An Improved DIP Denoising Model Based on Internal and External Image Priors and Image Fusion
-
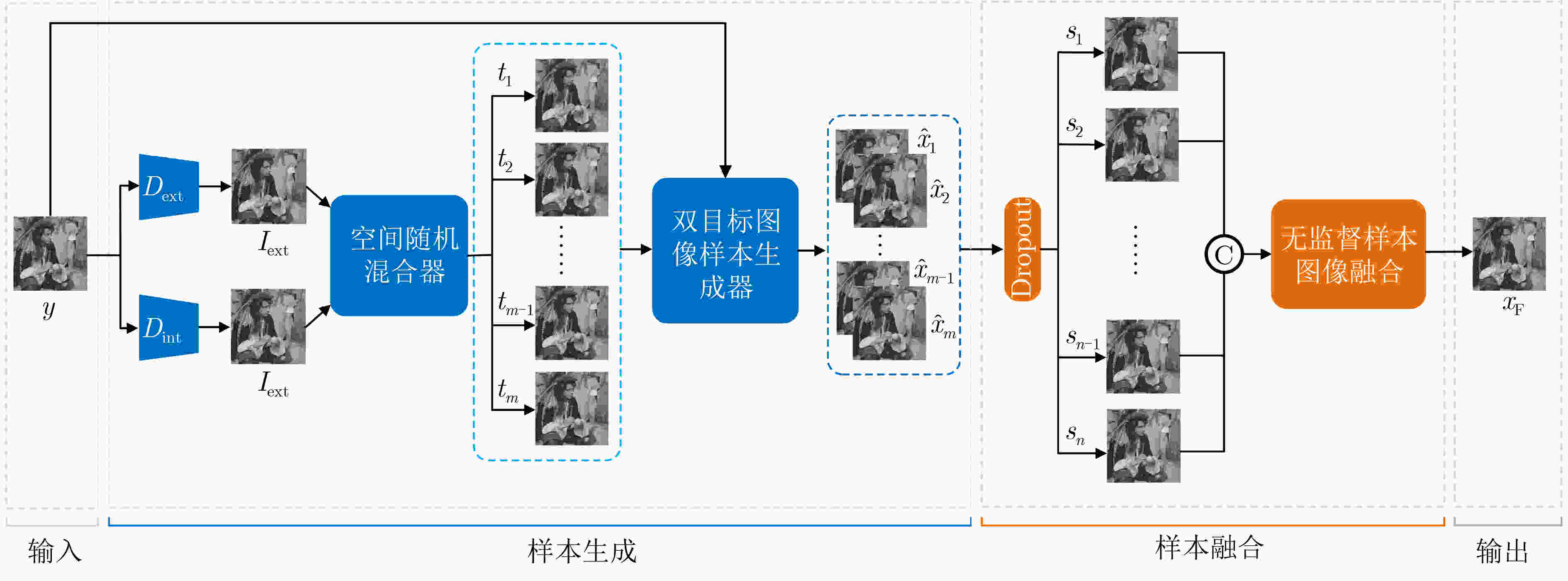
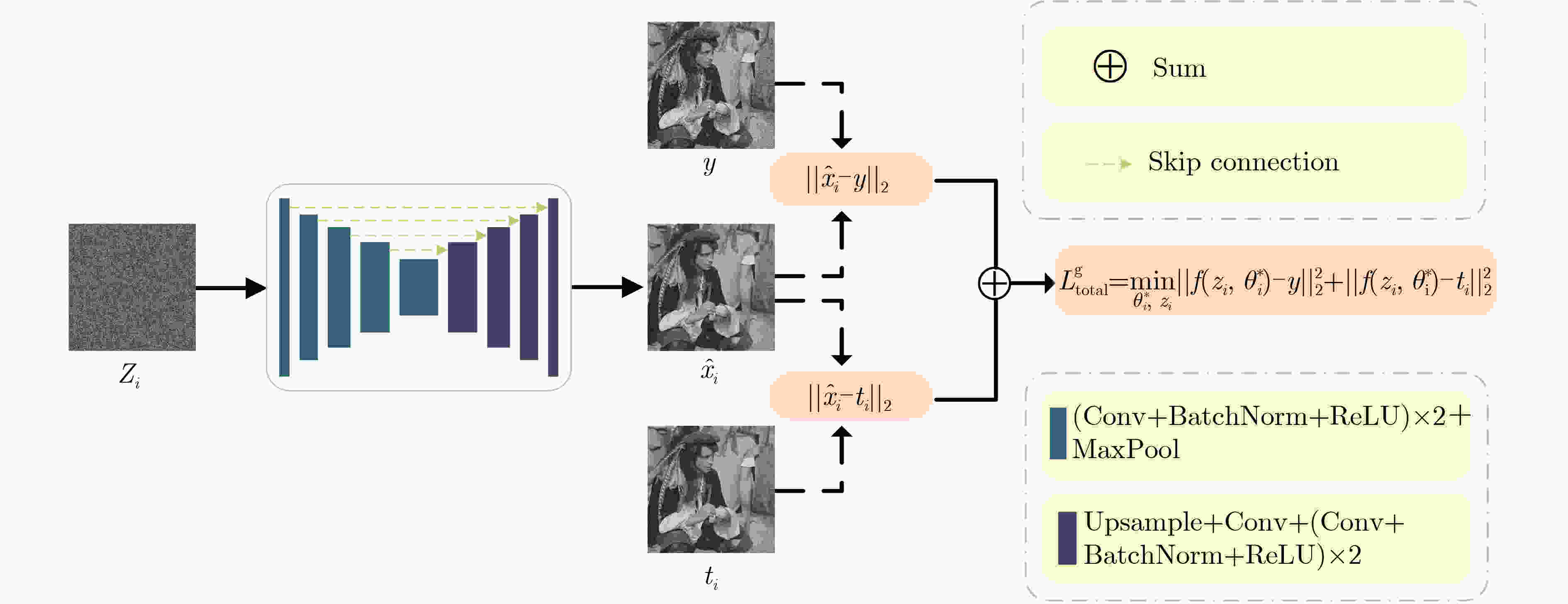
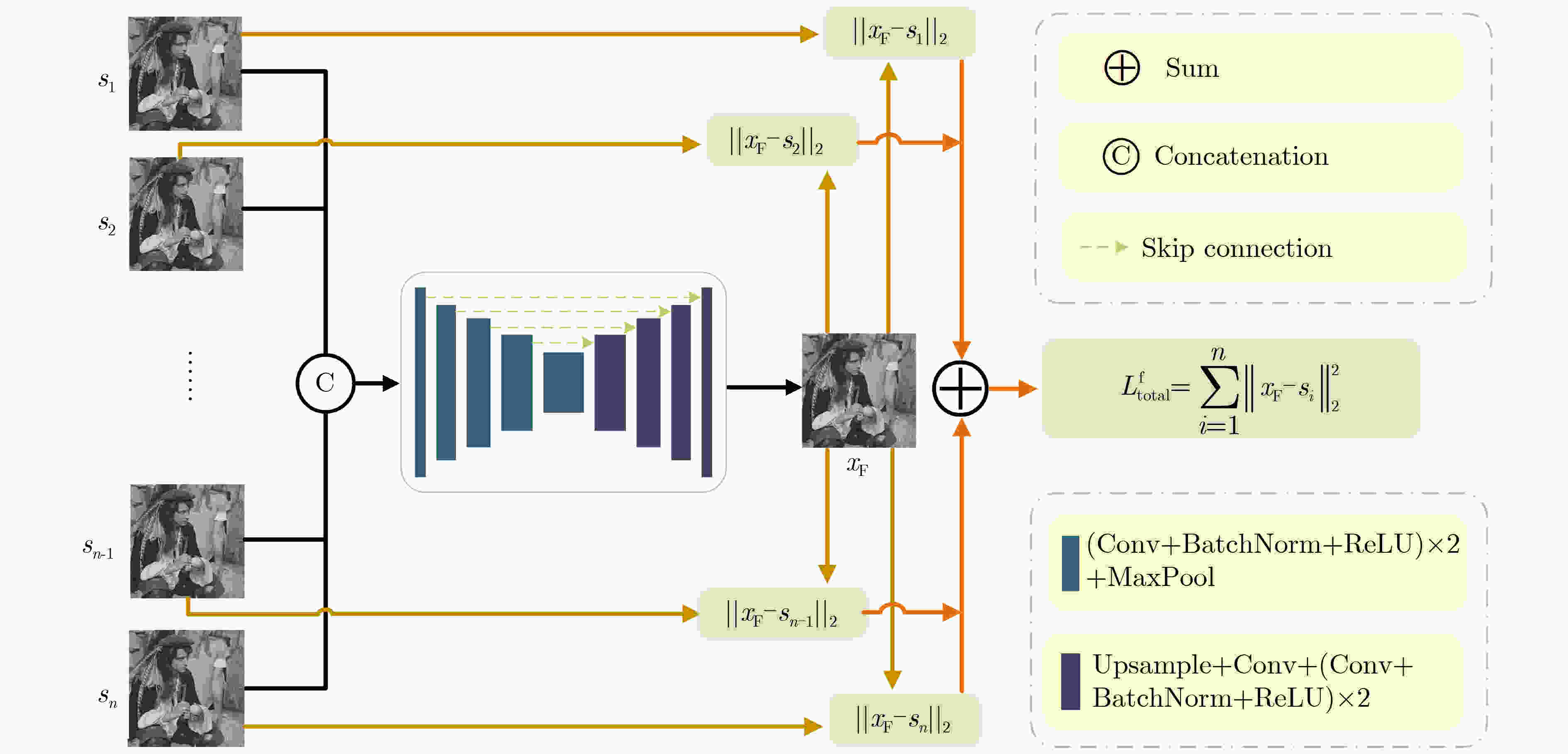
摘要: 为提高无监督深度图像先验(DIP)降噪模型的降噪性能,该文提出了一种基于内外混合图像先验与图像融合的DIP改进降噪模型(IDIP),该模型由样本生成和样本融合两个相继执行的模块组成。在样本生成阶段,首先利用2个分别来自内部和外部先验且有代表性的降噪算法(模型)处理噪声图像以产生2张初始降噪图像。基于这2张初始降噪图像,使用空间随机混合器按照各自50%混合比例随机生成足够多的混合图像作为DIP降噪模型的第2目标图像并与第1目标图像(即噪声图像)构成双目标图像。然后,每次使用不同的随机输入和双目标图像,多次执行标准DIP降噪流程生成多张具有互补性的样本图像;在样本融合阶段,首先为了获得更好的随机性和稳定性,随机丢弃50%的样本图像。然后,采用无监督融合网络在样本图像上完成自适应融合,获得的融合图像的图像质量相对参与融合的样本图像得到再次提升,作为最终降噪图像。在人工合成噪声图像上实验表明:IDIP降噪模型较原DIP降噪模型在峰值信噪比评价指标上有约2 dB的提升,且较大幅度超过了其他无监督降噪模型,逼近了有监督降噪模型。而在实际真实噪声图像上,其降噪性能较各对比方法更具鲁棒性。Abstract: To enhance the denoising performance of an unsupervised Deep Image Prior (DIP) model, an improved approach known as the Improved Deep Image Prior (IDIP) is proposed, which comprises sample generation and sample fusion modules, and leverages a prior hybrid image that combines internal and external factors, along with image fusion techniques. In the sample generation module, two representative denoising models are utilized, which capture internal and external priors and process the noisy image to produce two initial denoised images. Subsequently, a spatially random mixer is implemented on these initial denoised images to generate a sufficient number of mixed images. These mixed images, along with the noisy image, form dual-target images with a 50% mixing ratio. Furthermore, executing the standard DIP denoising process multiple times with different random inputs and dual-target images generates a set of diverse sample images with complementary characteristics. In the sample fusion module, to enhance randomness and stability, 50% of the sample images are randomly discarded using dropout. Next, an unsupervised fusion network is used, which performs adaptive fusion on the remaining sample images. The resulting fused image exhibits improved image quality compared to the individual sample images and serves as the final denoised output. The experimental results on artificially generated noisy images reveal that the IDIP model is effective, with an improvement of approximately 2 dB in terms of Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) compared to the original DIP model. Moreover, the IDIP model outperforms other unsupervised denoising models by a significant margin and approaches the performance level of supervised denoising models. When evaluated on real-world noisy images, the IDIP model exhibits superior denoising performance to the compared methods, thus verifying its robustness.
-
表 1 以不同目标图像所获得样本图像的PSNR均值比较(dB)
目标图像 平均值 目标图像 平均值 N 28.86 N+F 29.56 B 28.92 N+ $t_i\left( {0.25,0.75} \right)$ 30.12 F 28.94 N+ $t_i\left( {0.75,0.25} \right)$ 30.22 $t_i\left( {0.5,0.5} \right)$ 29.54 N+ $t_i\left( {0.5,0.5} \right)$ 30.65 N+B 29.11 注:其中符号N,B,F和$t_i$分别代表以噪声图像、BM3D预处理图像、FFDNet预处理图像和混合图像单个图像作为目标图像,而N+$t_i\left( {m,n} \right)$代表以噪声图像和混合图像两个图像作为双目标图像,其中$ m $和$ n $分别代表FFDNet和BM3D两张图像混合时所占的比例。 表 2 使用不同样本数量参与融合所获得降噪后图像的PSNR均值比较(dB)
样本数量 平均值 样本数量 平均值 2 30.74 6 30.87 3 30.82 7 30.86 4 30.87 8 30.82 5 30.89 表 3 各对比方法在Set12和BSD68数据集上的平均降噪性能比较(dB)
数据集 BM3D NCSR WNNM DnCNN FFDNet VDNet CsNet DIP N2V Restormer IDIP Set12 29.09 29.21 29.33 29.64 29.72 29.58 29.62 27.93 27.42 30.29 29.92 BSD68 28.52 28.47 28.55 29.12 29.09 28.23 29.32 27.26 27.03 29.43 29.47 -
[1] 米泽田, 晋洁, 李圆圆, 等. 基于多尺度级联网络的水下图像增强方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3353–3362. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220375MI Zetian, JIN Jie, LI Yuanyuan, et al. Underwater image enhancement method based on multi-scale cascade network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3353–3362. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220375 [2] 张雄, 杨琳琳, 上官宏, 等. 基于生成对抗网络和噪声水平估计的低剂量CT图像降噪方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8): 2404–2413. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200591ZHANG Xiong, YANG Linlin, SHANGGUAN Hong, et al. A low-dose CT image denoising method based on generative adversarial network and noise level estimation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2404–2413. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200591 [3] BIALER O, GARNETT N, and TIRER T. Performance advantages of deep neural networks for angle of arrival estimation[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brighton, UK, 2019: 3907–3911. [4] KIM S. Deep recurrent neural networks with layer-wise multi-head attentions for punctuation restoration[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brighton, UK, 2019: 7280–7284. [5] ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, and ZHANG Lei. FFDNet: Toward a fast and flexible solution for CNN-based image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(9): 4608–4622. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2839891 [6] ANWAR S and BARNES N. Real image denoising with feature attention[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 3155–3164. [7] VALSESIA D, FRACASTORO G, and MAGLI E. Deep graph-convolutional image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 8226–8237. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3013166 [8] ZAMIR S W, ARORA A, KHAN S, et al. Restormer: Efficient transformer for high-resolution image restoration[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 5718–5729. [9] ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, CHEN Yunjin, et al. Beyond a Gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7): 3142–3155. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2662206 [10] LEHTINEN J, MUNKBERG J, HASSELGREN J, et al. Noise2Noise: Learning image restoration without clean data[C]. Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 2971–2980. [11] KRULL A, BUCHHOLZ T O, and JUG F. Noise2Void-learning denoising from single noisy images[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 2124–2132. [12] HUANG Tao, LI Songjiang, JIA Xu, et al. Neighbor2Neighbor: Self-supervised denoising from single noisy images[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 14776–14785. [13] LEMPITSKY V, VEDALDI A, and ULYANOV D. Deep image prior[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 9446–9454. [14] ULYANOV D, VEDALDI A, and LEMPITSKY V. Deep image prior[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(7): 1867–1888. doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01303-4 [15] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. [16] DABOV K, FOI A, KATKOVNIK V, et al. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(8): 2080–2095. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.901238 [17] MA Kede, LI Hui, YONG Hongwei, et al. Robust multi-exposure image fusion: A structural patch decomposition approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(5): 2519–2532. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2671921 [18] LUO Jingyu, XU Shaoping, and LI Chongxi. A fast denoising fusion network using internal and external priors[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2021, 15(6): 1275–1283. doi: 10.1007/s11760-021-01858-w [19] DONG Weisheng, ZHANG Lei, SHI Guangming, et al. Nonlocally centralized sparse representation for image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(4): 1620–1630. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2235847 [20] GU Shuhang, ZHANG Lei, ZUO Wangmeng, et al. Weighted nuclear norm minimization with application to image denoising[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 2862–2869. [21] YUE Zongsheng, YONG Hongwei, ZHAO Qian, et al. Variational denoising network: Toward blind noise modeling and removal[C]. Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 1688–1699. [22] CHOI J H, ELGENDY O A, and CHAN S H. Optimal combination of image denoisers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(8): 4016–4031. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2903321 [23] ABDELHAMED A, LIN S, and BROWN M S. A high-quality denoising dataset for smartphone cameras[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1692–1700. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
