Adaptive Image Interpolation Algorithm and Acceleration Engine Co-Design
-
摘要: 为提高高清彩色图像超分辨率重建效果,该文提出了一种基于边缘对比度的新型自适应图像插值算法。使用边缘对比度检测和不同尺度的感受野来自适应选择Lanczos插值的系数,自适应性和不同感受野可以进一步提升图像放大质量,图像质量相比于双线性插值平均峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高1.1 dB,结构相似度(SSIM)提高0.025,图像感知相似度(LPIPS)提高0.051,相比于双三次插值平均PSNR提高0.34 dB,SSIM提高0.01,LPIPS提高0.033。同时为减少硬件资源以及提高存储效率协同设计了一种高并行、高能效的加速插值引擎架构,通过两级数据重用和系数脉动机制极大提高计算访存比。加速引擎在16 nm工艺库的综合结果达到2 GHz时钟频率;在Xilinx Zynq Ultra scale+ xczu15eg FPGA上工作频率达到200 MHz,帧速度(fps)达到60的实时性能。Abstract: In order to improve the super-resolution reconstruction effect of the high-definition color image, a new adaptive image interpolation algorithm based on edge contrast is proposed, which chooses adaptively the coefficients of Lanczos interpolation by edge contrast detection and receptive fields with different scales. Adaptability and diverse receptive fields can further improve the quality of image magnification. Compared with the bilinear interpolation algorithm, the Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR), Structural SIMilarity (SSIM) and Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (LPIPS) are improved by 1.1 dB, 0.025, 0.051, respectively. Compared with the bicubic interpolation algorithm, the PSNR, SSIM and LPIPS are improved by 0.34 dB, 0.01, 0.033, respectively. Moreover, in order to reduce the hardware resources and improve the storage efficiency, a high parallelized and high efficiency accelerated architecture is proposed. A 2-level data reuse and coefficients pulsation mechanism are employed to improve the computation-memory access ratio greatly. The synthesis result of the acceleration engine in the 16nm process library can reach the 2 GHz clock frequency. The operating frequency of FPGA project deployed in Xilinx Zynq Ultra scale+ xczu15eg can reach up to 200 MHz as well, which means that the algorithm can adapt to the frame rate (fps) up to 60.
-
Key words:
- Interpolation algorithm /
- Adaptive /
- Parallelism /
- Energy efficiency /
- Acceleration engine
-
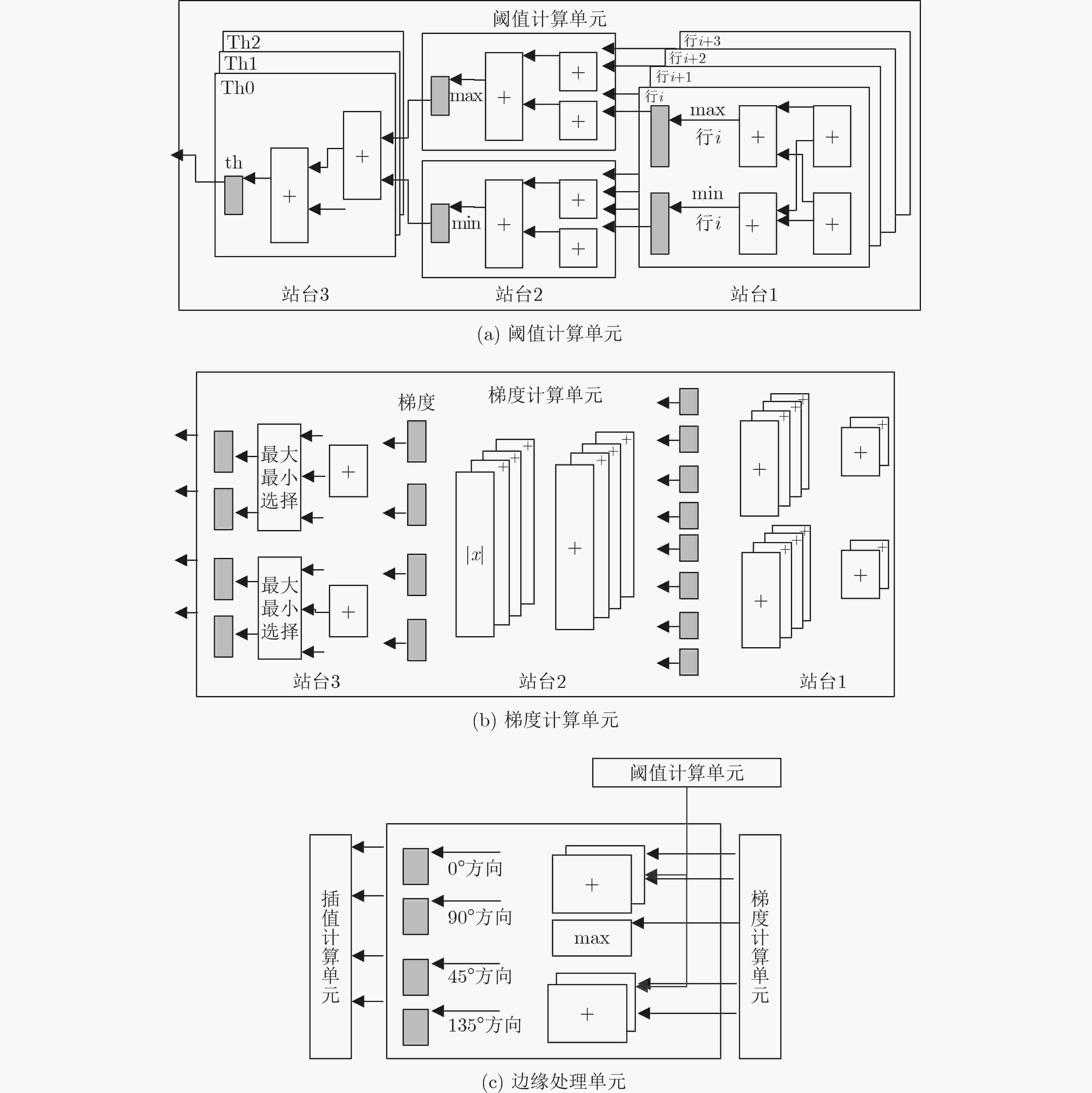
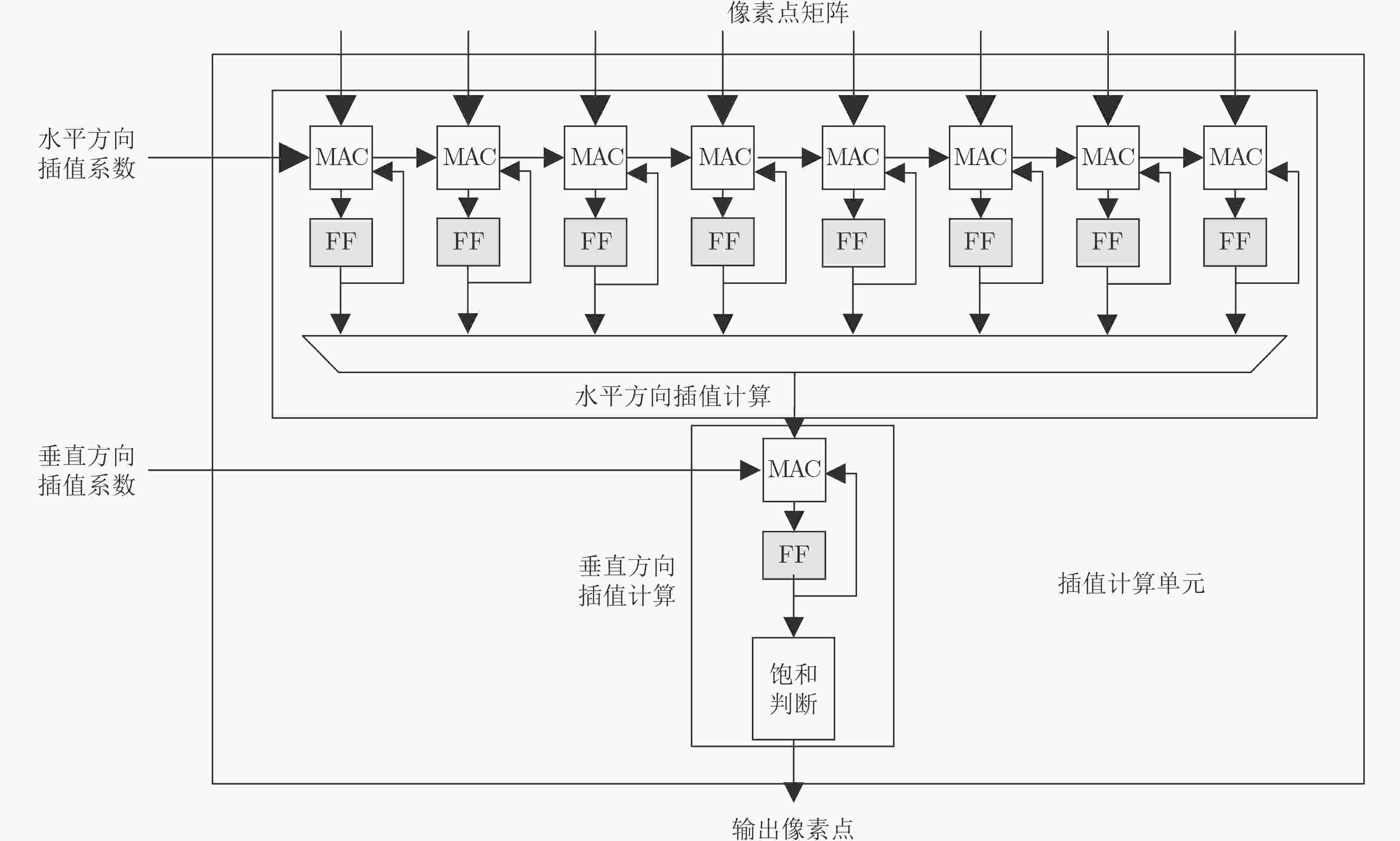
表 1 乘加器单元数目
模块名 数量 备注 水平插值计算单元 8×3 int8×int16+int24/
int16×int16+int32竖直插值计算单元 1×3 int8×int16+int24/
int16×int16+int32表 2 加法器单元数目
模块名 数量 位宽 阈值计算单元 24 Int8 梯度计算单元 4 Int8 8 Int9 4+4(绝对值) Int10 2 Int11 边缘处理单元 4 Int12 近似灰度转换 21 Int8 表 3 插值引擎的RAM容量表
模块名 数量 容量 插值系数 4 8×4×2B 共计 256B 表 4 插值引擎的寄存器数目表
模块名 数量 位宽 总数 像素寄存器阵列 88 3B 264 Byte 近似灰度阵列 42 1B 42 Byte 乘累加结果缓存 51 4B+2B 306 Byte 控制+边缘检测 80 Byte 共计 692 Byte 表 5 不同算法的复杂度对比
算法 时间复杂度 乘法次数 像素点数量 双线性插值 O( n) 6 4 双三次插值 O(n) 20 16 Lanczos3插值 O(n) 42 36 Lanczos4插值 O(n) 72 64 本文算法 O(n) 72 64 表 6 不同算法的PSNR对比(dB)
算法 平均PSNR 最佳PSNR 最差PSNR 双线性插值 30.88 35.08 23.15 双三次插值 31.59 36.00 23.66 Lanczos3插值 31.82 36.34 23.82 Lanczos4插值 31.84 36.39 23.83 本文算法 31.93 36.42 23.94 表 7 不同算法的SSIM对比
算法 平均SSIM 最佳SSIM 最差SSIM 双线性插值 0.849 0.920 0.599 双三次插值 0.864 0.936 0.625 Lanczos3插值 0.868 0.942 0.631 Lanczos4插值 0.869 0.944 0.632 本文算法 0.874 0.947 0.650 表 8 不同算法的LPIPS对比
算法 平均LPIPS 最佳LPIPS 最差LPIPS 双线性插值 0.291 0.133 0.517 双三次插值 0.273 0.104 0.513 Lanczos3插值 0.276 0.098 0.523 Lanczos4插值 0.275 0.096 0.520 本文算法 0.244 0.079 0.479 表 9 FPGA硬件实现的指标对比
-
[1] MEIJERING E H W, ZUIDERVELD K J, and VIERGEVER M A. Image reconstruction by convolution with symmetrical piecewise nth-order polynomial kernels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1999, 8(2): 192–201. doi: 10.1109/83.743854 [2] KEYS R G. Cubic convolution interpolation for digital image processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1981, 29(6): 1153–1160. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1981.1163711 [3] KWOK W and SUN H. Multi-directional interpolation for spatial error concealment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 1993, 39(3): 455–460. doi: 10.1109/30.234620 [4] LI Xin and ORCHARD M T. New edge-directed interpolation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(10): 1521–1527. doi: 10.1109/83.951537 [5] CHEN Meijuan, HUANG C H, and LEE W L. A fast edge-oriented algorithm for image interpolation[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2005, 23(9): 791–798. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2005.05.005 [6] ZHANG Xiangjun and WU Xiaolin. Image interpolation by adaptive 2-D autoregressive modeling and soft-decision estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2008, 28(6): 887–896. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2008.924279 [7] JAKHETIYA V, KUMAR A, and TIWARI A K. Image interpolation by adaptive 2-D autoregressive modeling[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 7546, Second International Conference on Digital Image Processing, Singapore, 2010. [8] LIU Yiwei, JIANG Zhuqing, WANG Yibo, et al. Single-frame reconstruction for improvement of off-axis digital holographic imaging based on image interpolation[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(24): 6623–6626. doi: 10.1364/OL.405578 [9] WANG Qiang, TANG Xiaoou, and SHUM H. Patch based blind image super resolution[C]. Proceedings of the Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Beijing, China, 2005: 709–716. [10] CHAN T M, ZHANG Junping, PU Jian, et al. Neighbor embedding based super-resolution algorithm through edge detection and feature selection[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2009, 30(5): 494–502. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2008.11.008 [11] GAO Xinbo, ZHANG Kaibing, TAO Dacheng, et al. Joint learning for single-image super-resolution via a coupled constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(2): 469–480. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2161482 [12] JI Jiahuan, ZHONG Baojiang, and MA Kaikuang. Image interpolation using multi-scale attention-aware inception network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 9413–9428. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3026632 [13] NIU Ben, WEN Weilei, REN Wenqi, et al. Single image super-resolution via a holistic attention network[C]. Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 191–207. [14] WEI Pengxu, XIE Ziwei, LU Hannan, et al. Component divide-and-conquer for real-world image super-resolution[C]. Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 101–117. [15] DENG Xin, ZHANG Yutong, XU Mai, et al. Deep coupled feedback network for joint exposure fusion and image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 3098–3112. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3058764 [16] LIN Yuting, LIU Wei, CAI Xiaowen, et al. A CNN-based quality model for image interpolation[C]. Proceedings of 2020 Cross Strait Radio Science & Wireless Technology Conference, Fuzhou, China, 2020: 1–3. [17] AMD. AMD FidelityFX super resolution (FSR): Changing the game in just 4 months[EB/OL]. https://www.amd.com/zh-hans/technologies/fidelityfx-super-resolution, 2021. [18] Andrew Burnes, nvidia-image-scaler-dlss-rtx-november-2021-updates[EB/OL]. https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/geforce/news/gfecnt/202111/nvidia-image-scaler-dlss-rtx-november-2021-updates/, 2021. [19] KHALEDYAN D, AMIRANY A, JAFARI K, et al. Low-cost implementation of bilinear and bicubic image interpolation for real-time image super-resolution[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE Global Humanitarian Technology Conference, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1–5. [20] 王康, 杨瑞祺, 杨依忠, 等. 基于二阶牛顿插值的图像自适应缩放设计及实现[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2020, 37(9): 126–132,138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2020.09.021WANG Kang, YANG Ruiqi, YANG Yizhong, et al. Design and implementation of image adaptive scaling based on second order newton interpolation[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2020, 37(9): 126–132,138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2020.09.021 [21] BOUKHTACHE S, BLAYSAT B, GRÉDIAC M, et al. FPGA-based architecture for bi-cubic interpolation: The best trade-off between precision and hardware resource consumption[J]. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing, 2021, 18(3): 901–911. doi: 10.1007/s11554-020-01035-1 [22] SHEN H Y, LEE Y C, TONG T W, et al. 4.7 A 91mW 90fps super-resolution processor for full HD images[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2021: 66–68. [23] 陆志芳, 钟宝江. 基于预测梯度的图像插值算法[J]. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(6): 1072–1085. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160793LU Zhifang and ZHONG Baojiang. Image interpolation with predicted gradients[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(6): 1072–1085. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160793 [24] ZHANG R, ISOLA P, EFROS A A, et al. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 586–595. [25] 吴世豪, 罗小华, 张建炜, 等. 基于FPGA的新边缘指导插值算法硬件实现[J]. 浙江大学学报:工学版, 2018, 52(11): 2226–2232. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2018.11.022WU Shihao, LUO Xiaohua, ZHANG Jianwei, et al. FPGA-based hardware implementation of new edge-directed interpolation algorithm[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University:Engineering Science, 2018, 52(11): 2226–2232. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2018.11.022 [26] LEE J, SHIN D, LEE J, et al. A full HD 60 fps CNN super resolution processor with selective caching based layer fusion for mobile devices[C]. Proceedings of 2019 Symposium on VLSI Circuits. Kyoto, Japan, 2019: C302–C303. -





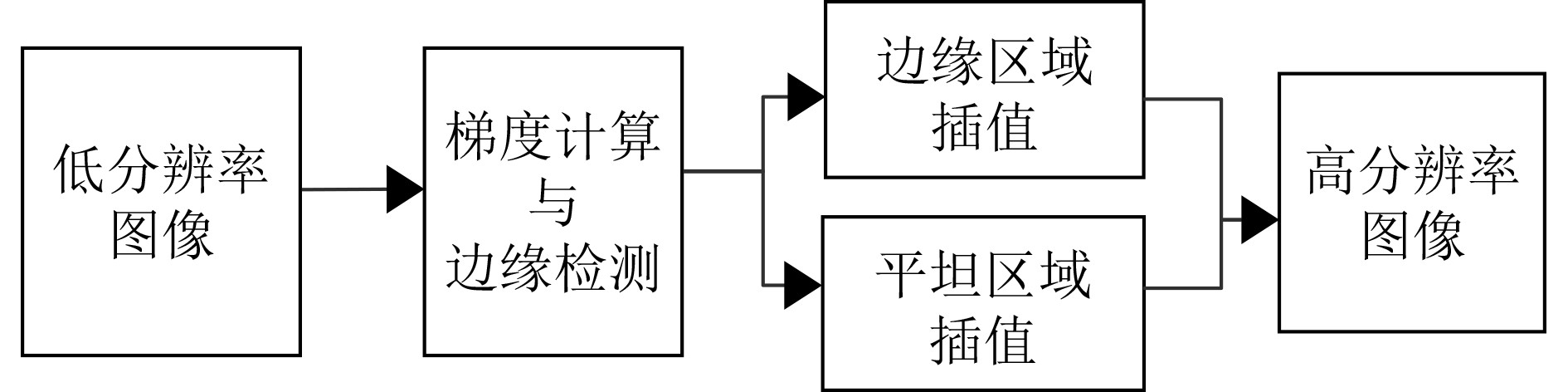
 下载:
下载:
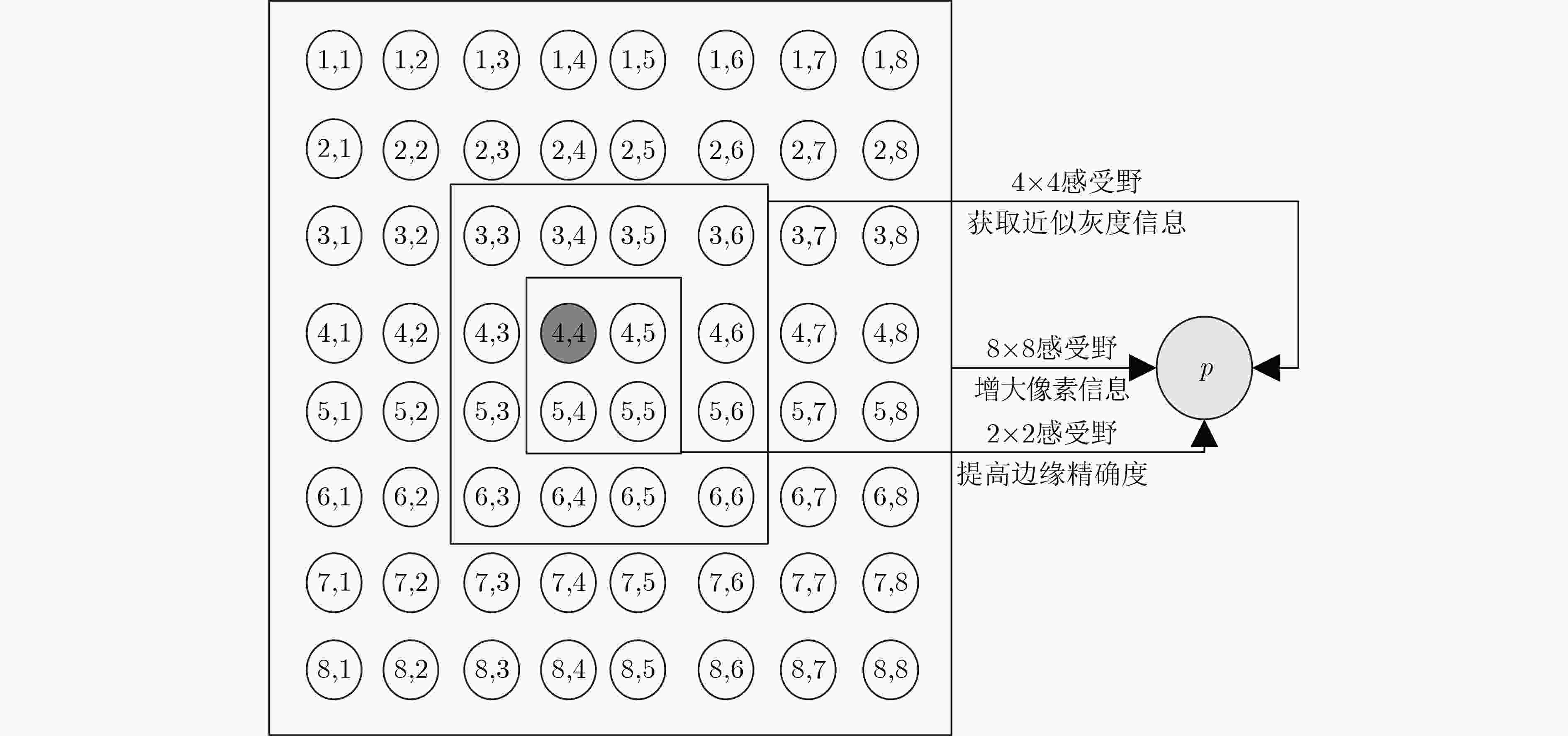
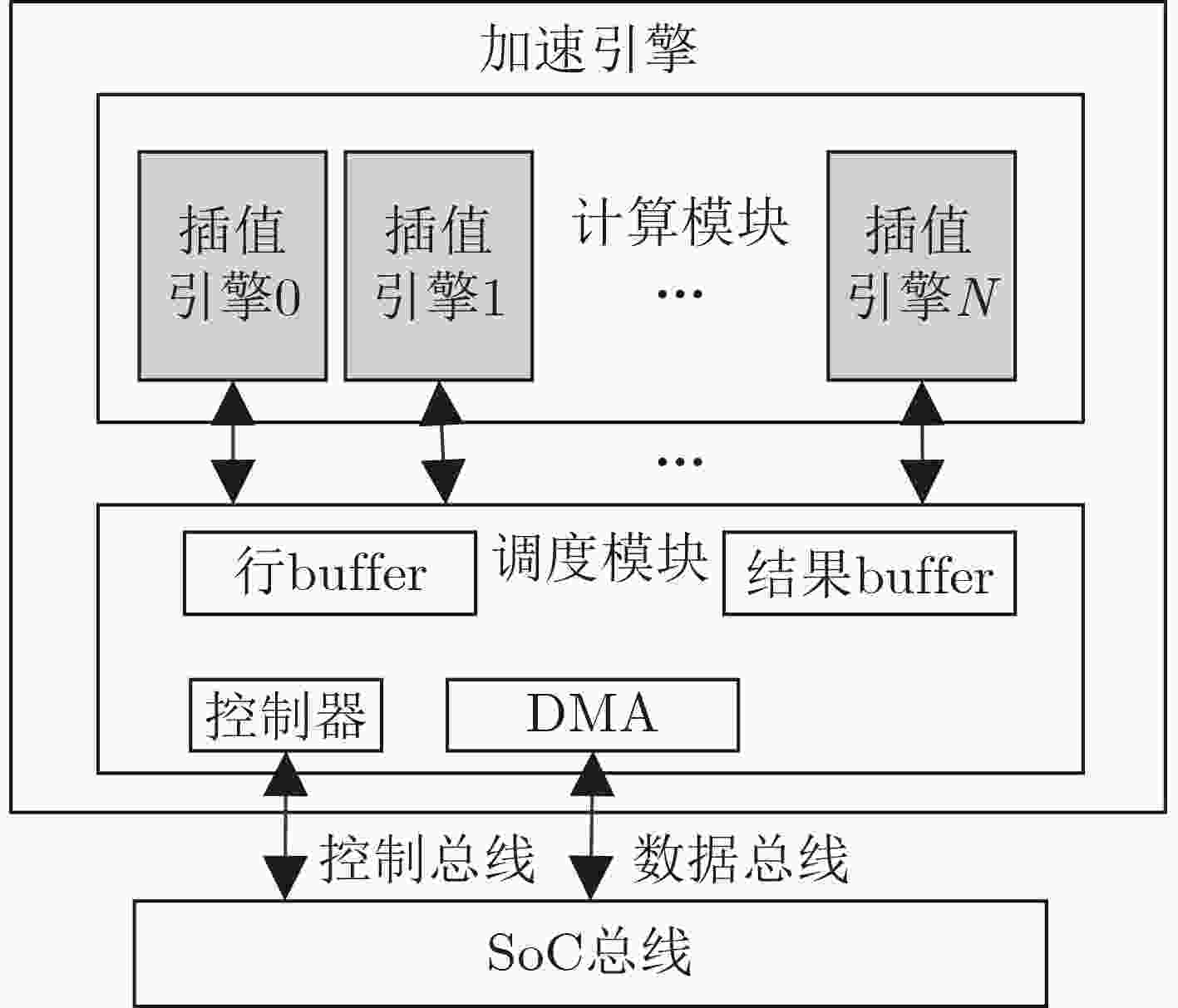
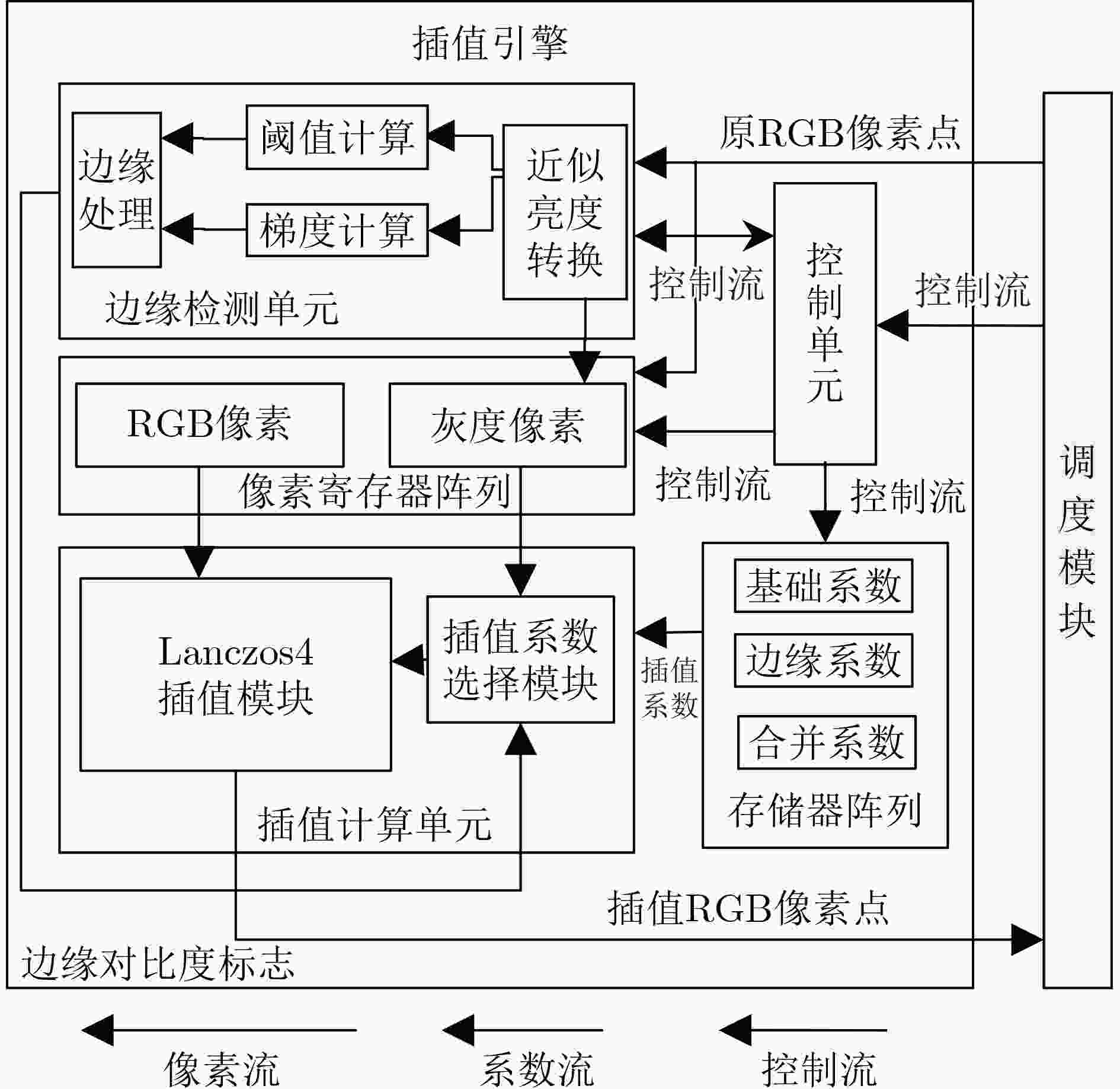


 下载:
下载:
