Design of Soft Physical Unclonable Functions Based on Tunneling Magnetic ResistanceMagnetometers
-
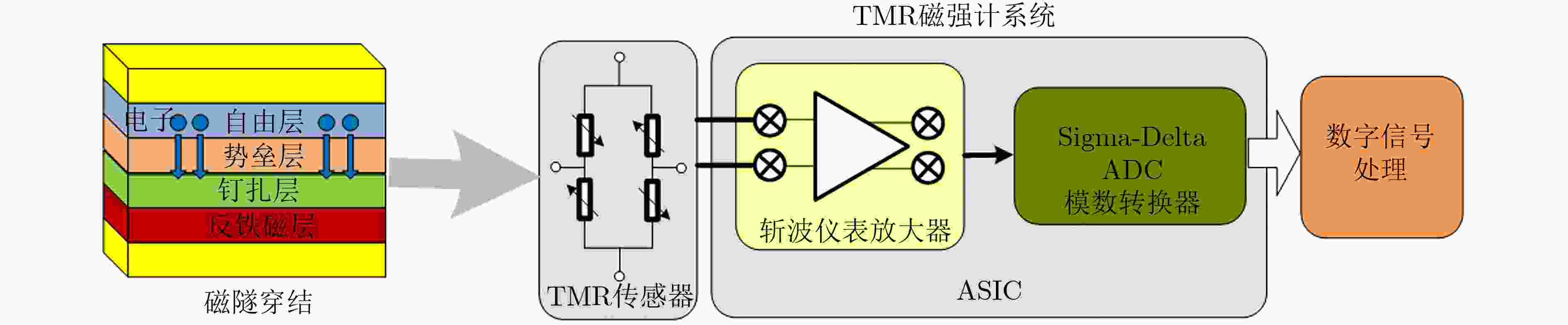
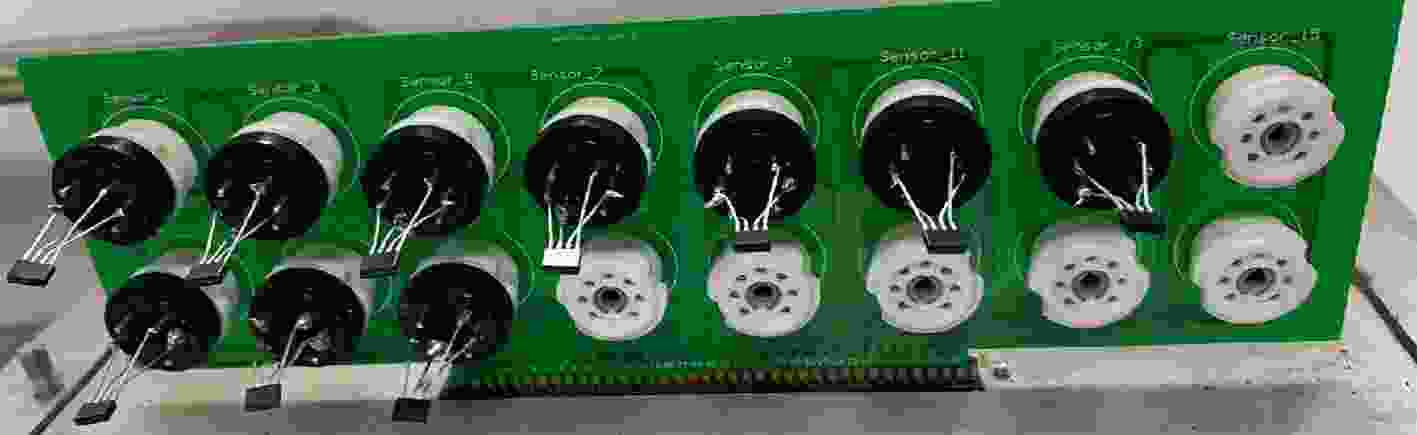
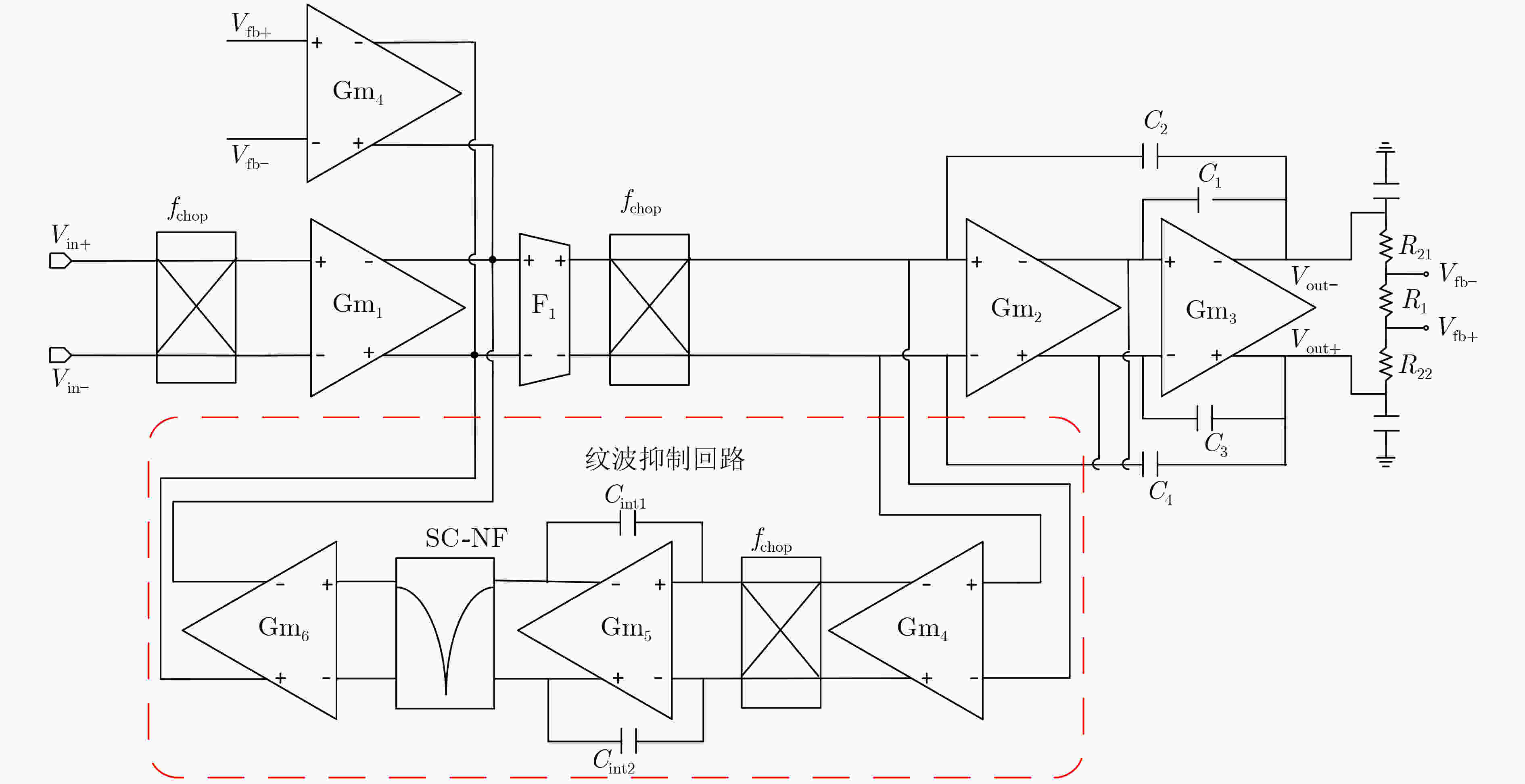
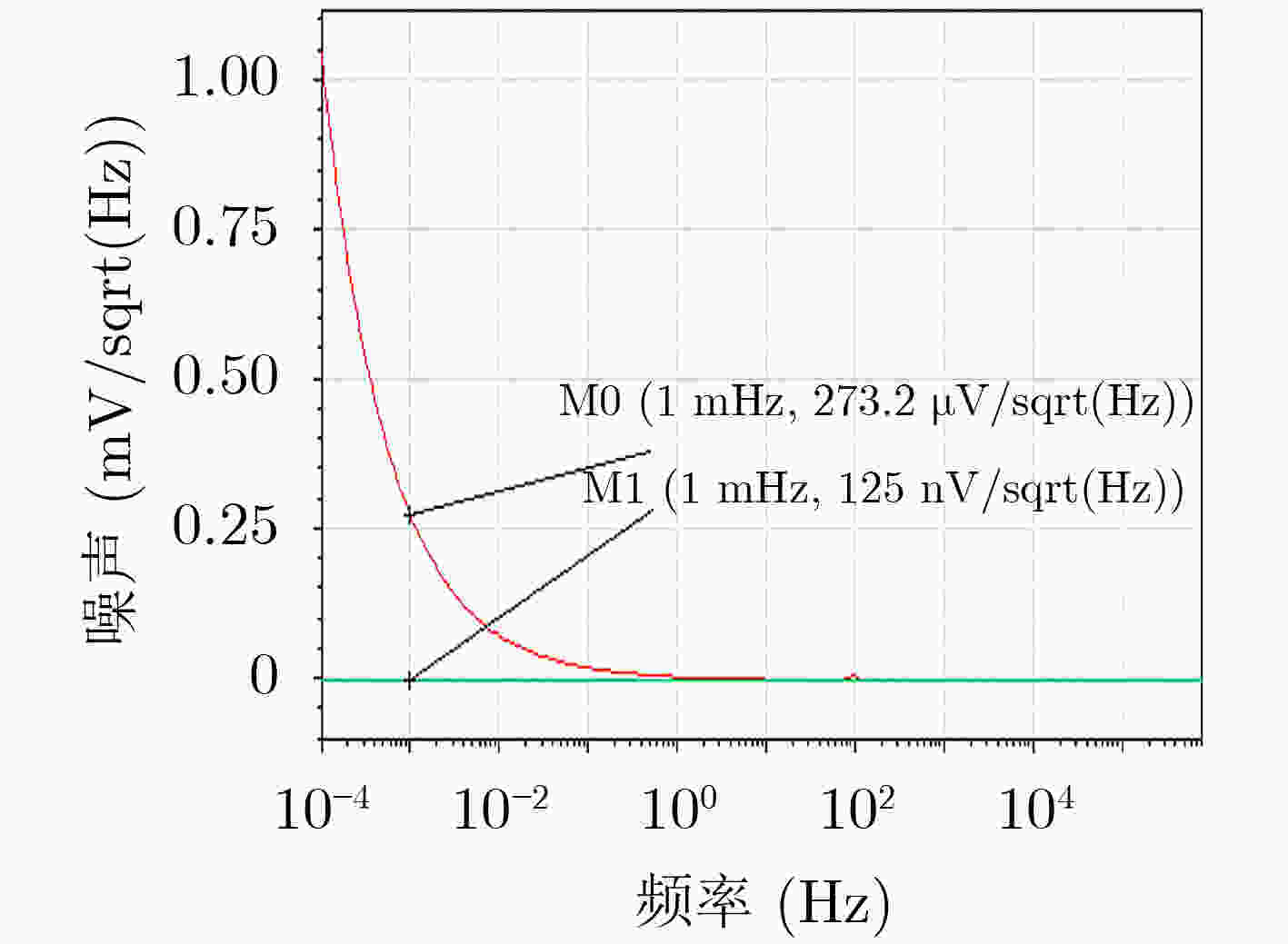
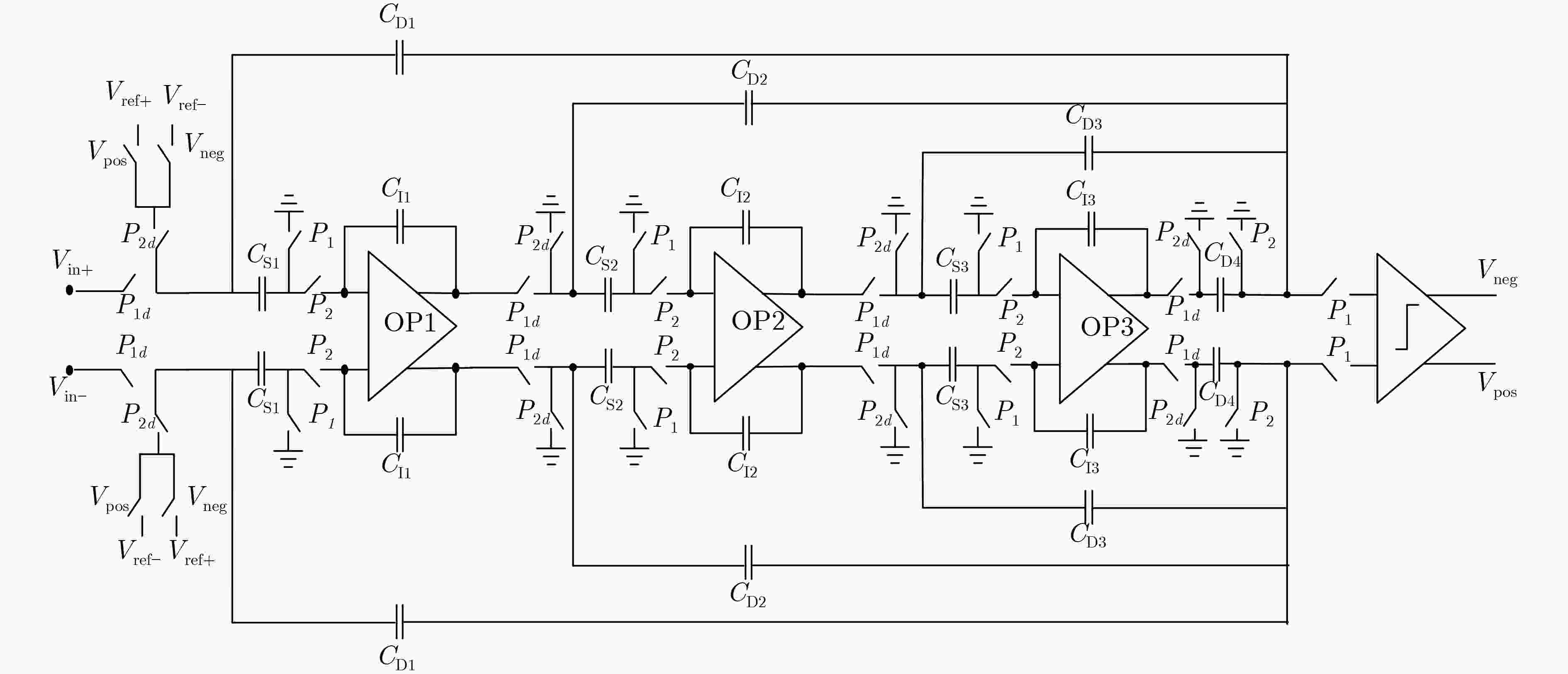
摘要: 隧穿磁阻(TMR)传感器相比于其他类型磁阻传感器功耗更低、灵敏度更高、可靠性更好,在军事和民用等领域有着广阔的应用前景。该文针对TMR传感器的微弱信号检测和安全防护等问题,提出一种高精度TMR传感器读取专用集成电路(ASIC)和提取传感器物理不可克隆函数(PUF)特性的设计方案。该方案通过设计前端低噪声仪表放大器和高精度模数转换器,并结合斩波技术和纹波抑制技术,实现高精度信号读取和模数转换;利用具备数字输出功能的TMR磁强计比较不同传感器零位偏差,采用多位随机平衡算法完成TMR磁强计的软PUF设计,可产生128 bit PUF响应。TMR传感器读取ASIC利用上海华虹0.35 μm CMOS工艺完成流片,并测试磁强计功能和TMR-PUF性能。实验结果表明,在5V电源电压下,TMR磁强计系统功耗约10 mW,噪底可达–140 dBV,3次谐波失真–107 dB;TMR-PUF的唯一性达到47.8%,稳定性为97.85%,与相关文献比较性能优异。Abstract: Tunneling Magnetic Resistance (TMR) sensors have lower power consumption, higher sensitivity, and better reliability than other types of magnetoresistive sensors and have broad application prospects in military and civilian fields. A design scheme for high-precision TMR sensor reading Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) and extracting the sensor’s Physical Unclonable Functions (PUF) characteristics is proposed in this paper, addressing issues such as weak signal detection and security protection of TMR sensors. A front-end low noise instrument amplifier and high-precision ADC are proposed, which is combined with chopping technology and ripple suppression technology to achieve high-precision signal reading and analog-to-digital conversion. The TMR magnetometer with digital output function is used to compare the zero position deviation of different sensors, and multi-bit random balance algorithm is used to complete the soft PUF design of TMR magnetometer, which can generate 128 bit PUF response. The readout ASIC for TMR sensor using the Shanghai Huahong of 0.35 μm CMOS process is completed, and magnetometer’s function and TMR-PUF performance are tested. The experimental results show that under 5V power supply voltage, the power consumption of the TMR magnetometer system is about 10 mW, the noise floor can reach –140 dBV and the third harmonic distortion is –107 dB; The uniqueness of TMR-PUF reaches 47.8%, and its stability is 97.85%, which shows excellent performance compared to relevant literature.
-
表 1 TMR传感器参数和接口电路的设计指标
参数 数值 传感器灵敏度 75 mV/Oe(5 V供电) 传感器电阻值 2 kΩ 传感器非线性 <0.2% FS 传感器噪底 1nT/Hz√@1 Hz 读取电路电源电压 5 V 集成电路工艺 0.35 μm CMOS 闪烁噪声转角频率 <5 mHz 等效输入噪声(PSD) <15 nV/√Hz@1 Hz 共模抑制比 120 dB 输入阻抗 20 MΩ 功耗 <10 mW 算法1 随机平衡算法伪代码 (1) int bit[place] (2) int lef[3] (3) int r[3] (4) double v[8] (5) i=0 (6) do {lsum = v[(i+lef[0]) mod 8]+v[(i+lef[1]) mod 8]+v[(i + lef[2]) mod 8] (7) rsum = v[(i + r[0]) mod 8]+v[(i + r[1]) mod 8]+v[(i + r[2]) mod 8] (8) if lsum > rsum (9) then bits[palce] = 1 (10) else bits[place] = 0 (11) place = place +1} (12) while(i<8) (13) return -
[1] LI Jiaxian, LIU Hao, and BI Tianshu. Tunnel magnetoresistance-based noncontact current sensing and measurement method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 9503609. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2022.3152240 [2] 韩秀峰, 刘厚方, 张佳, 等. 新型磁性隧道结材料及其隧穿磁电阻效应[J]. 中国材料进展, 2013, 32(6): 339–353. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.2013.06.02HAN Xiufeng, LIU Houfang, ZHANG Jia, et al. A typical magnetic tunnel junction material and effects of tunnel magneto-resistance[J]. Materials China, 2013, 32(6): 339–353. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.2013.06.02 [3] CHINENKOV M, DJUZHEV N, BESPALOV V, et al. Magnetoresistive sensor with high sensitivity: Self-aligned magnetic structures[C]. 2017 IEEE International Magnetics Conference, Dublin, Ireland, 2017. [4] 张朝阳, 虞伟乔, 陆鹏飞. 基于远场等效磁矩的潜艇磁防护技术[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2015, 37(2): 97–100. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2015.02.020ZHANG Zhaoyang, YU Weiqiao, and LU Pengfei. Research on the submarine's magnetic defense technology based on the far field equivalent magnetic moment[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2015, 37(2): 97–100. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2015.02.020 [5] YANG Huiwen, WENG Ling, WANG Bowen, et al. Design and characterization of high-sensitivity magnetostrictive tactile sensor array[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(5): 4004–4013. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3145822 [6] CAI Hao, GUO Yanan, LIU Bo, et al. Proposal of analog in-memory computing with magnified tunnel magnetoresistance ratio and universal STT-MRAM cell[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2022, 69(4): 1519–1531. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3140769 [7] EBRAHIMABADI M, YOUNIS M, and KARIMI N. A PUF-based modeling-attack resilient authentication protocol for IoT devices[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(5): 3684–3703. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3098496 [8] LEWIS J A. Economic impact of cybercrime[EB/OL]. https://www.csis.org/analysis/economic-impact-cybercrime, 2018. [9] 龚越, 叶靖, 胡瑜, 等. 内建自调整的仲裁器物理不可克隆函数[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2017, 29(9): 1734–1739. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9775.2017.09.018GONG Yue, YE Jing, HU Yu, et al. Built-in self adjustable arbiter PUF[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design &Computer Graphics, 2017, 29(9): 1734–1739. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9775.2017.09.018 [10] 孙子文, 叶乔. 利用震荡环频率特性提取多位可靠信息熵的物理不可克隆函数研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 234–241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT191013SUN Ziwen and YE Qiao. Study on the physical unclonable function of the reliable information entropy extracted by the frequency characteristic of oscillating ring[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 234–241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT191013 [11] LI Gang, WANG Pengjun, MA Xuejiao, et al. A 215-F2 bistable physically unclonable function with an ACF of <0.005 and a native bit instability of 2.05% in 65-nm CMOS process[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2020, 28(11): 2290–2299. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2020.3014892 [12] GOLANBARI M S, KIAMEHR S, BISHNOI R, et al. Reliable memory PUF design for low-power applications[C]. The 19th International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design, Santa Clara, USA, 2018: 207–213. [13] 张培勇, 袁晓东, 王雪洁, 等. 基于D触发器的物理不可克隆函数[J]. 浙江大学学报:理学版, 2019, 46(1): 32–38. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9497.2019.01.005ZHANG Peiyong, YUAN Xiaodong, WANG Xuejie, et al. D flip-flop based physical unclonable functions[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University:Science Edition, 2019, 46(1): 32–38. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9497.2019.01.005 [14] LEE J W, LIM D, GASSEND B, et al. A technique to build a secret key in integrated circuits for identification and authentication applications[C]. 2004 Symposium on VLSI Circuits. Digest of Technical Papers, Honolulu, USA, 2004: 176–179. [15] WILLERS O, HUTH C, GUAJARDO J, et al. MEMS gyroscopes as physical unclonable functions[C]. The 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Vienna, Austria, 2016: 591–602. [16] LABRADO C and THAPLIYAL H. Design of a piezoelectric-based physically unclonable function for IoT security[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 2770–2777. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2874626 [17] 吴少兵, 陈实, 李海, 等. TMR与GMR传感器1/f噪声的研究进展[J]. 物理学报, 2012, 61(9): 550–559. doi: 10.7498/aps.61.097504WU Shaobing, CHEN Shi, LI Hai, et al. Researching progress of the 1/f noise in TMR and GMR sensors[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61(9): 550–559. doi: 10.7498/aps.61.097504 [18] KUSUDA Y. Auto correction feedback for ripple suppression in a chopper amplifier[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(8): 1436–1445. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2048142 [19] KUMAR R S A and KRISHNAPURA N. Multi-channel analog-to-digital conversion techniques using a continuous-time delta-sigma modulator without reset[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2020, 67(11): 3693–3703. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.3013691 [20] LIM D, LEE J W, GASSEND B, et al. Extracting secret keys from integrated circuits[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2005, 13(10): 1200–1205. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2005.859470 [21] 张跃军, 汪鹏君, 李刚, 等. 基于信号传输理论的Glitch物理不可克隆函数电路设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(9): 2391–2396. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151312ZHANG Yuejun, WANG Pengjun, LI Gang, et al. Design of glitch physical unclonable functions circuit based on signal transmission theory[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(9): 2391–2396. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151312 [22] SU Y, HOLLEMAN J, and OTIS B. A 1.6pJ/bit 96% stable chip-ID generating circuit using process variations[C]. 2007 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference. Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, USA, 2007: 406–411. [23] ZHANG Jiliang, SHEN Chaoqun, GUO Zhiyang, et al. CT PUF: Configurable tristate PUF against machine learning attacks for IoT security[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(16): 14452–14462. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3090475 [24] QIU Pengfei, LYU Yongqiang, ZHANG Jiliang, et al. Physical unclonable functions-based linear encryption against code reuse attacks[C]. The 53rd Annual Design Automation Conference, Austin, USA, 2016: 75. -





 下载:
下载:


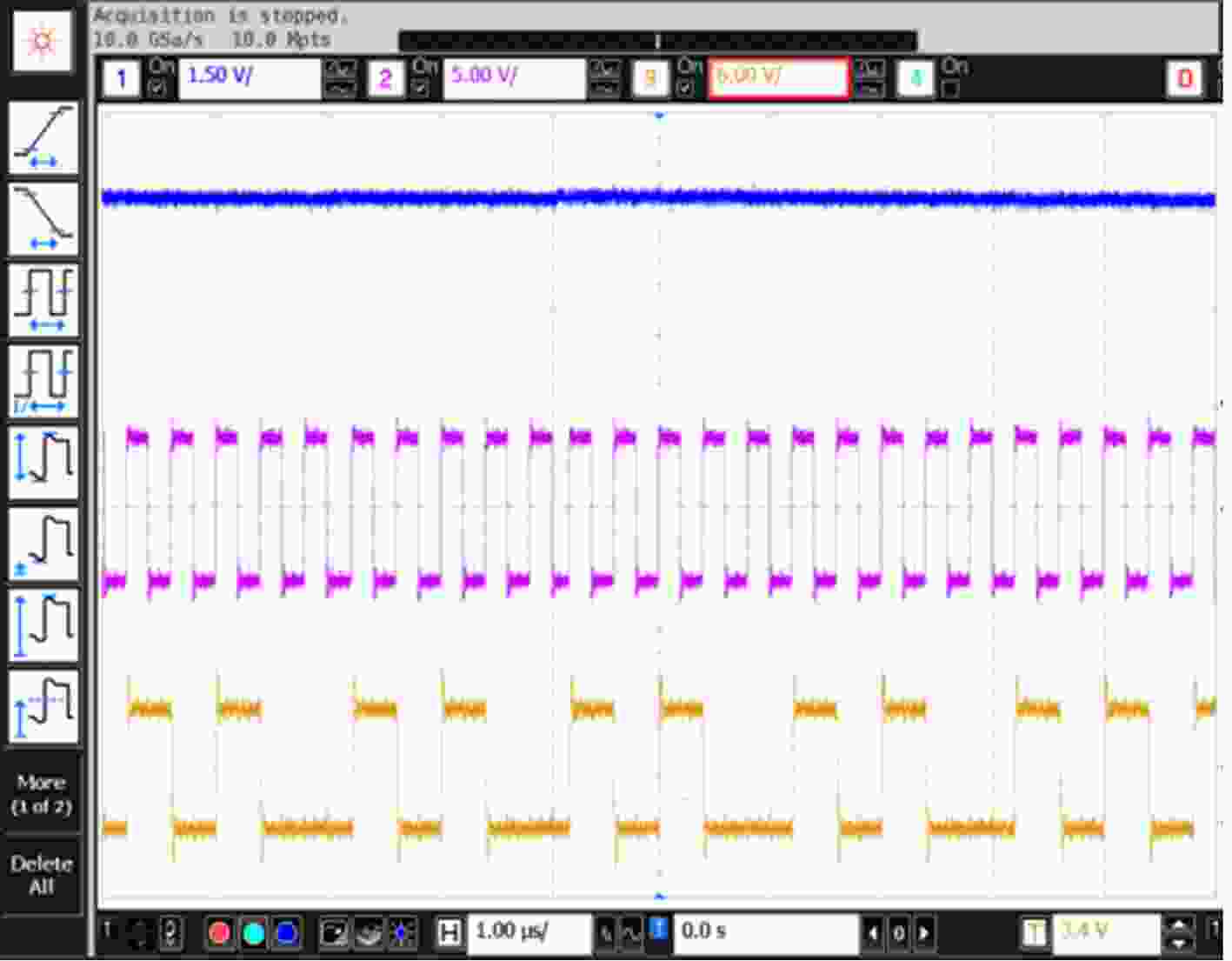
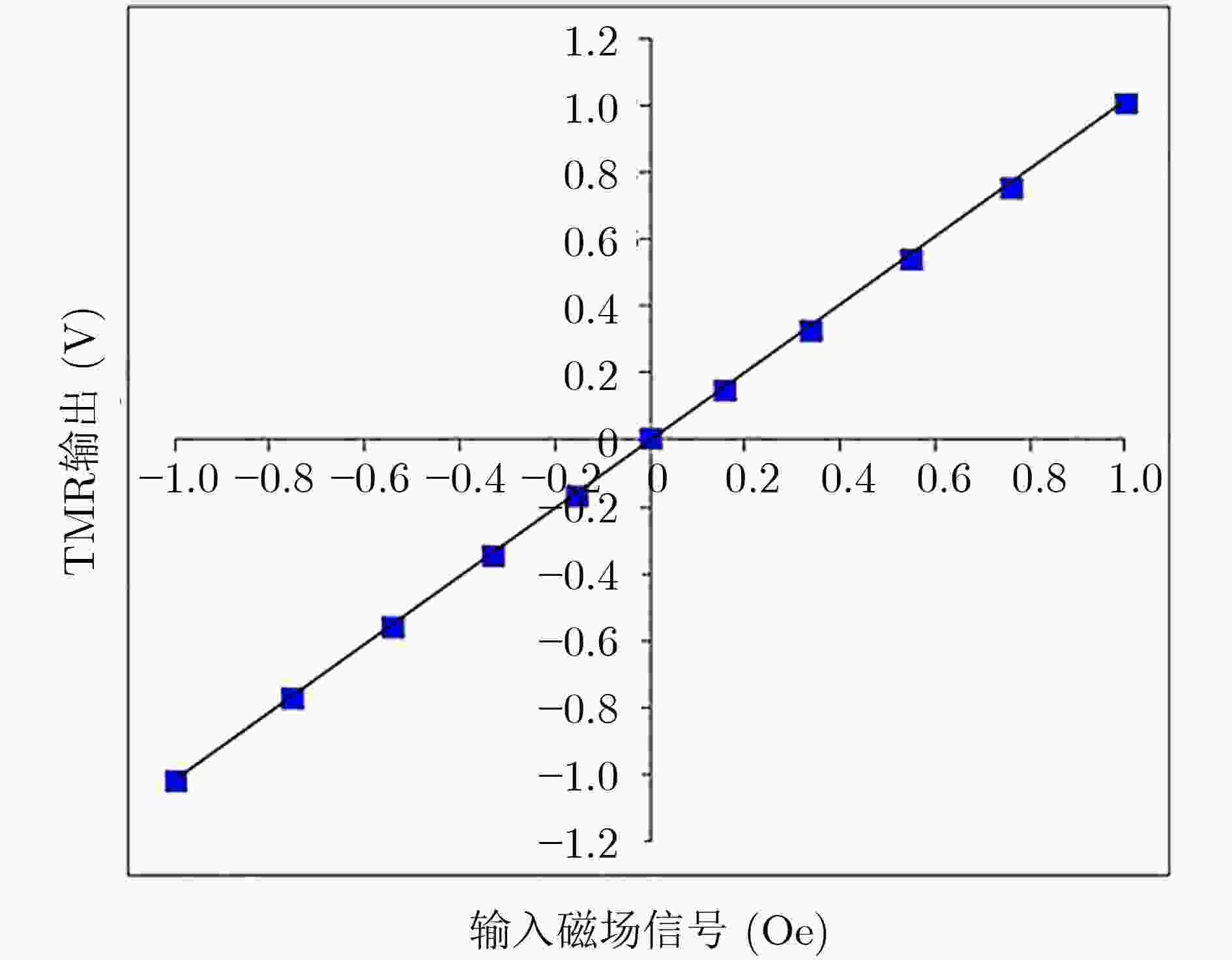
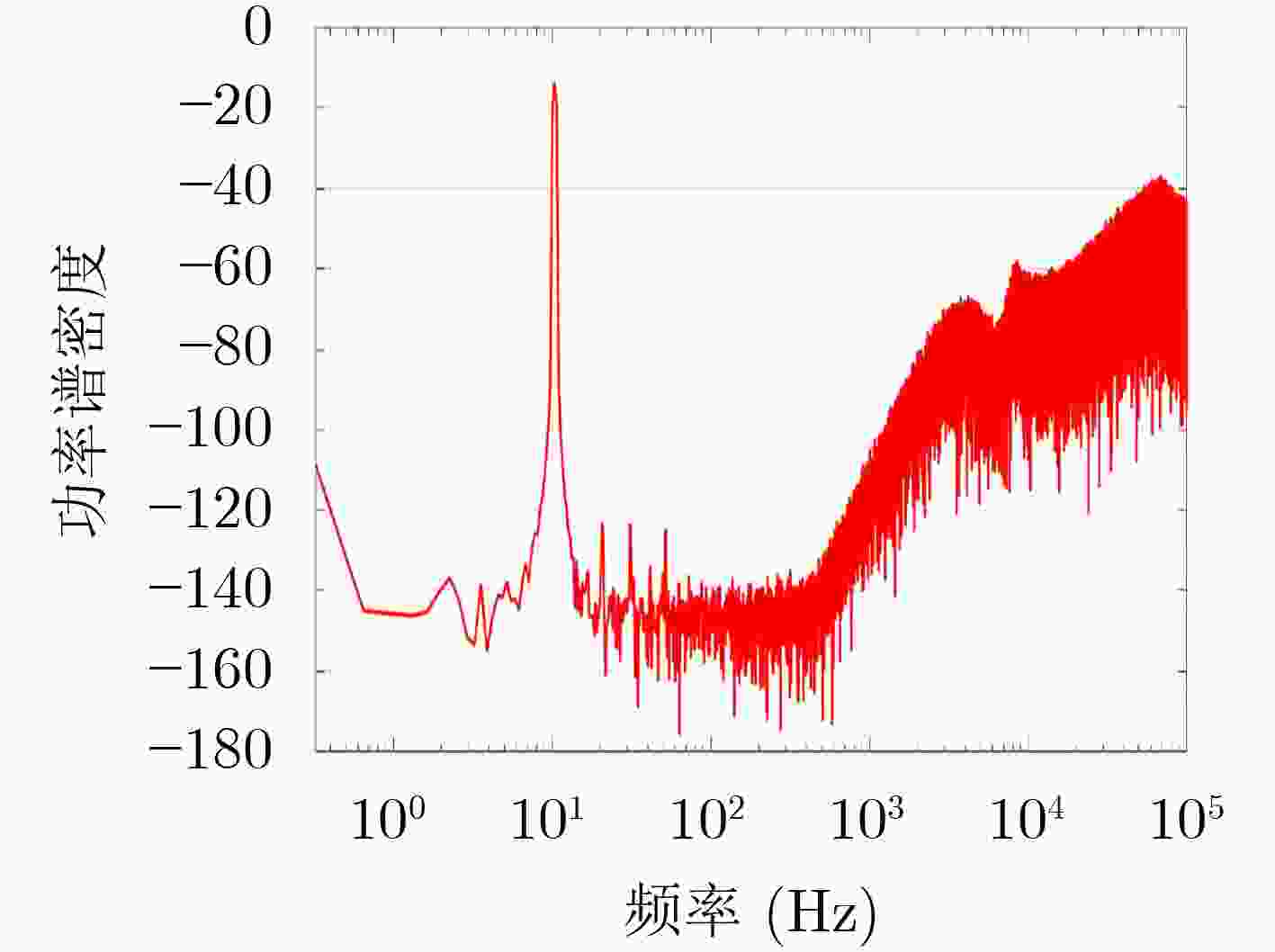
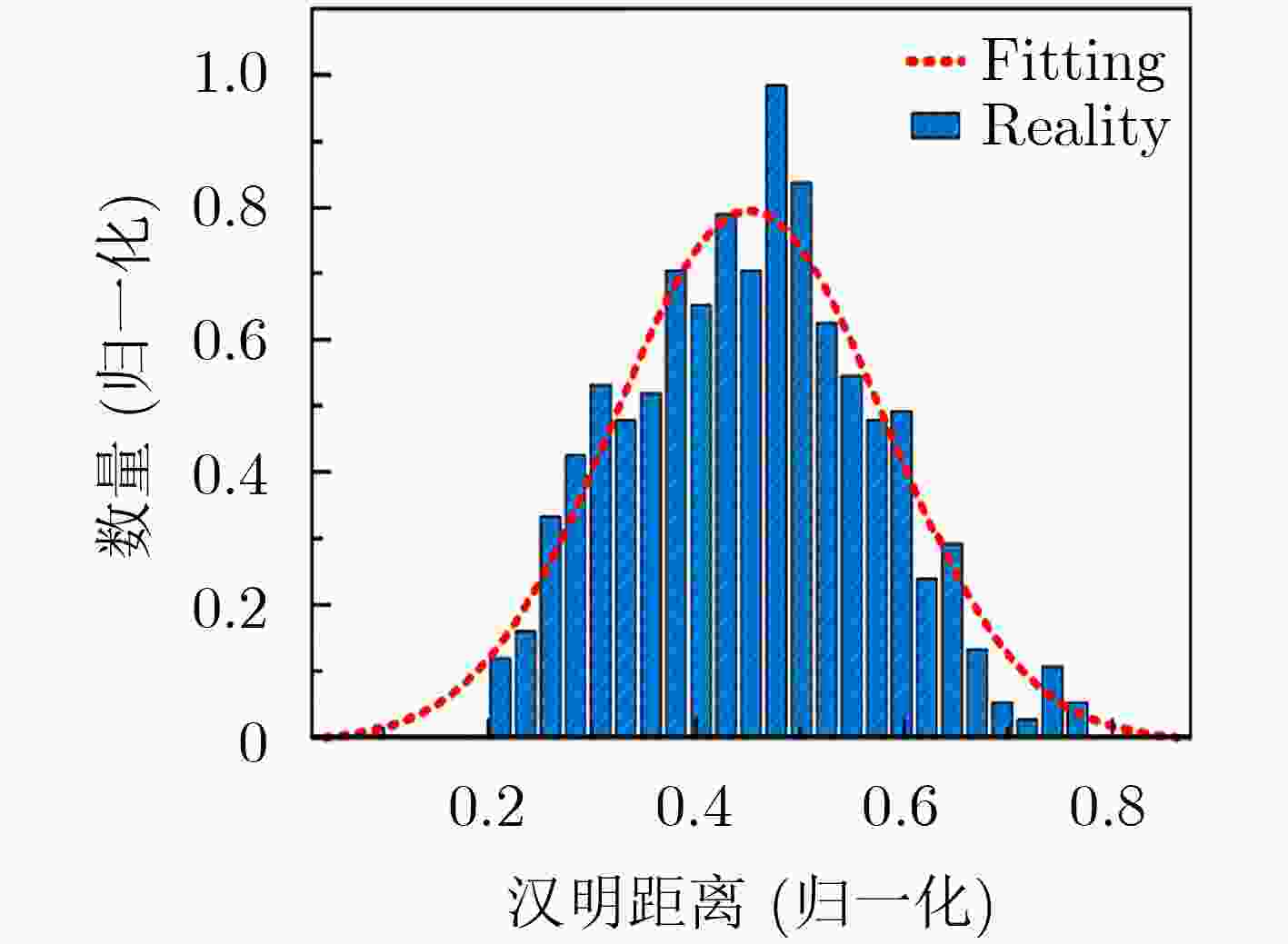
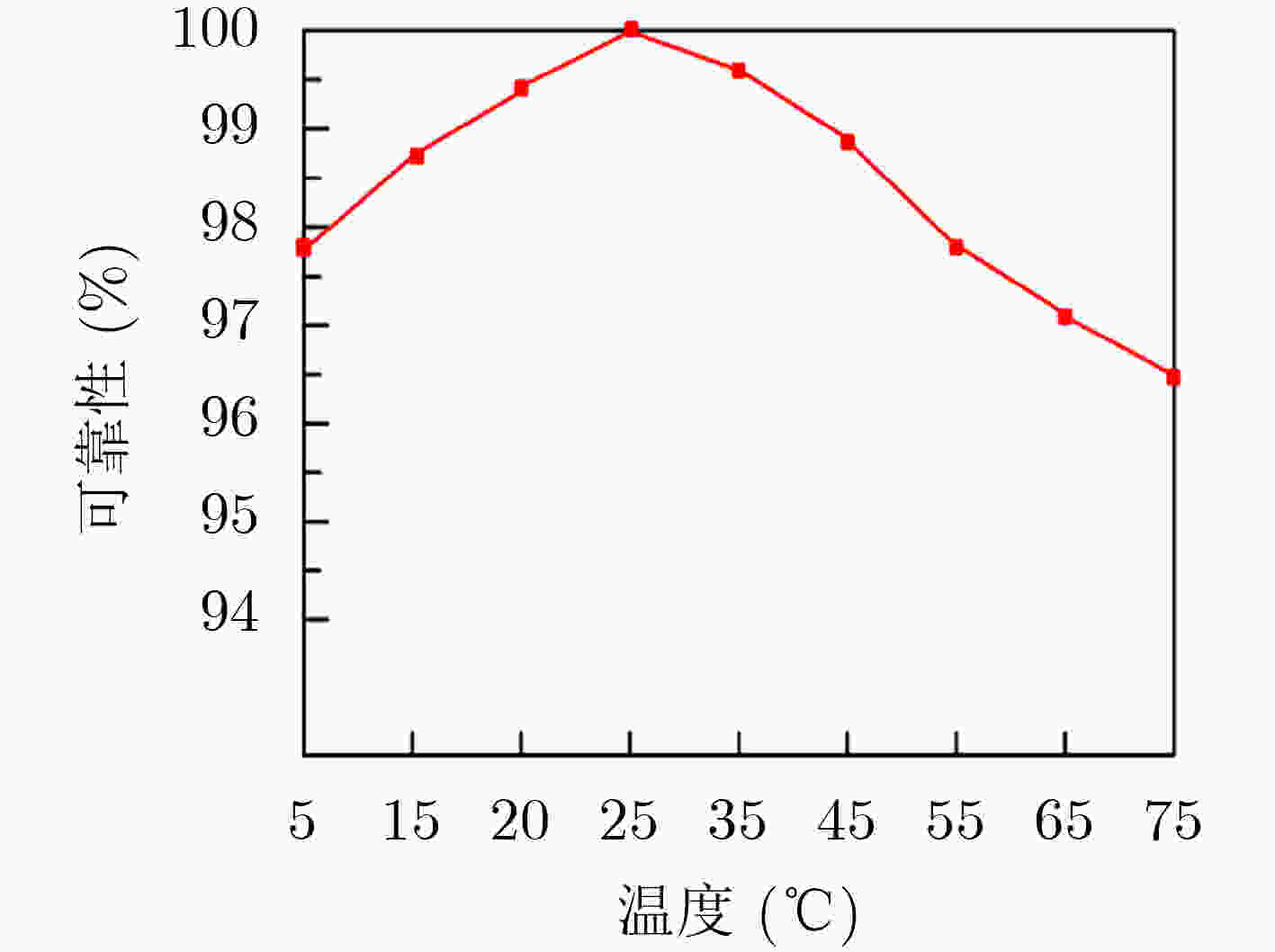
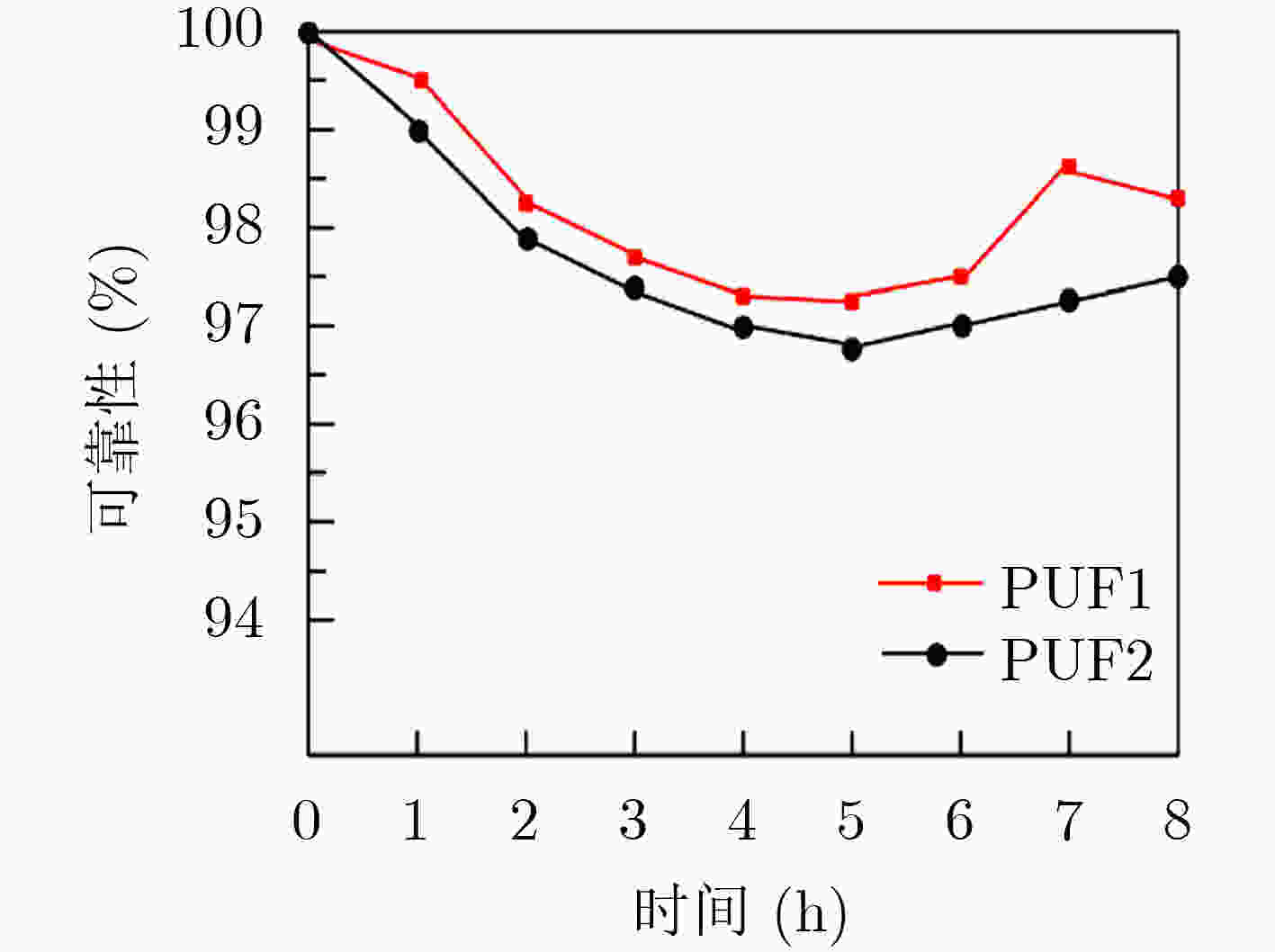
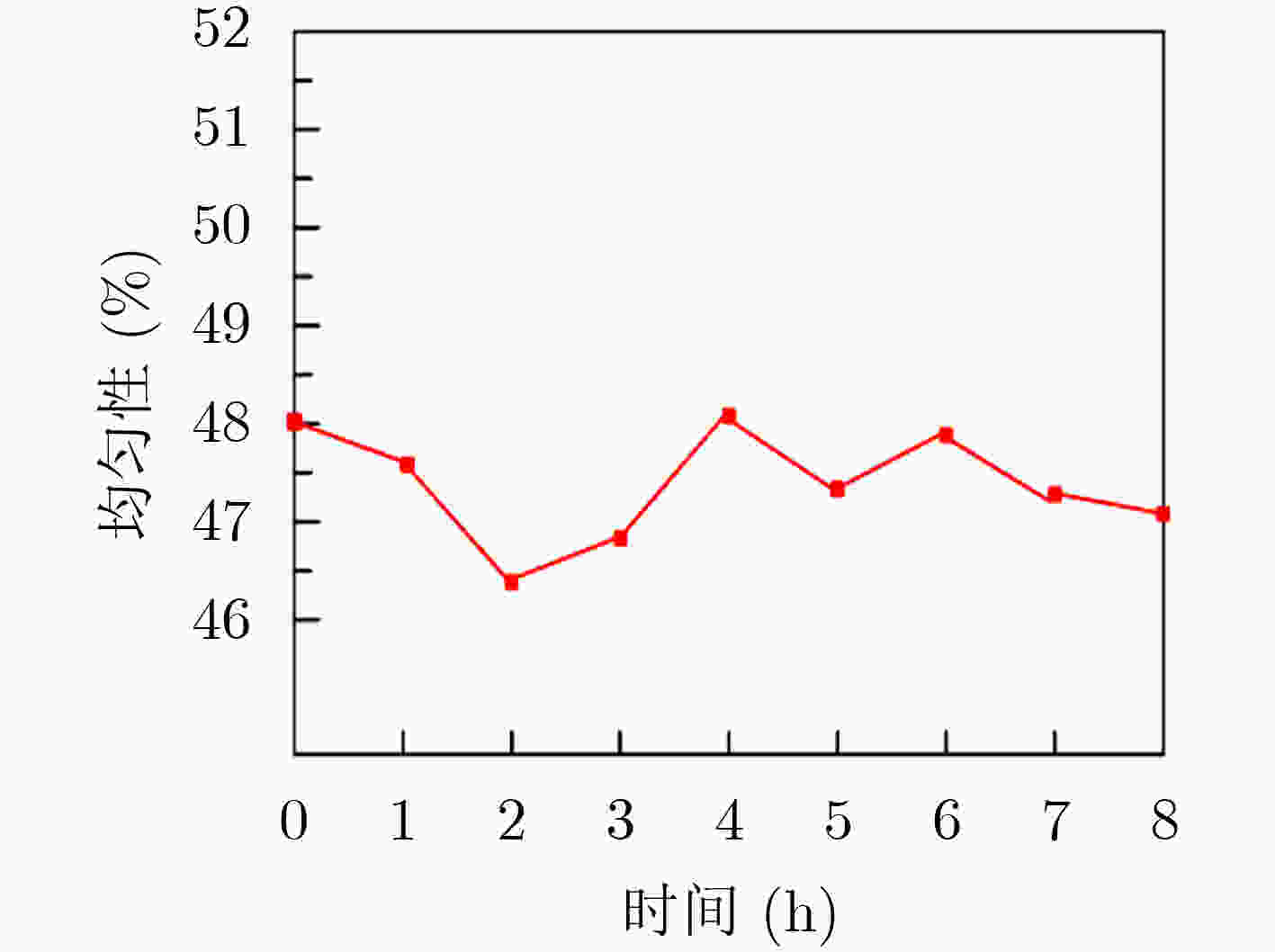


 下载:
下载:
