Spiking Neural Network Recognition Method Based on Dynamic Visual Motion Features
-
摘要: 针对现有脉冲神经网络(SNN)对动态视觉事件流识别精度低与实时性差等问题,该文提出一种基于动态视觉运动特征的脉冲神经网络识别方法。首先利用基于事件的运动历史信息表示与梯度方向计算提取事件流中的动态运动特征;然后引入时空池化操作来消除事件在时间和空间上的冗余,保留显著的运动特征;最后,将特征事件流输入脉冲神经网络进行学习与识别。在基准的动态视觉数据集上的实验结果表明,动态视觉运动特征可显著提升SNN对于事件流的识别精度与计算速度。Abstract: Considering the shortcomings of the low recognition accuracy and poor real-time performance of existing Spiking Neural Networks (SNN) for dynamic visual event streams, a SNN recognition method based on dynamic visual motion features is proposed in this paper. First, the dynamic motion features in the event stream are extracted using the event-based motion history information representation and gradient direction calculation. Then, the spatiotemporal pooling operation is introduced to eliminate the redundancy of events in the temporal and spatial domain, further retaining the significant motion features. Finally, the feature event streams are fed into the SNN for learning and recognition. Experiments conducted on benchmark dynamic visual datasets show that dynamic visual motion features can significantly improve the recognition accuracy and computational speed of SNN for event streams.
-
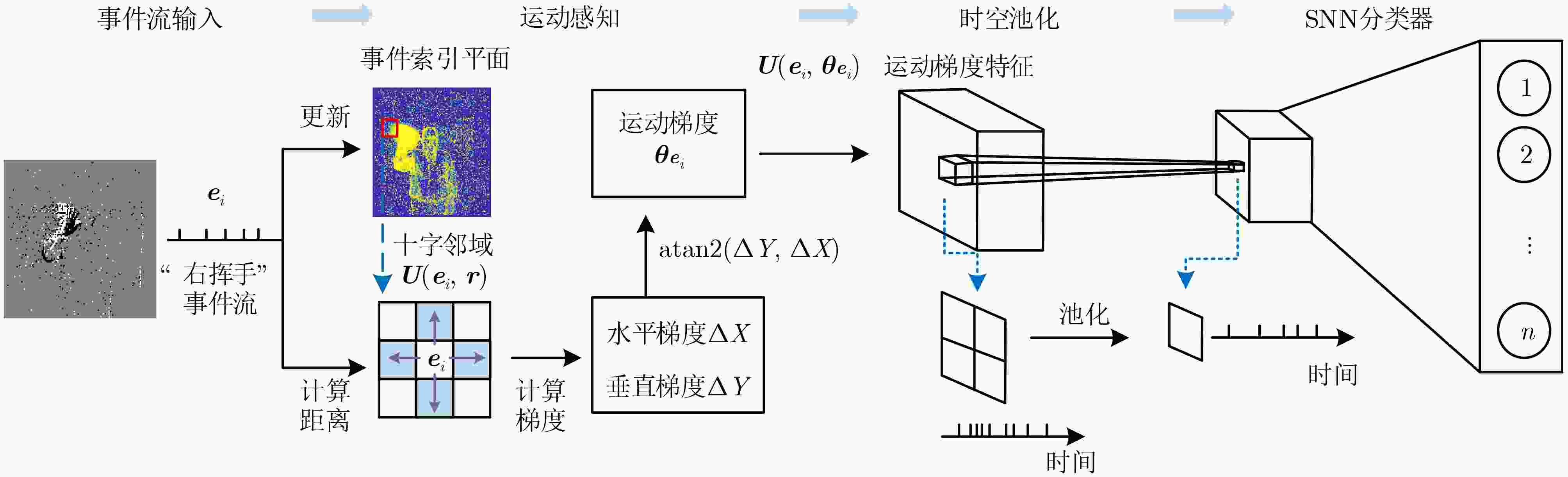
算法1 动态视觉运动特征算法 1: 输出: $ ({e_i},{\theta _{{e_i}}}) $ 2: 输入: $ r,\tau $,初始化$ {\bf{IS}}(x,y,p) \leftarrow 0 $ 3: for 每个到来的事件 ${{\boldsymbol{e}}_i}$ do 4: $ {\bf{IS}}({x_i},{y_i},{p_i}) \leftarrow i $ // 更新$ {\bf{IS}} $ 5: 计算十字邻域$U({{\boldsymbol{e}}_i},r)$,式(3)—式(6) 6: 利用式(8)、式(9)计算$ \Delta X $和$ \Delta Y $ 7: 计算当前事件的运动梯度方向$ {\theta _{{e_i}}} $,式(7)—式(10) 8: $ ({x_i},{y_i}) \leftarrow ({x_i}/4,{y_i}/4) $ // 时空池化 9: if ${{\boldsymbol{e}}_i}$不在不应期内 then 10: 输出$({{\boldsymbol{e}}_i},{\theta _{ {e_i} } })$ 11: end if 12: end for 表 1 数据集信息与划分情况
数据集 类别数 分辨率 训练集 测试集 DVS128 Gesture 11 128×128 1151 191 Action Recognition 10 346×260 250 41 DailyAction-DVS 12 128×128 1235 205 表 2 基于事件的动作识别算法比较(%)
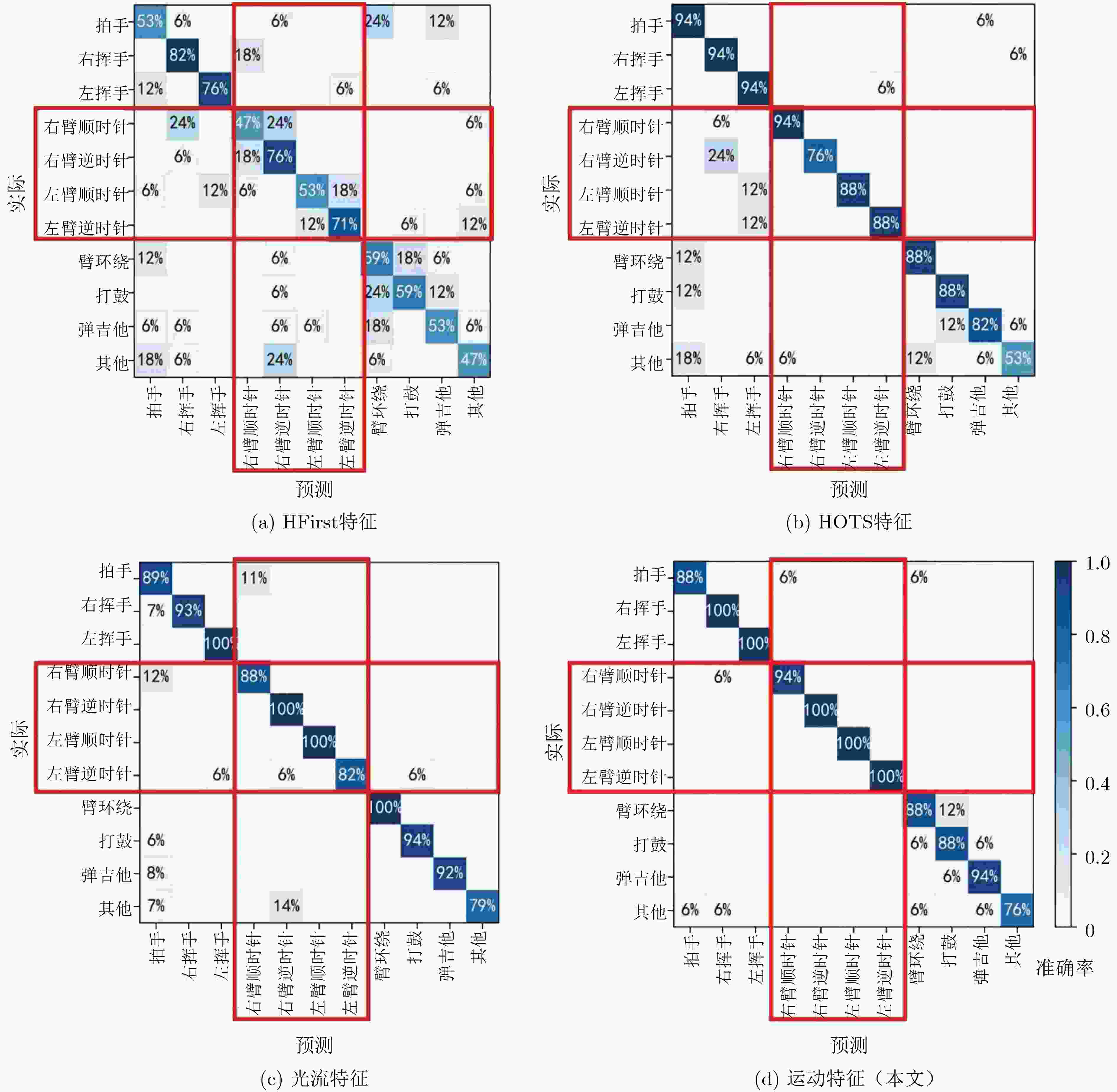
方法 结构 DVS128 Gesture Action Recognition DailyAction-DVS SLAYER[12] 深度SNN (8层) 93.6 – – STBP[13] 深度SNN (6层) 93.4 – – DECOLLE[14] 深度SNN (6层) 95.5 79.6 91.7 SCRNN[21] 脉冲卷积循环网络(5层) 92.0 – – 文献[22] 基于卷积和储层计算的SNN 65.0 – – 文献[9] HFirst特征+单层SNN 61.5 55.0 68.3 SPA [18] HFirst特征+单层SNN 70.1 – 76.9 文献[15] 光流特征+单层SNN 92.7 78.1 90.3 本文 运动特征+单层SNN 94.7 79.5 96.1 注: 加粗字体表示各列最优结果;“–”表示此处数据为空 表 3 不同特征表示方法的性能比较
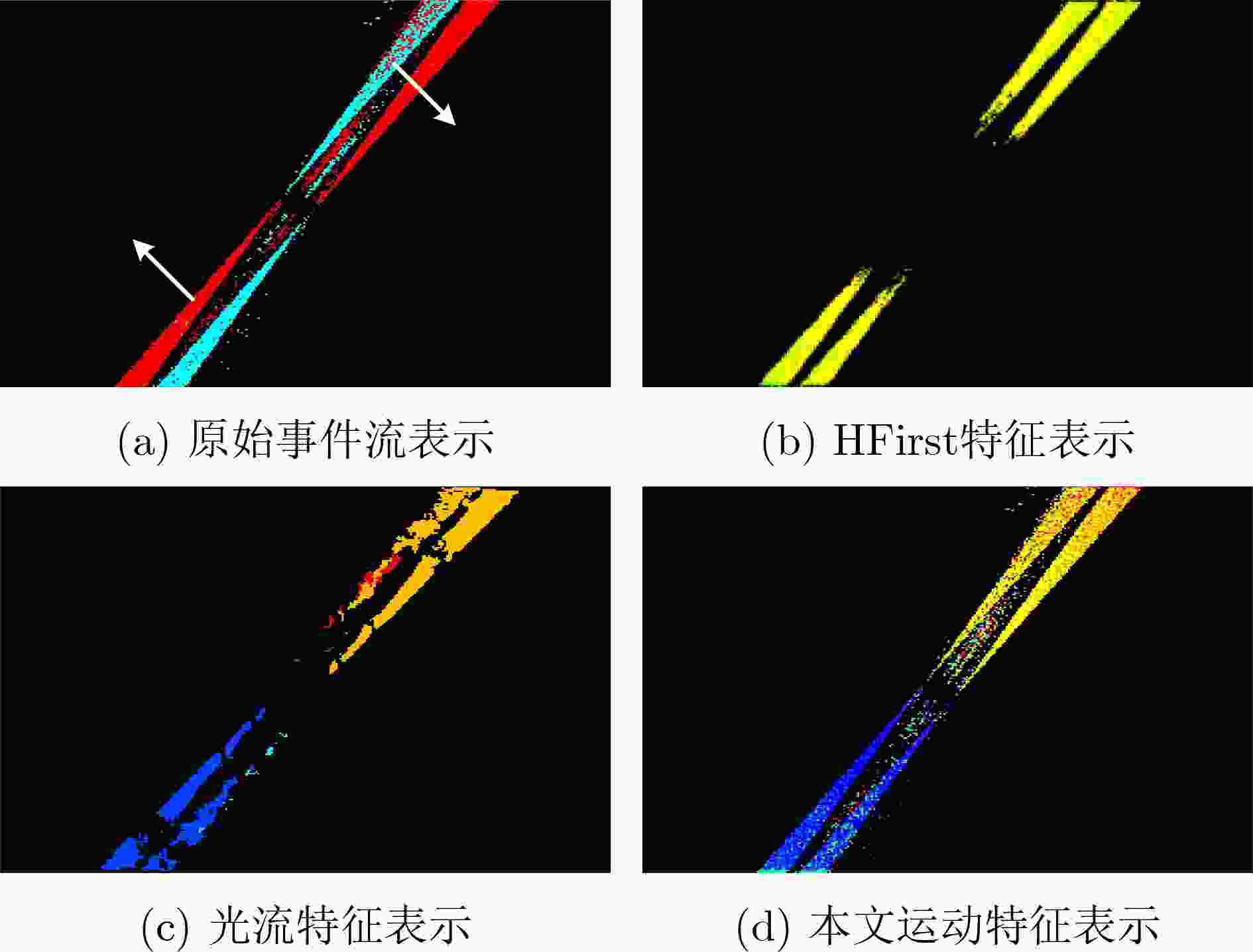
特征表示方法 识别精度(%) 处理速度(kev/s) HFirst特征 61.50 32.9 HOTS特征 85.56 54.7 光流运动特征 91.53 3.67 运动特征(本文) 94.65 913 注: 加粗字体表示各列最优结果 表 4 不同运动历史信息表示方法的性能比较(%)
运动历史信息 时间平面 计数平面 索引平面 DVS128
Gesture93.58 91.44 94.65 Action Recognition 76.92 74.36 79.49 DailyAction -DVS 94.63 93.66 96.10 注: 加粗字体表示各列最优结果 -
[1] GALLEGO G, DELBRÜCK T, ORCHARD G, et al. Event-based vision: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(1): 154–180. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3008413 [2] 张宇豪, 袁孟雯, 陆宇婧, 等. 面向动态事件流的神经网络转换方法[J]. 计算机应用, 2022, 42(10): 3033–3039. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021091607ZHANG Yuhao, YUAN Mengwen, LU Yujing, et al. Neural network conversion method for dynamic event stream[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2022, 42(10): 3033–3039. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021091607 [3] 李家宁, 田永鸿. 神经形态视觉传感器的研究进展及应用综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(6): 1258–1286.LI Jianing and TIAN Yonghong, Recent advances in neuromorphic vision sensors: A survey[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(6): 1258–1286. [4] ROY K, JAISWAL A, and PANDA P. Towards spike-based machine intelligence with neuromorphic computing[J]. Nature, 2019, 575(7784): 607–617. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1677-2 [5] 张铁林, 徐波. 脉冲神经网络研究现状及展望[J]. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(9): 1767–1785.ZHANG Tielin and XU Bo. Research advances and perspectives on spiking neural networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(9): 1767–1785. [6] 胡一凡, 李国齐, 吴郁杰, 等. 脉冲神经网络研究进展综述[J]. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(1): 1–26. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.1006HU Yifan, LI Guoqi, WU Yujie, et al. Spiking neural networks: A survey on recent advances and new directions[J]. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(1): 1–26. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.1006 [7] ORCHARD G, MEYER C, ETIENNE-CUMMINGS R, et al. HFirst: A temporal approach to object recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(10): 2028–2040. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2392947 [8] ZHAO Bo, DING Ruoxi, CHEN Shoushun, et al. Feedforward categorization on AER motion events using cortex-like features in a spiking neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(9): 1963–1978. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2362542 [9] XIAO Rong, TANG Huajin, MA Yuhao, et al. An event-driven categorization model for AER image sensors using multispike encoding and learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(9): 3649–3657. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2945630 [10] LIU Qianhui, PAN Gang, RUAN Haibo, et al. Unsupervised AER object recognition based on multiscale spatio-temporal features and spiking neurons[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(12): 5300–5311. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2966058 [11] LIU Qianhui, RUAN Haibo, XING Dong, et al. Effective AER object classification using segmented probability-maximization learning in spiking neural networks[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 1308–1315. [12] HE Weihua, WU Yujie, DENG Lei, et al. Comparing SNNs and RNNs on neuromorphic vision datasets: Similarities and differences[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 132: 108–120. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2020.08.001 [13] SHRESTHA S B and ORCHARD G. SLAYER: Spike layer error reassignment in time[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2018: 1419–1428. [14] KAISER J, MOSTAFA H, and NEFTCI E. Synaptic plasticity dynamics for deep continuous local learning (DECOLLE)[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2020, 14: 424. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00424 [15] LIU Qianhui, XING Dong, TANG Huajin, et al. Event-based action recognition using motion information and spiking neural networks[C]. The Thirtieth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 1743–1749. [16] AFSHAR S, HAMILTON T J, TAPSON J, et al. Investigation of event-based surfaces for high-speed detection, unsupervised feature extraction, and object recognition[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2019, 12: 1047. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.01047 [17] MANDERSCHEID J, SIRONI A, BOURDIS N, et al. Speed invariant time surface for learning to detect corner points with event-based cameras[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 10237–10246. [18] ZHAO Bo, YU Qiang, DING Ruoxi, et al. Event-driven simulation of the tempotron spiking neuron[C]. 2014 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS) Proceedings, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2014: 667–670. [19] AMIR A, TABA B, BERG D, et al. A low power, fully event-based gesture recognition system[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 7388–7397. [20] MIAO Shu, CHEN Guang, NING Xiangyu, et al. Neuromorphic vision datasets for pedestrian detection, action recognition, and fall detection[J]. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2019, 13: 38. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2019.00038 [21] XING Yannan, DI CATERINA G, and SORAGHAN J. A new spiking convolutional recurrent neural network (SCRNN) with applications to event-based hand gesture recognition[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2020, 14: 590164. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.590164 [22] GEORGE A M, BANERJEE D, DEY S, et al. A reservoir-based convolutional spiking neural network for gesture recognition from DVS input[C]. 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Glasgow, United Kingdom, 2020: 1–9. [23] LU Junwei, DONG Junfei, YAN Rui, et al. An event-based categorization model using spatio-temporal features in a spiking neural network[C]. 2020 12th International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI), Dali, China, 2020: 385–390. [24] LAGORCE X, ORCHARD G, GALLUPPI F, et al. HOTS: A hierarchy of event-based time-surfaces for pattern recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(7): 1346–1359. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2574707 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
