Line Spectrum Enhancement of Underwater Acoustic Targets Based on a Time-Frequency Attention Network
-
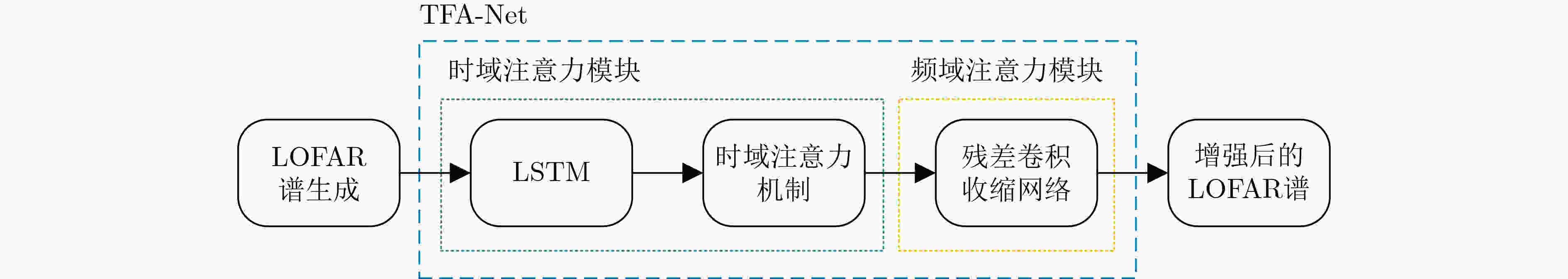
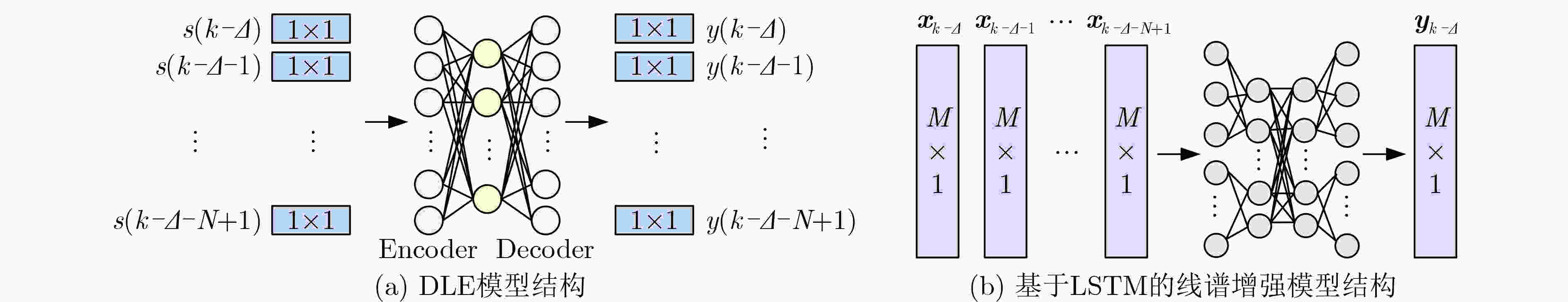
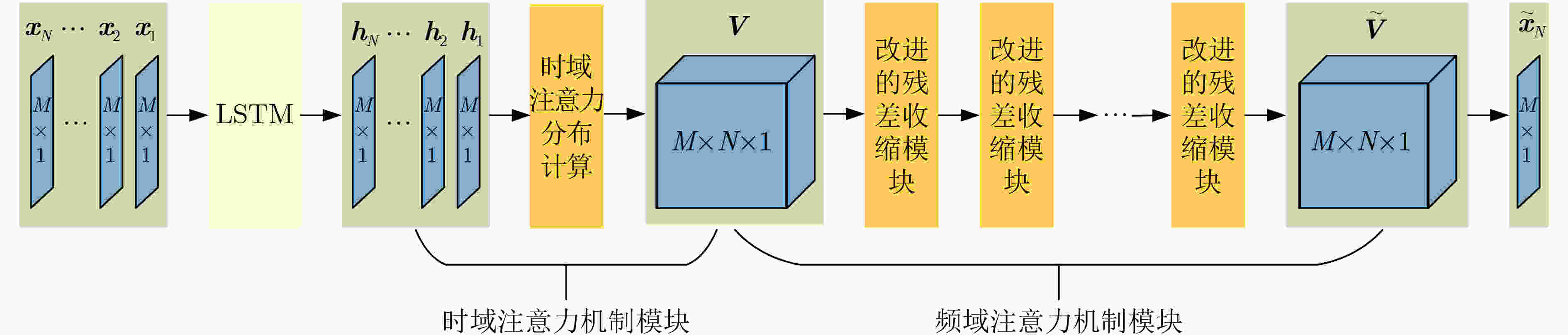
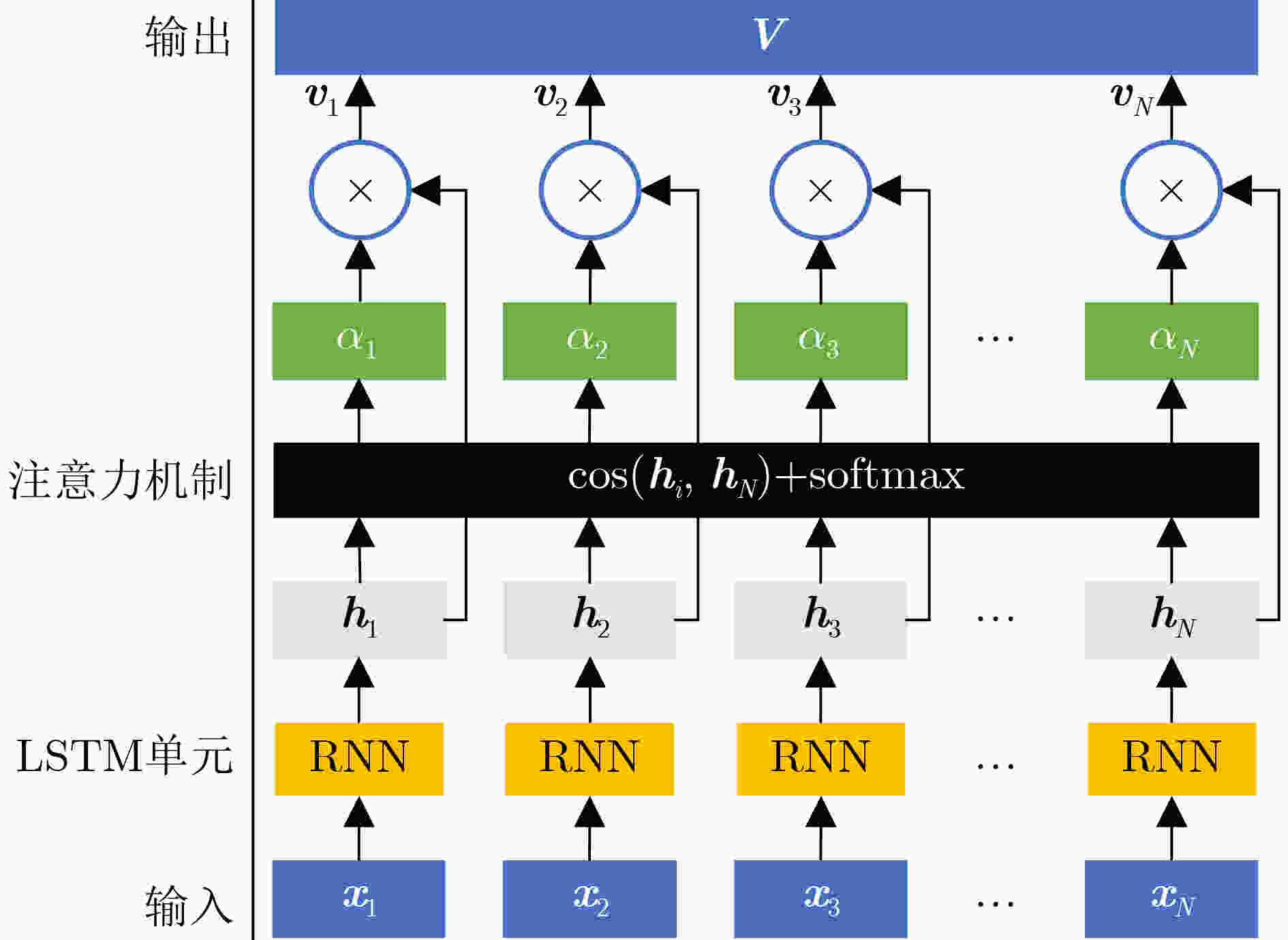
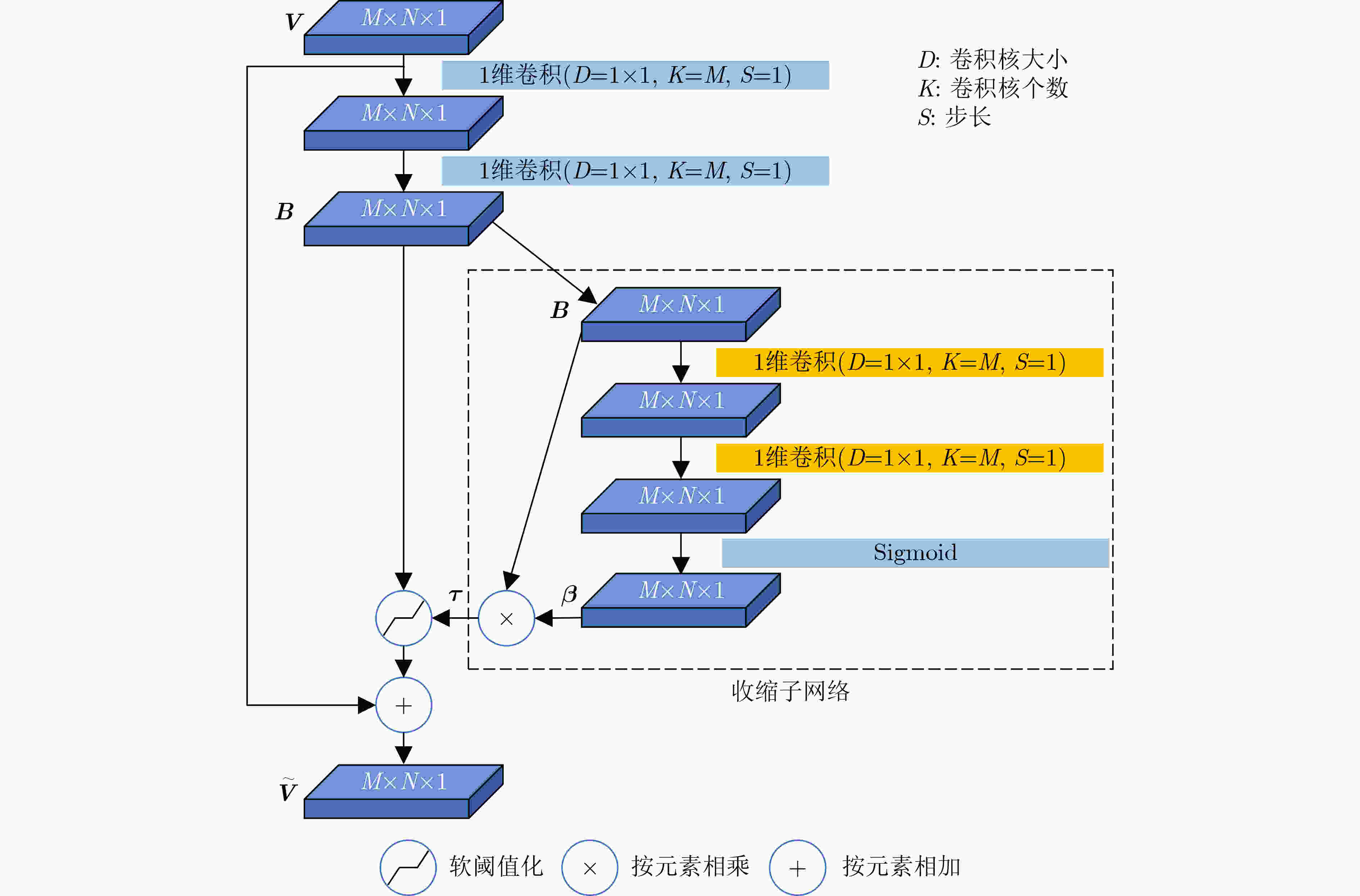
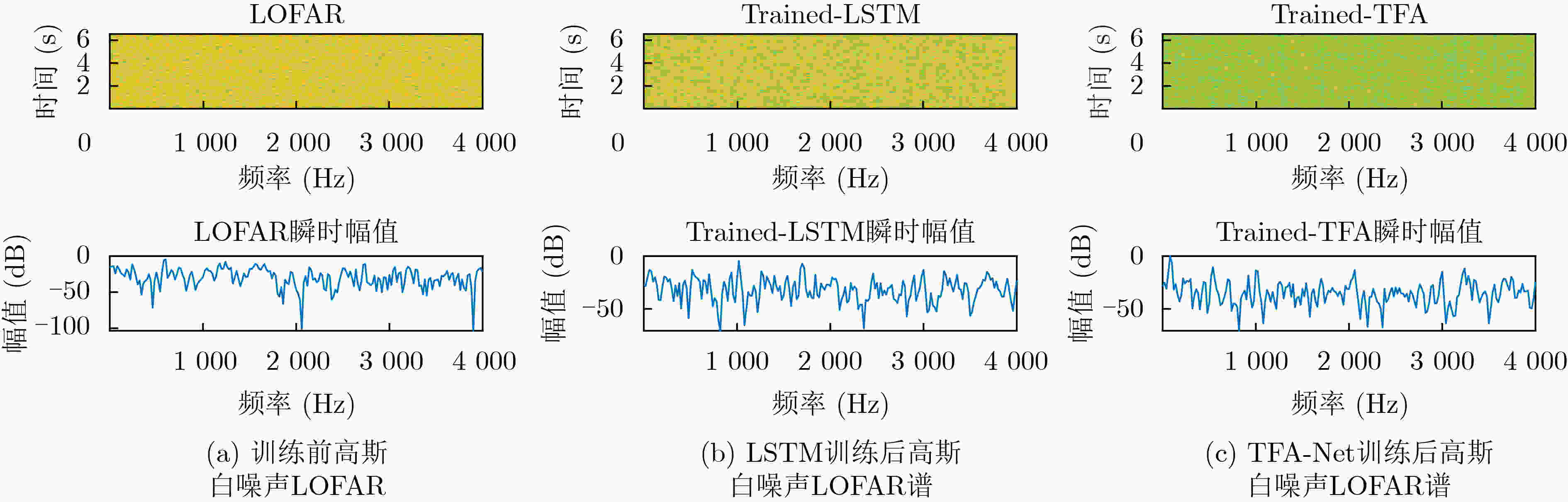
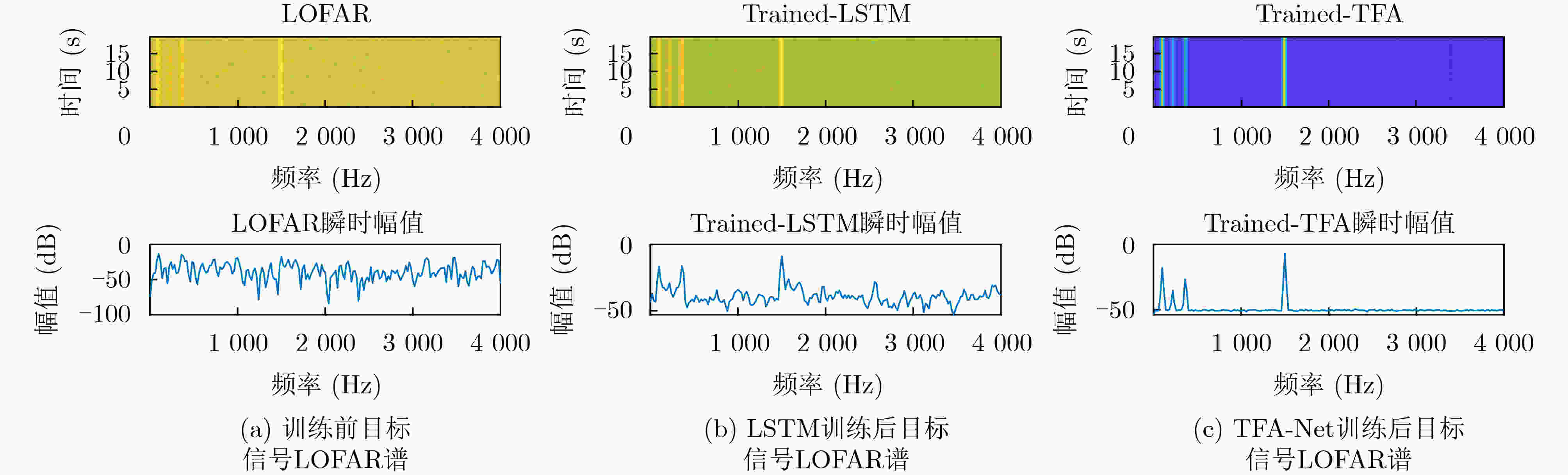
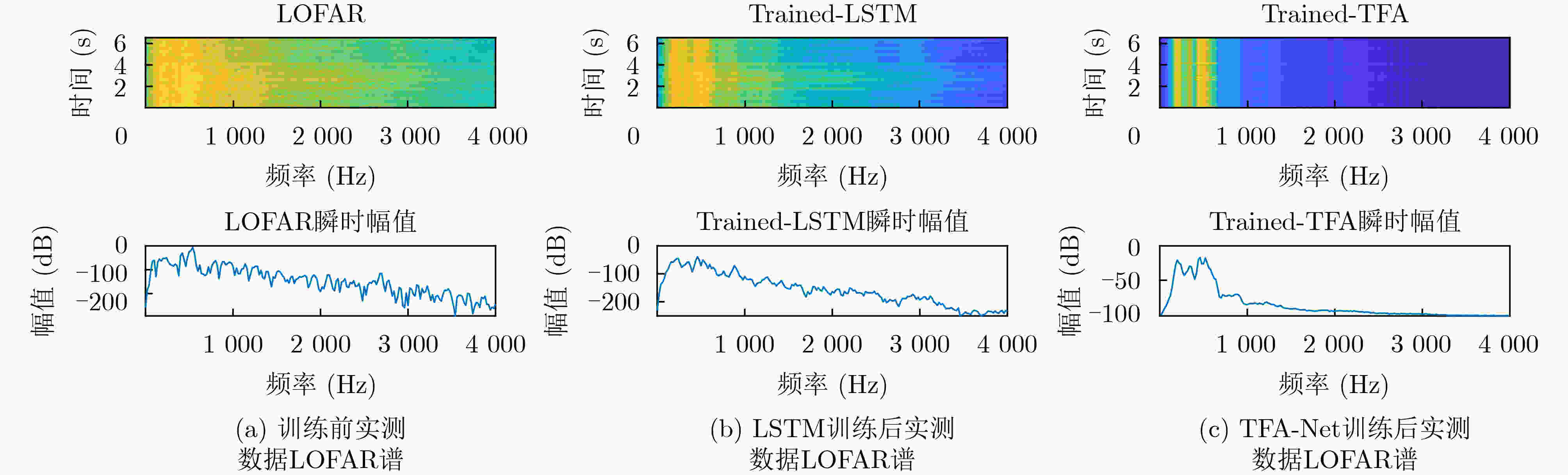
摘要: 为提高被动声纳对水下低噪声安静型目标的检测,研究者开始关注基于深度学习的线谱增强方法,其中,基于LSTM的线谱增强网络由于同时具有时域和频域的非线性处理能力,具有很强的灵活性,然而其性能还需要进一步提升。为此,该文提出了基于时-频注意力机制的网络模型(TFA-Net),通过在LSTM模型的基础上同时增加时域注意力机制和频域注意力机制,充分利用了目标信号在时域和频域的双重重要特征,提升了对LOFAR谱的线谱增强效果。TFA-Net中的时域注意力机制利用LSTM隐藏状态之间的关联性,增加了模型在时域的注意力,频率注意力机制通过将深度残差收缩网络中收缩子网络的全链接层设计为1维卷积层,增加了模型在频域的注意力。相比于LSTM,TFA-Net具有更高的系统信噪比增益:在输入信噪比为–3 dB的情况下,将系统信噪比增益由2.17 dB提升到12.56 dB;在输入信噪比为–11 dB的情况下,将系统信噪比增益由0.71 dB提升到10.6 dB。仿真和实测数据的实验结果表明,TFA-Net可以有效提升LOFAR谱的线谱增强效果,解决低信噪比下水下目标的检测问题。Abstract: Deep learning-based line spectrum enhancement methods have received increasing attention for improving the detection performance of underwater low-noise targets using passive sonar. Among them, Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)-based line spectrum enhancement networks have high flexibility due to their nonlinear processing capabilities in time and frequency domains. However, their performance requires further improvement. Therefore, a Time-Frequency Attention Network (TFA-Net) is proposed herein. The line spectrum enhancement effect of the LOw-Frequency Analysis Record (LOFAR) spectrum can be improved by incorporating the time and frequency-domain attention mechanisms into LSTM networks, In TFA-Net, the time-domain attention mechanism utilizes the correlation between the hidden states of LSTM to increase the model’s attention in the time domain, while the frequency-domain attention mechanism increases the model’s attention in the frequency domain by designing the full link layer of the shrinkage sub-network in deep residual shrinkage networks as a one-dimensional convolutional layer. Compared to LSTM, TFA-Net has a higher system signal-to-noise ratio gain: when the input signal-to-noise ratio is –3 dB and –11 dB, the system signal-to-noise ratio gain is increased from 2.17 to 12.56 dB and from 0.71 to 10.6 dB, respectively. Experimental results based on simulated and real data show that TFA-Net could effectively improve the line spectrum enhancement effect of the LOFAR spectrum and address the problem of detecting underwater low-noise targets.
-
Key words:
- Underwater target detection /
- LOFAR /
- Line spectrum enhancement /
- LSTM /
- Attention mechanism
-
表 1 TFA-Net模型超参数设置
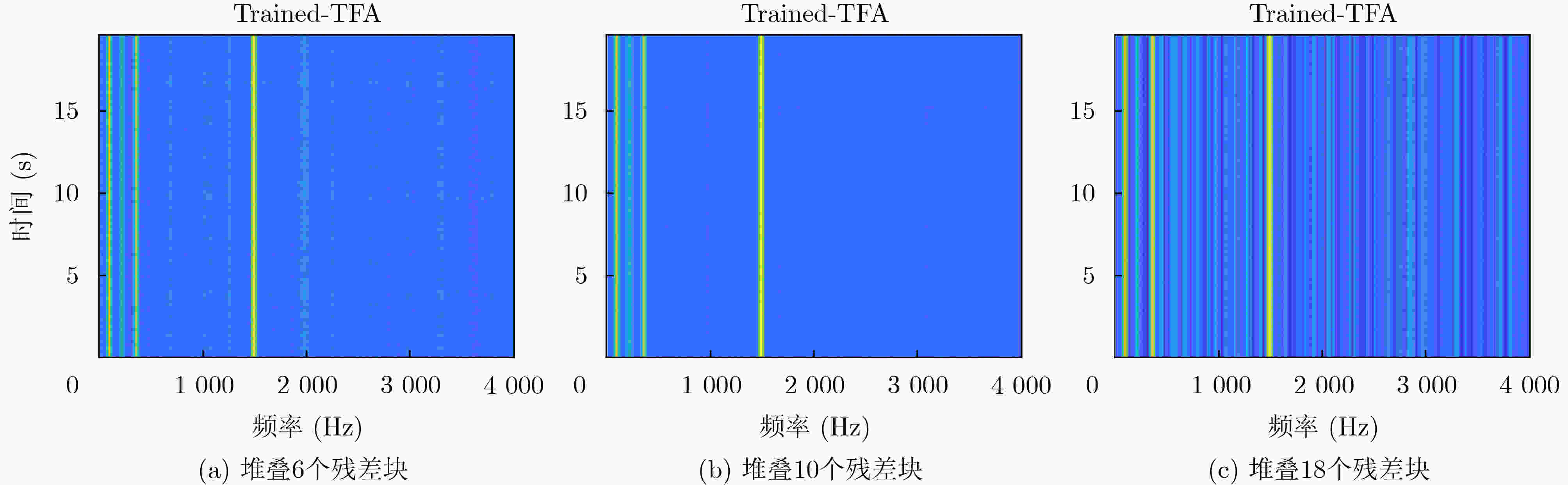
模块 参数名称 参数值 LSTM 隐藏层神经元个数 200 频域注意力机制模块 残差卷积收缩模块个数 10 全局参数 激活函数(activate function) ReLU 损失函数(loss function) MSE 优化器(optimizer) Adam 迭代次数(epoch) 200 学习率(learning rate) 0.0015 表 2 输入信噪比为–3 dB时的系统信噪比增益对比
线谱增强效果量化指标 训练前 LSTM训练后 TFA-Net训练后 图像信噪比(dB) 5.04 8.3394 90.92 系统信噪比增益(dB) – 2.17 12.56 表 3 消融实验结果
模型 –3 dB –5 dB –7 dB –9 dB –11 dB TFA-Net 12.56 11.84 11.47 11.10 10.60 (w/o)时域注意力 11.46 11.19 10.55 10.47 9.99 (w/o)卷积改进 10.84 10.70 10.54 9.18 8.35 (w/o)时域注意力&卷积改进 10.29 9.56 8.70 8.10 7.74 (w/o)频域注意力 6.55 5.68 5.34 4.45 3.59 (w/o)时域&频域注意力 2.17 1.68 1.45 0.73 0.71 注:TFA-Net包含LSTM、时域注意力机制模块及频域注意力机制模块,其中频域注意力机制模块包含深度残差收缩模块和卷积改进模块。 -
[1] ALI M F, JAYAKODY D N K, CHURSIN Y A, et al. Recent advances and future directions on underwater wireless communications[J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2020, 27(5): 1379–1412. doi: 10.1007/s11831-019-09354-8 [2] ISLAM K Y, AHMAD I, HABIBI D, et al. A survey on energy efficiency in underwater wireless communications[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2022, 198: 103295. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2021.103295 [3] LI Sichun, JIN Xin, YAO Sibing, et al. Underwater small target recognition based on convolutional neural network[C]. Global Oceans 2020: Singapore – U. S. Gulf Coast, Biloxi, USA, 2020: 1–7. [4] JIN Guanghao, LIU Fan, WU Hao, et al. Deep learning-based framework for expansion, recognition and classification of underwater acoustic signal[J]. Journal of Experimental & Theoretical Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 32(2): 205–218. doi: 10.1080/0952813X.2019.1647560 [5] BIANCO M J, GERSTOFT P, TRAER J, et al. Machine learning in acoustics: Theory and applications[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2019, 146(5): 3590–3628. doi: 10.1121/1.5133944 [6] VIVEK V S, VIDHYA S, and MADHANMOHAN P. Acoustic scene classification in hearing aid using deep learning[C]. 2020 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing, Chennai, India, 2020: 695–699. [7] WANG Peibing and PENG Yuan. Research on feature extraction and recognition method of underwater acoustic target based on deep convolutional network[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Advances in Electrical Engineering and Computer Applications, Dalian, China, 2020: 863–868. [8] RAO S K and JAGAN B O L. Passive target tracking in underwater environment using bearing and frequency measurements[C]. OCEANS 2022-Chennai, Chennai, India, 2022: 1–4. [9] KOGEKAR A P, NAYAK R, and PATI U C. A CNN-BiLSTM-SVR based deep hybrid model for water quality forecasting of the river Ganga[C]. 2021 IEEE 18th India Council International Conference, Guwahati, India, 2021: 1–6. [10] 朱雨男, 解方彤, 张明亮, 等. 基于多层双向长短时记忆网络的水声多载波通信索引检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(6): 1984–1990. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210949ZHU Yunan, XIE Fangtong, ZHANG Mingliang, et al. Index detection for underwater acoustic multi-carrier communication based on deep bidirectional long short-term memory network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(6): 1984–1990. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210949 [11] 鞠东豪, 迟骋, 李宇, 等. 基于无监督深度学习的线谱增强算法[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2020, 42(23): 117–120. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2020.12.023JU Donghao, CHI Cheng, LI Yu, et al. Line enhancement algorithm based on unsupervised deep learning for passive sonars[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2020, 42(23): 117–120. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2020.12.023 [12] JU Donghao, CHI Cheng, LI Zigao, et al. Deep-learning-based line enhancer for passive sonar systems[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2022, 16(3): 589–601. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12205 [13] WIDROW B, GLOVER J R, MCCOOL J M, et al. Adaptive noise cancelling: Principles and applications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1975, 63(12): 1692–1716. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1975.10036 [14] 杨路飞, 章新华, 吴秉坤. 基于长短时记忆网络的被动声纳目标信号LOFAR谱增强研究[J]. 电声技术, 2020, 44(6): 101–103. doi: 10.16311/j.audioe.2020.06.024YANG Lufei, ZHANG Xinhua, and WU Bingkun. A study on signal LOFAR spectrum enhancement of passive sonar target based on short and short time memory network[J]. Audio Engineering, 2020, 44(6): 101–103. doi: 10.16311/j.audioe.2020.06.024 [15] YANGZHOU Jianyun, MA Zhengyu, and HUANG Xun. A deep neural network approach to acoustic source localization in a shallow water tank experiment[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2019, 146(6): 4802–4811. doi: 10.1121/1.5138596 [16] SAMEK W, MONTAVON G, LAPUSCHKIN S, et al. Explaining deep neural networks and beyond: A review of methods and applications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2021, 109(3): 247–278. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2021.3060483 [17] SIAMI-NAMINI S, TAVAKOLI N, and NAMIN A S. The performance of LSTM and BiLSTM in forecasting time series[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Los Angeles, USA, 2019: 3285–3292. [18] 王同, 苏林, 任群言, 等. 基于注意力机制的全海深声速剖面预测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(3): 726–736. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210078WANG Tong, SU Lin, REN Qunyan et al. Full-sea depth sound speed profiles prediction using RNN and attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(3): 726–736. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210078 [19] 李文洁, 葛凤培, 张鹏远, 等. 双向长短时记忆模型训练中的空间平滑正则化方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(3): 544–550. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180314LI Wenjie, GE Fengpei, ZHANG Pengyuan, et al. Spatial smoothing regularization for bi-direction long short-term memory model[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(3): 544–550. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180314 [20] RICKARD J and ZEIDLER J. Second-order output statistics of the adaptive line enhancer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1979, 27(1): 31–39. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1979.1163203 [21] NEHORAI A and MALAH D. On the stability and performance of the adaptive line enhancer[C]. ICASSP'80. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Denver, USA, 1980: 478–481. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
