Dynamic Scheduling Method for Video Intelligent Analysis Tasks Based on Edge Computing Power Collaborative System
-
摘要: 对监控视频数据进行基于深度学习模型的智能分析可提升文物博物馆单位的文物安全风险防范能力。针对文物博物馆单位希望充分利用现有空闲可用计算资源完成更多视频数据智能分析的需求,该文提出一种视频智能分析任务动态调度方法,将边缘侧文物博物馆单位内拥有空闲可用计算资源的设备作为计算节点组建边缘算力协同系统进行视频智能分析任务的处理。该文把要解决的问题建模为2维多重背包问题,并采用动态规划的方法,求解如何在边缘算力协同系统上动态分配视频分析任务使得每一个时间周期内系统执行任务获得的安全价值效益最大化的问题。仿真实验结果表明,所提方法能在不干扰文物博物馆单位正常业务应用服务的情况下,根据对系统当前资源使用状态监控与分析,动态分配视频智能分析任务,达到了最大化安全价值效益的目的。Abstract: Intelligent analysis of surveillance video data based on deep learning models can improve the cultural relics security risk prevention capabilities of cultural relics museum units. In view of the needs of cultural relics museum units to make full use of existing free and available computing resources to complete more intelligent analysis of video data, a dynamic scheduling method for video intelligent analysis tasks is proposed. The device serves as a computing node to form an edge computing power collaborative system to process intelligent video analysis tasks. In this paper, the problem to be solved is modeled as a two-dimensional multiple knapsack problem, and the method of dynamic programming is used to solve how to allocate dynamically video analysis tasks on the edge computing power collaborative system so that the security value and benefits obtained by the system execution tasks in each time period problem of maximization. The simulation results show that the proposed method can dynamically allocate video intelligent analysis tasks based on the monitoring and analysis of the current resource usage status of the system without interfering with the normal business application services of cultural relics museum units, achieving the goal of maximizing security value and benefits purpose.
-
算法1 任务调度算法 1. each $ {t}_{\tau }:C={C}_{{f}_{i}}^{\text{a}}({t}_{\tau })={\lambda }_{c}{C}_{{f}_{i}}-{C}_{{f}_{i}}^{\text{b}}({t}_{\tau }) $,
$M = M_{{f_i}}^{\text{a}}({t_\tau }) = {\lambda _m}{M_{{f_i}}} - M_{{f_i}}^{\text{b}}({t_\tau })$, $ {\text{TN = SUM(}}T{\text{)}} $2. for($j$ = 1 to TN) do 3. for(${c_1}$ = C to $ C[j] $) do 4. for(${m_{\text{1}}}$ = M to $M[j]$) do 5. if (${c_{\text{1} } } \ge C[j]\& \& {m_1} \ge M[j]$) 6. then ${\text{dp[} }{c_1}{\text{][} }{m_1}{\text{] = max[dp[} }{c_1}{\text{][} }{m_1}]$,
${\rm{dp}}[ {c_1}{{ - {\rm{C}}[} }j{\text{]][} }{m_1}{-\text{M[} }j{\text{]] + } }{V_{ {T_j} } }{\text{] } } $7. end if 8. end for 9. end for 10. end for 11. $ {{\boldsymbol I}_{{{f}_{i}}}} = {\text{findResult(TN,}}C{\text{,}}M{\text{)}} $ 12. ${\text{max}}{V_{{t_\tau }}}{\text{ = dp[}}C{\text{][}}M{\text{]}}$ 13. return ${{\boldsymbol I}_{{{f}_{i}}}}$ and $\max {V_{{t_\tau }{f_i}}}{\text{ = dp[}}C{\text{][}}M{\text{]}}$ 表 1 实验所调度的job定义
类别(任务编号) 第1类(model-05) 第2类(model-15) 第3类(model-20) 第4类(model-30) 第5类(model-40) 模型应用功能 人脸识别 消防通道拥堵 徘徊行为识别 攀爬行为识别 挖掘行为识别 所需CPU资源(m) 600 1800 2400 3600 4800 所需内存资源(Mi) 800 2000 2500 4000 5200 安全价值效益 20 90 100 120 150 最大任务个数 2 3 2 2 1 -
[1] DENG Ruilong, LU Rongxing, LAI Chengzhe, et al. Optimal workload allocation in fog-cloud computing toward balanced delay and power consumption[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2016, 3(6): 1171–1181. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2016.2565516 [2] FAN Qiang and ANSARI N. Towards workload balancing in fog computing empowered IoT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2020, 7(1): 253–262. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2018.2852762 [3] YOUSEFPOUR A, ISHIGAKI G, GOUR R, et al. On reducing IoT service delay via fog offloading[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(2): 998–1010. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2788802 [4] KIM W S and CHUNG S H. User-participatory fog computing architecture and its management schemes for improving feasibility[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 20262–20278. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2815629 [5] AL-KHAFAJIY M, BAKER T, AL-LIBAWY H, et al. Fog computing framework for internet of things applications[C]. The 11th International Conference on Developments in eSystems Engineering, Cambridge, UK, 2018: 71–77. [6] BONOMI F, MILITO R, ZHU Jiang, et al. Fog computing and its role in the internet of things[C]. The First Edition of the MCC Workshop on Mobile Cloud Computing, Helsinki, Finland, 2012: 13–16. [7] 许方敏, 伍丽娇, 王翔, 等. 5G上行链路中基于预测的紧急资源分配方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(2): 611–619. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201050XU Fangmin, WU Lijiao, WANG Xiang, et al. Research on prediction based emergency resource allocation in 5G uplink[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(2): 611–619. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201050 [8] KATTEPUR A, DOHARE H, MUSHUNURI V, et al. Resource constrained offloading in fog computing[C]. The 1st Workshop on Middleware for Edge Clouds & Cloudlets, Trento, Italy, 2016: 1–6. [9] MENNES R, SPINNEWYN B, LATRÉ S, et al. GRECO: A distributed genetic algorithm for reliable application placement in hybrid clouds[C]. The 5th IEEE International Conference on Cloud Networking, Pisa, Italy, 2016: 14–20. [10] SKARLAT O, NARDELLI M, SCHULTE S, et al. Towards QoS-aware fog service placement[C]. The 1st International Conference on Fog and Edge Computing, Madrid, Spain, 2017: 89–96. [11] BROGI A and FORTI S. QoS-aware deployment of IoT applications through the fog[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2017, 4(5): 1185–1192. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2701408 [12] 卢为党, 詹悦者, 花俏枝, 等. 基于无人机无线能量传输的边缘计算系统能耗优化方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(3): 899–905. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211314LU Weidang, ZHAN Yuezhe, HUA Qiaozhi, et al. Energy consumption optimization in UAV wireless power transfer based mobile edge computing system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(3): 899–905. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211314 [13] MENG Jiaying, TAN Haisheng, LI Xiangyang, et al. Online deadline-aware task dispatching and scheduling in edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2020, 31(6): 1270–1286. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2019.2961905 [14] LIU Shengyu, QI Xiaogang, and LIU Lifang. Multi-objective task scheduling of circuit repair[J]. Axioms, 2022, 11(12): 714. doi: 10.3390/axioms11120714 [15] 张翀宇, 陈彦明, 李炜. 边缘计算中面向数据流的实时任务调度算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2022, 49(7): 263–270. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210300195ZHANG Chongyu, CHEN Yanming, and LI Wei. Task offloading online algorithm for data stream edge computing[J]. Computer Science, 2022, 49(7): 263–270. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210300195 [16] CHEBIL K and KHEMAKHEM M. A dynamic programming algorithm for the knapsack problem with setup[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2015, 64: 40–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2015.05.005 [17] HE Yichao, WANG Xizhao, and HE Yulin, et al. Exact and approximate algorithms for discounted {0-1} knapsack problem[J]. Information Sciences, 2016, 369: 634–647. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2016.07.037 -





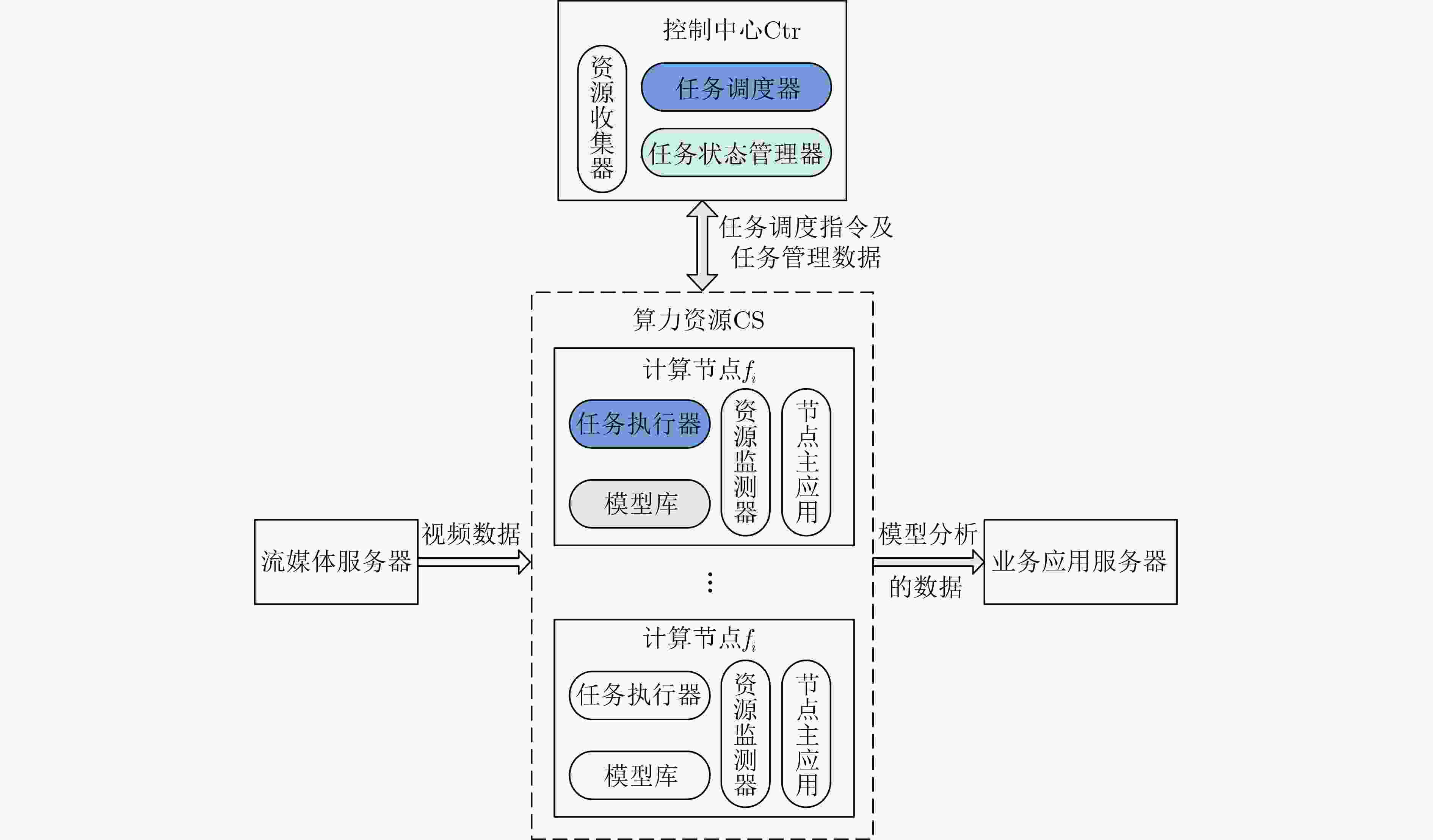
 下载:
下载:

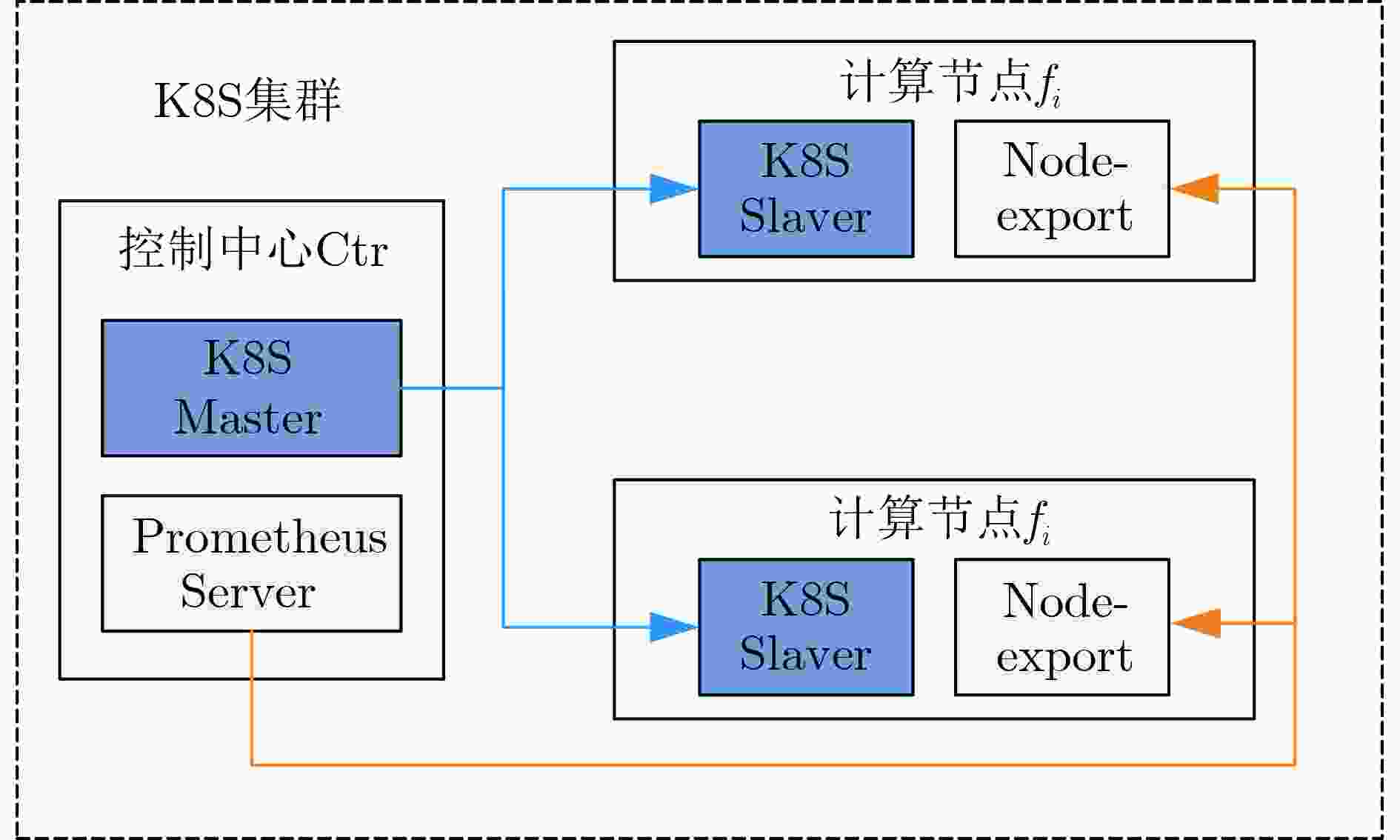
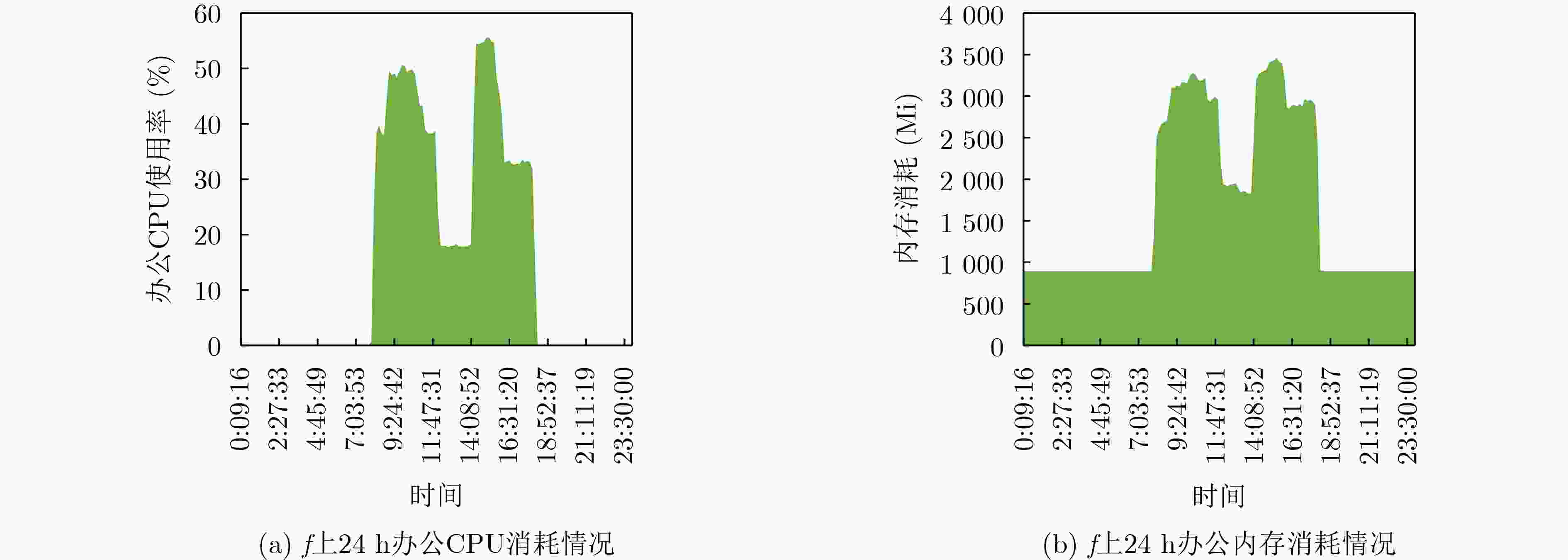
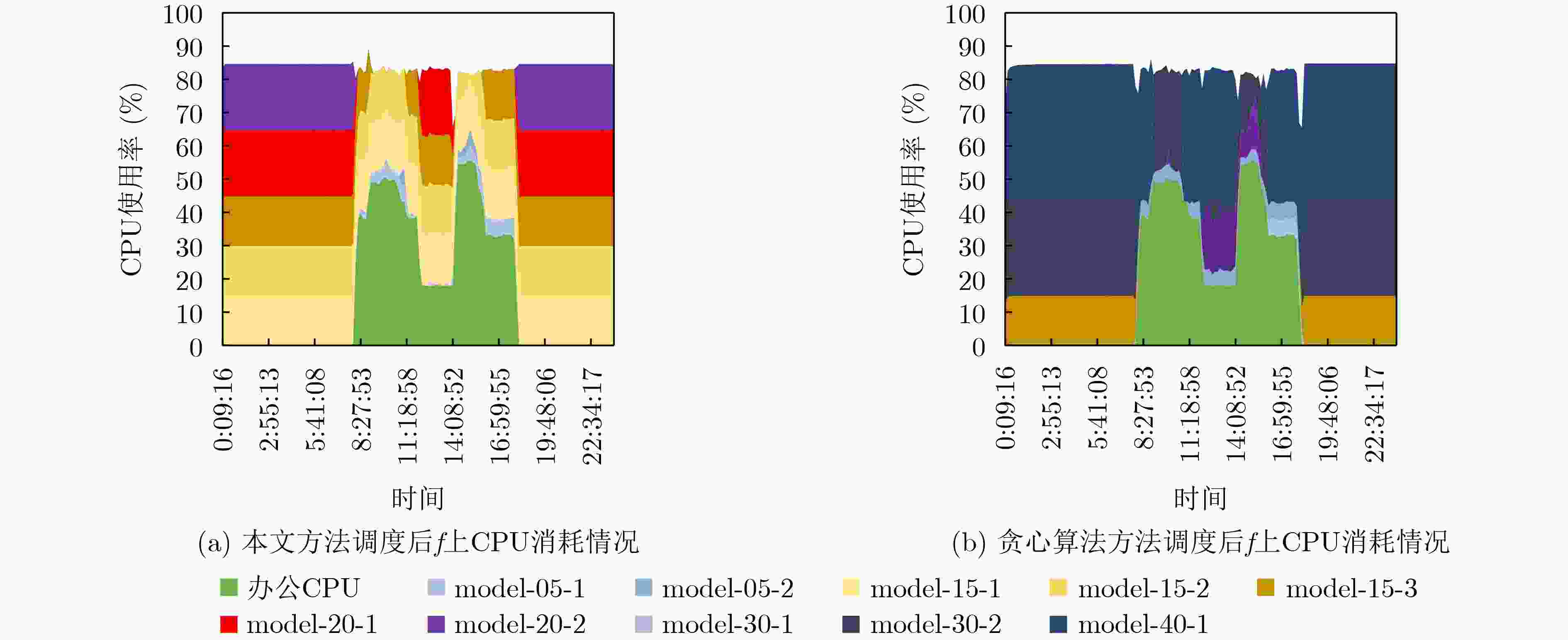
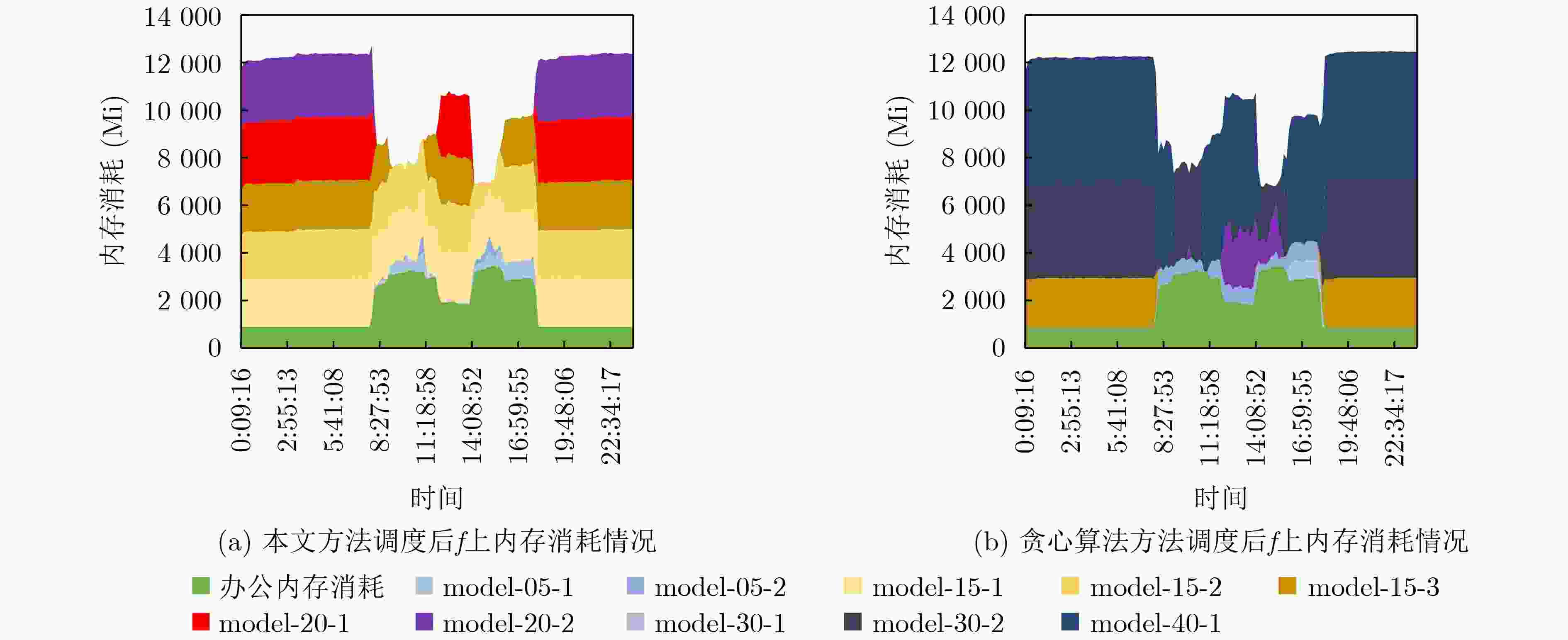
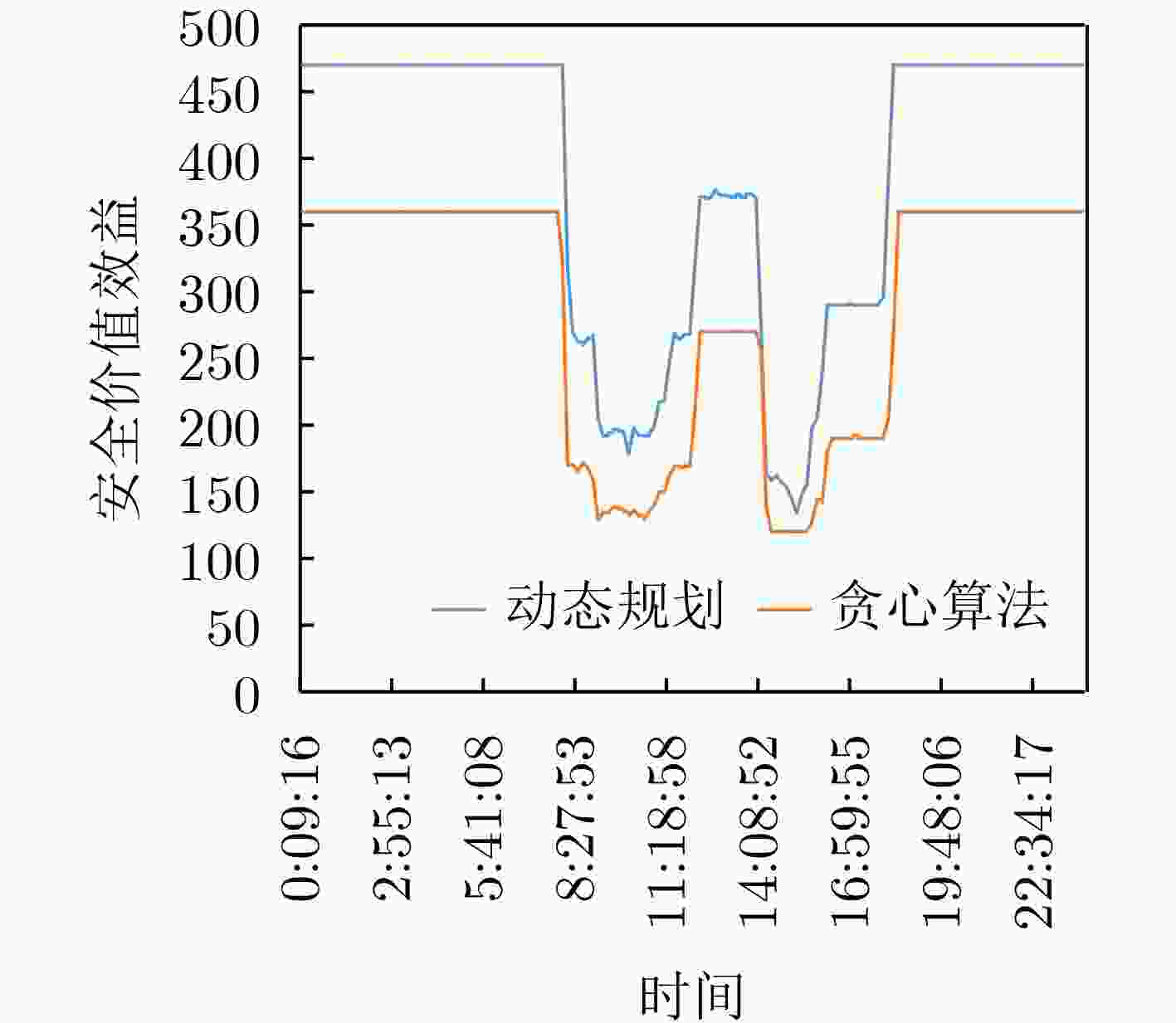
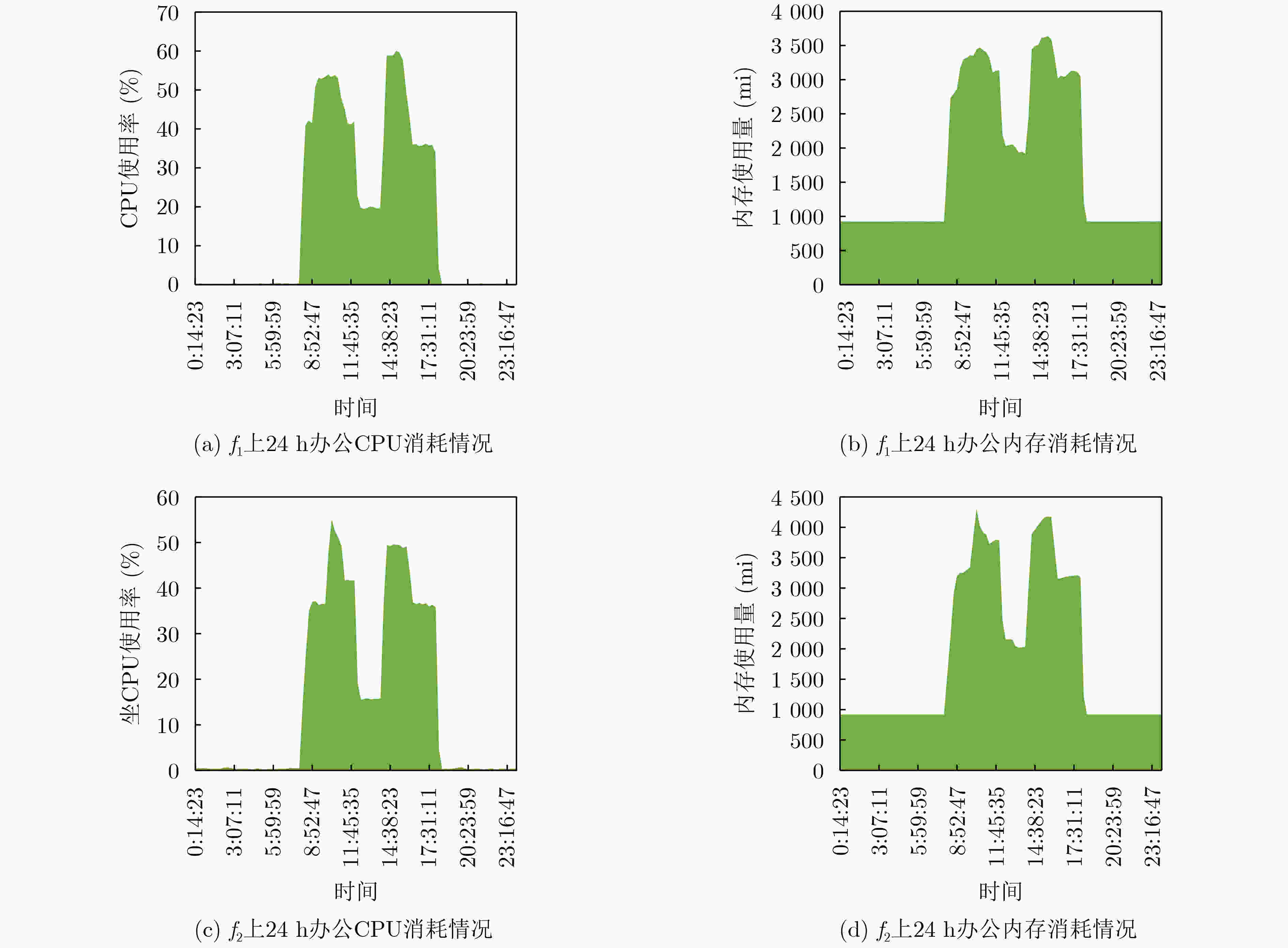
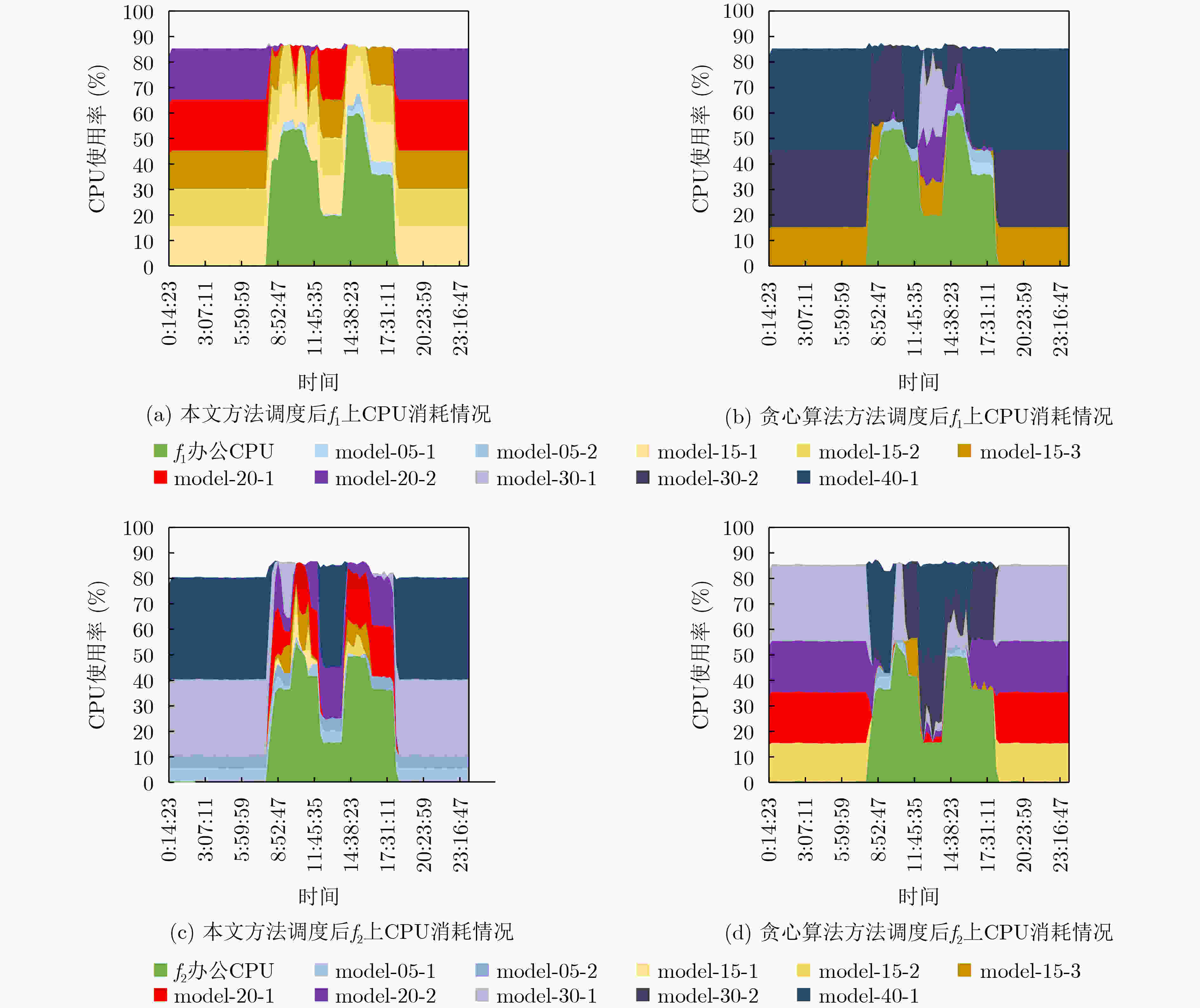
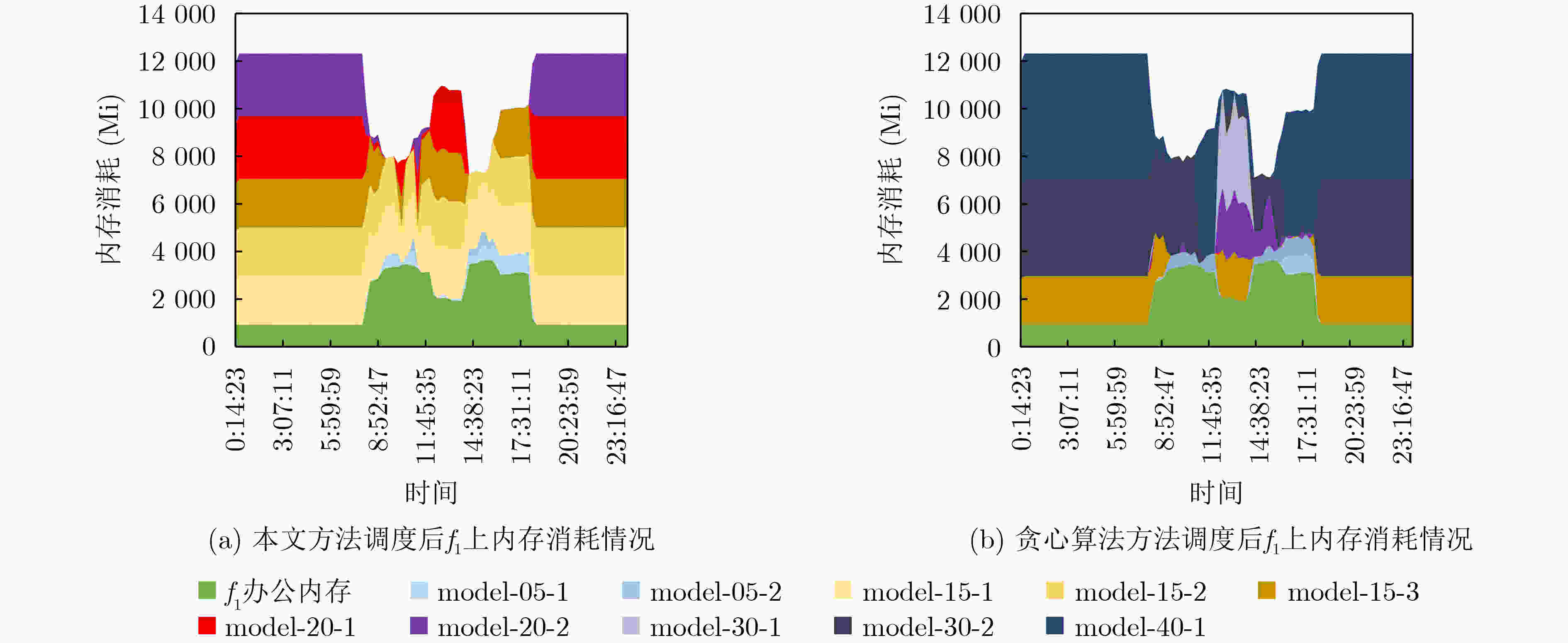
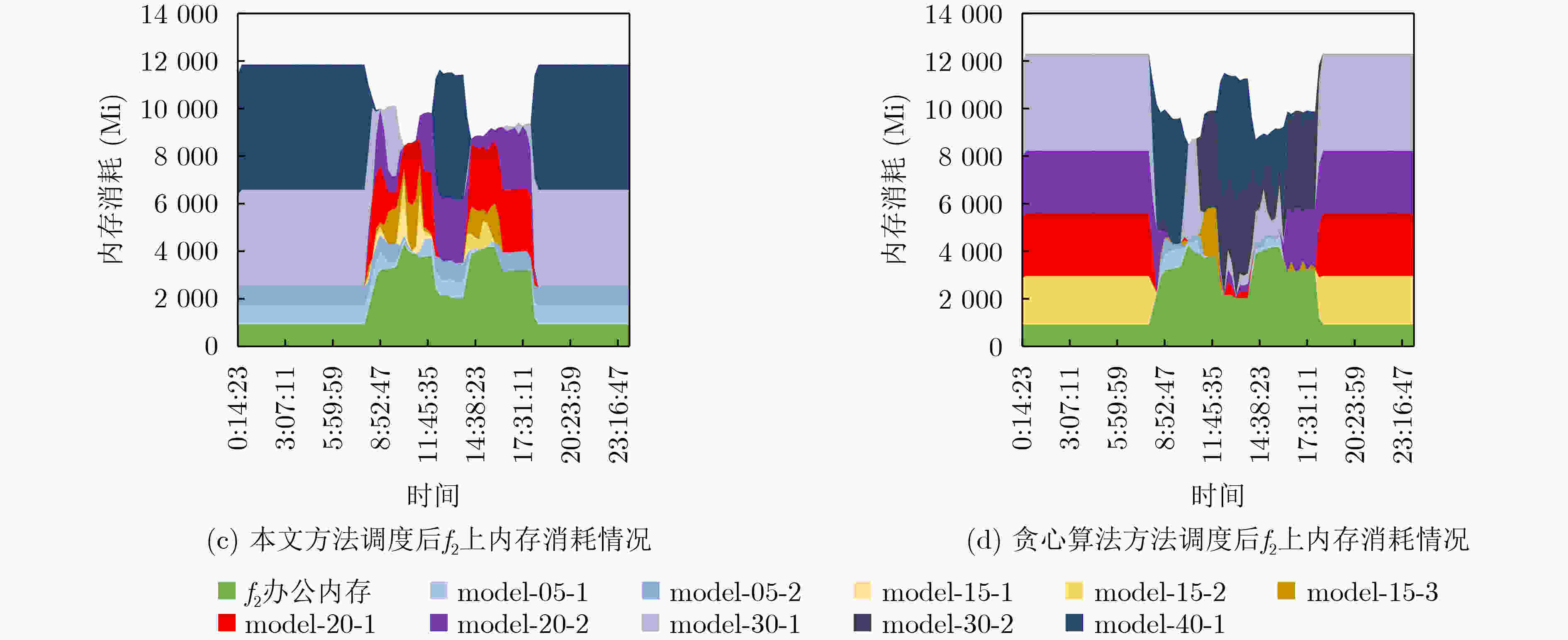
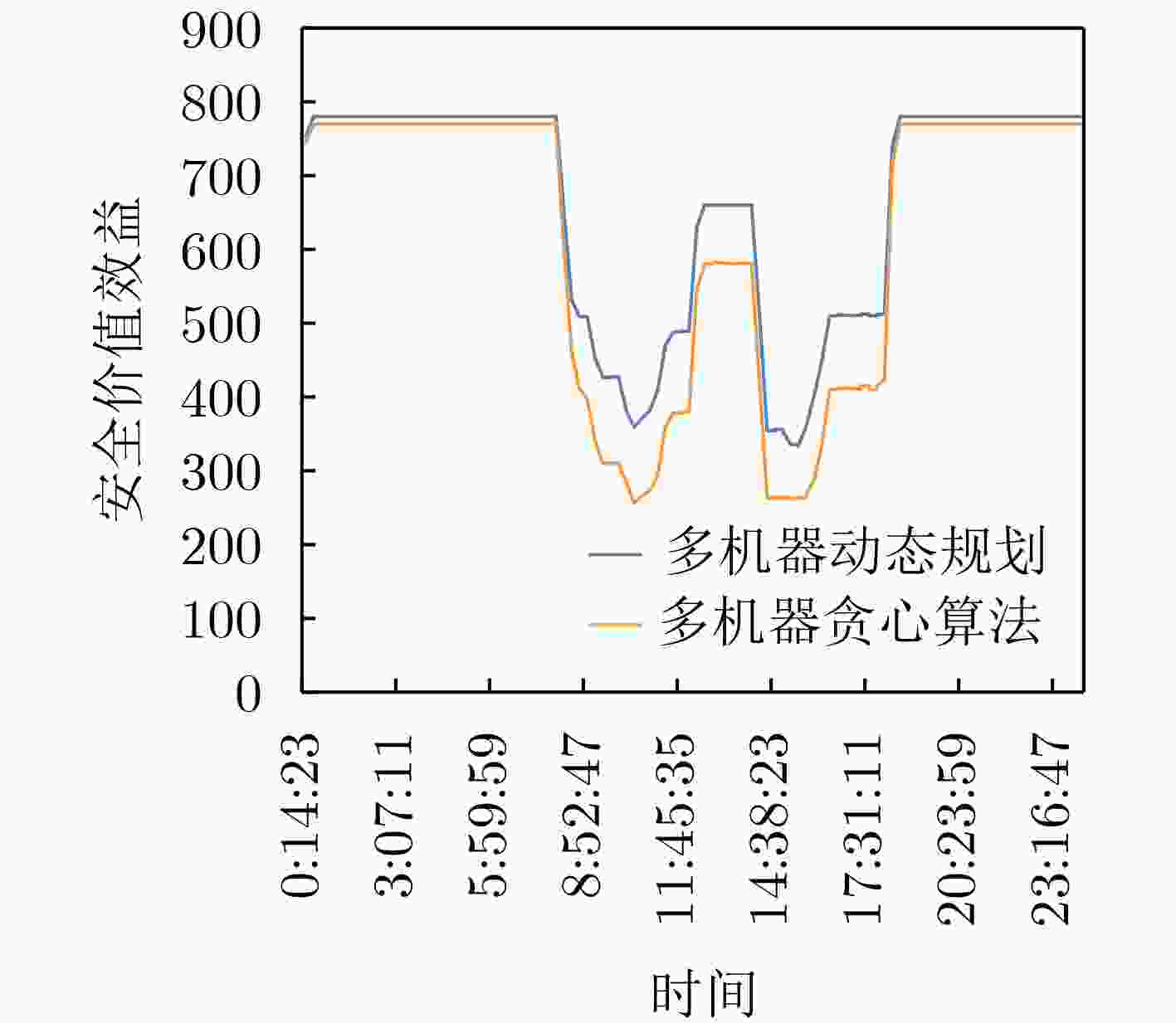


 下载:
下载:
