Research on Reflection and Transmission Characteristics of the Millimeter Wave Channel at 40~50 GHz for 6G ISAC
-
摘要: 为解决毫米波信道反射和透射特性测量数据不足、多层材料传播系数计算不准确和传播特性表征不明的问题,该文开展面向6G通信感知一体化(ISAC)的40~50 GHz毫米波信道反射和透射特性研究。首先,基于菲涅尔理论和射线弹跳追踪原理,提出一种室内多层建筑材料传播系数计算方法;然后,利用基于矢量网络分析仪的毫米波信道测量平台,开展40~50 GHz频率范围内多层木板和多层玻璃的反射和透射系数测量活动。结果表明,该方法与测量值间高度吻合,传播系数误差低于0.1,能够准确地刻画毫米波信道反射和透射特性变化规律。此外,研究还发现反射系数谐振特性和有效布儒斯特角特性依赖于电波极化、入射角和材料厚度。Abstract: Considering the insufficient measurements for reflection and transmission characteristics of millimeter-wave channel and inaccurate calculation methods for propagation coefficients of multilayer building materials, an extensive investigation on the reflection and transmission characteristics of millimeter-wave channel at 40–50 GHz is conducted for 6G Integrated Sensing And Communications (ISAC). Firstly, a method for calculating propagation coefficients of multilayer building materials is proposed based on Fresnel theory and shooting and bouncing ray principle. Furthermore, extensive measurement campaigns at 40–50 GHz are carried out to obtain reflection and transmission coefficients of multilayer wood and glass using VNA-based millimeter-wave channel sounder. The results show that the measured values are in good agreement with the theoretical values and the propagation coefficient error is less than 0.1, which verify the accuracy and effectiveness of the proposed method. Besides, it is also found that the resonant period and effective brewster angle of reflection coefficient are dependent on polarization, incident angle, and material thickness.
-
表 1 测量参数设置
测量参数 取值 测量参数 取值 中心频率(GHz) 45 天线类型 喇叭天线 频率带宽(GHz) 10 极化类型 水平/垂直 扫频点数 1001 天线高度(cm) 60 频点间隔(MHz) 10 发射功率(dBm) 0 中频带宽(kHz) 2 测量半径(cm) 50 表 2 多层材料几何参数和电磁参数
被测材料 几何参数 电磁参数 长度(cm) 宽度(cm) 粗糙度(μm) 总厚度(mm) 各层厚度(mm) ${\varepsilon _r}$ $\sigma $ (S/m) 3层木板 76.8 42.0 0.349 13.58 第1层:2.52 2.17 0.60 第2层:8.54 2.06 0.20 第3层:2.52 2.17 0.60 3层玻璃1 60.0 60.0 0.192 15.33 第1层:4.40 6.34 0.14 第2层:6.53 1.00 0 第3层:4.40 6.34 0.14 3层玻璃2 60.0 60.0 0.192 20.41 第1层:4.40 6.34 0.14 第2层:11.61 1.00 0 第3层:4.40 6.34 0.14 表 3 TE极化不同入射角下传播系数波动区间与拟合误差
被测
材料入射角
(°)传播系数波动区间 误差PCE Γmea Tmea Smea 3层
木板15 0.22-0.32 0.74-0.75 0.60-0.62 0.0480 30 0.28-0.36 0.67-0.68 0.68-0.71 0.0559 45 0.34-0.40 0.56-0.59 0.71-0.73 0.0675 60 0.42-0.55 0.43-0.51 0.72-0.75 0.0768 75 0.56-0.63 0.34-0.39 0.70-0.76 0.0801 3层
玻璃115 0.22-0.75 0.50-0.72 0.40-0.66 0.0247 30 0.24-0.85 0.39-0.70 0.39-0.75 0.0285 45 0.20-0.90 0.37-0.52 0.36-0.80 0.0328 60 0.35-0.91 0.05-0.48 0.24-0.84 0.0641 75 0.39-0.97 0.02-0.65 0.29-0.65 0.0594 3层
玻璃215 0.17-0.83 0.48-0.75 0.26-0.67 0.0480 30 0.21-0.90 0.38-0.68 0.35-0.74 0.0559 45 0.21-0.91 0.37-0.52 0.25-0.83 0.0675 60 0.39-0.91 0.08-0.59 0.31-0.91 0.0768 75 0.31-0.98 0.02-0.28 0.26-0.92 0.0801 表 4 毫米波信道反射系数的谐振周期
被测材料 谐振频率
间隔 (GHz)入射角(°) 15 30 45 60 75 3层木板 测量值 4.47 4.56 4.86 5.21 5.94 理论值 4.45 4.51 4.80 5.15 5.83 3层玻璃1 测量值 5.62 6.07 7.09 6.38 >10 理论值 5.60 6.04 7.02 6.30 >10 3层玻璃2 测量值 4.06 4.17 4.30 5.24 >10 理论值 4.03 4.10 4.20 5.13 >10 -
[1] IMT-2030(6G)推进组. 6G总体愿景与潜在关键技术白皮书[R]. 2021.IMT-2030 (6G) Promotion Group. White paper on 6G Vision and Candidate Technologies[R]. 2021. [2] WANG Jian, VARSHNEY N, GENTILE C, et al. Integrated sensing and communication: Enabling techniques, applications, tools and data sets, standardization, and future directions[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(23): 23416–23440. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3190845 [3] LIU Fan, CUI Yuanhao, MASOUROS C, et al. Integrated sensing and communications: Toward dual-functional wireless networks for 6G and beyond[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(6): 1728–1767. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3156632 [4] WANG Xiong, KONG Linghe, KONG Fanxin, et al. Millimeter wave communication: A comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(3): 1616–1653. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2844322 [5] HONG Wei, JIANG Zhihao, YU Chao, et al. The role of millimeter-wave technologies in 5G/6G wireless communications[J]. IEEE Journal of Microwaves, 2021, 1(1): 101–122. doi: 10.1109/JMW.2020.3035541 [6] CHANG Bo, TANG Wei, YAN Xiaoyu, et al. Integrated scheduling of sensing, communication, and control for mmWave/THz communications in cellular connected UAV networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(7): 2103–2113. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3157366 [7] EL FAITORI S and SALOUS S. Reflection and penetration loss wideband measurements of building materials at 28 GHz and 39 GHz[C]. The 2022 16th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Madrid, Spain, 2022: 1–4. [8] YANG Wenfei, HUANG Jie, ZHANG Jiliang, et al. Measurements of reflection and penetration loss in indoor environments in the 39-GHz band[C]. The 2021 15th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Dusseldorf, Germany, 2021: 1–5. [9] XING Yunchou, KANHERE O, JU Shihao, et al. Indoor wireless channel properties at millimeter wave and sub-terahertz frequencies[C]. 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Waikoloa, USA, 2019: 1–6. [10] LUO Jiangui, SHAO Yu, LIAO Xi, et al. Complex permittivity estimation for cloths based on QPSO method over (40 to 50) GHz[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(1): 600–605. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3005032 [11] ITU. Recommendation ITU-R P. 2040-1 Effects of building materials and structures on radiowave propagation above about 100 MHz[S]. 2015. [12] TEH C H, CHUNG B K, and LIM E H. Multilayer wall correction factors for indoor ray-tracing radio propagation modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(1): 604–608. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2943397 [13] BALASUBRAMANIAN M, CAMPBELL S D, WERNER P L, et al. Geometrical optics solution for periodic multilayer anisotropic slab scattering[C]. The 2020 Fourteenth International Congress on Artificial Materials for Novel Wave Phenomena, New York, USA, 2020: 130–132. [14] BORN M and WOLF E. Principles of Optics[M]. 7th expanded ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1999. [15] SHEIKH F, GAO Yuan, and KAISER T. A study of diffuse scattering in massive MIMO channels at terahertz frequencies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(2): 997–1008. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2944536 [16] 罗健桂. 典型建筑材料在毫米波频段下的电磁特性研究[D]. [硕士论文], 重庆邮电大学, 2020.LUO Jiangui. Electromagnetic property of typical building materials at millimeter-wave band[D]. [Master dissertation], Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2020. [17] DEGLI-ESPOSTI V, ZOLI M, VITUCCI E M, et al. A method for the electromagnetic characterization of construction materials based on Fabry–Pérot resonance[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 24938–24943. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2767278 -






 下载:
下载:
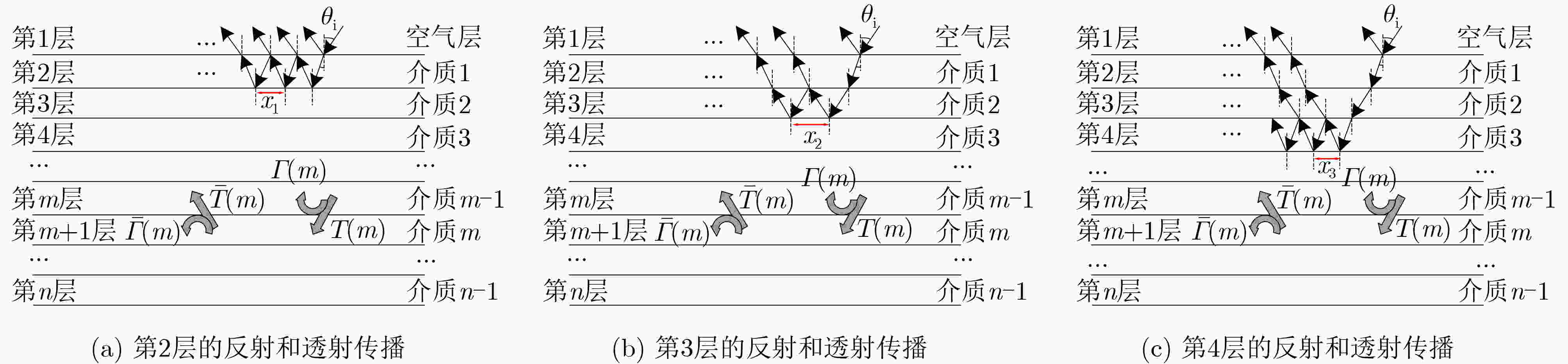


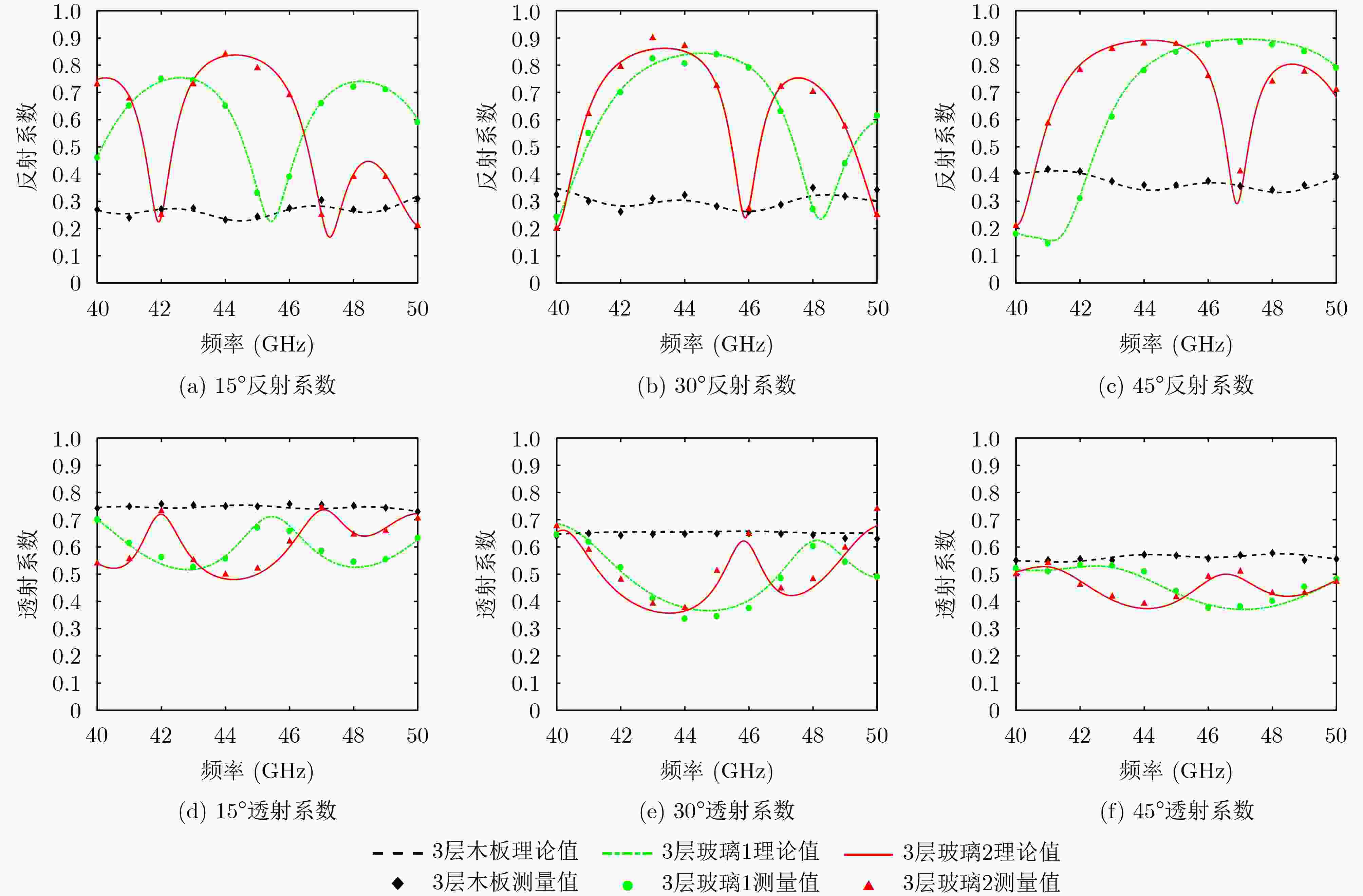




 下载:
下载:
