Research on Dispersion Strategy for Multiple Unmanned Ground Vehicles Based on Auction Multi-agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient
-
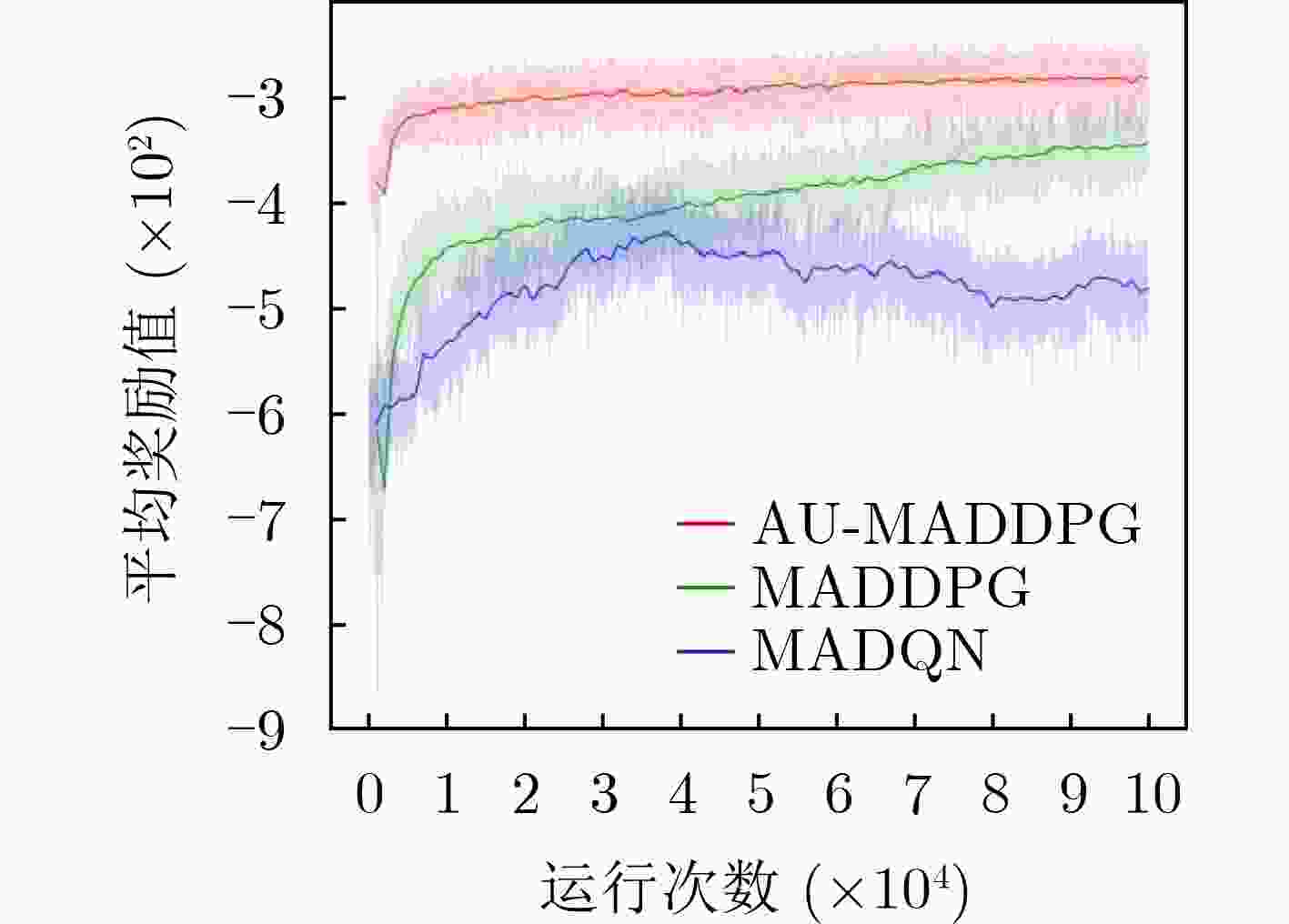
摘要: 多无人车(multi-UGV)分散在军事作战任务中应用非常广泛,现有方法较为复杂,规划时间较长,且适用性不强。针对此问题,该文提出一种基于拍卖多智能体深度确定性策略梯度(AU-MADDPG)算法的多无人车分散策略。在单无人车模型的基础上,建立基于深度强化学习的多无人车分散模型。对MADDPG结构进行优化,采用拍卖算法计算总路径最短时各无人车所对应的分散点,降低分散点分配的随机性,结合MADDPG算法规划路径,提高训练效率及运行效率;优化奖励函数,考虑训练过程中及结束两个阶段,全面考虑约束,将多约束问题转化为奖励函数设计问题,实现奖励函数最大化。仿真结果表明:与传统MADDPG算法相比,所提算法在训练时间上缩短了3.96%,路径总长度减少14.50%,解决分散问题时更为有效,可作为此类问题的通用解决方案。Abstract: Multiple Unmanned Ground Vehicle (multi-UGV) dispersion is commonly used in military combat missions. The existing conventional methods of dispersion are complex, long time-consuming, and have limited applicability. To address these problems, a multi-UGV dispersion strategy is proposed based on the AUction Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (AU-MADDPG) algorithm. Founded on the single unmanned vehicle model, the multi-UGV dispersion model is established based on deep reinforcement learning. Then, the MADDPG structure is optimized, and the auction algorithm is used to calculate the dispersion points corresponding to each unmanned vehicle when the absolute path is shortest to reduce the randomness of dispersion points allocation. Plan the path according to the MADDPG algorithm to improve training efficiency and running efficiency. The reward function is optimized by taking into account both during and the end of training process to consider the constraints comprehensively. The multi-constraint problem is converted into the reward function design problem to realize maximization of the reward f unction. The simulation results show that, compared with the traditional MADDPG algorithms, the proposed algorithm has a 3.96% reduction in training time-consuming and a 14.5% reduction in total path length, which is more effective in solving the decentralized problems, and can be used as a general solution for dispersion problems.
-
Key words:
- Path planning /
- Deep reinforcement learning /
- Multi-UGVs /
- Dispersion strategy /
- Auction algorithm
-
表 1 AU-MADDPG算法参数设置
参数 值 经验池大小M 1000 actor学习率la 0.01 critic学习率lc 0.01 最小批学习数N 32 迭代总次数E 105 每次迭代的最大步数T 25 网络更新率τ 0.01 运行采样时间δt (s) 0.1 表 2 测试100次路径长度对比
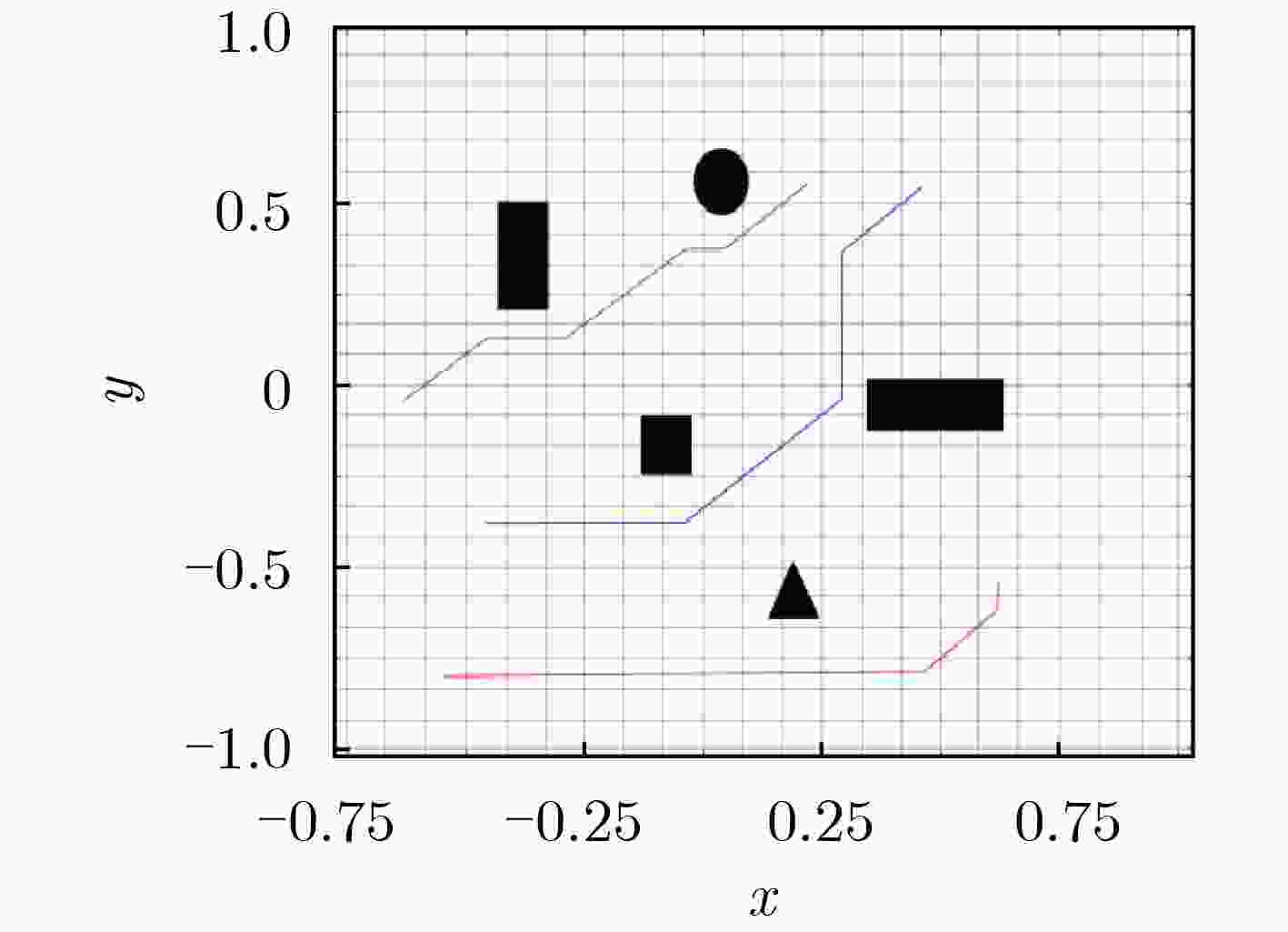
MADQN MADDPG AU-MADDPG 无障碍环境 总长度 545.272 240.915 205.959 最长路径 13.284 5.482 5.618 最短路径 1.883 0.138 0.220 越野
环境总长度 602.498 285.717 258.436 最长路径 13.875 5.836 5.661 最短路径 2.132 0.299 0.282 城市
环境总长度 692.331 346.120 288.96 最长路径 15.062 7.053 6.915 最短路径 2.125 0.526 0.469 表 3 算法耗时对比
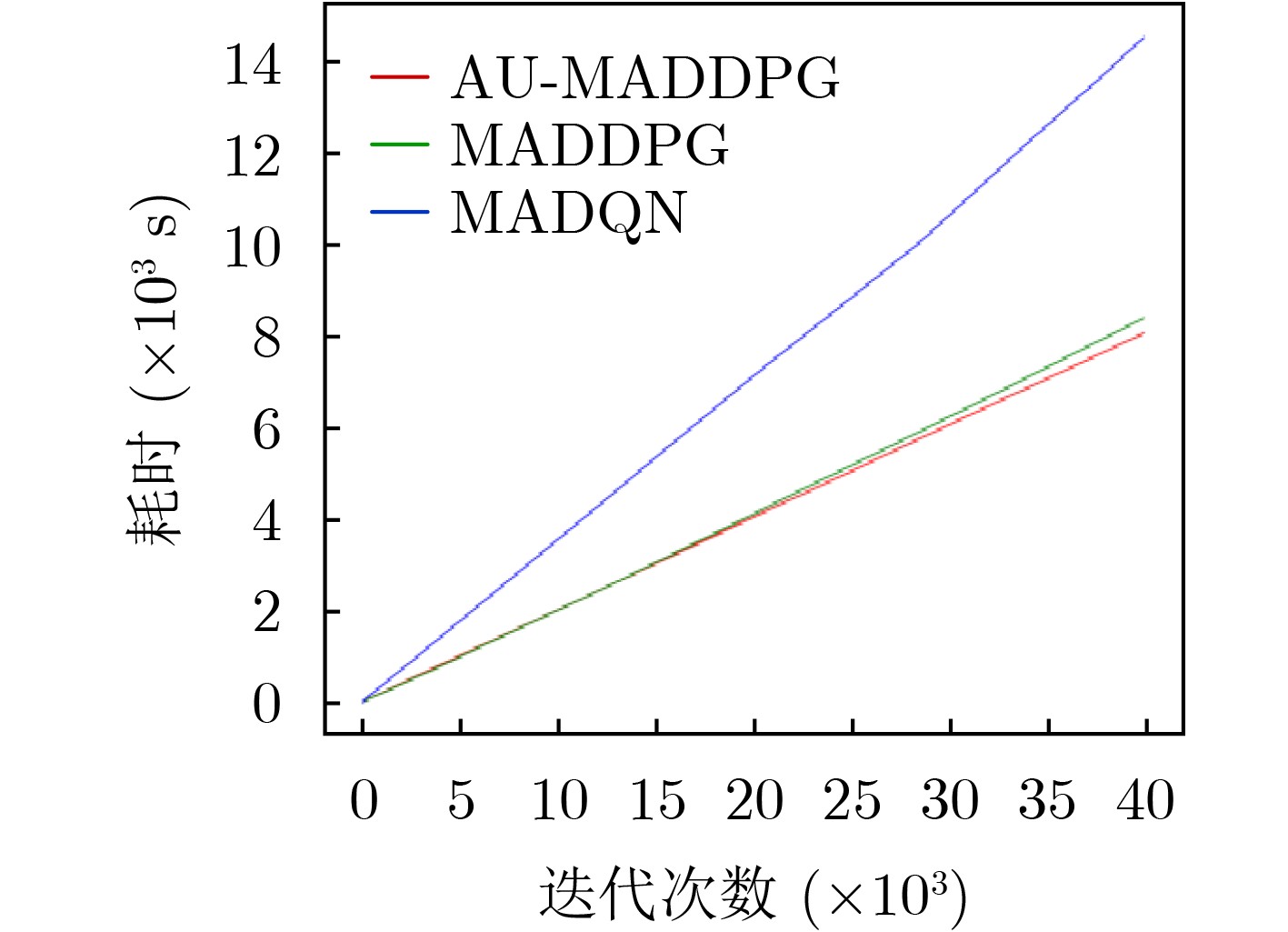
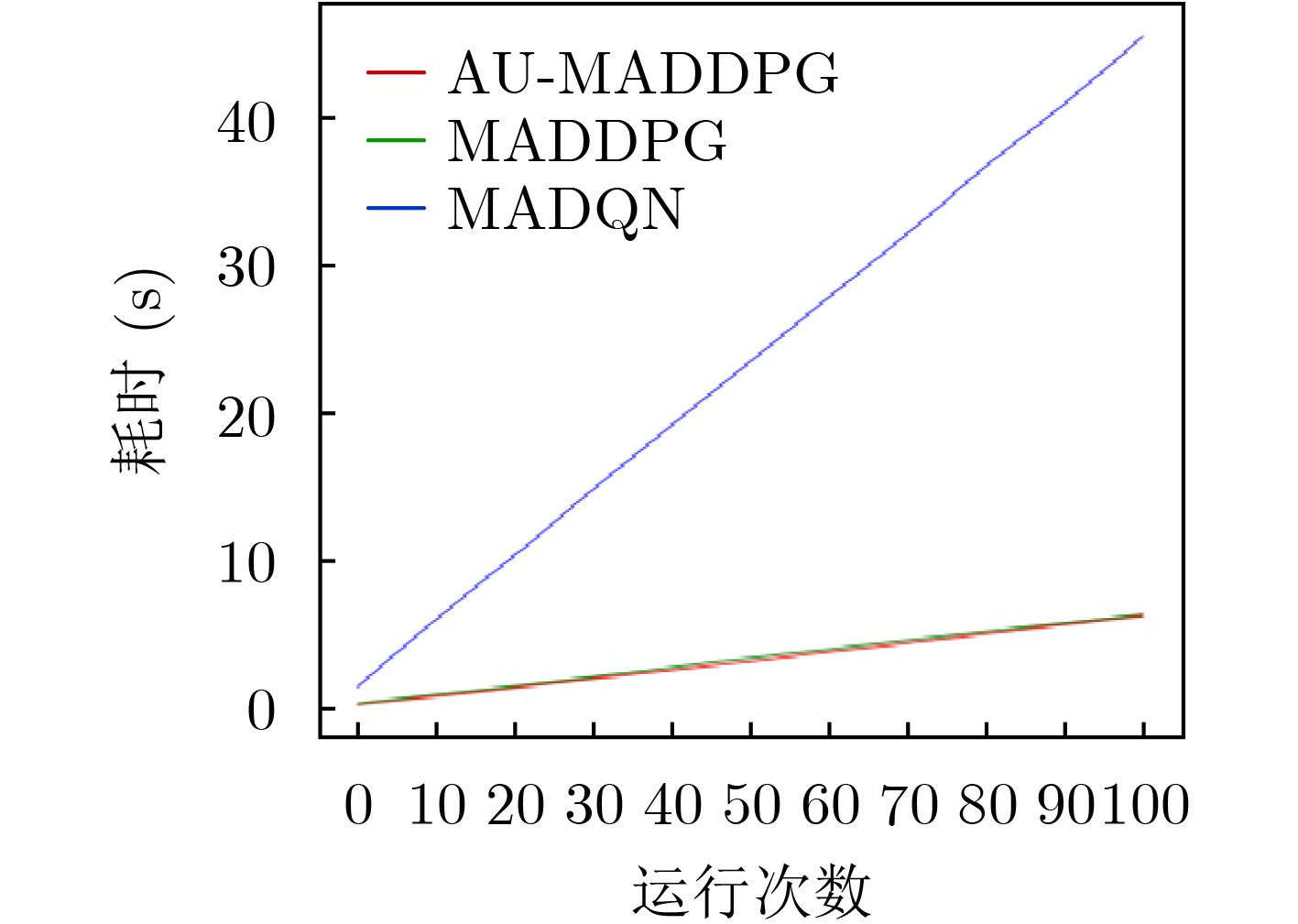
MADQN MADDPG AU-MADDPG 无障碍
环境训练迭代40000次(s) 14548.709 8417.064 8083.574 测试100次(s) 45.626 6.441 6.324 越野
环境训练迭代40000次(s) 15129.661 8852.918 8366.883 测试100次(s) 50.770 7.397 6.935 城市
环境训练迭代40000次(s) 14998.758 8997.201 8401.293 测试100次(s) 51.215 7.459 7.061 表 4 MADDPG单方面优化性能
优化奖励函数 引入拍卖算法 训练迭代40000次 耗时(s) 8151.701 8305.227 平均奖励 –310.411 –382.506 测试100次 耗时(s) 6.353 6.409 总长度 235.881 210.680 表 5 遗传算法测试结果
迭代次数 耗时(s) 总路径 最短路径 最长路径 100 64.323 395.670 0.352 10.557 -
[1] 解少博, 屈鹏程, 李嘉诚, 等. 跟驰场景中网联混合电动货车速度规划和能量管理协同控制的研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2022, 44(8): 1136–1143,1152. doi: 10.19562/j.chinasae.qcgc.2022.08.003XIE Shaobo, QU Pengcheng, LI Jiacheng, et al. Study on coordinated control of speed planning and energy management for connected hybrid electric truck in vehicle following scene[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(8): 1136–1143,1152. doi: 10.19562/j.chinasae.qcgc.2022.08.003 [2] 张立雄, 郭艳, 李宁, 等. 基于多智能体强化学习的无人车分布式路径规划方法[J]. 电声技术, 2021, 45(3): 52–57. doi: 10.16311/j.audioe.2021.03.010ZHANG Lixiong, GUO Yan, LI Ning, et al. Path planning method of autonomous vehicles based on multi agent reinforcement learning[J]. Audio Engineering, 2021, 45(3): 52–57. doi: 10.16311/j.audioe.2021.03.010 [3] 孟磊, 吴芝亮, 王轶强. POMDP模型在多机器人环境探测中的应用研究[J]. 机械科学与技术, 2022, 41(2): 178–185. doi: 10.13433/j.cnki.1003-8728.20200318MENG Lei, WU Zhiliang, and WANG Yiqiang. Research on multi-robot environment exploration using POMDP[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2022, 41(2): 178–185. doi: 10.13433/j.cnki.1003-8728.20200318 [4] 李瑞珍, 杨惠珍, 萧丛杉. 基于动态围捕点的多机器人协同策略[J]. 控制工程, 2019, 26(3): 510–514. doi: 10.14107/j.cnki.kzgc.161174LI Ruizhen, YANG Huizhen, and XIAO Congshan. Cooperative hunting strategy for multi-mobile robot systems based on dynamic hunting points[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2019, 26(3): 510–514. doi: 10.14107/j.cnki.kzgc.161174 [5] 王平, 白昕, 解成超. 基于蜂群与A*混合算法的三维多无人机协同[J]. 航天控制, 2019, 37(6): 29–34,65. doi: 10.16804/j.cnki.issn1006-3242.2019.06.006WANG Ping, BAI Xin, and XIE Chengchao. 3D Multi-UAV collabaration based on the hybrid algorithm of artificial bee colony and A*[J]. Aerospace Control, 2019, 37(6): 29–34,65. doi: 10.16804/j.cnki.issn1006-3242.2019.06.006 [6] 董程博, 陈恩民, 杨坤, 等. 多目标点同时到达约束下的集群四维轨迹规划设计[J]. 控制与信息技术, 2019(4): 23–28,38. doi: 10.13889/j.issn.2096-5427.2019.04.005DONG Chengbo, CHEN Enmin, YANG Kun, et al. Four-dimensional drone cluster route planning under the constraint of simultaneous multi-obiective arrival[J]. Control and Information Technology, 2019(4): 23–28,38. doi: 10.13889/j.issn.2096-5427.2019.04.005 [7] 赵明明, 李彬, 王敏立. 不确定信息下基于拍卖算法的多无人机同时到达攻击多目标[J]. 电光与控制, 2015, 22(2): 89–93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2015.02.020ZHAO Mingming, LI Bin, and WANG Minli. Auction algorithm based Multi-UAV arriving simultaneously to attack multiple targets with uncertain informatio[J]. Electronics Optics &Control, 2015, 22(2): 89–93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2015.02.020 [8] 徐国艳, 宗孝鹏, 余贵珍, 等. 基于DDPG的无人车智能避障方法研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2019, 41(2): 206–212. doi: 10.19562/j.chinasae.qcgc.2019.02.013XU Guoyan, ZONG Xiaopeng, YU Guizhen, et al. A research on intelligent obstacle avoidance of unmanned vehicle based on DDPG algorithm[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2019, 41(2): 206–212. doi: 10.19562/j.chinasae.qcgc.2019.02.013 [9] LILLICRAP T P, HUNT J J, PRITZEL A, et al. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning[C]. The 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2016: 1–14. [10] LOWE R, WU Yi, TAMAR A, et al. Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6382–6393. [11] 唐伦, 李质萱, 蒲昊, 等. 基于多智能体深度强化学习的无人机动态预部署策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022.TANG Lun, LI Zhixuan, PU Hao, et al. A dynamic pre-deployment strategy of uavs based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022. [12] 张建行, 康凯, 钱骅, 等. 面向物联网的深度Q网络无人机路径规划[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(11): 3850–3857. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210962ZHANG Jianhang, KANG Kai, QIAN Hua, et al. UAV trajectory planning based on deep Q-network for internet of things[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(11): 3850–3857. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210962 [13] 赵辉, 郝梦雅, 王红君, 等. 基于资源拍卖的农业多机器人任务分配[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2021, 38(12): 286–290,313. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2021.12.046ZHAO Hui, HAO Mengya, WANG Hongjun, et al. Cooperative task allocation of agricultural multi-robot based on resource auction[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2021, 38(12): 286–290,313. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2021.12.046 [14] ELGIBREEN H and YOUCEF-TOUMI K. Dynamic task allocation in an uncertain environment with heterogeneous multi-agents[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2019, 43(7): 1639–1664. doi: 10.1007/s10514-018-09820-5 [15] VAN HASSELT H. Double Q-learning[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2010: 2613–2621. [16] 万逸飞, 彭力. 基于协同多目标算法的多机器人路径规划[J]. 信息与控制, 2020, 49(2): 139–146.WAN Yifei and PENG Li. Multi-robot path planning based on cooperative multi-objective algorithm[J]. Information and Control. 2020, 49(2): 139–146. [17] 陈宝, 田斌, 周占伟, 等. 基于改进遗传算法的多直角贴装机器人路径协同规划[J]. 机械工程与自动化, 2022(5): 57–58,61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6413.2022.05.020CHEN Bao, TIAN Bin, ZHOU Zhanwei, et al. Path collaborative planning of multi right angle mounting robot based on improved genetic algorithm[J]. Mechanical Engineering &Automation, 2022(5): 57–58,61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6413.2022.05.020 -





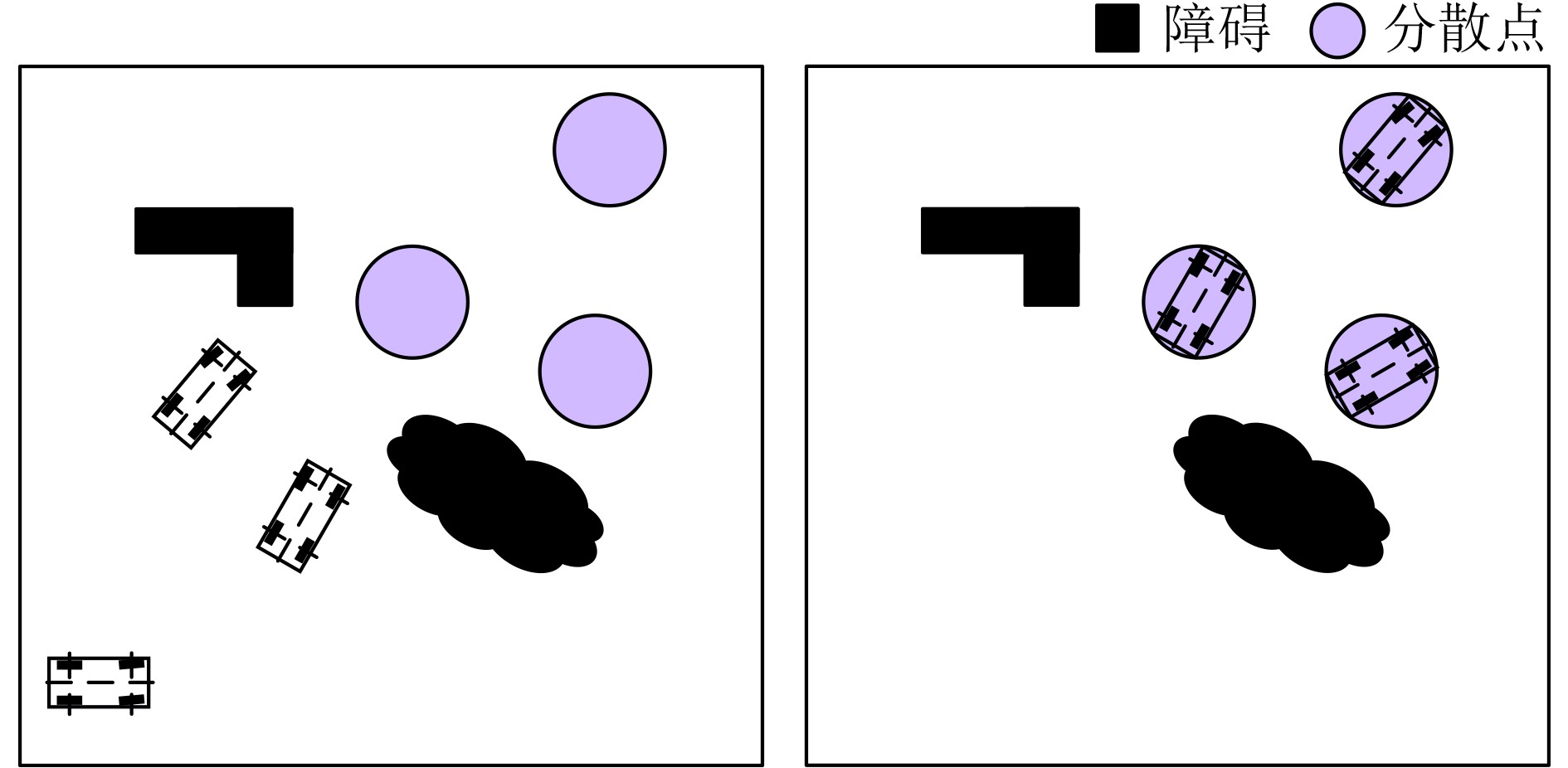
 下载:
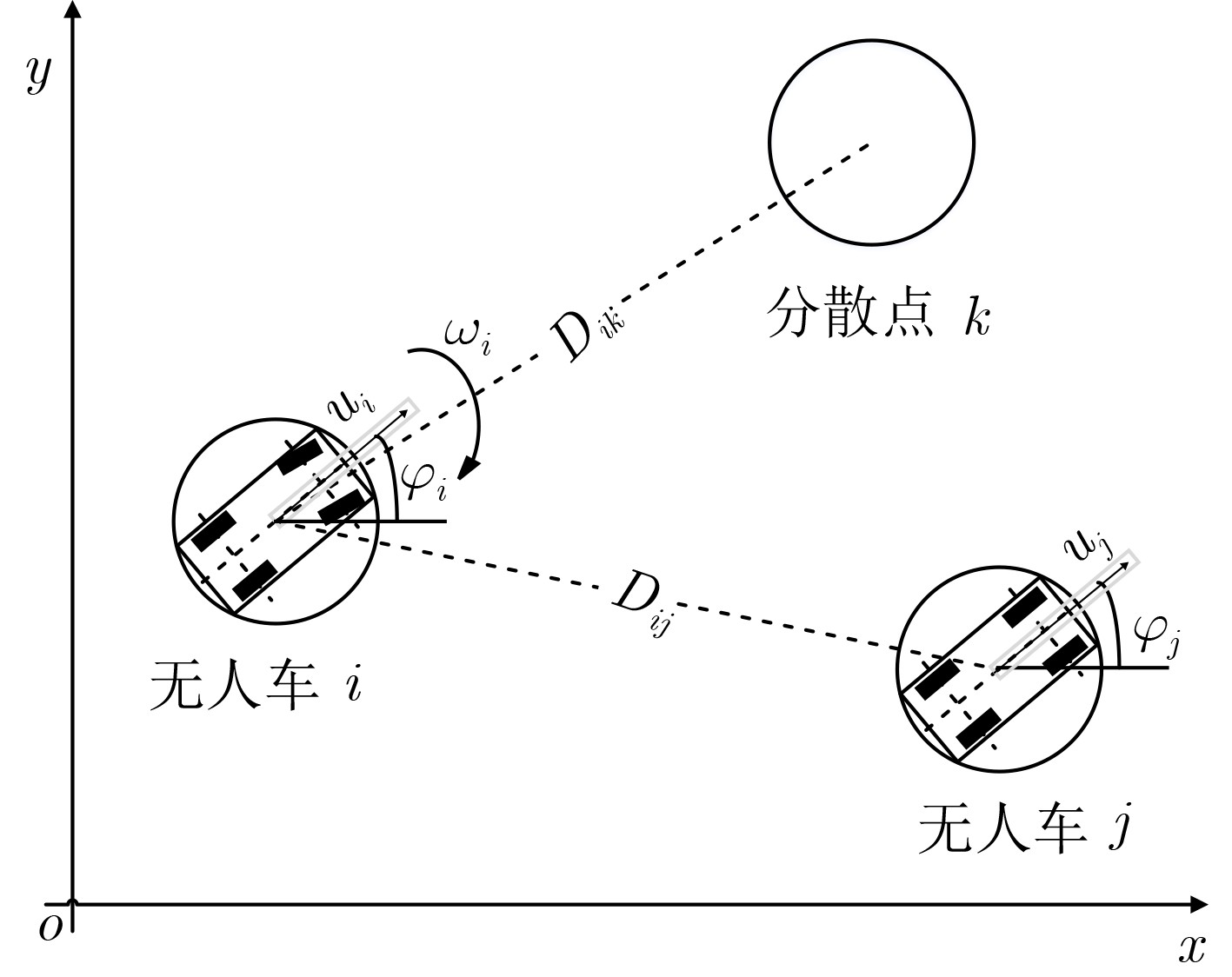
下载:
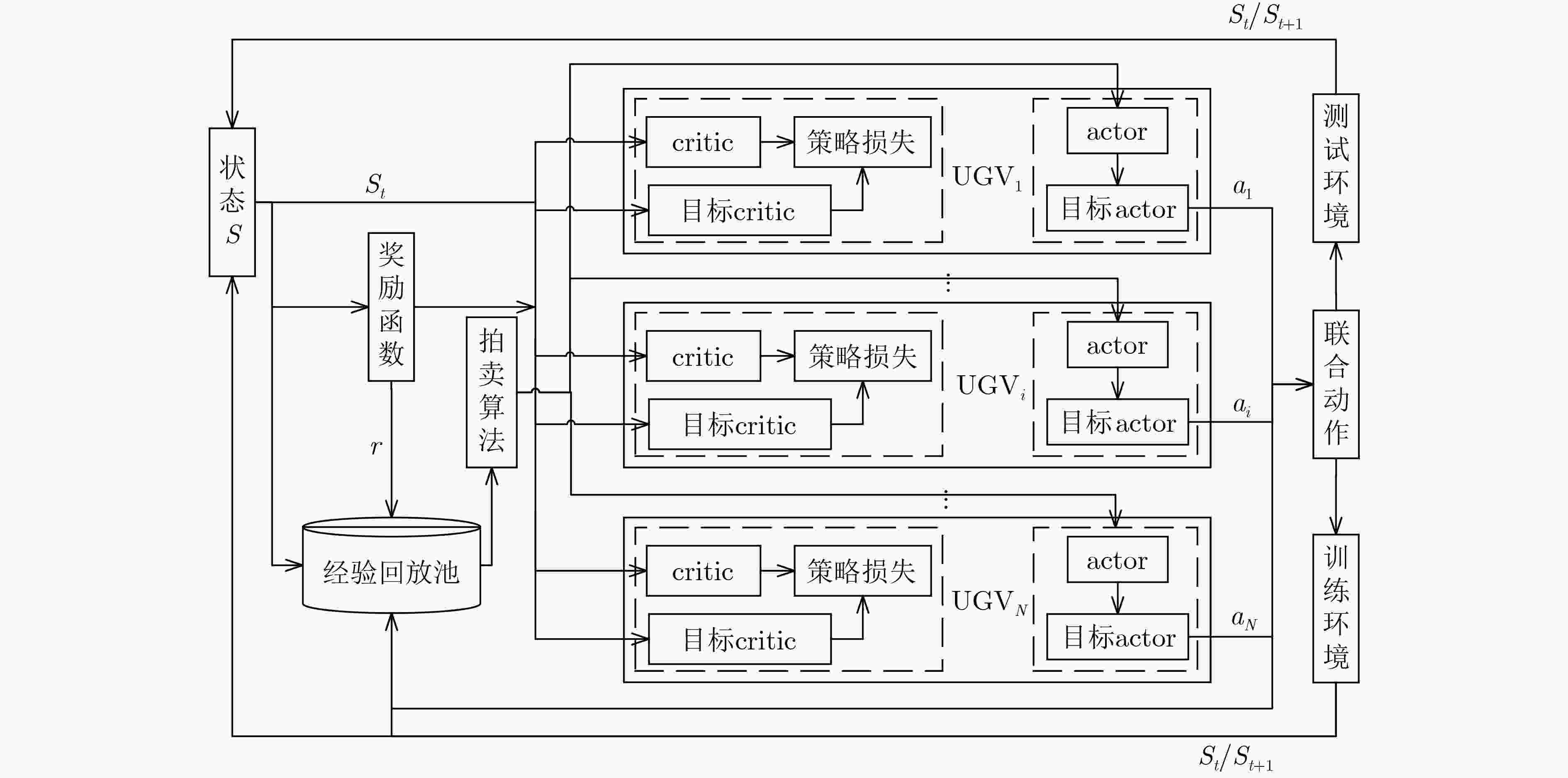
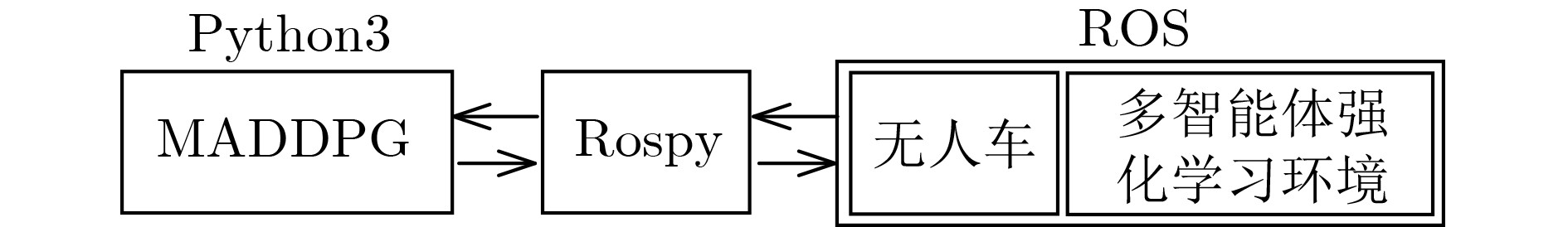
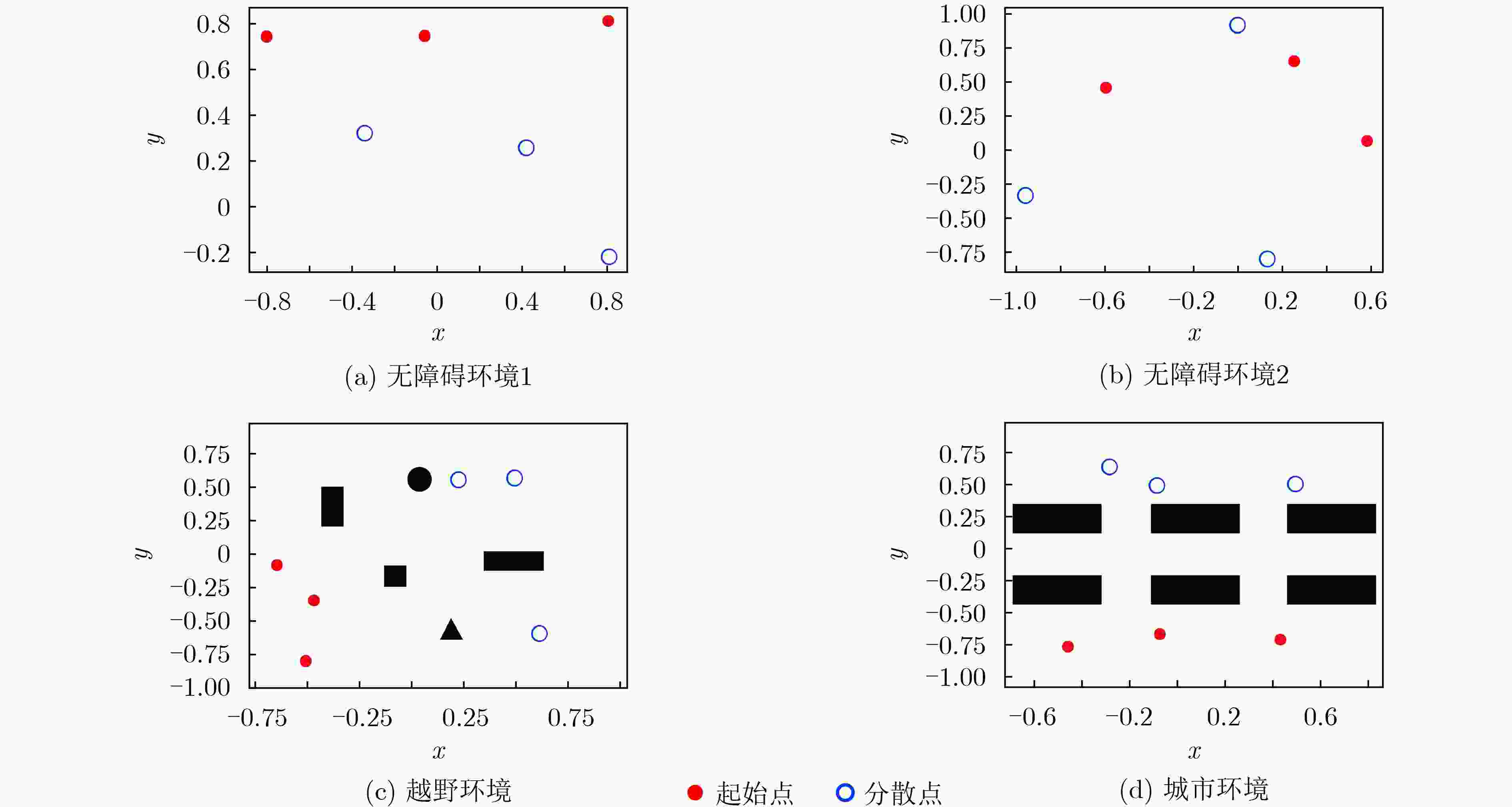
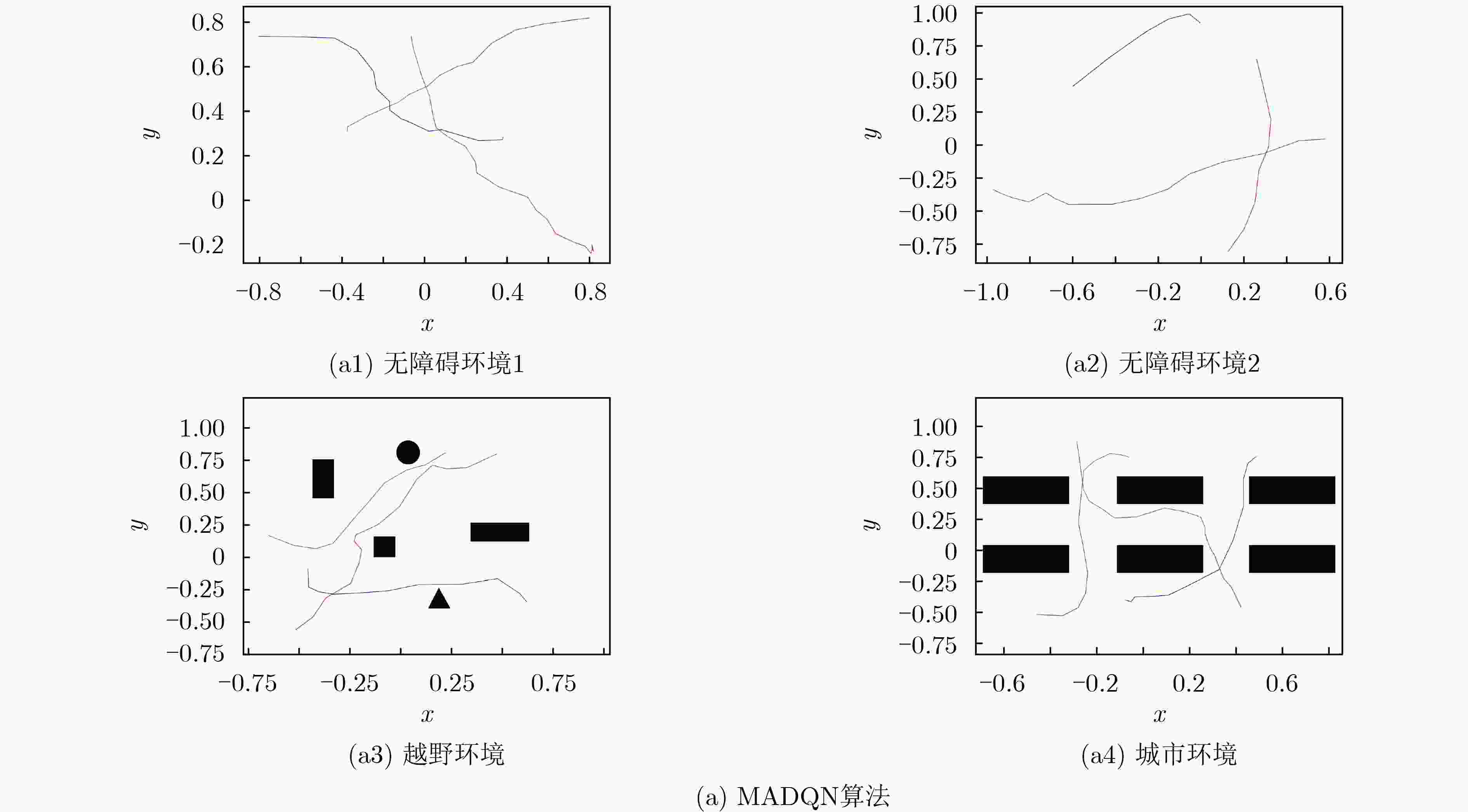
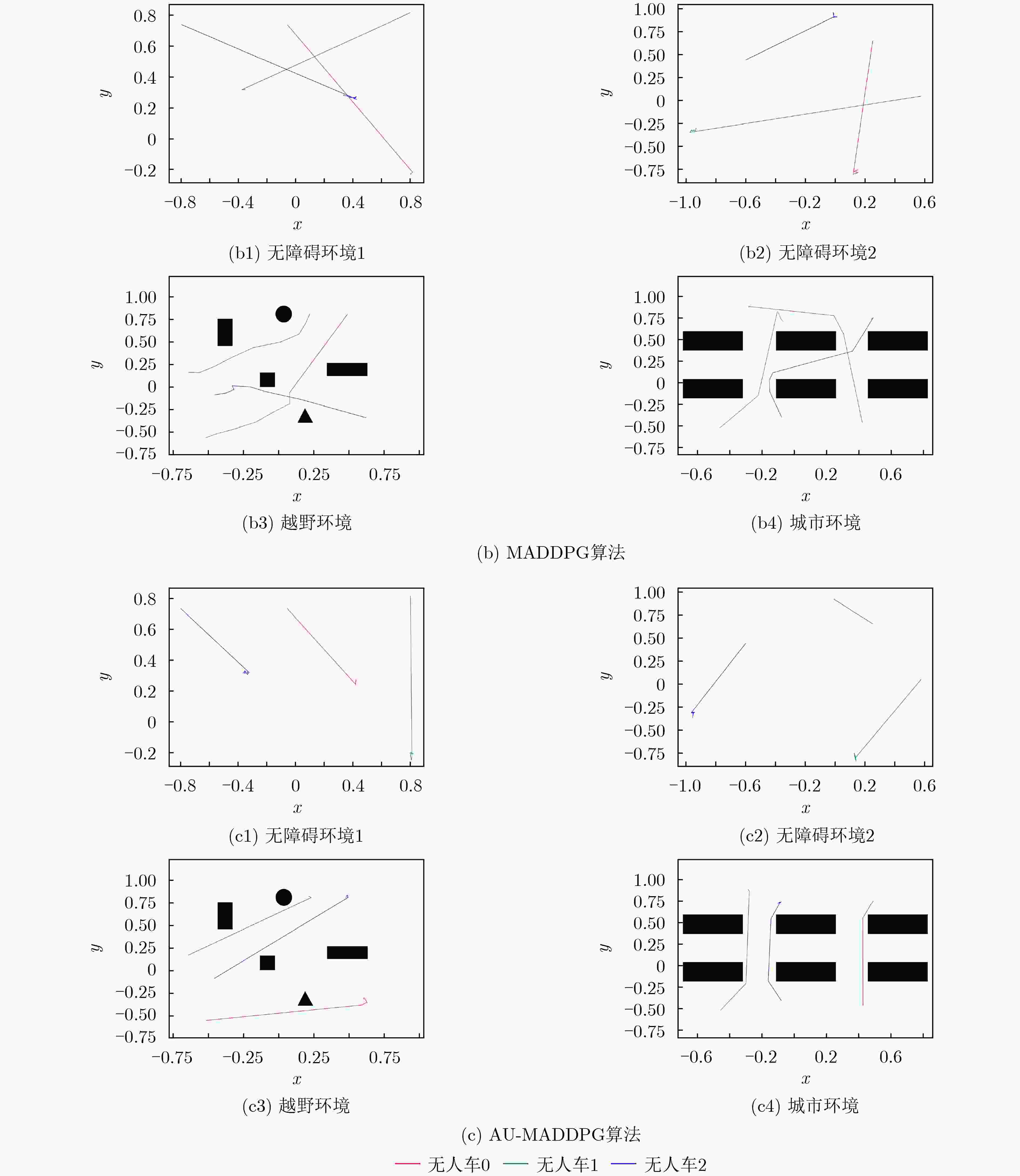


 下载:
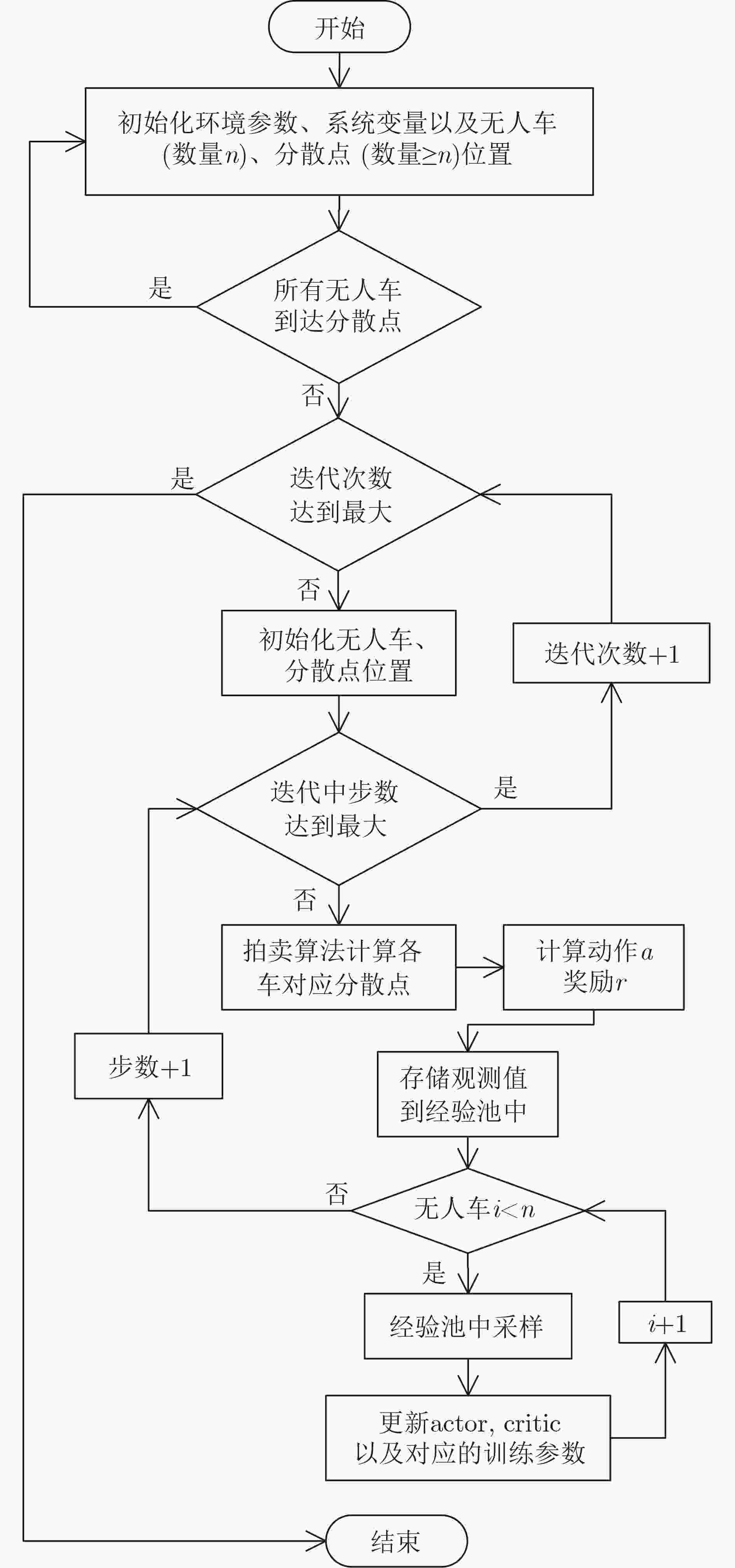
下载:
