Orthogonal Time Frequency Space Channel Estimation Based on Model-driven Deep Learning
-
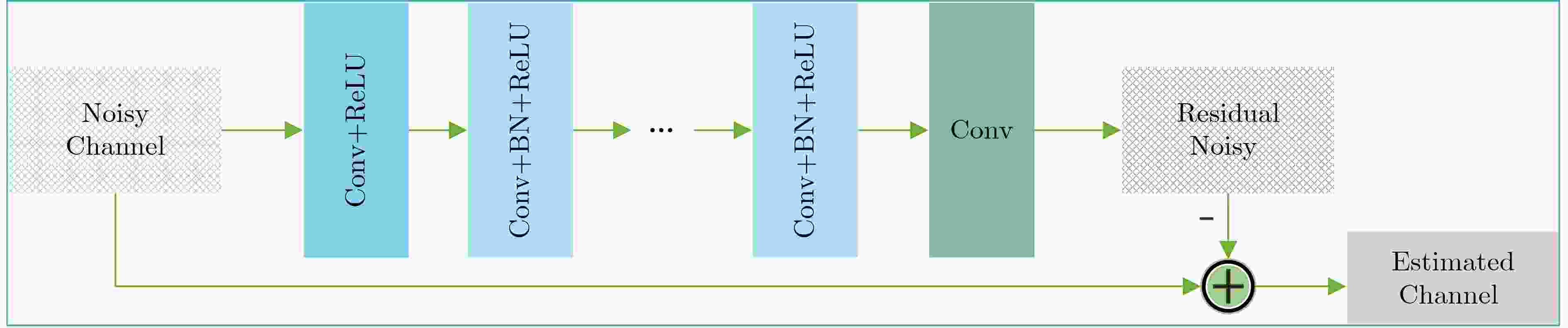
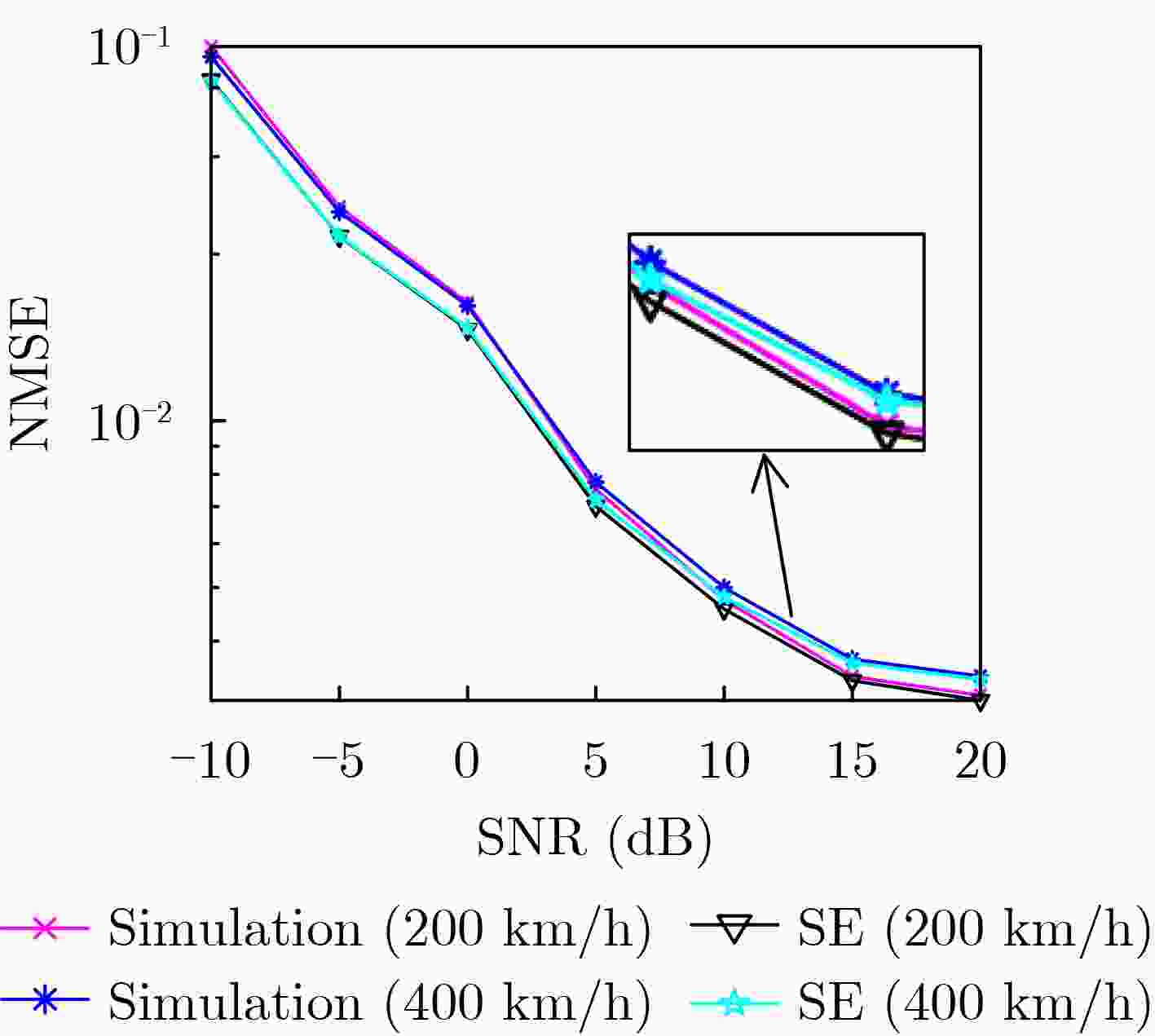
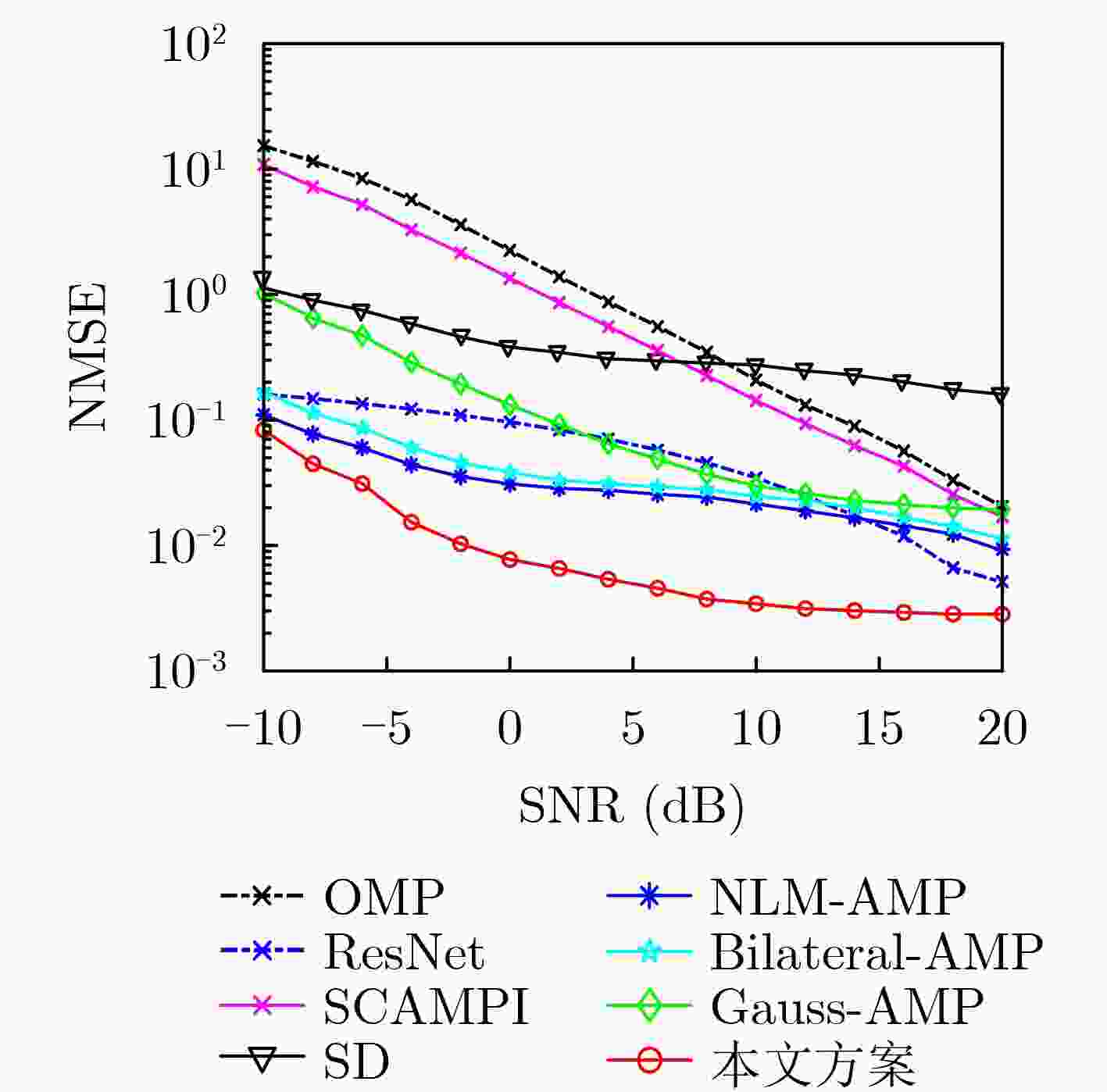
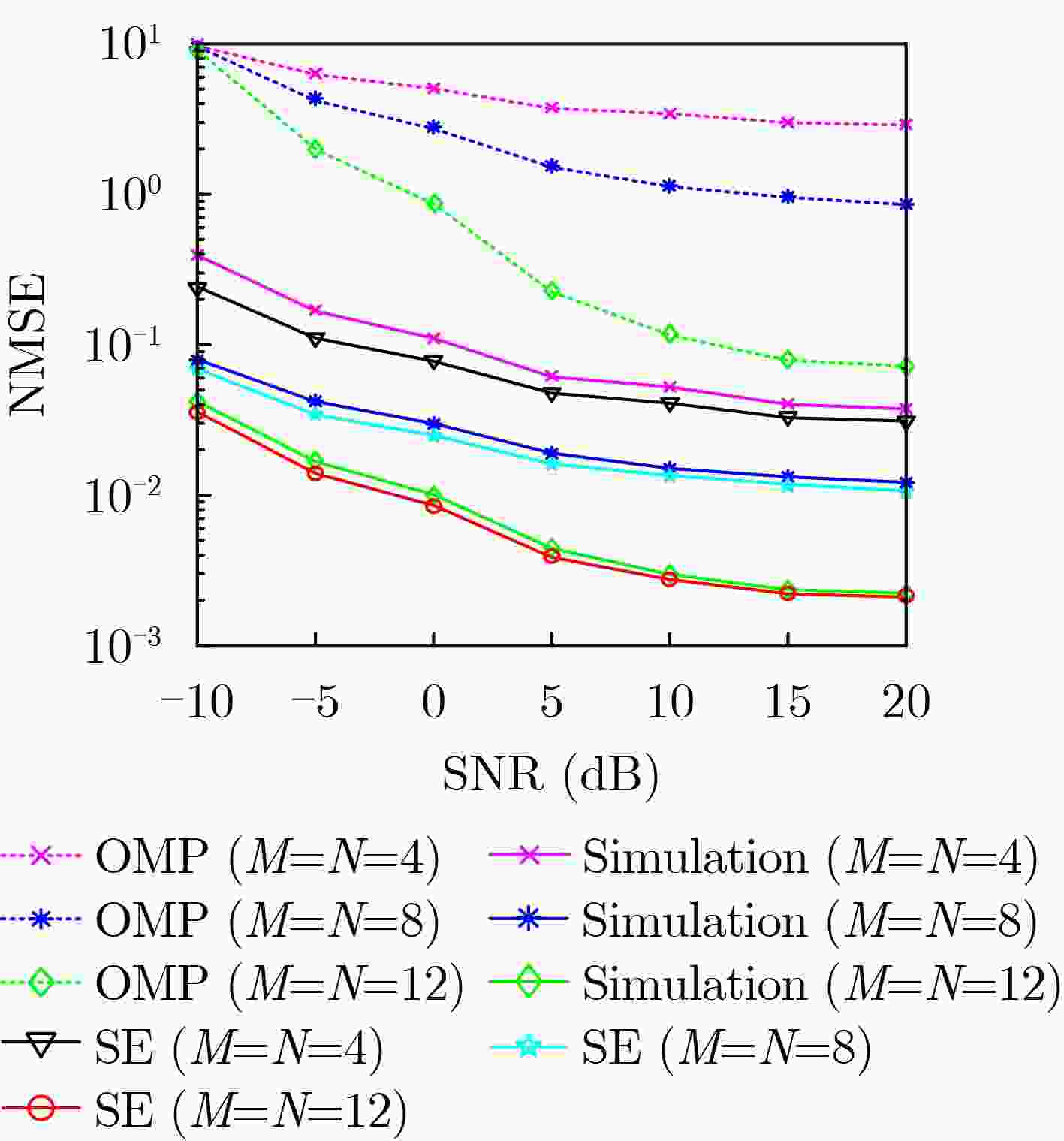
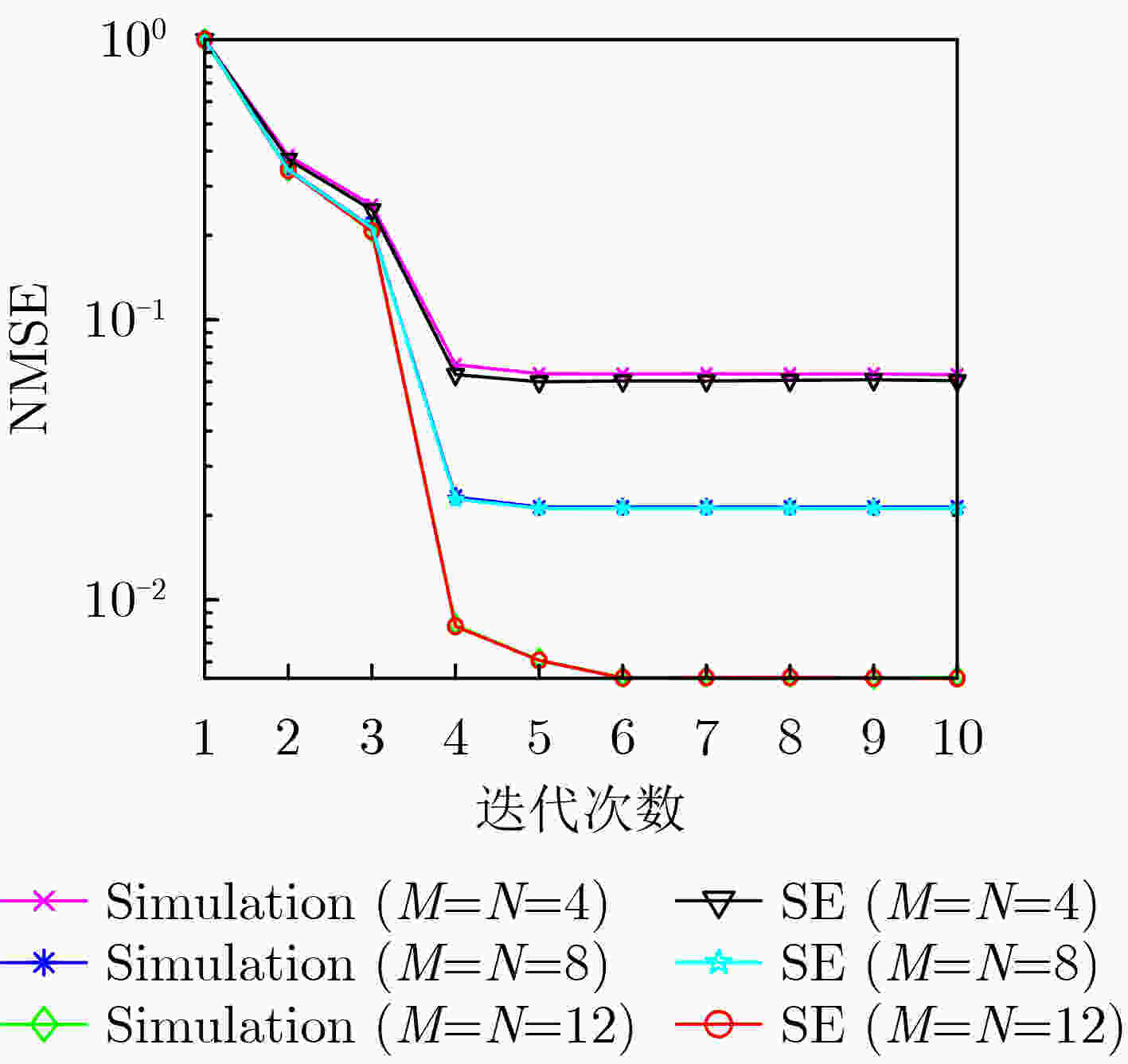
摘要: 针对单输入单输出(SISO)的正交时频空间(OTFS)调制系统,该文利用一种模型驱动深度学习算法进行OTFS信道估计。该方案首先将去噪近似消息传递(DAMP)算法进行深度展开,利用去噪卷积神经网络代替传统的去噪器,对含噪的时延多普勒信道进行去噪估计,然后提供了状态演化方程来预测可学习去噪近似消息传递(LDAMP)算法的理论归一化均方误差性能。仿真结果表明,相比于其他估计方案,该方案不仅在低信噪比条件下具有优越的性能表现,而且还具有非常好的鲁棒性,在信道路径总数不变时,增加OTFS 2维网格点数量,可以有效提升信道估计精确度。Abstract: In this paper, a channel estimation scheme based on model-driven deep learning algorithm is proposed for Single Input Single Output (SISO) Orthogonal Time Frequency Space (OTFS) modulation systems. First, the Denoising Approximate Message Passing (DAMP) algorithm is considerably expanded. Then the traditional denoiser is replaced by the Denoising Convolutional Neural Network (DnCNN) to estimate the delay-Doppler channel with additive white Gaussian noise. The State Evolution (SE) equation is provided to predict the theoretical Normalized Mean Square Error (NMSE) performance of the Learned Denoising based Approximate Message Passing (LDAMP) algorithm. Simulation results show that the scheme performs well under a low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and has great robustness compared with other estimation schemes. When the total number of channel paths is invariant, increasing the number of OTFS two-dimensional grid points can effectively improve channel estimation accuracy.
-
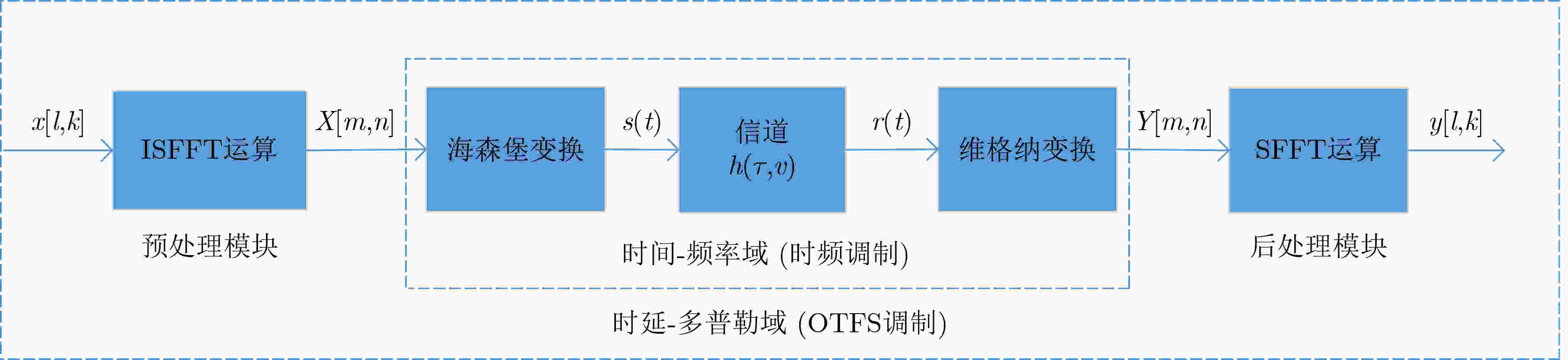
图 1 OTFS调制系统模型框图[17]
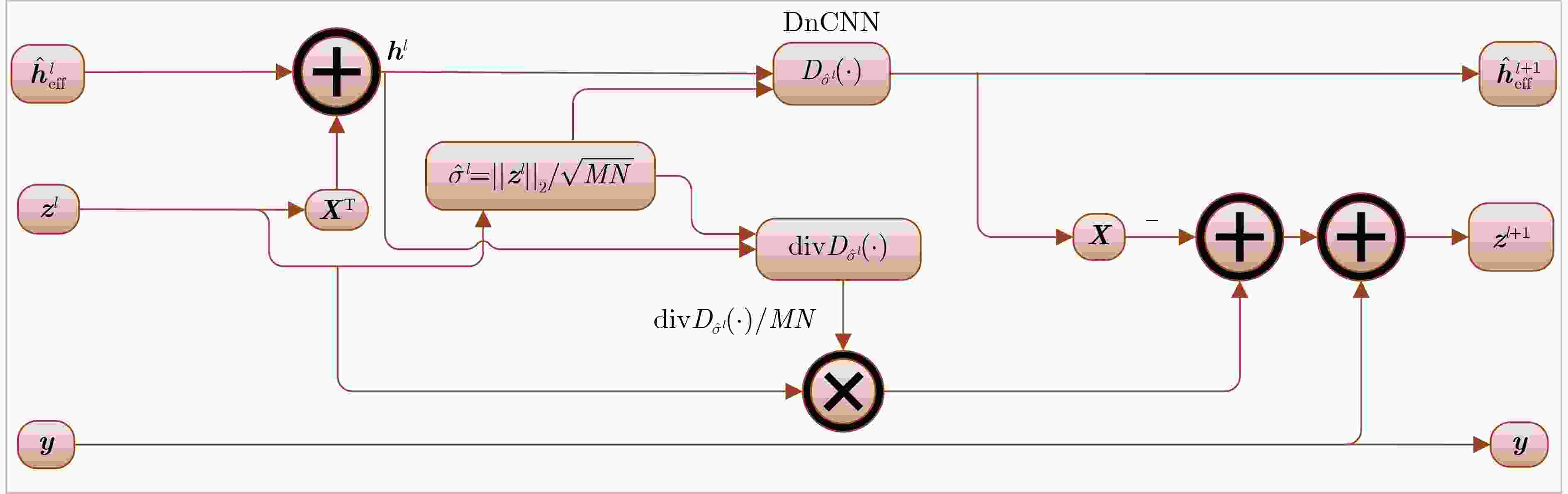
算法1 基于OTFS系统的LDAMP算法 输入:测量矩阵:$ {\mathbf{X}} $;观测矢量:$ {\mathbf{y}} $;迭代次数:$ L $ 初始化:$ {{\mathbf{z}}^0} = {\mathbf{y}} $,$ {\hat \sigma ^0} = ||{{\mathbf{z}}^0}|{|_2}/\sqrt {MN} $, $ {\mathbf{\hat h}}_{{\text{eff}}}^0 = 0 $ for $ l = 0,1, \cdots ,L - 1 $ do (1) $ {\mathbf{\hat h}}_{{\text{eff}}}^{l + 1} = {D_{{{\hat \sigma }^l}}}({\mathbf{\hat h}}_{{\text{eff}}}^l + {{\mathbf{X}}^{\text{T}}}{{\mathbf{z}}^l}) $ (2) $ {{\mathbf{c}}^{l + 1}} = {{\mathbf{z}}^l}{\text{div}}{D_{{{\hat \sigma }^l}}}({\mathbf{\hat h}}_{{\text{eff}}}^l + {{\mathbf{X}}^{\text{T}}}{{\mathbf{z}}^l})/MN $ (3) $ {{\mathbf{z}}^{l{\text{ + }}1}} = {\mathbf{y}} - {\mathbf{X\hat h}}_{{\text{eff}}}^{l{\text{ + }}1} + {{\mathbf{c}}^{l + 1}} $ (4) $ {\hat \sigma ^{l{\text{ + }}1}} = ||{{\mathbf{z}}^{l{\text{ + }}1}}|{|_2}/\sqrt {MN} $ end for 输出:时延多普勒信道估计值$ {{\mathbf{\hat h}}_{{\text{eff}}}} = {\mathbf{\hat h}}_{{\text{eff}}}^L $ 表 1 不同算法复杂度对比结果
所用算法 复杂度 LDAMP O(L(MN+M2N2)) DAMP O(L(MN+M2N2)) OMP O(L(M6N6)) 表 2 主要仿真参数设置
参数名称 参数设置 载波数$ M $ $ 4,8,12 $ 符号数$ N $ $ 4,8,12 $ 子载波间隔$ \Delta f $ $15{\text{ kHz} }$ 载波频率$ {f_{\text{c}}} $ $ 4{\text{ GHz}} $ 带宽B 0.18 MHz 波长 75 mm 调制方式 4-QAM 信道模型 EVA -
[1] WEI Zhiqiang, LI Shuangyang, YUAN Weijie, et al. Orthogonal time frequency space modulation–Part I: Fundamentals and challenges ahead[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(1): 4–8. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3209689. [2] HADANI R, RAKIB S, TSATSANIS M, et al. Orthogonal time frequency space modulation[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 1–6. [3] WEI Zhiqiang, YUAN Weijie, LI Shuangyang, et al. Orthogonal time-frequency space modulation: A promising next-generation waveform[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(4): 136–144. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2000408. [4] ZHANG Mingchen, WANG Fanggang, YUAN Xiaojun, et al. 2D structured turbo compressed sensing for channel estimation in OTFS systems[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communication Systems, Chengdu, China, 2018: 45–49. [5] YUAN Weijie, WEI Zhiqiang, LI Shuangyang, et al. Integrated sensing and communication-assisted orthogonal time frequency space transmission for vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(6): 1515–1528. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3117404. [6] YUAN Weijie, WEI Zhiqiang, LI Shuangyang, et al. Orthogonal time frequency space modulation–Part III: ISAC and potential applications[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(1): 14–18. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3209651. [7] RAMACHANDRAN M K and CHOCKALINGAM A. MIMO-OTFS in high-Doppler fading channels: Signal detection and channel estimation[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2018: 206–212. [8] ZHAO Hang, KANG Ziqi, and WANG Hua. A novel channel estimation scheme for OTFS[C]. Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 20th International Conference on Communication Technology, Nanning, China, 2020: 12–16. [9] RAVITEJA P, PHAN K T, and HONG Yi. Embedded pilot-aided channel estimation for OTFS in delay–Doppler channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(5): 4906–4917. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2906357. [10] YUAN Weijie, LI Shuangyang, WEI Zhiqiang, et al. Data-aided channel estimation for OTFS systems with a superimposed pilot and data transmission scheme[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(9): 1954–1958. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3088836. [11] LIU Wei, ZOU Liyi, BAI Baoming, et al. Low PAPR channel estimation for OTFS with scattered superimposed pilots[J]. China Communications, 2023, 20(1): 79–87. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2023.01.007. [12] WU Xianda, MA Shaodan, and YANG Xi. Tensor-based low-complexity channel estimation for mmWave massive MIMO-OTFS systems[J]. Journal of Communications and Information Networks, 2020, 5(3): 324–334. doi: 10.23919/JCIN.2020.9200896. [13] LIAO Yong and LI Xue. Joint multi-domain channel estimation based on sparse Bayesian learning for OTFS system[J]. China Communications, 2023, 20(1): 14–23. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2023.01.002. [14] ZHANG Yang, ZHANG Qunfei, HE Chengbing, et al. Channel estimation for OTFS system over doubly spread sparse acoustic channels[J]. China Communications, 2023, 20(1): 50–65. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2023.01.005. [15] WANG Tianqi, WEN Chaokai, WANG Hanqing, et al. Deep learning for wireless physical layer: Opportunities and challenges[J]. China Communications, 2017, 14(11): 92–111. doi: 10.1109/CC.2017.8233654. [16] LI Qingyu, GONG Yi, MENG Fanke, et al. Residual learning based channel estimation for OTFS system[C]. Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China, Foshan, China, 2022: 275–280. [17] LIU Fei, YUAN Zhengdao, GUO Qinghua, et al. Message passing-based structured sparse signal recovery for estimation of OTFS channels with fractional Doppler shifts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(12): 7773–7785. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3087501. [18] SRIVASTAVA S, SINGH R K, JAGANNATHAM A K, et al. Bayesian learning aided simultaneous row and group sparse channel estimation in orthogonal time frequency space modulated MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(1): 635–648. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3123354. [19] METZLER C A, MALEKI A, and BARANIUK R G. From denoising to compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2016, 62(9): 5117–5144. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2016.2556683. [20] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84–90. doi: 10.1145/3065386. [21] METZLER C A, MOUSAVI A, and BARANIUK R G. Learned D-AMP: Principled neural network based compressive image recovery[C]. Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 1770–1781. [22] HE Hengtao, WEN Chaokai, JIN Shi, et al. Deep learning-based channel estimation for beamspace mmWave massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, 7(5): 852–855. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2832128. [23] SHEN Wenqian, DAI Linglong, AN Jianping, et al. Channel estimation for orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) massive MIMO[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(16): 4204–4217. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2919411. [24] YANG Jie, WEN Chaokai, JIN Shi, et al. Beamspace channel estimation in mmWave systems via cosparse image reconstruction technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(10): 4767–4782. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2805359. [25] GAO Xinyu, DAI Linglong, HAN Shuangfeng, et al. Reliable beamspace channel estimation for millimeter-wave massive MIMO systems with lens antenna array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(9): 6010–6021. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2718502. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
