A Fast Recognition Method of SSVEP Signals Based on Time-Frequency Multiscale
-
摘要: 目前基于稳态视觉诱发电位(SSVEP)的脑机接口在人机协作中受到广泛关注,但较短时长 SSVEP 信号仍面临信噪比较低、特征提取不充分的问题。该文从频域、时域以及空域3个角度分析并提取SSVEP信号特征。首先该方法从由频域实部信息和虚部信息整合的3维重校正特征矩阵中提取幅值和相位特征信息。然后在时域中通过训练多个刺激时窗尺度的样本增强模型表征能力。最后利用不同尺度的1维卷积核,并行提取通道空间和频域上的多尺度特征信息。该文在两种不同的视觉刺激频率和频率间隔的公开数据集上进行实验,在时窗为1 s时的平均准确率和平均信息传输率(ITR)均优于现有的其他方法。Abstract: A brain-computer interface based on Steady-State Visual Evoked Potential (SSVEP) has recently garnered considerable interest in human-computer cooperation. Nevertheless, SSVEP signals with short time windows suffer from a low signal-to-noise ratio and insufficient feature extraction. This study examines and extracts the SSVEP signal characteristics from three perspectives: frequency domain, time domain and spatial domain. The proposed method extracts the amplitude and phase feature information from a three-dimensional recalibrated feature matrix developed by incorporating the real part and the imaginary part information in the frequency domain. Subsequently, the model’s representation ability is enhanced by training samples across multiple stimulus time window scales in the time domain. Finally, multiscale feature information in the channel space and frequency domain is extracted in parallel by using distinct scaled one-dimensional convolution kernels with. In this paper, experiments are conducted on two open datasets characterized by different visual stimulus frequencies and frequency intervals. The average accuracy and average information transfer rate at a time window of 1 s surpass the performance of existing methods.
-
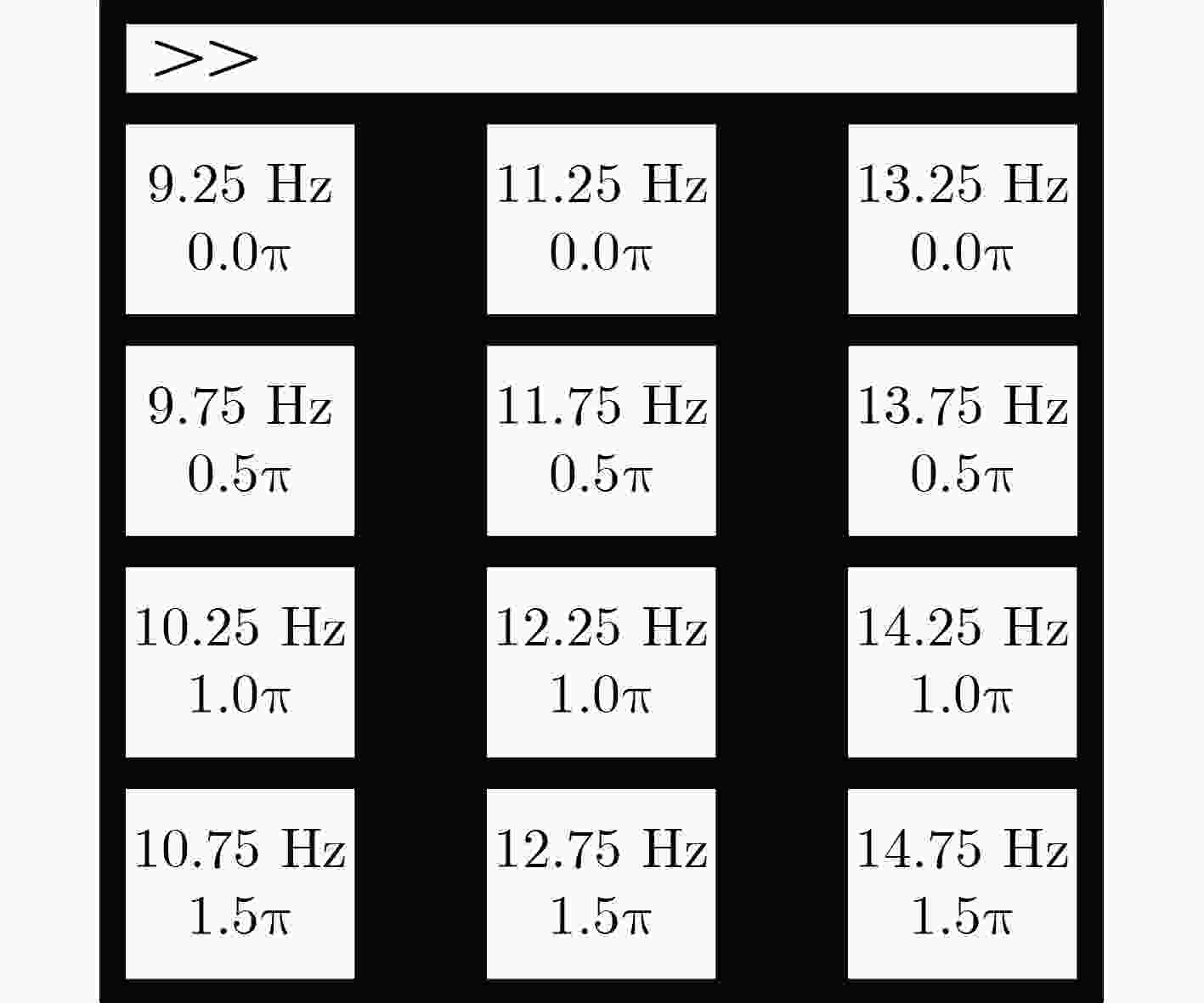
图 2 数据集1的SSVEP刺激范式[14]
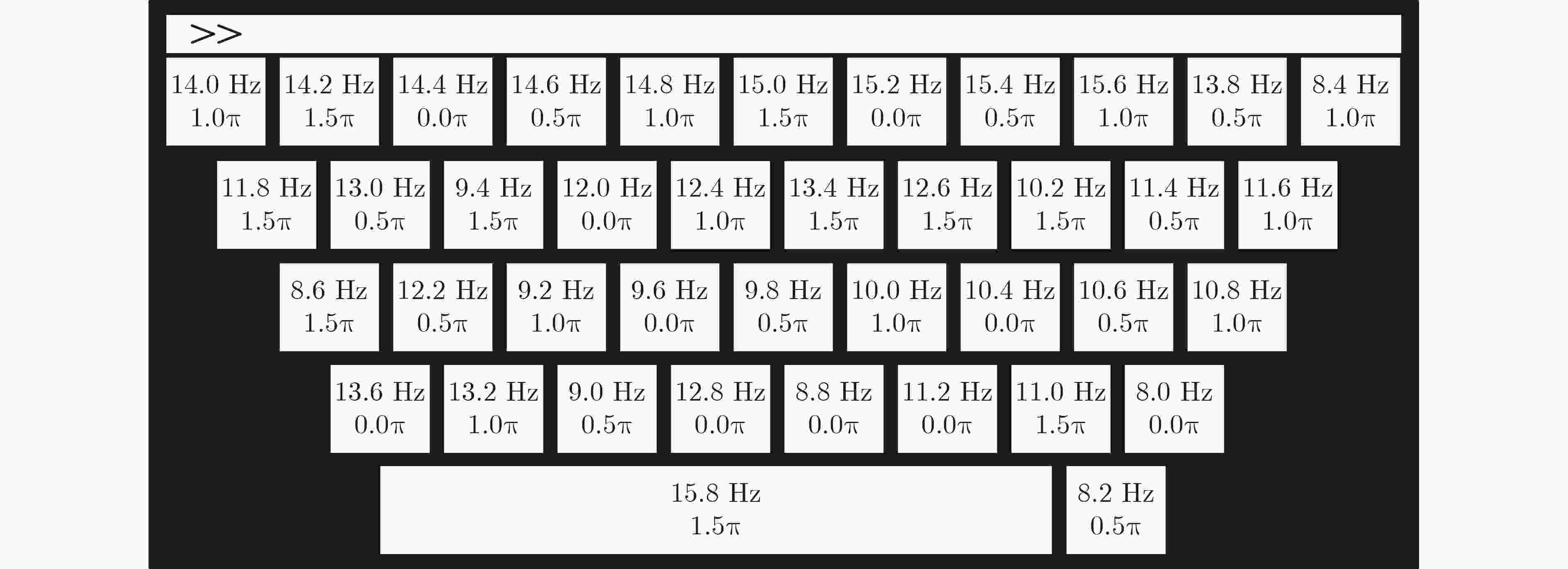
图 3 数据集2的SSVEP刺激范式[15]
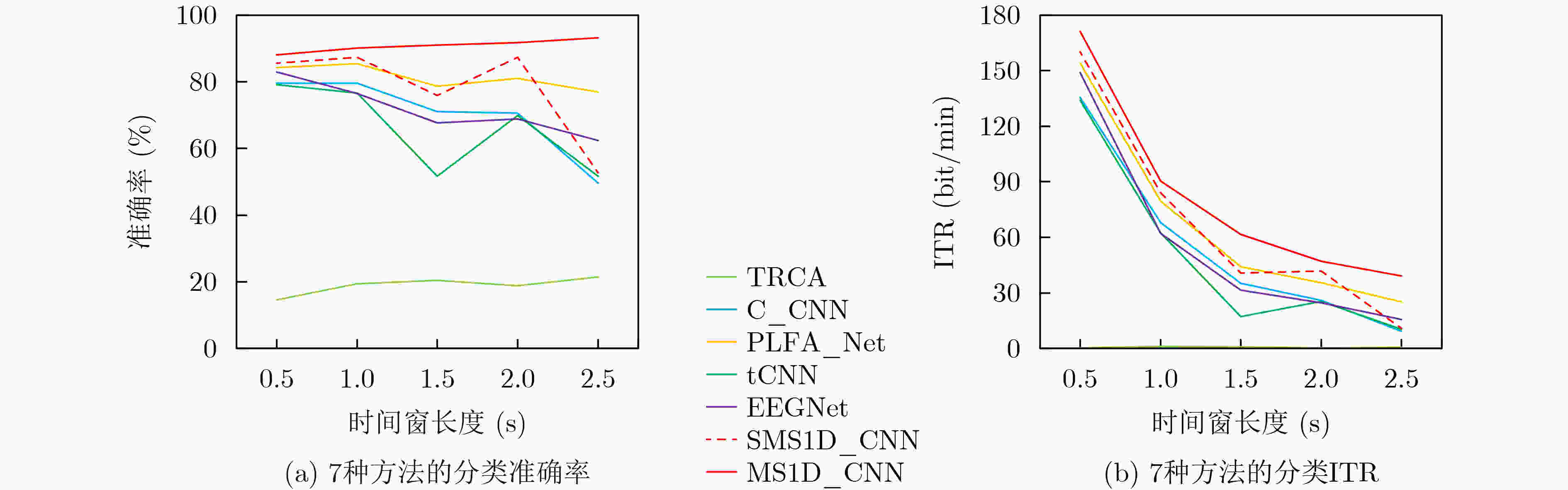
表 1 不同方法在数据集1(时间窗口长度为1 s)上的平均实验结果
方法 Acc(%) ITR(bit/min) TRCA 19.34 3.44 C_CNN 88.61 107.17 PLFA_Net 66.03 59.41 tCNN 85.24 98.82 EEGNet 87.25 103.72 SMS1D_CNN 89.22 108.75 MS1D_CNN 89.35 109.09 表 2 不同方法在数据集2(时间窗口长度为1 s)上的平均实验结果
方法 Acc(%) ITR(bit/min) TRCA 19.48 1.12 C_CNN 79.58 67.86 PLFA_Net 85.42 79.66 tCNN 76.60 62.33 EEGNet 76.51 62.16 SMS1D_CNN 87.37 83.93 MS1D_CNN 90.17 90.42 表 3 不同方法在数据集1(跨被试)上的平均实验结果
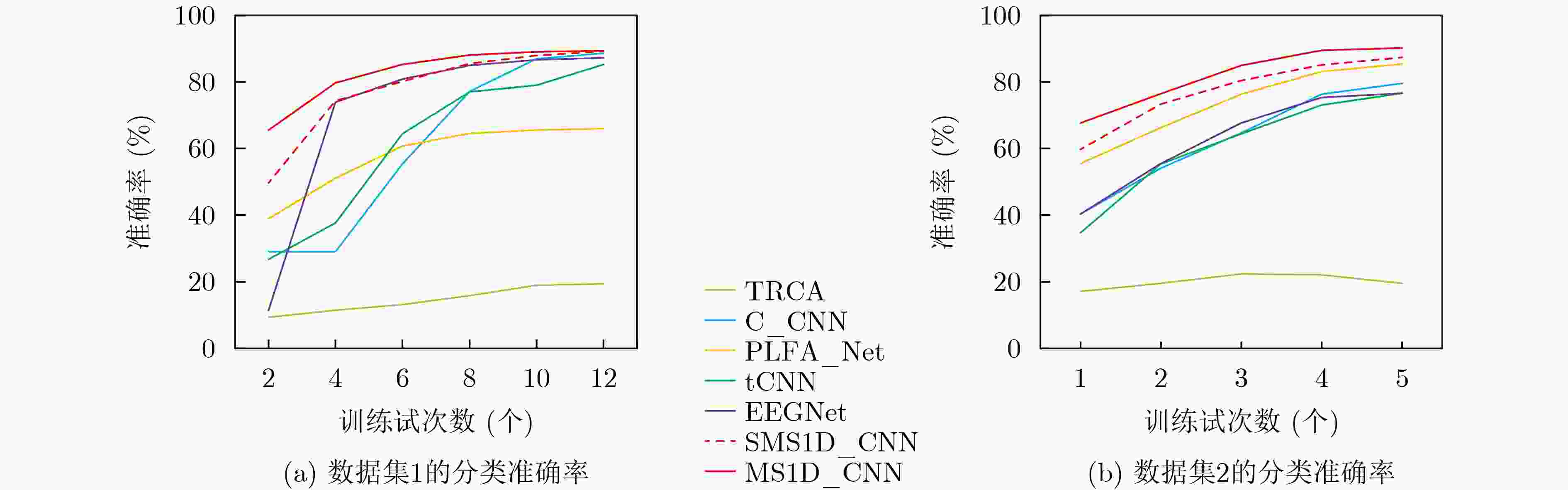
方法 Acc(%) ITR(bit/min) TRCA 23.44 6.03 C_CNN 74.73 75.81 PLFA_Net 58.59 46.95 tCNN 74.44 75.23 EEGNet 75.39 77.14 SMS1D_CNN 76.69 79.81 MS1D_CNN 77.46 81.41 表 4 不同方法在数据集2(跨被试)上的平均实验结果
方法 Acc(%) ITR(bit/min) TRCA 21.29 1.73 C_CNN 93.10 97.76 PLFA_Net 87.99 85.33 tCNN 82.42 73.43 EEGNet 93.67 99.28 SMS1D_CNN 94.41 101.28 MS1D_CNN 96.06 105.99 -
[1] CHEN Xiaogang, HUANG Xiaoshan, WANG Yijun, et al. Combination of augmented reality based brain-computer interface and computer vision for high-level control of a robotic arm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2020, 28(12): 3140–3147. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2020.3038209 [2] CHIUZBAIAN A, JAKOBSEN J, and PUTHUSSERYPADY S. Mind controlled drone: An innovative multiclass SSVEP based brain computer interface[C]. 2019 7th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), Gangwon, Korea (South), 2019: 1–5. [3] LIN Zhonglin, ZHANG Changshui, WU Wei, et al. Frequency recognition based on canonical correlation analysis for SSVEP-based BCIs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2006, 53(12): 2610–2614. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2006.886577 [4] CHEN Xiaogang, WANG Yijun, GAO Shangkai, et al. Filter bank canonical correlation analysis for implementing a high-speed SSVEP-based brain-computer interface[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2015, 12(4): 046008. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/12/4/046008 [5] NAKANISHI M, WANG Yijun, CHEN Xiaogang, et al. Enhancing detection of SSVEPs for a high-speed brain speller using task-related component analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 65(1): 104–112. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2017.2694818 [6] JIAO Yong, ZHANG Yu, WANG Yu, et al. A novel multilayer correlation maximization model for improving CCA-based frequency recognition in SSVEP brain–computer interface[J]. International Journal of Neural Systems, 2018, 28(4): 1750039. doi: 10.1142/S0129065717500393 [7] MIAO Runfeng, ZHANG Li, and SUN Qiang. Hybrid template canonical correlation analysis method for enhancing SSVEP recognition under data-limited condition[C]. 2021 10th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, Italy, 2021: 65–68. [8] WAYTOWICH N, LAWHERN V J, GARCIA J O, et al. Compact convolutional neural networks for classification of asynchronous steady-state visual evoked potentials[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2018, 15(6): 066031. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aae5d8 [9] RAVI A, BENI N H, MANUEL J, et al. Comparing user-dependent and user-independent training of CNN for SSVEP BCI[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2020, 17(2): 026028. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ab6a67 [10] CECOTTI H. A time-frequency convolutional neural network for the offline classification of steady-state visual evoked potential responses[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2011, 32(8): 1145–1153. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2011.02.022 [11] NGUYEN T H and CHUNG W Y. A single-channel SSVEP-based BCI speller using deep learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 1752–1763. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2886759 [12] KWAK N S, MÜLLER K R, and LEE S W. A convolutional neural network for steady state visual evoked potential classification under ambulatory environment[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(2): e0172578. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172578 [13] 林艳飞, 臧博宇, 郭嵘骁, 等. 基于相频特性的稳态视觉诱发电位深度学习分类模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(2): 446–454. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210816LIN Yanfei, ZANG Boyu, GUO Rongxiao, et al. A deep learning method for SSVEP classification based on phase and frequency characteristics[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(2): 446–454. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210816 [14] NAKANISHI M, WANG Yujun, WANG Yute, et al. A comparison study of canonical correlation analysis based methods for detecting steady-state visual evoked potentials[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(10): e0140703. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140703 [15] LIU Bingchuan, HUANG Xiaoshan, WANG Yijun, et al. BETA: A large benchmark database toward SSVEP-BCI application[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2020, 14: 627. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00627 [16] PAN Yudong, CHEN Jianbo, ZHANG Yangsong, et al. An efficient CNN-LSTM network with spectral normalization and label smoothing technologies for SSVEP frequency recognition[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2022, 19(5): 056014. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac8dc5 [17] JIE Hu, LI Shen, and GANG Sun. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. [18] DING Wenlong, SHAN Jianhua, FANG Bin, et al. Filter bank convolutional neural network for short time-window steady-state visual evoked potential classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2021, 29: 2615–2624. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2021.3132162 -





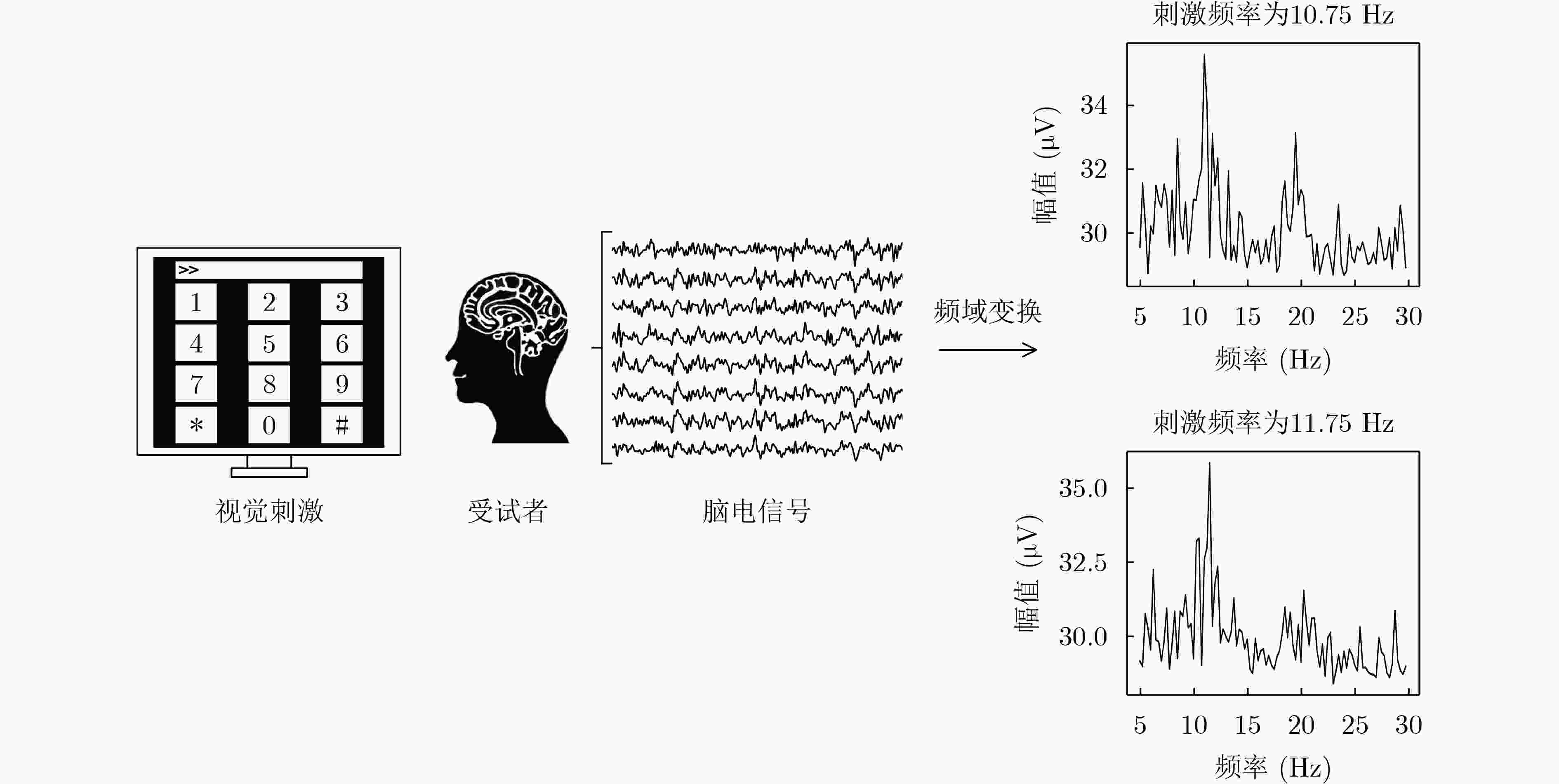
 下载:
下载:
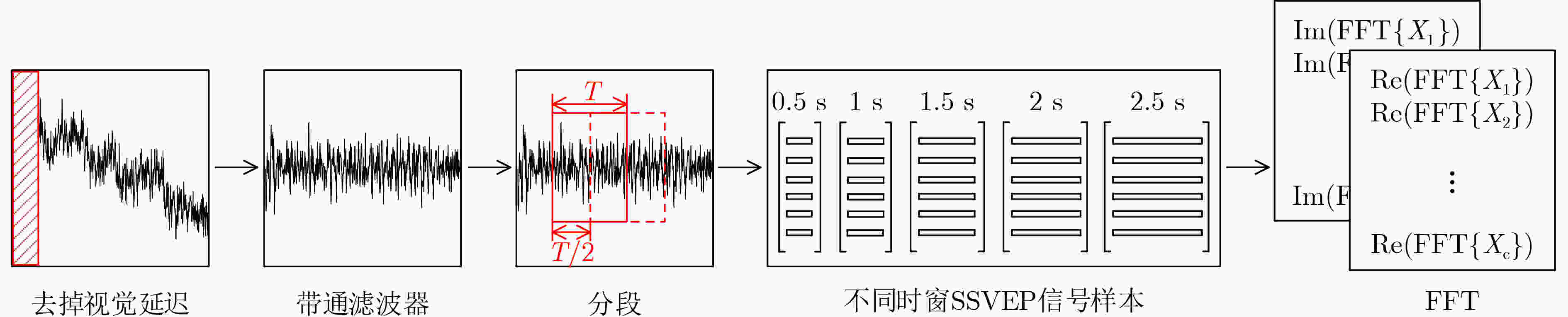
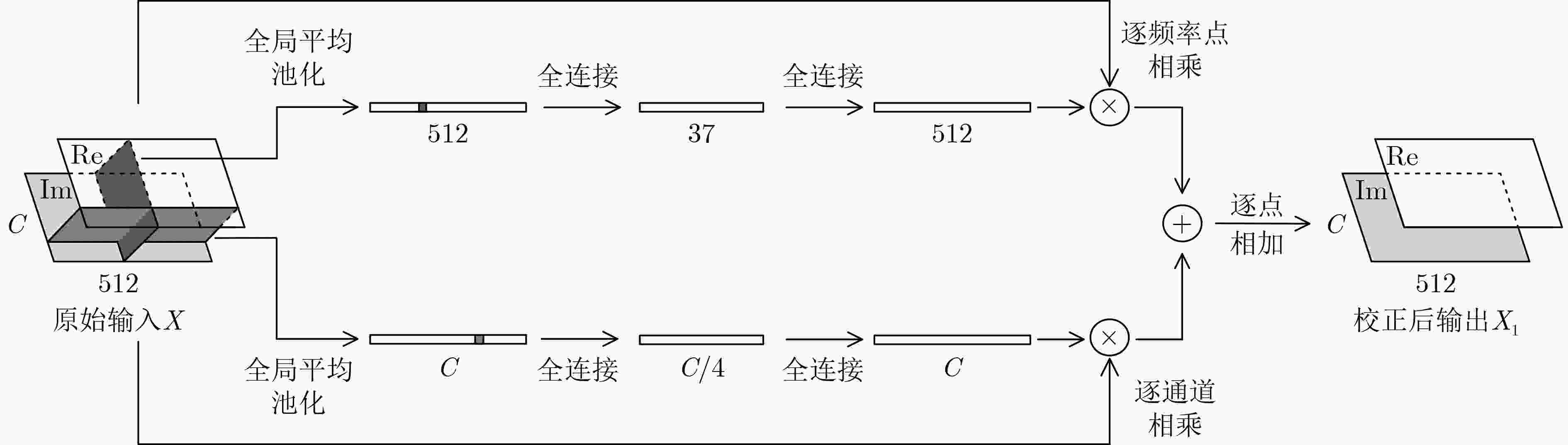
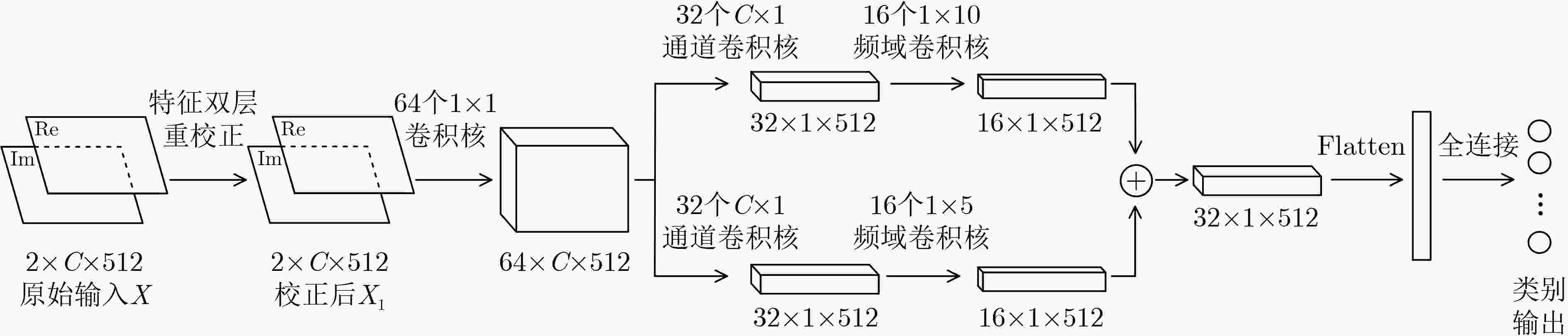



 下载:
下载:
