A Method for Offloading Vehicle Collaborative Tasks for Green Computing
-
摘要: 车辆边缘计算(VEC)为处理计算密集、延迟敏感型任务提供了新的范式,然而边缘服务器在整合可再生能源方面的能力较差。因此,为了提高边缘服务器的能效,该文设计了一种面向绿色计算的车辆协同任务卸载框架。在该框架中,车辆配备能源收集(EH)设备,通过彼此间共享绿色能源和计算资源协作执行任务。为有效促进车辆的参与积极性,该文通过动态定价激励车辆,并综合考虑了车辆的移动性、任务优先级等。为了使卸载决策适应动态环境的变化,该文提出了一种基于双延迟深度确定性策略梯度(TD3)的任务卸载方法,以在最大化所有车辆平均任务完成效用的同时减少边缘端电网电力的使用。最后,仿真结果验证了该方法的有效性,相比基于深度确定性策略梯度(DDPG)和基于贪心原则(GPE)的方法在性能上分别提升了7.34%和37.47%。Abstract: Vehicular Edge Computing (VEC) has become a promising and prospective paradigm for computation-intensive and delay-sensitive tasks. However, edge servers are less capable of integrating renewable energy. Therefore, in order to improve the energy efficiency of edge servers, a green computing oriented vehicle collaborative task offloading framework is proposed. In this framework, vehicles equipped with Energy Harvest (EH) devices cooperate to perform tasks by sharing green energy and computing resources with each other. To effectively enhance the participation enthusiasm of vehicles, dynamic pricing is adopted to motivate vehicles, and the mobility and task priority are also considered comprehensively. In order to adapt the offloading decisions to the dynamic environment, a Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic policy gradient (TD3) based task offloading method is proposed to maximize the average task completion utility of all vehicles while reducing the use of grid power. Finally, simulation results verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, and the performance achieves 7.34% and 37.47% improvement respectively compared with Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) based method and Greedy Principle Execution (GPE) method.
-
算法1 基于TD3的车辆协同任务卸载方法 初始化VEC环境,包括:基站的位置信息$ (0,h) $,所有车辆的计算能力$ {F_m} $,车辆的移动模式$\left\{ {\left( { {x_m},0} \right),{{\boldsymbol{v}}_m} } \right\}$和EH模块初始能源存储
$Q_m^0,m \in M$。for 迭代次数$v = 1,2,\cdots,V$ do 初始化一个随机过程用于动作探索,即产生一个随机噪声$\varepsilon \sim N\left( {0,\delta } \right)$。 for $l = 0,1,\cdots,{l_{\rm{max}}}$ do 基站从车辆处接收任务请求,并从环境收集状态信息${{\boldsymbol{s}}^l}$,依据当前策略及探索噪声生成动作${ {\boldsymbol{a} }^l} = {\mu ^\theta }\left( { {{\boldsymbol{s}}^l} } \right) + \varepsilon$,发送任务执行和资源
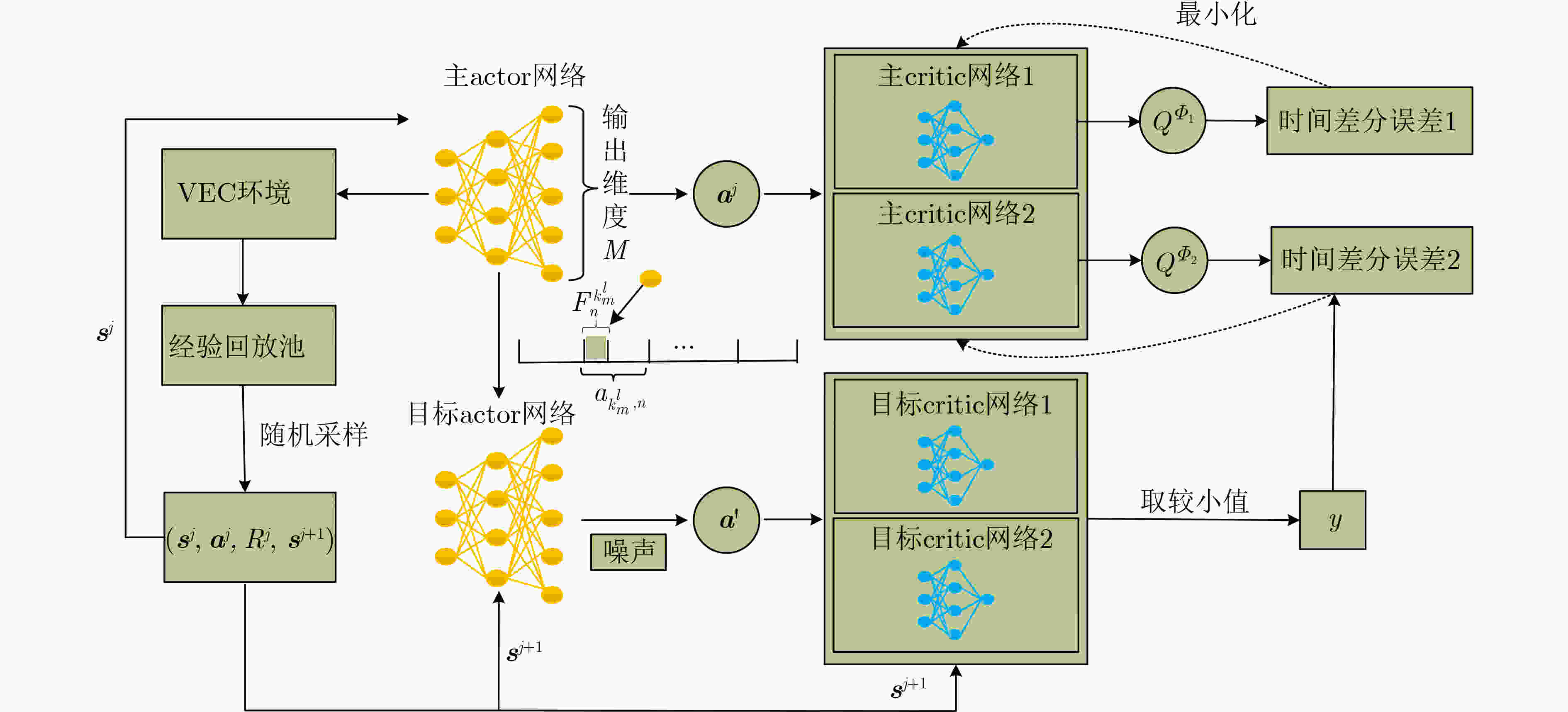
分配信息给车辆,执行动作获得环境反馈的即时奖励${R^l}$及新状态${{\boldsymbol{s}}^{l + 1} }$,添加经验$\left( { { {\boldsymbol{s} }^l},{ {\boldsymbol{a} }^l},{ {{R} }^l},{ {\boldsymbol{s} }^{l + 1} } } \right)$到回放池中。if $v \ge$训练开始阈值 then 从池中随机抽取一小批经验作为样本集$\psi = \left\{ {\left( { { {\boldsymbol{s} }^j},{ {\boldsymbol{a} }^j},{ {{R} }^j},{ {\boldsymbol{s} }^{j + 1} } } \right)} \right\}$。 根据式(24)更新主critic网络。 if $ l{\rm{mod}} $更新频率$ = 0 $ then 根据式(28)更新主actor网络。 以软更新方式更新目标critic网络和目标actor网络。 end for end for 表 1 仿真参数设置
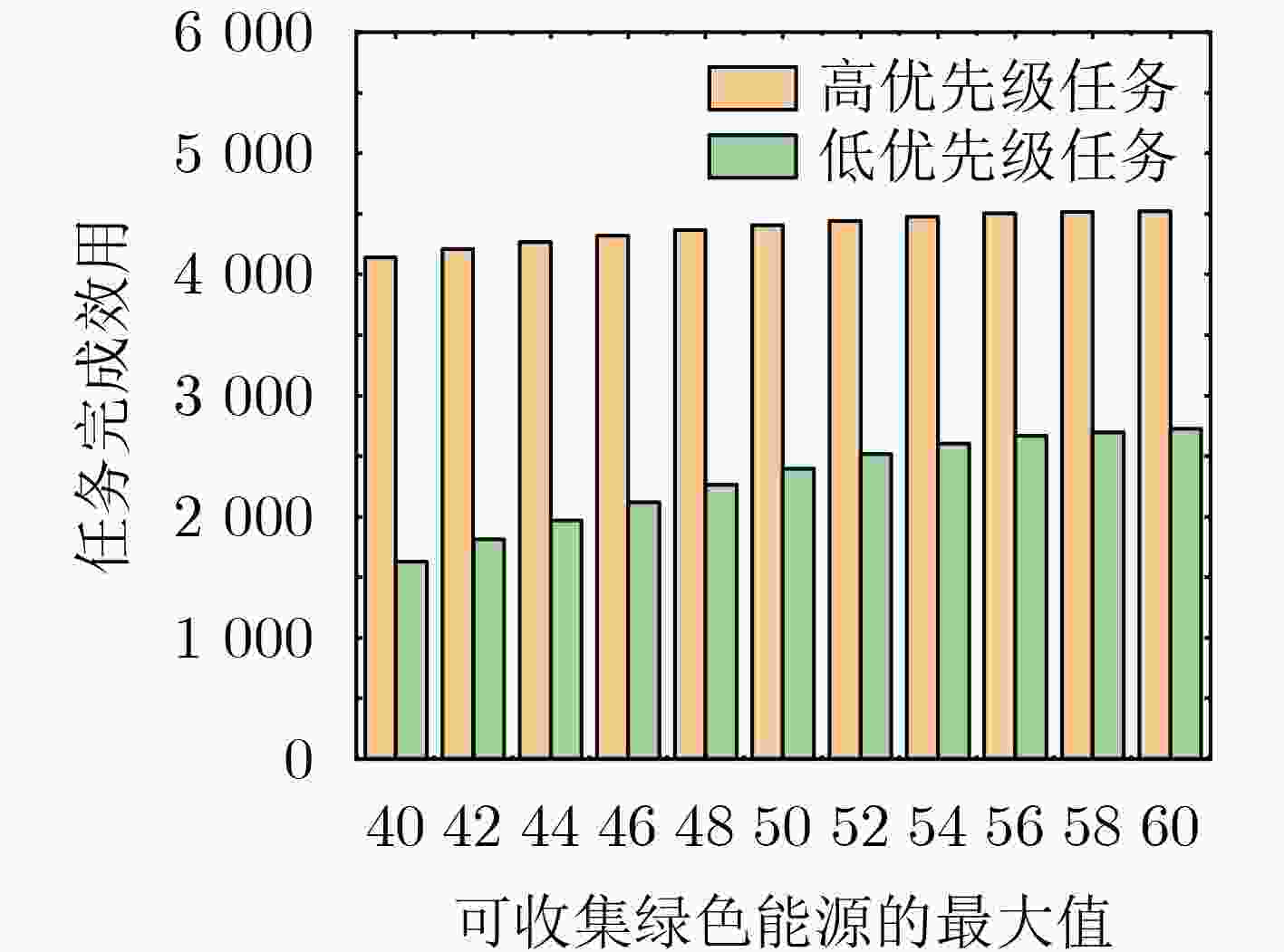
参数 值 车辆速度(km/h) 40~80 车辆计算能力(GHz) 5~10 EH模块初始能源(J) 50~4000 任务大小(kbit) 200~1000 任务所需计算资源(cycles/bit) 500~1000 最大延迟容忍(ms) 高优先级:200
低优先级:1000最大V2V链路传输范围(m) 100 边缘服务器处理一个CPU周期能耗(W) $ 4 \times 1{0^{ - 9}} $ -
[1] BAI Shengxi and LIU Chunhua. Overview of energy harvesting and emission reduction technologies in hybrid electric vehicles[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 147: 111188. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2021.111188 [2] LIU Lei, CHEN Chen, PEI Qingqi, et al. Vehicular edge computing and networking: A survey[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2021, 26(3): 1145–1168. doi: 10.1007/s11036-020-01624-1 [3] 马惠荣, 陈旭, 周知, 等. 绿色能源驱动的移动边缘计算动态任务卸载[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2020, 57(9): 1823–1838. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20200184MA Huirong, CHEN Xu, ZHOU Zhi, et al. Dynamic task offloading for mobile edge computing with green energy[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2020, 57(9): 1823–1838. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20200184 [4] SHI Jinming, DU Jun, WANG Jingjing, et al. Priority-aware task offloading in vehicular fog computing based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(12): 16067–16081. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3041929 [5] LIN Yan, ZHANG Yijin, LI Jun, et al. Popularity-aware online task offloading for heterogeneous vehicular edge computing using contextual clustering of bandits[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(7): 5422–5433. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3109003 [6] FUJIMOTO S, HOOF H, and MEGER D. Addressing function approximation error in actor-critic methods[C]. The 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 1587–1596. [7] WANG Haipeng, LV Tiejun, LIN Zhipeng, et al. Energy-delay minimization of task migration based on game theory in MEC-assisted vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(8): 8175–8188. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3175238 [8] LUO Quyuan, LI Changle, LUAN T H, et al. Collaborative data scheduling for vehicular edge computing via deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(10): 9637–9650. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2983660 [9] MIN Minghui, XIAO Liang, CHEN Ye, et al. Learning-based computation offloading for IoT devices with energy harvesting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(2): 1930–1941. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2890685 [10] MA Huirong, HUANG Peng, ZHOU Zhi, et al. GreenEdge: Joint green energy scheduling and dynamic task offloading in multi-tier edge computing systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(4): 4322–4335. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3147027 [11] LEE J and KO H. Neighbor-aware distributed task offloading algorithm in energy-harvesting internet of things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(10): 8744–8753. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3232710 [12] KAZMI S M A, DANG T N, YAQOOB I, et al. A novel contract theory-based incentive mechanism for cooperative task-offloading in electrical vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(7): 8380–8395. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3078913 [13] LIWANG Minghui, DAI Shijie, GAO Zhibin, et al. A truthful reverse-auction mechanism for computation offloading in cloud-enabled vehicular network[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(3): 4214–4227. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2875507 [14] 孙慧婷, 范艳芳, 马孟晓, 等. VEC中基于动态定价的车辆协同计算卸载方案[J]. 计算机科学, 2022, 49(9): 242–248. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210700166SUN Huiting, FAN Yanfang, MA Mengxiao, et al. Dynamic pricing-based vehicle collaborative computation offloading scheme in VEC[J]. Computer Science, 2022, 49(9): 242–248. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210700166 [15] XU Huiying, QIU Xiaoyu, ZHANG Weikun, et al. Privacy-preserving incentive mechanism for multi-leader multi-follower IoT-edge computing market: A reinforcement learning approach[J]. Journal of Systems Architecture, 2021, 114: 101932. doi: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2020.101932 -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
