Research on Symmetrically Resonant VLF Transmit/Receive Magnetoelectric Antenna Coupling Performance
-
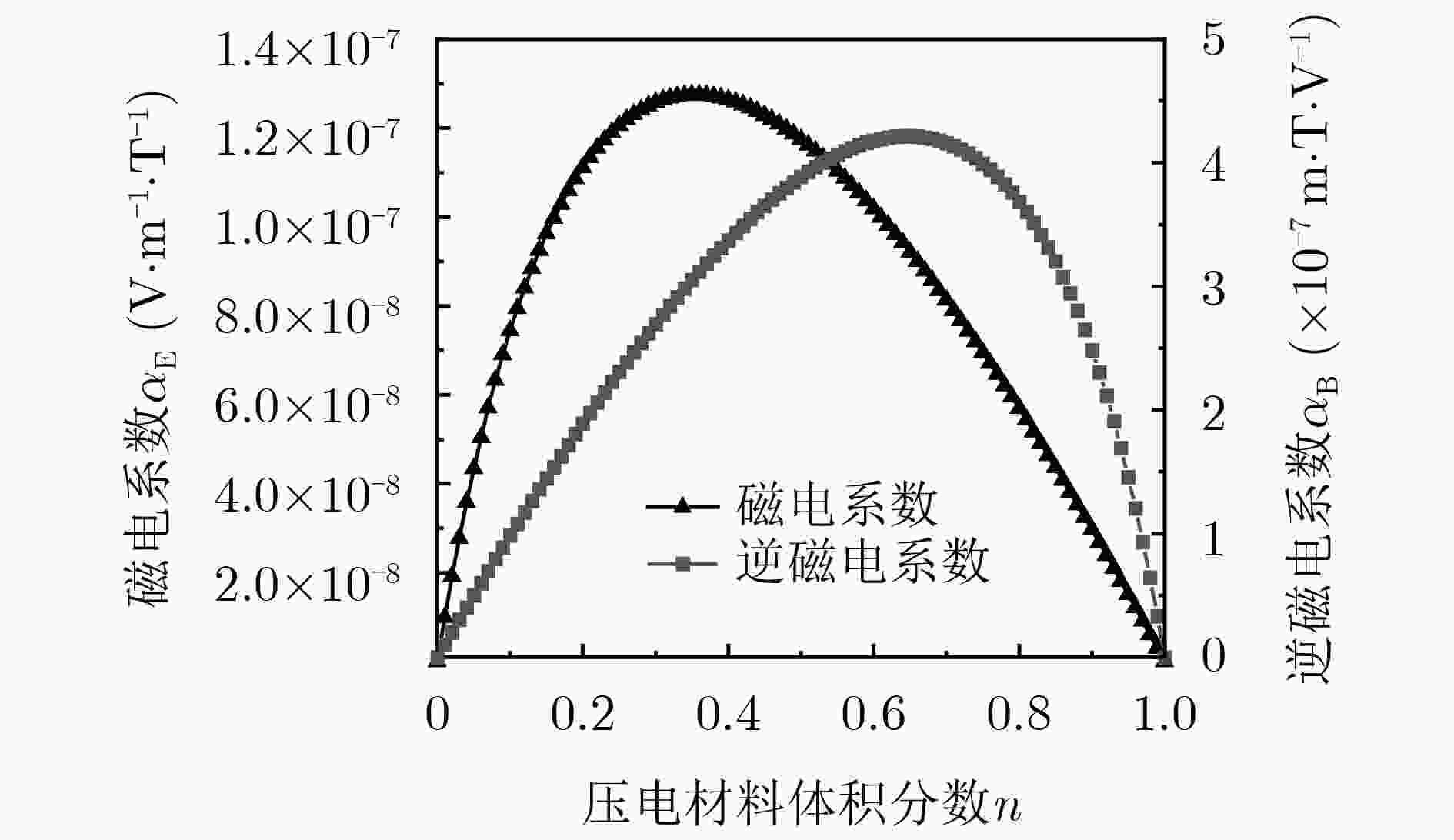
摘要: 甚低频段由于低传播损耗特性,在远距离信号传输及军事通信方面有巨大潜力。传统天线庞大物理尺寸以及复杂网络匹配限制了低频天线通信的发展。磁电(ME)天线基于声波谐振原理可以突破尺寸极限且易于阻抗匹配,在甚低频段传输具有独特优势。基于此设计了P/T/P结构的发射天线和T/P/T结构的接收天线组成的新型ME天线系统。依据磁机电耦合模型分析天线在接收/发射电磁波时的规律;依据辐射模型研究近场范围内天线磁场分布情况;以声波介导激励,实现ME天线在甚低频段的发/收通信实验。实验得到在谐振频率下,ME发射/接收天线在压电占比分别在0.66, 0.34时,结构优化前较于优化后输出电压提升82.6%,通信距离提升42.2%;相较于同等尺寸电小天线辐射效率提高3个数量级;可实现传输速率为5bit/s的调制通信,依据结构优化实现了天线性能的提升。Abstract: Very low frequency has great potential for long distance signal transmission and military communications due to its low propagation loss characteristics. Magneto-Electric (ME) antennas, based on the acoustic resonance principle, can push the limits of size and are easily impedance matched, offering unique advantages for transmission in the very low frequency band. Based on this, a new ME antenna system consisting of a transmitting antenna of P/T/P structure and a receiving antenna of T/P/T structure is designed. The structural pattern of the antenna in receiving/transmitting electromagnetic waves is analyzed based on the magneto-mechanical coupling model. The magnetic field distribution of the antenna in the near-field range is investigated based on the radiation model. An experiment on the transmission/receiving of ME antennas in the very low frequency band is realized with acoustic wave mediated excitation. Experimental results indicate that obtained at resonant frequencies, the ME transmit/receive antenna is improved by 82.6% in output voltage and by 42.2% in communication range before the structure optimization compared to after the optimization when the piezoelectricity ratio is 0.66 and 0.34, respectively. Magnitude higher radiation efficiency is improved by three orders compared to the same size electric small antenna. Modulated communication with a transmission rate of 5 bit/s is possible and the performance of the antenna is improved based on structural optimization.
-
表 1 ME天线材料参数
Volume (mm3) $ {s}_{33}^{{\mathrm{H}}},\;{s}_{11}^{{\mathrm{E}}} $(m2/N) $ {d}_{33}^{{\mathrm{m}}} $ (m/A)
$ {d}_{31}^{{\mathrm{P}}} $ (C/N)$ {\rho }_{{\mathrm{m}}},\;{\rho }_{{\mathrm{P}}} $
(g/cm3)$ {Q}_{{\mathrm{m}}}、{Q}_{{\mathrm{P}}} $ $\mu _{33}^{\mathrm{T}}$, ${\varepsilon _{33}}$ Terfenol-D 35×10×1 1.638×10-11 14.86×10–9 9250 10 62.8×10–7 PZT-5 38×10×1 4.7×10-11 1.53×10–8 7800 65 38×10–8 表 2 ME天线类型参数表
类型 Volume of T Volume of P 压电体积分数 T1 35×15×1 38×15×2 0.66 T2 35×15×1.5 38×15×1.5 0.5 T3 35×15×2 38×15×1 0.34 -
[1] KRAMER B A, CHEN C C, LEE M, et al. Fundamental limits and design guidelines for miniaturizing ultra-wideband antennas[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2009, 51(4): 57–69. doi: 10.1109/MAP.2009.5338684. [2] SKRIVERVIK A K, ZURCHER J F, STAUB O, et al. PCS antenna design: The challenge of miniaturization[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2001, 43(4): 12–27. doi: 10.1109/74.951556. [3] NAN Tianxiang, LIN H, GAO Yuan, et al. Acoustically actuated ultra-compact NEMS magnetoelectric antennas[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 296. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00343-8. [4] 丁宏. DARPA机械天线项目或掀起军事通信革命[J]. 现代军事, 2017(4): 71–73. [5] BURCH H C, GARRAUD A, MITCHELL M F, et al. Experimental generation of ELF radio signals using a rotating magnet[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(11): 6265–6272. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2869205. [6] GONG Shuhong, LIU Yu, and LIU Yi. A rotating-magnet based mechanical antenna (Rmbma) for Elf-Ulf wireless communication[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research M, 2018, 72: 125–133. doi: 10.2528/PIERM18070204. [7] LUONG K Q T and WANG Yuanxun. Analysis of dynamic magnetoelastic coupling in mechanically driven magnetoelectric antennas[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(2): 455. doi: 10.3390/s22020455. [8] WAITZ T, SCHRANZ W, and TRÖSTER A. Nanoscale phase transformations in functional materials[M]. SAXENA A and PLANES A. Mesoscopic Phenomena in Multifunctional Materials. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 23–56. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-55375-2_2. [9] ZAEIMBASHI M, NASROLLAHPOUR M, KHALIFA A, et al. Ultra-compact dual-band smart NEMS magnetoelectric antennas for simultaneous wireless energy harvesting and magnetic field sensing[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 3141. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23256-z. [10] KEMP M A, FRANZI M, HAASE A, et al. A high Q piezoelectric resonator as a portable VLF transmitter[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1715. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09680-2. [11] HASSANIEN A E, BREEN M, LI Minghuang, et al. Acoustically driven electromagnetic radiating elements[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 17006. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73973-6. [12] XU Jianchun, CAO Jinqing, GUO Menghao, et al. Metamaterial mechanical antenna for very low frequency wireless communication[J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2021, 4(3): 761–767. doi: 10.1007/s42114-021-00278-1. [13] DONG Cunzheng, HE Yifan, LI Menghui, et al. A portable very low frequency (VLF) communication system based on acoustically actuated magnetoelectric antennas[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2020, 19(3): 398–402. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2020.2968604. [14] 彭春瑞, 李君儒, 钟慧, 等. 体声波磁电天线辐射性能的解析计算[J]. 压电与声光, 2020, 42(1): 34–37. doi: 10.11977/j.issn.1004-2474.2020.01.009. [15] XU Guokai, XIAO Shaoqiu, LI Yan, et al. Modeling of electromagnetic radiation-induced from a magnetostrictive/piezoelectric laminated composite[J]. Physics Letters A, 2021, 385: 126959. doi: 10.1016/j.physleta.2020.126959. [16] XIAO Ning, WANG Yao, CHEN Lei, et al. Low-frequency dual-driven magnetoelectric antennas with enhanced transmission efficiency and broad bandwidth[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2023, 22(1): 34–38. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2022.3201070. [17] 阳昌海. 偏置磁场对超磁致伸缩/压电复合材料磁电效应影响的研究[D]. [硕士论文], 重庆大学, 2008.YANG Changhai. Study on the influence of bias magnetic field on magnetoelectric effect of giant magnetostrictive/piezoelectric composite material[D]. [Master dissertation], Chongqing University, 2008. [18] 郁国良. 基于磁致伸缩/压电层状复合材料的磁电效应研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2018. [19] ZHOU Jianping, MA Yuanjun, ZHANG Guangbin, et al. A uniform model for direct and converse magnetoelectric effect in laminated composite[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104(20): 202904. doi: 10.1063/1.4878559. [20] LEI Lei and CHEN Xiangming. Magnetoelectric characteristics of a dual-mode magnetostrictive/piezoelectric bilayered composite[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(7): 072903. doi: 10.1063/1.2840177. [21] XU Junran, LEUNG C M, ZHUANG Xin, et al. A low frequency mechanical transmitter based on magnetoelectric heterostructures operated at their resonance frequency[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(4): 853. doi: 10.3390/s19040853. -






 下载:
下载:












 下载:
下载:
