A Power Side-channel Attack Framework for Lattice-based Post Quantum Cryptography
-
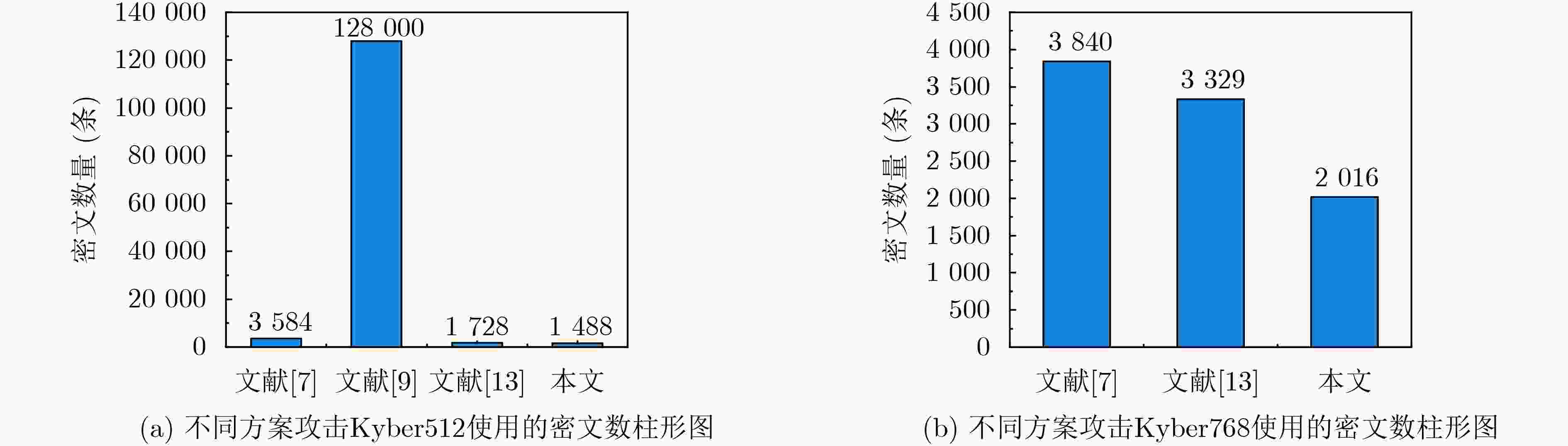
摘要: 为应对量子计算对传统公钥密码的安全威胁,后量子密码(PQC)已逐渐成为新一代密码技术。虽然后量子密码通过数学理论保证了算法的安全性,但在密码实现运算过程中易发生侧信道信息泄漏。该文提出一种针对格基PQC的能量侧信道分析攻击框架,利用秘密多项式系数与能耗之间的关系创建侧信道攻击模板,实现了对Kyber算法的侧信道攻击。该文还首次提出一种高阶选择密文攻击方法,成功实现了对Kyber算法的能量侧信道分析,与现有工作相比该方法恢复Kyber512和Kyber768的密钥所需密文条数分别降低了58.48%和47.5%。实验结果表明了该文构建的能量侧信道分析框架的可行性,验证了高阶选择密文攻击方法的有效性,可为后续PQC算法实现侧信道安全风险评估提供方法与工具支撑。Abstract: To address the security threat of quantum commutating on classic public key cryptography. Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) has gradually become a new generation cryptography technology. Although PQC ensures the security strength of the algorithms through mathematical theory, it can still be vulnerable to side-channel attacks during the execution of cipher implementation. A power side channel attack framework for lattice-based PQC is developped. By investigating the relationship between secret polynomial coefficient and power consumption, a template is created for the side-channel analysis of the Kyber algorithm. A novel high-order chosen ciphertext attack method is proposed, and power side channel attack on Kyber is realized successfully. Compared with existing work, the number of ciphertexts required to recover the entire Kyber512 key and Kyber768 key is reduced by 58.48% and 47.5% respectively. The feasibility of the proposed power side channel attack framework and the effectiveness of the proposed high-order chosen ciphertext attack method have been verified by experimental results. The method and tool support required for subsequent evaluation of the side channel security threat encountered by PQC is provided by this work.
-
表 1 Kyber PKE算法组成
算法名称 输入 输出 算法主要特点 CPAPKE.KeyGen() 输入:无 输出:公钥${\rm{pk}}$,私钥${\text{sk}}$ 对${\mathbf{s}}$进行编码变换得到${\rm{sk}}$,${\rm{pk}}$与算法
中间变量$e$和${\mathbf{s}}$相关。CPAPKE.Enc(${\rm{pk}}$, $m$, $r$) 输入:公钥${\rm{pk}}$,加密信息$m$,随机数$r$ 输出:密文结果$c$ $c$包含$ {c_1} $和${c_2}$两部分,$ {c_1} $与算法中间变量$u$相关,
${c_2}$与算法中间变量$v$相关,(${\boldsymbol{u}}$, $v$)与${\rm{pk}}$和$m$相关。CPAPKE.Dec(${\rm{sk}}$,$c$) 输入:私钥${\rm{sk}}$,密文$c$ 输出:解密信息$m$ 解码$c$获(${\boldsymbol{u}}$, $v$),解码${\rm{sk}}$获${\mathbf{s}}$,(${\boldsymbol{u}}$,$v$, ${\mathbf{s}}$)编码获得$m$。 算法1 Kyber.CPAPKE.Dec(sk, c) 输入:密文$c$,私钥${\rm{sk}}$ 输出:解密信息 $m'$ (1) ${({\boldsymbol{u} },v) = {\text{ DecodeCT(} }c{\text{)} } }$ (2) ${\mathbf{s } }{\text{ = DecodeSK(} }{\rm{sk}}{\text{)} }$ (3) $m' = {\text{ Poly\_to\_Msg} }(v - {\boldsymbol{u}} \cdot {\boldsymbol{s}}{\text{ } })$ 表 2 Kyber的选择密文攻击表
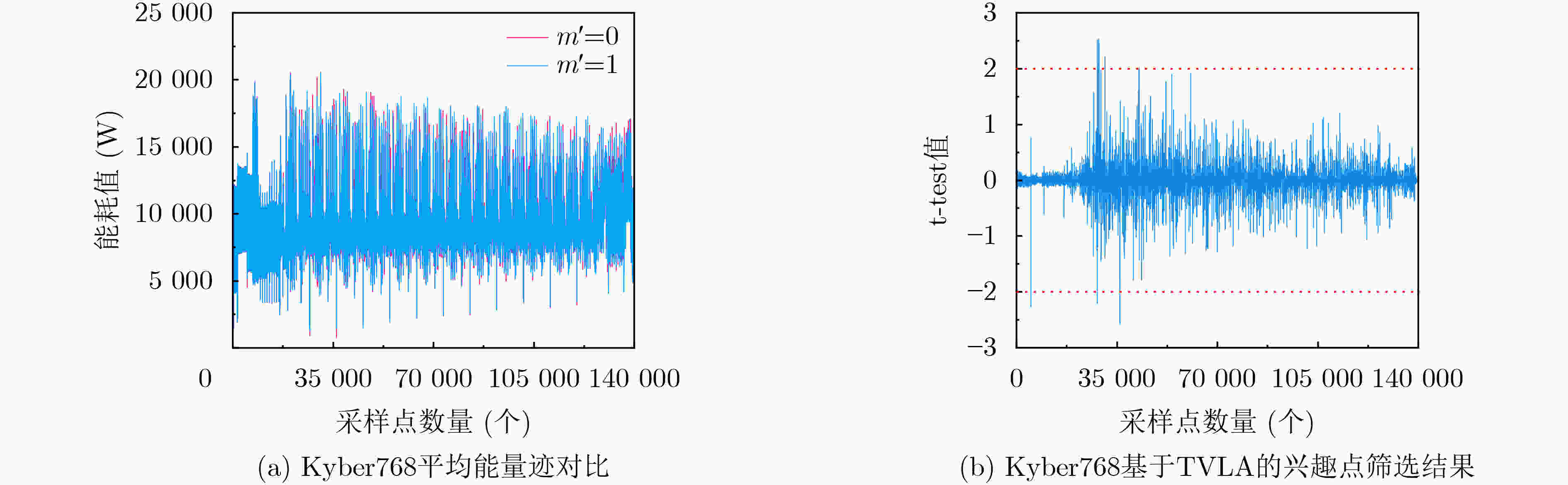
$ {\boldsymbol{s}} $的系数$m' = 0/m' = 1$ ($ {k_{\mathbf{u}}} $,${k_v}$) ($ {k_{{\mathbf{u}}0}} $,${k_{v0}}$) ($ {k_{{\mathbf{u}}1}} $,${k_{v1}}$) ($ {k_{{\mathbf{u}}2}} $,${k_{v2}}$) ($ {k_{{\mathbf{u}}3}} $,${k_{v3}}$) ($ {k_{{\mathbf{u}}4}} $,${k_{v4}}$) $ - \eta $ 1 0 1 0 1 $ - (\eta - 1) $ 0 0 1 0 1 $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ 0 0 0 0 0 1 $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $ \eta - 1 $ 0 0 0 1 0 $ \eta $ 0 1 0 1 0 表 3 测试案例实验环境
硬件环境 软件环境 编程语言 Pico 6406E示波器,stm32开发板,个人电脑(i7处理器, 16 GB内存) Arduino,PyCharm C语言,python 表 4 Kyber512选择密文攻击表
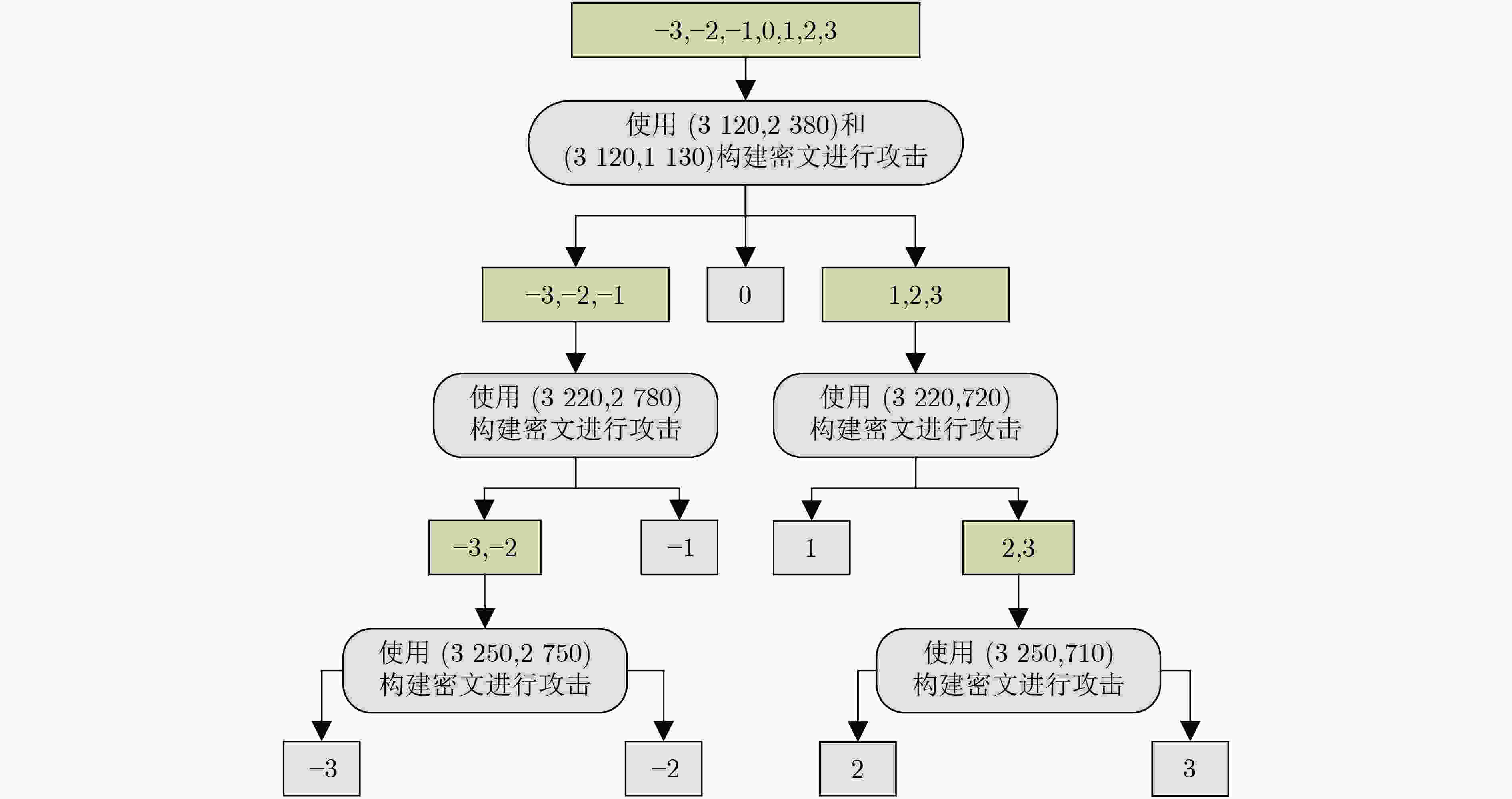
$ {\boldsymbol{s}} $的系数 ($ {k_{\mathbf{u}}} $,${k_v}$) (3120, 2380) (3120, 1130) (3220, 2780) (3220, 720) (3250, 2750) (3250, 710) –3 1 0 1 0 1 0 –2 1 0 1 0 0 0 –1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 2 0 1 0 1 0 0 3 0 1 0 1 0 1 表 5 Kyber768选择密文攻击表
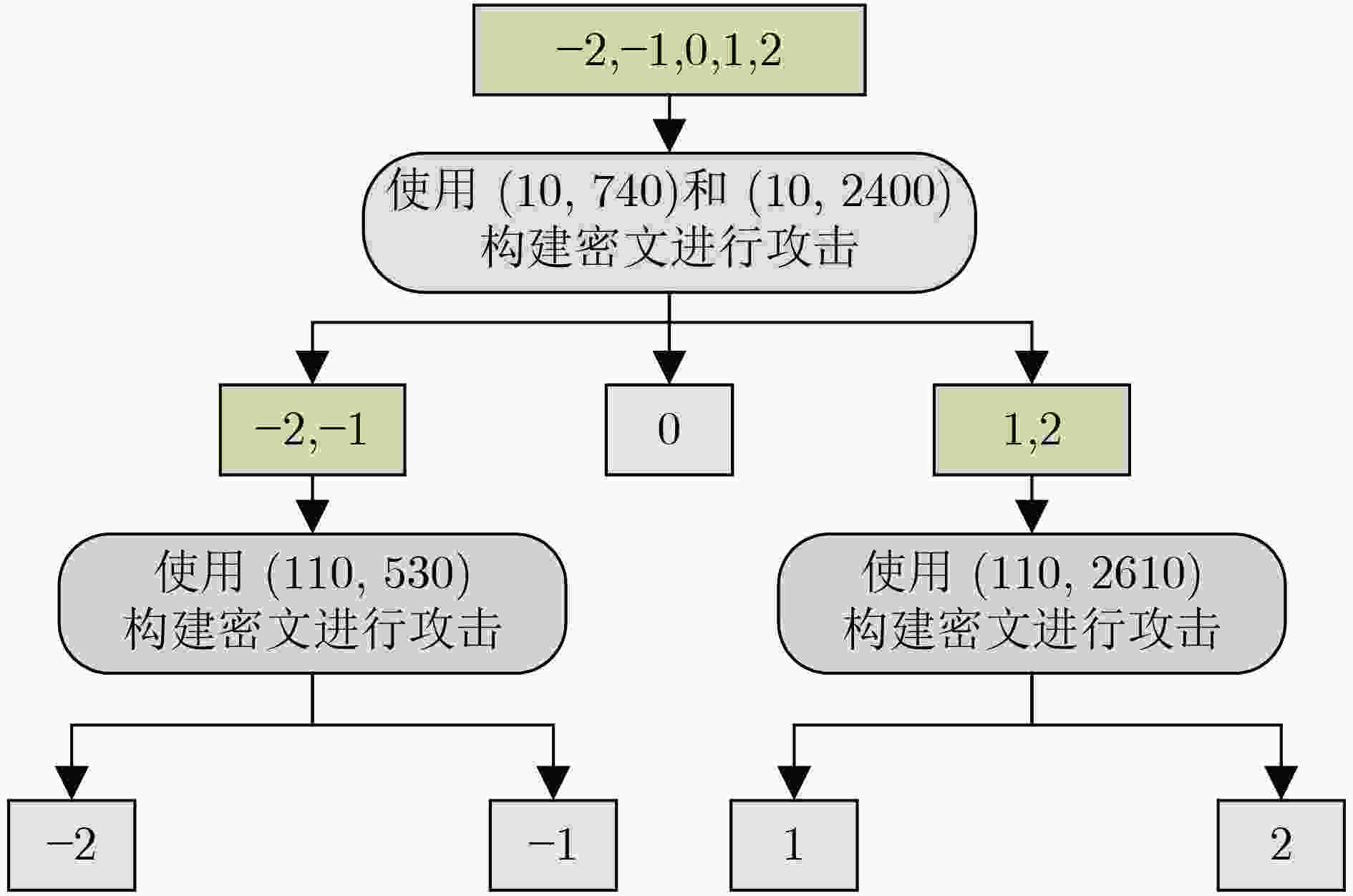
$ {\boldsymbol{s}} $的系数 ($ {k_{\mathbf{u}}} $,${k_v}$) (10, 740) (10, 2400) (110, 530) (110, 2610) –2 1 0 1 0 –1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 2 0 1 0 1 -
[1] 王潮, 姚皓南, 王宝楠, 等. 量子计算密码攻击进展[J]. 计算机学报, 2020, 43(9): 1691–1707. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.01691WANG Chao, YAO Haonan, WANG Baonan, et al. Progress in quantum computing cryptography attacks[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020, 43(9): 1691–1707. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.01691 [2] PRIMAS R, PESSL P, and MANGARD S. Single-trace side-channel attacks on masked lattice-based encryption[C]. The 19th International Conference on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Taipei, China, 2017: 513–533. [3] KIM S and HONG S. Single trace analysis on constant time CDT sampler and its countermeasure[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(10): 1809. doi: 10.3390/app8101809 [4] DING Jintai, CHENG Chi, and QIN Yue. A simple key reuse attack on LWE and ring LWE encryption schemes as key encapsulation mechanisms (KEMs)[J]. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2019, page: 271. [5] BĂETU C, DURAK F B, HUGUENIN-DUMITTAN L, et al. Misuse attacks on post-quantum cryptosystems[C]. The 38th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Darmstadt, Germany, 2019: 747–776. [6] PESSL P and PRIMAS R. More practical single-trace attacks on the number theoretic transform[C]. The 6th International Conference on Cryptology and Information Security in Latin America, Santiago de Chile, Chile, 2019: 130–149. [7] RAVI P, ROY S S, CHATTOPADHYAY A, et al. Generic side-channel attacks on CCA-secure lattice-based PKE and KEMS[J]. IACR Transactions on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, 2020, 2020(3): 307–335. doi: 10.13154/tches.v2020.i3.307-335 [8] AMIET D, CURIGER A, LEUENBERGER L, et al. Defeating NEWHOPE with a single trace[C]. Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Post-Quantum Cryptography, Paris, France, 2020: 189–205. [9] RAVI P, BHASIN S, ROY S S, et al. On exploiting message leakage in (few) NIST PQC candidates for practical message recovery attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17: 684–699. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2021.3139268 [10] NGO K, DUBROVA E, GUO Qiao, et al. A side-channel attack on a masked IND-CCA secure saber KEM implementation[J]. IACR Transactions on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, 2021, 2021(4): 676–707. doi: 10.46586/tches.v2021.i4.676-707 [11] NGO K, DUBROVA E, and JOHANSSON T. Breaking masked and shuffled CCA secure saber KEM by power analysis[C]. The 5th Workshop on Attacks and Solutions in Hardware Security, Seoul, Korea, 2021: 51–61. [12] XU Zhuang, PEMBERTON O, ROY S S, et al. Magnifying side-channel leakage of lattice-based cryptosystems with chosen ciphertexts: The case study of Kyber[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2022, 71(9): 2163–2176. doi: 10.1109/TC.2021.3122997 [13] TANAKA Y, UENO R, XAGAWA K, et al. Multiple-valued plaintext-checking side-channel attacks on post-quantum KEMs[J]. IACR Transactions on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, 2023(3): 473–503. doi: 10.46586/tches.v2023.i3.473-503 [14] BOCK E A, BANEGAS G, BRZUSKA C, et al. Breaking DPA-protected Kyber via the pair-pointwise multiplication[J]. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2023, page: 551. [15] GUO Qian, NABOKOV D, NILSSON A, et al. SCA-LDPC: A code-based framework for key-recovery side-channel attacks on post-quantum encryption schemes[J]. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2023, page: 294. -





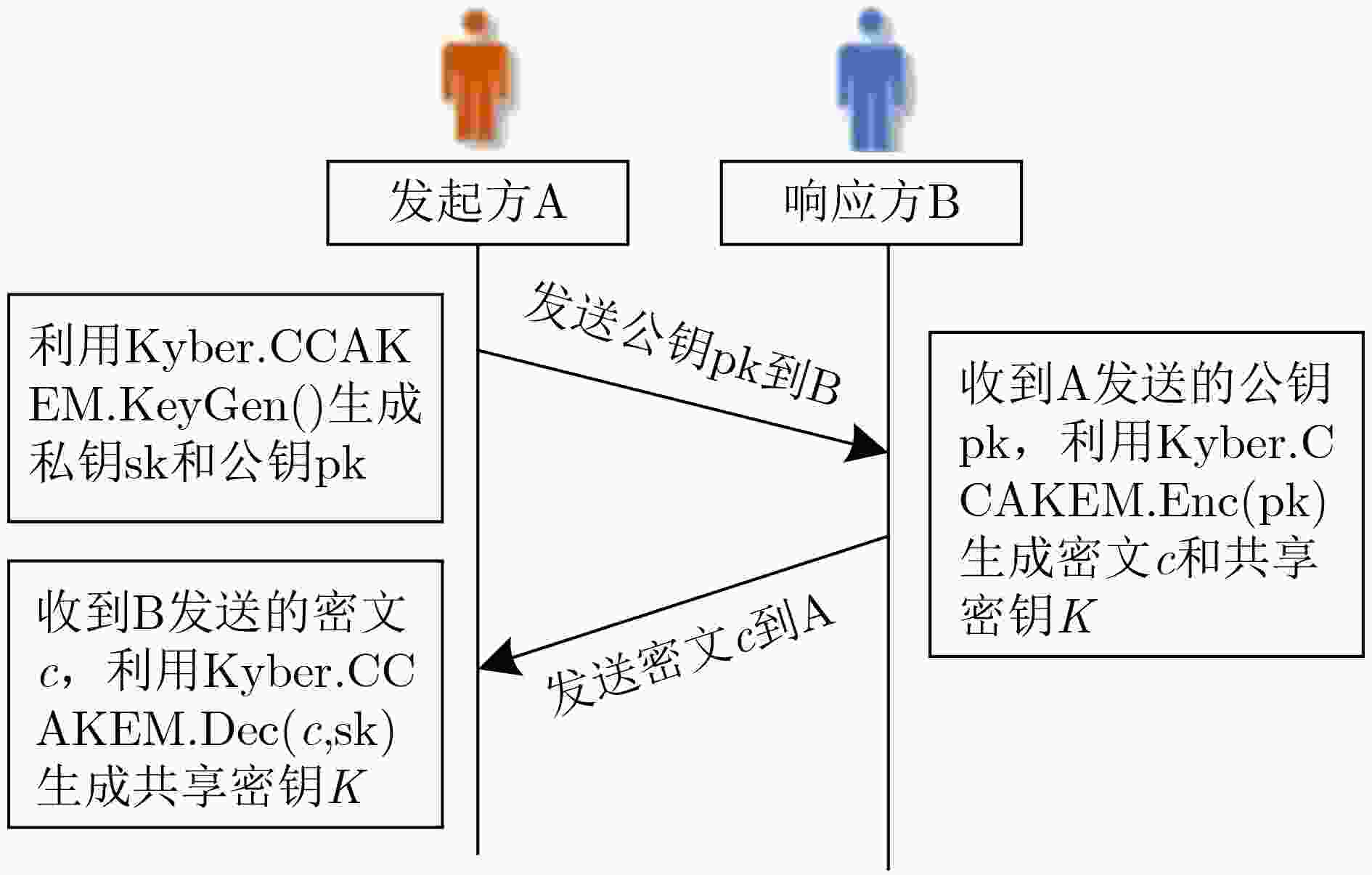
 下载:
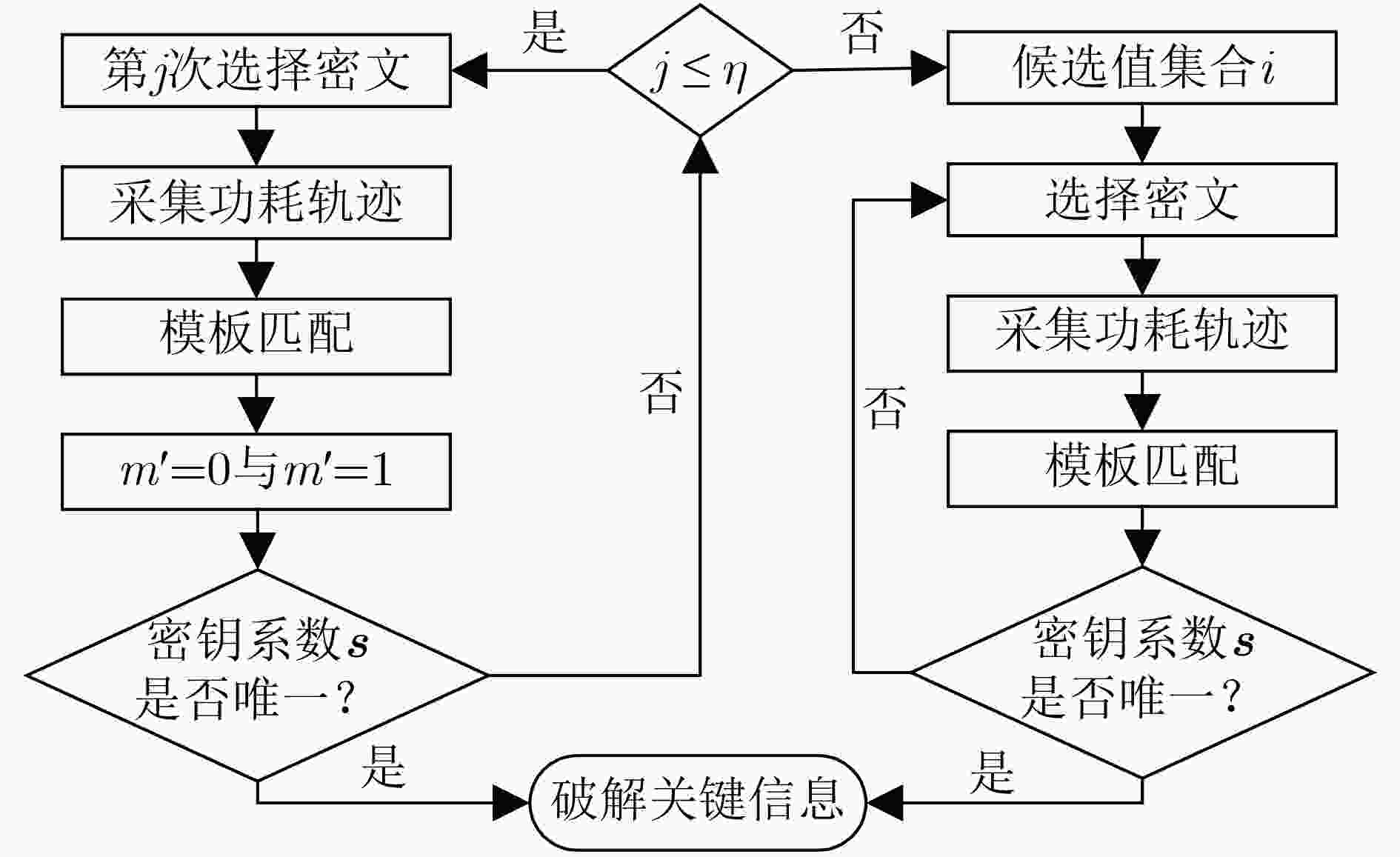
下载:

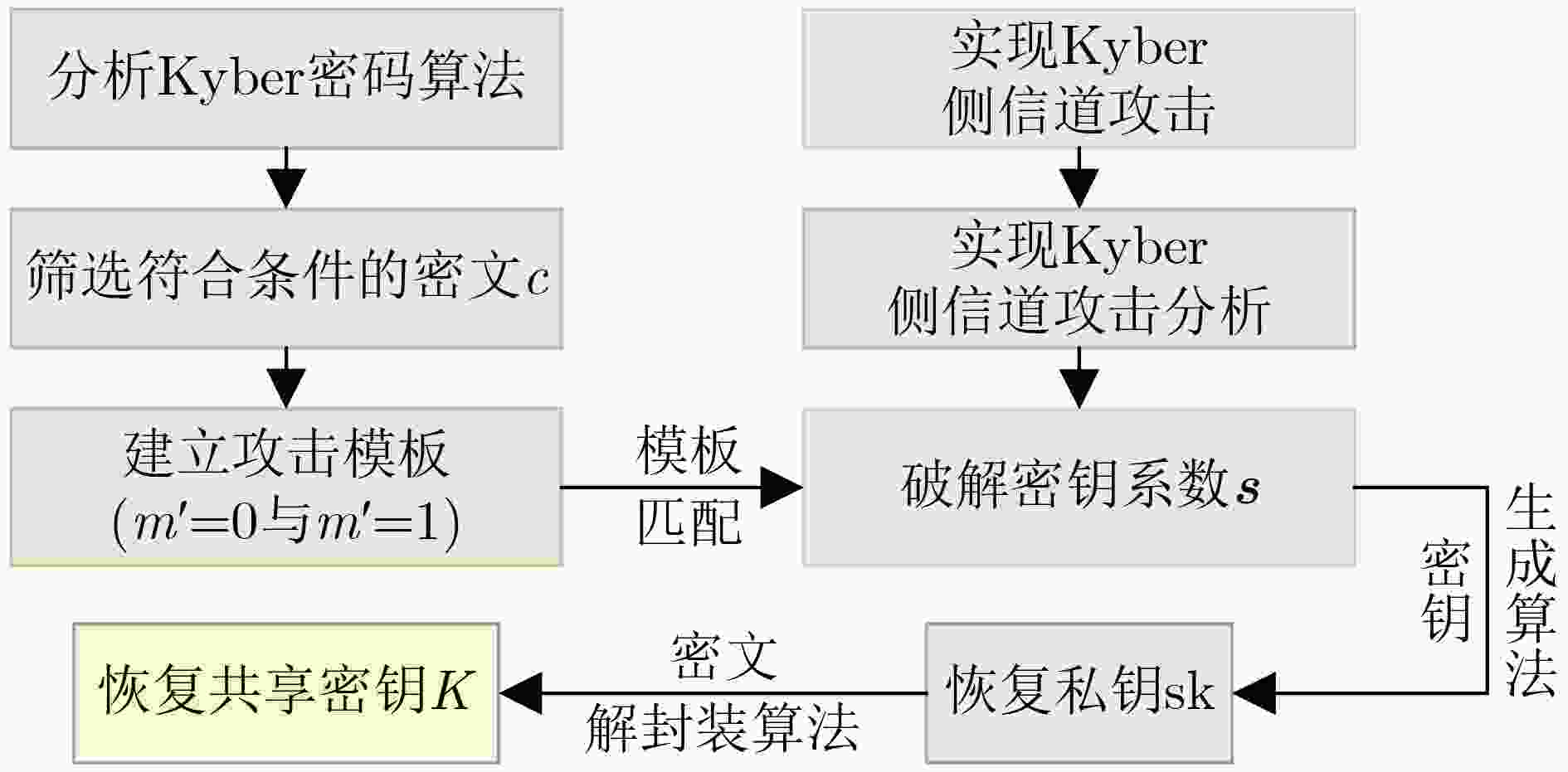
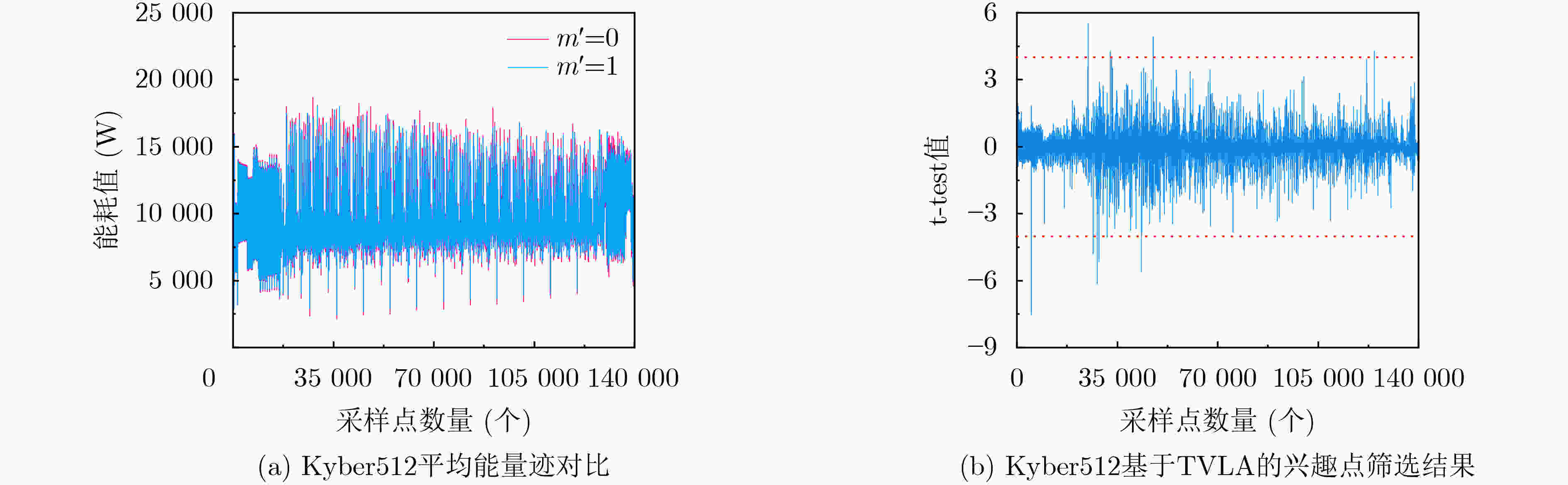


 下载:
下载:
