Opportunistic Routing in Underwater Acoustic Networks Fusing Depth Adjustment and Adaptive Forwarding
-
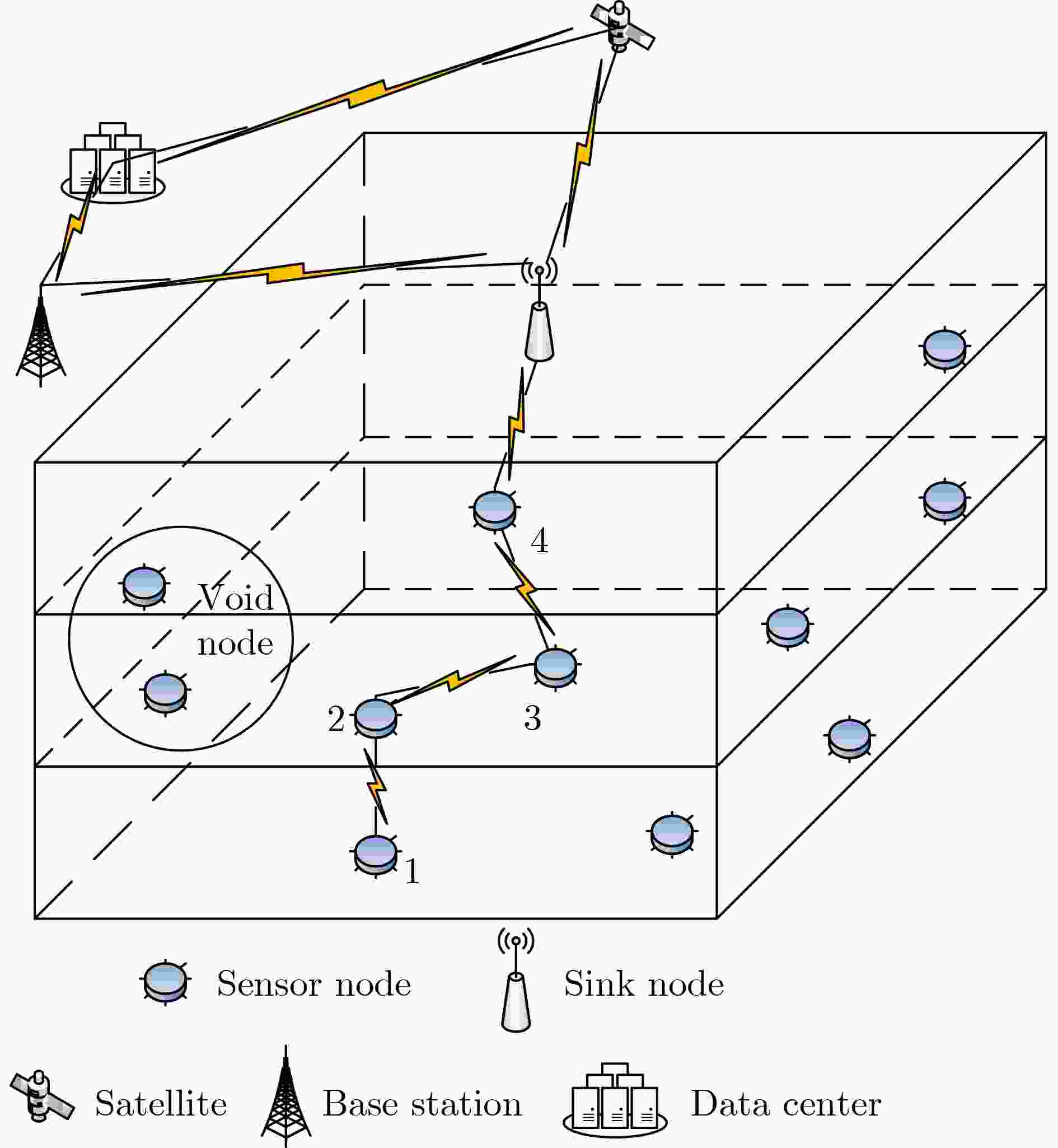
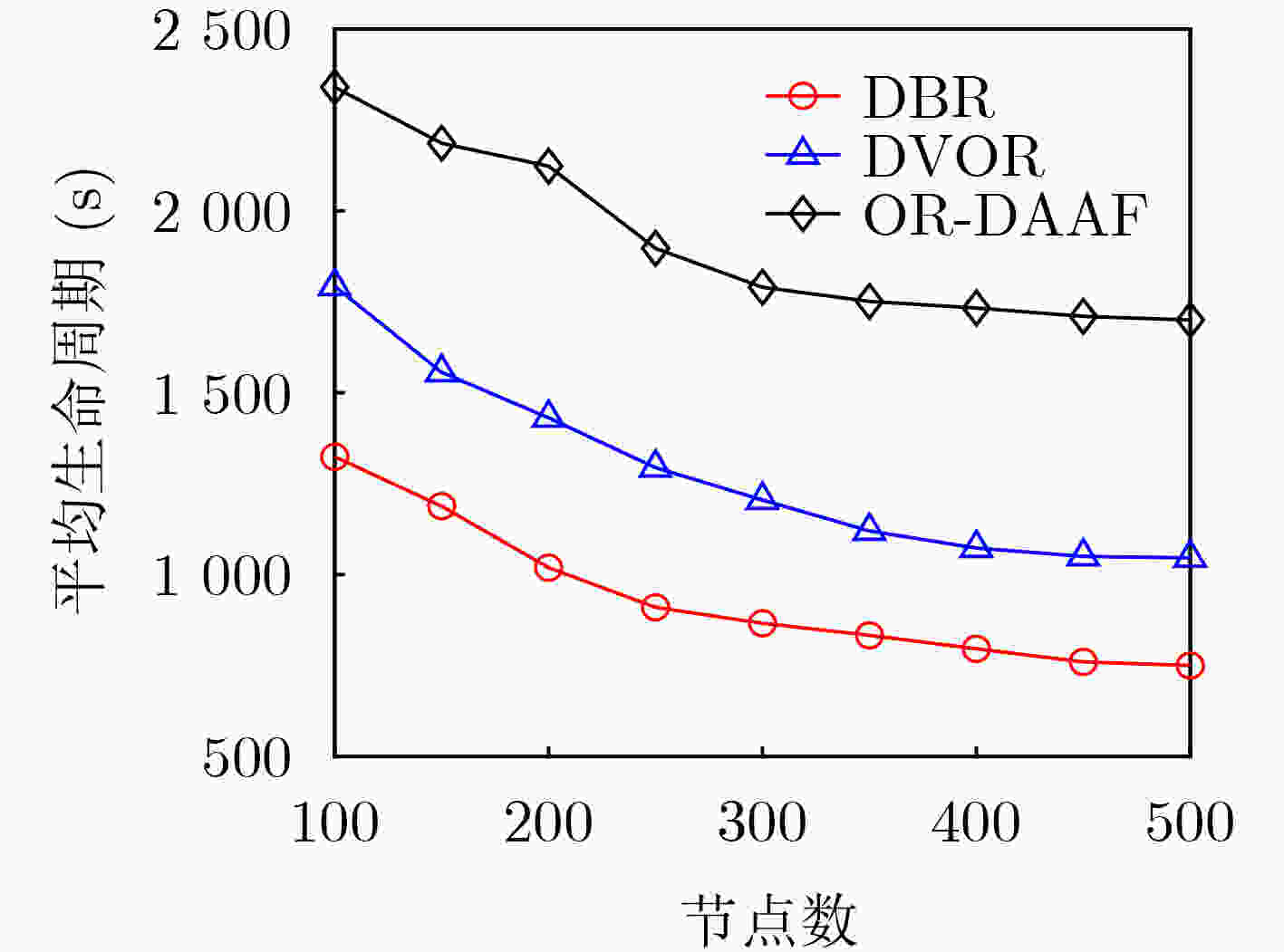
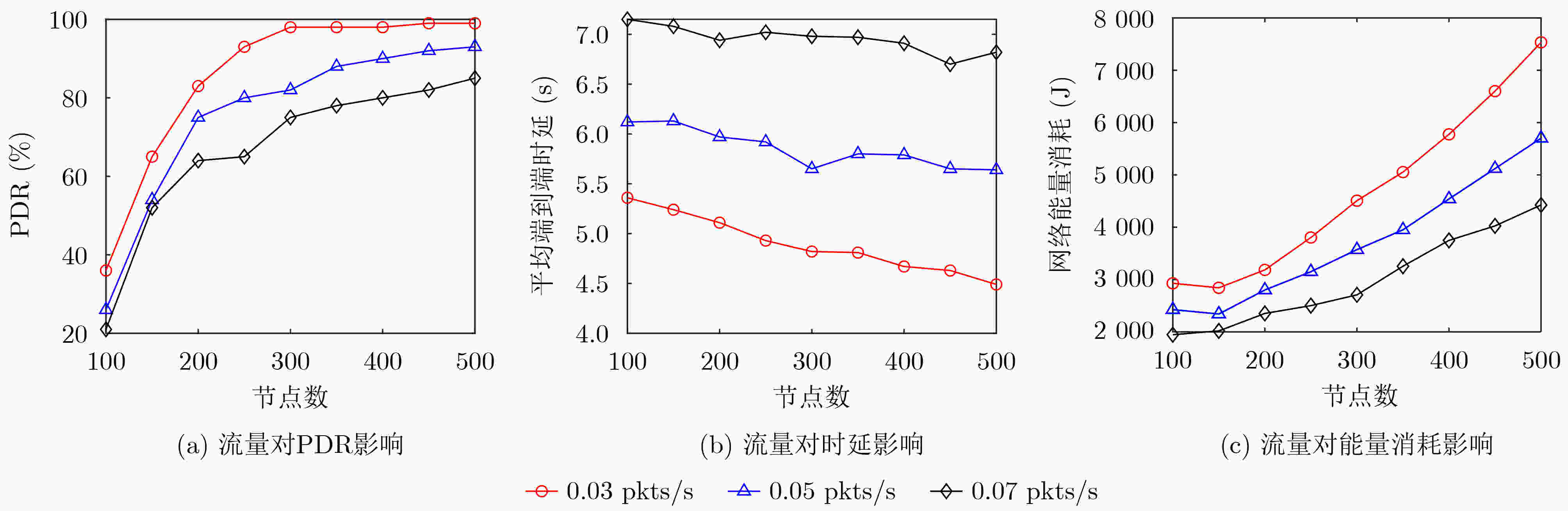
摘要: 针对水声传感器网络路由过程中的空洞问题和数据传输中能效低下的问题,该文提出了融合深度调整和自适应转发的水声网络机会路由(OR-DAAF)。针对路由空洞,区别于传统绕路策略,OR-DAAF提出一种基于拓扑控制的空洞恢复模式算法—利用剩余能量对空洞节点分级,先后调整空洞节点到新的深度以克服路由空洞,恢复网络联通。针对数据传输中的能效低下问题,OR-DAAF提出了转发区域划分机制,通过转发区域的选择自适应转发面积以抑制冗余包,并提出基于加权推进距离,能量和链路质量的多跳多目标路由决策指标,综合考虑区域能量,链路质量和推进距离实现能效平衡。实验数据表明,相比DVOR协议,OR-DAAF的包投递率和生命周期分别提高10%和48.7%,端到端时延减少22%。Abstract: Considering voids in the routing process of underwater acoustic sensor networks and low energy efficiency in data transmission, An Opportunistic Routing fusing Depth Adjustment and Adaptive Forwarding (OR-DAAF) technique is developed. Aiming at routing voids, instead of adopting the traditional detour strategy, OR-DAAF proposes a topology control-based void recovery mode algorithm, which uses the residual energy to grade void nodes and successively adjusts them to the new depth to overcome routing voids and restore network connectivity. Aiming at low energy efficiency in data transmission, OR-DAAF proposes a forwarding area division mechanism that selects the forwarding area to suppress redundant packets. It also puts forward a multi-hop and multi-objective routing decision index based on weighted advance distance, energy and link quality, comprehensively considering regional energy, link quality and advance distance to achieve an energy efficiency balance. Experimental results show that compared with a Doppler VHF omnidirectional range, OR-DAAF improves packet delivery rate by 10% and network lifetime by 48.7%, respectively and reduces delay by 22%.
-
表 1 符号集
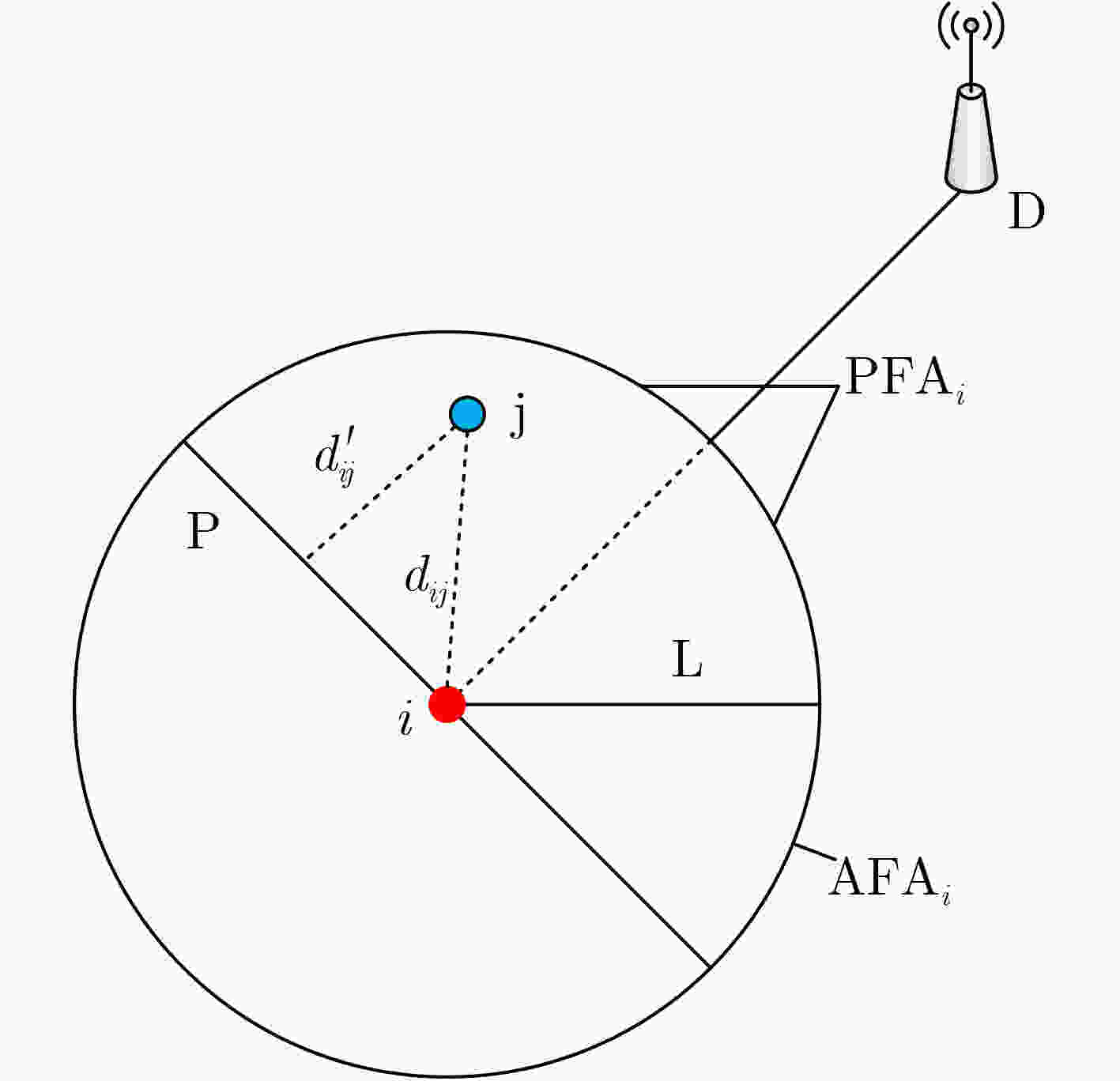
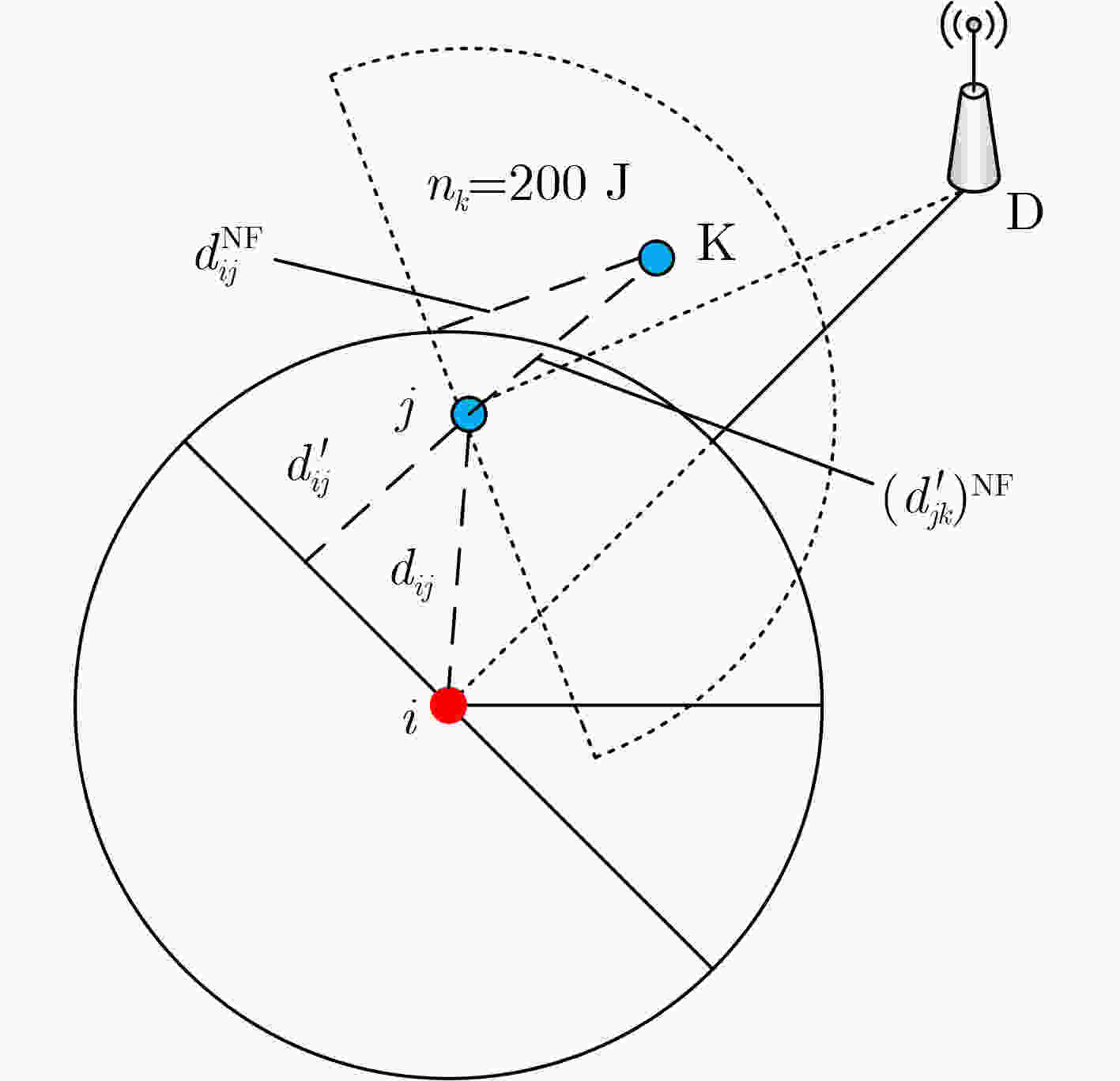
符号 含义 ${n_i}$ 第i个节点 $ {\text{PF}}{{\text{A}}_i} $, $ {\text{AF}}{{\text{A}}_i} $ ni的主、辅助转发区域 ${\text{N}}{{\text{e}}_i}$, ${\text{Nsn}}{{\text{r}}_i}$ ni的能量、信噪比候选集 ${\text{Npf}}{{\text{a}}_i}$, ${\text{Naf}}{{\text{a}}_i}$ ni的主、辅助转发候选集 $G({n_i})$, $E({n_i})$ ni的邻居数、剩余能量 $\varOmega , \;\varPhi$ ni的两跳邻居集、深度集 $E{{\text{(}}{n_i}{\text{)}}^{{\text{NF}}}}$ ni的邻居集能量 $ {\text{TF}}{{\text{A}}_i} $ ni的综合转发区域 $d_{ {{jk} } }^{ {\text{NF} } }$ nj的所有邻居节点nk到nj的距离 ${(d'_{ {{jk} } })^{ {\text{NF} } } }$ nj的所有邻居节点nk到平面P的距离 算法1: 构建候选集 1: for each node ${n_j} \in {N_i}(t)$ 2: if ${n_j} \in {\text{PF}}{{\text{A}}_i}$ 3: then add ${n_j} \to {\text{Npf}}{{\text{a}}_i}$
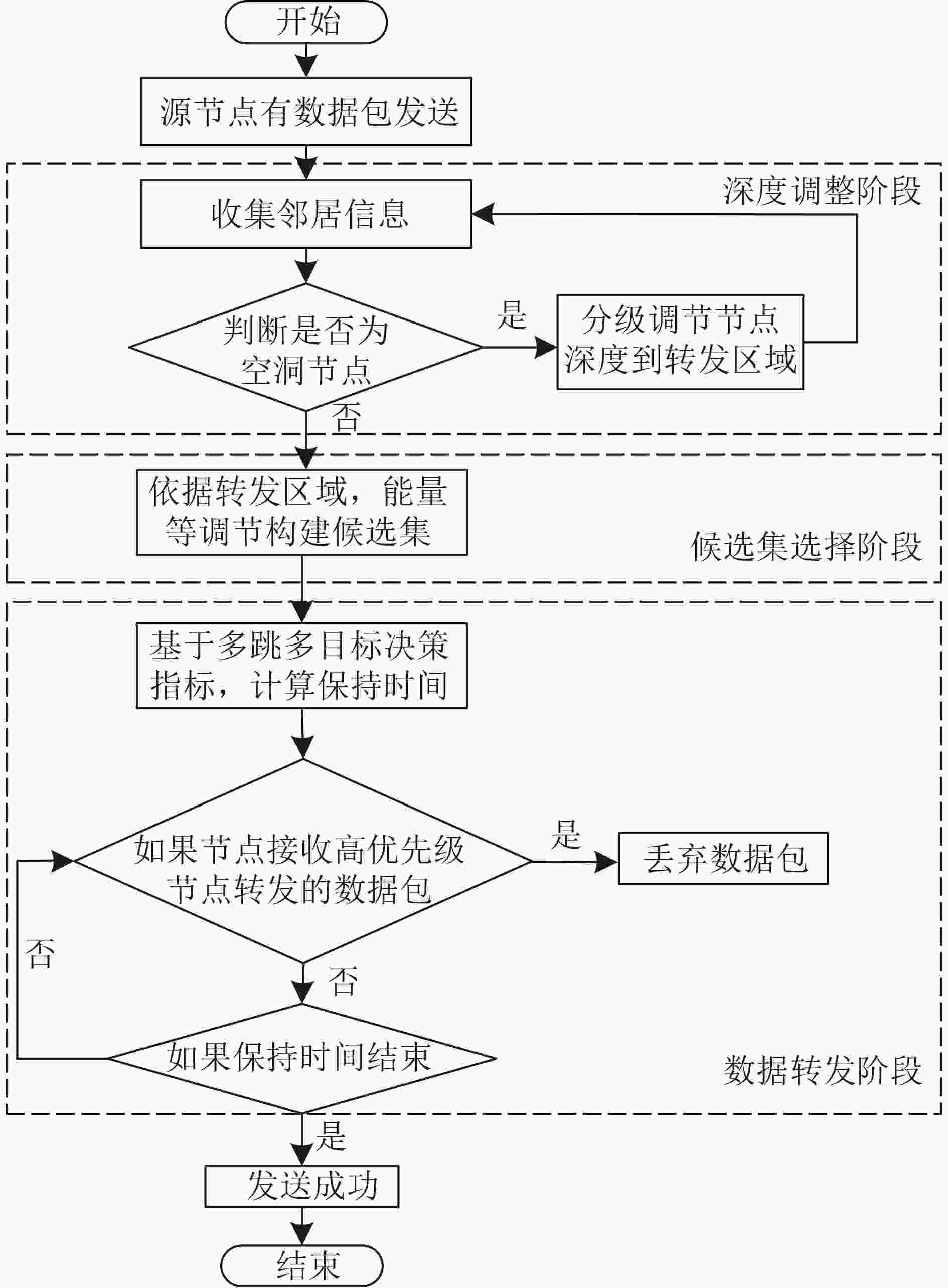
4: if $E({n_j}) \ge \displaystyle\sum\limits_k {E({n_k})/2G({n_i})}$5: then add $n_{j} \rightarrow {\rm{N} }e_{i}$ 6: if ${\text{SNR} }({n_i},{n_j}) \ge \displaystyle\sum\limits_k { {\text{SNR} }({n_i},{n_k})/2{{G} }({n_i})}$ 7: then add $n_{j} \rightarrow {\rm{Nsnr} }_{i}$ 8: if $[{n_j} \in {\text{Npf} }{ {\text{a} }_i}] \vee [{n_j} \in {\text{N} }{ {{e} }_i}] \vee [{n_j} \in {\text{Nsn} }{ {\text{r} }_i}]$ 9: then add $ n_{j} \rightarrow C(i) $ 10: end for 11: if $C(i) = \varnothing $ the forwarding area is $ {\text{PF}}{{\text{A}}_i} $ 12: then replace $ {\text{PF}}{{\text{A}}_i} $ to $ {\text{TF}}{{\text{A}}_i} $ 13: and switch to Algorithm 1 again 14: else if $C(i) = \varnothing $ the forwarding area is $ {\text{TF}}{{\text{A}}_i} $ 15: switch to the Algorithm 2 算法 2: 空洞恢复算法 1: if $|\varOmega| > 0$ 2: for $n_{k} \in \varOmega$ 3: if $ E(n)<0.5 E_{\text {mat }} $ 4: then wait $ 2R/{v_0} $ and switch to Algorithm 2 5: else if
$ \left\{\begin{array}{c}\left(x_{D}-x_{i}\right)\left(x_{k}-x_{i}\right)+\left(y_{D}-y_{i}\right)\left(y_{k}-y_{i}\right) \\+\left(z_{D}-z_{i}^{*}\right)\left(z_{k}-z_{i}^{*}\right)>0 \\0<\sqrt{\left(x_{k}-x_{i}\right)^{2}+\left(y_{k}-y_{i}\right)^{2}+\left(z_{k}-z_{i}^{*}\right)^{2}} \\\leq R\end{array}\right\} $6: then $z_{i}^{*} \rightarrow \varPhi$ 7: end if 8: end for 9: $\hat z = \arg {\min _{\forall z_i^* \in \varPhi } }\{ |z_i^* - {z_i}|\}$ 表 2 实验参数设置
参数 取值 通信范围 1.5 km 发送功率 2 W 接收功率 0.75 W 待机功率 0.008 W 深度移动能耗 1.2 J/m 数据包大小 100 Byte -
[1] SHEN Zhongwei, YIN Hongxi, JING Lianyou, et al. A cooperative routing protocol based on Q-learning for underwater optical-acoustic hybrid wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(1): 1041–1050. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3128594 [2] 黄沛烁, 王易因, 关新平, 等. 面向水声传感网的自主水下航行器辅助定位动态路径规划[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(6): 1927–1936. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211432HUANG Peishuo, WANG Yiyin, GUAN Xinping, et al. Dynamic path planning for autonomous underwater vehicle assisted localization of underwater acoustic aensor networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(6): 1927–1936. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211432 [3] WANG Qingwen, LI Jianghui, QI Qian, et al. An adaptive-location-based routing protocol for 3-D underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(8): 6853–6864. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3034880 [4] HAO Kun, DING Yuying, LI Cheng, et al. An energy-efficient routing void repair method based on an autonomous underwater vehicle for UWSNs[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(4): 5502–5511. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3030019 [5] STOJANOVIC M and PREISIG J. Underwater acoustic communication channels: Propagation models and statistical characterization[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2009, 47(1): 84–89. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2009.4752682 [6] SU Yishan, GUO Lei, JIN Zhigang, et al. A voronoi-based optimized depth adjustment deployment scheme for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(22): 13849–13860. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3005685 [7] NOH Y, LEE U, WANG P, et al. VAPR: Void-aware pressure routing for underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2013, 12(5): 895–908. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2012.53 [8] GUAN Quansheng, JI Fei, LIU Yun, et al. Distance-vector-based opportunistic routing for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 3831–3839. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2891910 [9] WANG Zhuo, HAN Guangjie, QIN Hongde, et al. An energy-aware and void-avoidable routing protocol for underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 7792–7801. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2805804 [10] COUTINHO R W L, BOUKERCHE A, VIEIRA L F M, et al. Design guidelines for opportunistic routing in underwater networks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2016, 54(2): 40–48. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2016.7402259 [11] YAN Hai, SHI Z J, and CUI J H. DBR: Depth-based routing for underwater sensor networks[C]. Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Research in Networking, Singapore, 2008: 72–86. [12] XIE Peng, CUI Junhong, and LAO Li. VBF: Vector-based forwarding protocol for underwater sensor networks[C]. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Research in Networking, Coimbra, Portugal, 2006: 1216–1221. [13] NICOLAOU N, SEE A, XIE P, et al. Improving the robustness of location-based routing for underwater sensor networks[C]. Proceedings of the Oceans 2007-Europe, Aberdeen, UK, 2007: 1–6. [14] COUTINHO R W L, BOUKERCHE A, VIEIRA L F M, et al. Geographic and opportunistic routing for underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2016, 65(2): 548–561. doi: 10.1109/TC.2015.2423677 [15] JAFFE J and SCHURGERS C. Sensor networks of freely drifting autonomous underwater explorers[C]. Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Underwater Networks, Los Angeles, USA, 2006: 93–96. [16] JIN Zhigang, DUAN Chenxu, YANG Qiuling, et al. Q-learning-Based Opportunistic Routing with an on-site architecture in UASNs[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2021, 119: 102553. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2021.102553 [17] HU Tiansi and FEI Yunsi. QELAR: A machine-learning-based adaptive routing protocol for energy-efficient and lifetime-extended underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2010, 9(6): 796–809. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2010.28 [18] YU Haitao, YAO Nianmin, WANG Tong, et al. WDFAD-DBR: Weighting depth and forwarding area division DBR routing protocol for UASNs[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2016, 37: 256–282. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2015.08.023 [19] BOUKERCHE A and DAREHSHOORZADEH A. Opportunistic routing in wireless networks: Models, algorithms, and classifications[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2014, 47(2): 22. doi: 10.1145/2635675 [20] ZHANG Ying, ZHANG Zheming, CHEN Lei, et al. Reinforcement learning-based opportunistic routing protocol for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(3): 2756–2770. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3058282 -





 下载:
下载:
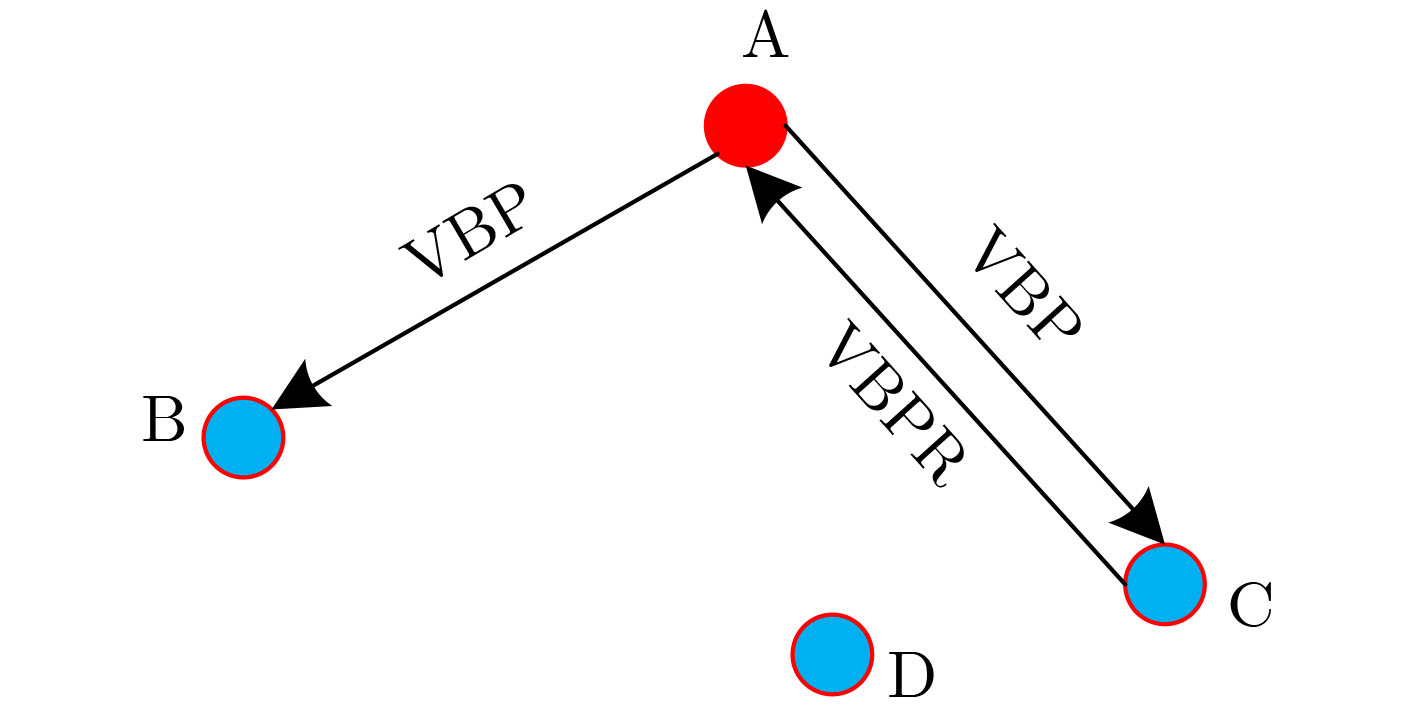
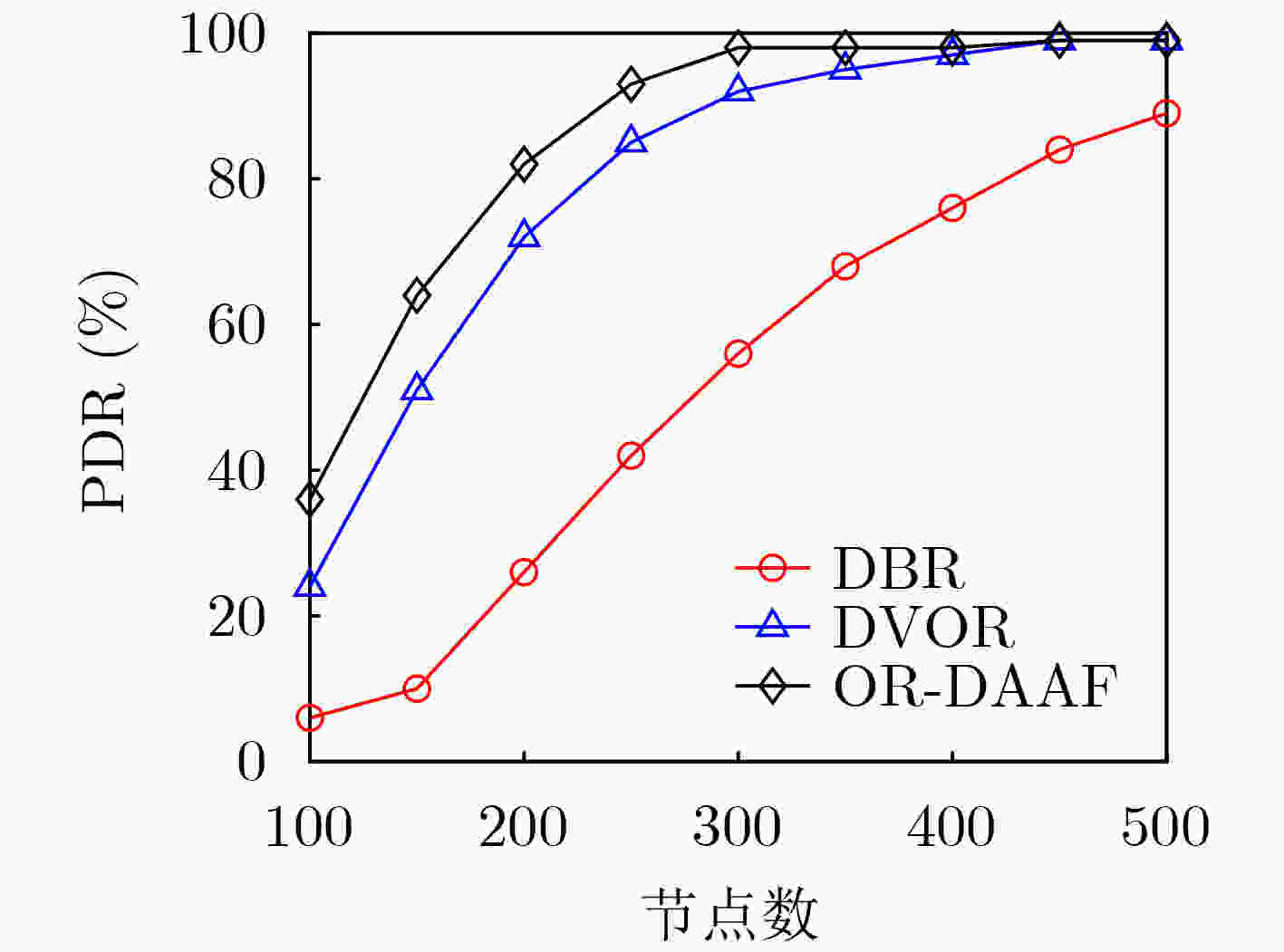
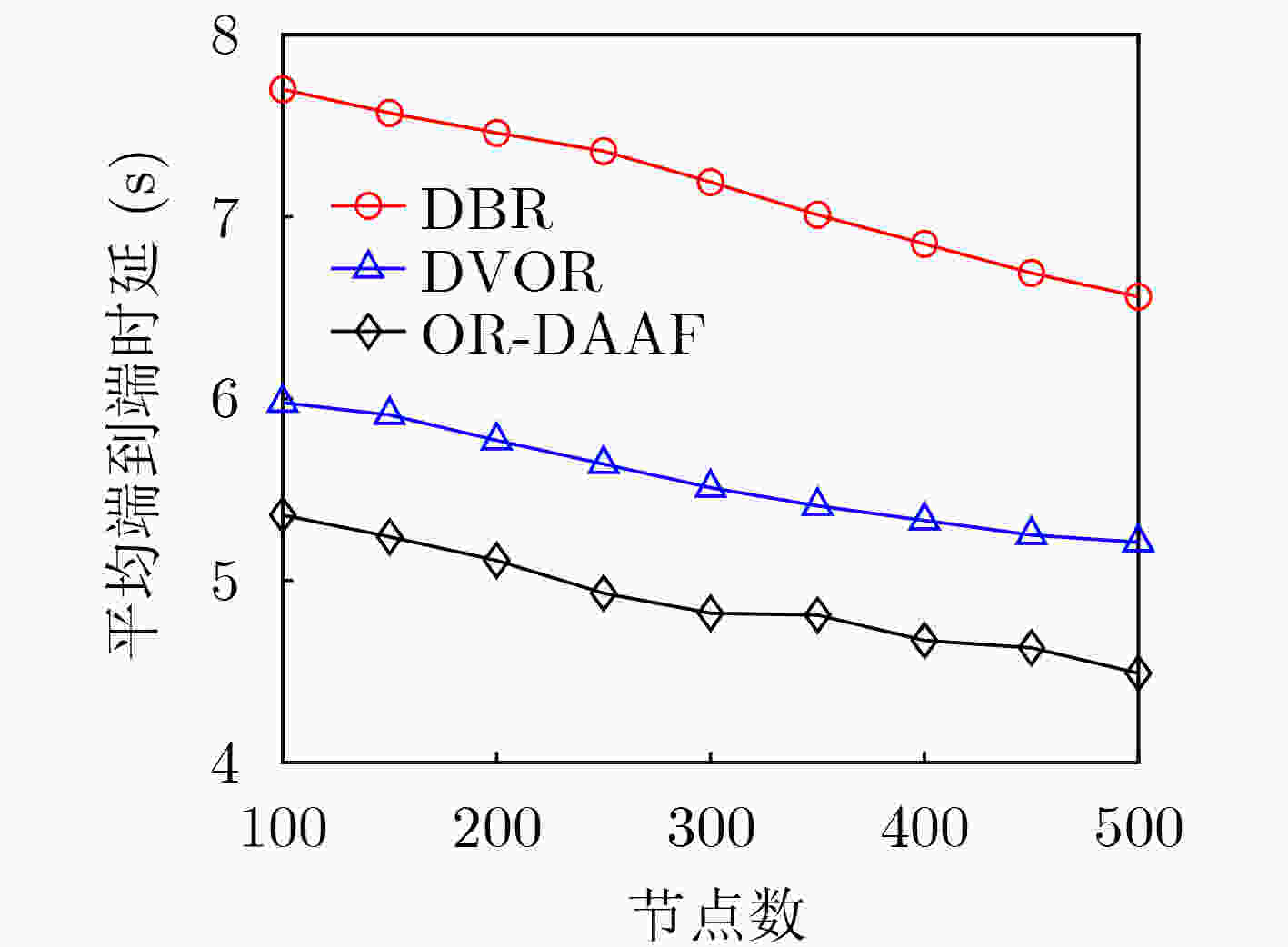
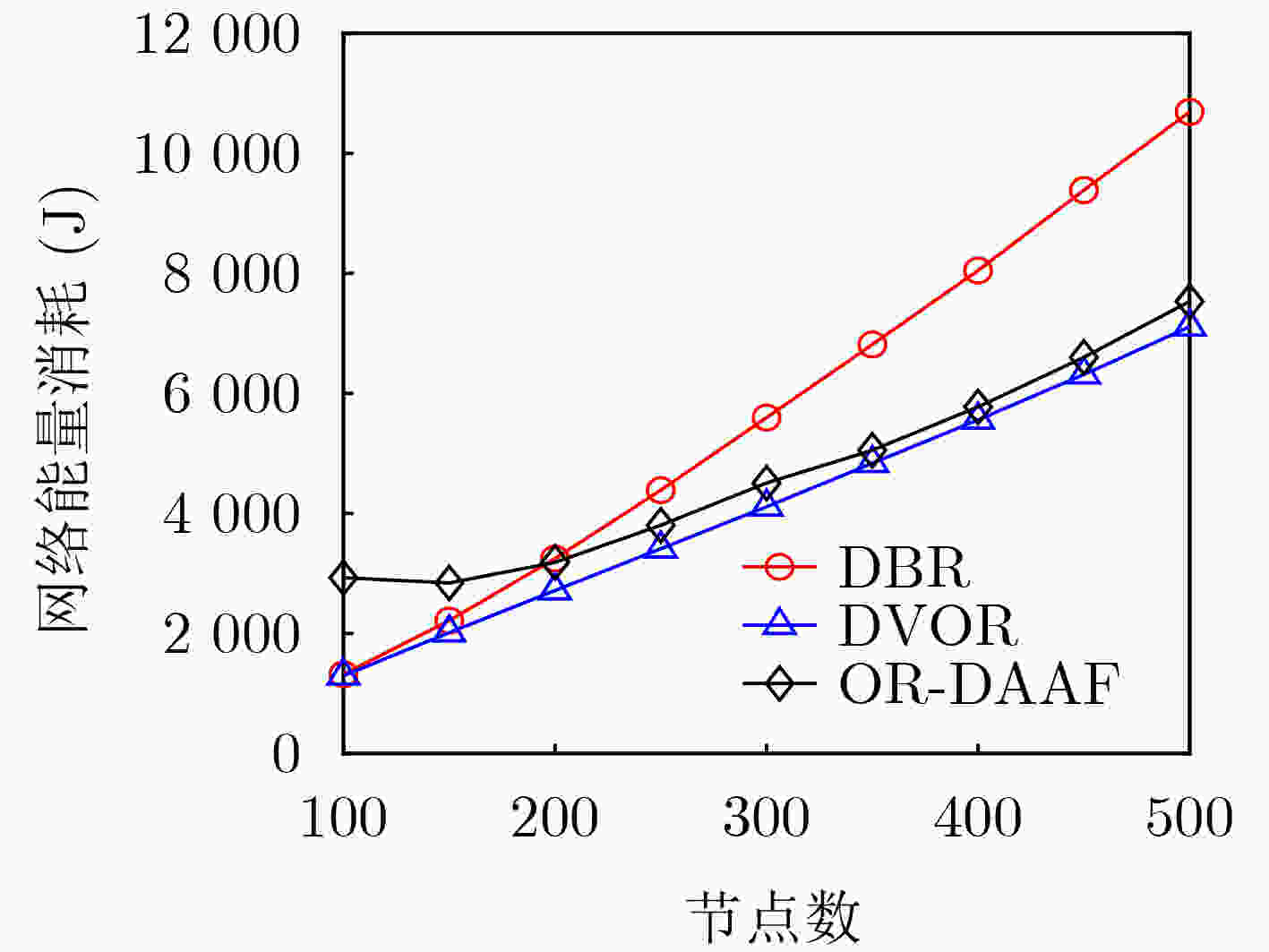


 下载:
下载:
