Dynamic Quantum Secret Sharing Scheme Based on Nonlocal Orthogonal Product States
-
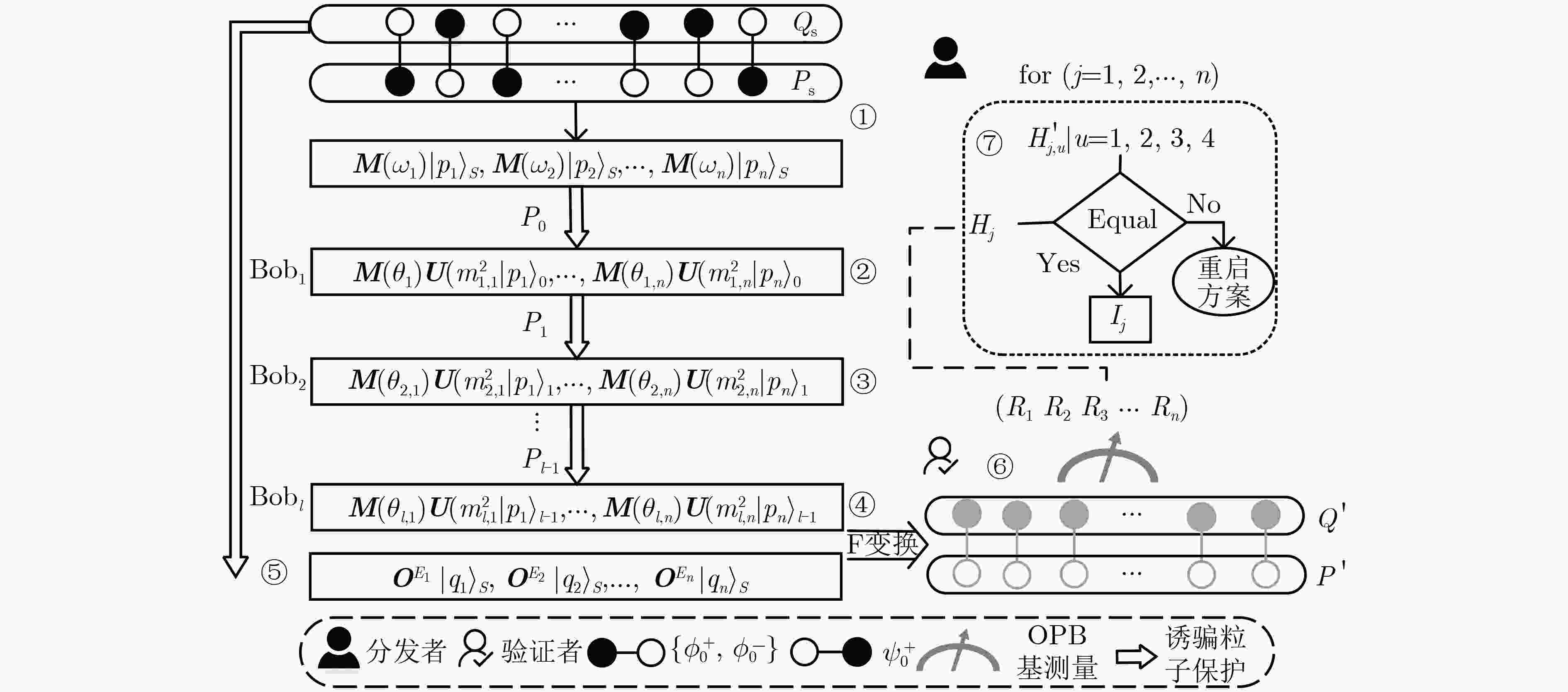
摘要: 当前的量子秘密共享(QSS)存在资源制备开销较大、安全性不强的问题,该文提出一种基于正交乘积态的可验证量子秘密共享方案弥补上述不足,且多方成员能动态地加入或退出秘密共享。该方案将正交乘积态的粒子分成两个序列,第1个序列在多个参与者之间传输,前一个参与者对其执行嵌入份额值的酉算子后传输给下一个参与者,直到全部份额聚合完成;对于另一个序列,只有最后一个参与者(验证者)对接收到的粒子执行Oracle算子。然后,验证者对两个序列中的粒子对执行全局测量,得到秘密值的平方剩余。最后,借鉴Rabin密码中密文与明文之间非单一映射的思想,验证者联合Alice验证测量结果的正确性,并从测量结果确定出秘密值。安全性分析表明,该方案能抵抗常见的外部攻击和内部攻击,且验证过程具有强安全性;由于非局域性正交乘积态以两个序列分开传输,因此增强了秘密重构过程的安全性。性能分析表明,该方案使用正交乘积态作为信息载体,量子资源开销较小,且将正交乘积基的维度从低维拓展到d维,参与者人数能动态地增加和减少,使得方案具有更好的灵活性和通用性。Abstract: Current Quantum Secret Sharing(QSS) has the drawbacks of high consumption of resource preparation and the security is not stronger. To overcome the above drawbacks, a verifiable quantum secret sharing scheme based on orthogonal product states is proposed, where multiple participants can dynamically join or leave the secret sharing. In the proposed scheme, the particle pairs of product states are divided into two sequences, the first sequence is transmitted among participants, and the previous participant performs the unitary operator to aggregate the shares on it and then transmits it to the next participant; for the other sequence, the last participant(verifier) performs the Oracle operator on the received particles. Afterward, the verifier uses global measurements on the particle pairs to obtain the quadratic residues of the secrets. Finally, learning from the idea of non-single mapping between ciphertext and plaintext in Rabin cipher, the verifier jointly with Alice verifies the correctness of the measurement results and identifies the secrets from the results. Security analysis shows that the proposed scheme can resist common external and internal attacks, and that the verification process is strongly secure. Since the nonlocal orthogonal product states are transmitted separately in two sequences, the security of the secret reconstruction process is enhanced. Performance analysis shows that the proposed scheme has low quantum resource consumption using orthogonal product state as information carriers, and extends the dimension of orthogonal product basis from low dimension to d dimension, and the number of participants can be dynamically increased or decreased, so it provides better flexibility and generality.
-
表 1 相似方案的性能比较
属性 文献[7] 文献[13] 本文方案 信息粒子类型 3维OPB态 2维OPB态 d维OPB态 粒子数量 m $ {2^{m - 1}} \cdot l $ 2m 计算消耗 $m({{\rm{QFT}}} + {{\rm{IQFT}}})/2$ – $l \cdot {\boldsymbol{U}} + (l + 1){\boldsymbol{M}} + {\boldsymbol{O}} + 1/3({\boldsymbol{F}} + {{\boldsymbol{F}}^\dagger } + {\boldsymbol{U}})$ 参与者人数 两方固定 多方固定 多方动态 测量消耗 $ m $次单粒子测量 $ l $次OPB测量 1次OPB测量 -
[1] HILLERY M, BUŽEK V, and BERTHIAUME A. Quantum secret sharing[J]. Physical Review A, 1999, 59(3): 1829–1834. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.59.1829. [2] KARLSSON A, KOASHI M, and IMOTO N. Quantum entanglement for secret sharing and secret splitting[J]. Physical Review A, 1999, 59(1): 162–168. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.59.162. [3] 杜宇韬, 鲍皖苏, 李坦. 基于秘密认证的可验证量子秘密共享协议[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 212–217. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190901.DU Yutao, BAO Wansu, and LI Tan. Verifiable quantum secret sharing protocol based on secret authentication[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 212–217. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190901. [4] BAI Chenming, ZHANG Sujuan, and LIU Lu. Verifiable quantum secret sharing scheme using d-dimensional GHZ state[J]. International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 2021, 60(10): 3993–4005. doi: 10.1007/s10773-021-04955-1. [5] HSU L Y and LI Cheming. Quantum secret sharing using product states[J]. Physical Review A, 2005, 71(2): 022321. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.A.71.022321. [6] YANG Yuguang, WEN Qiaoyun, and ZHU Fuchen. An efficient quantum secret sharing protocol with orthogonal product states[J]. Science in China Series G:Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy, 2007, 50(3): 331–338. doi: 10.1007/s11433-007-0028-8. [7] XU Juan and YUAN Jiabing. Improvement and extension of quantum secret sharing using orthogonal product states[J]. International Journal of Quantum Information, 2014, 12(1): 1450008. doi: 10.1142/S0219749914500087. [8] BENNETT C H, DIVINCENZO D P, MOR T, et al. Unextendible product bases and bound entanglement[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1999, 82(26): 5385–5388. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.82.5385. [9] WALGATE J and HARDY L. Nonlocality, asymmetry, and distinguishing bipartite states[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2002, 89(14): 147901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.147901. [10] ZHEN Xiaofan, FEI Shaoming, and ZUO Huijuan. Nonlocality without entanglement in general multipartite quantum systems[J]. Physical Review A, 2022, 106(6): 062432. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.106.062432. [11] XU Guangbao and JIANG Donghuan. Novel methods to construct nonlocal sets of orthogonal product states in an arbitrary bipartite high-dimensional system[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2021, 20(4): 128. doi: 10.1007/s11128-021-03062-8. [12] JIANG Donghuan, YUAN Fei, and XU Guangbao. Novel quantum group signature scheme based on orthogonal product states[J]. Modern Physics Letters B, 2021, 35(26): 2150418. doi: 10.1142/S0217984921504182. [13] FU Sijia, ZHANG Kejia, ZHANG Long, et al. A new non-entangled quantum secret sharing protocol among different nodes in further quantum networks[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2022, 10: 1021113. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2022.1021113. [14] HSU J L, CHONG Songkong, HWANG T, et al. Dynamic quantum secret sharing[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2013, 12(1): 331–344. doi: 10.1007/s11128-012-0380-0. [15] WANG Tianying and LI Yanping. Cryptanalysis of dynamic quantum secret sharing[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2013, 12(5): 1991–1997. doi: 10.1007/s11128-012-0508-2. [16] DU Yutao and BAO Wansu. Dynamic quantum secret sharing protocol based on two-particle transform of Bell states[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2018, 27(8): 080304. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/27/8/080304. [17] GAO Gan, WEI Changcheng, and WANG Dong. Cryptanalysis and improvement of dynamic quantum secret sharing protocol based on two-particle transform of Bell states[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2019, 18(6): 186. doi: 10.1007/s11128-019-2301-y. [18] LI Fulin, CHEN Tingyan, and ZHU Shixin. Dynamic (t, n) threshold quantum secret sharing based on d-dimensional Bell state[J]. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2022, 606: 128122. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2022.128122. [19] SMALL C. A simple proof of the four-squares theorem[J]. The American Mathematical Monthly, 1982, 89(1): 59–61. doi: 10.1080/00029890.1982.11995381. [20] DE VOS A and DE BAERDEMACKER S. From reversible computation to quantum computation by Lagrange interpolation[EB/OL]. http://arXiv.org/abs/1502.00819, 2015. [21] YANG Chunwei and TSAI C W. Efficient and secure dynamic quantum secret sharing protocol based on bell states[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2020, 19(5): 162. doi: 10.1007/s11128-020-02662-0. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
