| [1] |
HAYKIN S. Cognitive radio: Brain-empowered wireless communications[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2005, 23(2): 201–220. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2004.839380
|
| [2] |
XU Yongjun, ZHAO Xiaohui, and LIANG Yingchang. Robust power control and beamforming in cognitive radio networks: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2015, 17(4): 1834–1857. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2015.2425040
|
| [3] |
LI Dong. Hybrid active and passive antenna selection for backscatter-assisted MISO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(11): 7258–7269. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3014917
|
| [4] |
徐勇军, 杨浩克, 叶迎晖, 等. 反向散射通信网络资源分配综述[J]. 物联网学报, 2021, 5(3): 56–69. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2021.00215XU Yongjun, YANG Haoke, YE Yinghui, et al. A survey on resource allocation in backscatter communication networks[J]. Chinese Journal on Internet of Things, 2021, 5(3): 56–69. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2021.00215
|
| [5] |
LI Dong. Backscatter communication powered by selective relaying[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(11): 14037–14042. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3029340
|
| [6] |
LI Dong. Two birds with one stone: Exploiting decode-and-forward relaying for opportunistic ambient backscattering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(3): 1405–1416. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2957490
|
| [7] |
XU Yongjun, GU Bowen, HU R Q, et al. Joint computation offloading and radio resource allocation in MEC-based wireless-powered backscatter communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(6): 6200–6205. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3077094
|
| [8] |
XU Yongjun, QIN Zhijin, GUI Guan, et al. Energy efficiency maximization in NOMA enabled backscatter communications with QoS guarantee[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(2): 353–357. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3031042
|
| [9] |
张倩倩. 认知反向散射通信互惠传输理论与资源配置方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2021.ZHANG Qianqian. Research on mutualistic transmission theory and resource allocation method in cognitive backscatter communications[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021.
|
| [10] |
LI Xingwang, ZHENG Yike, KHAN W U, et al. Physical layer security of cognitive ambient backscatter communications for green internet-of-things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2021, 5(3): 1066–1076. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2021.3062060
|
| [11] |
LU Xiao, WANG Ping, LI Guangxia, et al. Short-packet backscatter assisted wireless-powered relaying with NOMA: Mode selection with performance estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2022, 8(1): 216–231. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2021.3108158
|
| [12] |
XIAO Sa, GUO Huayan, and LIANG Yingchang. Resource allocation for full-duplex-enabled cognitive backscatter networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(6): 3222–3235. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2912203
|
| [13] |
KANG Xin, LIANG Yingchang, and YANG Jing. Riding on the primary: A new spectrum sharing paradigm for wireless-powered IoT devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(9): 6335–6347. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2859389
|
| [14] |
ZHUANG Yuandong, LI Xi, JI Hong, et al. Optimal resource allocation for RF-powered underlay cognitive radio networks with ambient backscatter communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(12): 15216–15228. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3037152
|
| [15] |
LIU Xiaolan, GAO Yue, and HU Fengye. Optimal time scheduling scheme for wireless powered ambient backscatter communications in IoT networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 2264–2272. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2889700
|
| [16] |
WANG Jie, YE Hanting, KANG Xin, et al. Cognitive backscatter NOMA networks with multi-slot energy causality[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(12): 2854–2858. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3019203
|
| [17] |
徐勇军, 杨浩克, 李国军, 等. 多标签无线供电反向散射通信网络能效优化算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3492–3498. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210772XU Yongjun, YANG Haoke, LI Guojun, et al. Energy-efficient optimization algorithm in multi-tag wireless-powered backscatter communication networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3492–3498. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210772
|
| [18] |
YANG Gang, ZHANG Jiapeng, and LIANG Yingchang. Optimal beamforming in cooperative cognitive backscatter networks for wireless-powered IoT[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communication Systems (ICCS), Chengdu, China, 2018: 56–61.
|
| [19] |
徐勇军. 下垫式认知无线电网络动态资源分配问题研究[D]. [博士论文], 吉林大学, 2015.XU Yongjun. Research on dynamic resource allocation for underlay cognitive radio networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Jilin University, 2015.
|
| [20] |
XU Yongjun, XIE Hao, LIANG Chengchao, et al. Robust secure energy-efficiency optimization in SWIPT-aided heterogeneous networks with a nonlinear energy-harvesting model[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(19): 14908–14919. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3072965
|
| [21] |
徐勇军, 谷博文, 杨洋, 等. 基于不完美CSI的D2D通信网络鲁棒能效资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8): 2189–2198. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200587XU Yongjun, GU Bowen, YANG Yang, et al. Robust energy-efficient resource allocation algorithm in D2D communication networks with imperfect CSI[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2189–2198. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200587
|
| [22] |
NG D W K, LO E S, and SCHOBER R. Robust beamforming for secure communication in systems with wireless information and power transfer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2014, 13(8): 4599–4615. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.2314654
|
| [23] |
BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004.
|
| [24] |
ZHENG Yuan, BI Suzhi, ZHANG Y J A, et al. Joint beamforming and power control for throughput maximization in IRS-assisted MISO WPCNs[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(10): 8399–8410. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3045703
|
| [25] |
CUI Miao, ZHANG Guangchi, and ZHANG Rui. Secure wireless communication via intelligent reflecting surface[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(5): 1410–1414. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2919685
|





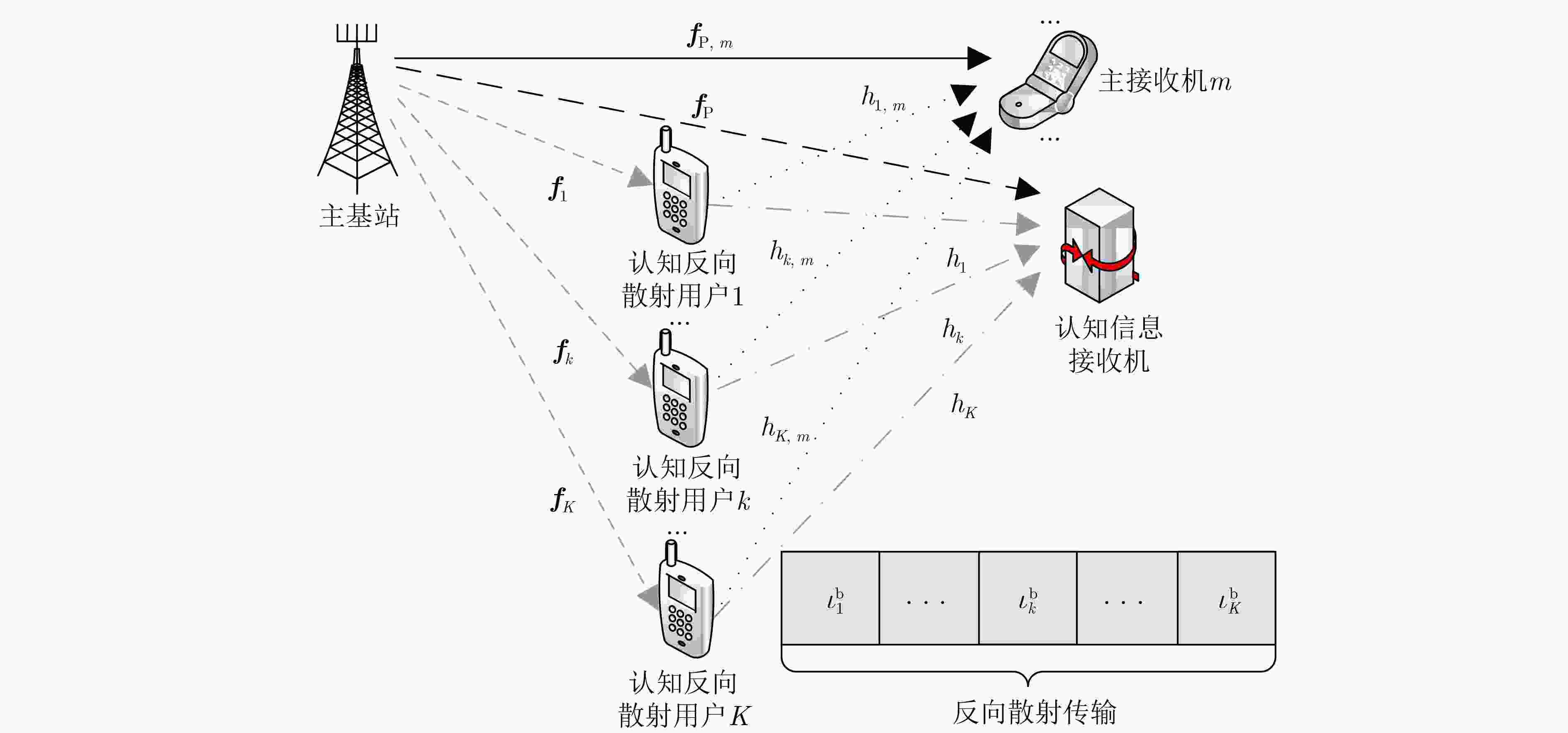
 下载:
下载:
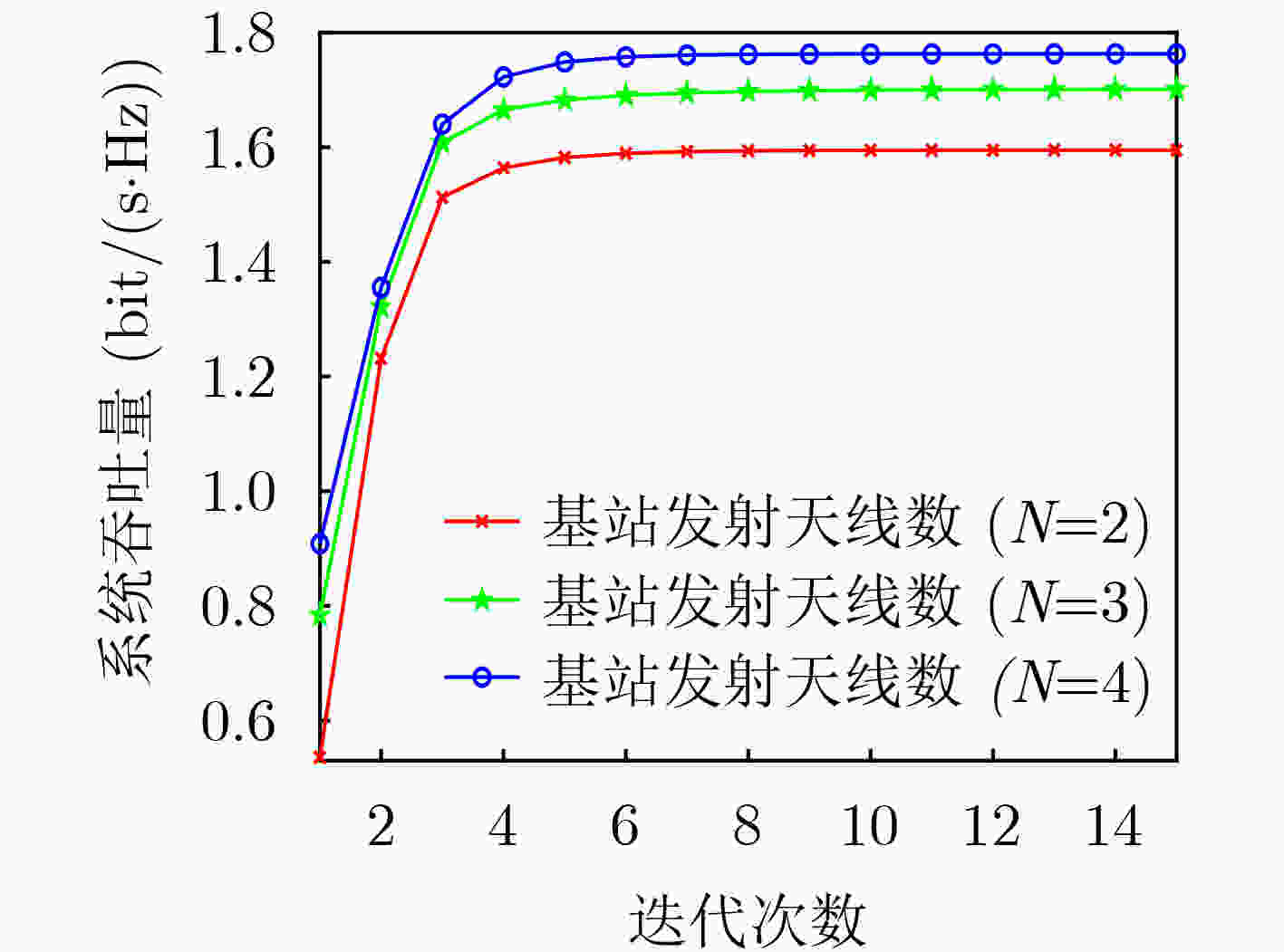
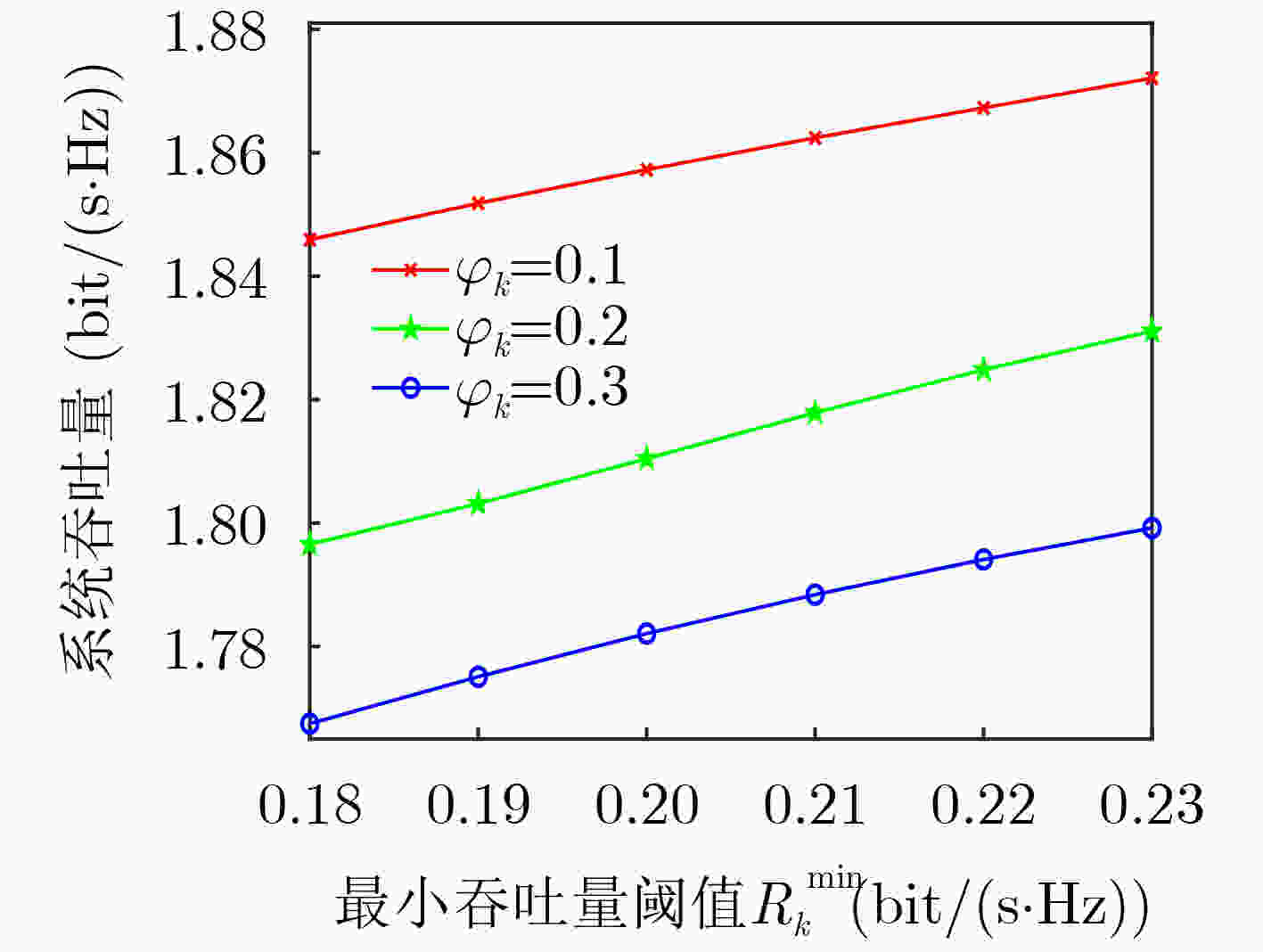
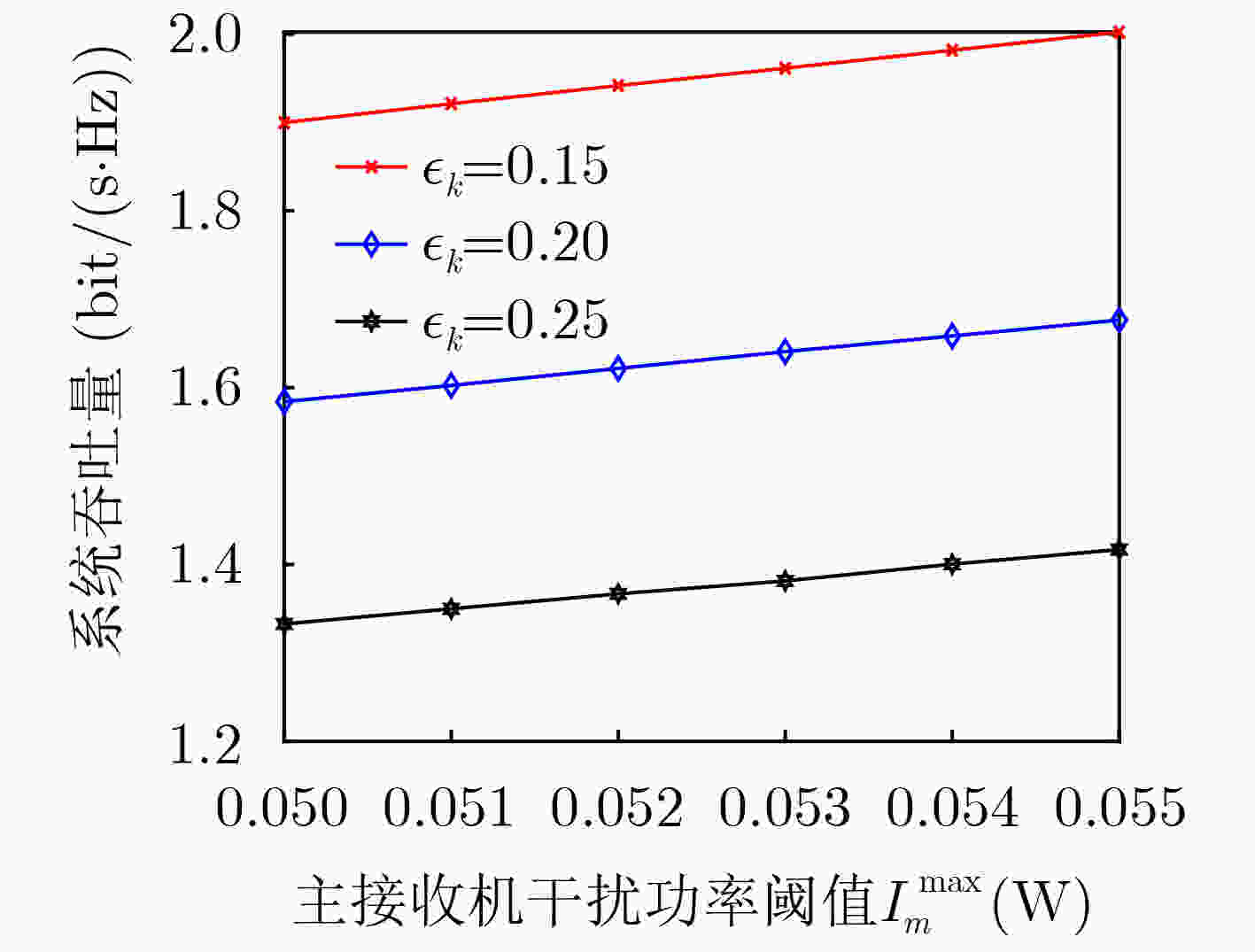


 下载:
下载:
