Frequency-Hopping Network Station Sorting Method Using Radio Polarization Characteristics
-
摘要: 针对现有方法在跳频通信用户“空时频能”域特征相近、跳频参数捷变等条件下,跳频网台分类识别效果不佳的问题,该文提出一种基于无线电极化特征的跳频用户分选方法。该方法将无线电双极化特征引入到跳频侦察,充分利用各用户的交叉极化鉴别度差异,实现了跳频网台精准分选。针对同类用户交叉极化鉴别度参数易受噪声污染的问题,构建了双通道双极化接收系统,抑制了信号噪声,保证了极化特征提取的精度。在此基础上,基于谱聚类思想,完成了极化特征的分类软判决,进一步提升了跳频网台分选效果,实现了跳频信号的精准识别。仿真实验表明,在5 dB信噪比条件下,所提方法可对同步正交和非正交组网方式下的多跳频网台准确识别,识别分类成功率达99%以上,验证了新方法的有效性。Abstract: The paper proposes a hopping signal sorting method based on radio polarization features to address the problem of poor classification and recognition performance of hopping network stations under the condition of similar characteristics in the “space-time-frequency-energy” domain of user and agile frequency hopping parameters using the existing methods. Radio dual-polarization features are introduced into hopping reconnaissance, fully utilizing the differences in cross-polarization discrimination of each user and achieving accurate hopping network station sorting. To address the issue that the cross-polarization discrimination parameter of users of the same type is susceptible to noise pollution, a dual-channel dual-polarization receiving system is constructed to suppress signal noise and ensure the accuracy of polarization feature extraction. Based on the spectral clustering idea, a soft classification decision of polarization characteristics is made, which further improves the network station selection effect and achieves accurate identification of hopping signals. Simulation experiments show that under a 5 dB signal-to-noise ratio, the proposed algorithm can accurately identify multiple hopping network stations under synchronous orthogonal and non-orthogonal networking modes, with a success rate of over 99% in identification and classification, verifying the effectiveness of the new method.
-
表 1 模拟数据集1参数
网台 采样率
(MHz)跳频网台参数 极化参数 跳速
(hop/s)驻留
时间(ms)跳频
带宽(kHz)跳频频率集
(kHz)跳频频率
数目(个)极化
幅度比极化
相位差(°)1 10 2000 0.1 200 [7002,12998]区间随机1000个点 1500 1/10 2 2 10 2000 0.1 200 [17002,22998]区间随机1000个点 1500 1/9 3.5 3 10 2000 0.1 200 [27002,32998]区间随机1000个点 1500 1/7 5 表 2 模拟数据集2参数
网台 采样率
(MHz)跳频网台参数 极化参数 跳速(hop/s) 驻留
时间(ms)跳频
带宽(Hz)跳频频率集
(kHz)跳频频率数目(个) 极化
幅度比极化
相位差(°)1 10 2000 0.1 2000 [7002,12998]区间随机3000个频点
(3部网台各1000个频点)1500 1/10 2 2 10 2000 0.1 2000 1500 1/9 3.5 3 10 2000 0.1 2000 1500 1/7 5 -
[1] 齐扬阳, 于淼. 基于EMD的单通道盲源分离跳频通信抗干扰方法[J]. 计算机科学, 2016, 43(1): 149–153. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2016.1.034.QI Yangyang and YU Miao. Anti-jamming method for frequency hopping communication based on single channel BSS and EMD[J]. Computer Science, 2016, 43(1): 149–153. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2016.1.034. [2] BAEK H and LIM J. Spectrum sharing for coexistence of fixed satellite services and frequency hopping tactical data link[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(10): 2642–2649. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2016.2605979. [3] 李静威, 刘广凯, 王川川. 复杂干扰条件对跳频系统中断概率的影响[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 45(4): 137–142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2018.04.024.LI Jingwei, LIU Guangkai, and WANG Chuanchuan. Effects of complicated interference environment on the outage probability of the frequency hopping system[J]. Journal of Xidian University (Natural Science), 2018, 45(4): 137–142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2018.04.024. [4] 刘荣, 余志勇, 韩佳, 等. 欠定盲源分离技术的研究进展综述[J]. 电子技术与软件工程, 2022(22): 84–89.LIU Rong, YU Zhiyong, HAN Jia, et al. A review of the research progress of underdetermined blind source separation technique[J]. Electronic Technology & Software Engineering, 2022(22): 84–89. [5] 贾可新. 通信侦察中的信号分选算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2011.JIA Kexin. Research on signal sorting algorithm for communication reconnaissance[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology, 2011. [6] LEI Ziwei, ZHENG Linhua, DING Hong, et al. Blind separation of synchronous-networking frequency hopping signals based on time-frequency analysis[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2014, 34: 31–38. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2014.07.016. [7] 任珂. 跳频电台分选关键技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2020.REN Ke. Research on key technologies of frequency hopping radio sorting[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020. [8] 翟海莹, 杨小牛, 王文勇. 基于盲源分离的跳频网台分选[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2008, 3(4): 398–402.ZHAI Haiying, YANG Xiaoniu, and WANG Wenyong. Frequency hopping signal sorting based on blind source separation[J]. Journal of China Academy of Electronics and Information Technology, 2008, 3(4): 398–402. [9] 陈超, 高宪军, 李德鑫. 基于独立分量分析的混叠跳频信号分离算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(信息科学版), 2008, 26(4): 347–351. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5896.2008.04.004.CHEN Chao, GAO Xianjun, and LI Dexin. Overlapped frequency-hopping communication signals separation algorithm based on independent component analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Information Science Edition), 2008, 26(4): 347–351. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5896.2008.04.004. [10] 杨芸丞, 孙雪丽, 钟兆根, 等. 一种改进的独立分量分析跳频网台分选方法[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2018, 13(4): 452–459. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2018.04.016.YANG Yuncheng, SUN Xueli, ZHONG Zhaogen, et al. An improved independent component analysis frequency-hopping network station sorting method[J]. Journal of China Academy of Electronics and Information Technology, 2018, 13(4): 452–459. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2018.04.016. [11] 李红光, 郭英, 张东伟, 等. 基于欠定盲源分离的同步跳频信号网台分选[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(2): 319–328. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190920.LI Hongguang, GUO Ying, ZHANG Dongwei, et al. Synchronous frequency hopping signal network station sorting based on underdetermined blind source separation[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information, 2021, 43(2): 319–328. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190920. [12] 崔伟. 非合作通信系统中盲源分离及关键算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 吉林大学, 2021. doi: 10.27162/d.cnki.gjlin.2021.000578.CUI Wei. The key algorithm research and blind source separation in non-cooperative communication system[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Jilin University, 2021. doi: 10.27162/d.cnki.gjlin.2021.000578. [13] 王淼, 蔡晓霞, 雷迎科. 改进的欠定变速跳频信号盲分离算法[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2020, 42(2): 79–85.WANG Miao, CAI Xiaoxia, and LEI Yingke. An improved blind separation algorithm for underdetermined variable speed frequency hopping signals[J]. Journal of Detection & Control, 2020, 42(2): 79–85. [14] 杨保平, 陈永光, 杨鸾, 等. 一种异步非正交跳频网台盲分选方法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27(10): 103251. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.103251.YANG Baoping, CHEN Yongguang, YANG Luan, et al. A blind separating method for asynchronous nonorthogonal frequency hopping network[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27(10): 103251. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.103251. [15] 郭英, 东润泽, 张坤峰, 等. 基于稀疏贝叶斯学习的多跳频信号DOA估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(3): 516–522. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180435.GUO Ying, DONG Runze, ZHANG Kunfeng, et al. Direction of arrival estimation for multiple frequency hopping signals based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2019, 41(3): 516–522. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180435. [16] 梁策, 郭英, 李红光. 基于CNN网络的跳频信号个体识别[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 21(3): 57–62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2020.03.010.LIANG Ce, GUO Ying, and LI Hongguang. Individual identification of frequency-hopping signals based on CNN network[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 21(3): 57–62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2020.03.010. [17] 胡展. 复杂电磁环境条件下的跳频网台分选技术研究与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2020.002187.HU Zhan. Research and implementation of frequency hopping network sorting technology in complex electromagnetic environment[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2020. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2020.002187. [18] 杨永杰. 辐射源极化信息的检测和识别技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2012.YANG Yongjie. Research on measuring and detecting polarization information of radiation sources[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2012. [19] 马慧慧. 先进极化阵列的稳健参数估计算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2020.003390.MA Huihui. Robust parameters estimation algorithm for advanced polarimetric array[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2020. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2020.003390. [20] 曾清平. 雷达极化技术与极化信息应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2006: 10–12.ZENG Qingping. Radar Polarization Techniques and Polarization Information Applications[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2006: 10–12. [21] 肖顺平. 雷达极化技术[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2022: 36–37.XIAO Shunping. Radar Polarization Techniques[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2022: 36–37. [22] PARK J, JANG J, IM S, et al. A sub-Nyquist radar electronic surveillance system[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 10080–10091. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2799304. [23] CHEN Tao, LIU Lizhi, ZHAO Zhongkai, et al. A frequency estimation method based on MWC discrete compressed sampling structure[C]. Proceedings of the 2016 Sixth International Conference on Instrumentation & Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control, Harbin, 2016: 274–278. doi: 10.1109/IMCCC.2016.84. [24] 许洪玮. 传统谱聚类算法概述[J]. 电脑知识与技术, 2022, 18(23): 76–78. doi: 10.14004/j.cnki.ckt.2022.1578.XU Hongwei. An overview of traditional spectral clustering algorithms[J]. Computer Knowledge and Technology, 2022, 18(23): 76–78. doi: 10.14004/j.cnki.ckt.2022.1578. [25] VON LUXBURG U. A tutorial on spectral clustering[J]. Statistics and Computing, 2007, 17(4): 395–416. doi: 10.1007/s11222-007-9033-z. -





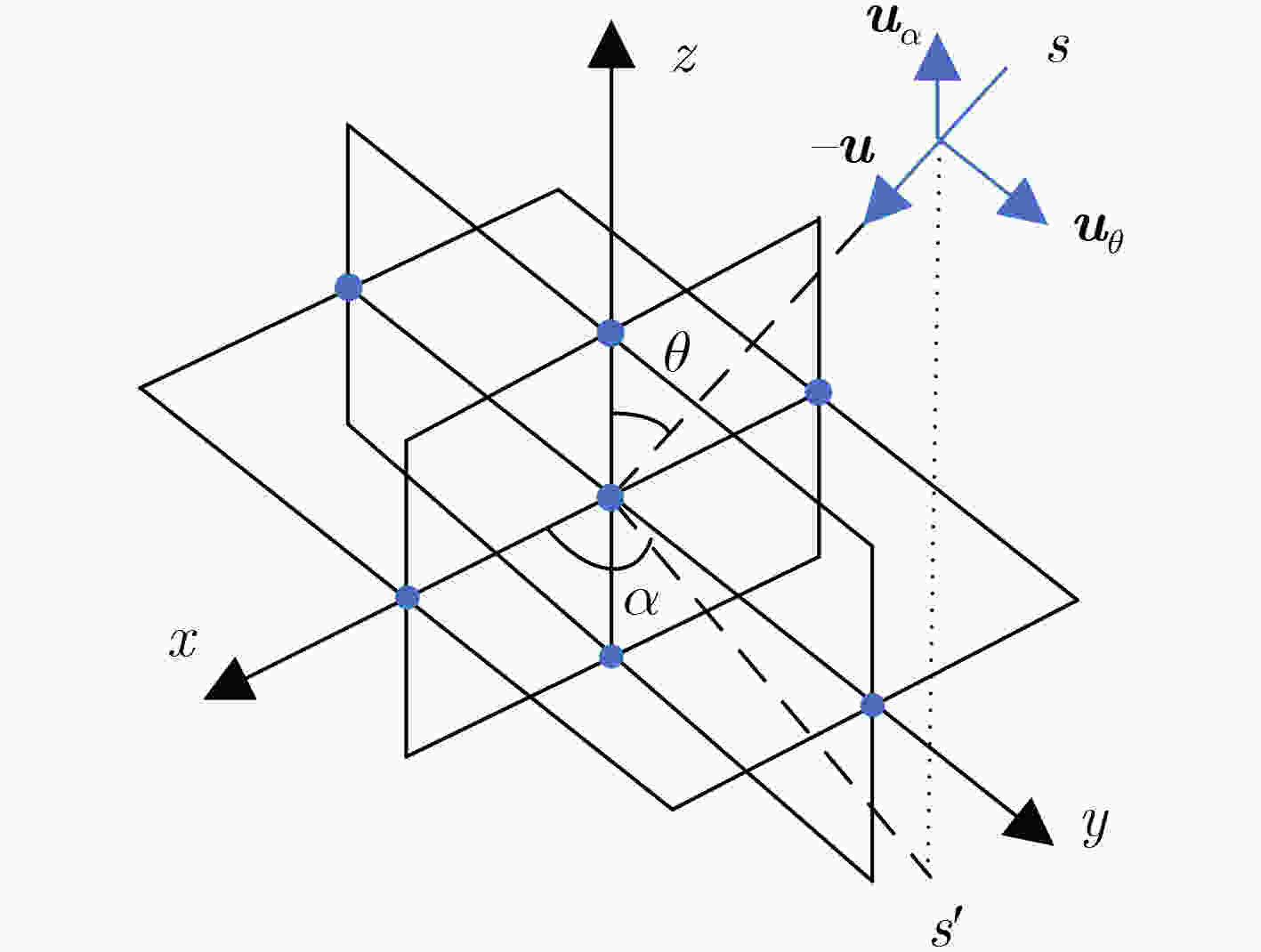
 下载:
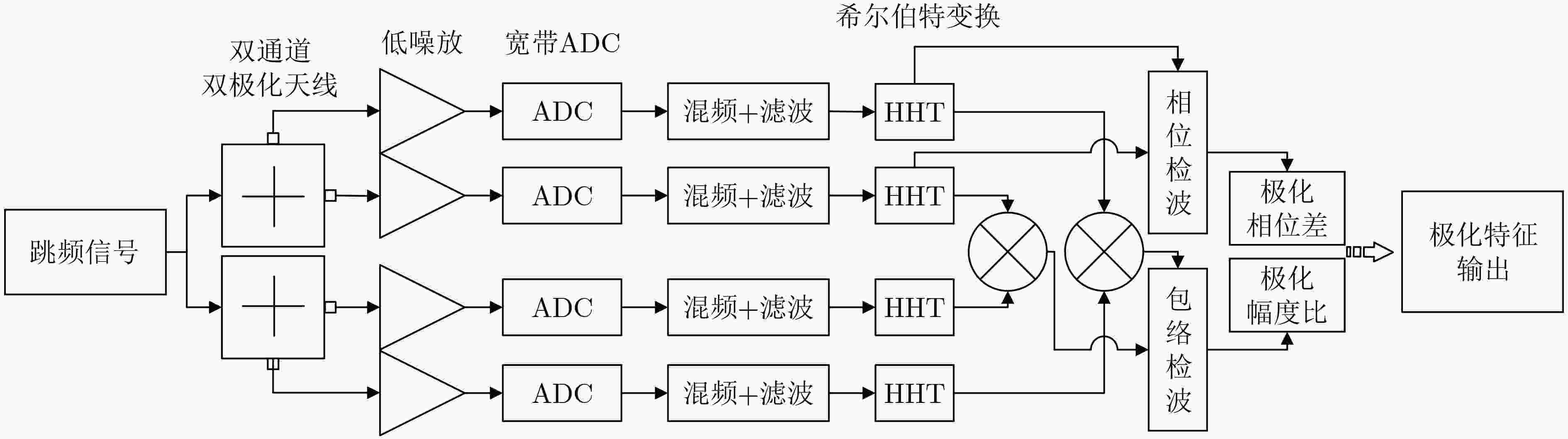
下载:
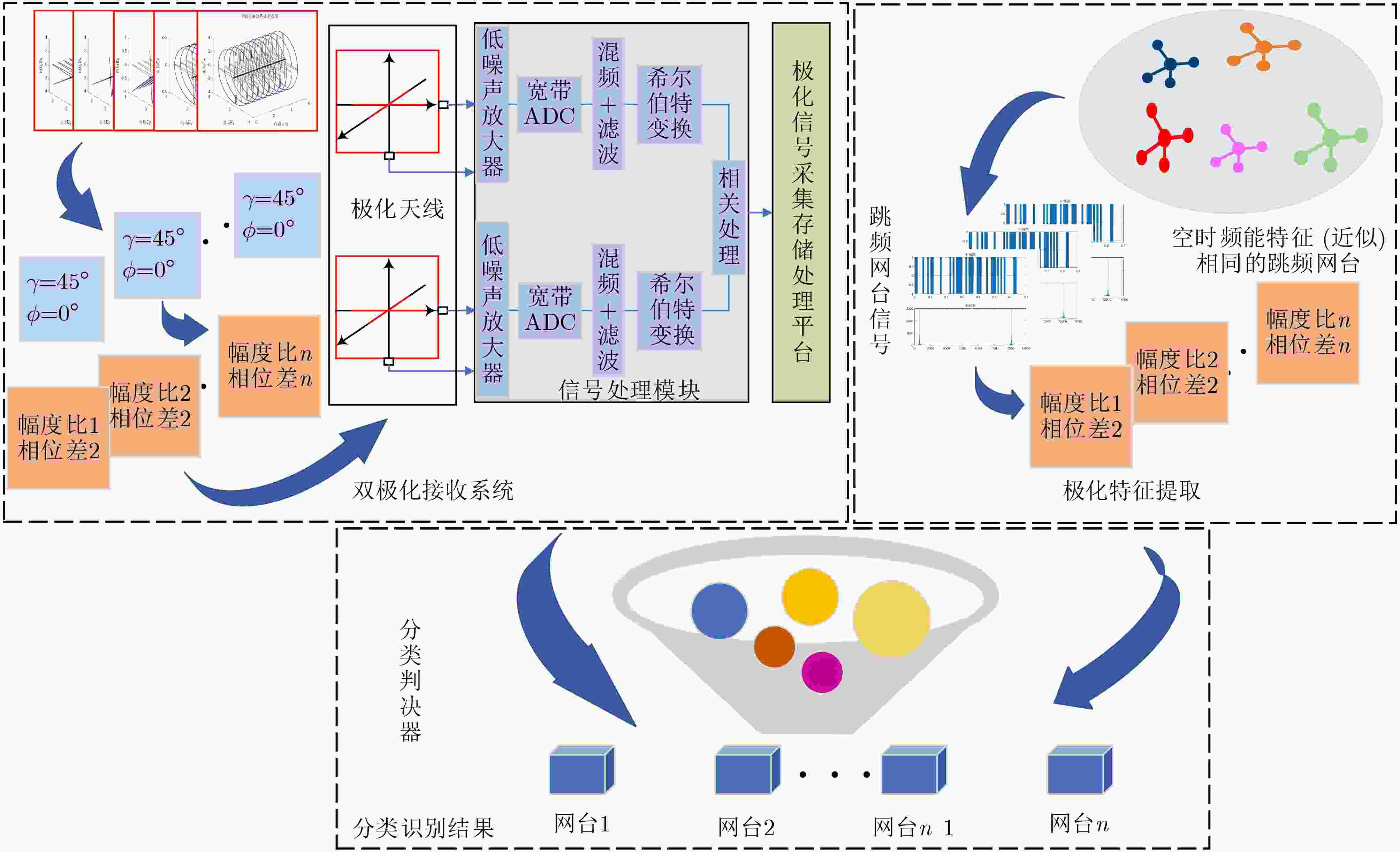
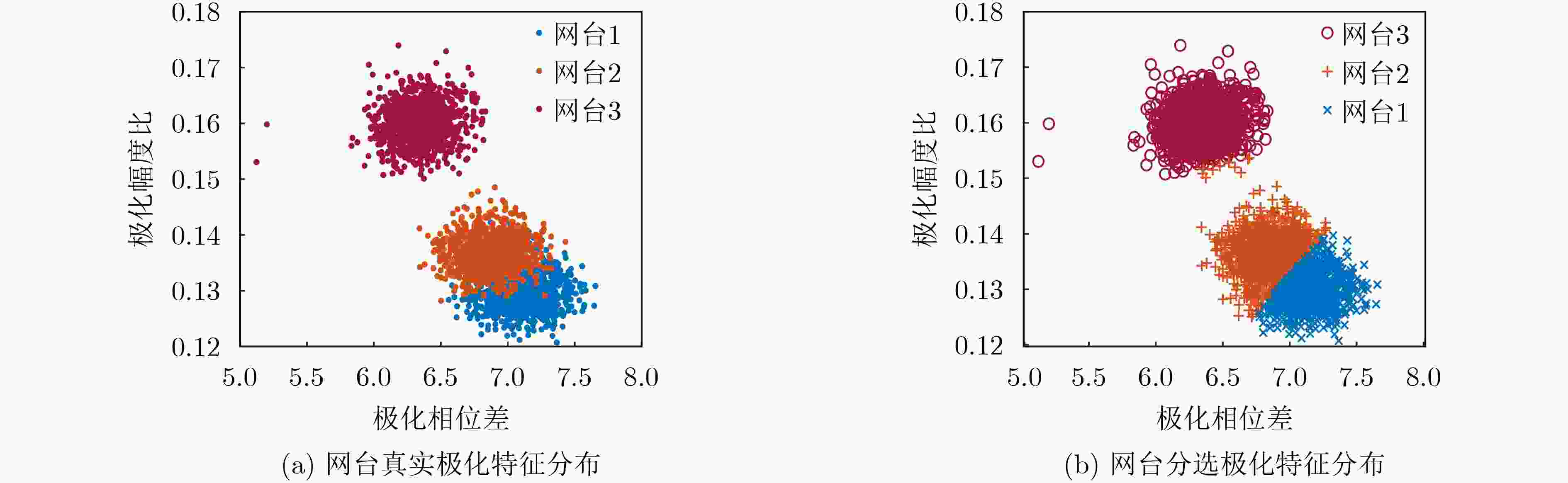
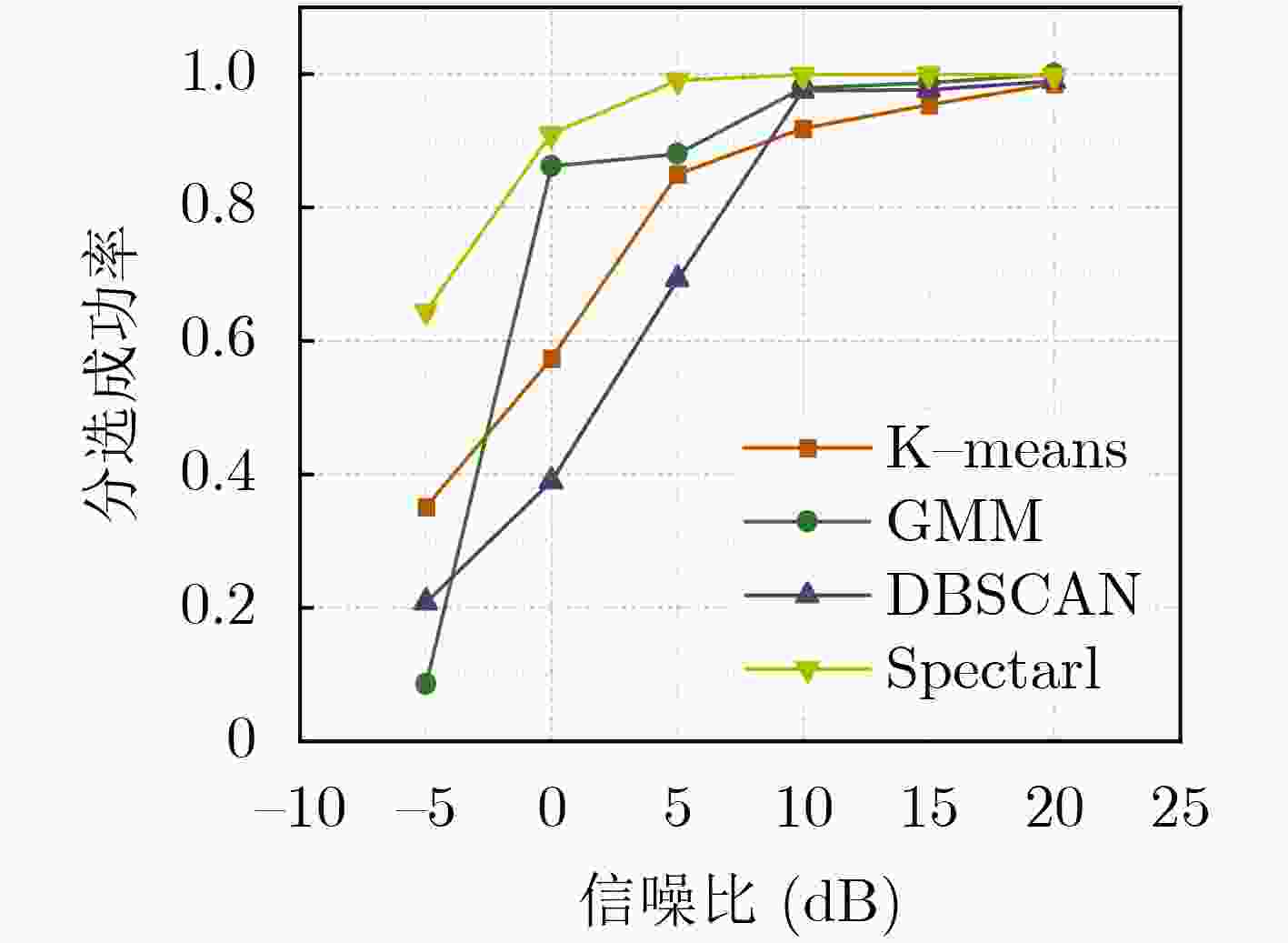
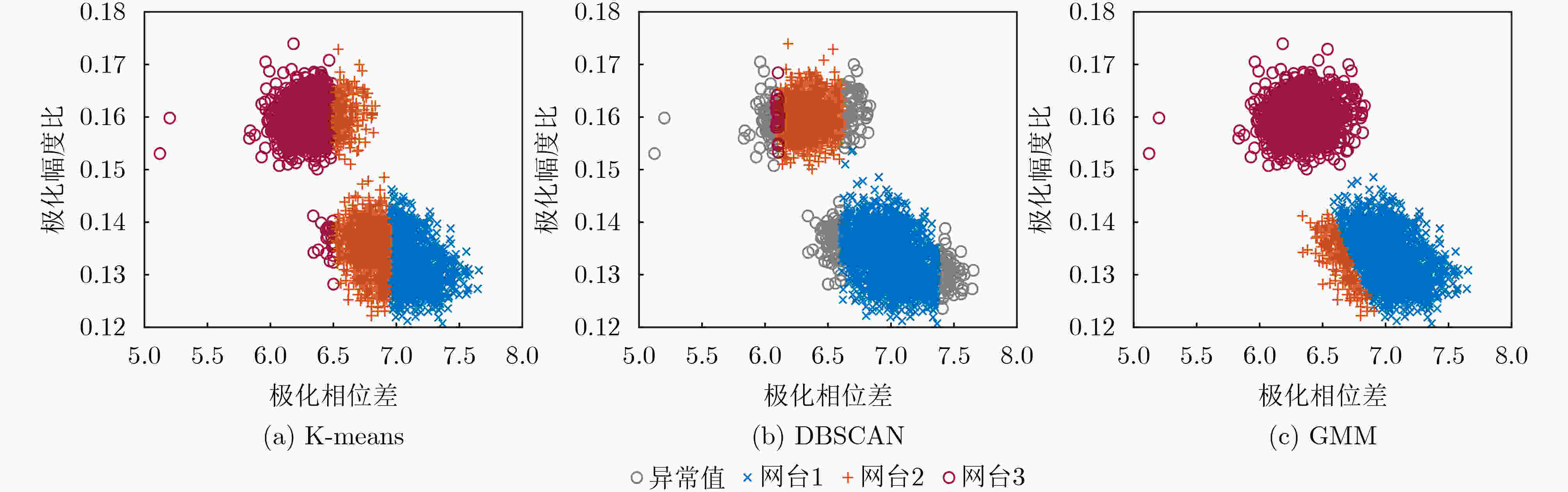
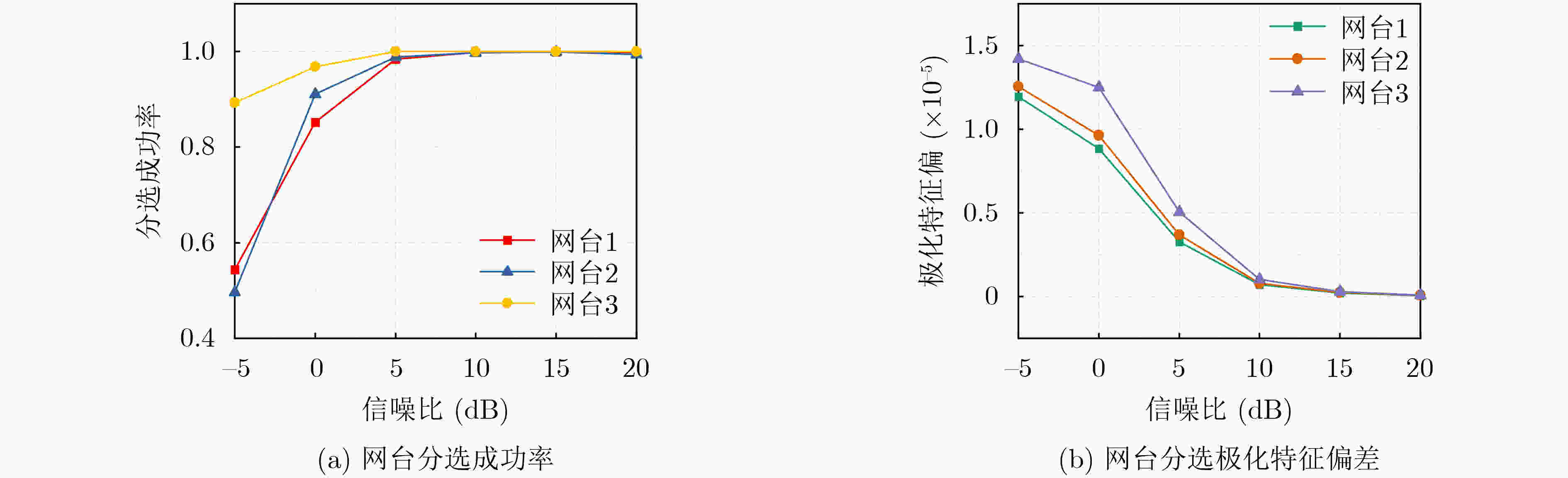
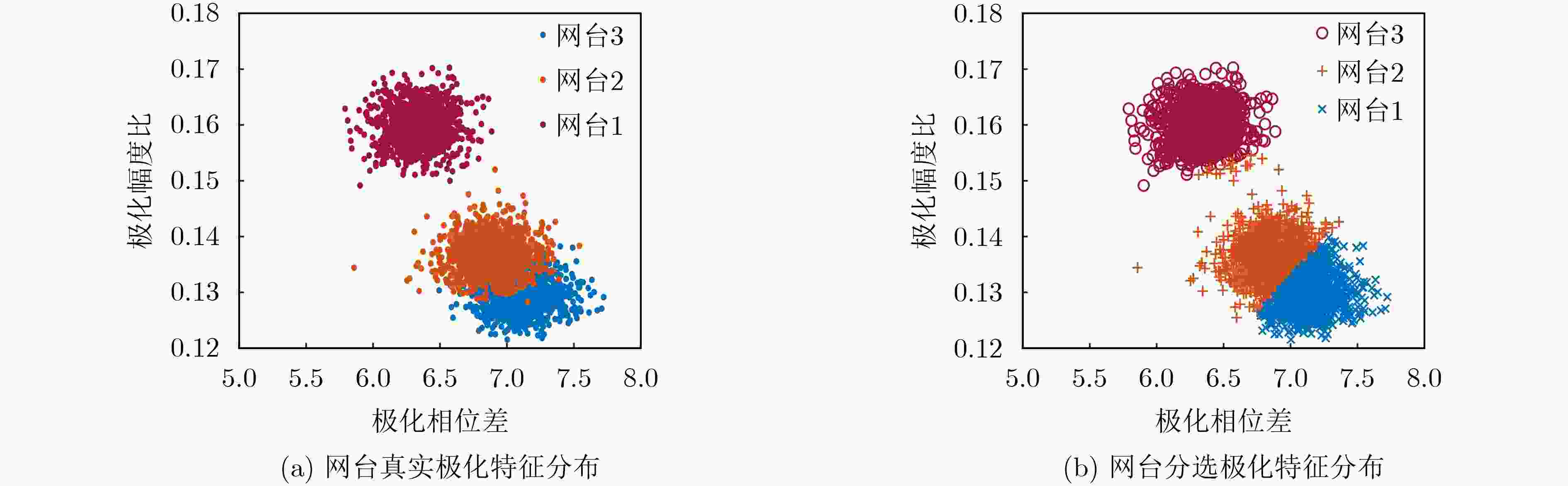
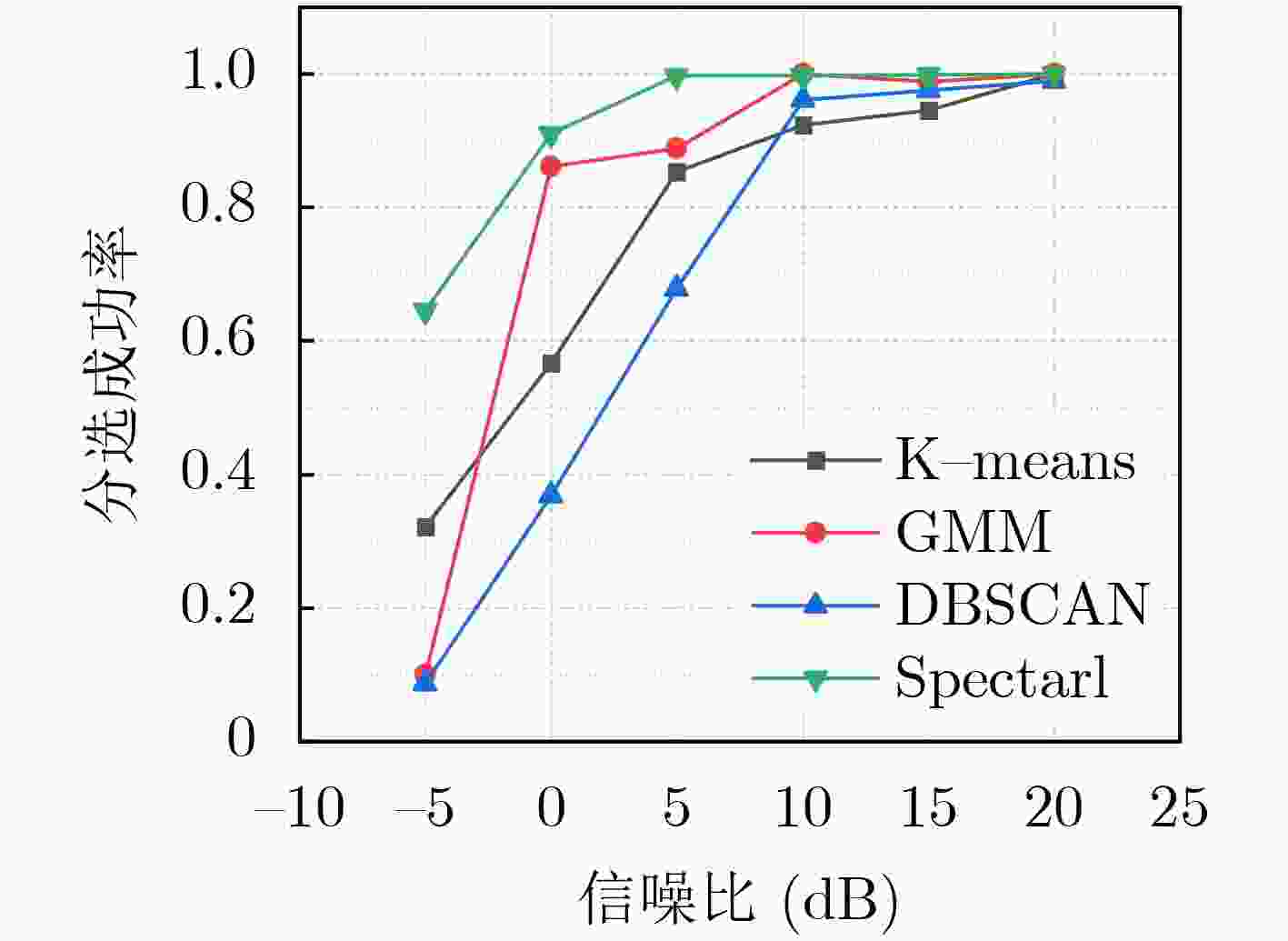
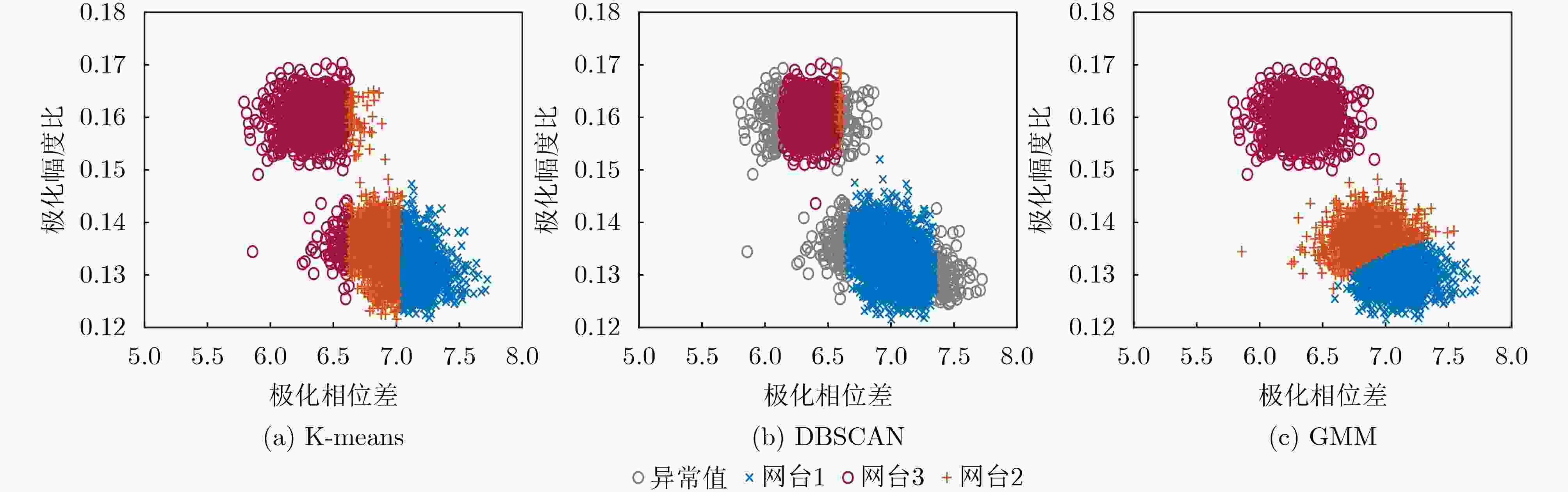


 下载:
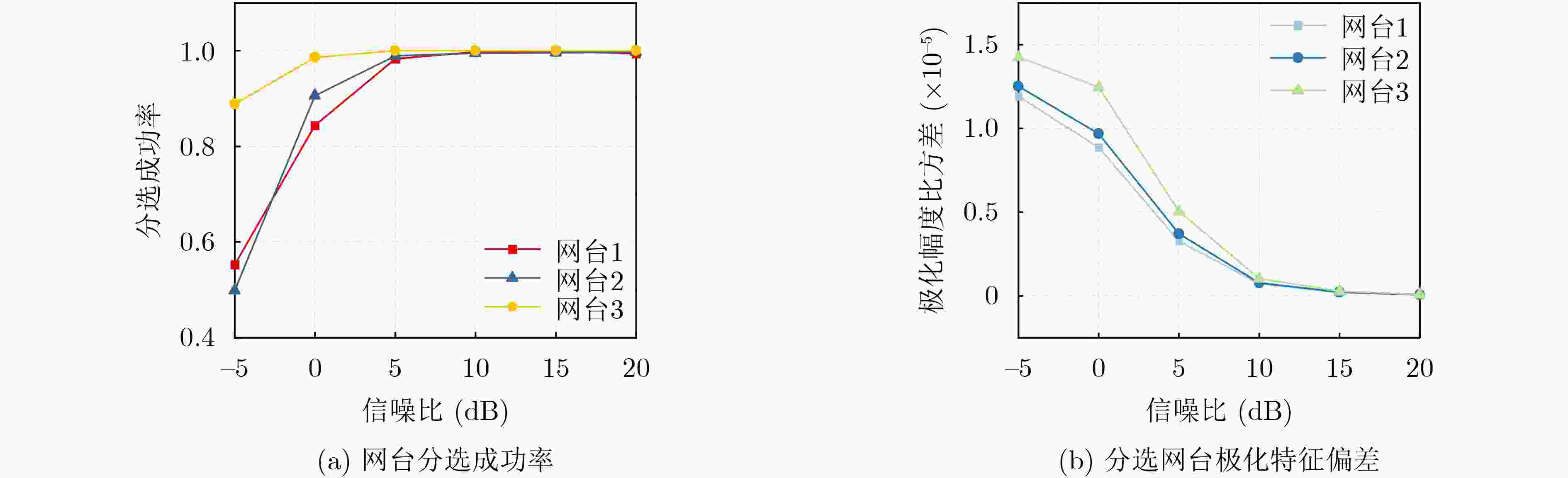
下载:
