Two-dimensional Hierarchical Mainlobe and Sidelobe Jamming Suppression Algorithm for Monopulse Angle Estimation
-
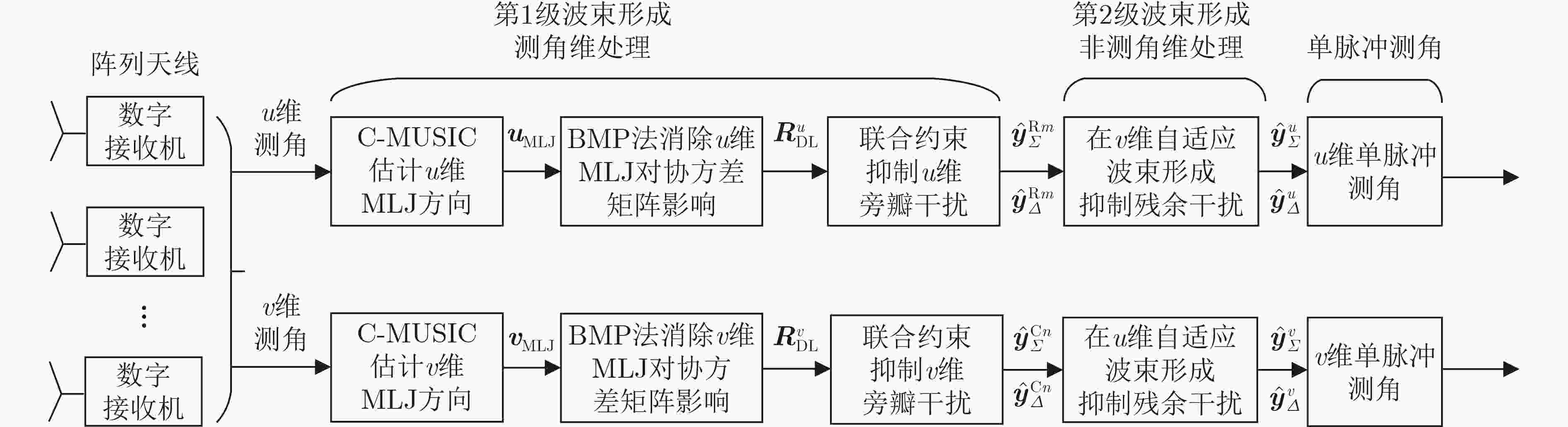
摘要: 针对矩形平面阵列天线同时存在主、旁瓣干扰的单脉冲测角问题,该文设计了2维分级自适应单脉冲波束形成算法(TDHJ-ADBF)。TDHJ-ADBF算法将矩形平面阵分为方位维和俯仰维两个正交维度,采用2维分级处理架构:第1级处理在测角维进行,采用低运算量的压缩多重信号分类法对测角维主瓣干扰进行快速识别与方向估计,构造阻塞矩阵滤除主瓣干扰,获得仅含旁瓣干扰和噪声的协方差矩阵,进而对和、差波束方向图进行指向与鉴角曲线联合约束,完成测角维旁瓣干扰抑制与波束形成处理;第2级在非测角维对残留的测角维主瓣干扰进行抑制。通过2维分级处理实现主、旁瓣干扰联合对抗,并保持单脉冲测角的鉴角曲线线性度。仿真结果表明,TDHJ-ADBF算法实现了对主、旁瓣干扰联合抑制,具有高精度的单脉冲测角性能。Abstract: In order to improve the monopulse angle measurement performance for the rectangular array when the mainlobe and sidelobe jammings exist, a Two-Dimensional Hierarchical Joint Adaptive Digital BeamForming (TDHJ-ADBF) method is proposed in this paper. The beamforming of TDHJ-ADBF method is divided into two stages. In the first stage, the mainlobe jamming corresponding to the angular measurement dimension is quickly estimated by the compressed multiple signal classification algorithm and pre-eliminated by a blocking matrix. Then the adaptive weights and beamforming are calculated using the joint constraint of beam direction and the linearity of monopulse response curve. The residue mainlobe jamming is further suppressed in orthogonal dimension at the second stage. Thereby both the mainlobe and sidelobe jammings are jointly suppressed, the linearity of the monopulse response curve is maintained. Simulation results demonstrate that the TDHJ-ADBF method exhibits an excellent jamming suppression capacity and a high precision of angle measurement.
-
表 1 仿真参数设置
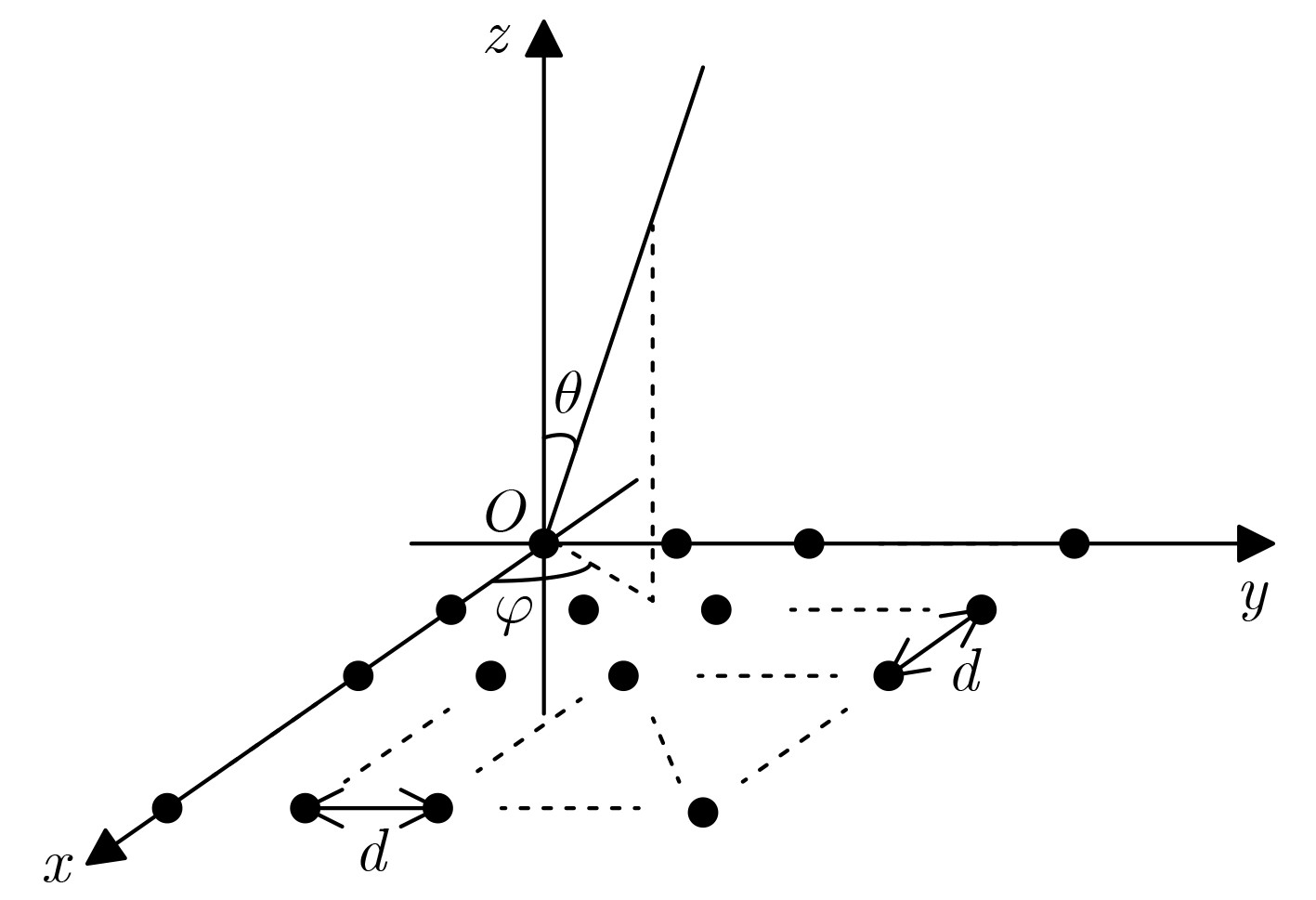
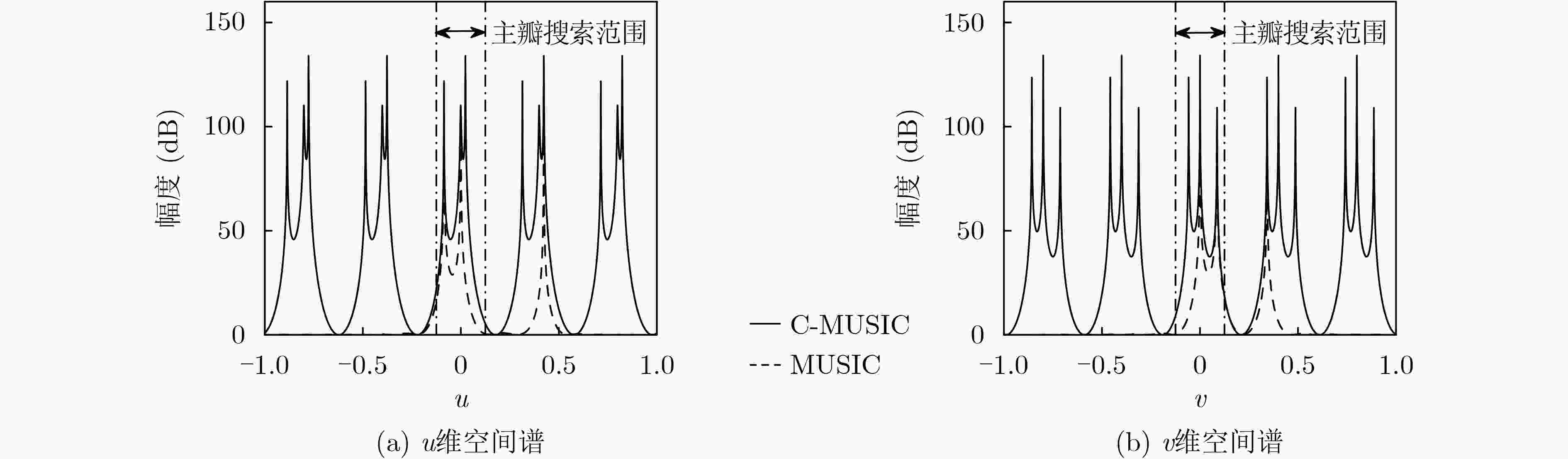
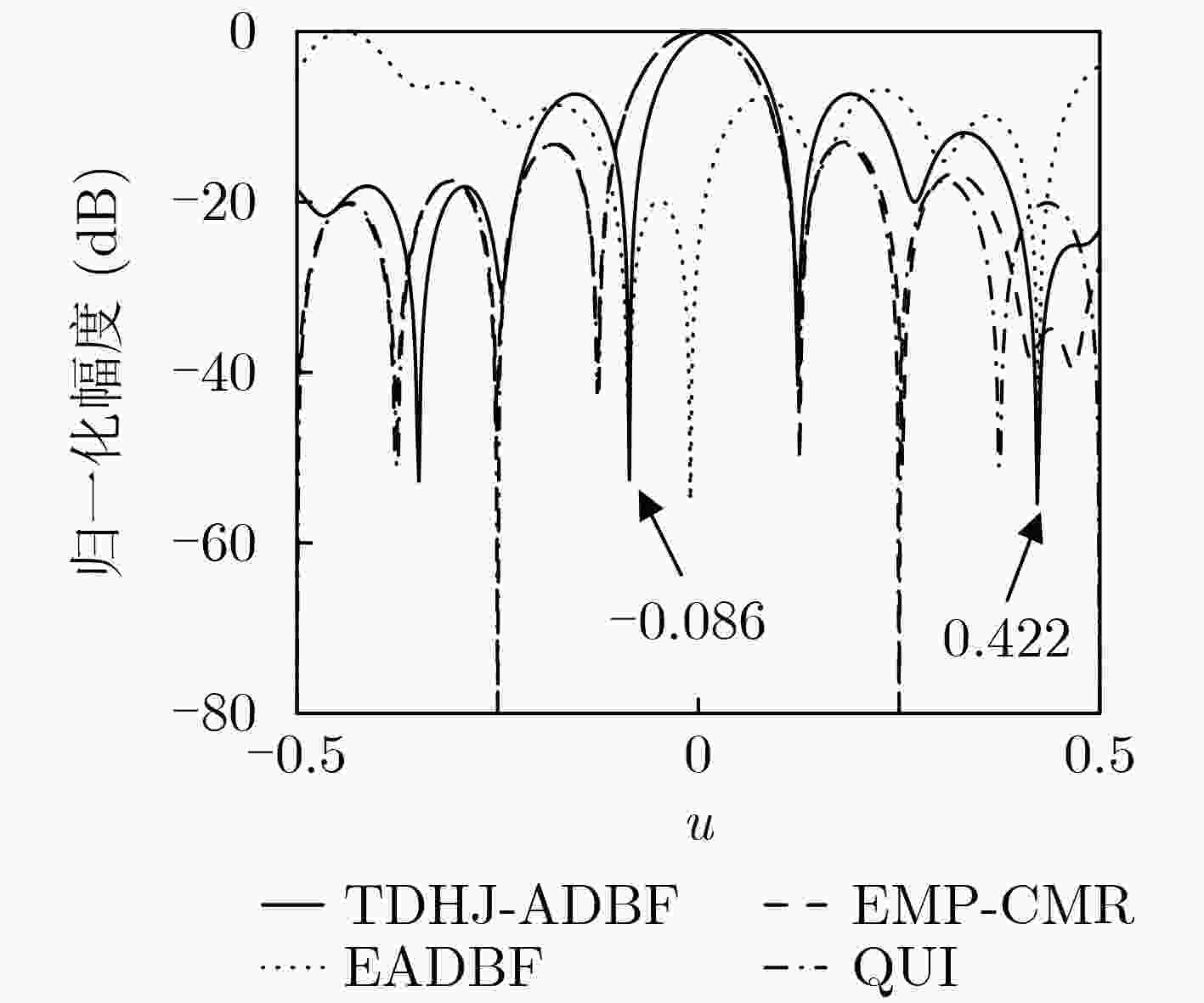
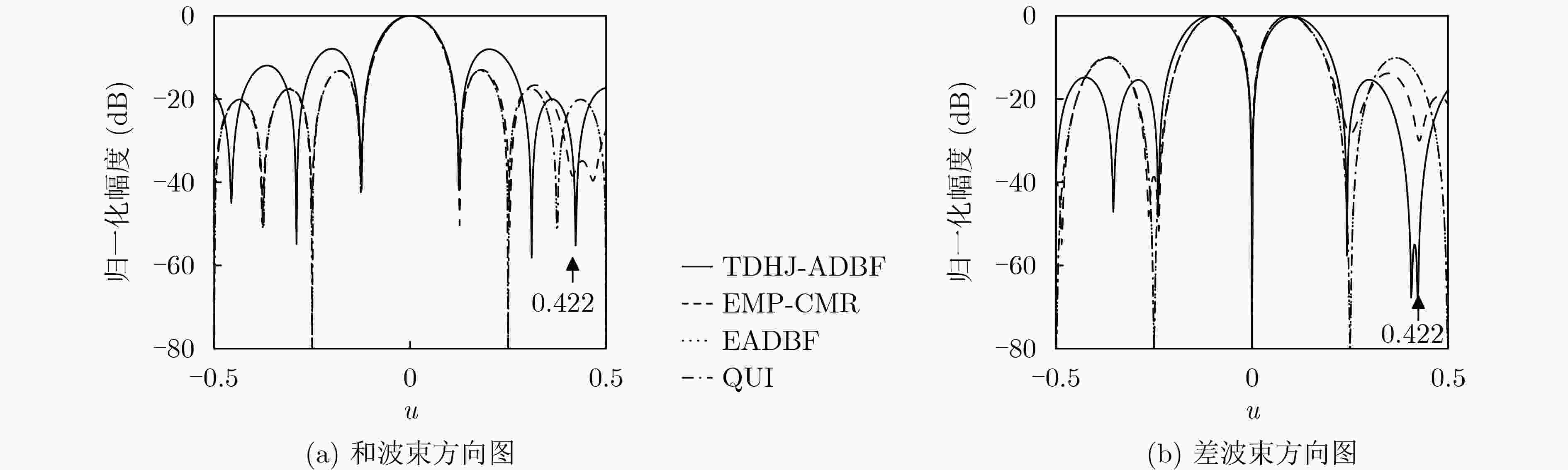
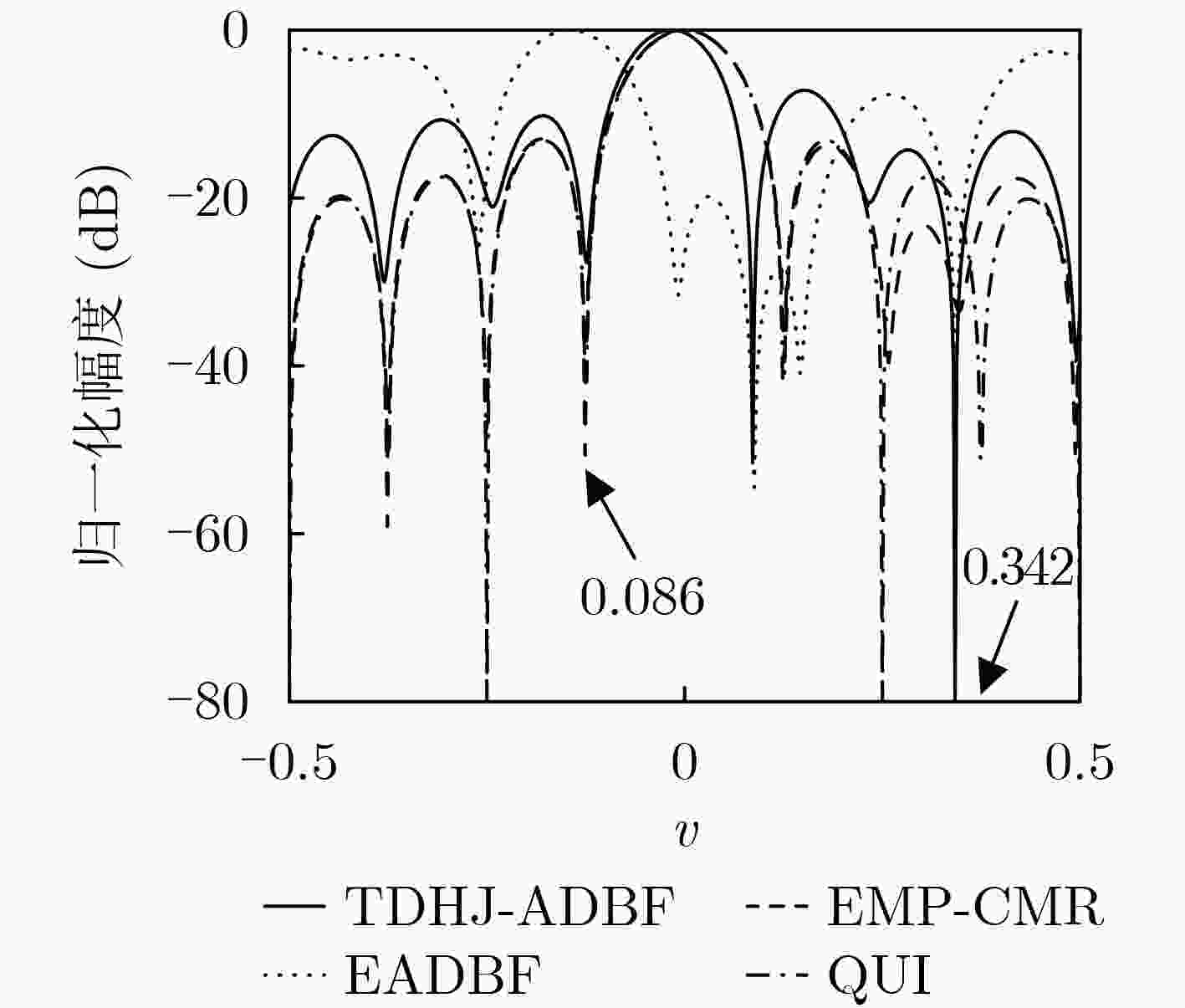
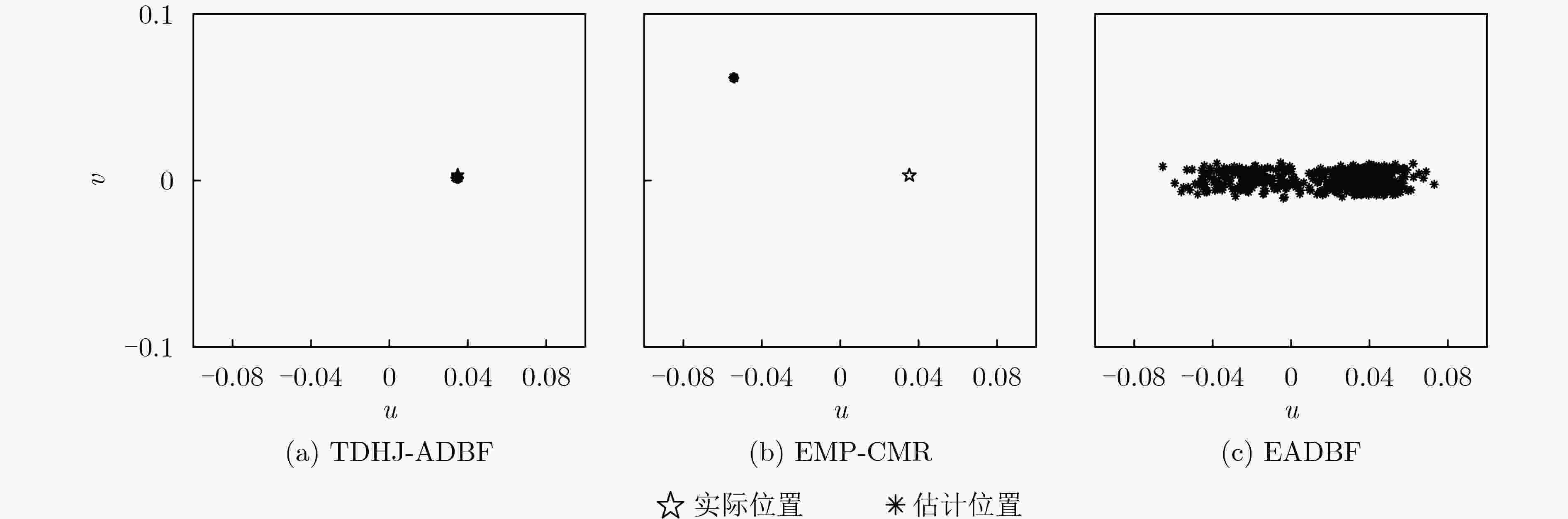
阵列参数 目标参数 干扰参数 阵元数:M=N=16 目标:方向(u,v) =(0.035, 0.002) 干扰J1:方向(u,v)= (–0.086,0.086)/JNR1=28 dB 波束指向:(u,v)= (0, 0) 目标SNR=0 dB 干扰J2:方向(u,v)= (0,0.342) /JNR2=30 dB 阵元间距:λ/2 干扰J3:方向(u,v)= (0.422,0) /JNR3=32 dB 表 2 C-MUSIC算法u维和v维正交性检验结果
干扰 u维估计
干扰位置与原始噪声子空间的
正交性值是否为u维主瓣干扰 v维估计
干扰位置与原始噪声子空间的
正交性值是否为v维主瓣干扰 J1 u维
检验–0.086 8194.8 是 v维
检验0.086 12230 是 J2 0 918.1 是 –0.058 0.185 否 J3 0.023 1.2 否 0 906.899 是 表 3 100次权重计算运行时间(s)
TDHJ-ADBF EADBF EMP-CMR 运行时间 0.6113 0.0186 1.4116 -
[1] WANG Yu, ZHU Daiyin, JIN Guodong, et al. A robust digital beamforming on receive in elevation for airborne MIMO SAR system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5233619. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3199424 [2] CHEN Peng, GAO Jingjie, and WANG Wei. Linear prediction-based covariance matrix reconstruction for robust adaptive beamforming[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 1848–1852. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3111582 [3] LU Yawei, MA Jiazhi, ZHOU Jian, et al. Adaptive polarization-constrained monopulse approach for dual-polarization array[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2021, 20(3): 289–292. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2020.3047684 [4] LU Yawei, MA Jiazhi, SHI Longfei, et al. Multiple interferences suppression with space-polarization null-decoupling for polarimetrie array[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 32(1): 44–52. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2021.000006 [5] YU K B. Enhanced monopulse angle estimation using 4-channel radar system[C]. Proceedings of the IET International Radar Conference 2015, Hangzhou, China, 2015: 1–6. [6] 苏保伟, 王永良, 李荣峰, 等. 阻塞矩阵方法对消主瓣干扰[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2005, 27(11): 1830–1832. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2005.11.004SU Baowei, WANG Yongliang, LI Rongfeng, et al. Mainlobe interference cancelling method via block matrix[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2005, 27(11): 1830–1832. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2005.11.004 [7] 陈卓, 贾维敏, 金伟, 等. 基于EMP的主瓣干扰抑制算法分析[J]. 现代雷达, 2020, 42(4): 55–60. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2020.04.012CHEN Zhuo, JIA Weimin, JIN Wei, et al. Analysis of mainlobe interference suppression algorithms based on Eigen-projection matrix preprocessing[J]. Modern Radar, 2020, 42(4): 55–60. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2020.04.012 [8] YANG Xiaopeng, ZHANG Zongao, ZENG Tao, et al. Mainlobe interference suppression based on Eigen-projection processing and covariance matrix reconstruction[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2014, 13: 1369–1372. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2014.2339224 [9] YANG Xiaopeng, YIN Pilei, ZENG Tao, et al. Applying auxiliary array to suppress mainlobe interference for ground-based radar[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2013, 12: 433–436. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2013.2254698 [10] 饶灿, 李荣锋. 主瓣干扰下多点约束自适应单脉冲测角方法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2011, 9(3): 232–236. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2011.03.007RAO Can and LI Rongfeng. Multipoint constraint adaptive monopulse estimation in the presence of mainlobe jamming[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2011, 9(3): 232–236. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2011.03.007 [11] CHENG Ziyang, HE Zishu, DUAN Xiang, et al. Adaptive monopulse approach with joint linear constraints for planar array at subarray level[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(3): 1432–1441. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2793318 [12] ZHU Lin, QIU Shuang, and HAN Yubing. Combined constrained adaptive sum and difference beamforming in monopulse angle estimation[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2018, 17(12): 2314–2318. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2018.2873818 [13] 夏德平, 张良, 吴涛, 等. 机载双基地极化敏感阵列多干扰抑制[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(3): 399–407. doi: 10.12000/JR21212XIA Deping, ZHANG Liang, WU Tao, et al. A multiple interference suppression algorithm based on airborne bistatic polarization radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(3): 399–407. doi: 10.12000/JR21212 [14] CHEN Xinzhu, SHU Ting, YU K B, et al. Enhanced ADBF architecture for monopulse angle estimation in multiple jammings[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2017, 16: 2684–2687. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2017.2740958 [15] YAN Fenggang, JIN Meng, and QIAO Xiaolin. Low-complexity DOA estimation based on compressed MUSIC and its performance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(8): 1915–1930. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2243442 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
