Memory and Compute-in-Memory Based on Ferroelectric Field Effect Transistors
-
摘要: 近年来,物联网和人工智能等技术的发展对片上存储与智能计算的能效、密度以及性能提出了更高的要求。面对传统CMOS处理器的能效与密度瓶颈,以及传统冯·诺伊曼架构的“存储墙”瓶颈,以铁电晶体管 (FeFET)为代表的新型非易失存储器 (NVM)提供了新的机遇。FeFET具有非易失、高能效、高开关比等特点,非常适合低功耗、高密度场景下的存储与存算一体 (CiM)应用,为数据密集型应用在边缘端的部署提供支持。该文回顾了FeFET的发展历程、结构、特性以及建模相关的工作,概述了FeFET存储器在电路结构和访存机制上的探索与优化。进一步地,该文还探讨了FeFET CiM在非易失计算、存内逻辑计算、矩阵向量乘法以及内容可寻址存储器上的应用。最后,该文从不同方面分析并展望了基于FeFET的存储与CiM电路的前景与挑战。Abstract: Recently, with the development of the Internet of Things and Artificial Intelligence, higher energy efficiency, density, and performance in on-chip memories and intelligent computing are required. Facing the energy efficiency and density bottleneck in conventional CMOS memories and the “memory wall” problem in the Von Neumann architecture, emerging Nonvolatile Memories (NVMs) such as Ferroelectric Field Effect Transistors (FeFETs) bring new opportunities to solve the challenges. FeFETs have the characteristics of non-volatility, ultra-low power, and high on-off ratio, which are very suitable for memories and Compute-in-Memory (CiM) in high-density, low-power scenarios and would support the implementation of data-intensive applications at the edge. This paper first reviews the development, structure, characteristics, and modeling of FeFETs. Then, the exploration and optimization of FeFET-based memories with different circuit structures and characteristics are discussed. Further, this paper summarizes the FeFET-based CiM circuits, including nonvolatile computing, logic-in-memory, matrix-vector multiplication, and content-addressable memories. Finally, the prospects and challenges of FeFET-based memory and CiM are analyzed.
-
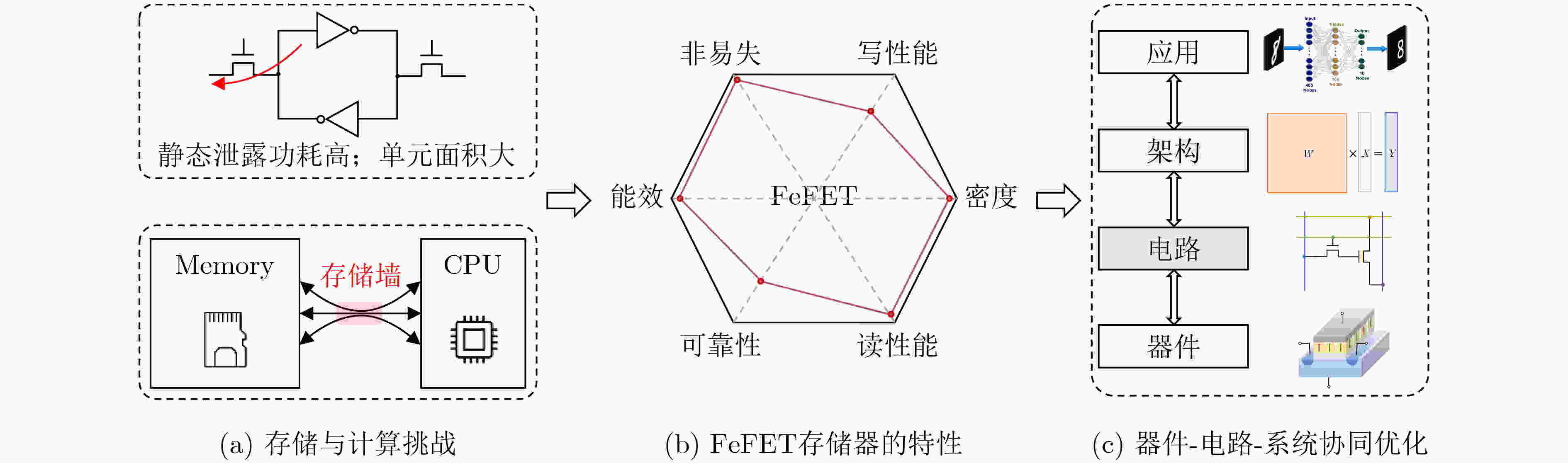
图 1 基于FeFET的存储与CiM电路的背景与挑战[12]
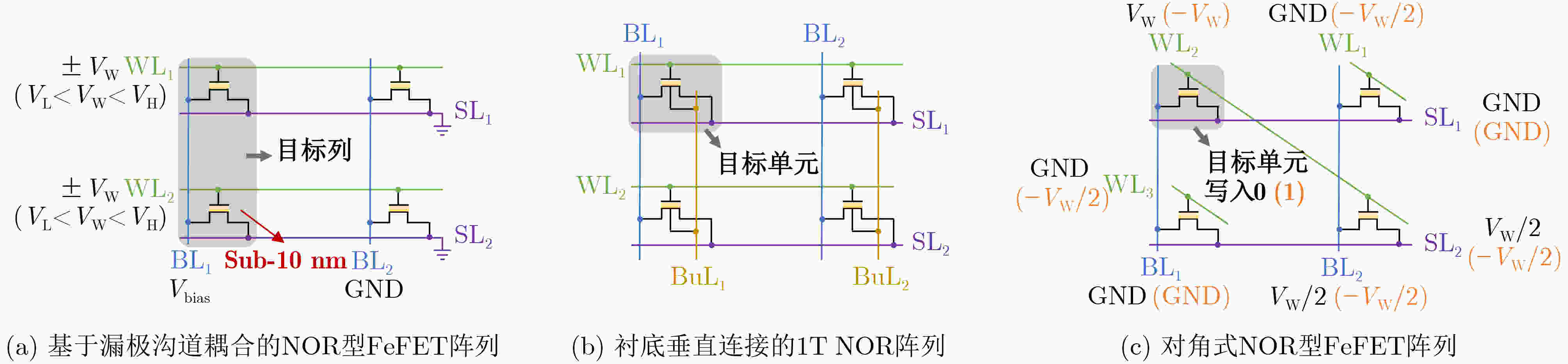
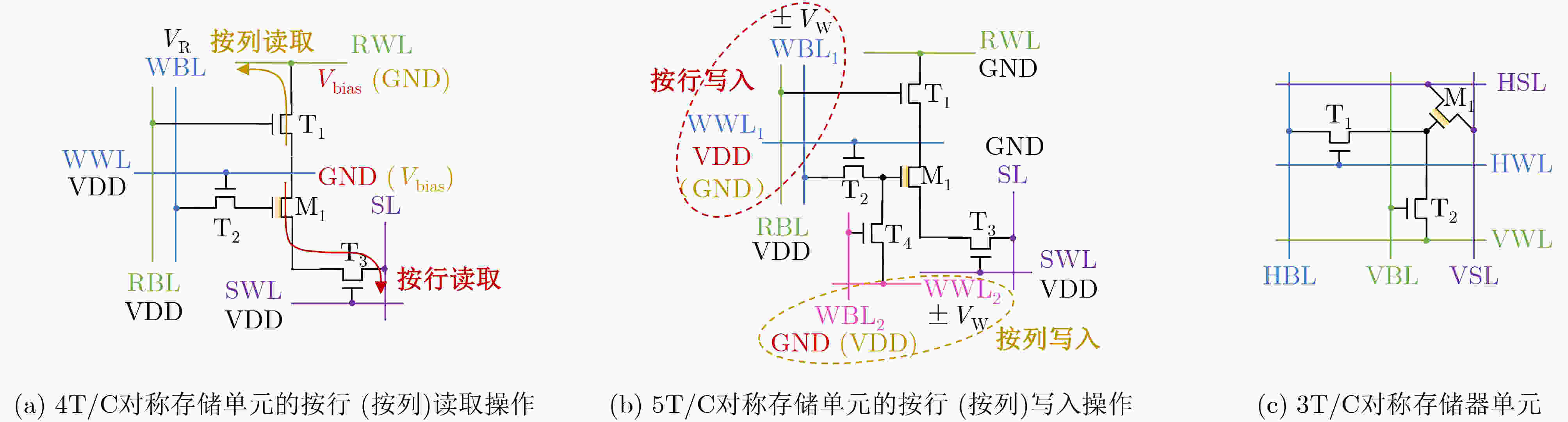
图 4 FeFET在3种1T/C典型存储阵列结构中的应用[39]
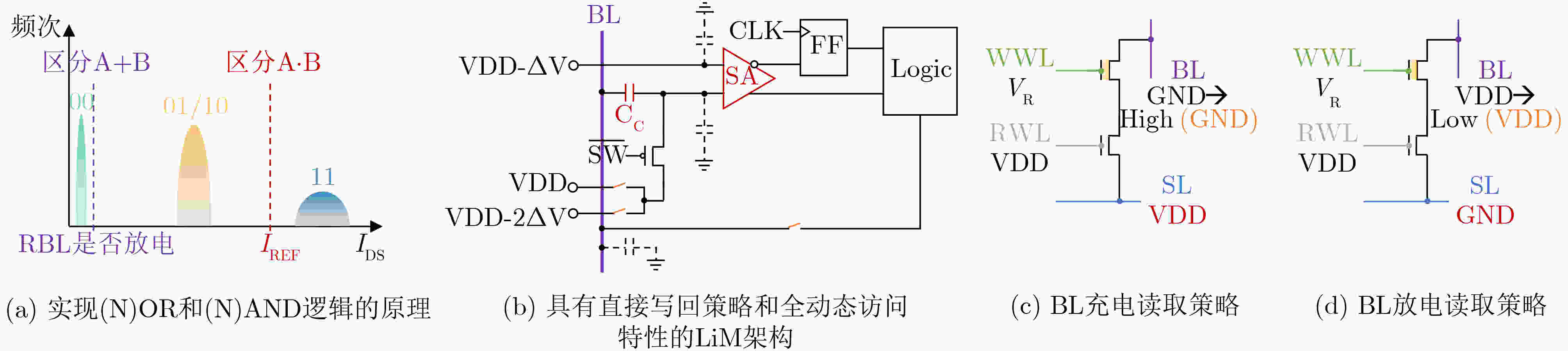
图 9 LiM实现逻辑计算的原理、全动态FeFET LiM架构及其不同读取操作[63]
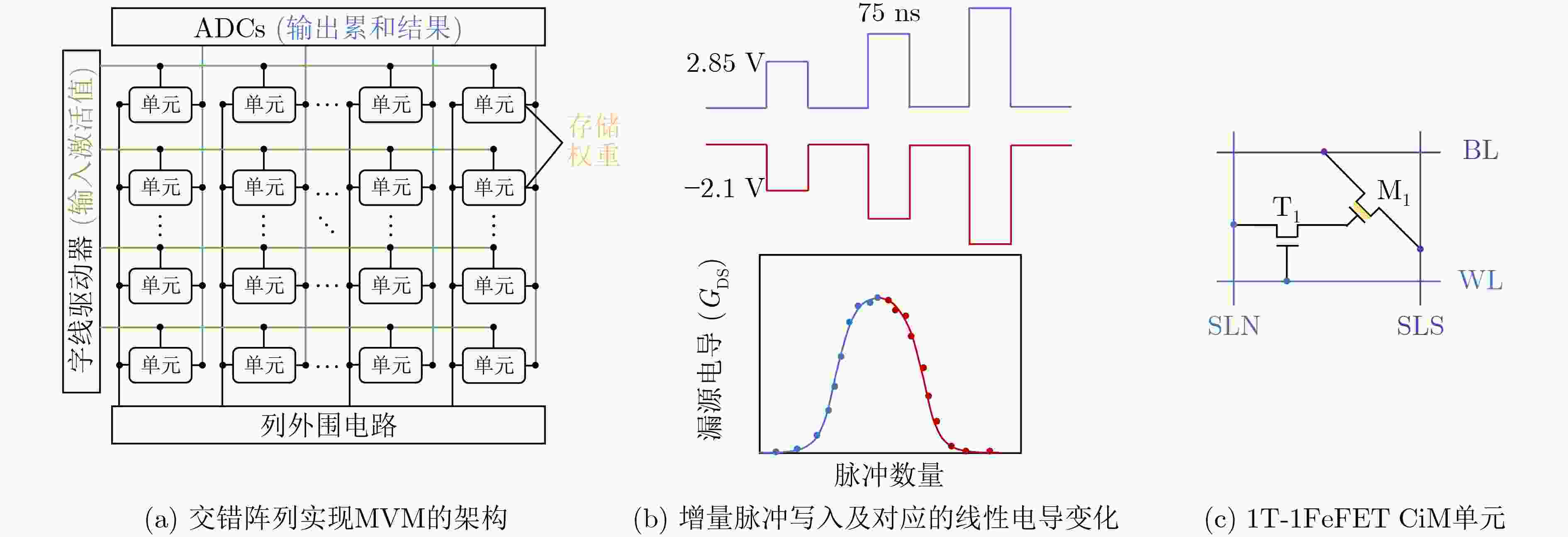
图 10 基于FeFET的MVM CiM架构、原理及单元[64]
表 1 不同存储阵列的关键参数和性能指标对比
存储器类型 SRAM[34] eDRAM[35] eFlash[36] RRAM[5,6] STT-MRAM[7,8] PCM[9,37] FeRAM[38] FeFET[21,25] 单元面积 (F2) 120~150 40 40~60 10~30 10~30 10~30 30~40 10~30 单元结构 6T 1T-1C 1T 1T-1R 1T-1MTJ 1T-1PCM 1T-1C 1T 易失/非易失性 易失 易失 非易失 非易失 非易失 非易失 非易失 非易失 写入电压 (V) 0.7-1.0 0.8-1.1 ~10 <2 ~1 <3 <3 <4 写入能量 ~1 fJ ~10 fJ ~100 pJ ~1 pJ ~5 pJ ~10 pJ ~100 fJ ~10 fJ 写入速度 0.5~0.8 ns ~0.8 ns 0.01-4 ms <10 ns <20 ns <100 ns <10 ns <10 ns 读取速度 (ns) 0.5~0.8 ~0.8 ~10 <10 <10 ~15 <10 <10 阵列寿命 >1016 >1016 104-105 >106 >1014 >108 >1012 >105 器件寿命 >1016 >1016 104-105 >1012 >1015 >1012 >1014 >1012 器件偏差 小 中 中 大 中 中 中 中 开关比 高 中 高 中 小 中 中 高 读破坏性 无 有 无 无 无 无 有 无 量产情况 TSMC 3 nm
三星 3 nm
Intel 4TSMC 40 nm
三星 45 nm
Intel 22 nmTSMC 40 nm
三星 45 nmTSMC
40/22 nmTSMC 22 nm
三星 28 nm
GF 28 nmIntel 3D
XPointFujitsu
130 nmGF 22 nm
未量产主要应用 缓存 大容量缓存 eNVM eNVM 缓存/eNVM 内存/SSD eNVM eNVM 表 2 不同结构的FeFET存储阵列特性对比
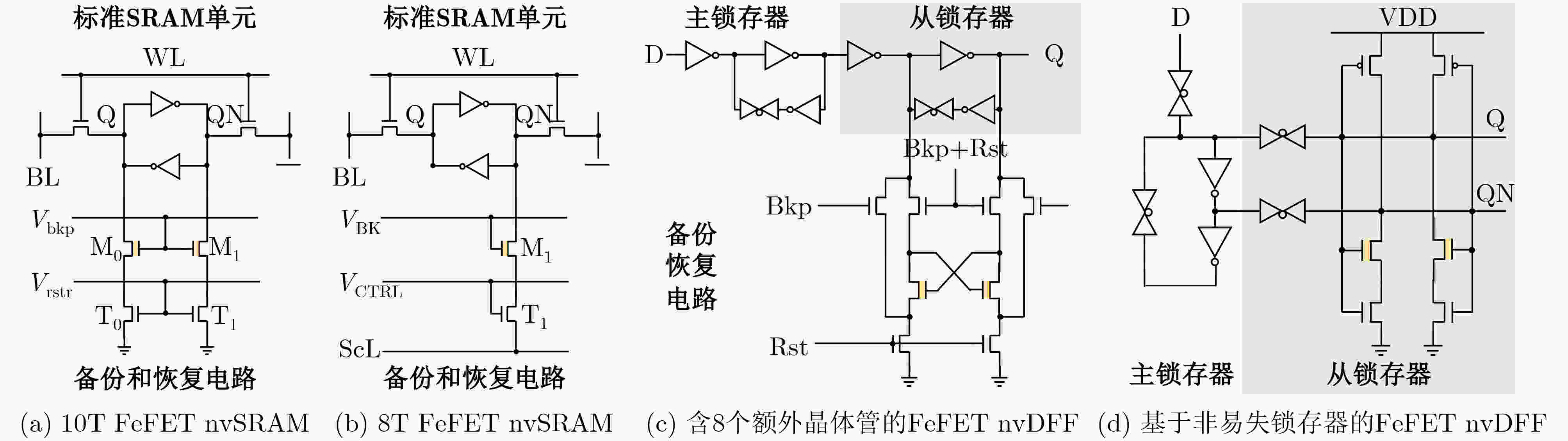
存储阵列结构 密度 写入策略 写入能效 电源电压 写干扰 其他特性 主要应用前景 技术成熟度 1T NAND[39] 极高 两步写 高 2VDD 有 读干扰严重 3D堆叠大容量存储 阵列制备 1T AND[39] 高 两步写 高 VDD 有 两种写入策略 eNVM/CiM 测试样片 传统1T NOR[39] 高 两步写 低 2VDD 有 \ CiM 阵列制备 漏极沟道耦合的1T NOR[40] 高 一步写 低 2VDD 有 仅限sub-10 nm 先进工艺存储 仿真 C-AND[41] 高 两步写 高 2VDD 有 无法写入LRS 无法应用 仿真 源/漏极浮空的1T NOR[42] 高 两步写 高 2VDD 有 不对称、速度慢 eNVM 器件 整行擦除的1T NOR[10] 高 两步写 高 2VDD 有 \ eNVM/CiM 器件 对角式1T NOR[10] 中 两步写 高 2VDD 有 \ eNVM 器件 栅极选通的2T[43] 中 一步写 高 2VDD 无 \ eNVM/CiM 仿真 源极选通的2T[44] 中 两步写 高 VDD 无 \ 非易失处理/eNVM 仿真 3T[44] 低 两步写 高 VDD 无 \ 非易失处理/eNVM 仿真 -
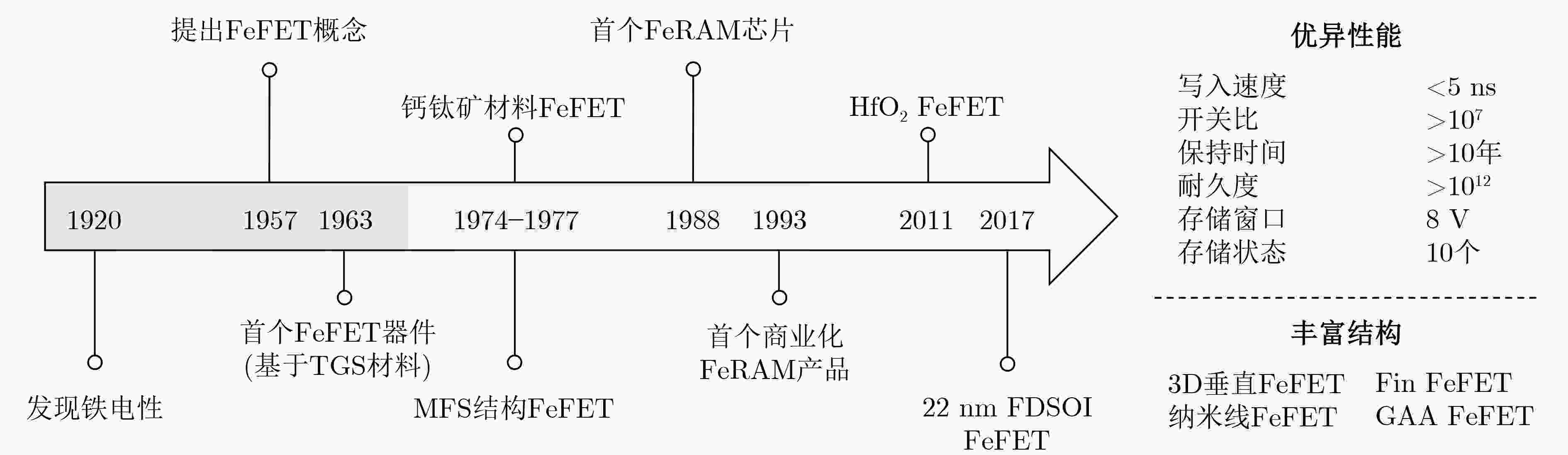
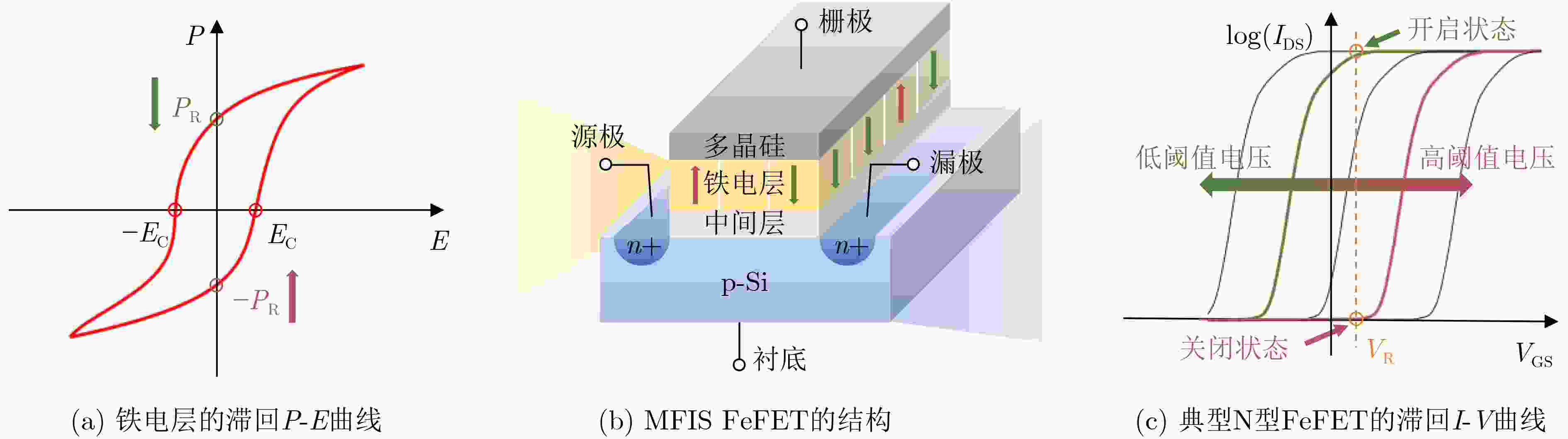
[1] SALAHUDDIN S, NI Kai, and DATTA S. The era of hyper-scaling in electronics[J]. Nature Electronics, 2018, 1(8): 442–450. doi: 10.1038/s41928-018-0117-x [2] REUTHER A, MICHALEAS P, JONES M, et al. AI accelerator survey and trends[C]. 2021 IEEE High Performance Extreme Computing Conference (HPEC), Waltham, USA, 2021: 1–9. [3] LI Xueqing and LAI Longqiang. Nonvolatile memory and computing using emerging ferroelectric transistors[C]. 2018 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI), Hong Kong, China, 2018: 750–755. [4] CHANG C H, CHANG V S, PAN K H, et al. Critical process features enabling aggressive contacted gate pitch scaling for 3nm CMOS technology and beyond[C]. 2022 International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA, 2022: 27.1. 1–27.1. 4. [5] REHMAN M M, REHMAN H M M U, GUL J Z, et al. Decade of 2D-materials-based RRAM devices: A review[J]. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2020, 21(1): 147–186. doi: 10.1080/14686996.2020.1730236 [6] CHEN Zixuan, WU Huaqiang, GAO Bin, et al. Performance improvements by SL-current limiter and novel programming methods on 16MB RRAM chip[C]. 2017 IEEE International Memory Workshop (IMW), Monterey, USA, 2017: 1–4. [7] IKEGAWA S, NAGEL K, MANCOFF F B, et al. High-speed (400MB/s) and low-BER STT-MRAM technology for industrial applications[C]. 2022 International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA, 2022: 10.4. 1–10.4. 4. [8] LEE T Y, LEE J M, KIM M K, et al. World-most energy-efficient MRAM technology for non-volatile RAM applications[C]. 2022 International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA, 2022: 10.7. 1–10.7. 4. [9] MIN D, PARK J, WEBER O, et al. 18nm FDSOI technology platform embedding PCM & innovative continuous-active construct enhancing performance for leading-edge MCU applications[C]. 2021 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA, 2021: 13.1. 1–13.1. 4. [10] XIAO Yi, XU Yixin, JIANG Zhouhang, et al. On the write schemes and efficiency of FeFET 1T NOR array for embedded nonvolatile memory and beyond[C]. 2022 International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA, 2022: 13.6. 1–13.6. 4. [11] DUTTA S, YE H, CHAKRABORTY W, et al. Monolithic 3D integration of high endurance multi-bit ferroelectric FET for accelerating compute-in-memory[C]. 2020 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA, 2020: 36.4. 1–36.4. 4. [12] MULAOSMANOVIC H, BREYER E T, DÜNKEL S, et al. Ferroelectric field-effect transistors based on HfO2: A review[J]. Nanotechnology, 2021, 32(50): 502002. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ac189f [13] VALASEK J. Piezo-electric and allied phenomena in Rochelle salt[J]. Physical Review, 1921, 17(4): 475–481. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.17.475 [14] MORTON J A. Electrical switching and storage[P]. US Patent, US-2791761-A, 1957-05-07. [15] MOLL J L and TARUI Y. A new solid state memory resistor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 1963, 10(5): 338. doi: 10.1109/T-ED.1963.15245 [16] HIGUMA Y, MATSUI Y, OKUYAMA M, et al. "MFS FET" -a new type of nonvolatile memory switch using PLZT film[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1978, 17(S1): 209–214. doi: 10.7567/JJAPS.17S1.209 [17] BATRA I P, WURFEL P, and SILVERMAN B D. Phase transition, stability, and depolarization field in ferroelectric thin films[J]. Physical Review B, 1973, 8(7): 3257–3265. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.8.3257 [18] WU S Y. A new ferroelectric memory device, metal-ferroelectric-semiconductor transistor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 1974, 21(8): 499–504. doi: 10.1109/T-ED.1974.17955 [19] KHAN A I, KESHAVARZI A, and DATTA S. The future of ferroelectric field-effect transistor technology[J]. Nature Electronics, 2020, 3(10): 588–597. doi: 10.1038/s41928-020-00492-7 [20] BÖSCKE T S, MÜLLER J, BRÄUHAUS D, et al. Ferroelectricity in hafnium oxide: CMOS compatible ferroelectric field effect transistors[C]. 2011 International Electron Devices Meeting, Washington, USA, 2011: 24.5. 1–24.5. 4. [21] DÜNKEL S, TRENTZSCH M, RICHTER R, et al. A FeFET based super-low-power ultra-fast embedded NVM technology for 22nm FDSOI and beyond[C]. 2017 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 19.7. 1–19.7. 4. [22] FU Tianyue, ZENG Min, LIU Shiyuan, et al. Record-high 2Pr=60 μC/cm2 by Sub-5ns switching pulse in ferroelectric lanthanum-doped HfO2 with large single grain of orthorhombic phase >38 nm[C]. 2022 International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA, 2022: 6.5. 1–6.5. 4. [23] JERRY M, AZIZ A, NI K, et al. A threshold switch augmented hybrid-FeFET(H-FeFET) with enhanced read distinguishability and reduced programming voltage for non-volatile memory applications[C]. 2018 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology, Honolulu, USA, 2018: 129–130. [24] ZHOU Yuejia, LIANG Zhongxin, LUO Wenpu, et al. Ferroelectric and interlayer co-optimization with in-depth analysis for high endurance FeFET[C]. 2022 International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA, 2022: 6.2. 1–6.2.4. [25] SHARMA A A, DOYLE B, YOO H J, et al. High speed memory operation in channel-last, back-gated ferroelectric transistors[C]. 2020 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA, 2020: 18.5. 1–18.5. 4. [26] ZHENG Zijie, SUN Chen, JIAO Leming, et al. Boosting the memory window of the BEOL-compatible MFMIS ferroelectric/ anti-ferroelectric FETs by charge injection[C]. 2022 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits, Honolulu, USA, 2022: 389–390. [27] MULAOSMANOVIC H, DÜNKEL S, TRENTZSCH M, et al. Investigation of accumulative switching in ferroelectric FETs: Enabling universal modeling of the switching behavior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2020, 67(12): 5804–5809. doi: 10.1109/TED.2020.3031249 [28] BAE J H, KWON D, JEON N, et al. Highly scaled, high endurance, Ω-gate, nanowire ferroelectric FET memory transistors[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2020, 41(11): 1637–1640. doi: 10.1109/LED.2020.3028339 [29] YAN S C, LAN G M, SUN C J, et al. High speed and large memory window ferroelectric HfZrO2 FinFET for high-density nonvolatile memory[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2021, 42(9): 1307–1310. doi: 10.1109/LED.2021.3097777 [30] LIAO C Y, HSIANG K Y, LOU Z F, et al. Endurance > 1011 cycling of 3D GAA nanosheet ferroelectric FET with stacked HfZrO2 to homogenize corner field toward mitigate dead zone for high-density eNVM[C]. 2022 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits, Honolulu, USA, 2022: 1–2. [31] AZIZ A, GHOSH S, DATTA S, et al. Physics-based circuit-compatible SPICE model for ferroelectric transistors[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2016, 37(6): 805–808. doi: 10.1109/LED.2016.2558149 [32] NI Kai, JERRY M, SMITH J A, et al. A circuit compatible accurate compact model for ferroelectric-FETs[C]. 2018 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology, Honolulu, USA, 2018: 131–132. [33] DENG Shan, YIN Guodong, CHAKRABORTY W, et al. A comprehensive model for ferroelectric FET capturing the key behaviors: Scalability, variation, stochasticity, and accumulation[C]. 2020 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology, Honolulu, USA, 2020: 1–2. [34] SONG T, RIM W, KIM H, et al. 24.3 a 3nm gate-all-around SRAM featuring an adaptive dual-BL and an adaptive cell-power assist circuit[C]. 2021 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2021: 338–340. [35] SALIGRAM R, DATTA S, and RAYCHOWDHURY A. CryoMem: A 4K-300K 1.3GHz eDRAM macro with hybrid 2T-gain-cell in a 28nm logic process for cryogenic applications[C]. 2021 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, Austin, USA, 2021: 1–2. [36] JOURBA S, BOLLON N, DECOBERT C, et al. Performance and reliability of 4 Mb eFLASH memory array featuring 28 nm split-gate cell with HKMG select transistor[C]. 2020 IEEE International Memory Workshop, Dresden, Germany, 2020: 1–4. [37] SONG Z T, CAI D L, LI X, et al. High endurance phase change memory chip implemented based on carbon-doped Ge2Sb2Te5 in 40 nm node for embedded application[C]. 2018 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 27.5. 1–27.5. 4. [38] YANG Jianguo, LUO Qing, XUE Xiaoyong, et al. A 9Mb HZO-based embedded FeRAM with 1012-cycle endurance and 5/7ns read/write using ECC-assisted data refresh and offset-canceled sense amplifier[C]. 2023 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2023: 1–3. [39] ULLMANN M, GOEBEL H, HOENIGSCHMID H, et al. Disturb free programming scheme for single transistor ferroelectric memory arrays[J]. Integrated Ferroelectrics, 2001, 34(1/4): 155–164. doi: 10.1080/10584580108012885 [40] SHARMA A and ROY K. 1T non-volatile memory design using sub-10nm ferroelectric FETs[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2018, 39(3): 359–362. doi: 10.1109/LED.2018.2797887 [41] DAHAN M M, BREYER E T, SLESAZECK S, et al. C-AND: Mixed writing scheme for disturb reduction in 1T ferroelectric FET memory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2022, 69(4): 1595–1605. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2021.3139736 [42] JIANG Zhouhang, ZHAO Zijian, DENG Shan, et al. On the feasibility of 1T ferroelectric FET memory array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2022, 69(12): 6722–6730. doi: 10.1109/TED.2022.3216819 [43] GEORGE S, MA Kaisheng, AZIZ A, et al. Nonvolatile memory design based on ferroelectric FETs[C]. 2016 53rd ACM/EDAC/IEEE Design Automation Conference, Austin, USA, 2016: 1–6. [44] LI Xueqing, WU Juejian, NI Kai, et al. Design of 2T/cell and 3T/cell nonvolatile memories with emerging ferroelectric FETs[J]. IEEE Design & Test, 2019, 36(3): 39–45. doi: 10.1109/MDAT.2019.2902094 [45] NI Kai, LI Xueqing, SMITH J A, et al. Write disturb in ferroelectric FETs and its implication for 1T-FeFET AND memory arrays[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2018, 39(11): 1656–1659. doi: 10.1109/LED.2018.2872347 [46] GEORGE S, LI Xueqing, LIAO M J, et al. Symmetric 2-D-memory access to multidimensional data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2018, 26(6): 1040–1050. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2018.2801302 [47] WU Juejian, ZHONG Hongtao, NI Kai, et al. A 3T/cell practical embedded nonvolatile memory supporting symmetric read and write access based on ferroelectric FETs[C]. The 56th Annual Design Automation Conference 2019, Las Vegas, USA, 2019: 82. [48] MULAOSMANOVIC H, SLESAZECK S, OCKER J, et al. Evidence of single domain switching in hafnium oxide based FeFETs: Enabler for multi-level FeFET memory cells[C]. 2015 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, Washington, USA, 2015: 26.8. 1–26.8. 3. [49] WU Juejian, XU Yixin, XUE Bowen, et al. Adaptive circuit approaches to low-power multi-level/cell FeFET memory[C]. 2020 25th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC), Beijing, China, 2020: 407–413. [50] GUO An, SI Xin, CHEN Xi, et al. A 28nm 64-kb 31.6-TFLOPS/W digital-domain floating-point-computing-unit and double-bit 6T-SRAM computing-in-memory macro for floating-point CNNs[C]. 2023 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2023: 128–130. [51] XIE Shanshan, NI Can, SAYAL A, et al. 16.2 eDRAM-CIM: Compute-in-memory design with reconfigurable embedded-dynamic-memory array realizing adaptive data converters and charge-domain computing[C]. 2021 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2021: 248–250. [52] YE Wang, WANG Linfang, ZHOU Zhidao, et al. A 28-nm RRAM computing-in-memory macro using weighted hybrid 2T1R cell array and reference subtracting sense amplifier for AI edge inference[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, To be published. [53] CAI Hao, BIAN Zhongjian, HOU Yaoru, et al. 33.4 A 28nm 2Mb STT-MRAM computing-in-memory macro with a refined bit-cell and 22.4 - 41.5TOPS/W for AI inference[C]. 2023 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2023: 500–502. [54] CAI Hao, GUO Yanan, LIU Bo, et al. Proposal of analog in-memory computing with magnified tunnel magnetoresistance ratio and universal STT-MRAM cell[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2022, 69(4): 1519–1531. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3140769 [55] CAI Hao, BIAN Zhongjian, FAN Zhonghua, et al. Commodity bit-cell sponsored MRAM interaction design for binary neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2022, 69(4): 1721–1726. doi: 10.1109/TED.2021.3134588 [56] REIS D, NIEMIER M, and HU X S. Computing in memory with FeFETs[C]. The International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design (ISLPED '18), Seattle, USA, 2018: 24. [57] YIN Xunzhao, AZIZ A, NAHAS J, et al. Exploiting ferroelectric FETs for low-power non-volatile logic-in-memory circuits[C]. 2016 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), Austin, USA, 2016: 1–8. [58] LI Xueqing, MA Kaisheng, GEORGE S, et al. Design of nonvolatile SRAM with ferroelectric FETs for energy-efficient backup and restore[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2017, 64(7): 3037–3040. doi: 10.1109/TED.2017.2707664 [59] WANG Jianfeng, XIU Nuo, WU Juejian, et al. An 8T/Cell FeFET-based nonvolatile SRAM with improved density and sub-fJ backup and restore energy[C]. 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Austin, USA, 2022: 3408–3412. [60] LI Xueqing, SAMPSON J, KHAN A, et al. Enabling energy-efficient nonvolatile computing with negative capacitance FET[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2017, 64(8): 3452–3458. doi: 10.1109/TED.2017.2716338 [61] LI Xueqing, GEORGE S, MA Kaisheng, et al. Advancing nonvolatile computing with nonvolatile NCFET latches and flip-flops[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2017, 64(11): 2907–2919. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2017.2702741 [62] LI Xueqing, GEORGE S, LIANG Yuhua, et al. Lowering area overheads for FeFET-based energy-efficient nonvolatile flip-flops[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2018, 65(6): 2670–2674. doi: 10.1109/TED.2018.2829348 [63] TANG Wenjun, LEE M, WU Juejian, et al. FeFET-based logic-in-memory supporting SA-free write-back and fully dynamic access with reduced bitline charging activity and recycled bitline charge[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2023, 70(6): 2398–2411. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2023.3251961 [64] JERRY M, CHEN P Y, ZHANG Jianchi, et al. Ferroelectric FET analog synapse for acceleration of deep neural network training[C]. 2017 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 6.2. 1–6.2. 4. [65] SOLIMAN T, MÜLLER F, KIRCHNER T, et al. Ultra-low power flexible precision FeFET based analog in-memory computing[C]. 2020 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, USA, 2020: 29.2. 1–29.2. 4. [66] SAITO D, KOBAYASHI T, KOGA H, et al. Analog in-memory computing in FeFET-based 1T1R array for edge AI applications[C]. 2021 Symposium on VLSI Technology, Kyoto, Japan, 2021: 1–2. [67] CHEN Xiaoming, YIN Xunzhao, NIEMIER M, et al. Design and optimization of FeFET-based crossbars for binary convolution neural networks[C]. 2018 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition, Dresden, Germany, 2018: 1205–1210. [68] YIN Guodong, CAI Yi, WU Juejian, et al. Enabling lower-power charge-domain nonvolatile in-memory computing with ferroelectric FETs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2021, 68(7): 2262–2266. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2021.3049844 [69] DE S, MÜLLER F, LALENI N, et al. Demonstration of multiply-accumulate operation with 28 nm FeFET crossbar array[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2022, 43(12): 2081–2084. doi: 10.1109/LED.2022.3216558 [70] SOLIMAN T, CHATTERJEE S, LALENI N, et al. First demonstration of in-memory computing crossbar using multi-level cell FeFET[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2948718/v1. [71] YIN Xunzhao, NIEMIER M, and HU X S. Design and benchmarking of ferroelectric FET based TCAM[C]. Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Lausanne, Switzerland, 2017: 1444–1449. [72] YIN Xunzhao, NI Kai, REIS D, et al. An ultra-dense 2FeFET TCAM design based on a multi-domain FeFET model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2019, 66(9): 1577–1581. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2018.2889225 [73] NI Kai, YIN Xunzhao, LAGUNA A F, et al. Ferroelectric ternary content-addressable memory for one-shot learning[J]. Nature Electronics, 2019, 2(11): 521–529. doi: 10.1038/s41928-019-0321-3 [74] MA Xiaoyang, ZHONG Hongtao, XIU Nuo, et al. CapCAM: A multilevel capacitive content addressable memory for high-accuracy and high-scalability search and compute applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2022, 30(11): 1770–1782. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2022.3198492 [75] GEORGE S, JAO N, RAMANATHAN A K, et al. Integrated CAM-RAM functionality using ferroelectric FETs[C]. 2020 21st International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design, Santa Clara, USA, 2020: 81–86. [76] KAZEMI A, MÜLLER F, SHARIFI M M, et al. Achieving software-equivalent accuracy for hyperdimensional computing with ferroelectric-based in-memory computing[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 19201. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23116-w [77] LIU Liu, KUMAR S, THOMANN S, et al. Compact and high-performance TCAM based on scaled double-gate FeFETs[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.03868.pdf.2023.4, 2023. [78] LIU Liu, LAGUNA A F, RAJAEI R, et al. A reconfigurable FeFET content addressable memory for multi-state hamming distance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2023, 70(6): 2356–2369. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2023.3259940 -





 下载:
下载:


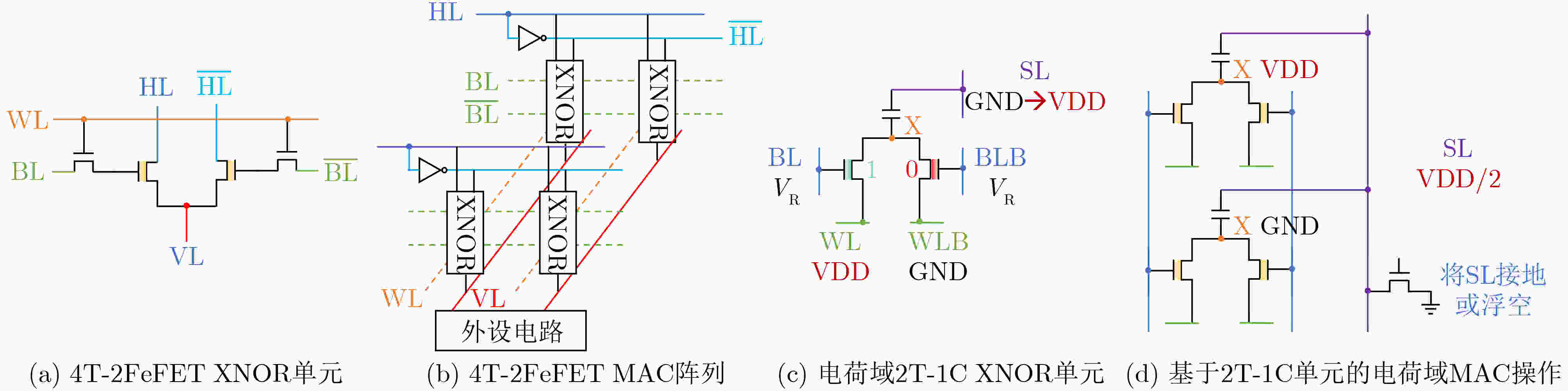
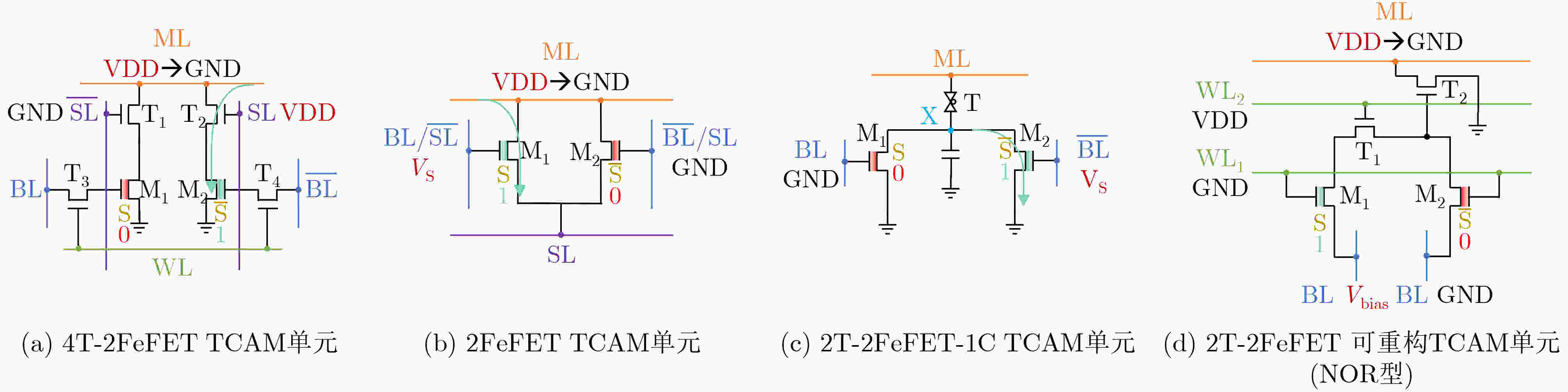


 下载:
下载:
