Solution Method of Line-of-sight Attitude in One-point to Multi-point Simultaneous Laser Communication System
-
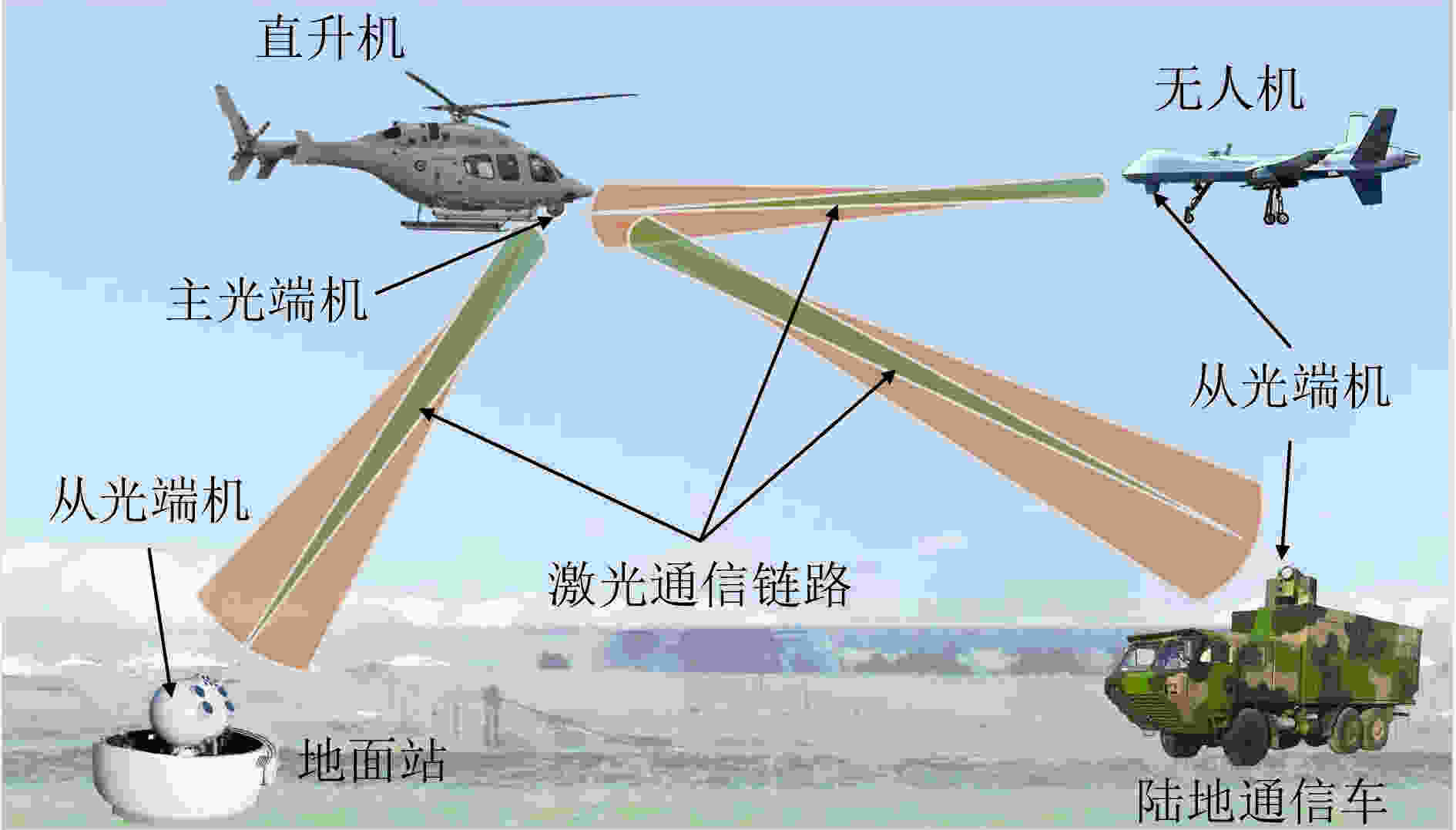
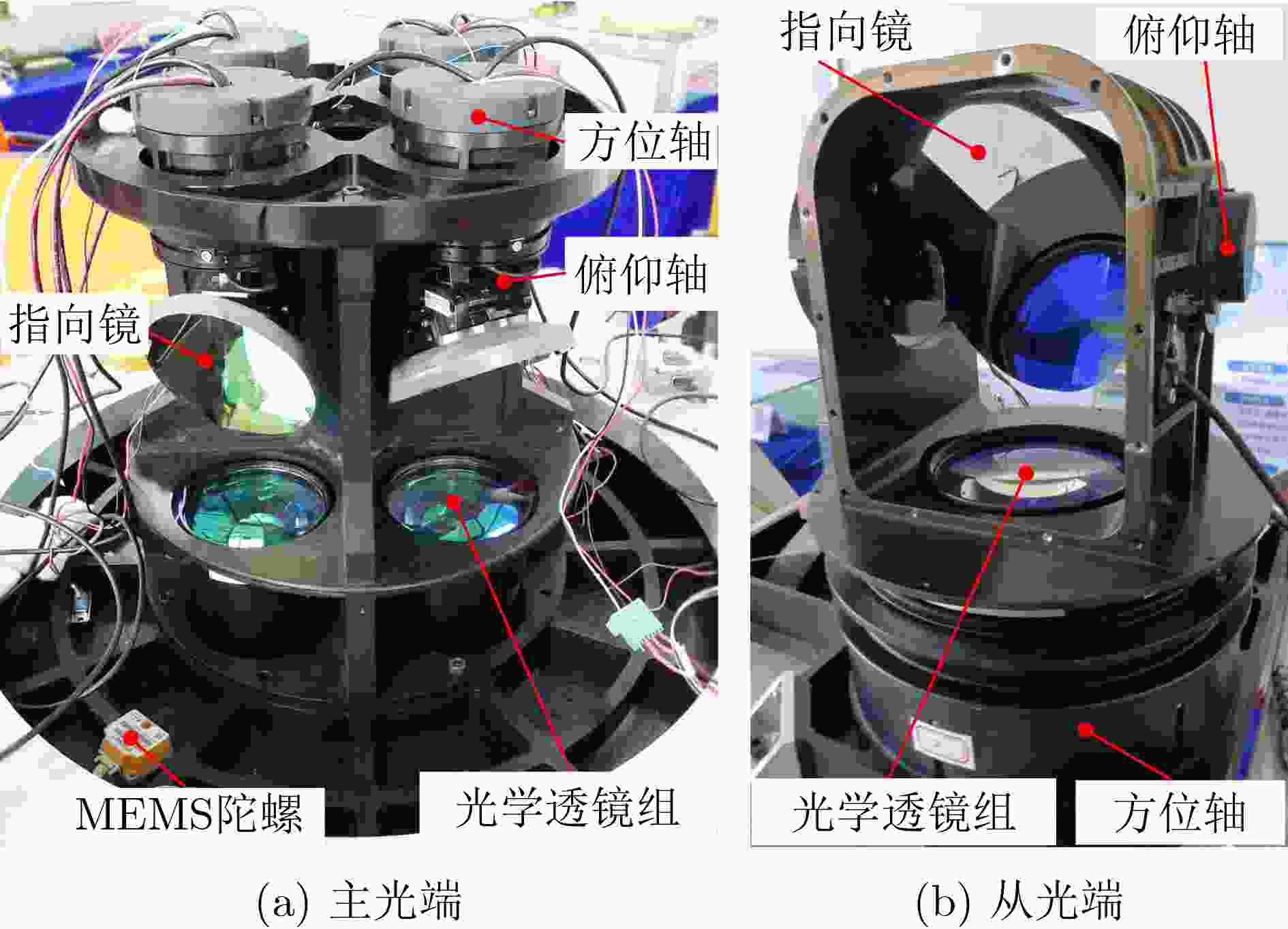
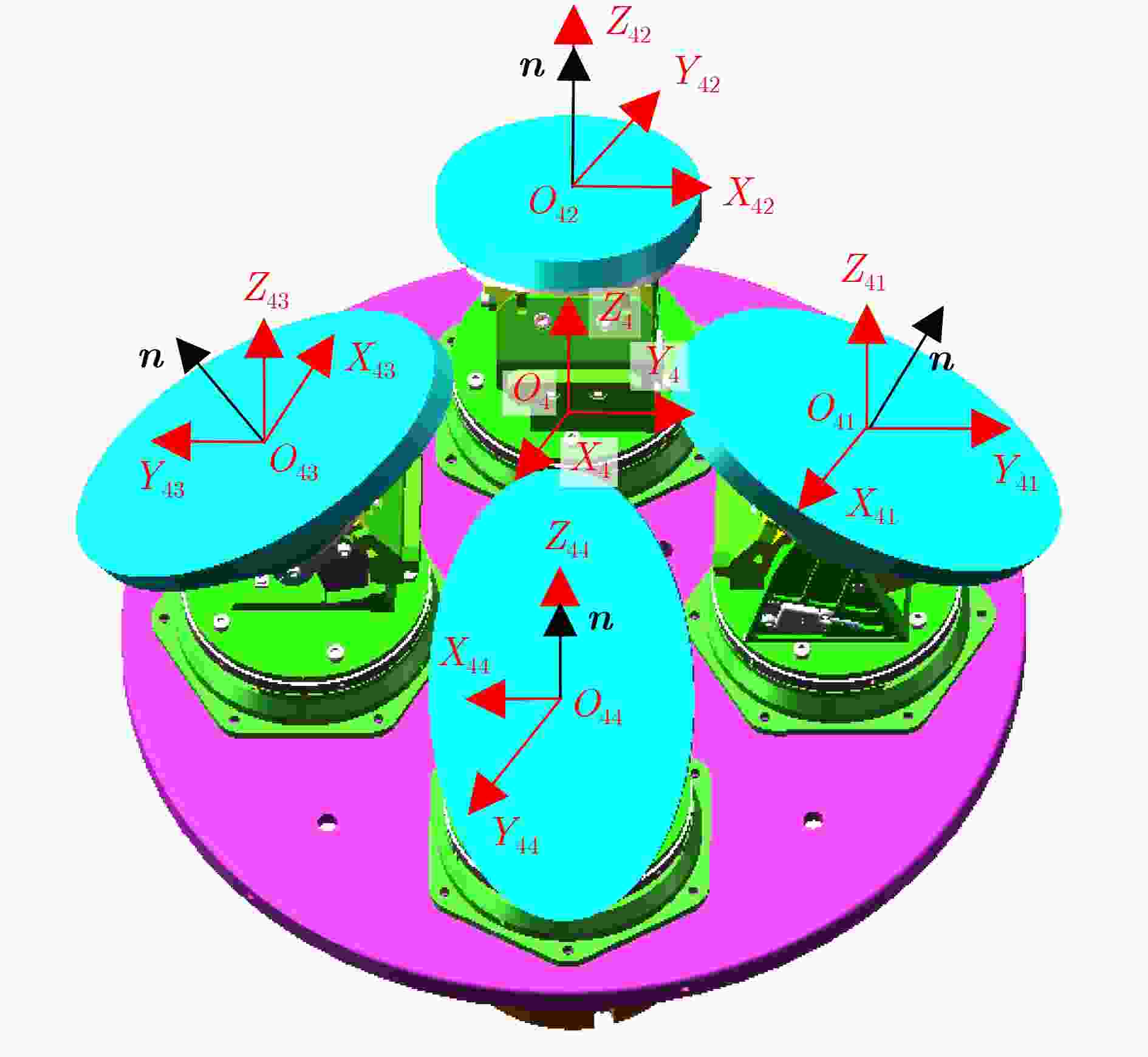
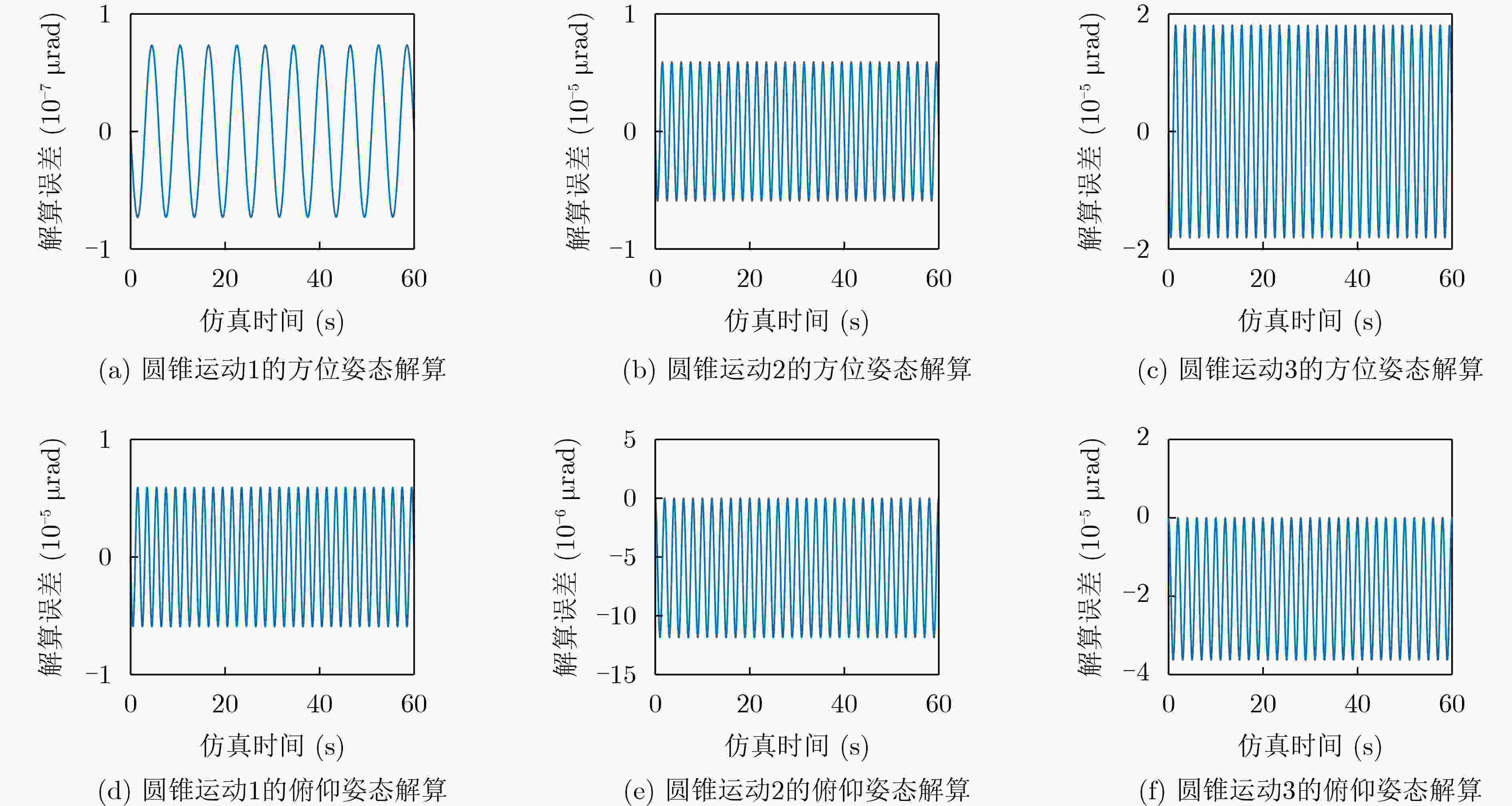
摘要: 针对1点对多点同时激光通信光端机的小型化、轻量化、网络化的技术需求,该文简化了光端机上的多个陀螺,提出一种利用单陀螺实现多个光学视轴同时稳定的方案。为求解多光学视轴姿态,根据欧拉定理重新定义了每个指向镜的坐标系,建立了基于转动4元数的多光学视轴姿态数学模型。为了求解该数学模型的参数,给出了相对应的4阶龙格库塔解算方法,并进行了“三子样”算法优化。最后,将数值解算结果与3种典型圆锥运动的真值进行比较,获得了不同指向镜视轴姿态的解算误差曲线。结果表明,在60 s仿真时间内4阶龙格库塔法对4个光学视轴姿态的联合解算精度优于10–4 μrad,验证了该模型的有效性。经过“三子样”算法优化后,3种典型圆锥运动的解算精度分别提高了3个数量级、3个数量级和1个数量级,达到了精度优化的目的。该方法的提出,为捷联稳定技术在激光通信组网中的应用提供了理论依据。Abstract: Considering the technical requirements of one-point to multi-point simultaneous laser communication for miniaturization, light weight and networking of optical transceiver, the multiple gyroscopes on the optical transceiver are simplified, and a scheme of realizing simultaneous stability of multiple optical line-of-sights by using a single gyroscope is proposed. In order to calculate the attitude of multiple optical line-of-sights, the coordinate system of each pointing mirror is redefined according to the Euler theorem, and the mathematical model of multiple optical line-of-sights attitude based on rotating quaternion is established. In order to calculate the parameters of the mathematical model, the fourth-order Runge-Kutta algorithm is given, and the three-sample algorithm is optimized. Finally, the numerical solution results are compared with the true values of three typical cone motions, and the solution error curves of different pointing mirror line-of-sight postures are obtained. The results show that the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method is superior to 10-4 μrad in the simulation time of 60 s, which verifies the effectiveness of the model. After the optimization of the three-sample algorithm, the accuracy of the joint solution of three typical conical motions is improved by 3 orders of magnitude, 3 orders of magnitude and 1 order of magnitude respectively, and the purpose of accuracy optimization is achieved. This method provides a theoretical basis for the application of strapdown stabilization technology to laser communication networking.
-
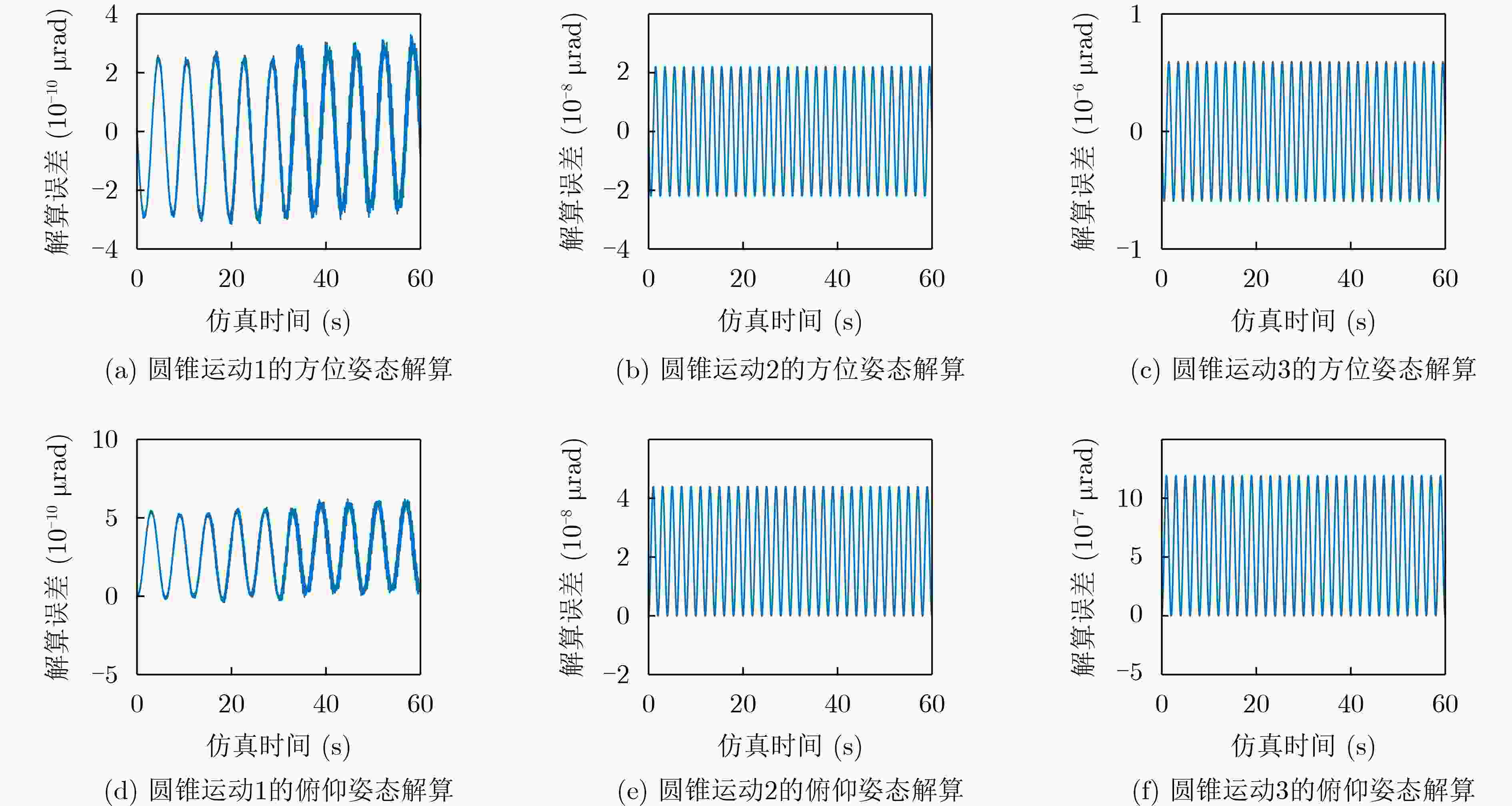
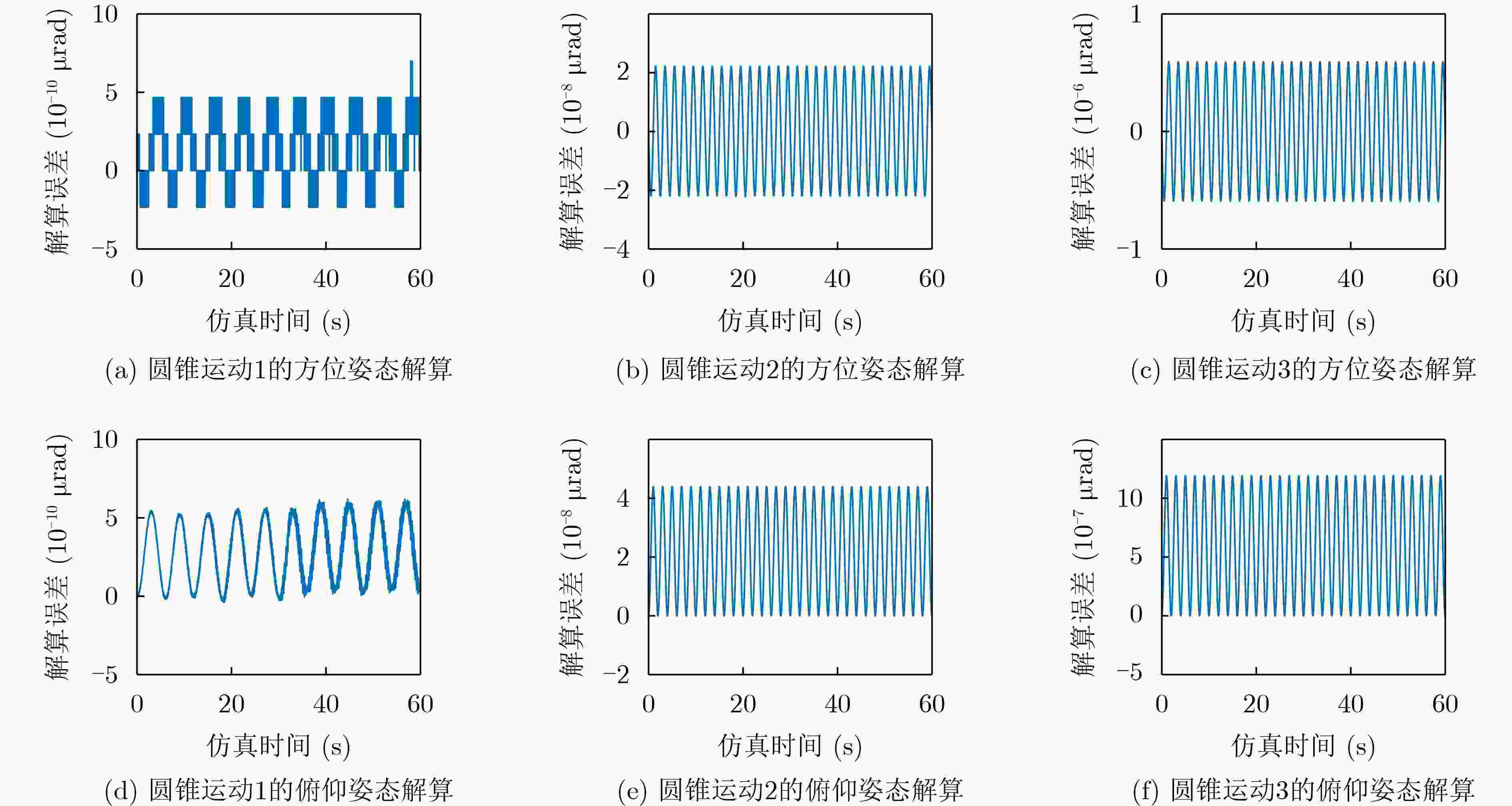
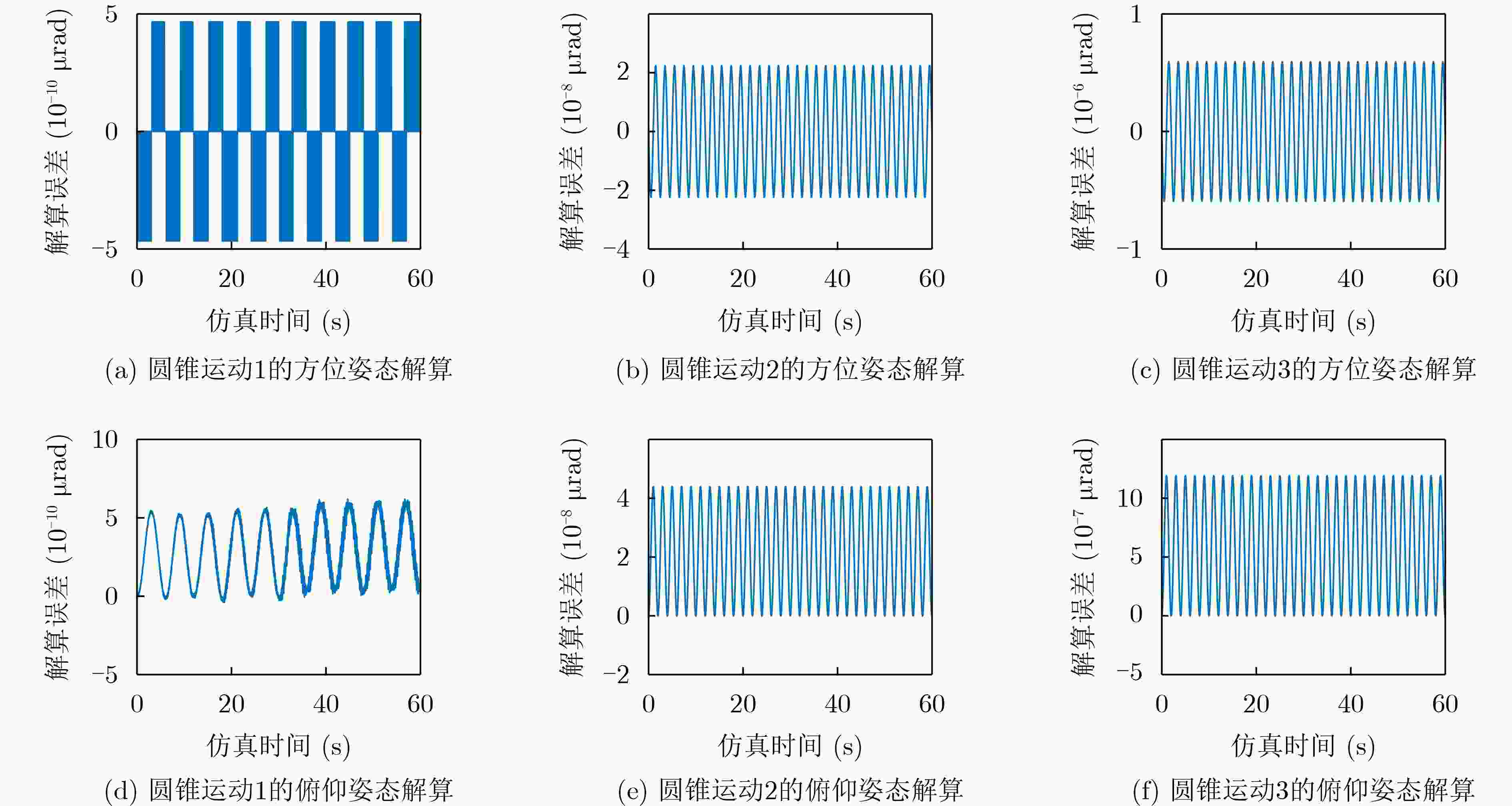
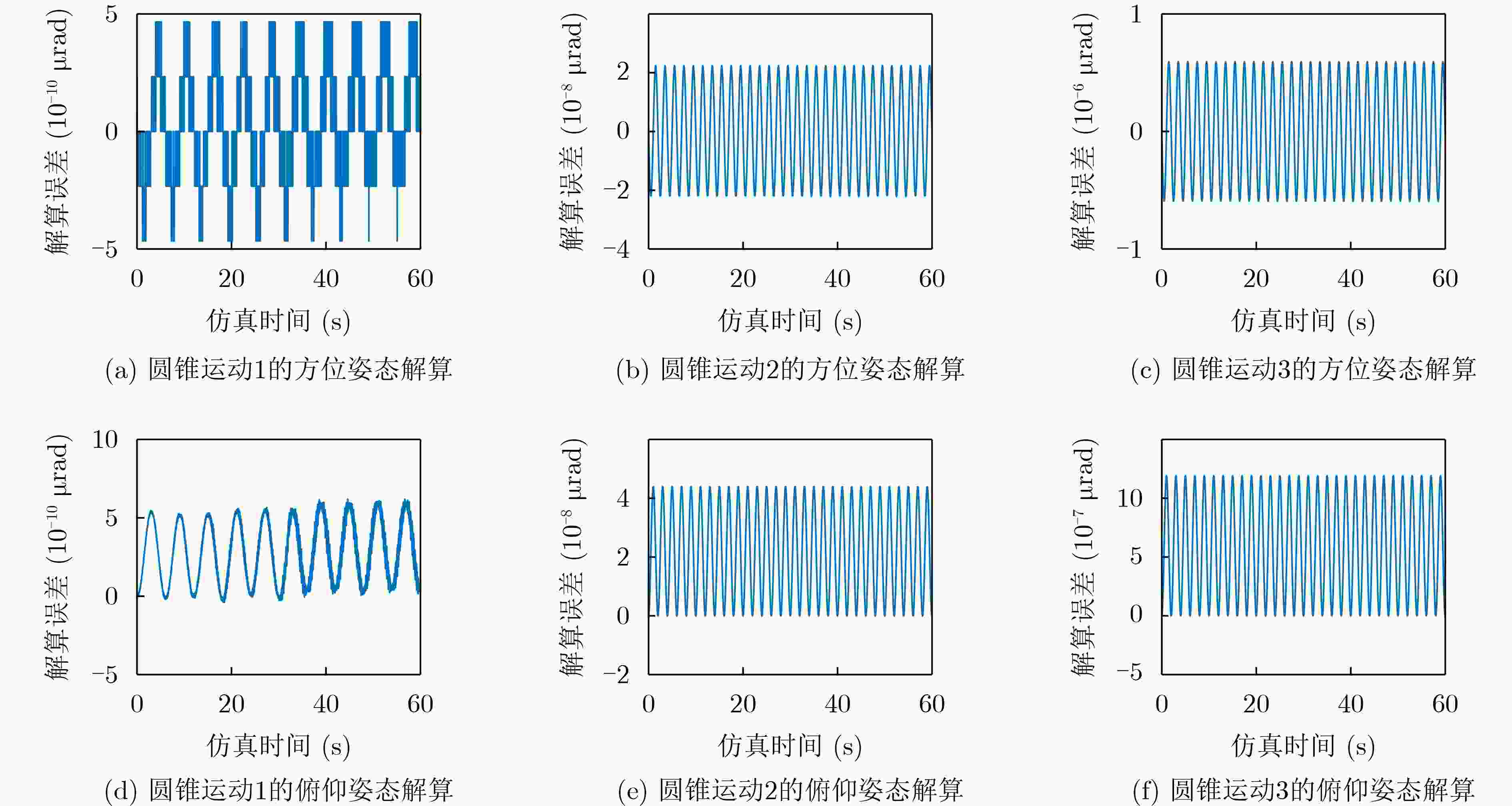
表 1 4阶龙格库塔法数值解算误差
圆锥运动 解算姿态 误差(μrad) 圆锥运动1 方位 7.3×10–8 俯仰 1.5×10–7 圆锥运动2 方位 5.9×10–6 俯仰 1.2×10–5 圆锥运动3 方位 1.8×10–5 俯仰 3.6×10–5 表 2 “三子样”优化算法数值解算误差(μrad)
指向镜坐标系 姿态 圆锥运动1 圆锥运动2 圆锥运动3 O41X41Y41Z41 方位 3.3×10–10 2.2×10–8 5.9×10–7 俯仰 6.2×10–10 4.4×10–8 1.2×10–6 O42X42Y42Z42 方位 7×10–10 2.2×10–8 5.9×10–7 俯仰 6.2×10–10 4.4×10–8 1.2×10–6 O43X43Y43Z43 方位 4.7×10–10 2.2×10–8 5.9×10–7 俯仰 6.2×10–10 4.4×10–8 1.2×10–6 O44X44Y44Z44 方位 4.7×10–10 2.2×10–8 5.9×10–7 俯仰 6.2×10–10 4.4×10–8 1.2×10–6 -
[1] WANG Chao, ZHANG Tao, TONG Shoufeng, et al. Pointing and tracking errors due to low-frequency deformation in inter-satellite laser communication[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 2019, 66(4): 430–437. doi: 10.1080/09500340.2018.1538467 [2] CHAUDHRY A U and YANIKOMEROGLU H. Laser intersatellite links in a starlink constellation: A classification and analysis[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2021, 16(2): 48–56. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2021.3063706 [3] LI Rui, LIN Baojun, LIU Yingchun, et al. A survey on laser space network: Terminals, links, and architectures[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 34815–34834. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3162917 [4] 徐常志, 靳一, 李立, 等. 面向6G的星地融合无线传输技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 28–36. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200363XU Changzhi, JIN Yi, LI Li, et al. Wireless transmission technology of satellite-terrestrial integration for 6G mobile communication[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 28–36. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200363 [5] 高铎瑞, 李天伦, 孙悦, 等. 空间激光通信最新进展与发展趋势[J]. 中国光学, 2018, 11(6): 901–913. doi: 10.3788/CO.20181106.0901GAO Duorui, LI Tianlun, SUN Yue, et al. Latest developments and trends of space laser communication[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(6): 901–913. doi: 10.3788/CO.20181106.0901 [6] ROSS M. Unique multiaccess laser communications transciever system[C]. SPIE 1218, Free-Space Laser Communication Technologies II, Los Angeles, USA, 1990: 585–596. [7] 姜会林, 胡源, 丁莹, 等. 空间激光通信组网光学原理研究[J]. 光学学报, 2012, 32(10): 1006003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201232.1006003JIANG Huilin, HU Yuan, DING Ying, et al. Optical principle research of space laser communication network[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2012, 32(10): 1006003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201232.1006003 [8] 赵佰秋, 于笑楠, 董岩, 等. 空间激光通信组网反射镜跟踪性能[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(9): 0906007. doi: 10.3788/LOP202158.0906007ZHAO Baiqiu, YU Xiaonan, DONG Yan, et al. Tracking performance of mirrors in space laser communication networking[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(9): 0906007. doi: 10.3788/LOP202158.0906007 [9] 宋江鹏, 孙广利, 周荻, 等. 反射镜光电平台视轴稳定技术研究[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2015, 44(6): 1904–1911. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2015.06.041SONG Jiangpeng, SUN Guangli, ZHOU Di, et al. Line-of-sight stabilization techniques for mirror electro-optical platform[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2015, 44(6): 1904–1911. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2015.06.041 [10] 王琦, 孙广利, 黎纯宁, 等. 基于半捷联方式的反射镜视轴稳定技术[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2015, 44(10): 3070–3075. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2015.10.035WANG Qi, SUN Guangli, LI Chunning, et al. Inertial line-of-sight stabilization technique of semi-strapdown control using mirrors[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2015, 44(10): 3070–3075. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2015.10.035 [11] 张荣辉, 贾宏光, 陈涛, 等. 基于四元数法的捷联式惯性导航系统的姿态解算[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2008, 16(10): 1963–1970. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.2008.10.029ZHANG Ronghui, JIA Hongguang, CHEN Tao, et al. Attitude solution for strapdown inertial navigation system based on quaternion algorithm[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2008, 16(10): 1963–1970. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.2008.10.029 [12] IGNAGNI M B. Efficient class of optimized coning compensation algorithms[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 1996, 19(2): 424–429. doi: 10.2514/3.21635 [13] 熊丽娟, 朱洪涛, 王志勇, 等. 圆锥运动下几种姿态算法的比较与误差建模[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2020, 40(3): 39–44. doi: 10.15892/j.cnki.djzdxb.2020.03.010XIONG Lijuan, ZHU Hongtao, WANG Zhiyong, et al. Compatison and Error Modeling of Several Altitude Algorithms Under Coning Motion[J]. Journal of Projectiles,Rockets,Missiles and Guidance, 2020, 40(3): 39–44. doi: 10.15892/j.cnki.djzdxb.2020.03.010 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
