Research on Multi-target Parameter Estimation Method for Overlapping-element Time Division Multiplexing MIMO Radar
-
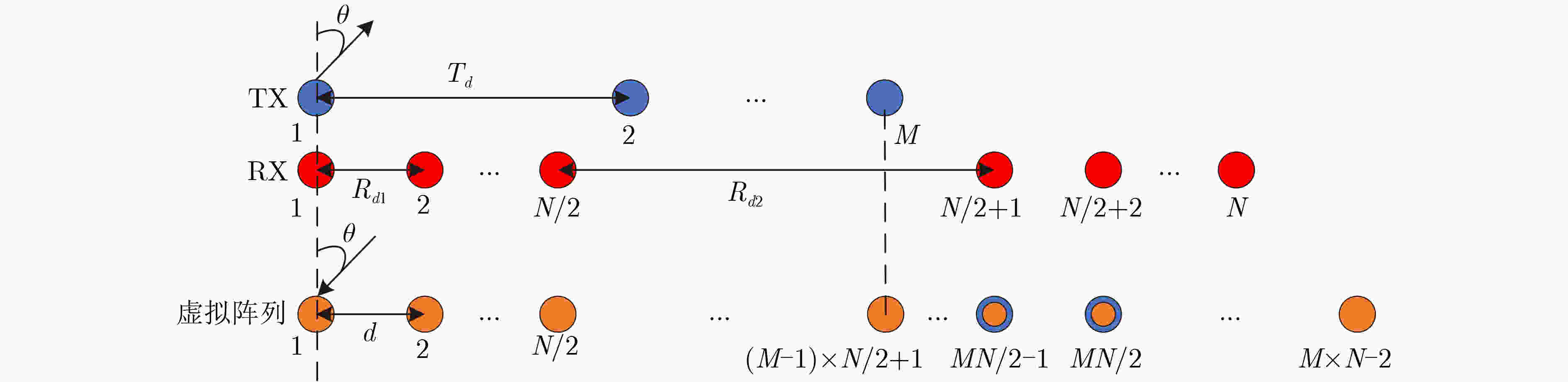
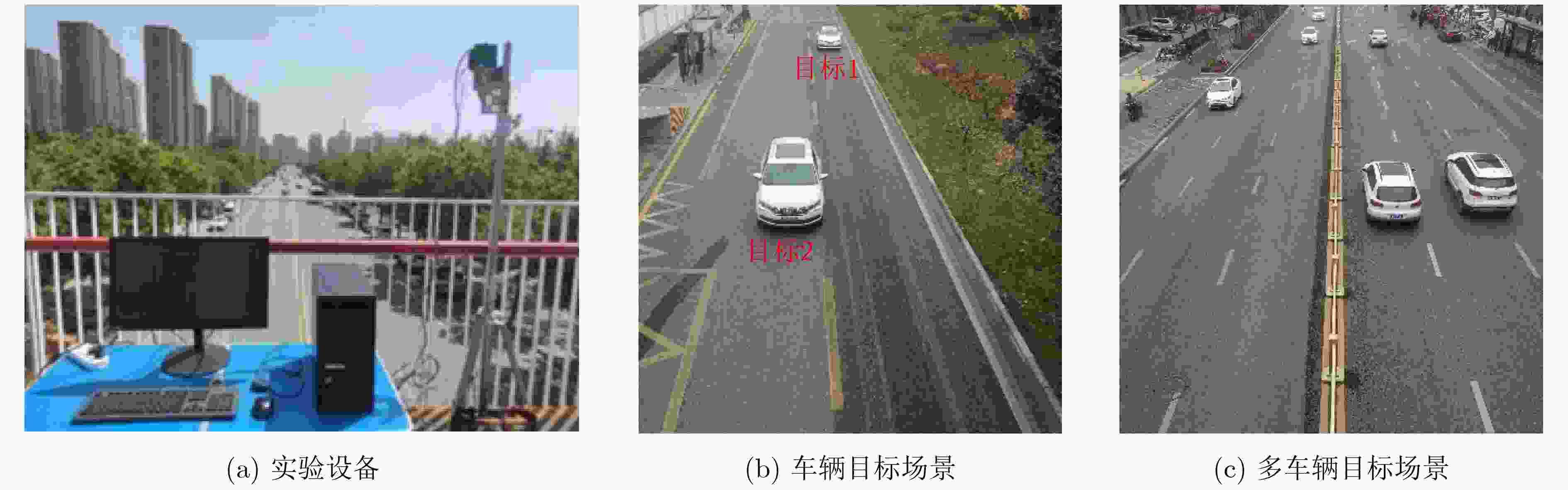
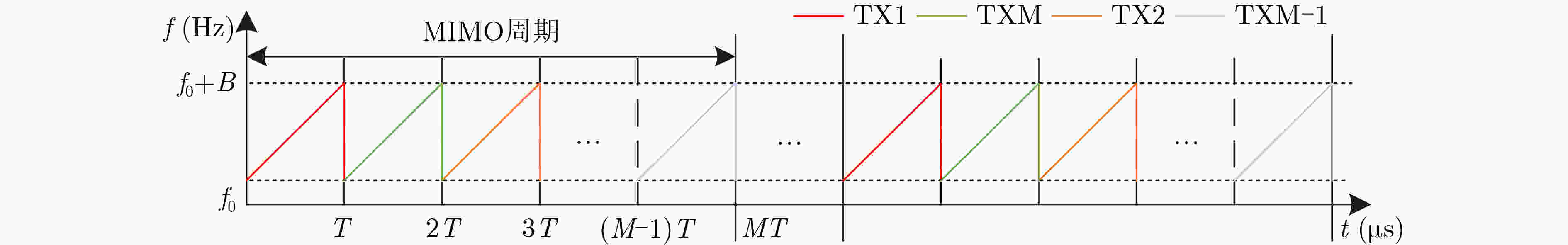
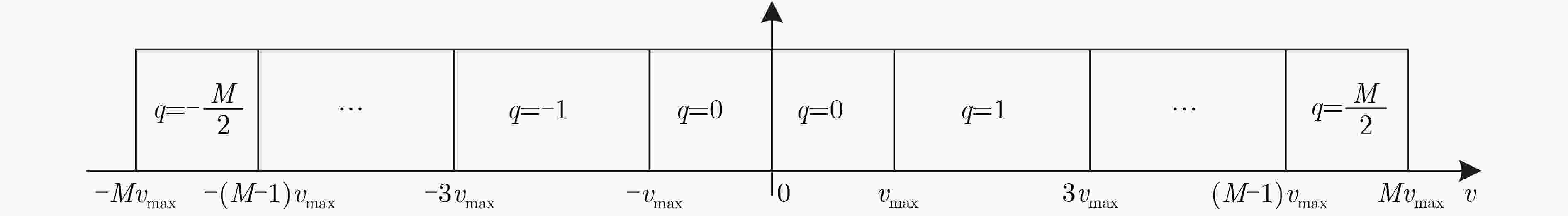
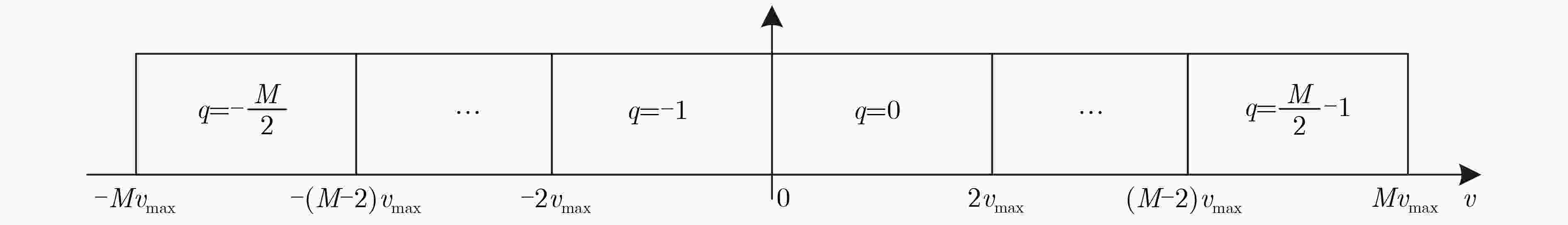
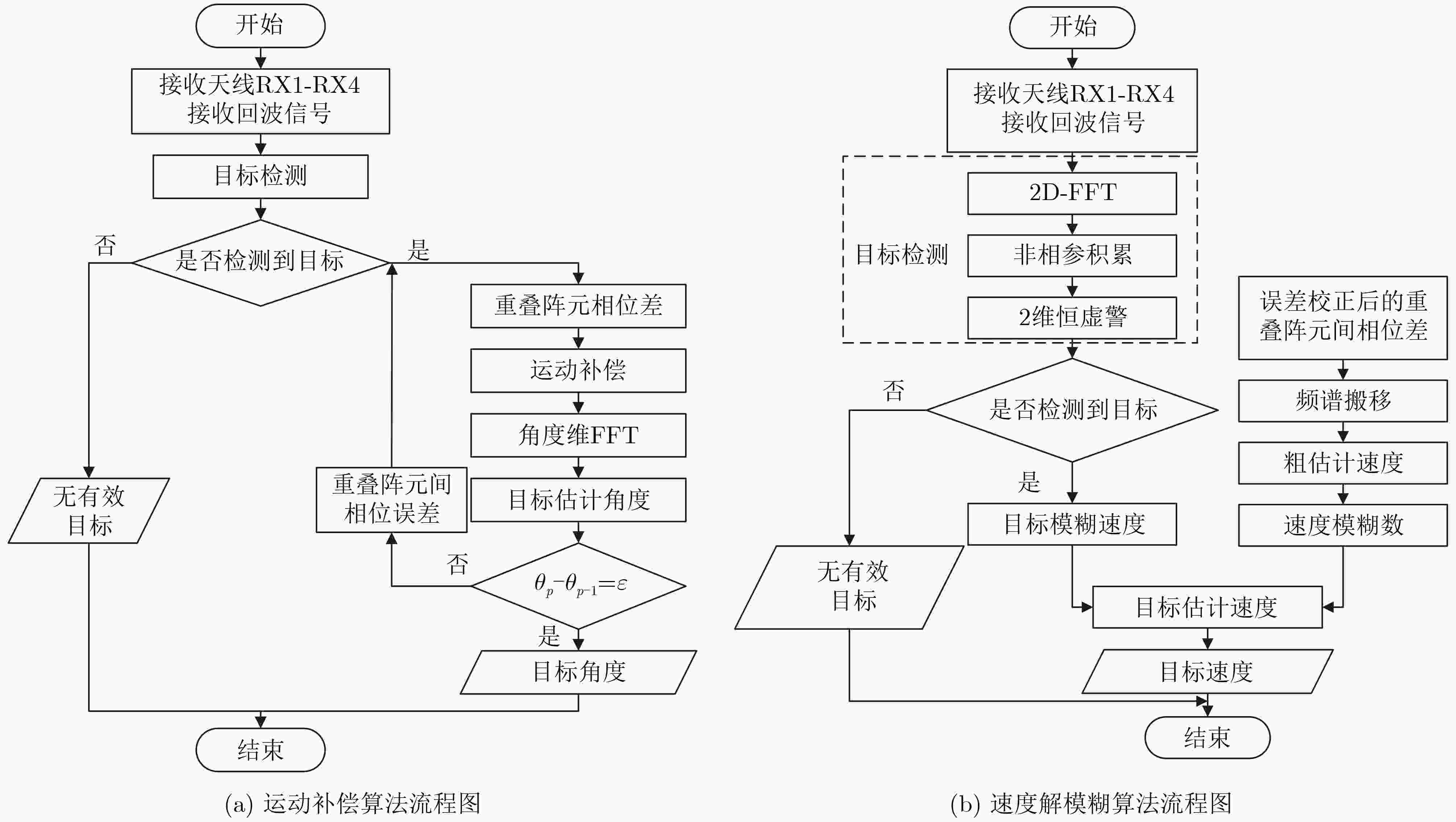
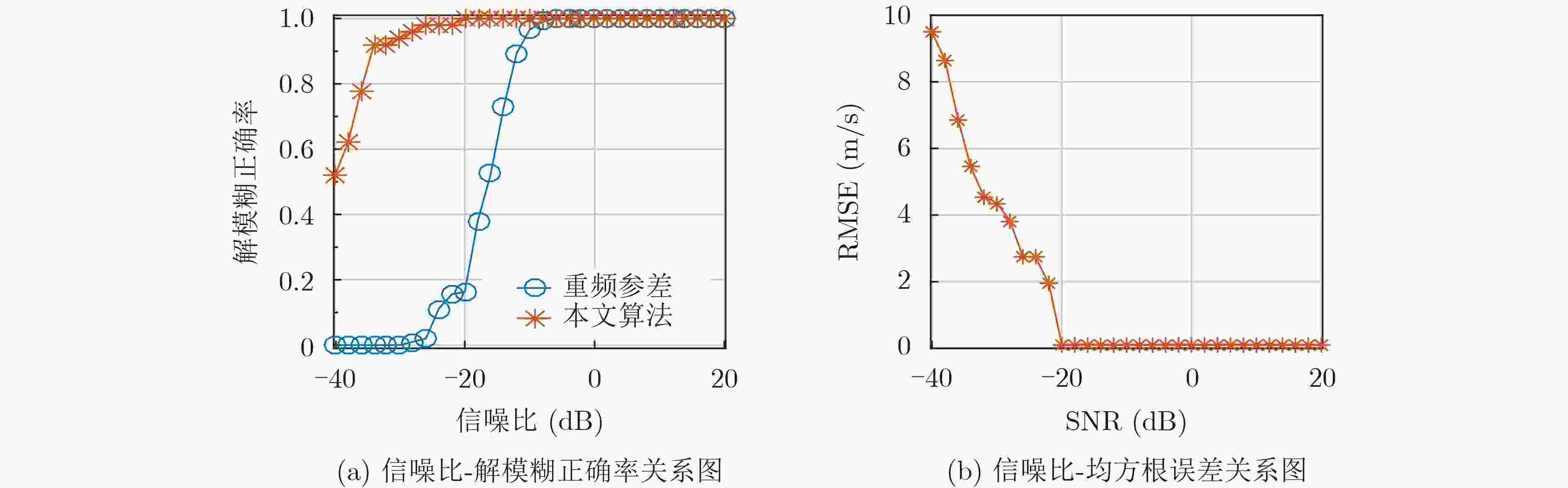
摘要: 针对多普勒-角度耦合和速度模糊问题,该文提出一种基于重叠阵元MIMO阵列的多目标参数估计方法。该方法基于虚拟孔径原理,在传统MIMO天线阵列中引入重叠阵元,构建重叠阵元MIMO天线阵列。通过在角度快速傅里叶变换(FFT)算法中引入循环迭代的方法估计阵列位置参数,利用重叠阵元回波信号的相位差值进行频率估计。同时,引入频谱搬移方法对速度区间进行转换,实现多目标的距离和速度估计。通过蒙特卡罗仿真实验,信噪比15 dB 的条件下,解模糊正确率为100%,速度误差为0.1 m/s,角度误差为0.1°。基于城市交通场景采集的车辆数据集进行测试,测试结果表明,该方法能够实现对车辆目标的速度和角度精确估计,可满足交通雷达对车辆信息监测的实时性和准确性需求。
-
关键词:
- 时分复用多输入多输出雷达 /
- 运动补偿 /
- 速度模糊 /
- 重叠阵元
Abstract: A multitarget parameter estimation method based on overlapping element MIMO arrays is presented for Doppler-angle coupling and velocity ambiguity. Based on the virtual aperture principle, overlapping elements are introduced into the traditional MIMO antenna array to construct the overlapping element MIMO antenna array. Array position parameters are estimated by introducing a cyclic iteration into the angular Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm, and the frequency is estimated by using the phase difference of the overlapping array element echo signals. The spectral shift method is introduced to convert the speed interval to achieve multi-objective distance and speed estimation. Under the Monte Carlo simulation with 15 dB signal-to-noise ratio, the blur resolution accuracy is 100%, the speed error is 0.1 m/s, and the angle error is 0.1 degree. Tests based on the self-collected data set of urban roads show that the method can accurately estimate the speed and angle of vehicle targets, and can meet the real-time and accuracy requirements of traffic radar for vehicle information monitoring. -
表 1 毫米波雷达参数
雷达参数 仿真数值 实测数值 载频${f_0}$(GHz) 60 60 调制周期$T$(μs) 45 45 调频带宽$B$(MHz) 200 200 慢时间维${N_d}$ 128 128 距离分辨率(${\rm{m}}$) 0.75 0.75 最大探测距离(${\rm{m}}$) 384 384 速度分辨率(${\rm{m}}/{\rm{s}}$) 0.108 0.108 最大不模糊速度(${\rm{m}}/{\rm{s}}$) ±20 ±20 角度分辨率(°) 2.7 2.7 表 2 模拟目标参数
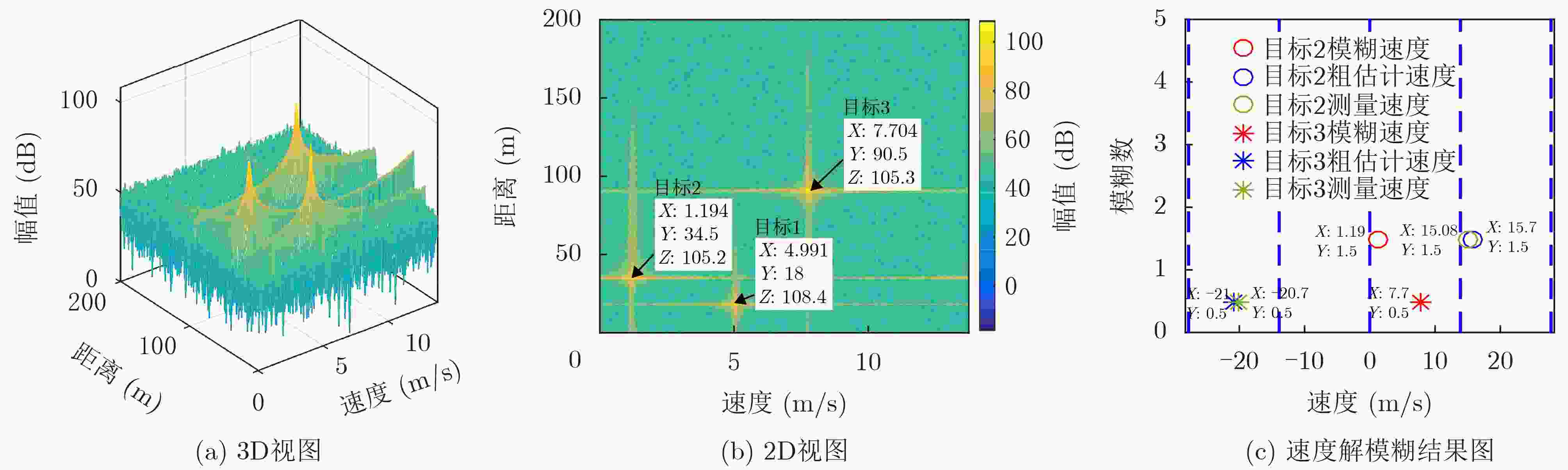
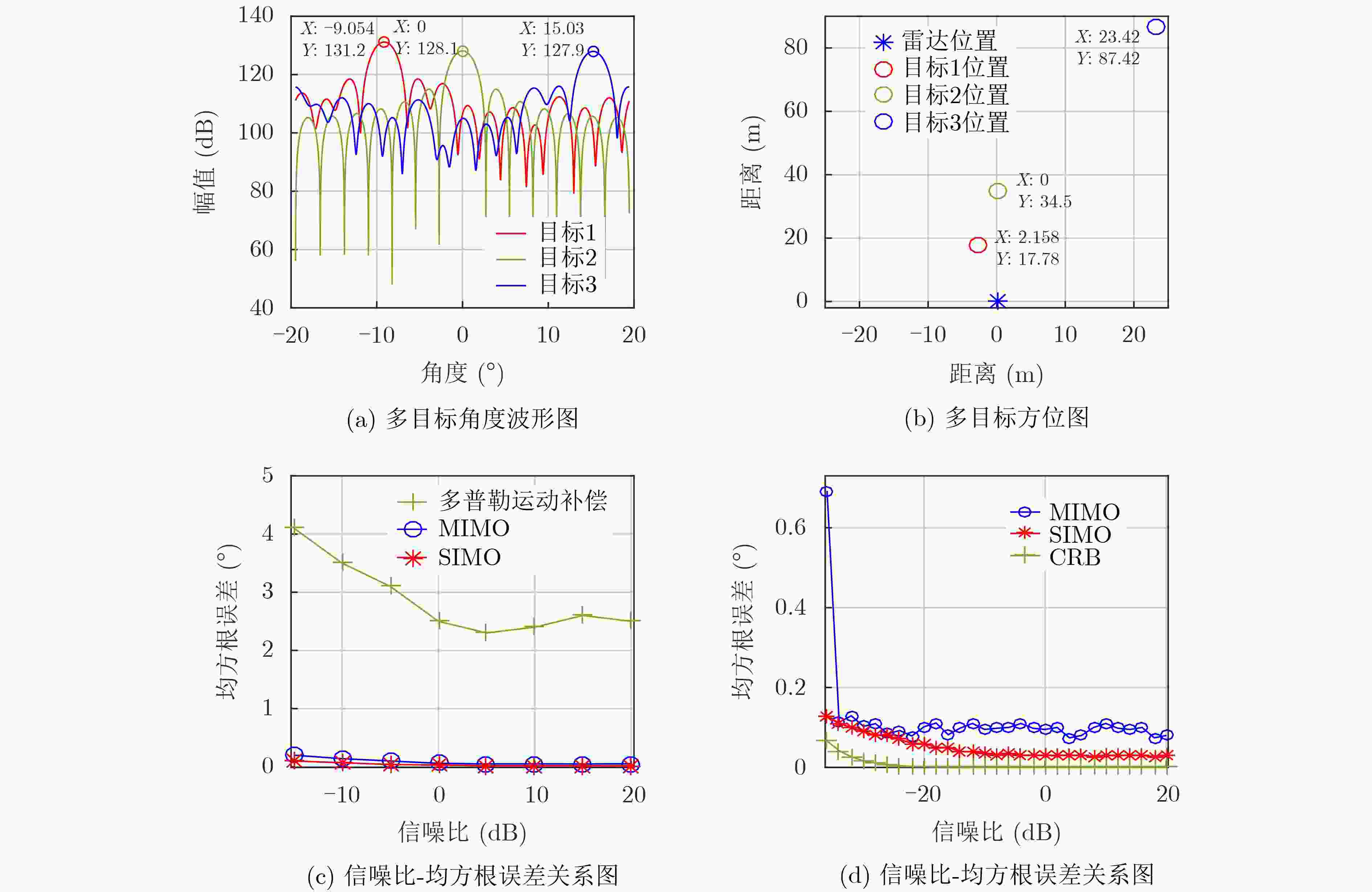
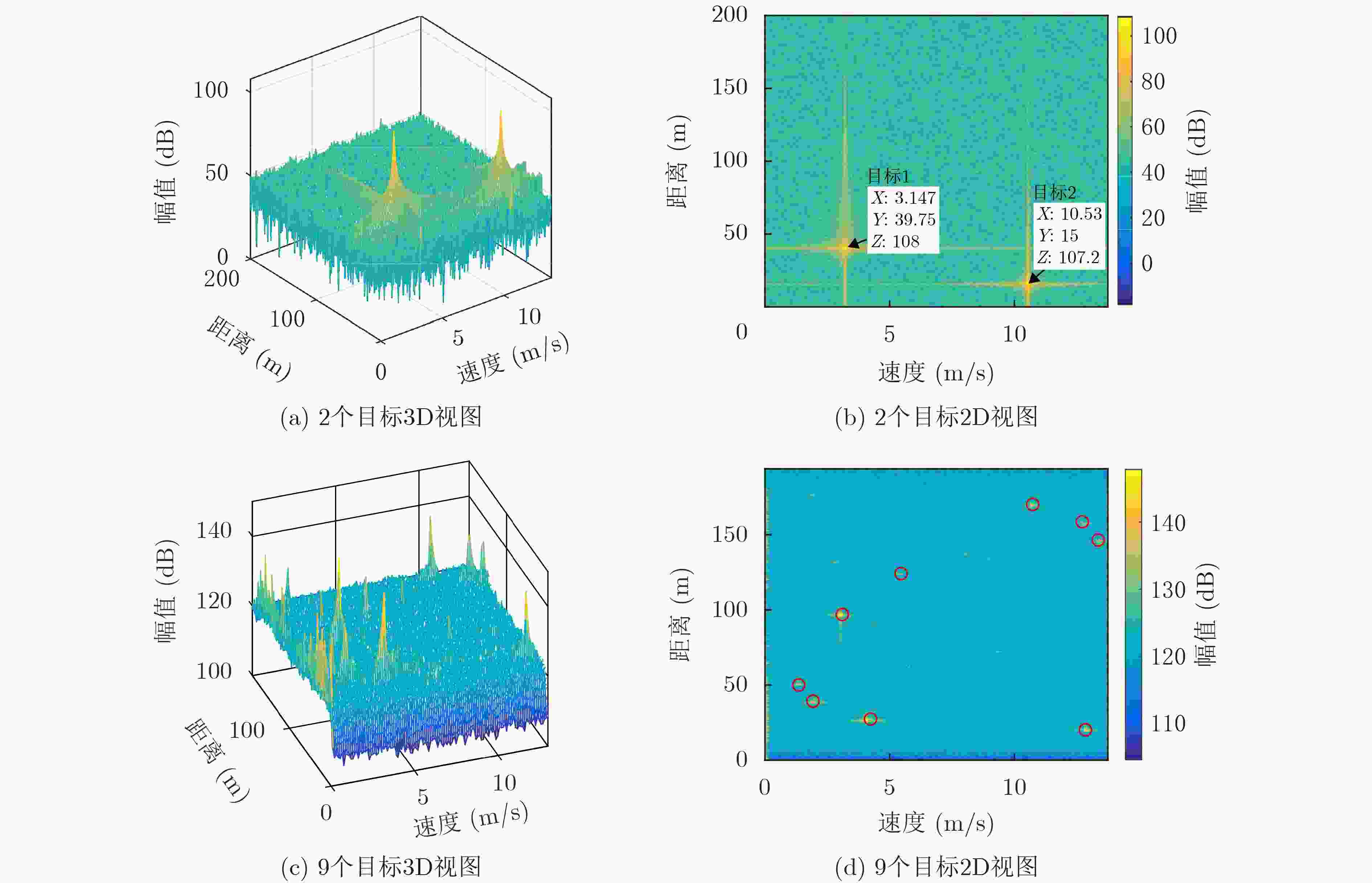
目标参数 目标距离(m) 目标速度(m/s) 目标角度(°) 目标1 18 5 –9 目标2 35 15 0 目标3 90 –20 15 表 3 多目标仿真结果
目标参数 距离测量值(m) 模糊速度(m/s) 模糊数 速度测量值(m/s) 角度测量值(°) 目标1 18.0 4.99 0 4.99 –9.05 目标2 34.5 1.19 1 15.08 0 目标3 90.5 7.70 –2 –20.07 15.03 表 4 目标参数
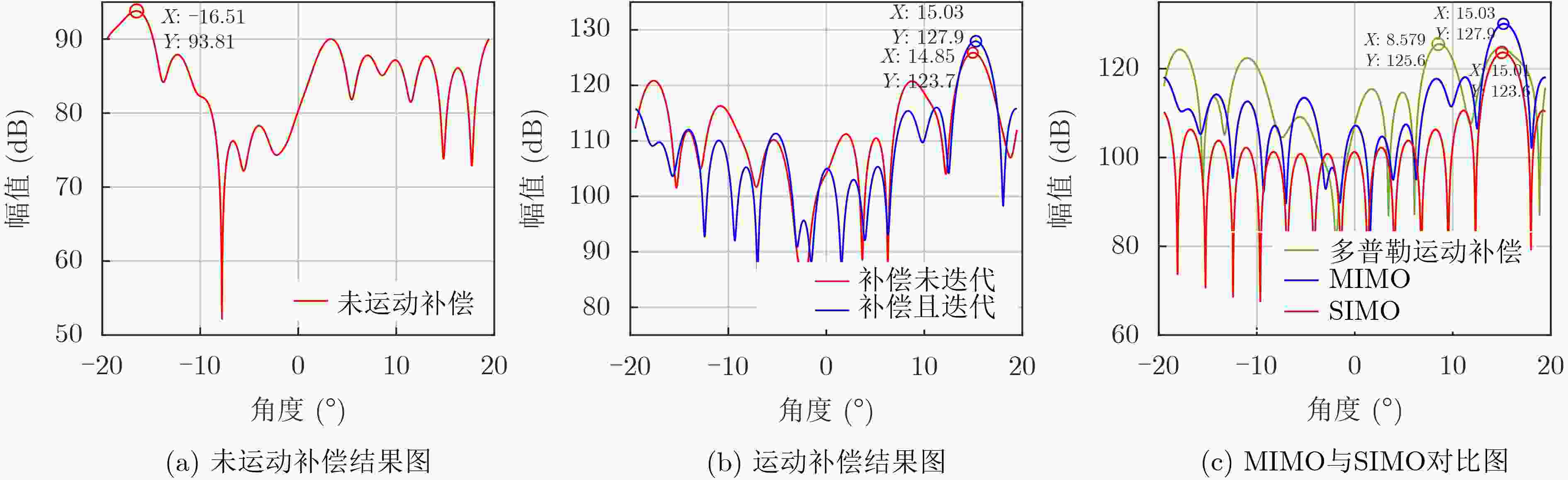
目标参数 目标1 目标2 真实距离(m) 40 15 真实速度(m/s) 17 10.5 真实角度(°) –1 –8 距离测量值(m) 39.75 15 模糊速度(m/s) 3.15 10.53 解得模糊数 1 0 速度测量值(m/s) 16.93 10.53 角度测量值(°) –0.85 –7.87 -
[1] SUN Shunqiao, PETROPULU A P, and POOR H V. MIMO radar for advanced driver-assistance systems and autonomous driving: Advantages and challenges[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2020, 37(4): 98–117. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2020.2978507 [2] ROOS F, BECHTER J, KNILL C, et al. Radar sensors for autonomous driving: Modulation schemes and interference mitigation[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2019, 20(9): 58–72. doi: 10.1109/MMM.2019.2922120 [3] WALDSCHMIDT C, HASCH J, and MENZEL W. Automotive radar — from first efforts to future systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Microwaves, 2021, 1(1): 135–148. doi: 10.1109/JMW.2020.3033616 [4] HU Xueyao, LU Man, LI Yang, et al. Motion compensation for TDM MIMO radar by sparse reconstruction[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(24): 1604–1606. doi: 10.1049/el.2017.3524 [5] BECHTER J, ROOS F, and WALDSCHMIDT C. Compensation of motion-induced phase errors in TDM MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2017, 27(12): 1164–1166. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2017.2751301 [6] LIN Yi, SUN Zhanshan, GUO Min, et al. Phase compensation method based on reference-element for SAA FMCW radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(12): 2097–2101. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3014363 [7] HU Xueyao, LI Yand, LU Man, et al. A multi-carrier-frequency random-transmission chirp sequence for TDM MIMO automotive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 3672–3685. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2900357 [8] HÄFNER S and THOMÄ R. Compensation of motion-induced phase errors and enhancement of Doppler unambiguity in TDM-MIMO systems by model-based estimation[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2020, 4(10): 7003504. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2020.3020700 [9] NEEMAT S, KRASNOV O, VAN DER ZWAN F, et al. Decoupling the Doppler ambiguity interval from the maximum operational range and range-resolution in FMCW radars[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(11): 5992–6003. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2972152 [10] JUNG J, LIM S, KIM S C, et al. Solving Doppler-angle ambiguity of BPSK-MIMO FMCW radar system[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 120347–120357. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3108783 [11] NGUYEN M Q, FEGER R, BECHTER J, et al. Fast-chirp FDMA MIMO radar system using range-division multiple-access and Doppler-division multiple-access[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(1): 1136–1148. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2020.3039795 [12] 王元恺, 肖泽龙, 许建中, 等. 一种改进的FMCW雷达线性调频序列波形[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(6): 1288–1293. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.06.002WANG Yuankai, XIAO Zelong, XU Jianzhong, et al. A modified chirp sequence waveform for FMCW radar[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(6): 1288–1293. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.06.002 [13] 周奇特, 李朝晖. 组合时延估计及人工时延方法用于脉冲相干多普勒测速去模糊[J]. 声学学报, 2018, 43(4): 582–591. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2018.04.018ZHOU Qite and LI Chaohui. An dealiasing method for pulse-to-pulse coherent Doppler velocimetry using combining time delay estimation and artificial delay[J]. Acta Acustica, 2018, 43(4): 582–591. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2018.04.018 [14] XU Luzhou, LIEN J, and LI Jian. Doppler-range processing for enhanced high-speed moving target detection using LFMCW automotive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(1): 568–580. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3101768 [15] SCHERHÄUFL M, HAMMER F, PICHLER-SCHEDER M, et al. Radar distance measurement with Viterbi algorithm to resolve phase ambiguity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2020, 68(9): 3784–3793. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2020.2985357 [16] GONZALEZ H A, LIU Chen, VOGGINGER B, et al. Doppler disambiguation in MIMO FMCW radars with binary phase modulation[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2021, 15(8): 884–901. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12063 [17] BARAL A B and TORLAK M. Joint Doppler frequency and direction of arrival estimation for TDM MIMO automotive radars[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(4): 980–995. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3073572 [18] XIONG Xiangyu, LIU Hui, DENG Zhenmiao, et al. Micro-Doppler ambiguity resolution with variable shrinkage ratio based on time-delayed cross correlation processing for wideband radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(4): 1906–1917. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2870149 [19] 王超, 王岩飞, 王琦, 等. 基于回波序列最小二乘拟合的高分辨率SAR运动目标速度估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1055–1062. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180695WANG Chao, WANG Yanfei, WANG Qi, et al. Velocity estimation of moving targets based on least square fitting of high-resolution SAR echo sequences[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1055–1062. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180695 [20] SUN Peilin, Tang Jun, and WAN Shuang. Cramer-Rao bound of joint estimation of target location and velocity for coherent MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 25(4): 566–572. doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2014.00066 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
