Design of High Area Efficiency Elliptic Curve Scalar Multiplier Based on Fast Modulo Reduction of Bit Reorganization
-
摘要: 针对现有椭圆曲线密码标量乘法器难以兼顾灵活性和面积效率的问题,该文设计了一种基于比特重组快速模约简的高面积效率标量乘法器。首先,根据椭圆曲线标量乘的运算特点,设计了一种可实现乘法和模逆两种运算的硬件复用运算单元以提高硬件资源使用率,并采用Karatsuba-Ofman算法提高计算性能。其次,设计了基于比特重组的快速模约简算法,并实现了支持secp256k1, secp256r1和SCA-256(SM2标准推荐曲线)快速模约简计算的硬件架构。最后,对点加和倍点的模运算操作调度进行了优化,提高乘法与快速模约简的利用率,降低了标量乘计算所需的周期数量。所设计的标量乘法器在55 nm CMOS工艺下需要275 k个等效门,标量乘运算速度为48309次/s,面积时间积达到5.7。Abstract: To solve the problem that existing elliptic curve cryptography scalar multipliers are difficult to balance flexibility and area efficiency, a scalar multiplier with high area efficiency based on bit reorganization fast modular reduction is designed. Firstly, according to the operation characteristics of elliptic curve scalar multiplication, a hardware multiplexing operation unit that can realize two operations of multiplication and modular inversion is designed to improve the utilization rate of hardware resources, and the Karatsuba-Ofman algorithm is used to improve the calculation performance. Secondly, a fast modular reduction algorithm based on bit reorganization is designed, and a hardware architecture supporting secp256k1, secp256r1 and SCA-256 (SM2 standard recommended curve) fast modular reduction calculation is implemented. Finally, the scheduling of modular operations for point addition and point doubling is optimized to improve the utilization of multiplication and fast modular reduction, and reduce the number of cycles required for scalar multiplication calculations. The designed scalar multiplier requires 275 k equivalent gates in 55 nm CMOS technology, the scalar multiplication operation speed is 48309 times/s, and the area-time product reaches 5.7.
-
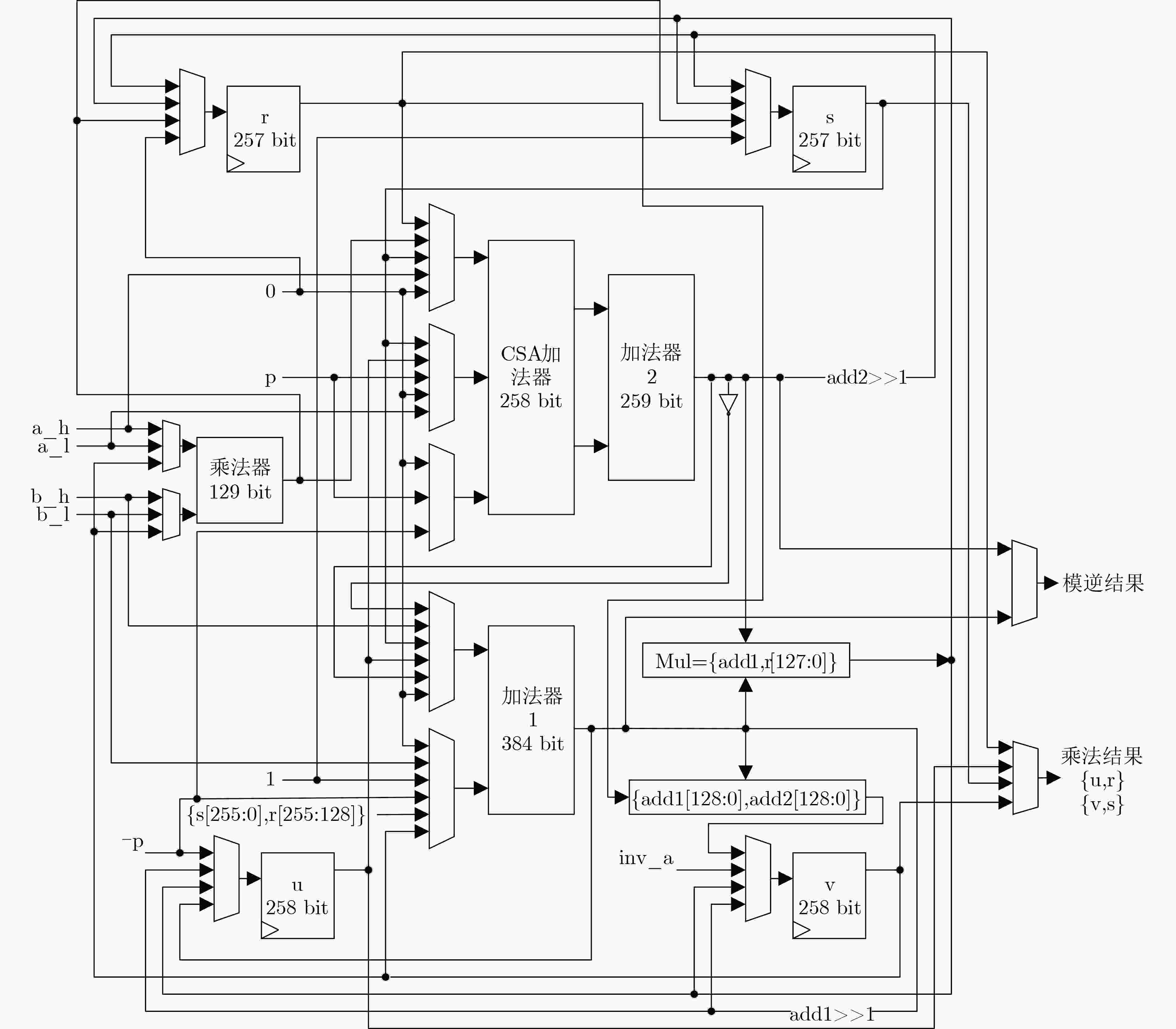
算法1 NAF标量乘算法 输入:$ k,P $ 输出:$ Q = kP $ 步骤1:计算${\text{NAF} }\left( k \right) = \left\{ { {k_{m - 1} }, \cdots ,{k_0} } \right\}$ 步骤2:$ Q \leftarrow \infty $ 步骤3:$ {\text{for }}i \leftarrow m - 1{\text{ down to }}0{\text{ do}} $ $ Q \leftarrow 2Q $ $ {\text{if }}{k_i} = 1{\text{ then}} $ $ Q \leftarrow Q + P $ $ {\text{if }}{k_i} = - 1{\text{ then}} $ $ Q \leftarrow Q - P $ 步骤4:返回$ Q $ 算法2 改进的Karatsuba算法操作调度 输入:$ A={a}_{1}{2}^{128}+{a}_{0},\;B={b}_{1}{2}^{128}+{b}_{0} $ 输出:$ C = A \cdot B $ 1:$ s = {a_1}\cdot{b_1} $;$ v\left[ {128:0} \right] = {\text{ }}{a_0} + {a_1} $;
$ v\left[ {257:129} \right] = {b_0} + {b_1} $;2:$ r = {a_0}\cdot{b_0} $;$ {c_1} = r + s $;$u = {\text{~}}{c_1} + 1$; 3:$ v = v\left[ {128:0} \right] \cdot v\left[ {257:129} \right] $;$ {c_1} = v + u $;
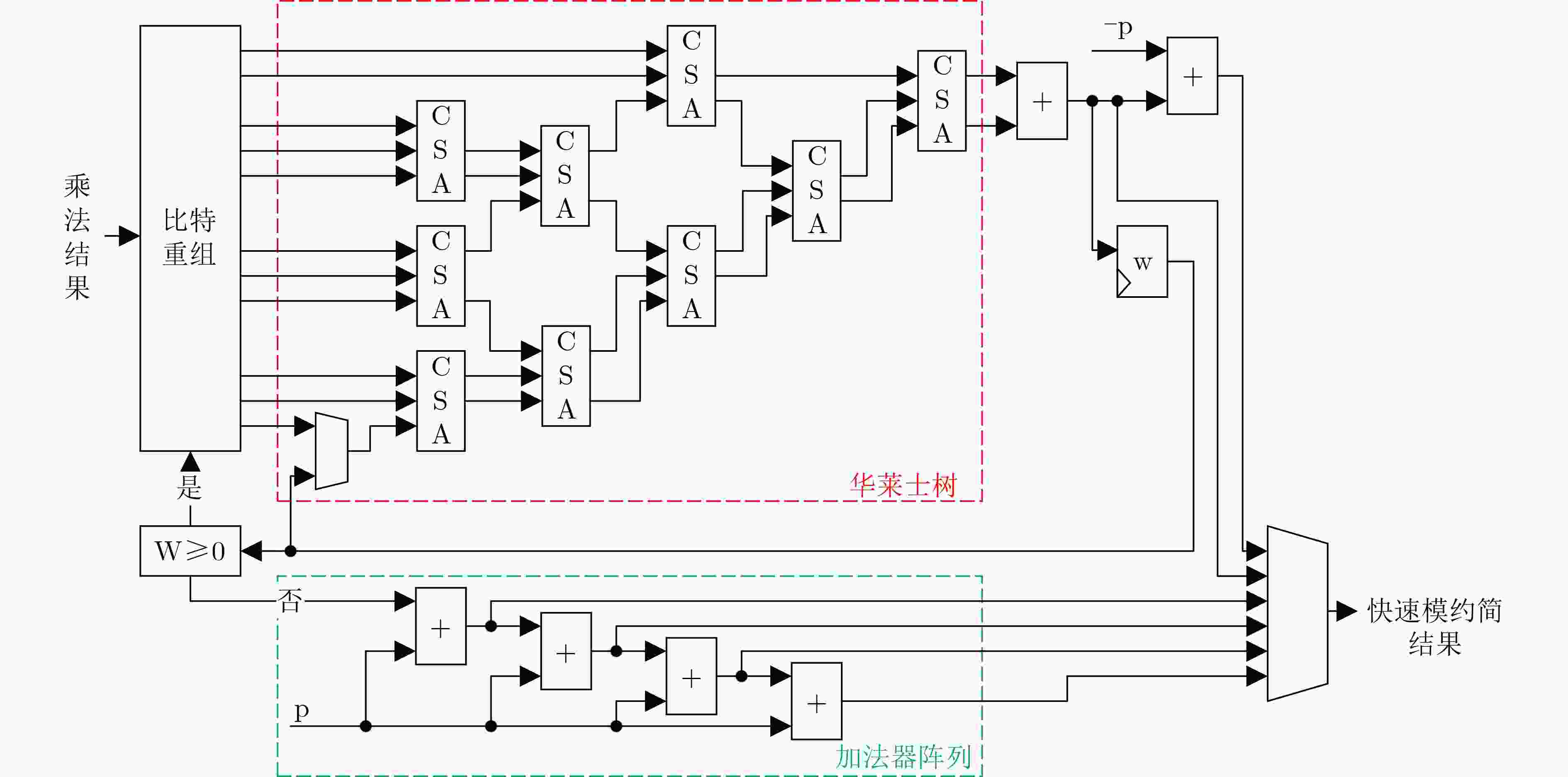
$ {c_2} = \left\{ {s,r\left[ {255:128} \right]} \right\} + {c_1} $;4:返回$ C = \{ {c_2},r\left[ {127:0} \right]\} $ 算法3 secp256k1快速模约简算法 输入:$ C = {c_{127}}{2^{508}} + {c_{126}}{2^{504}} + \cdots + {c_1}{2^4} + {c_0} $, $0 \le C < {p^2}$ 输出:$ C\text{mod} p $ (1) $ {s_1} = ({c_{63}}, \cdots ,{c_0}) $; $ {s_2} = ({c_{127}}, \cdots ,{c_{64}}) $; $ {s_3} = ({c_{126}}, \cdots ,{c_{64}},{c_{127}}) $; $ {s_4} = (2'h0,{c_{124}}, \cdots ,{c_{64}},2'h0,{c_{127}},4'h0) $; $ {s_5} = ({c_{119}}, \cdots ,{c_{64}},{c_{127}}, \cdots ,{c_{120}}) $; $ {s_6} = (214'h0,{c_{127}},2'h0,{c_{127}}, \cdots ,{c_{120}},4'h0) $; $ {s_7} = (214'h0,{c_{127}}, \cdots ,{c_{120}},{c_{126}},{c_{126}},2'h0) $; $ {s_8} = (192'h0,{c_{127}}, \cdots ,{c_{120}},12'h0,{c_{127}},2'h0,$
${c_{127}},10'h0) $;$ {s_9} = (218'h0,{c_{126}},18'h0,{c_{126}},{c_{127}},8'h0) $; $ {s_{10}} = (220'h0,{c_{127}},18'h0,{c_{127}},10'h0) $; $ {s_{11}} = ({c_{125}},254'h0) $; $ {s_{12}} = (2'h0,{c_{125}}, \cdots ,{c_{64}},{c_{127}},2'h0) $; $ {s_{13}} = (218'h0,{c_{127}}, \cdots ,{c_{120}},6'h0) $; $ {s_{14}} = (218'h0,{c_{127}},18'h0,{c_{127}},2'h0,{c_{127}},6'h0) $; $ {s_{15}} = (240'h0,{c_{127}},{c_{126}},8'h0) $; $ {s_{16}} = ({c_{126}},254'h0) $; $ {{\text{z}}_1} = {s_1} + {s_2} + {s_3} + {s_4} + {s_5} + {s_6} + {s_7} + {s_8} + {s_9} + {s_{10}} + $
${s_{11}} - {s_{12}} - {s_{13}} - {s_{14}} - {s_{15}} - {s_{16}} $;$ = ({r_{65}}, \cdots ,{r_0}) $ (2) $ {t_1} = ({r_{63}}, \ldots ,{r_0}) $; $ {t_2} = \left( {216'h0,{\text{ }}{r_{65}},{r_{64}},20'h0,{\text{ }}{r_{65}},{r_{65}},{r_{64}}} \right) $; $ {t_3} = \left( {235'h0,{\text{ }}{r_{65}},{r_{64}},2'h0,{\text{ }}{r_{64}},4'h0} \right) $; $ {t_4} = \left( {242'h0,{\text{ }}{r_{65}},{r_{64}},6'h0} \right) $; $ {z_2} = {\text{ }}{t_1} + {t_2} + {t_3} - {t_4} $ (3)若$({z_1} \ge 0)$,返回$ \left( {{z_2}\text{mod} p} \right) $; 若$ ( - p < {z_1} < 0) $,返回$ \left( {{z_1} + p} \right) $; 若$( - 2p < {z_1} \le - p)$,返回$ \left( {{z_1} + 2p} \right) $; 若$( - 3p < {z_1} \le- 2p)$,返回$ \left( {{z_1} + 3p} \right) $; 表 1 主要模块面积
模块 NAF编码器 资源共享
运算单元模约简 标量乘法器 面积(K·Gates/LUTs) 16 151 45 275 表 2 椭圆曲线操作周期
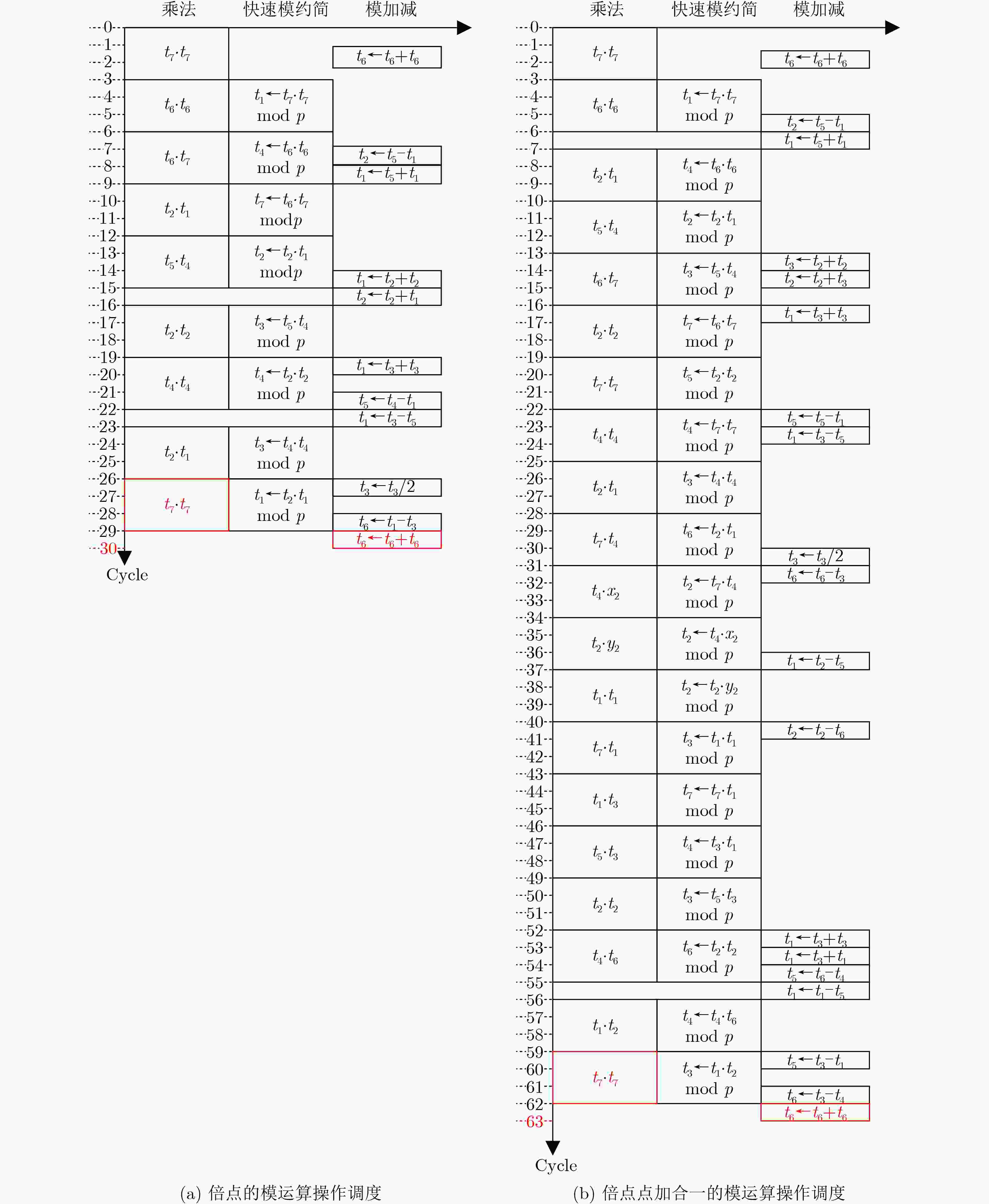
乘法 模约简 模加/减 模逆 NAF编码 倍点 倍点点加 标量乘 周期 3 3 1 360 256 27 60 10366 表 3 256位素数域下椭圆曲线标量乘法器的性能比较
方案 工艺(nm) 曲线 主频(MHz) 周期 面积(K·Gates/LUTs) 单次时间(μs) 吞吐量(次/s) AT 本文 55 secp256k1/r1, SCA-256 500 10366 275 20.7 48309 5.7 文献[22] 55 secp256r1 300 7955 306 27 37712 8.1 文献[9] 55 256 136 458200 189 1450 690 274 文献[10] 65 256 546.5 397300 447 730 1370 326.3 文献[11] 65 secp256r1 188 2300 3500 12.5 80000 43.7 本文 130 secp256k1/r1, SCA-256 243 10366 314 42.5 23529 13.3 文献[6] 130 SCA-256 250 14240 280 57 17544 15.9 文献[12] 130 256 150 610000 57.1 4070 246 232 文献[14] 130 SCA-256 214 45500 208 211 4740 44.2 文献[13] 180 secp256r1 185 36800 144.8 71 14084 28.9 本文 Virtex-7 secp256k1/r1, SCA-256 37 10366 47.4 279 3584 13.2 文献[24] Virtex-7 256 177.7 262.7 32.7 1471 679 48.5 文献[25] Virtex-7 256 72.9 215.9 96.9 2957 338 286.8 -
[1] ANSI. ANSI X9.63 Public key cryptography for the financial services industry: Elliptic curve key agreement and key transport protocols[S]. 2000. [2] BARKER E. Digital signature standard[R]. Gaithersburg: National Institute of Standards and Technology, 2000. [3] Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers. 1363-2000 IEEE standard specifications for public-key cryptography[S]. IEEE, 2000. [4] JAVEED K, SAEED K, and GREGG D. High-speed parallel reconfigurable Fp multipliers for elliptic curve cryptography applications[J]. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 2022, 50(4): 1160–1173. doi: 10.1002/cta.3206 [5] WANG Huaqun, HE Debiao, and JI Yimu. Designated-verifier proof of assets for bitcoin exchange using elliptic curve cryptography[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 107: 854–862. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2017.06.028 [6] HU Xianghong, ZHENG Xin, ZHANG Shengshi, et al. A high-performance elliptic curve cryptographic processor of SM2 over GF(p)[J]. Electronics, 2019, 8(4): 431. doi: 10.3390/electronics8040431 [7] HUANG Hai, NA Ning, XING Lin, et al. An improved wNAF Scalar-multiplication algorithm with low computational complexity by using prime precomputation[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 31546–31552. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3061124 [8] 赵石磊, 杨晓秋, 刘志伟, 等. 一种低复杂度的改进wNAF标量乘算法[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(4): 977–983. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20211016ZHAO Shilei, YANG Xiaoqiu, LIU Zhiwei, et al. An Improved wNAF Scalar-Multiplication Algorithm With Low Computational Complexity[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(4): 977–983. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20211016 [9] LIU Zilong, LIU Dongsheng, and ZOU Xuecheng. An efficient and flexible hardware implementation of the dual-field elliptic curve cryptographic processor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(3): 2353–2362. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2625241 [10] HOSSAIN M S, KONG Yinan, SAEEDI E, et al. High-performance elliptic curve cryptography processor over NIST prime fields[J]. IET Computers & Digital Techniques, 2017, 11(1): 33–42. doi: 10.1049/iet-cdt.2016.0033 [11] LIU Jianwei, CHENG Dongxu, GUAN Zhenyu, et al. A high speed VLSI implementation of 256-bit scalar point multiplier for ECC over GF(p)[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Conference on Intelligence and Safety for Robotics, Shenyang, China, 2018: 184–191. [12] HU Xianghong, ZHENG Xin, ZHANG Shengshi, et al. A low hardware consumption elliptic curve cryptographic architecture over GF(p) in embedded application[J]. Electronics, 2018, 7(7): 104. doi: 10.3390/electronics7070104 [13] CHOI P, LEE M K, KIM J H, et al. Low-complexity elliptic curve cryptography processor based on configurable partial modular reduction over NIST prime fields[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2018, 65(11): 1703–1707. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2017.2756680 [14] ZHANG Dan and BAI Guoqiang. Ultra high-performance ASIC implementation of SM2 with power-analysis resistance[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits (EDSSC), Singapore, 2015: 523–526. [15] ISLAM M M, HOSSAIN M S, SHAHJALAL M, et al. Area-time efficient hardware implementation of modular multiplication for elliptic curve cryptography[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 73898–73906. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988379 [16] HANKERSON D, VANSTONE S, and MENEZES A. Guide to Elliptic Curve Cryptography[M]. New York: Springer, 2004: 312. [17] LUCCA A V, SBORZ G A M, LEITHARDT V R Q, et al. A review of techniques for implementing elliptic curve point multiplication on hardware[J]. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks, 2021, 10(1): 3. doi: 10.3390/jsan10010003 [18] 王敏, 吴震. 抗SPA攻击的椭圆曲线NAF标量乘实现算法[J]. 通信学报, 2012, 33(S1): 228–232.WANG Min and WU Zhen. Algorithm of NAF scalar multiplication on ECC against SPA[J]. Journal on Communications, 2012, 33(S1): 228–232. [19] SOLINAS J A. Efficient arithmetic on Koblitz curves[J]. Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 2000, 19(2): 195–249. doi: 10.1023/A:1008306223194 [20] KARATSUBA A. Multiplication of multidigit numbers on automata[J]. Soviet Physics Doklady, 1963, 7: 595–596. [21] CHOI P, LEE M K, KONG J T, et al. Efficient design and performance analysis of a hardware right-shift binary modular inversion algorithm in GF(p)[J]. Journal of Semiconductor Technology and Science, 2017, 17(3): 425–437. doi: 10.5573/JSTS.2017.17.3.425 [22] HU Xianghong, LI Xueming, ZHENG Xin, et al. A high speed processor for elliptic curve cryptography over NIST prime field[J]. IET Circuits, Devices & Systems, 2022, 16(4): 350–359. doi: 10.1049/CDS2.12110 [23] 于斌, 黄海, 刘志伟, 等. 面向多椭圆曲线的高速标量乘法器设计与实现[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(12): 100–109. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-463X.2020226YU Bin, HUANG Hai, LIU Zhiwei, et al. Design and implementation of high-speed scalar multiplier for multi-elliptic curve[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(12): 100–109. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-463X.2020226 [24] ISLAM M M, HOSSAIN M S, HASAN M K, et al. FPGA implementation of high-speed area-efficient processor for elliptic curve point multiplication over prime field[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 178811–178826. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2958491 [25] ASIF S, HOSSAIN M S, and KONG Yinan. High-throughput multi-key elliptic curve cryptosystem based on residue number system[J]. IET Computers & Digital Techniques, 2017, 11(5): 165–172. doi: 10.1049/iet-cdt.2016.0141 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
