| [1] |
STOCKMAN H. Communication by means of reflected power[J]. Proceedings of the IRE, 1948, 36(10): 1196–1204. doi: 10.1109/JRPROC.1948.226245
|
| [2] |
BLETSAS A, SIACHALOU S, and SAHALOS J N. Anti-collision tags for backscatter sensor networks[C]. The 38th European Microwave Conference, Amsterdam, Netherlands: IEEE, 2008: 179–182.
|
| [3] |
KIMIONIS J, BLETSAS A, and SAHALOS J N. Bistatic backscatter radio for power-limited sensor networks[C]. 2013 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Atlanta, USA: IEEE, 2013: 353–358.
|
| [4] |
LIU V, PARKS A, TALLA V, et al. Ambient backscatter: Wireless communication out of thin air[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2013, 43(4): 39–50. doi: 10.1145/2534169.2486015
|
| [5] |
BHARADIA D, JOSHI K R, KOTARU M, et al. BackFi: High throughput WiFi backscatter[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2015, 45(4): 283–296. doi: 10.1145/2829988.2787490
|
| [6] |
ZHANG Pengyu, BHARADIA D, JOSHI K, et al. HitchHike: Practical backscatter using commodity WiFi[C]. The 14th ACM Conference on Embedded Network Sensor Systems CD-ROM, Stanford, USA, 2016: 259–271.
|
| [7] |
ZHENG Guangyuan, WEN Miaowen, CHEN Yingyang, et al. Interference exploitation for ambient backscatter communication networks via symbol level precoding[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(6): 1166–1170. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2022.3159777
|
| [8] |
GUO Wenbo, ZHAO Hongzhi, SONG Changqing, et al. Direct-link interference cancellation design for backscatter communications over ambient DVB signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2022, 68(2): 317–330. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2022.3142962
|
| [9] |
BISWAS R, SHEIKH M U, YIĞITLER H, et al. Direct path interference suppression requirements for bistatic backscatter communication system[C]. 2021 IEEE 93rd Vehicular Technology Conference, Helsinki, Finland, 2021: 1–5.
|
| [10] |
CHI Zicheng, LIU Xin, WANG Wei, et al. Leveraging ambient LTE traffic for ubiquitous passive communication[C/OL]. The Annual Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication on the Applications, Technologies, Architectures, and Protocols for Computer Communication, 2020: 172–185.
|
| [11] |
GU Bowen, LI Dong, XU Yongjun, et al. Many a little makes a mickle: Probing backscattering energy recycling for backscatter communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(1): 1343–1348. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3205888
|
| [12] |
ROSENTHAL J D and REYNOLDS M S. Hardware-efficient all-digital architectures for OFDM backscatter modulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(1): 803–811. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2020.3038860
|
| [13] |
LONG Ruizhe, LIANG Yingchang, GUO Huayan, et al. Symbiotic radio: A new communication paradigm for passive internet of things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(2): 1350–1363. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2954678
|
| [14] |
YE Yinghui, SHI Liqin, CHU Xiaoli, et al. Mutualistic cooperative ambient backscatter communications under hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(11): 7656–7668. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3201119
|
| [15] |
ZHANG Qianqian, ZHANG Lin, LIANG Yingchang, et al. Backscatter-NOMA: A symbiotic system of cellular and internet-of-things networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 20000–20013. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2897822
|
| [16] |
JAFAR S A and SHAMAI S. Degrees of freedom region of the MIMO X channel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2008, 54(1): 151–170. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2007.911262
|
| [17] |
SUH C and TSE D. Interference alignment for cellular networks[C]. The 46th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, Monticello, USA, 2008: 1037–1044.
|
| [18] |
MUNGARA R K, TÖLLI A, and JUNTTI M. Degrees of freedom and interference mitigation for MIMO interfering broadcast channels[C]. 2011 IEEE GLOBECOM Workshops, Houston, USA, 2011: 441–446.
|
| [19] |
LI Jingfu, FENG Wenjiang, YU F R, et al. Two new kinds of interference alignment schemes for cellular K-user MIMO downlink networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(11): 11827–11842. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3115806
|
| [20] |
SUO Long, LI Hongyan, ZHANG Shun, et al. Successive interference cancellation and alignment in K-user MIMO interference channels with partial unidirectional strong interference[J]. China Communications, 2022, 19(2): 118–130. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2022.02.010
|
| [21] |
LIU Guoqing, SHENG Min, WANG Xijun, et al. Interference alignment for partially connected downlink MIMO heterogeneous networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2015, 63(2): 551–564. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2015.2388450
|
| [22] |
MISHRA D and LARSSON E G. Multi-tag backscattering to MIMO reader: Channel estimation and throughput fairness[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(12): 5584–5599. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2937763
|





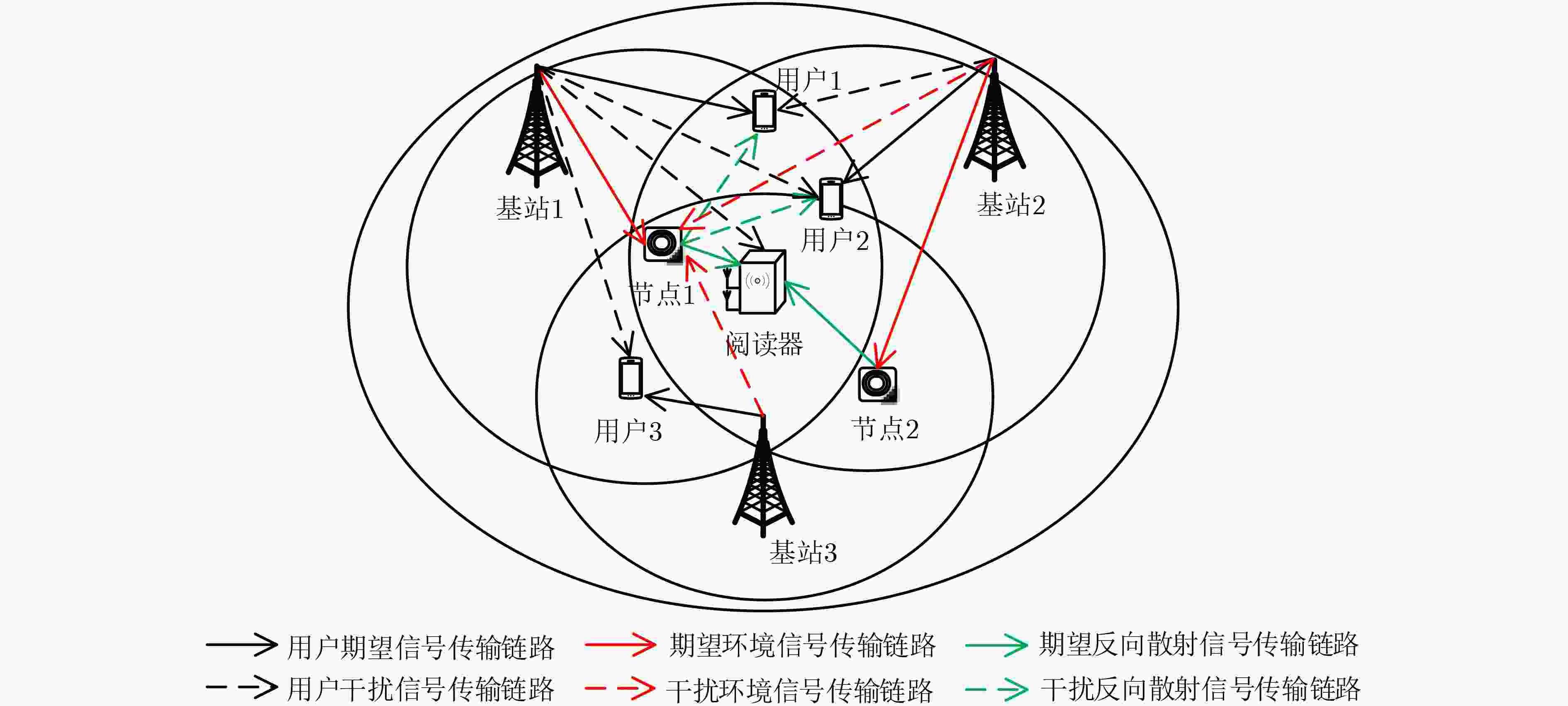
 下载:
下载:
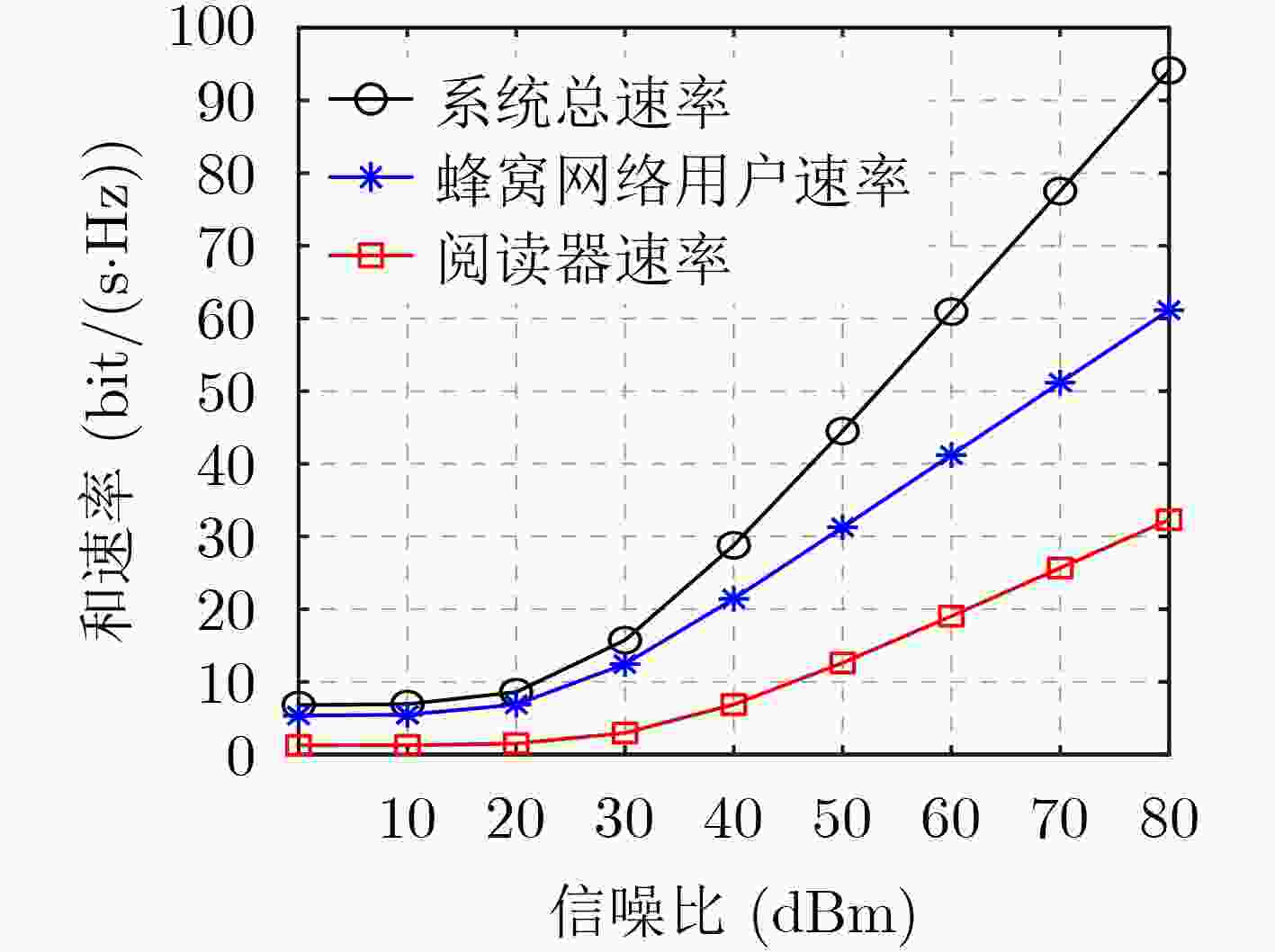
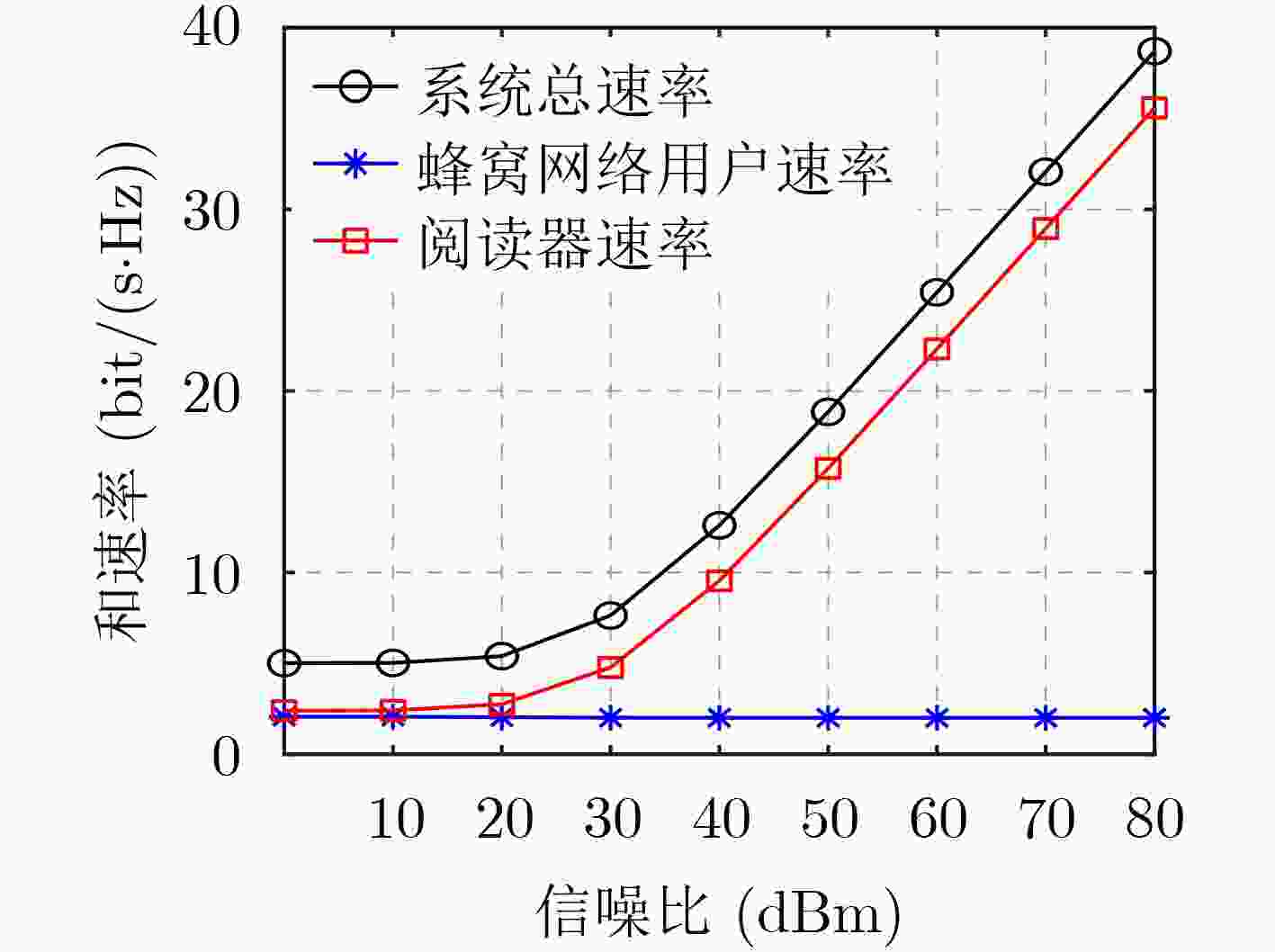
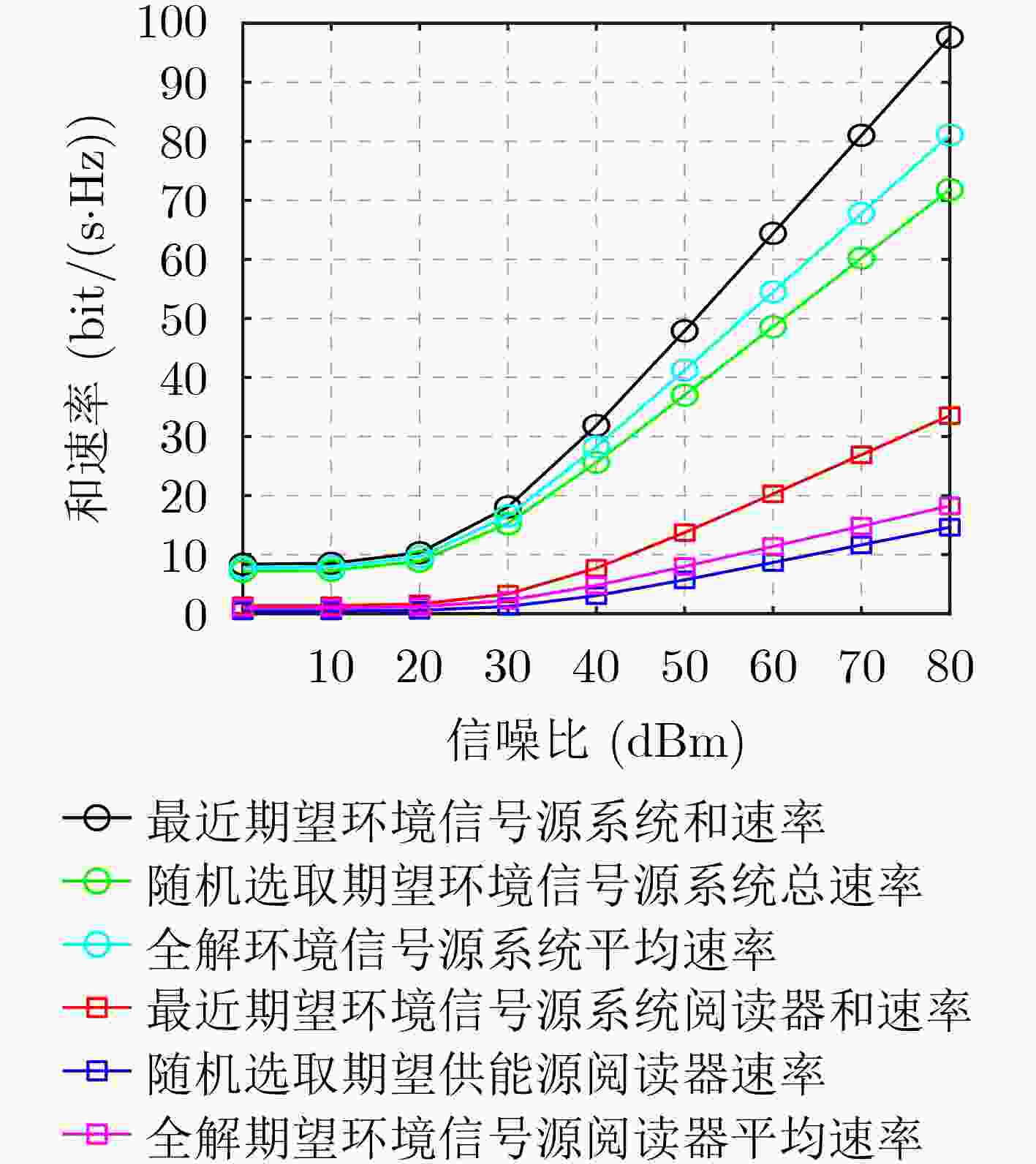


 下载:
下载:
