Robust Beamforming Algorithm for Terahertz Communication Systems Aided by Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
-
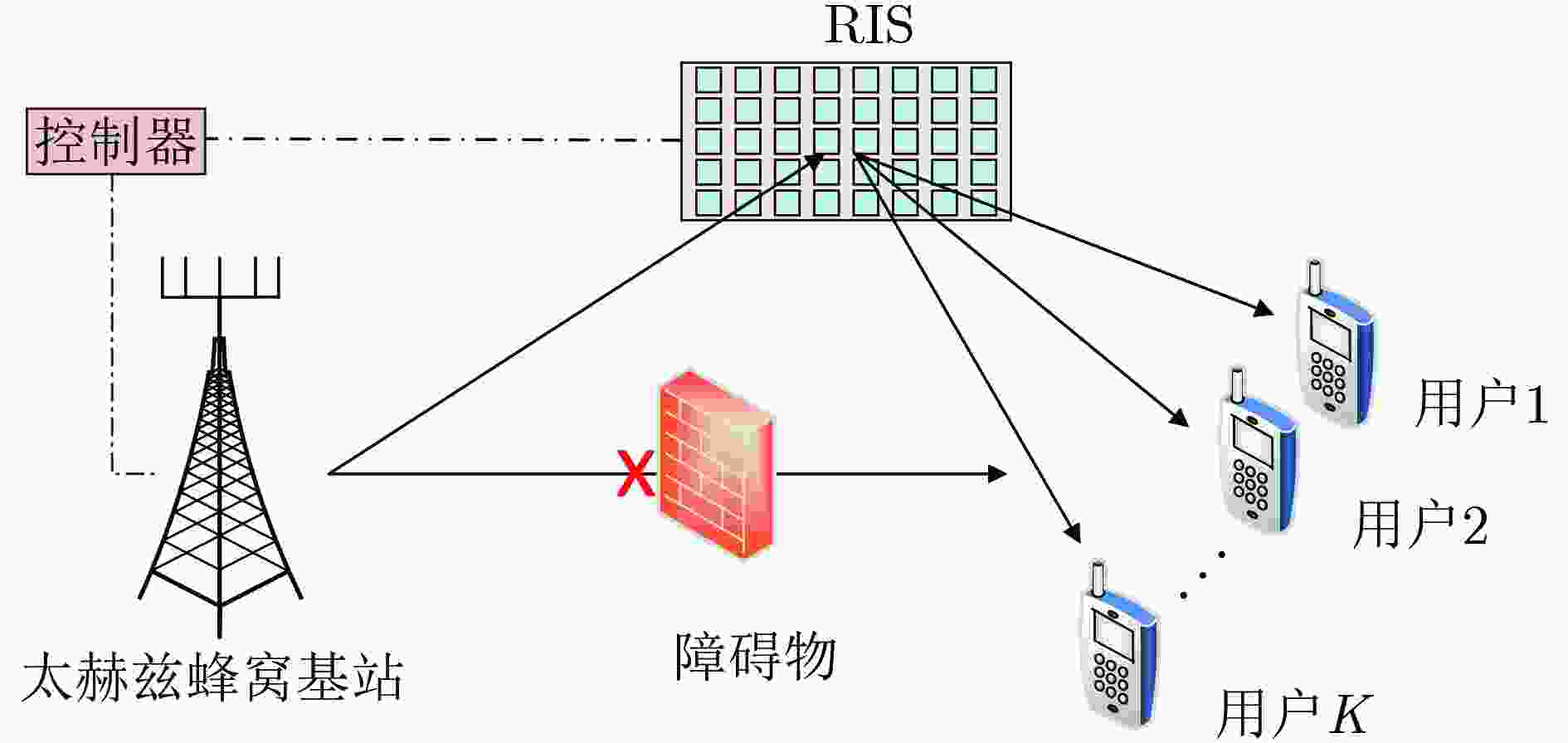
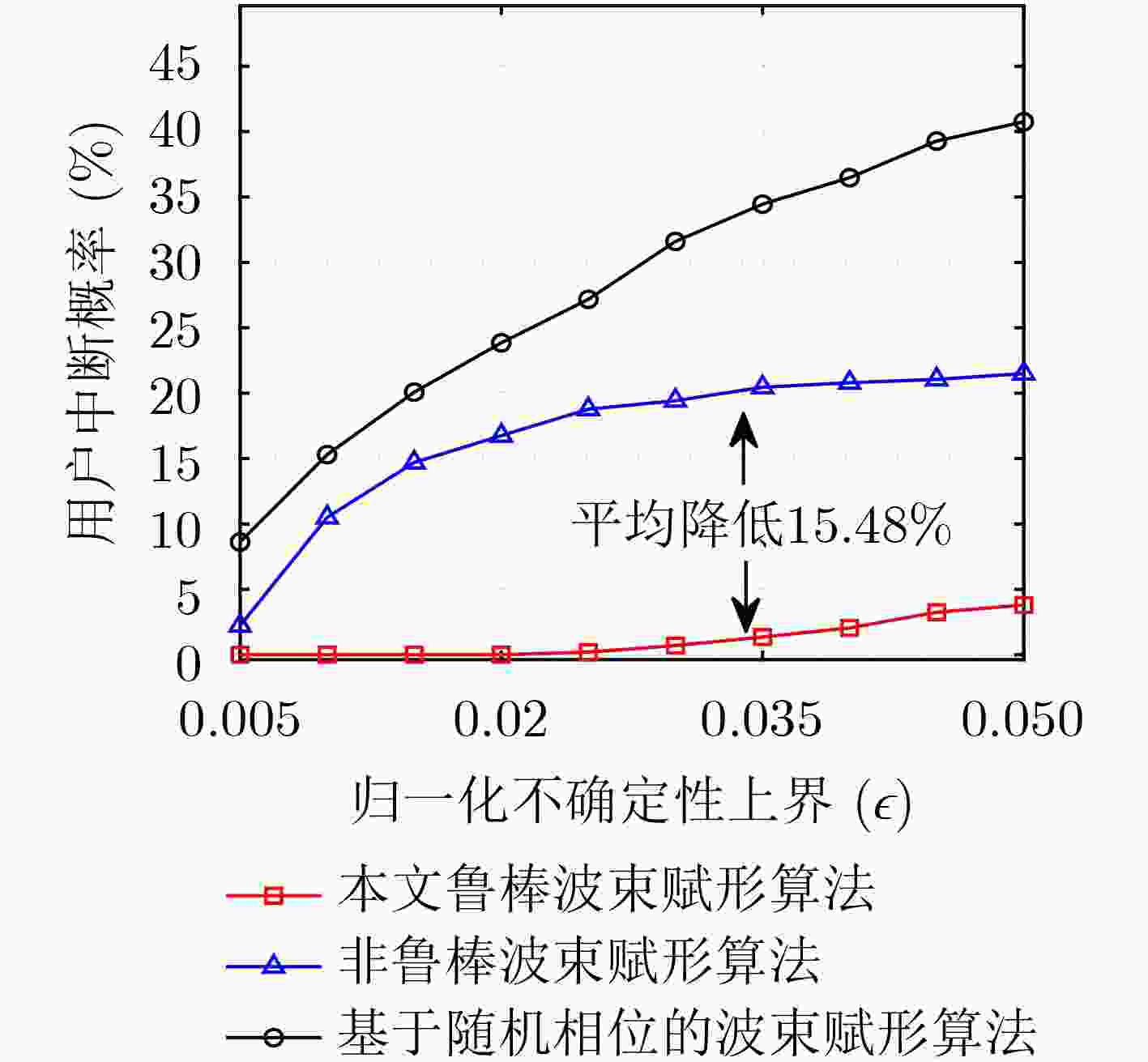
摘要: 太赫兹通信作为6G的关键技术之一,被认为是能够解决频谱资源短缺、提升系统容量的有效手段。然而,由于路径损耗极高和分子的吸收作用,太赫兹容易被障碍物阻挡导致通信中断。为了解决该问题,该文将可重构智能反射面(RIS)引入到太赫兹通信系统中,且考虑信道不确定性对传输稳定性的影响,基于用户服务质量约束、基站发射功率约束及RIS离散相移约束,建立多用户能效最大化波束赋形模型。利用丁克尔巴赫、连续凸近似、S-程序、半正定松弛、相位映射和块坐标下降将原非凸优化问题转化为凸优化问题进行求解。仿真结果表明,与传统非鲁棒波束赋形对比,所提算法能效提升了15.4%,中断概率减小了15.48%。Abstract: Terahertz communication, as one of the key technologies for 6G, is considered an effective means of addressing the scarcity of spectrum resources and improving system capacity. However, due to high path loss and the molecule absorption, terahertz is easily blocked by obstacles leading to communication interruptions. To address this problem, Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) is introduced into terahertz communication systems and the impact of channel uncertainty on transmission stability is considered to establish a multi-user energy-efficiency maximization beamforming model based on user quality of service constraints, base station transmit power constraints and RIS discrete phase shift constraints. The original nonconvex optimization problem is solved by transforming it into a convex optimization problem using Dinkelbach, continuous convex approximation, S-procedure, semi-positive definite relaxation, phase mapping and block coordinate descent. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm improves the energy efficiency by 15.4% and reduces the outage probability by 15.48% compared with the traditional non-robust beamforming algorithm.
-
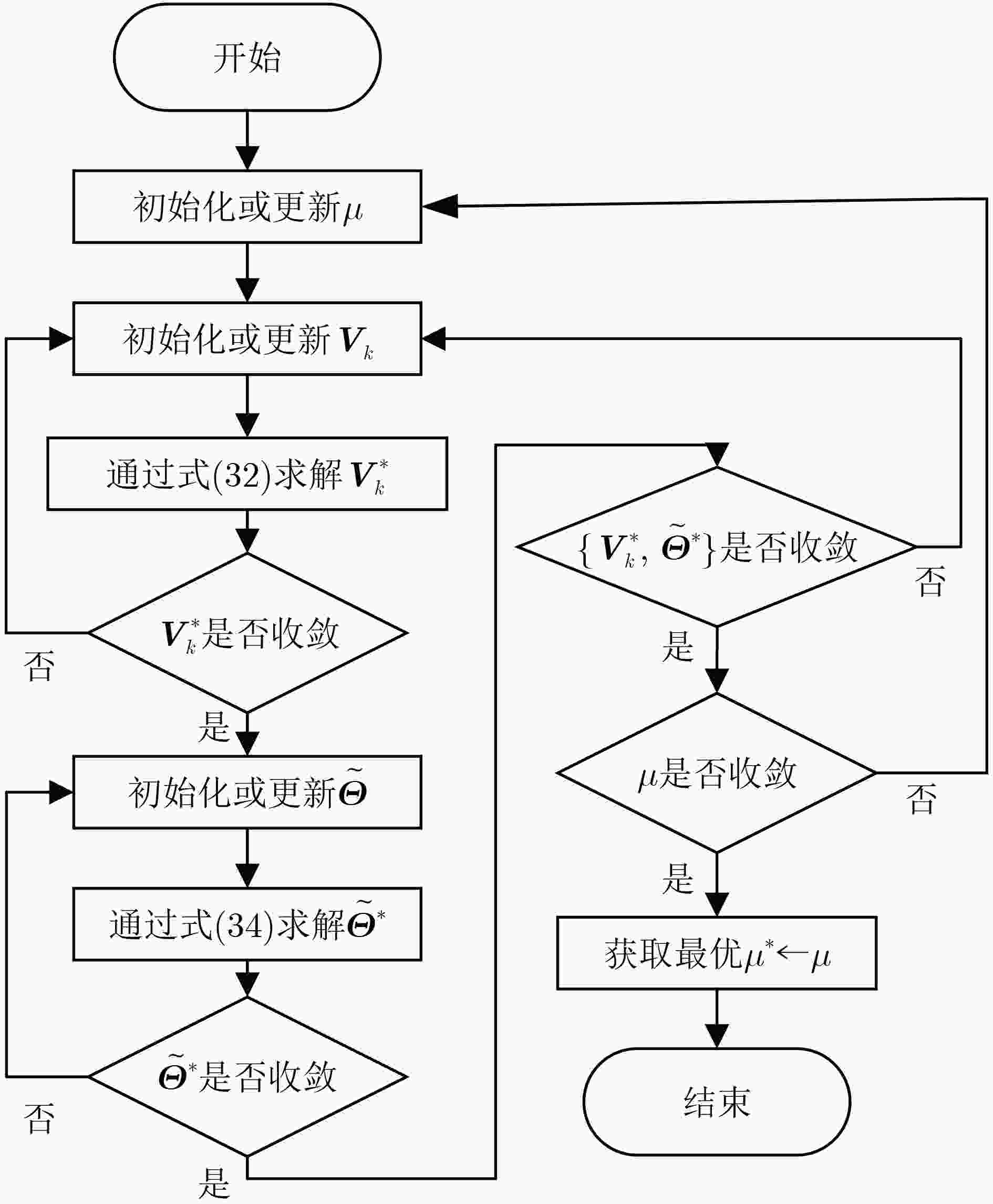
算法1 基于BCD的鲁棒波束赋形算法 初始化系统参数:$M,N,K,\sigma _k^2,{P^{\max } },{P_{ {\text{BS} } } },{P_{ {\text{RIS} } } },R_k^{\min },\bar x_k^{(2)}$,
$\bar x_k^{(3)},\bar \eta ,{\varepsilon _k},\mu $;设置$ \mu $的上界和下界使之满足$ {\mu ^{\min }} < = {\mu ^ * } < = {\mu ^{\max }} $; 设置最大迭代次数$ {L_{\max }} $,收敛精度$ \varpi $,迭代索引$ l = 0 $; (1) While $ l < = {L_{\max }} $do (2) $ \mu (l) = ({\mu ^{\min }} + {\mu ^{\max }})/2 $; (3) 初始化$ {{\boldsymbol{V}}_k} $,$ {\boldsymbol{\tilde \varTheta }} $; (4) 重复 (5) 给定$ {\boldsymbol{\tilde \varTheta }} $,求解问题式(32)得到$ {{\boldsymbol{V}}_k}^{} $; (6) 更新$ {{\boldsymbol{V}}_k}^{} $; (7) 直到 收敛 (8) 重复 (9) 给定$ {{\boldsymbol{V}}_k}^{} $,求解问题式(34)得到$ {\boldsymbol{\tilde \varTheta }} $; (10) 更新$ {\boldsymbol{\tilde \varTheta }} $; (11) 直到 收敛 (12) if $f(\mu (l)) \le \varpi$ then (13) $ {{\boldsymbol{V}}_k}^ * = {{\boldsymbol{V}}_k}(l) $, $ {{\boldsymbol{\tilde \varTheta }}^{\boldsymbol{*}}} = {\boldsymbol{\tilde \varTheta }}(l) $,通过式(35)、式(16)分别得
到$ {{\boldsymbol{\hat \varTheta }}^{\boldsymbol{*}}} $, $ \mu (l) $;(14) break (15) else (16) if $ f(\mu (l)) < 0 $ then (17) $ {\mu ^{\max }} = \mu (l); $ (18) else (19) $ {\mu ^{\min }} = \mu (l); $ (20) end if (21) end if (22) 设置迭代次数$ l = l + 1 $; (23) end while 表 1 仿真参数
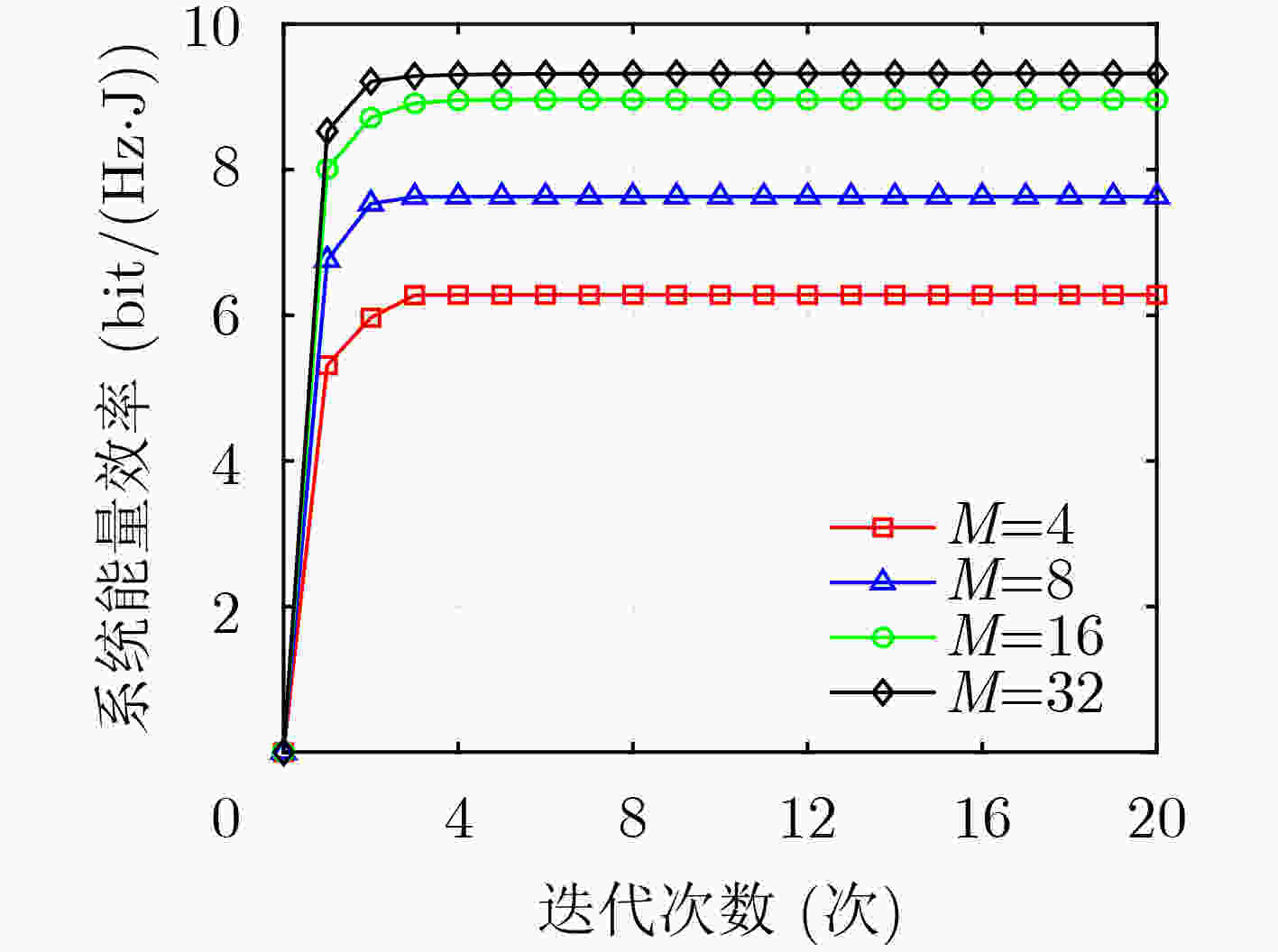
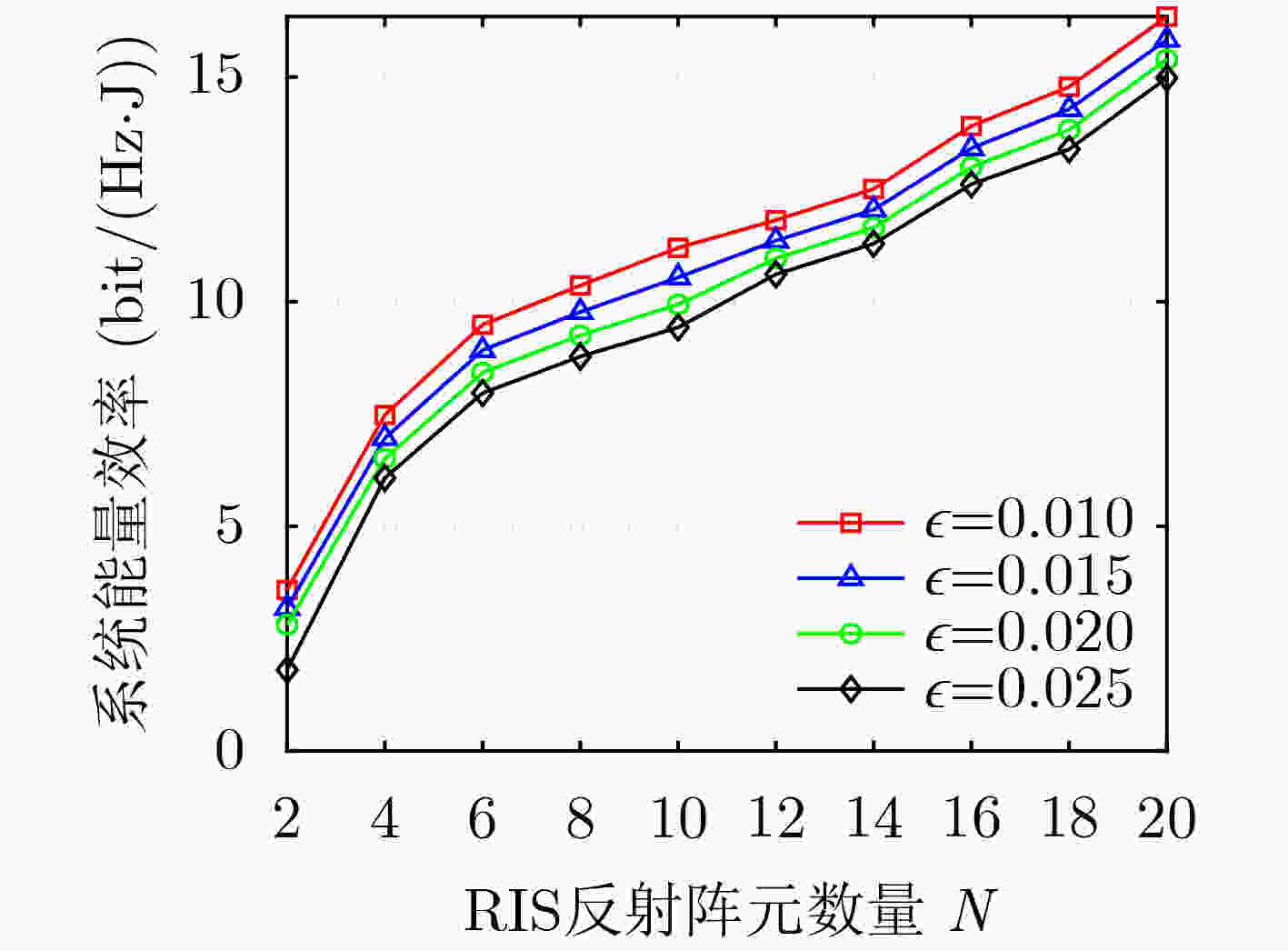
参数 值 参数 值 $ f $ 340 GHz ${P^{\max } }$ 10 W ${G_{\rm{t}}}$ 1 $\sigma _{}^2$ 10–8 W ${G_{\rm{r}}}$ $ 4 + 20\lg \sqrt M $ c $ 3 \times {10^8} \;({\text{m/s)}}$ $ \varpi $ 10–3 $ {L_{\max }} $ 20 $ \tau (f) $ 0.0033 m $ K $ 2 -
[1] CHEN Zhi, HAN Chong, WU Yongzhi, et al. Terahertz wireless communications for 2030 and beyond: A cutting-edge frontier[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2021, 59(11): 66–72. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.011.2100195. [2] XU Yongjun, GAO Zhengnian, WANG Zhengqiang, et al. RIS-enhanced WPCNs: Joint radio resource allocation and passive beamforming optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(8): 7980–7991. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3096603. [3] 智能超表面技术联盟. 智能超表面技术白皮书[R]. 杭州, 中国, 2023.RIS TECH Alliance. Reconfigurable intelligent surface technology white paper[R]. Hangzhou, China, 2023. [4] SONG D, SHIN W, and LEE J. A maximum throughput design for wireless powered communication networks with IRS-NOMA[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(4): 849–853. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3046722. [5] HUA Meng and WU Qingqing. Joint dynamic passive beamforming and resource allocation for IRS-aided full-duplex WPCN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(7): 4829–4843. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3133491. [6] 徐勇军, 徐然, 周继华, 等. 面向窃听用户的RIS-MISO系统鲁棒资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(7): 2253–2263. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211537.XU Yongjun, XU Ran, ZHOU Jihua, et al. Robust Resource Allocation Algorithm for RIS-Assisted MISO Systems with Eavesdroppers[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(7): 2253–2263. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211537. [7] 刘志新, 赵松晗, 杨毅, 等. 智能反射面辅助的无人机无线携能通信网络吞吐量最大化算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(7): 2325–2331. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220195.LIU Zhixin, ZHAO Songhan, YANG Yi, et al. Throughput maximization algorithm for intelligent reflecting surface-aided unmanned aerial vehicle communication networks with wireless energy transfer[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(7): 2325–2331. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220195. [8] HUANG Chongwen, YANG Zhaohui, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Multi-hop RIS-empowered terahertz communications: A DRL-based hybrid beamforming design[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(6): 1663–1677. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2021.3071836. [9] NING Boyu, WANG Peilan, LI Lingxiang, et al. Multi-IRS-aided multi-user MIMO in mmWave/THz communications: A space-orthogonal scheme[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(12): 8138–8152. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3216344. [10] MAMAGHANI M T and HONG Yi. Aerial intelligent reflecting surface-enabled terahertz covert communications in beyond-5G internet of things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(19): 19012–19033. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3163396. [11] HAO Wanming, SUN Gangcan, ZENG Ming, et al. Robust design for intelligent reflecting surface-assisted MIMO-OFDMA terahertz IoT networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(16): 13052–13064. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3064069. [12] ZHU Zhengyu, XU Jinlei, SUN Gangcan, et al. Robust beamforming design for IRS-aided secure SWIPT terahertz systems with non-linear EH model[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(4): 746–750. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2022.3142098. [13] QIAO Jingping, ZHANG Chuanting, DONG Anming, et al. Securing intelligent reflecting surface assisted terahertz systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(8): 8519–8533. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3172763. [14] GAO Zhengnian, XU Yongjun, WANG Qianzhu, et al. Outage-constrained energy efficiency maximization for RIS-assisted WPCNs[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(10): 3370–3374. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3101657. [15] XU Yongjun, GUI Guan, GACANIN H, et al. A survey on resource allocation for 5G heterogeneous networks: Current research, future trends, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 668–695. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3059896. [16] XU Yongjun, XIE Hao, WU Qingqing, et al. Robust max-min energy efficiency for RIS-aided HetNets with distortion noises[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(2): 1457–1471. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3141798. [17] XU Yongjun, XIE Hao, LIANG Chengchao, et al. Robust secure energy-efficiency optimization in Swipt-aided heterogeneous networks with a nonlinear energy-harvesting model[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(19): 14908–14919. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3072965. [18] DINKELBACH W. On nonlinear fractional programming[J]. Management Science, 1967, 13(7): 492–498. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.13.7.492. [19] BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004. [20] LUO Zhiquan, MA W K, SO A M C, et al. Semidefinite relaxation of quadratic optimization problems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2010, 27(3): 20–34. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2010.936019. [21] QIAO Jingping and ALOUINI M S, Secure transmission for intelligent reflecting surface-assisted mmWave and terahertz systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(10): 1743–1747. [22] WANG Kunyu, SO A M C, CHANG T H, et al. Outage constrained robust transmit optimization for multiuser MISO downlinks: Tractable approximations by conic optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(21): 5690–5705. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2354312. -





 下载:
下载:
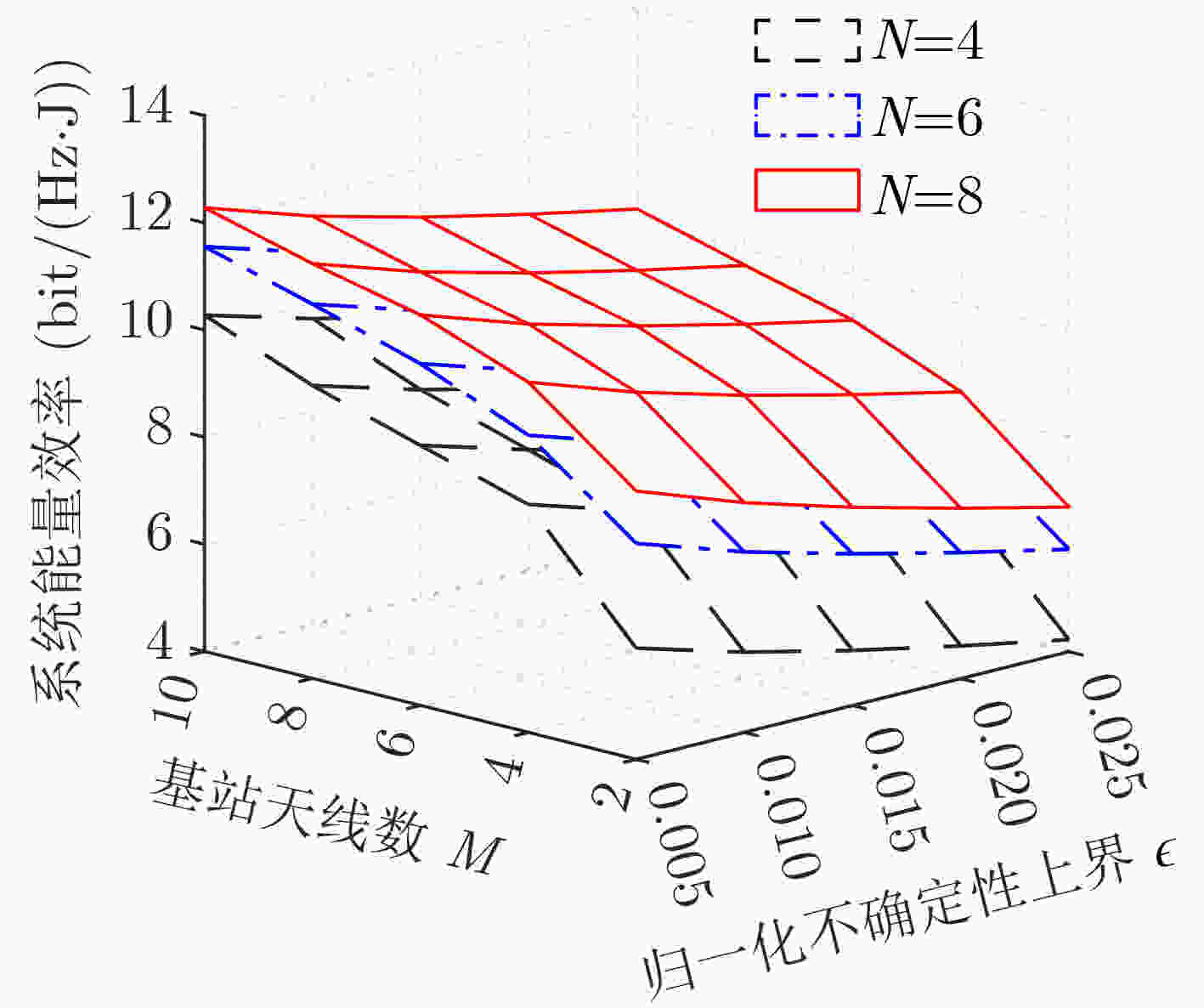
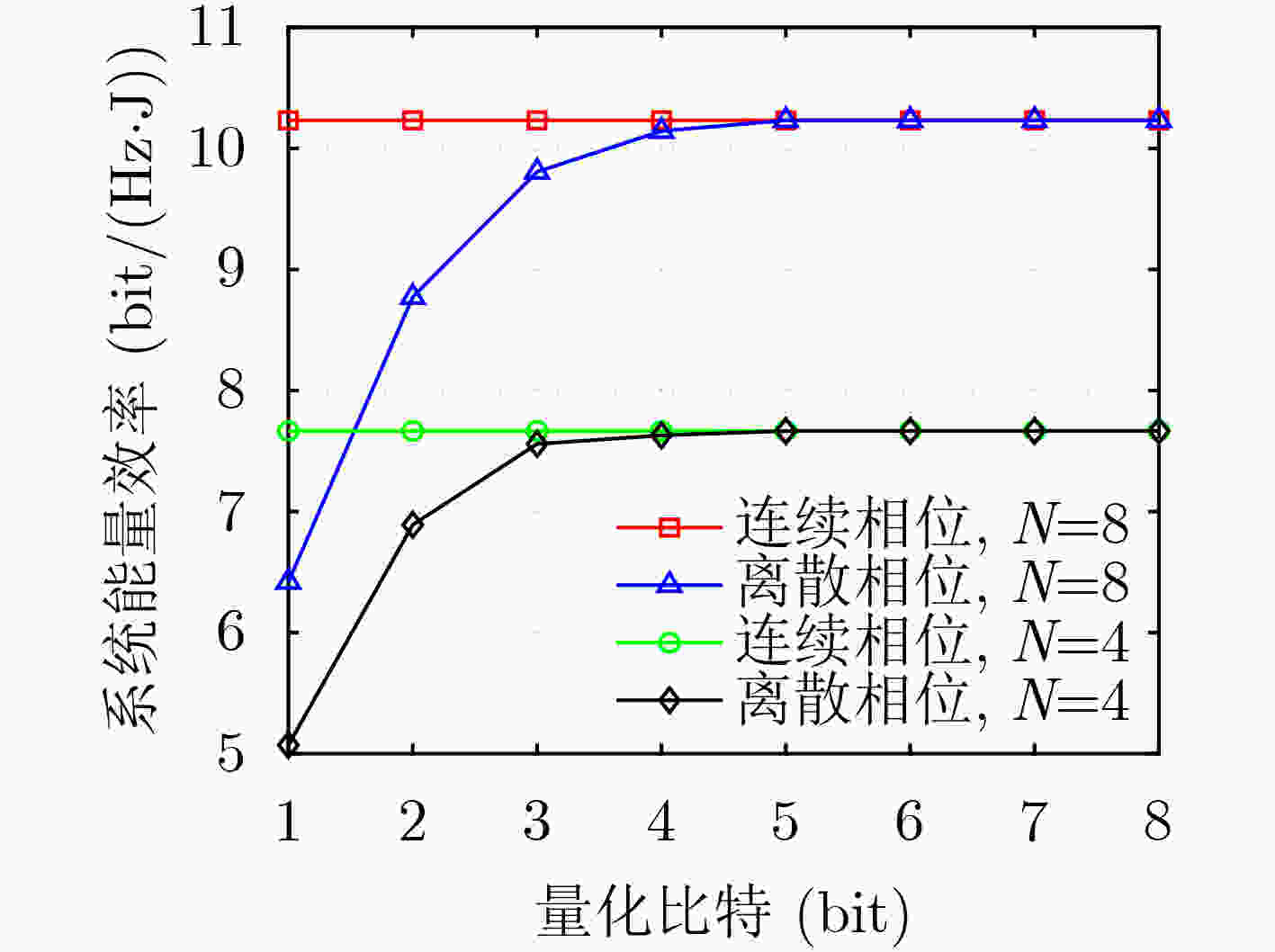
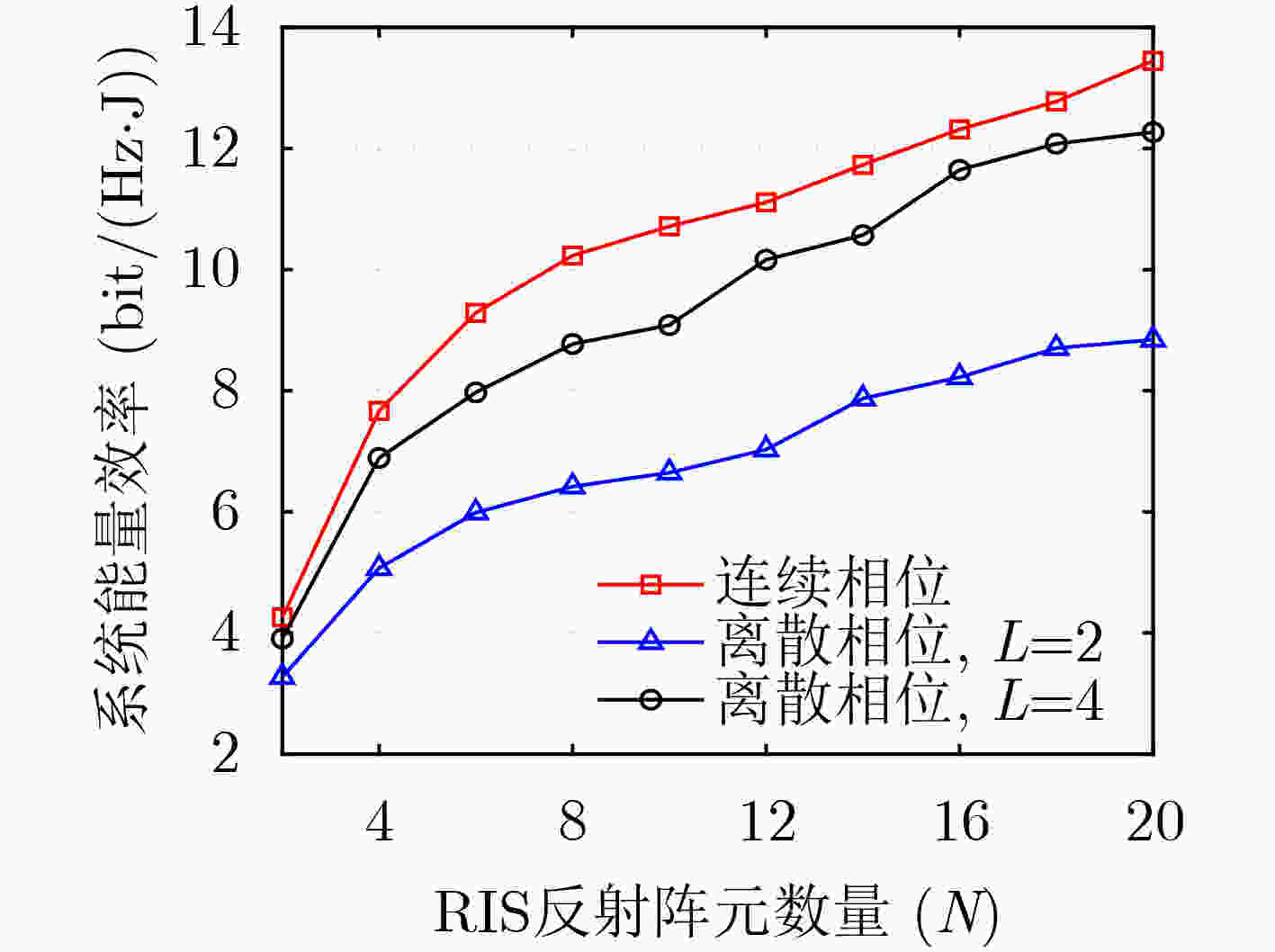
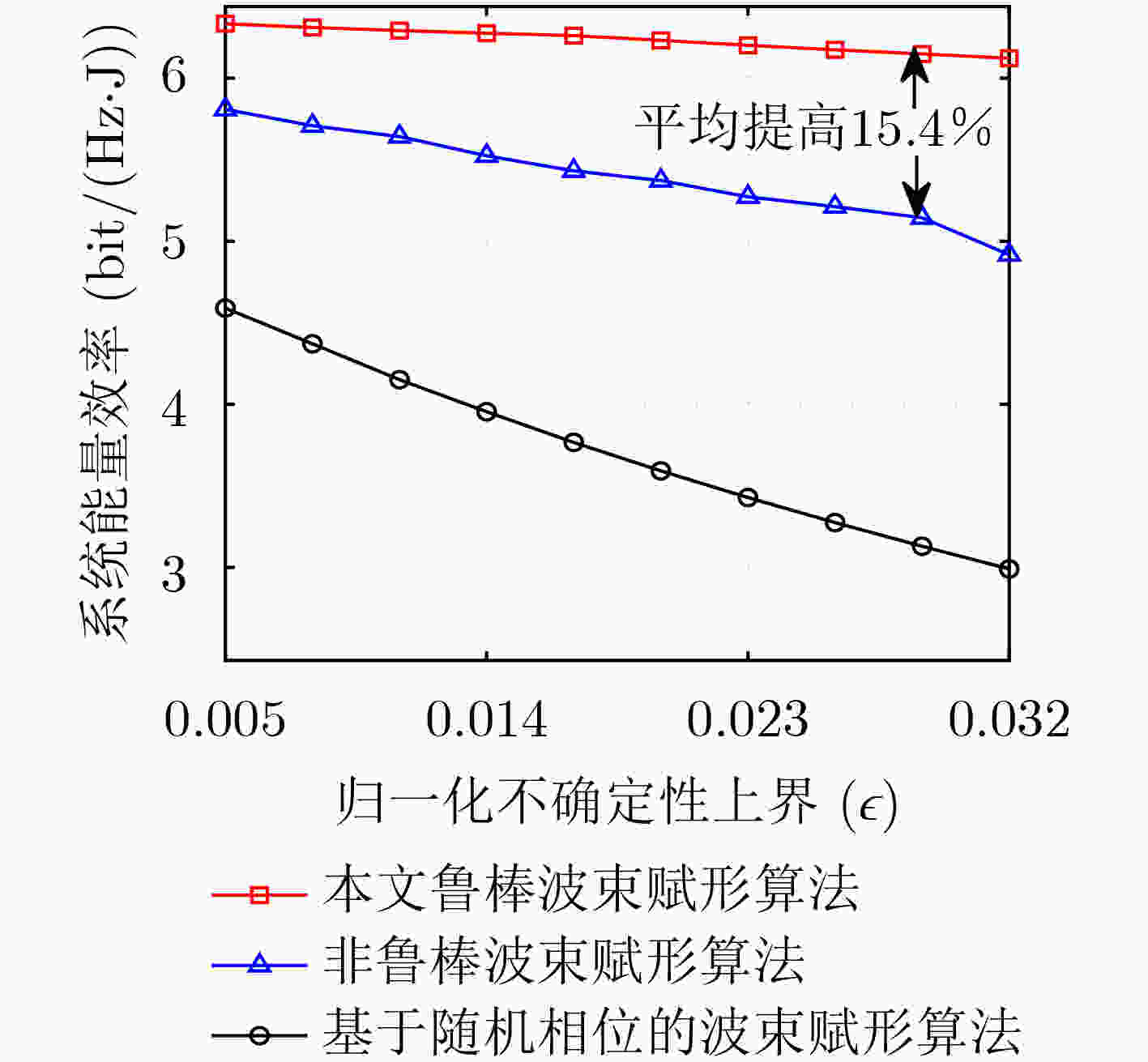


 下载:
下载:
