Power Allocation Method Based on Overlapping Visibility Region in Extra Large Scale MIMO System
-
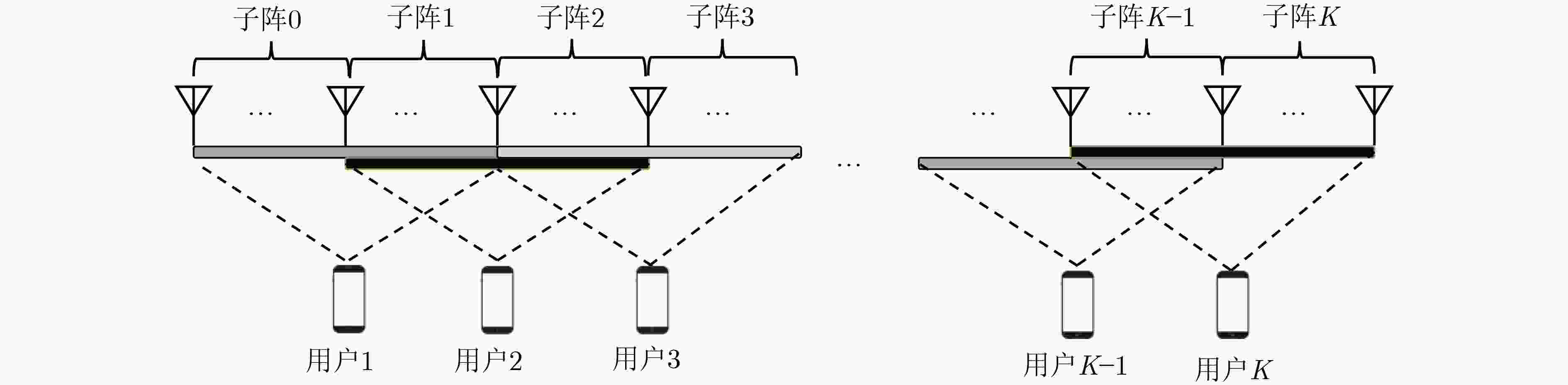
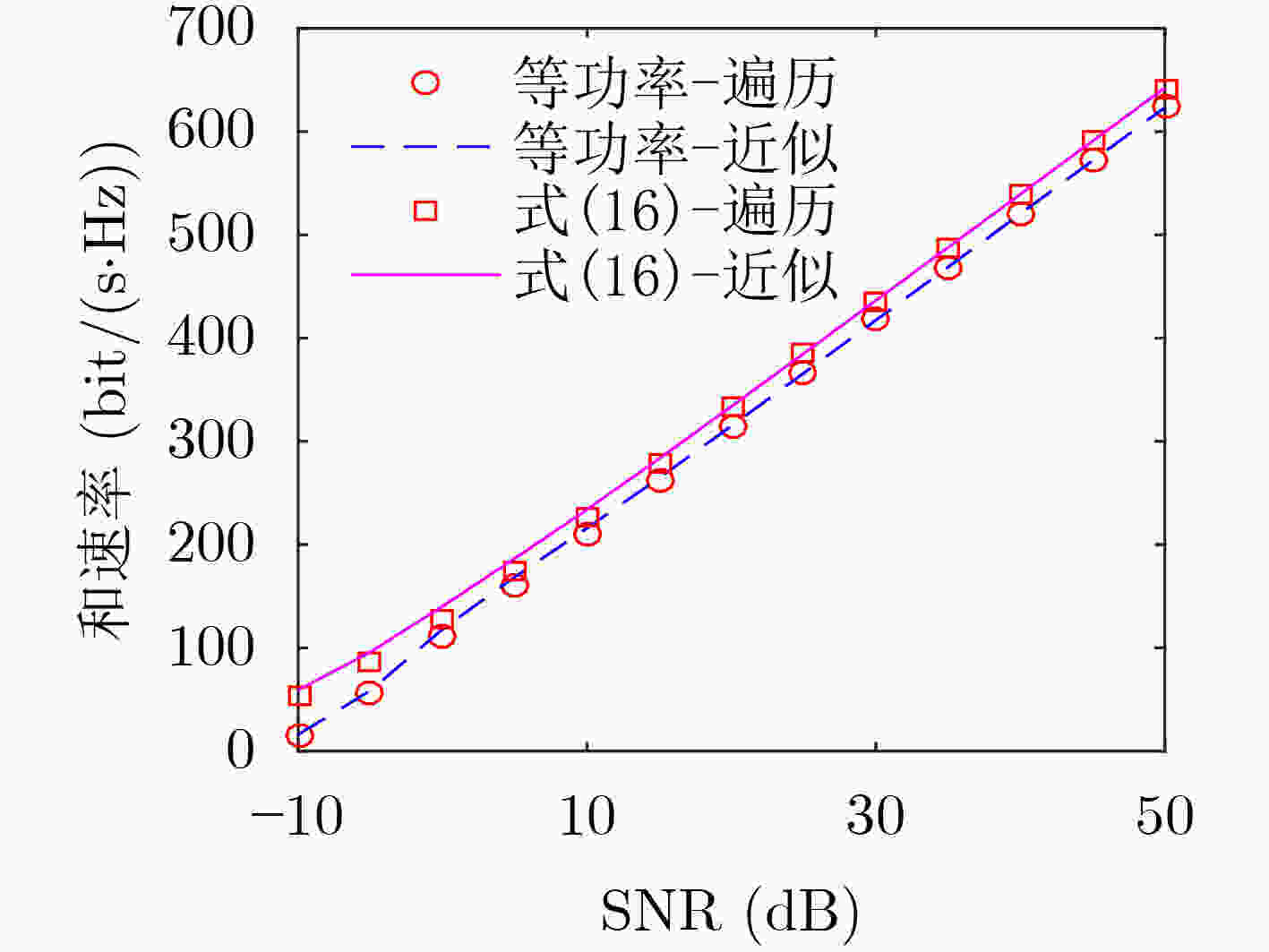
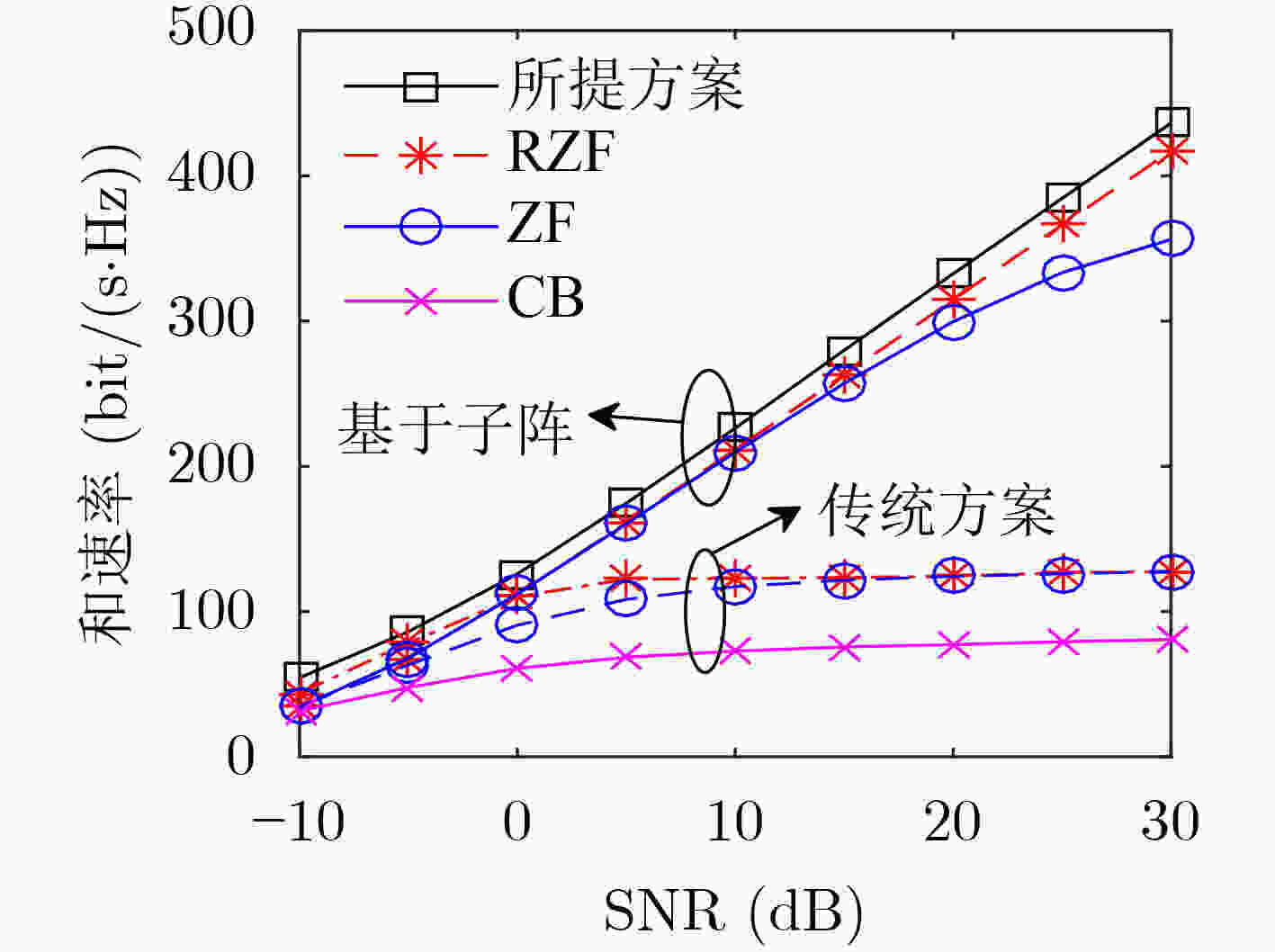
摘要: 该文解决了超大规模多输入多输出(MIMO)系统中不同用户的可视区域(VR)存在相互交叠时的下行功率分配问题。考虑单个基站服务多个单天线用户的超大规模MIMO通信场景,由于基站配备的阵列较大,各个用户受障碍物遮挡仅能与基站部分天线进行通信,这部分天线即为各用户的可视区域。该文考虑不同用户的可视区域分布两两交叠,并依此划分子阵,并在各子阵上进行规则化迫零预编码以降低复杂度。接着基于大维随机矩阵理论,推导了系统下行遍历和速率的确定性近似表达式。然后,通过最大化该表达式,给出了基于统计信道状态信息的最优用户功率分配方法的闭式解。最后,仿真结果表明,和速率近似表达式的精度很高,所提功率分配方法能有效提高系统性能。Abstract: In an extra large scale Multiple-Input Multiple-Output(MIMO) system where the Visibility Regions(VR) of different users are overlapping, the ergodic sum-rate is maximized by designing power allocation. Specifically, one base station equipped with an extra large scale array serves multiple users equipped with single-antenna, and their VRs are overlapped with adjacent users’. To reduce the inter-users interference and precoding complexity, the base station array is divided into several subarrays by the VR distributions, and then the regularized zero forcing precoding is employed for different subarray respectively. Furthermore, by exploiting the statistical channel state information, an approximation of the ergodic sum-rate is derived based on the large-dimensional random matrix theory. Based on the approximations, an optimal power allocation solution for different users is given in closed-form. Simulations illustrate that the proposed approximation fits the ergodic results well, and the proposed power allocation method can effectively improve system performances.
-
表 1 仿真参数设置[11]
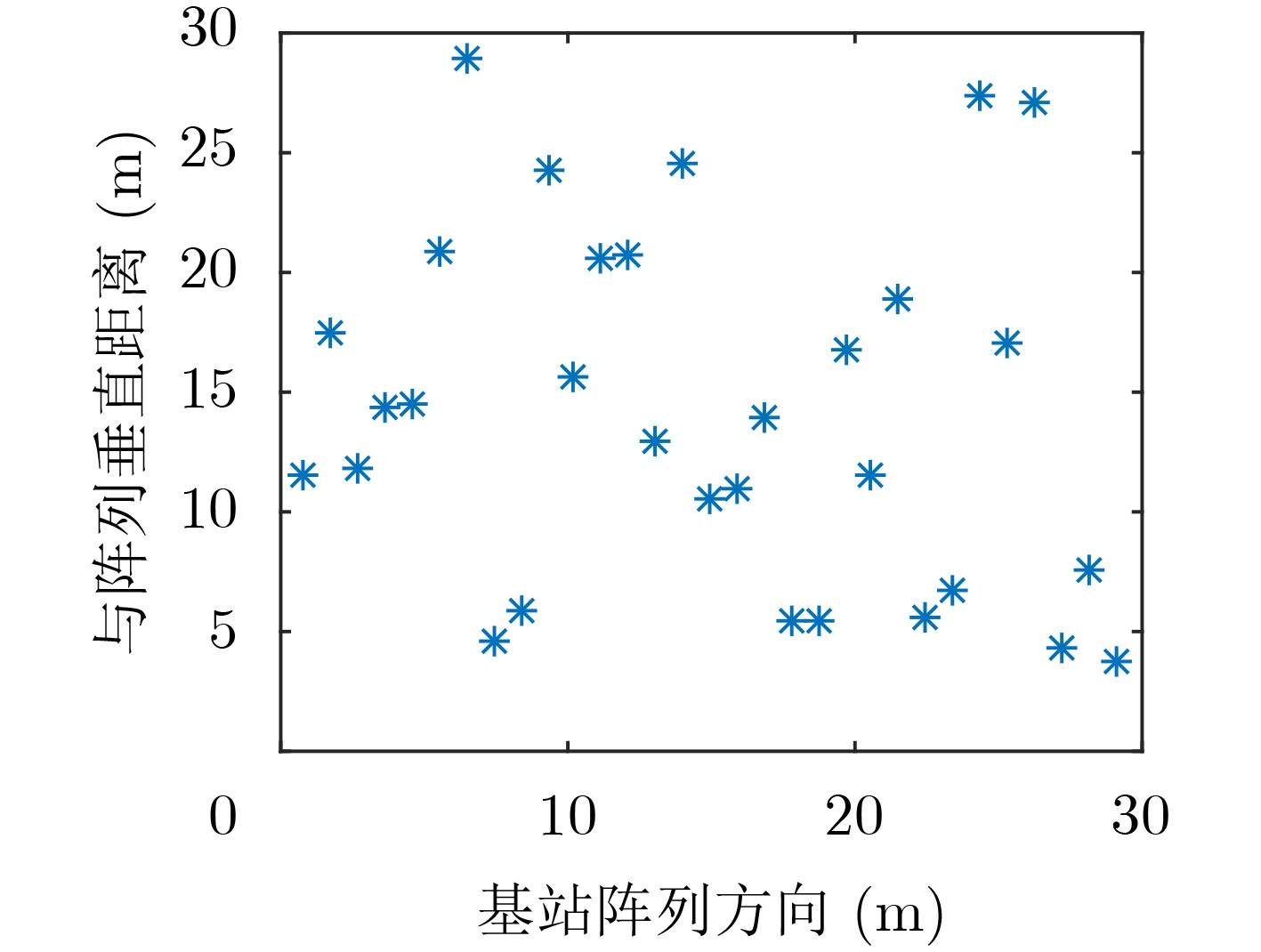
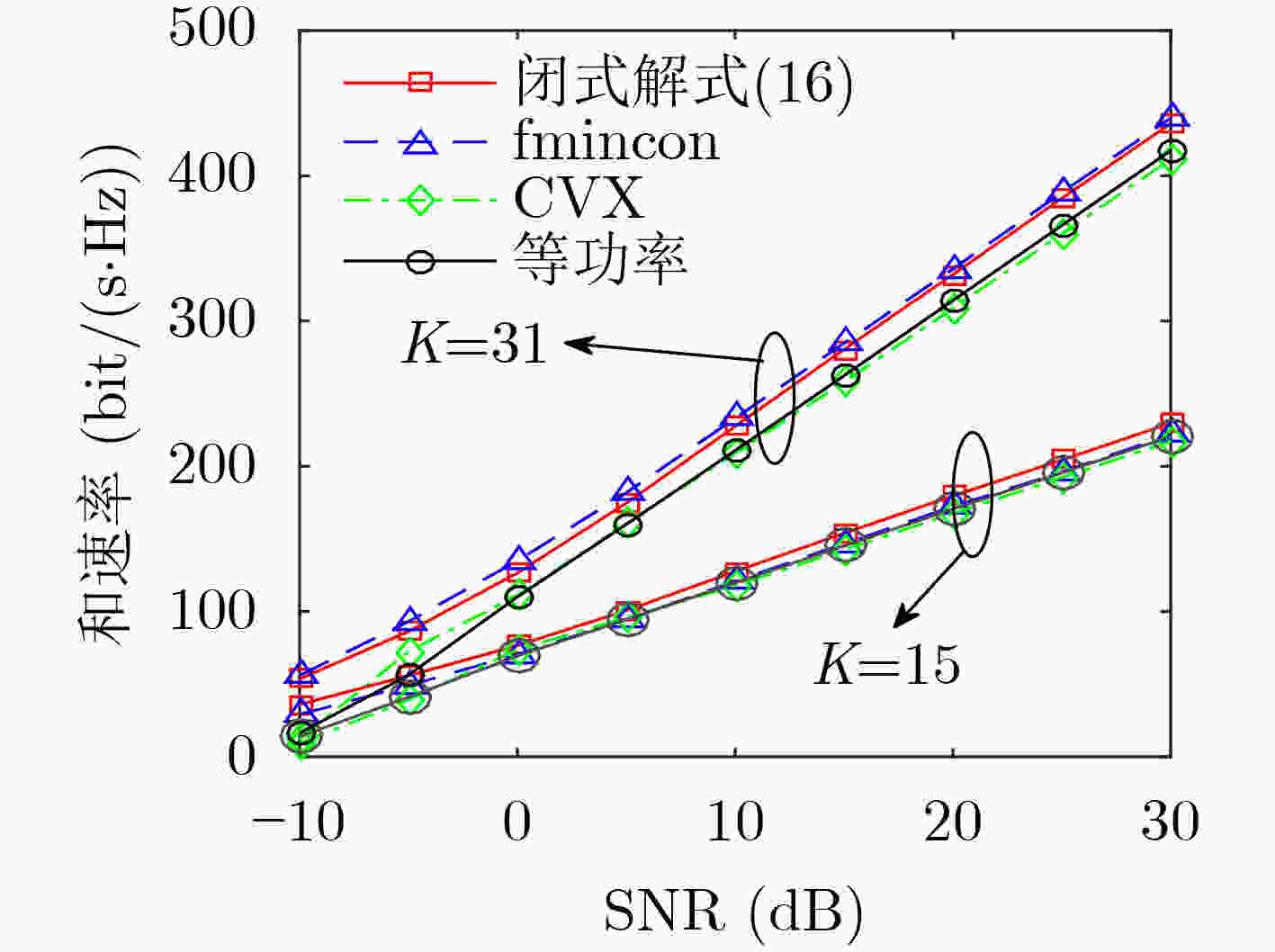
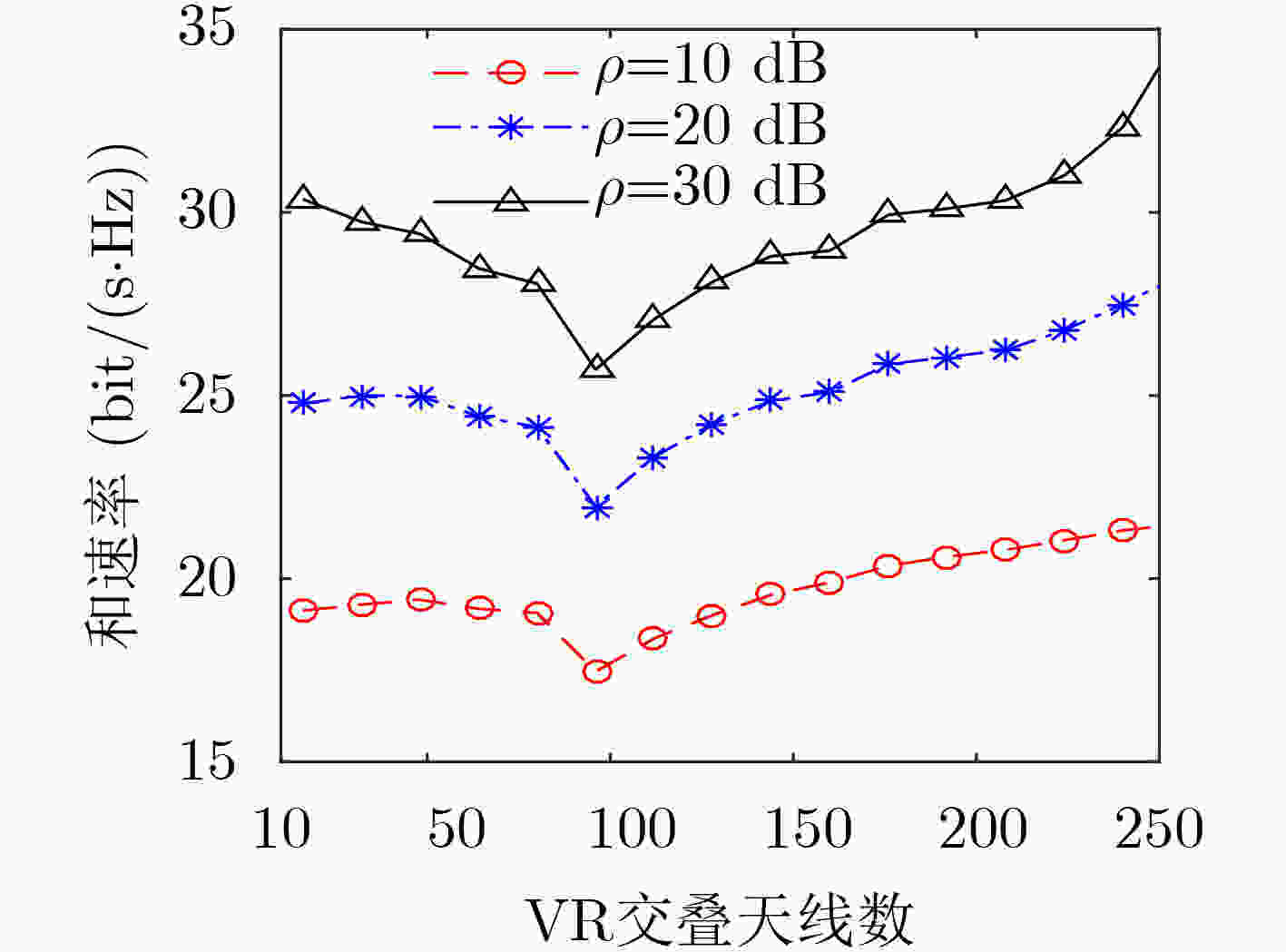
参数 天线数$ M $ 用户数$ K $ 阵列长$ L $ 参考损耗$ {\beta _0} $ 损耗因子$ \mathcal{K} $ VR长度$ D $ 实验次数 数值 256 31 30 m $ {10^{ - 3.53}} $ 3 16 $ {10^4} $ -
[1] 尤肖虎, 尹浩, 邬贺铨. 6G与广域物联网[J]. 物联网学报, 2020, 4(1): 3–11. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2020.00158YOU Xiaohu, YIN Hao, and WU Hequan. On 6G and wide-area IoT[J]. Chinese Journal on Internet of Things, 2020, 4(1): 3–11. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2020.00158 [2] CHEN Xiaoming, NG D W K, YU Wei, et al. Massive access for 5G and beyond[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(3): 615–637. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3019724 [3] LU Haiquan and ZENG Yong. Near-field modeling and performance analysis for multi-user extremely large-scale MIMO communication[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(2): 277–281. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3129317 [4] IMT-2030(6G)推进组. 6G总体愿景与潜在关键技术[R]. IMT-2030(6G)推进组, 2021. [5] HAN Yu, JIN Shi, WEN Chaokai, et al. Localization and channel reconstruction for extra large RIS-assisted massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2022, 16(5): 1011–1025. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2022.3174654 [6] GONZÁLEZ-COMA J P, LÓPEZ-MARTÍNEZ F J, and CASTEDO L. Low-complexity distance-based scheduling for multi-user XL-MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(11): 2407–2411. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3101940 [7] CUI Mingyao and DAI Linglong. Channel estimation for extremely large-scale MIMO: Far-field or near-field?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(4): 2663–2677. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3146400 [8] FILHO J C, BRANTE G, SOUZA R D, et al. Exploring the non-overlapping visibility regions in XL-MIMO random access and scheduling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(8): 6597–6610. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3151329 [9] HUANG Chongwen, ZAPPONE A, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(8): 4157–4170. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2922609 [10] LI Xueru, ZHOU Shidong, BJÖRNSON E, et al. Capacity analysis for spatially non-wide sense stationary uplink massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(12): 7044–7056. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2464219 [11] ALI A, DE CARVALHO E, and HEATH R W. Linear receivers in non-stationary massive MIMO channels with visibility regions[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(3): 885–888. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2898572 [12] MARINELLO J C, ABRÃO T, AMIRI A, et al. Antenna selection for improving energy efficiency in XL-MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(11): 13305–13318. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3022708 [13] ZHANG Jun, WEN Chaokai, JIN Shi, et al. Large system analysis of cooperative multi-cell downlink transmission via regularized channel inversion with imperfect CSIT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2013, 12(10): 4801–4813. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2013.081413.120460 [14] BAI Zhidong, FANG Zhaoben, and LIANG Yingchang. Spectral Theory of Large Dimensional Random Matrices and its Applications to Wireless Communications and Finance Statistics: Random Matrix Theory and its Applications[M]. Singapore: World Scientific, 2014: 11–16. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
