Research on Blind Super-resolution Reconstruction with Double Discriminator
-
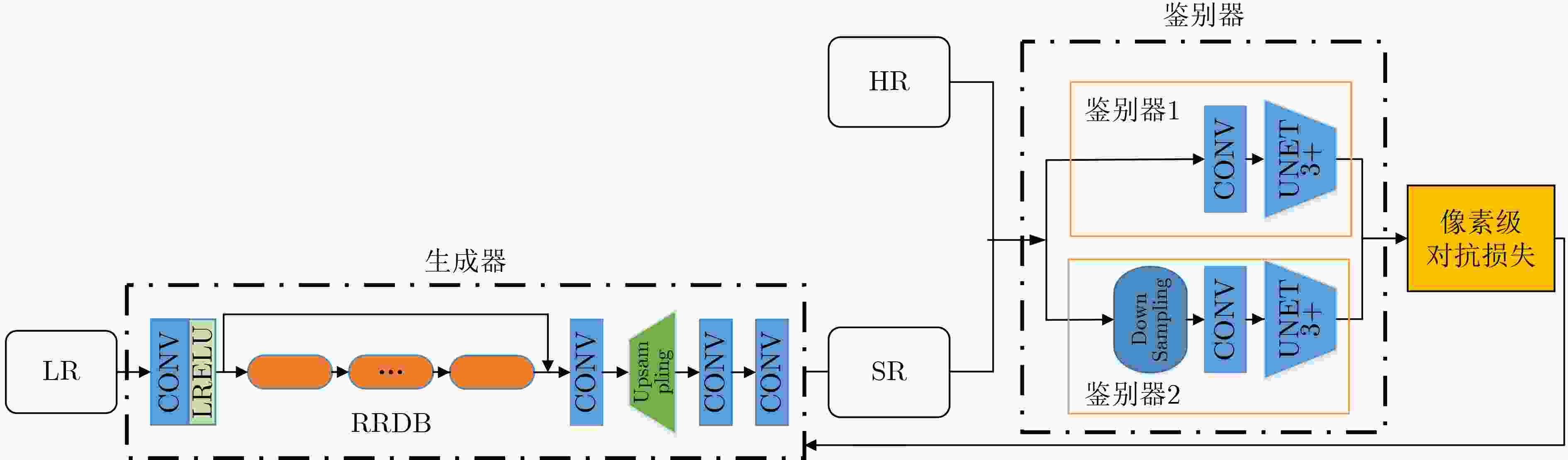
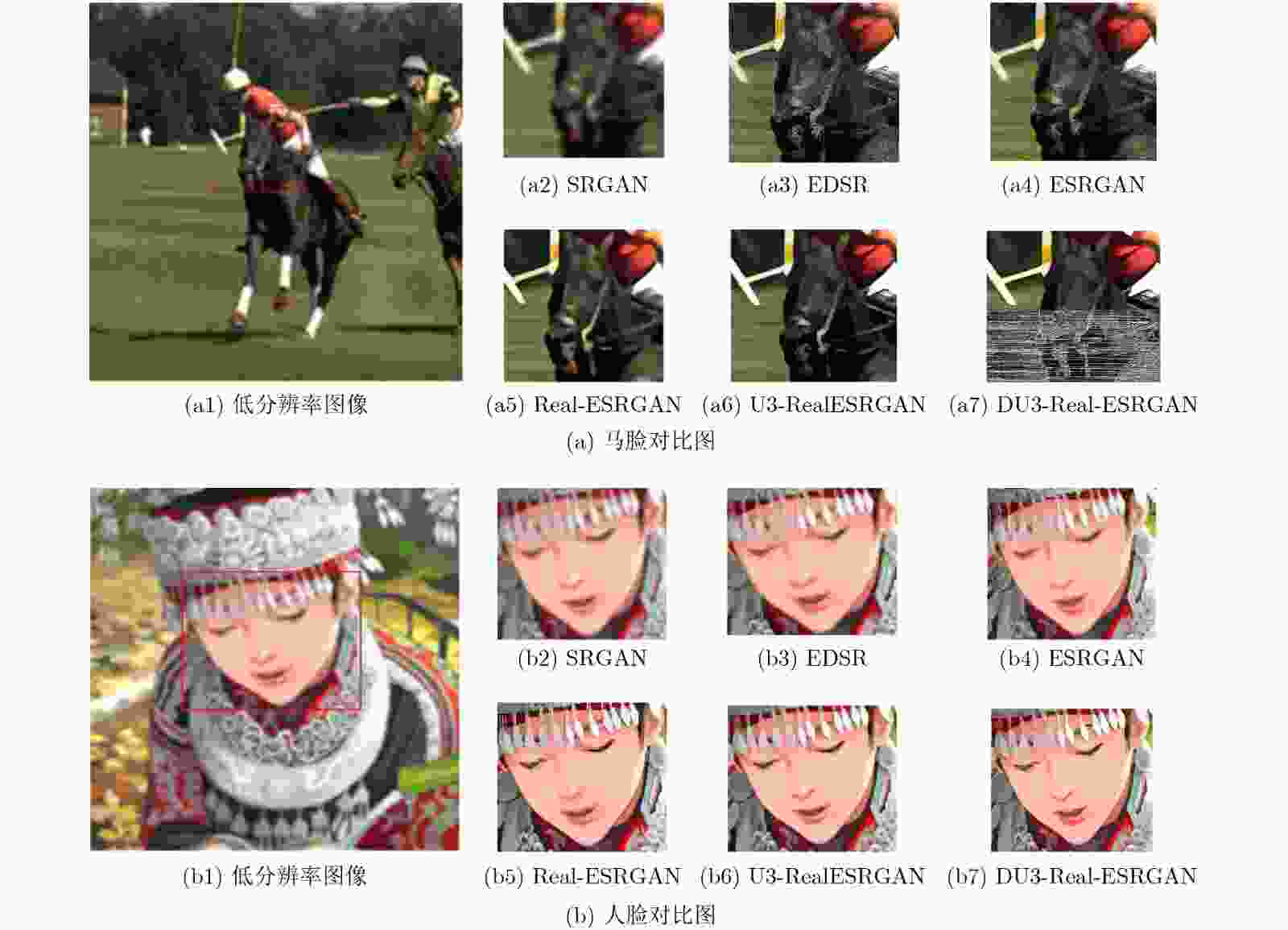
摘要: 图像超分变率重建方法在公共安全检测、卫星成像、医学和照片恢复等方面有着十分重要的用途。该文对基于生成对抗网络的超分辨率重建方法进行研究,提出一种基于纯合成数据训练的真实世界盲超分算法(Real-ESRGAN)的UNet3+双鉴别器Real-ESRGAN方法(Double Unet3+ Real-ESRGAN, DU3-Real-ESRGAN)。首先,在鉴别器中引入UNet3+结构,从全尺度捕捉细粒度的细节和粗粒度的语义。其次,采用双鉴别器结构,一个鉴别器学习图像纹理细节,另一个鉴别器关注图像边缘,实现图像信息互补。在Set5, Set14, BSD100和Urban100数据集上,与多种基于生成对抗网络的超分重建方法相比,除Set5数据集外,DU3-Real-ESRGAN方法在峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性(SSIM)和无参图像考评价指标(NIQE)都优于其他方法,产生了更直观逼真的高分辨率图像。
-
关键词:
- 超分辨率重建 /
- 纯合成数据训练的真实世界盲超分算法 /
- UNet3+ /
- 双鉴别器
Abstract: Image super-resolution reconstruction methods have very important uses in public safety detection, satellite imaging, medicine and photo restoration. In this paper, super-resolution reconstruction methods based on generative adversarial networks are investigated, from the training Real-world blind Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Networks pure synthetic data (Real-ESRGAN) method, a double UNet3+ discriminators Real-ESRGAN (DU3-Real-ESRGAN) method is proposed. Firstly, a UNet3+ structure is introduced in the discriminator to capture fine-grained details and coarse-grained semantics from the full scale. Secondly, a dual discriminator structure is adopted, with one discriminator learning image texture details and the other focusing on image edges to achieve complementary image information. Compared with several methods based on generative adversarial networks on Set5, Set14, BSD100 and Urban100 data sets, except for Set5, the Peak Signal to Noise Ration (PSNR), Structure SIMilarity (SSIM) and Natural Image Quality Evaluator (NIQE) values of the DU3-Real-ESRGAN method are superior to those of other methods to produce more intuitive and realistic high-resolution images. -
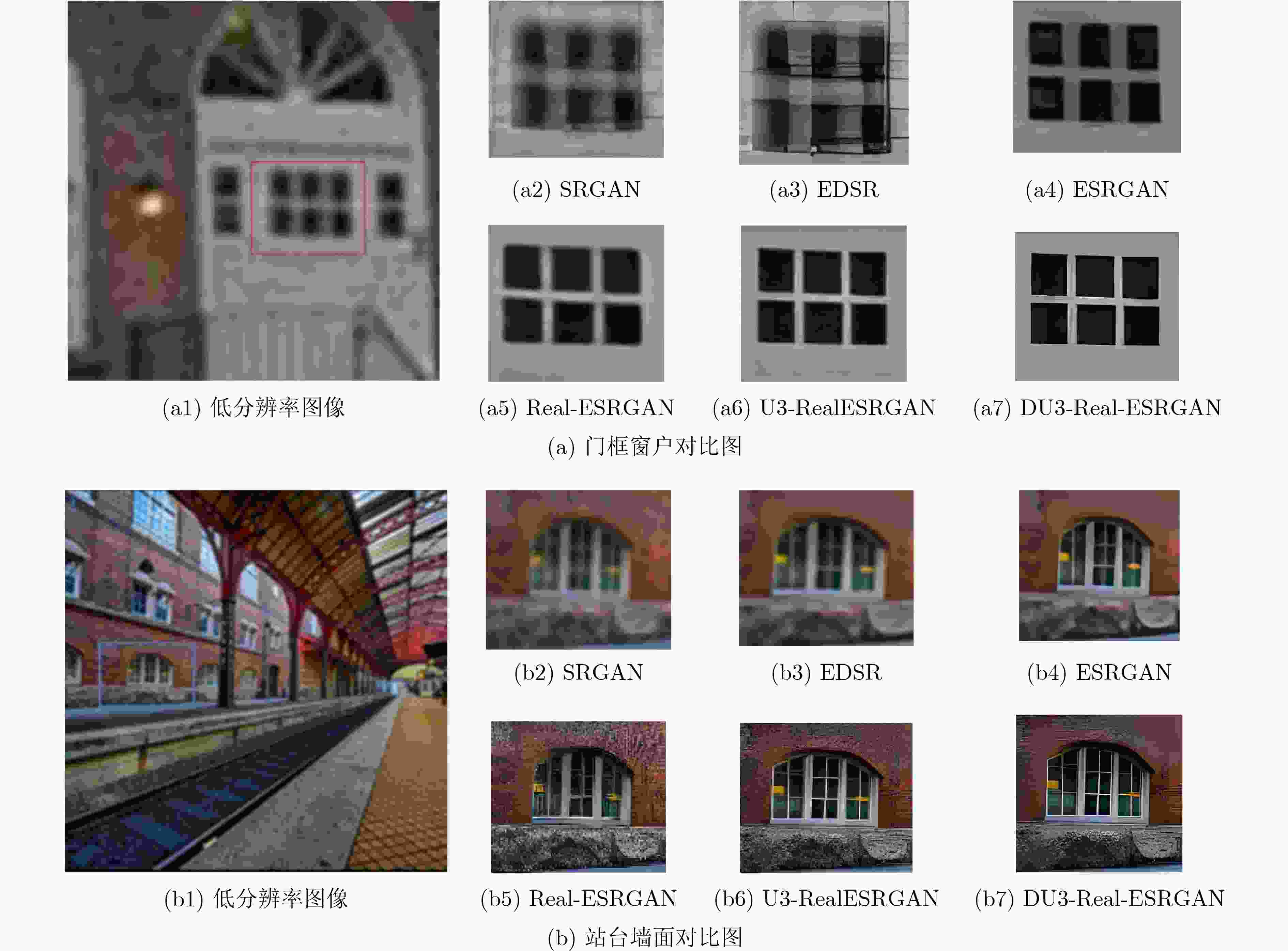
表 1 PSNR/SSIM值对比
数据集 算法 SRGAN EDSR ESRGAN Real-ESRGAN U3-RealESRGAN DU3-Real-ESRGAN Set5 28.99/0.791 28.80/0.787 28.81/0.7868 30.52/0.878 30.01/0.868 30.24/0.870 Set14 27.03/0.815 26.64/0.803 27.13/0.741 28.71/0.830 28.55/0.845 29.57/0.847 BSD100 27.85/0.745 28.34/0.827 27.33/0.808 29.14/0.855 29.25/0.851 30.19/0.859 Urban100 27.45/0.825 27.71/0.7420 27.29/0.836 28.82/0.850 29.15/0.795 30.05/0.857 表 2 NIQE值对比
数据集 算法 SRGAN EDSR ESRGAN Real-ESRGAN U3-RealESRGN DU3-Real-ESRGAN Set5 5.671 2 5.137 2 4.580 6 3.506 4 3.602 1 3.840 0 Set14 7.559 3 5.158 8 4.409 6 3.541 3 3.533 2 3.516 8 BSD100 7.341 3 6.271 5 3.817 2 3.691 6 3.267 5 3.247 4 Urban100 7.108 9 6.563 2 4.199 6 3.929 0 3.454 3 3.399 3 -
[1] 陶状, 廖晓东, 沈江红. 双路径反馈网络的图像超分辨重建算法[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2020, 29(4): 181–186. doi: 10.15888/j.cnki.csa.007344TAO Zhuang, LIAO Xiaodong, and SHEN Jianghong. Dual stream feedback network for image super-resolution reconstruction[J]. Computer Systems &Applications, 2020, 29(4): 181–186. doi: 10.15888/j.cnki.csa.007344 [2] 陈栋. 单幅图像超分辨率重建算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 华南理工大学, 2020.CHEN Dong. Research on single image super-resolution reconstruction algorithm[D]. [Master dissertation], South China University of Technology, 2020. [3] KAPPELER A, YOO S, DAI Qiqin, et al. Video super-resolution with convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2016, 2(2): 109–122. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2016.2532323 [4] JADERBERG M, SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A, et al. Spatial transformer networks[C]. The 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 2017–2025. [5] IRANI M and PELEG S. Super resolution from image sequences[C]. [1990] Proceedings. 10th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Atlantic City, USA, 1990: 115–120. [6] STARK H and OSKOUI P. High-resolution image recovery from image-plane arrays, using convex projections[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1989, 6(11): 1715–1726. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.6.001715 [7] DONG Chao, LOY C C, HE Kaiming, et al. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]. 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 184–199. [8] DONG Chao, LOY C C, and TANG Xiaoou. Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 391–407. [9] PARK S J, SON H, CHO S, et al. SRFeat: Single image super-resolution with feature discrimination[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 455–471. [10] ZHANG Yulun, LI Kunpeng, LI Kai, et al. Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 294–310. [11] LEDIG C, THEIS L, HUSZÁR F, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 105–114. [12] LIM B, SON S, KIM H, et al. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1132–1140. [13] WANG Xintao, YU Ke, WU Shixiang, et al. ESRGAN: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 63–79. [14] SOH J W, PARK G Y, JO J, et al. Natural and realistic single image super-resolution with explicit natural manifold discrimination[C]. The 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 8114-8123. [15] WANG Xintao, XIE Liangbin, DONG Chao, et al. Real-ESRGAN: Training real-world blind super-resolution with pure synthetic data[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 1905–1914. [16] SAJJADI M S M, SCHÖLKOPF B, and HIRSCH M. EnhanceNet: Single image super-resolution through automated texture synthesis[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 4501–4510. [17] ZHANG Kai, LI Yawei, ZUO Wangmeng, et al. Plug-and-play image restoration with deep denoiser prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(10): 6360–6376. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3088914 [18] HUANG Huimin, LIN Lanfen, TONG Ruofeng, et al. UNet 3+: A full-scale connected UNet for medical image segmentation[C]. ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 1055–1059. [19] ZHOU Zongwei, SIDDIQUEE M M R, TAJBAKHSH N, et al. Unet++: A nested U-Net architecture for medical image segmentation[M]. Stoyanov D, Taylor Z, Carneiro G, et al. Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support. Cham: Springer, 2018: 3–11. [20] MITTAL A, SOUNDARARAJAN R, and BOVIK A C. Making a “Completely Blind” image quality analyzer[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(3): 209–212. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2012.2227726 -





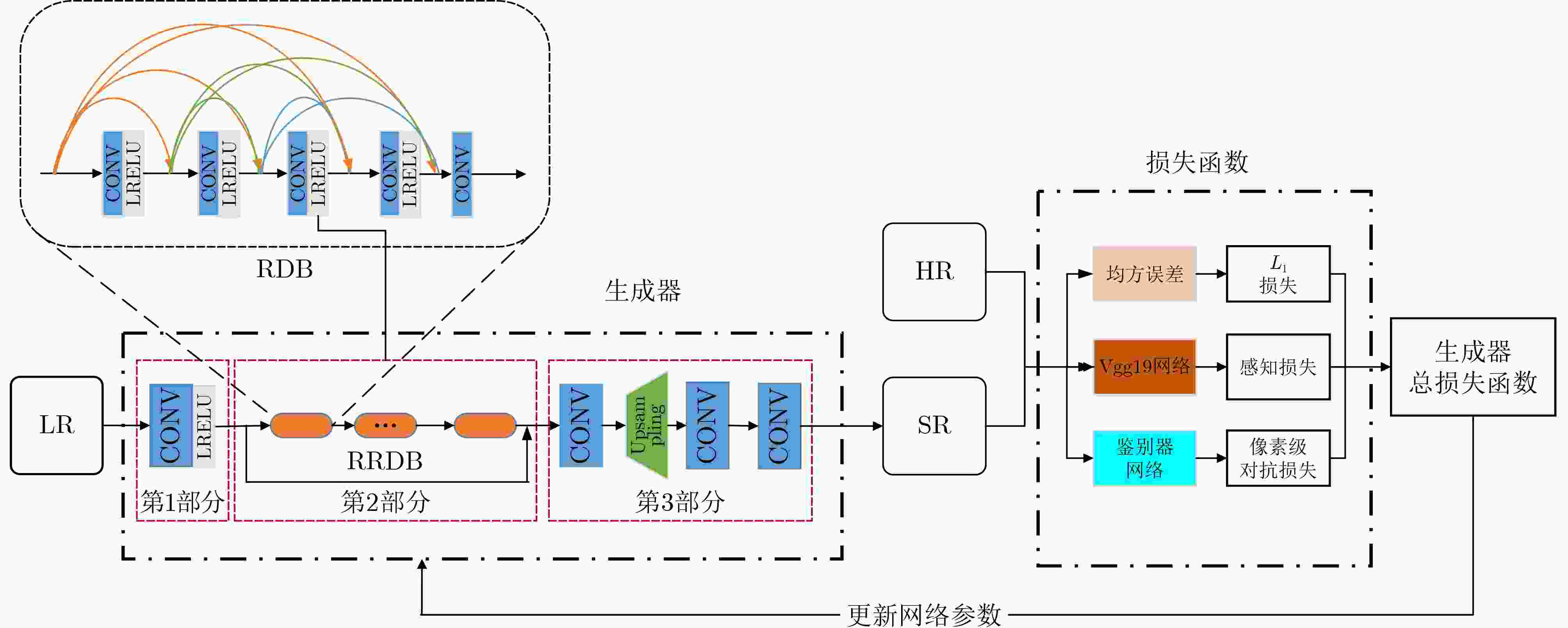
 下载:
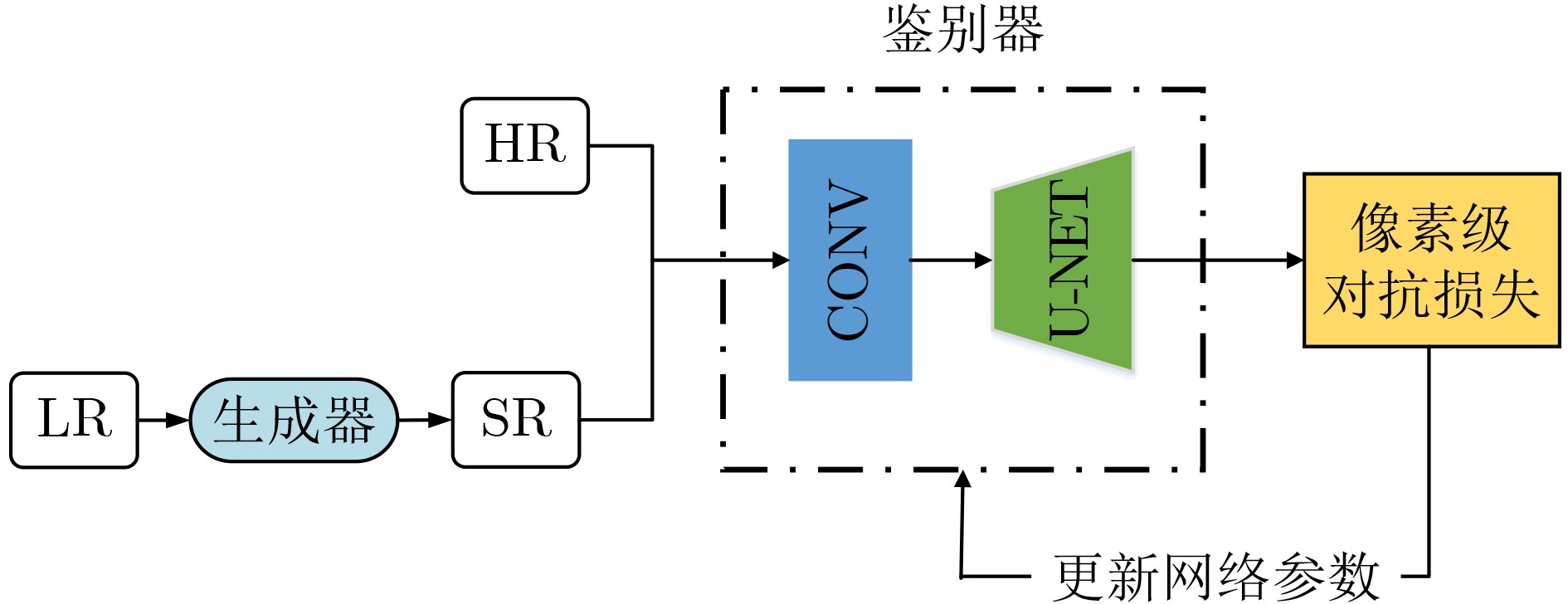
下载:
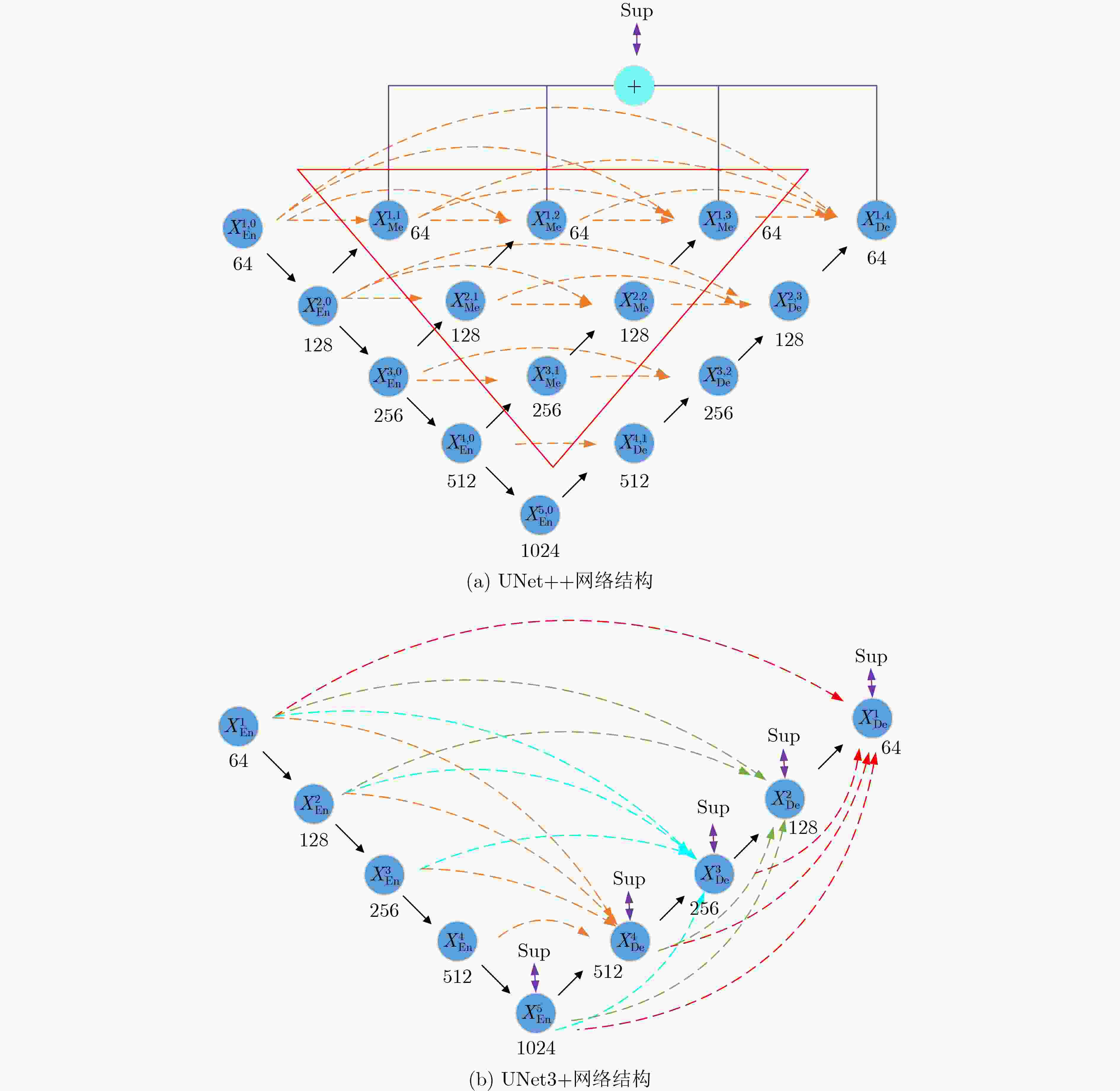
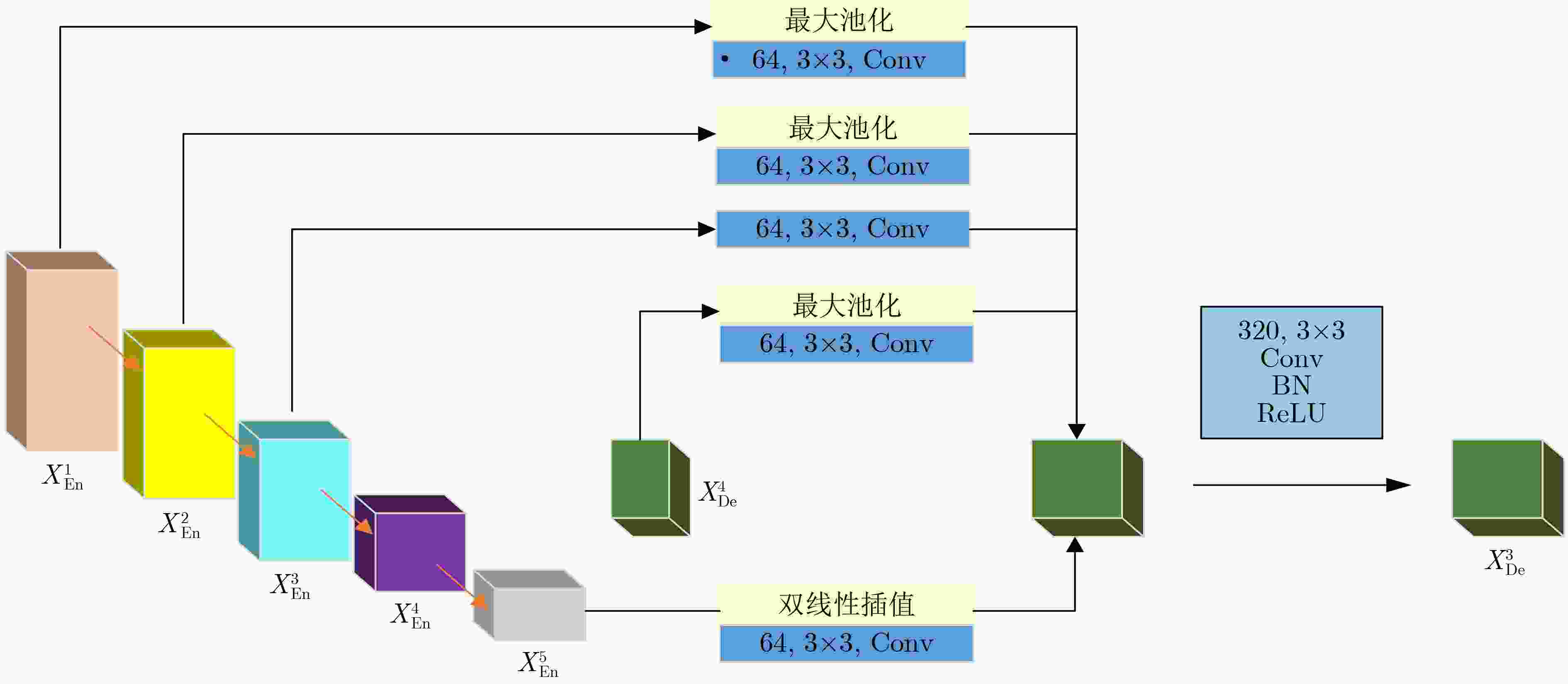






 下载:
下载:
