Joint Optimization of Data Value and Age of Information in Multi-cluster System with Mixed Data
-
摘要: 信息年龄(AoI)是一种业界新兴的时间相关指标,其经常用于评估接收数据的新鲜度。该文考虑了一个视频数据与环境数据混合的多集群视频直播系统,并制定调度策略以联合优化系统数据价值与信息年龄。为克服优化问题中动作空间过大导致难以实现有效求解的问题,该文将优化问题的调度策略分解为相互关联的内外两层策略,外层策略利用深度强化学习实现集群间的信道分配,内层策略则基于构造的虚拟队列实现集群内的链路选择。双层调度策略将每个集群的内层策略嵌入到外层策略中进行训练,仿真结果显示,与现有调度策略相比,该文所提的调度策略可以提高时间平均的接收数据价值并降低时间平均的信息年龄。Abstract: Age of Information (AoI) is an emerging time-related indicator in the industry. It is often used to evaluate the freshness of received data. Considering a multi-cluster live streaming system with mixed video data and environmental data, a scheduling policy is formulated to jointly optimize the system data value and AoI. To overcome the problem that the effective solution to the optimization problem is difficult to achieve due to the action space being too large, the scheduling policy of the optimization problem is decomposed into two interrelated internal layer and external layer policies. The external layer policy utilizes deep reinforcement learning for channel allocation between clusters. The internal layer policy implements the link selection in the cluster on the basis of the constructed virtual queue. The two-layer policy embeds the internal layer policy of each cluster into the external layer policy for training. Simulation results show that compared with the existing scheduling policy, the proposed scheduling policy can increase the time-averaged data value of received data and reduce the time-averaged AoI.
-
算法1 求解问题$ {\mathcal{P}}_{3} $的TS策略 输入:全局神经网络参数集$ {\theta } $和$ {{\theta }}_{\mathrm{c}} $,全局计数器$ T=0 $,线程独有神经网络参数集$ {{\theta }}^{'} $和$ {{\theta }}_{\mathrm{c}}^{'} $,线程独有计数器$ t=0,\tilde{T},{T}_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{x}} $ 输出:动作向量$ \boldsymbol{a}\left(t\right) $ Repeat: 重置全局神经网络参数集的梯度:$ \mathrm{d}{\theta }=0 $,$ \mathrm{d}{{\theta }}_{\mathrm{c}}=0 $。同步线程独有神经网络参数集:$ {{\theta }}^{'}={\theta },{{\theta }}_{\mathrm{c}}^{'}={{\theta }}_{\mathrm{c}} $。获得当前时隙状态$ {\boldsymbol{s}}_{t} $,$ {t}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}=t $ Repeat: 根据策略$ \pi \left(\left.\boldsymbol{a}\left(t\right)\right|\boldsymbol{s}\left(t\right),{{\theta }}^{'}\right) $选择动作$ \boldsymbol{a}\left(t\right) $ For $n\in \left\{\mathrm{1,2},\cdots ,N\right\}$ do For $l\in \left\{N+1,N+2, \cdots ,L\right\}$ do If $ {\varphi }_{n}^{\mathrm{s}}\left(t\right)=l $ Then 基于以下原则选择集群$ n $内的传感器$ {m}^{*} $与信道$ l $进行配对
${m}^{*}=\underset{m\in \left[2,M\right]}{\mathrm{arg}\mathrm{max} }\displaystyle\sum\limits_{f=1}^{F}{\beta }_{n,m}^{f}f+\frac{q\left(t\right){\varDelta }_{n,m}\left(t\right)}{\displaystyle\sum\limits _{j=1}^{Y}{\omega }_{n,m}^{ {y}_{j} }\left\lceil { {y}_{j}/\left({R}_{l}b\right)} \right\rceil }$End If End For End For 执行动作$ \boldsymbol{a}\left(t\right) $与上述集群内链路选择决策 获得更新后的状态$ \boldsymbol{s}\left(t+1\right) $以及即时奖励函数$ r\left(\boldsymbol{s}\left(t\right),\boldsymbol{a}\left(t\right),\boldsymbol{s}\left(t+1\right)\right) $ $ t:=t+1,T:=T+1 $ Until $ t=={t}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}+\tilde{T} $ $ G=V\left(\boldsymbol{s}\left(t\right),{{\theta }}_{\mathrm{c}}^{'}\right) $ For $ h\in \left\{t-1,t-2,\cdots ,{t}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\right\} $ do $ G:=r\left(\boldsymbol{s}\left(h\right),\boldsymbol{a}\left(h\right),\boldsymbol{s}\left(h+1\right)\right)+\gamma G $ 累加线程独有的神经网络梯度: $\mathrm{d}{{\theta } }_{\rm{c} }:=\mathrm{d}{{\theta } }_{\rm{c} }+\partial {\left(G-V\left(\boldsymbol{s}\left(h\right),{{\theta } }_{\rm{c} }^{'}\right)\right)}^{2}/\partial {{\theta } }_{\rm{c} }^{'}$ $\mathrm{d}{\theta }:=\mathrm{d}{\theta }+{ {\boldsymbol{ {\text{∇} } } } }_{ {{\theta } }^{'} }\mathrm{l}\mathrm{n}\pi \left(\left.\boldsymbol{a}\left(h\right)\right|\boldsymbol{s}\left(h\right),{{\theta } }^{'}\right)\left(G-V\left(\boldsymbol{s}\left(h\right),{{\theta } }_{\rm{c} }^{'}\right)\right)$ End For 利用累积梯度$ \mathrm{d}{\theta } $和$\mathrm{d}{{\theta } }_{\rm{c} }$异步更新全局神经网络参数集$ {\theta } $和${{\theta } }_{\rm{c} }$ Until $ T > {T}_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{x}} $ -
[1] KAUL S, YATES R, and GRUTESER M. Real-time status: How often should one update?[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM, Orlando, USA, 2012: 2731–2735. [2] ZHANG Shuhang, ZHANG Hongliang, HAN Zhu, et al. Age of information in a cellular Internet of UAVs: Sensing and communication trade-off design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(10): 6578–6592. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3004162 [3] HU Huimin, XIONG Ke, QU Gang, et al. AoI-minimal trajectory planning and data collection in UAV-assisted wireless powered IoT networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(2): 1211–1223. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3012835 [4] TANG Haoyue, WANG Jintao, SONG Linqi, et al. Minimizing age of information with power constraints: Multi-user opportunistic scheduling in multi-state time-varying channels[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(5): 854–868. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.2980911 [5] XIE Xin, WANG Heng, YU Lei, et al. Online algorithms for optimizing age of information in the IoT systems with multi-slot status delivery[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(5): 971–975. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3052569 [6] UITTO M and HEIKKINEN A. Evaluating 5G uplink performance in low latency video streaming[C]. Joint European Conference on Networks and Communications & 6G Summit (EuCNC/6G Summit), Grenoble, France, 2022: 393–398. [7] ZHANG Zhilong, ZENG Minyin, CHEN Mingzhe et al. Joint user grouping, version selection, and bandwidth allocation for live video multicasting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(1): 350–365. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3115480 [8] LIU Junquan, ZHANG Weizhan, HUANG Shouqin, et al. QoE-driven HAS live video channel placement in the media cloud[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2021, 23: 1530–1541. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2020.2999176 [9] WEI Bo, SONG Hang, and KATTO J. High-QoE DASH live streaming using reinforcement learning[C]. IEEE/ACM 29th International Symposium on Quality of Service (IWQOS), Tokyo, Japan, 2021: 1–2. [10] MA Xiaoteng, LI Qing, ZOU Longhao, et al. QAVA: QoE-aware adaptive video bitrate aggregation for HTTP live streaming based on smart edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2022, 68(3): 661–676. [11] LIU Dongzhu, ZHU Guangxu, ZENG Qunsong, et al. Wireless data acquisition for edge learning: Data-importance aware retransmission[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(1): 406–420. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3024980 [12] LIU Dongzhu, ZHU Guangxu, ZHANG Jun, et al. Data-importance aware user scheduling for communication-efficient edge machine learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2021, 7(1): 265–278. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2020.2999606 [13] YATES R D. Lazy is timely: Status updates by an energy harvesting source[C]. IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Hong Kong, China, 2015: 3008–3012. [14] ZHOU Zhenyu, YU Haijun, MUMTAZ S, et al. Power control optimization for large-scale multi-antenna systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(11): 7339–7352. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3010701 [15] DU Jianbo, CHENG Wenjie, LU Guangyue, et al. Resource pricing and allocation in MEC enabled blockchain systems: An A3C deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2022, 9(1): 33–44. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2021.3068340 -





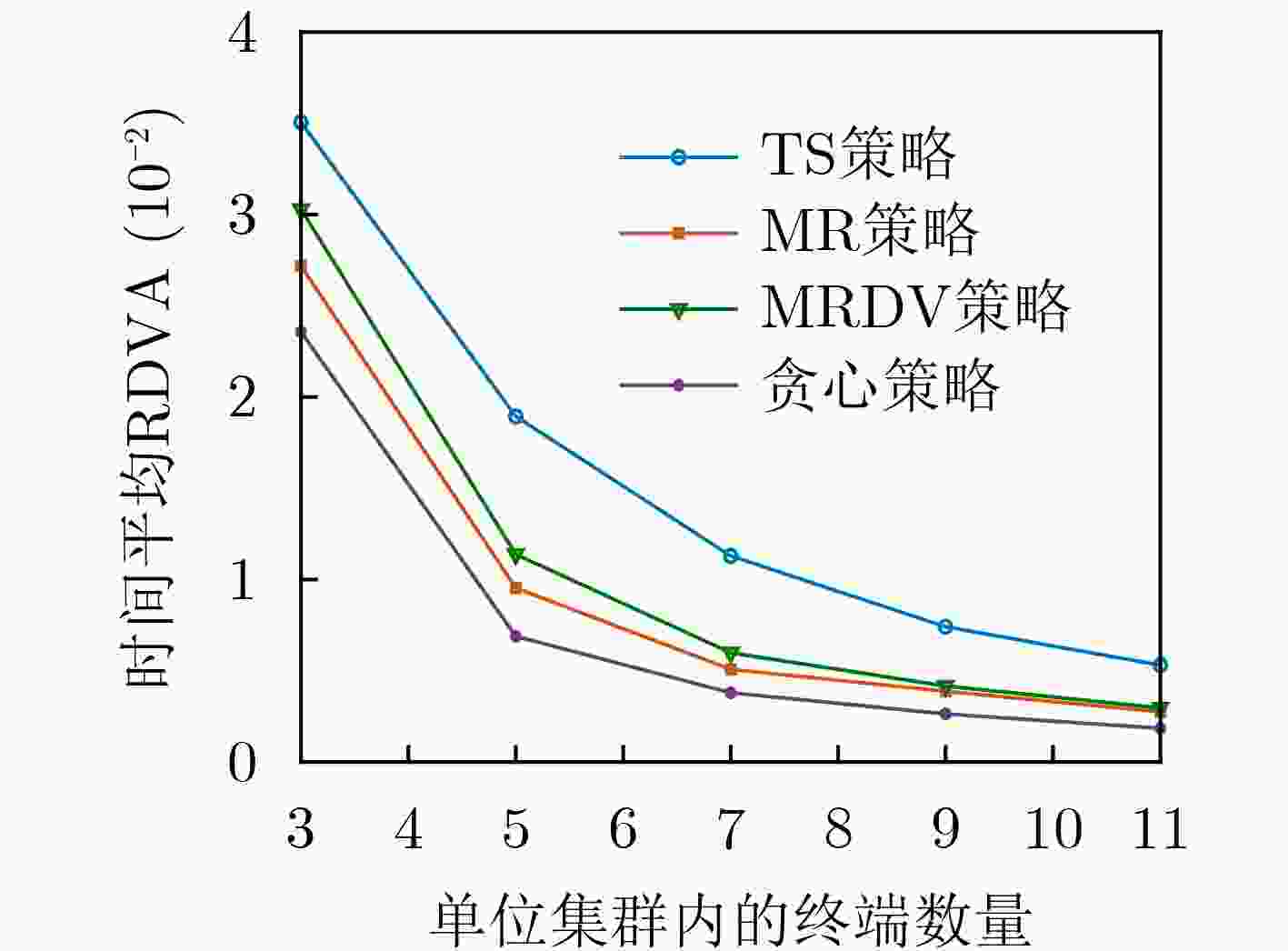
 下载:
下载:
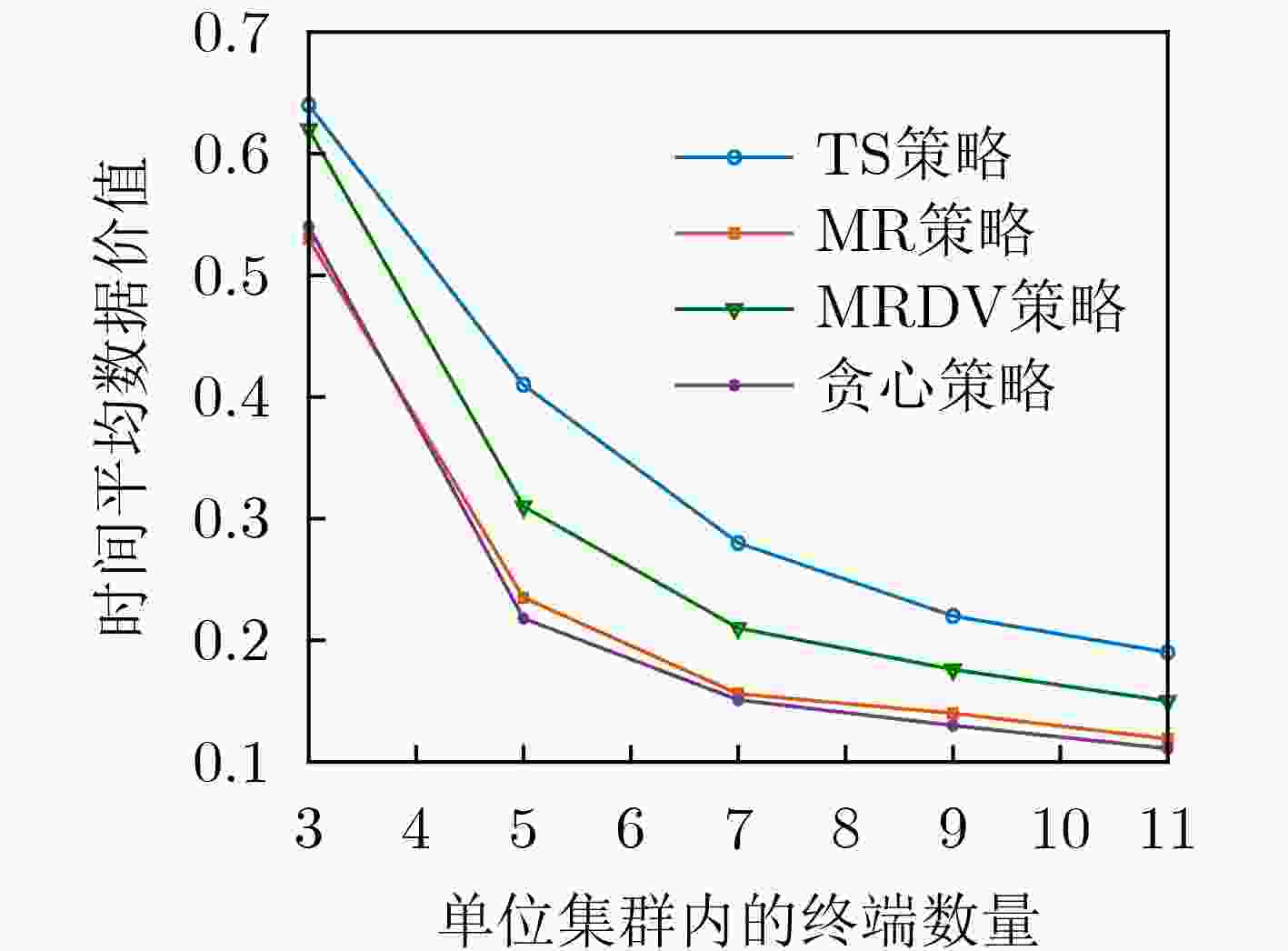
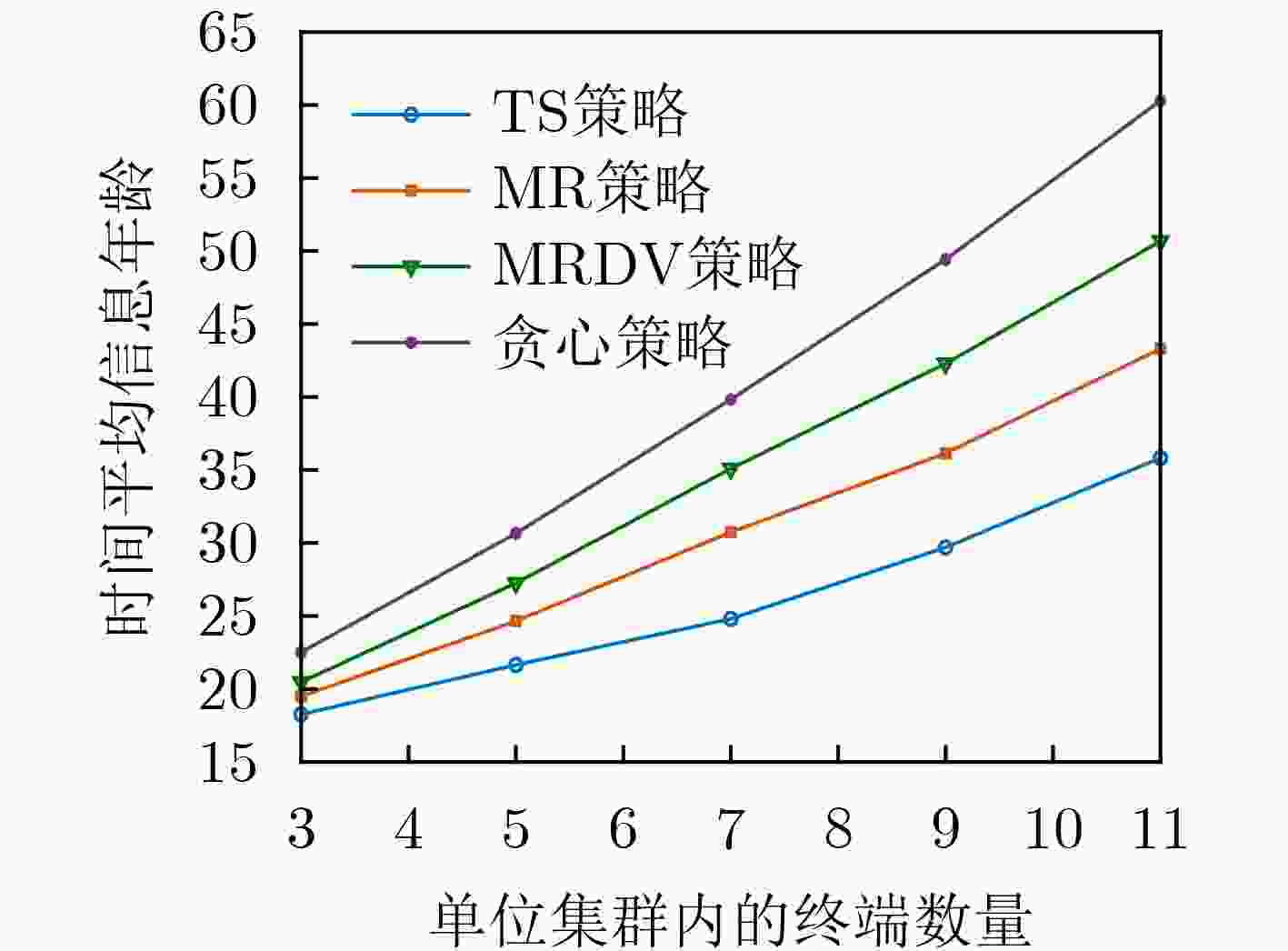


 下载:
下载:
