Underwater Acoustic Signal Detection using Similarity Network Construction and Representation
-
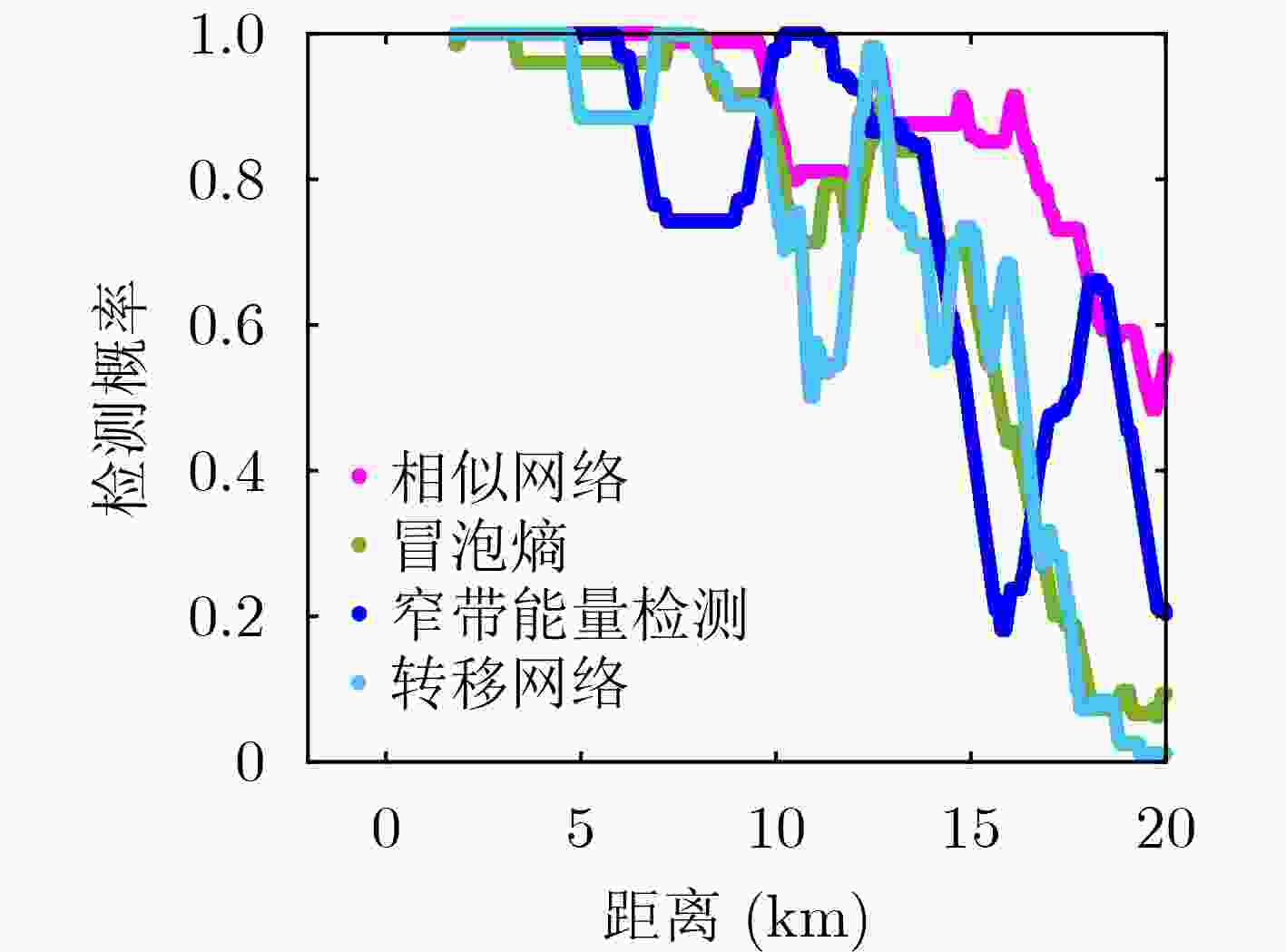
摘要: 水下声信号检测在海洋防御系统中扮演着不可或缺的角色,同时也广泛应用于民用领域。然而,在没有目标信号先验信息的情况下,目前仍缺乏行之有效的水下声信号检测方法。为此,该文提出了一种新的算法—相似网络,以解决在复杂海洋背景下水下目标检测的难题。该方法结合了信息几何和复杂网络理论,通过将节点相似度度量问题转化为矩阵流形上的几何问题,测量不同时间尺度上数据之间的相似性,并构建时间序列数据的网络表示。同时还引入了图信号处理理论,以提取目标信号内部隐藏的动力学特性,从而实现无目标先验信息下的水下声信号检测。通过对仿真和实测数据的研究验证,证明了该方法的有效性。结果表明,相似网络方法优于现有的网络构建和目标信号被动检测方法,能够更有效地检测水下声信号,实现无目标先验信息下的水下声信号检测。Abstract: Underwater acoustic signal detection plays a crucial role in ocean defense systems and has broad applications in civilian domains. However, contemporary underwater acoustic signal detection methods need to be improved for effectiveness when prior information about the target is unavailable. This paper proposes a new algorithm - a similarity network - to address the challenge of underwater target detection in complex oceanic backgrounds. In this method, information geometry and complex network theory are combined, and the problem of measuring node similarity is converted into a geometric problem on a matrix manifold, wherein the similarity between data at different time scales is determined, and a network representation of the time series data is achieved. Concurrently, a graph signal processing theory is introduced to extract the hidden dynamic characteristics of the target signal, thereby achieving underwater acoustic signal detection without prior target information. Further, the effectiveness of this method is demonstrated through research and verification of the simulated and actual. Our results show that the similarity network method is superior to existing network construction and passive target detection methods, can detect underwater acoustic signals more effectively, and can achieve underwater acoustic signal detection without any prior target information.
-
Key words:
- Complex network /
- Information geometry /
- Similarity network /
- Acoustic signal detection
-
表 1 试验数据记录表
时间 试验船经纬度 航速(kn) 与水听器布放点距离(km) 走航路线对应点 17:18 19°21.694$' $N/115°5.30$' $E 8.7 10 A点 17:50 水听器正横位置 8.7 2 水听器正横位置 18:34 19°27.903$' $N/115°14.579$' $E 8.0 10 B点 19:15 水听器正横位置 8.0 2 水听器正横位置 19:55 19°20.765$' $N/115°5.981$' $E 8.5 10 C点 20:30 水听器正横位置 8.5 2 水听器正横位置 21:10 19°24.888$' $N/115°15.986$' $E 8.5 10 D点 22:05 E点位置 8.5 20 E点 00:30 18°58.785$' $N/115°28.206$' $E 8.5 56 终点 -
[1] LEROY E C, SAMARAN F, STAFFORD K M, et al. Broad-scale study of the seasonal and geographic occurrence of blue and fin whales in the Southern Indian Ocean[J]. Endangered Species Research, 2018, 37: 289–300. doi: 10.3354/esr00927 [2] 马石磊, 王海燕, 申晓红, 等. 复杂海洋环境噪声下甚低频声信号检测方法[J]. 兵工学报, 2020, 41(12): 2495–2503. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.12.015MA Shilei, WANG Haiyan, SHEN Xiaohong, et al. Detection method of VLF acoustic signal in complex marine environmental noise[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(12): 2495–2503. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.12.015 [3] YANG Hong, LI Lulu, LI Guohui, et al. A novel feature extraction method for ship-radiated noise[J]. Defence Technology, 2022, 18(4): 604–617. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2021.03.012 [4] WAGHMARE R G, NALBALWAR S L, and DAS A. Transient signal detection on the basis of energy and zero crossing detectors[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2012, 30: 129–134. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2012.01.843 [5] ALMOUNAJJED A, SAHOO A K, KUMAR M K, et al. Stator fault diagnosis of induction motor based on discrete wavelet analysis and neural network technique[J]. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2023, 9(1): 142–157. doi: 10.23919/CJEE.2023.000003 [6] WANG Xiaojuan, CHEN Feng, ZHOU Hongyuan, et al. Structural damage detection based on cross-correlation function with data fusion of various dynamic measurements[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2022, 541: 117373. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2022.117373 [7] HE Kaiming, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]. Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2980–2988. [8] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Region-based convolutional networks for accurate object detection and segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(1): 142–158. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2437384 [9] SHI Peiming, LI Mengdi, ZHANG Wenyue, et al. Weak signal enhancement for machinery fault diagnosis based on a novel adaptive multi-parameter unsaturated stochastic resonance[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2022, 189: 108609. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2021.108609 [10] 闫源江, 甘新年, 胡光波. 舰船辐射噪声的混沌特性检验[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2011, 31(1): 61–63,155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2011.01.020YAN Yuanjiang, GAN Xinnian, and HU Guangbo. Testing for chaotic property for ship radiated noise[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2011, 31(1): 61–63,155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2011.01.020 [11] SUN Yilin and ZHANG Xiaomin. Analysis of chaotic characteristics of ship radiated noise signals with different data lengths[C]. OCEANS 2022-Chennai, Chennai, India, 2022: 1–7. [12] LI Yuxing, GAO Peiyuan, TANG Bingzhao, et al. Double feature extraction method of ship-radiated noise signal based on slope entropy and permutation entropy[J]. Entropy, 2022, 24(1): 22. doi: 10.3390/e24010022 [13] SONG Xingjian and XIAO Fuyuan. Combining time-series evidence: A complex network model based on a visibility graph and belief entropy[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2022, 52(9): 10706–10715. doi: 10.1007/s10489-021-02956-5 [14] GAO Jianxi, BARZEL B, and BARABÁSI A L. Universal resilience patterns in complex networks[J]. Nature, 2016, 530(7590): 307–312. doi: 10.1038/nature16948 [15] LI Aming, CORNELIUS S P, LIU Yangyu, et al. The fundamental advantages of temporal networks[J]. Science, 2017, 358(6366): 1042–1046. doi: 10.1126/science.aai7488 [16] ZHANG J and SMALL M. Complex network from pseudoperiodic time series: Topology versus dynamics[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 96(23): 238701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.238701 [17] ZOU Yong, DONNER R V, MARWAN N, et al. Complex network approaches to nonlinear time series analysis[J]. Physics Reports, 2019, 787: 1–97. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2018.10.005 [18] HU Jun, ZHANG Yujie, WU Peng, et al. An analysis of the global fuel-trading market based on the visibility graph approach[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2022, 154: 111613. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2021.111613 [19] GAO Zhongke, CAI Qing, YANG Yuxuan, et al. Time-dependent limited penetrable visibility graph analysis of nonstationary time series[J]. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2017, 476: 43–48. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2017.02.038 [20] ZHANG Hongwei, WANG Haiyan, YAN Yongsheng, et al. Weighted dynamic transfer network and spectral entropy for weak nonlinear time series detection[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2023, 111(10): 9345–9359. doi: 10.1007/s11071-023-08310-3 [21] AKBARI H, SADIQ M T, UR REHMAN A, et al. Depression recognition based on the reconstruction of phase space of EEG signals and geometrical features[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2021, 179: 108078. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2021.108078 [22] 华小强, 程永强, 王宏强, 等. 矩阵信息几何中值检测器[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(2): 284–294. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200684HUA Xiaoqiang, CHENG Yongqiang, WANG Hongqiang, et al. Matrix information geometric median detectors[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(2): 284–294. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200684 [23] ZHANG Hongwei, WANG Haiyan, YAN Yongsheng, et al. Remote passive sonar detection by relative multiscale change entropy[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(18): 18066–18075. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3195994 [24] TOOTOONI M S, RAO P K, CHOU C A, et al. A spectral graph theoretic approach for monitoring multivariate time series data from complex dynamical processes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2018, 15(1): 127–144. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2016.2598094 [25] ZHANG Hongwei, WANG Haiyan, LIANG Xuanming, et al. Weighted undirected similarity network construction and application for nonlinear time series detection[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2023, 30: 728–732. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2023.3286809 [26] MANIS G, AKTARUZZAMAN M D, and SASSI R. Bubble entropy: An entropy almost free of parameters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 64(11): 2711–2718. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2017.2664105 [27] ZHANG Zhen, WANG Minggang, XU Hua, et al. Research on the co-movement between high-end talent and economic growth: A complex network approach[J]. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2018, 492: 1216–1225. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2017.11.049 -





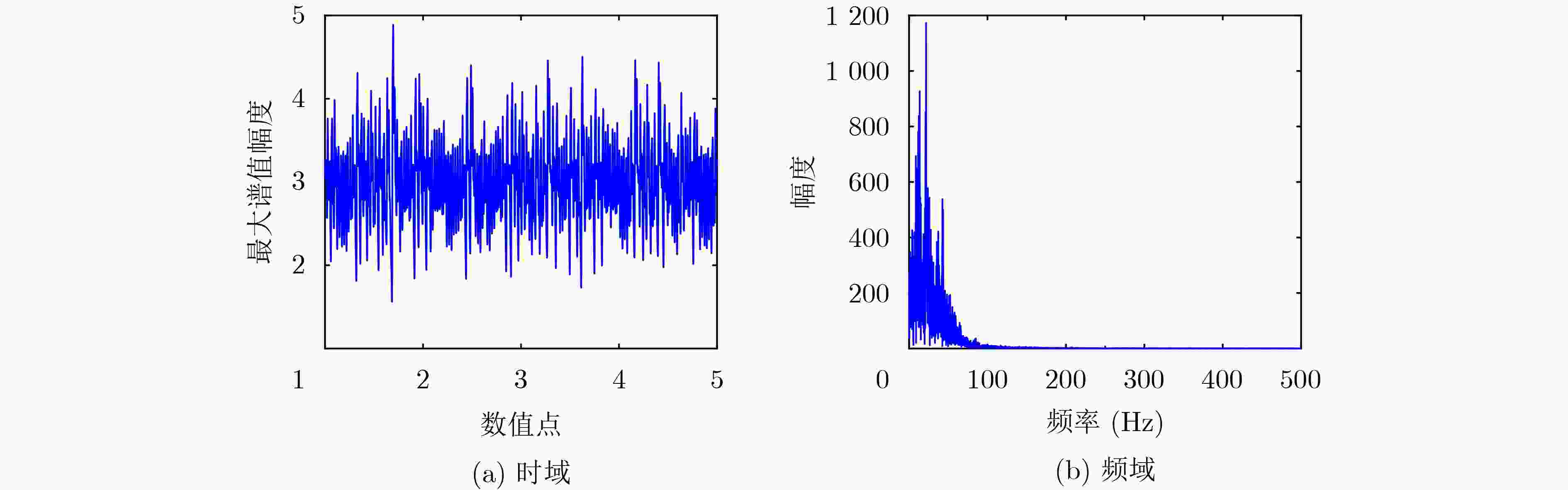
 下载:
下载:
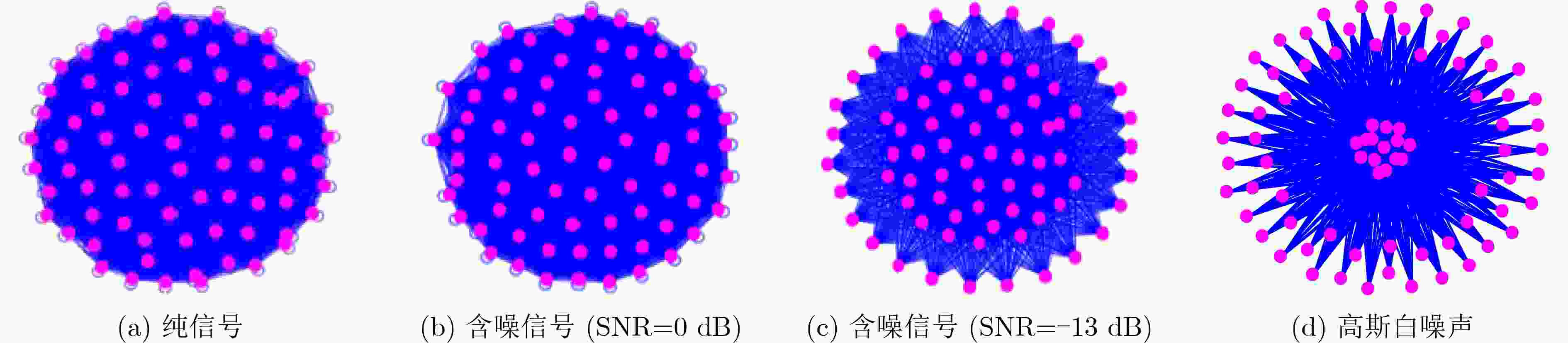
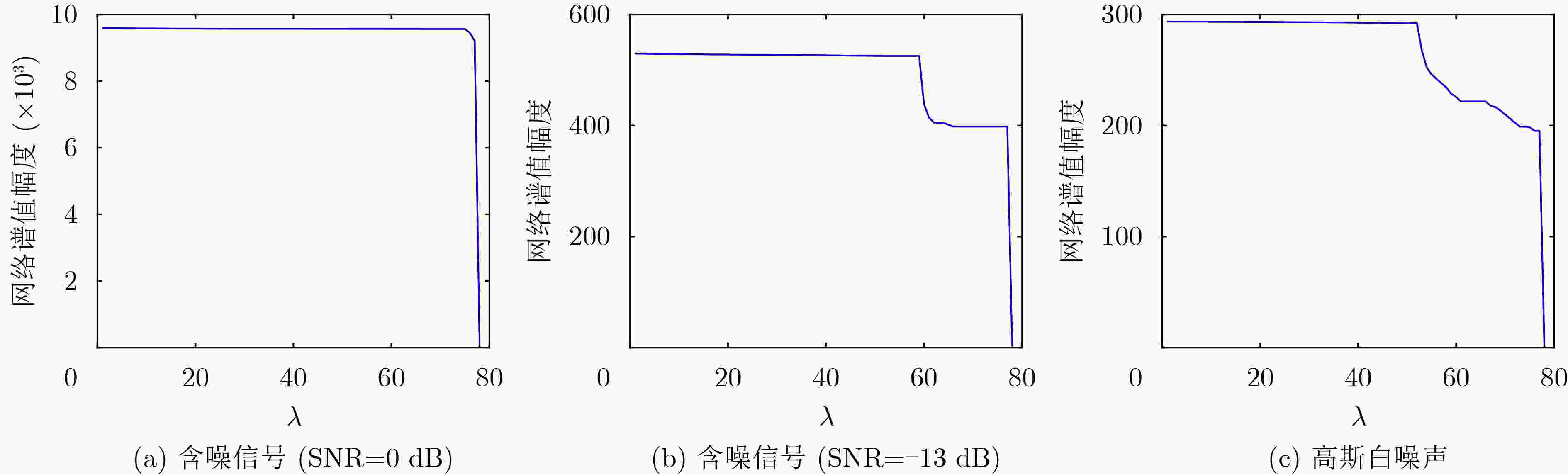
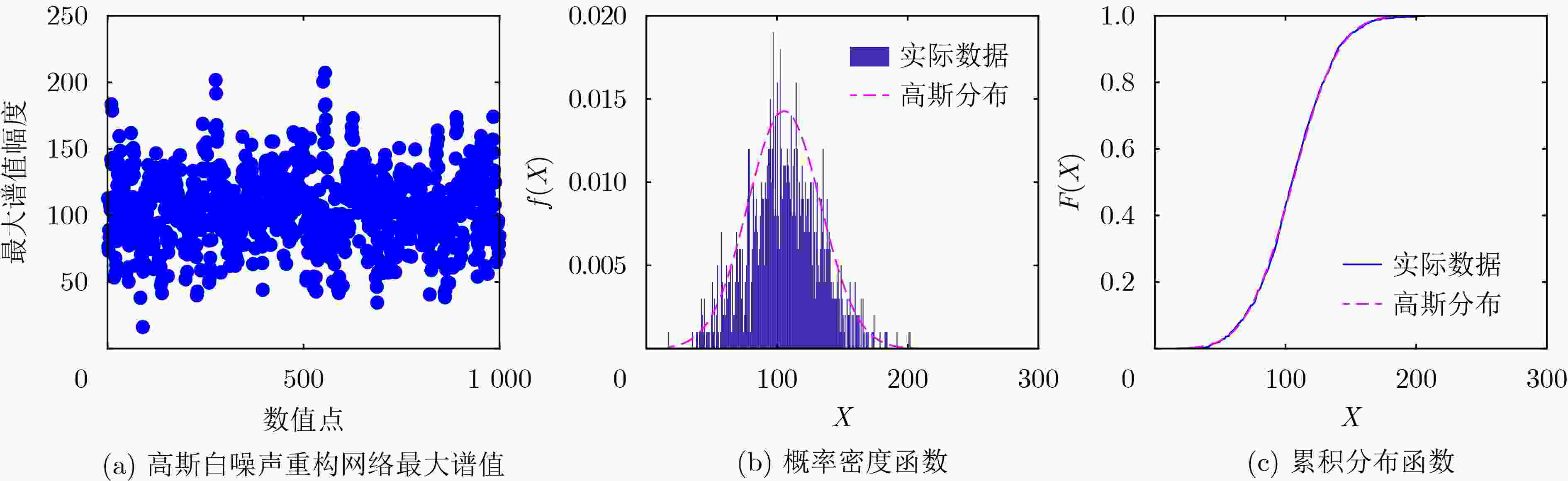
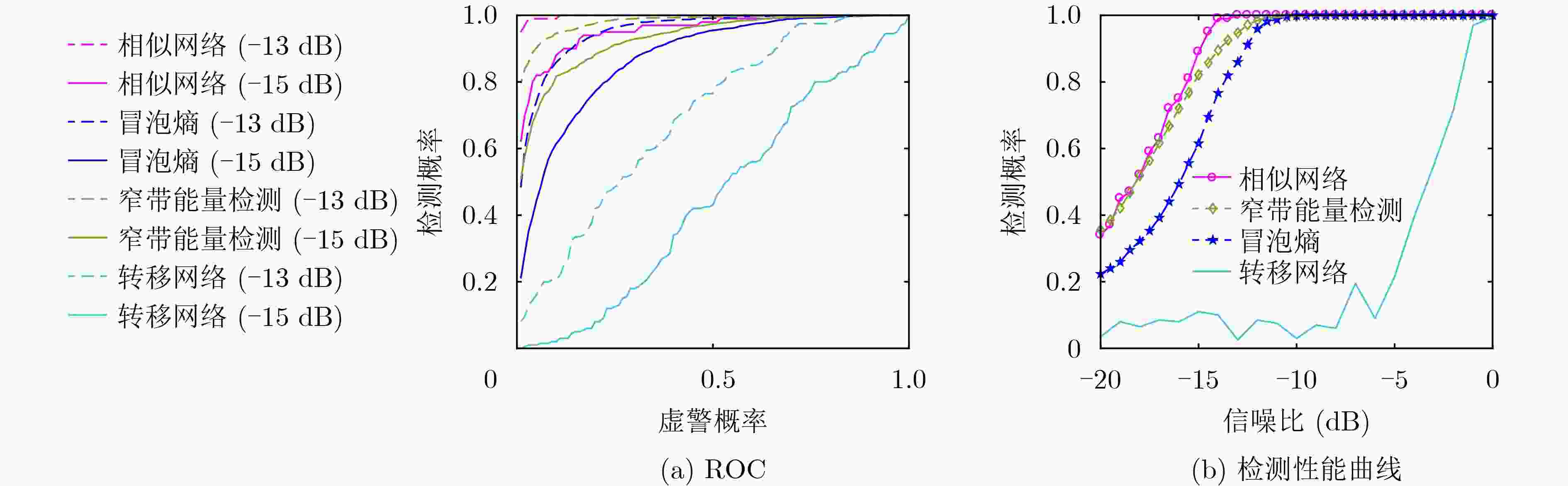
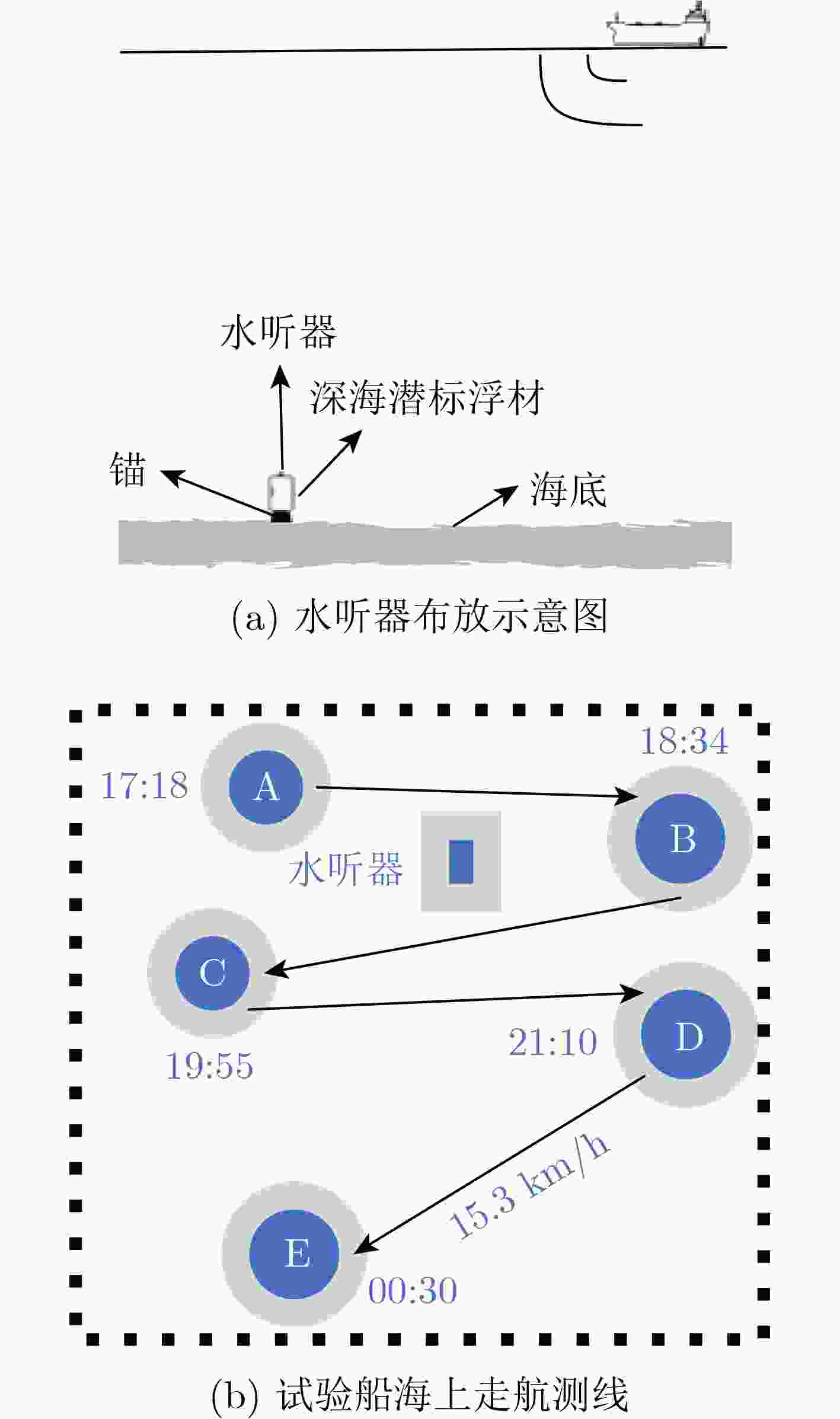
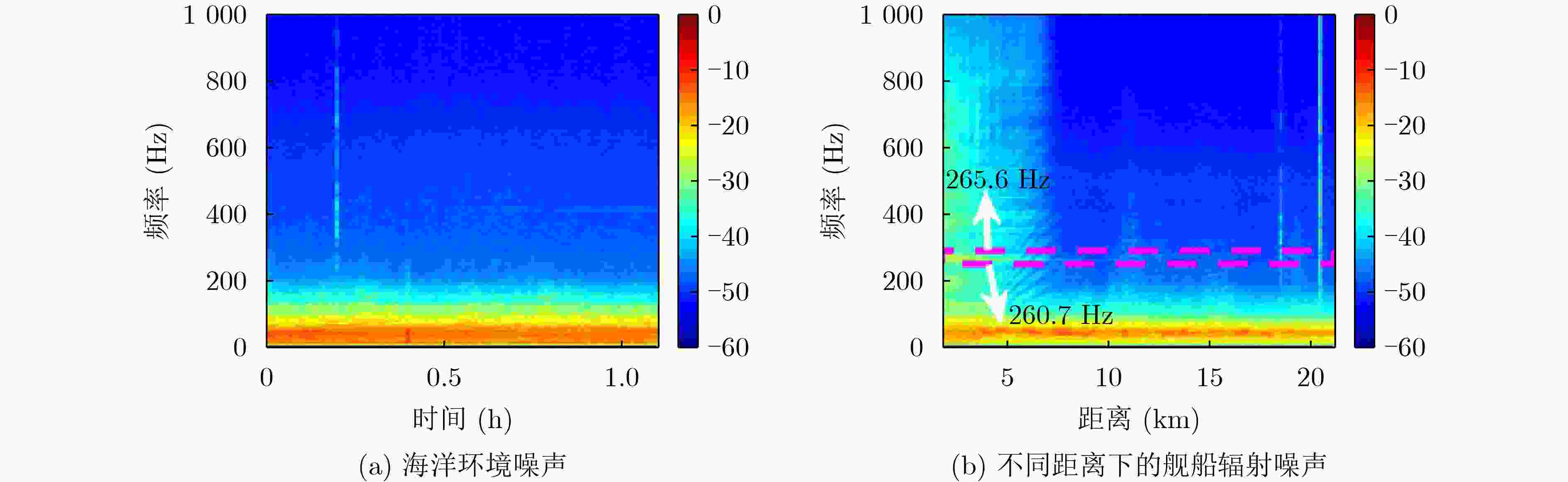
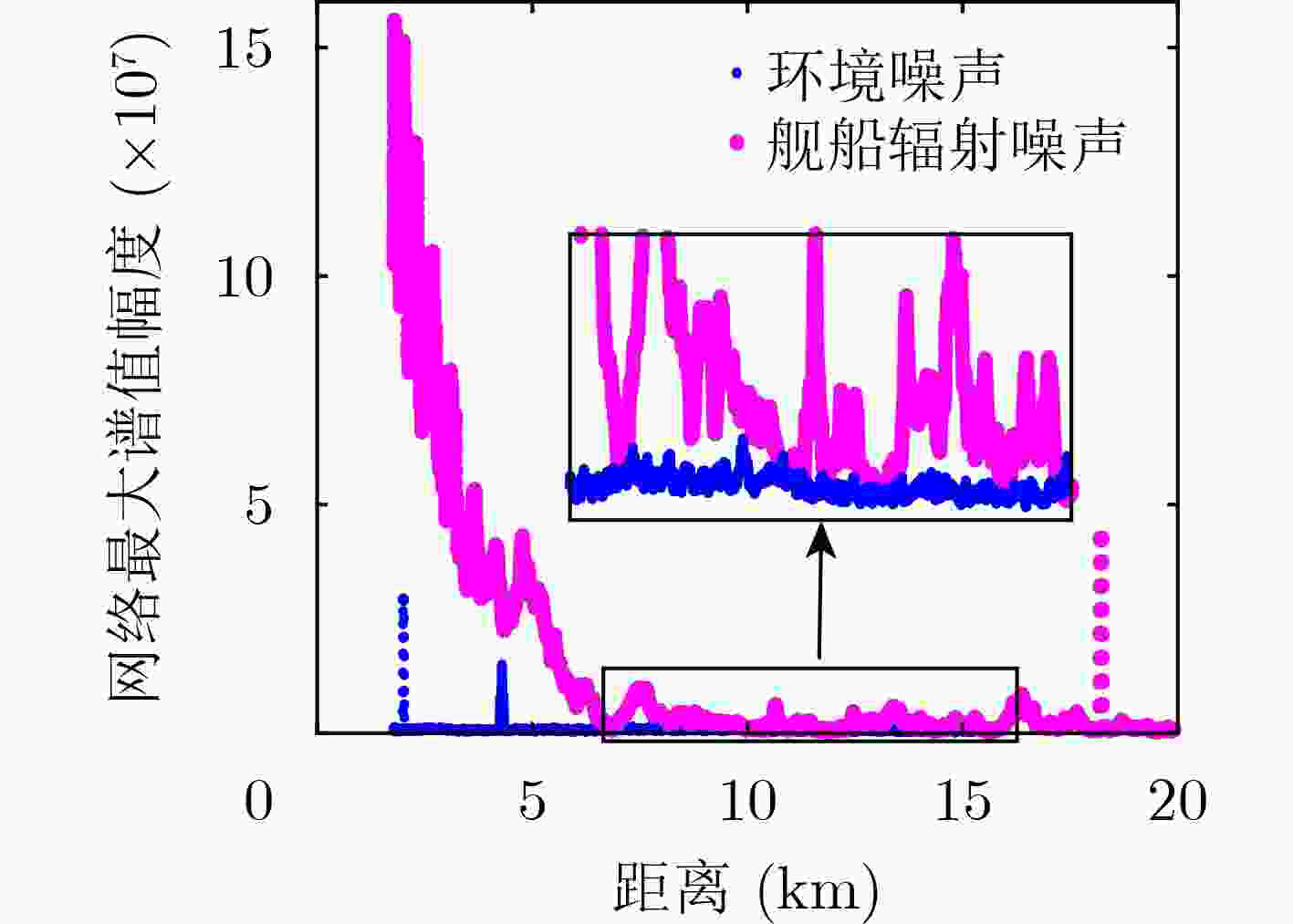


 下载:
下载:
