANG Yu, WANG Xin, SHEN Bin, et al. Clustering optimization and hog feature extraction based primary user activity scene recognition scheme[C]. 2022 IEEE 95th Vehicular Technology Conference: (VTC2022-Spring). Helsinki, Finland: IEEE, 2022: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/VTC2022-Spring54318.2022.9860431. [9] SONG Yisheng, WANG Tingyuan, CAI Puyu, et al. A comprehensive survey of few-shot learning: Evolution, applications, challenges, and opportunities[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(13s): 271. doi: 10.1145/3582688. [10] TIAN Pinzhuo and GAO Yang. Improving meta-learning model via meta-contrastive loss[J]. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2022, 16(5): 165331. doi: 10.1007/s11704-021-1188-9. [11] VINYALS O, BLUNDELL C, LILLICRAP T, et al. Matching networks for one shot learning[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: Curran Associates Inc., 2016. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1606.04080. [12] LIU Yongfei, ZHANG Xiangyi, ZHANG Songyang, et al. Part-aware prototype network for few-shot semantic segmentation[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58545-7_9. [13] RAVI S and LAROCHELLE H. Optimization as a model for few-shot learning[C]. 5th International Conference on Learning Representations. Toulon, France: OpenReview. net, 2017. [14] FINN C, ABBEEL P, and LEVINE S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks[C]. The 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research(PMLR). PMLR, 2017: 1126-1135. [15] BATENI P, GOYAL R, MASRANI V, et al. Improved few-shot visual classification[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020: 14481–14490. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01450. [16] ZHANG Chi, CAI Yujun, LIN Guosheng, et al. DeepEMD: Few-shot image classification with differentiable earth mover’s distance and structured classifiers[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020: 12200–12210. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01222. [17] SUNG F, YANG Yongxin, ZHANG Li, et al. Learning to compare: Relation network for few-shot learning[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018: 1199–1208. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00131. [18] WANG Yaqing, YAO Quanming, KWOK J T, et al. Generalizing from a few examples: A survey on few-shot learning[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2021, 53(3): 63. doi: 10.1145/3386252. [19] ESHEL A, OSTROMETZKY J, GAT S, et al. Spatial reconstruction of rain fields from wireless telecommunication networks—scenario-dependent analysis of idw-based algorithms[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(5): 770–774. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2935348. [20] DIAGO-MOSQUERA M, ARAGÓN-ZAVALA A, AZPILICUETA L, et al. A 3-D indoor analysis of path loss modeling using kriging techniques[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2022, 21(6): 1218–1222. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2022.3162160. -





 下载:
下载:

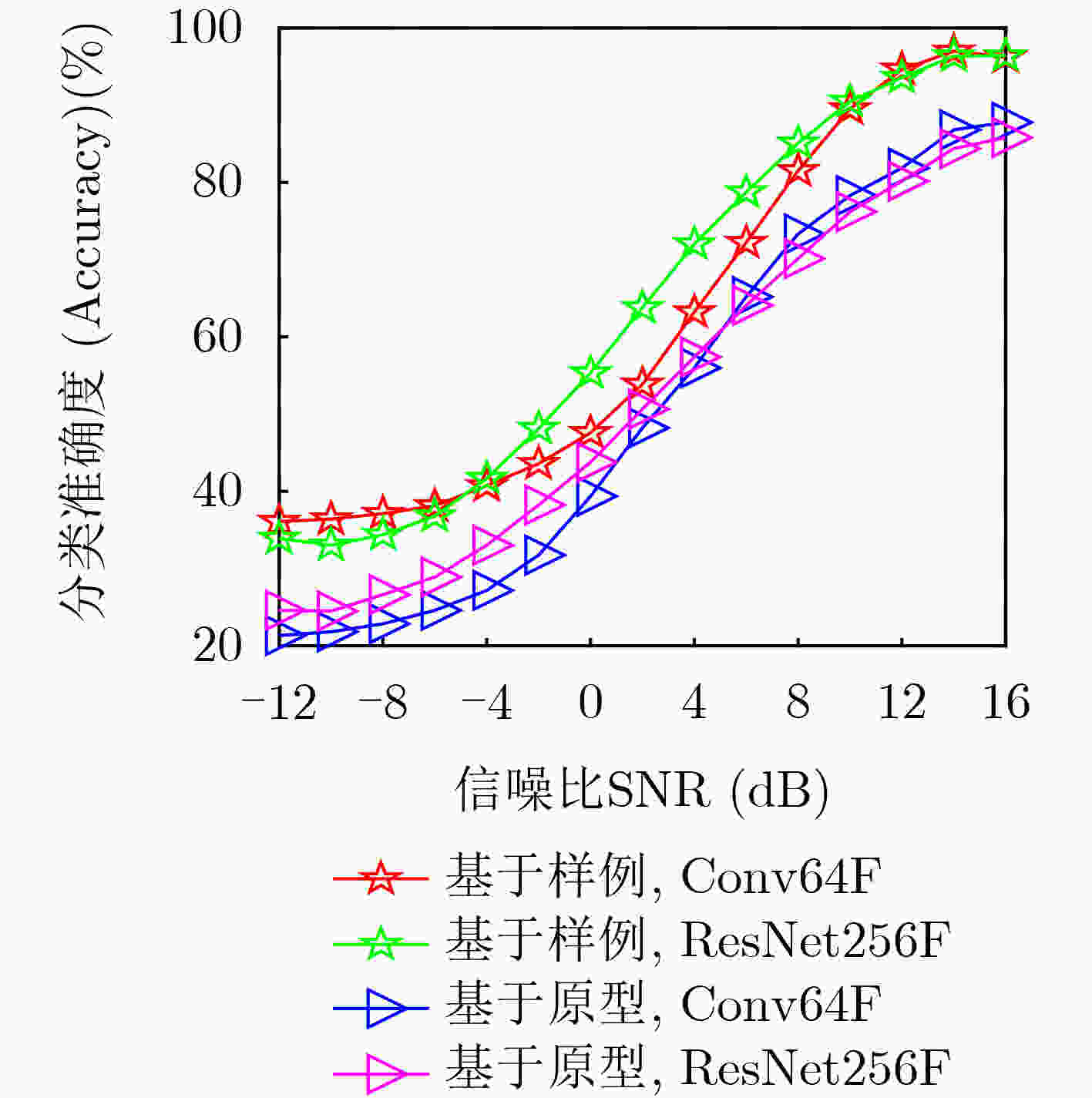
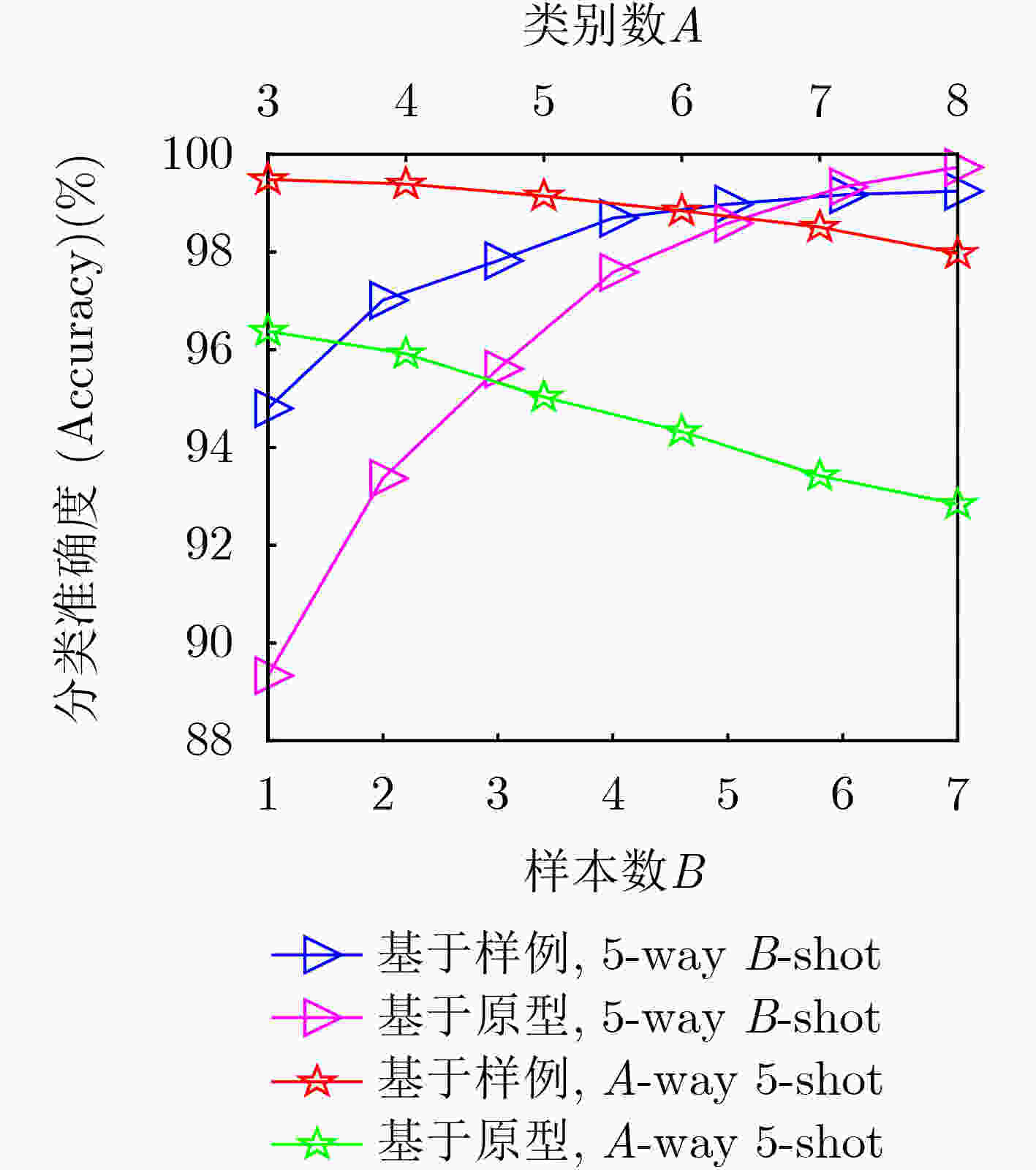


 下载:
下载:
