Concurrent Decision Directed and Constant Modulus Equalization Algorithm Based on Quaternion
-
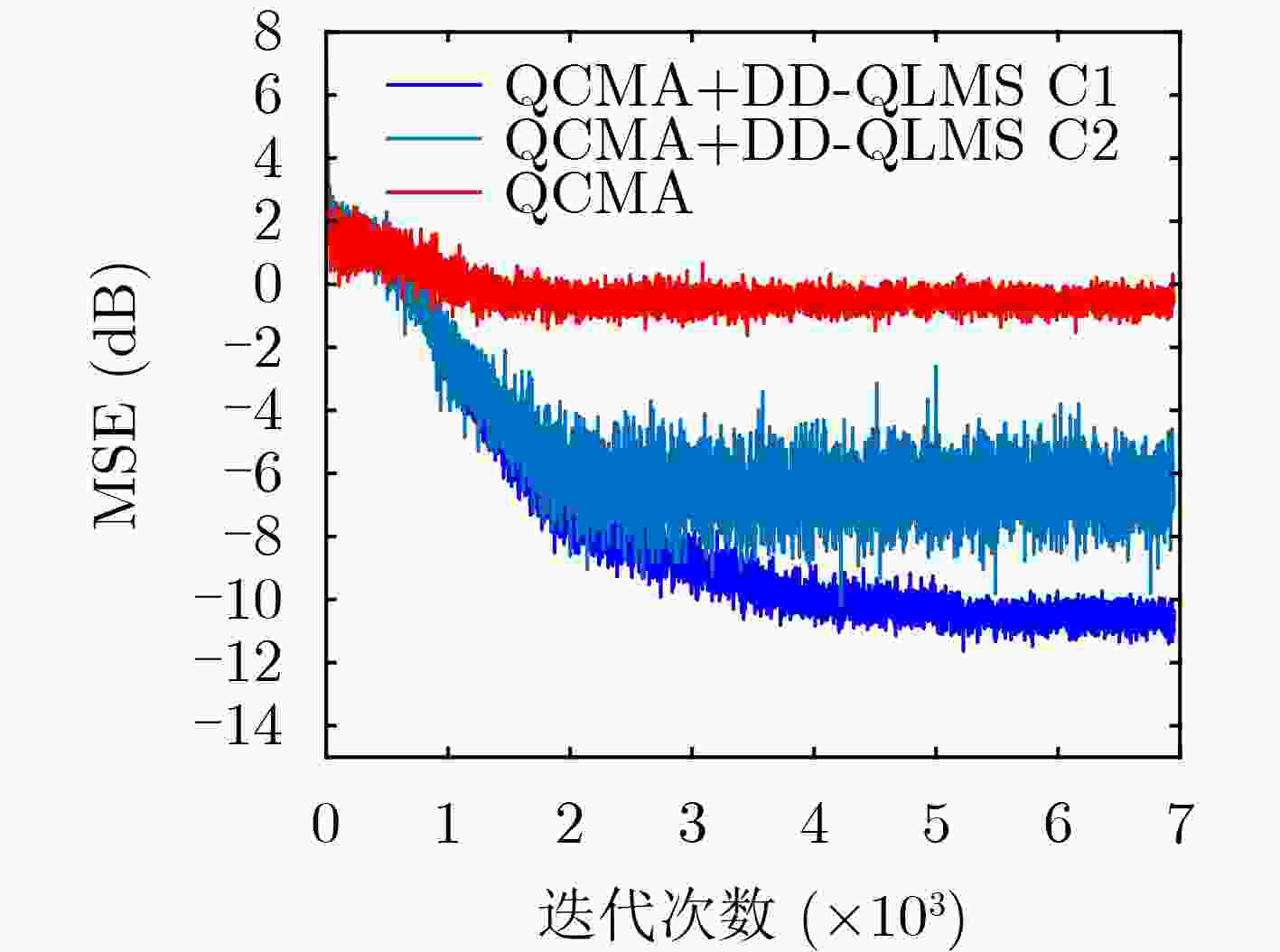
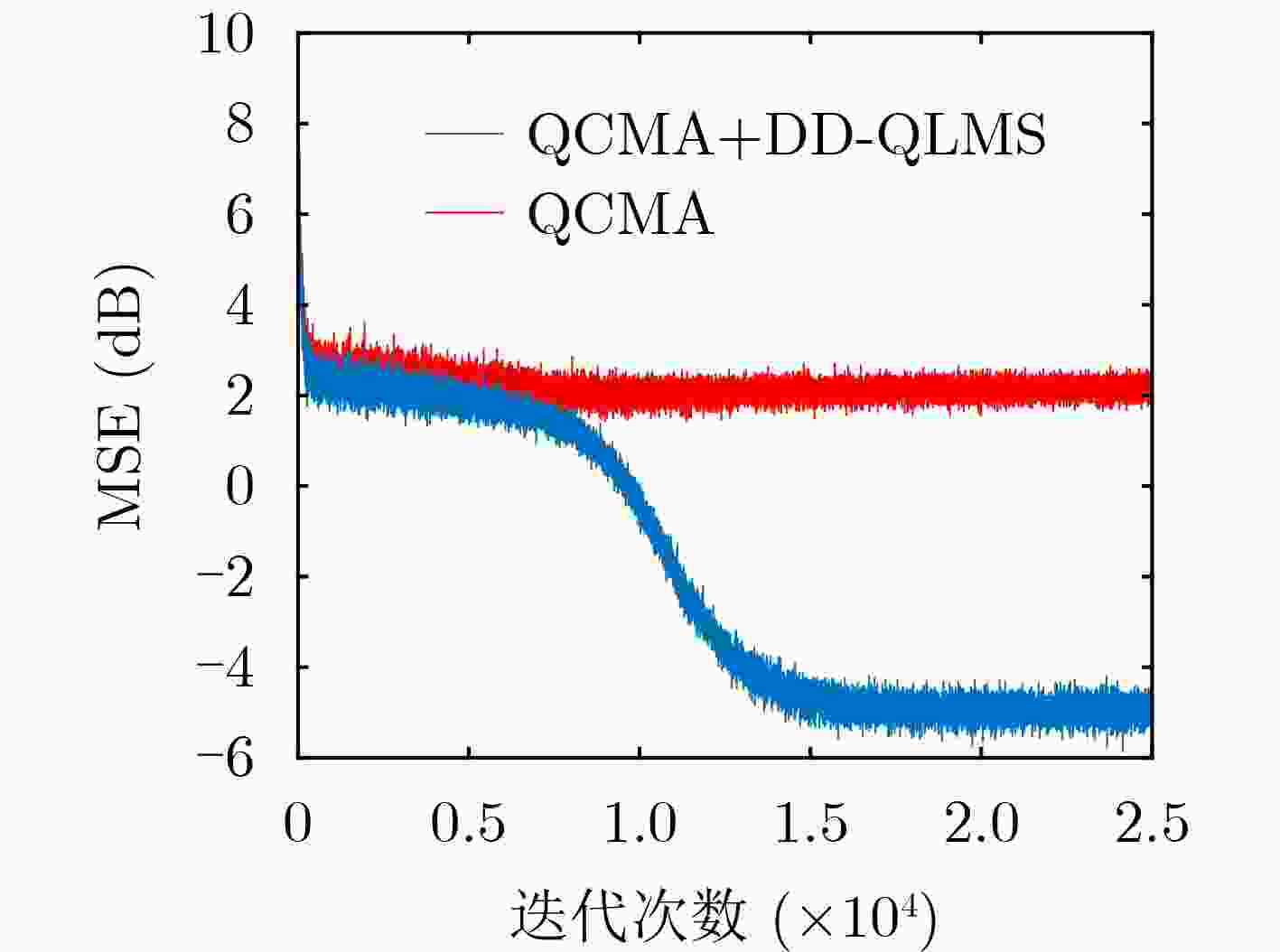
摘要: 近年来4元数理论成为各界学者研究的热点并被应用到许多领域。该文基于4元数自适应滤波算法对正交极化信道均衡问题进行研究。为了解决4元数恒模(QCMA)算法的相位模糊问题,该文将QCMA算法与4元数最小均方算法(QLMS)相结合提出一种4元数直接判决并行恒模(QCMA+DD-QLMS) 算法。基于广义哈密顿实演算(GHR)的梯度运算规则对新的算法做了理论推导并进行MATLAB实验仿真,仿真结果表明该文所提算法不但能够解决QCMA算法相位模糊问题,还具有更小的稳态均方误差(MSE)。
-
关键词:
- 4元数 /
- 正交极化信道均衡 /
- 4元数最小均方算法 /
- 4元数恒模算法 /
- 4元数直接判决并行恒模算法
Abstract: In recent years, quaternion theory has become a research hotspot for scholars and has been applied to many fields. In this paper, the quadrature polarization channel equalization problem is studied based on quaternion adaptive filtering algorithm. In order to solve the phase ambiguity problem of Quaternion Constant Modulus Algorithm (QCMA), a concurrent quaternion Direct Decision constant modulus algorithm (QCMA+DD-QLMS) is proposed by combining QCMA algorithm with Quaternion Least Mean Square (QLMS) algorithm. Based on the gradient operation rules of Generalized Hamilton-Real (GHR), the new algorithm is theoretically deduced and simulated by MATLAB. The simulation results show that the algorithm proposed in this paper can not only solve the phase ambiguity problem of the QCMA, but also has smaller steady-state Mean Square Error (MSE). -
表 1 4-抽头4元数信道脉冲响应
抽头数 实部 i部 j部 k部 0 –1.1696 –0.1135 0.0958 –0.9583 1 0.4989 –0.3639 –0.2515 –0.6047 2 1.0571 –0.3791 1.4957 0.5183 3 0.4911 0.8653 0.1552 –0.8966 -
[1] ISAEVA O M and SARYTCHEV V A. Quaternion presentations polarization state[C]. The 2nd Topical Symposium on Combined Optical-Microwave Earth and Atmosphere Sensing, Atlanta, US, 1995: 195–196. [2] 周珂, 吴成茂, 李昌兴. 基于四元数傅里叶变换的盲彩色图像质量评价[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(18): 181021. doi: 10.3788/LOP57.181021ZHOU Ke, WU Chengmao, and LI Changxing. Quality assessment of blind color images using quaternion Fourier transform[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(18): 181021. doi: 10.3788/LOP57.181021 [3] SAOUD L S, AL-MARZOUQI H, and DERICHE M. Wind speed forecasting using the stationary wavelet transform and quaternion adaptive-gradient methods[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 127356–127367. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3111667 [4] JIANG Mengdi, LIU Wei, and LI Yi. Adaptive beamforming for vector-sensor arrays based on a reweighted zero-attracting quaternion-valued LMS algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2016, 63(3): 274–278. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2015.2482464 [5] GAUDET C J and MAIDA A S. Deep quaternion networks[C]. 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2018: 1–8. [6] 田新宇. 基于四元数的神经网络算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2022.TIAN Xinyu. Research on neural network algorithm based on quaternion[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022. [7] TOOK C C and MANDIC D P. The quaternion LMS algorithm for adaptive filtering of hypercomplex processes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(4): 1316–1327. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2010600 [8] XU Dongpo, JAHANCHAHI C, TOOK C C, et al. Quaternion derivatives: The GHR calculus[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.8168, 2014. [9] MENGÜÇ E C. Novel quaternion-valued least-mean kurtosis adaptive filtering algorithm based on the GHR calculus[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2018, 12(4): 487–495. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2017.0340 [10] MENGÜÇ E C, ACIR N, and MANDIC D P. Widely linear quaternion-valued least-mean kurtosis algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 5914–5922. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3029959 [11] OGUNFUNMI T and SAFARIAN C. The quaternion stochastic information gradient algorithm for nonlinear adaptive systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(23): 5909–5921. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2944757 [12] STERN S and FISCHER R F H. Quaternion-valued multi-user MIMO transmission via dual-polarized antennas and QLLL reduction[C]. 2018 25th International Conference on Telecommunications (ICT), Saint Malo, France, 2018: 63–69. [13] WYSOCKI B J, WYSOCKI T A, and SEBERRY J. Modeling dual polarization wireless fading channels using quaternions[C]. Joint IST Workshop on Mobile Future, 2006 and the Symposium on Trends in Communications. SympoTIC '06, Bratislava, Slovakia, 2006: 68–71. [14] LIU Wei. Antenna array signal processing for quaternion-valued wireless communication systems[C]. 2014 IEEE Benjamin Franklin Symposium on Microwave and Antenna Sub-systems for Radar, Telecommunications, and Biomedical Applications (BenMAS), Philadelphia, USA, 2014: 1–3. [15] LIU Wei. Channel equalization and beamforming for quaternion-valued wireless communication systems[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2017, 354(18): 8721–8733. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2016.10.043 [16] 曾乐雅, 许华, 王天睿. 自适应切换双模盲均衡算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(11): 2780–2786. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160099ZENG Leya, XU Hua, and WANG Tianrui. Dual mode blind equalization algorithm based on adaptive switching[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(11): 2780–2786. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160099 [17] XU Tongtong, XIANG Zheng, YANG Hua, et al. Concurrent modified constant modulus algorithm and decision directed scheme with Barzilai-Borwein method[J]. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2021, 15: 699221. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2021.699221 [18] LI Sen, WANG Yan, and LIN Bin. Concurrent blind channel equalization in impulsive noise environments[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2013, 22(4): 741–746. [19] 胡婉如, 梅如如, 崔健, 等. 一种基于CMA和DDLMS算法的双模式盲均衡算法[J]. 电讯技术, 2021, 61(1): 83–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2021.01.013HU Wanru, MEI Ruru, CUI Jian, et al. A dual-mode blind equalization algorithm based on CMA and DDLMS algorithm[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2021, 61(1): 83–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2021.01.013 [20] 陈康. 室内可见光通信自适应均衡技术的研究[D]. [硕士论文], 长春理工大学, 2019.CHEN Kang. Research on adaptive equalization technology of indoor visible light communication[D]. [Master dissertation], Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2019. [21] CHEN S, COOK T B, and ANDERSON L C. A comparative study of two blind FIR equalizers[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2004, 14(1): 18–36. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2003.04.001 -





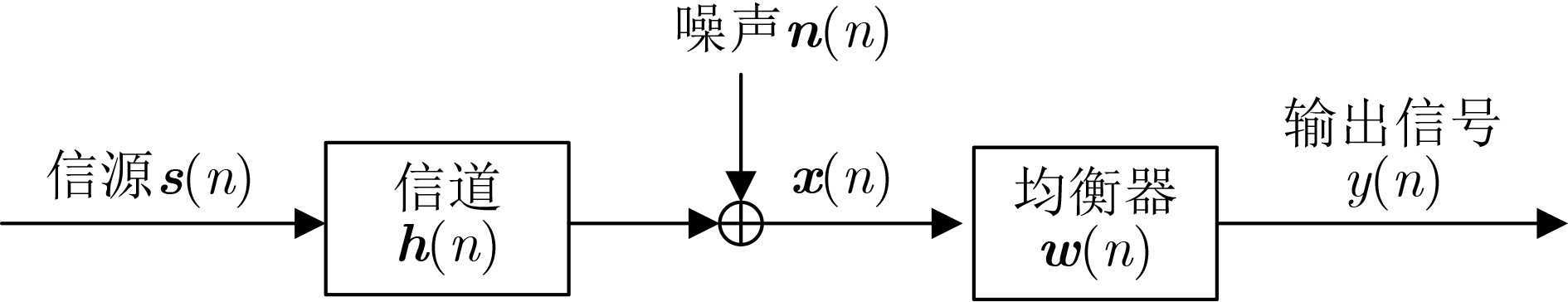
 下载:
下载:
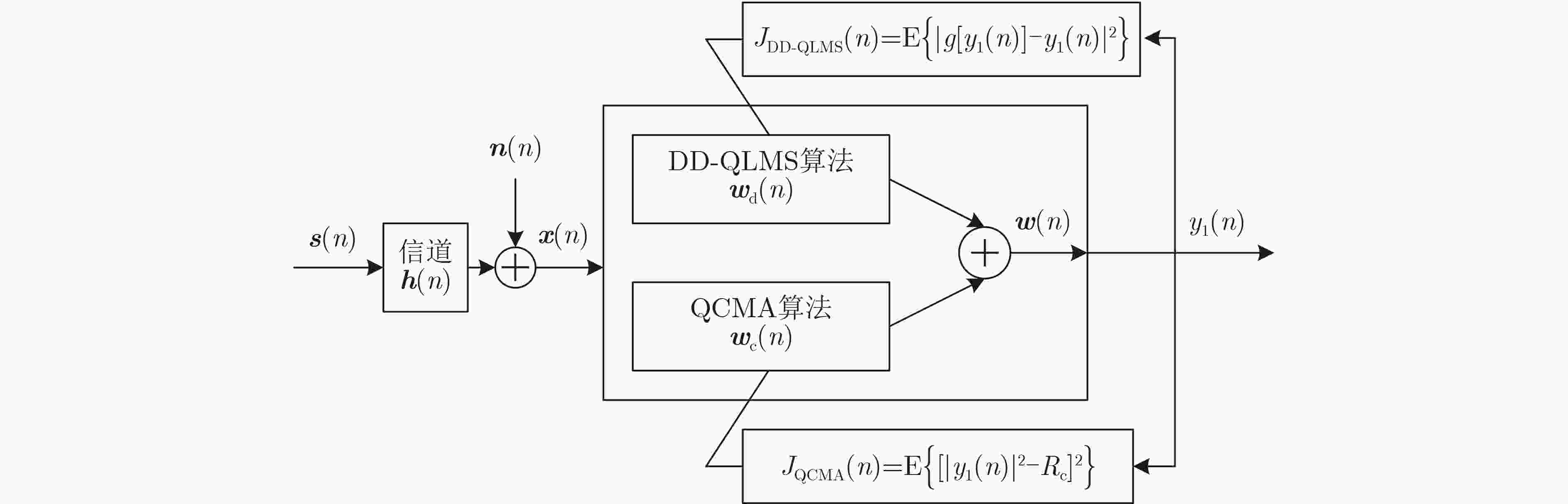
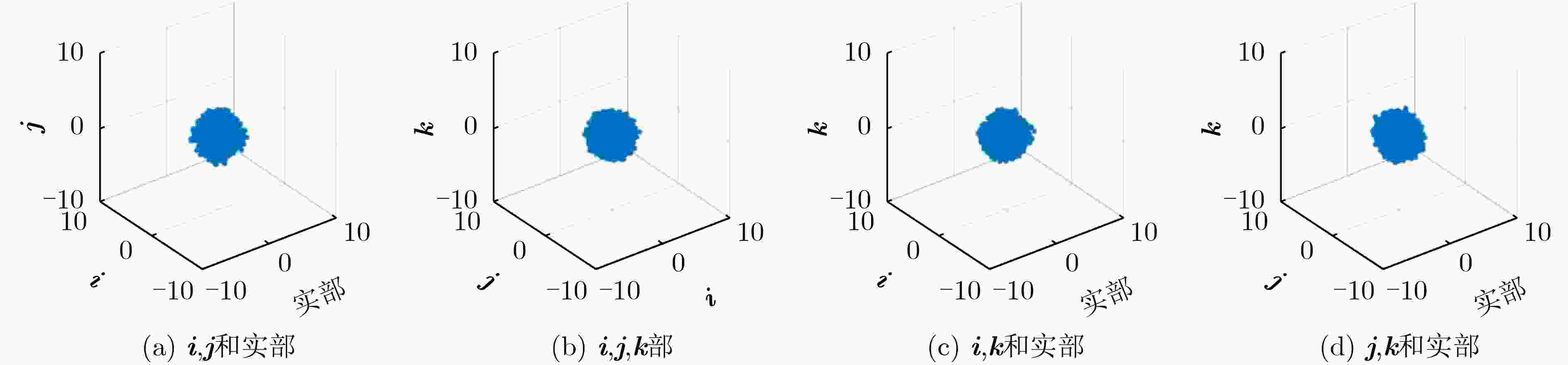
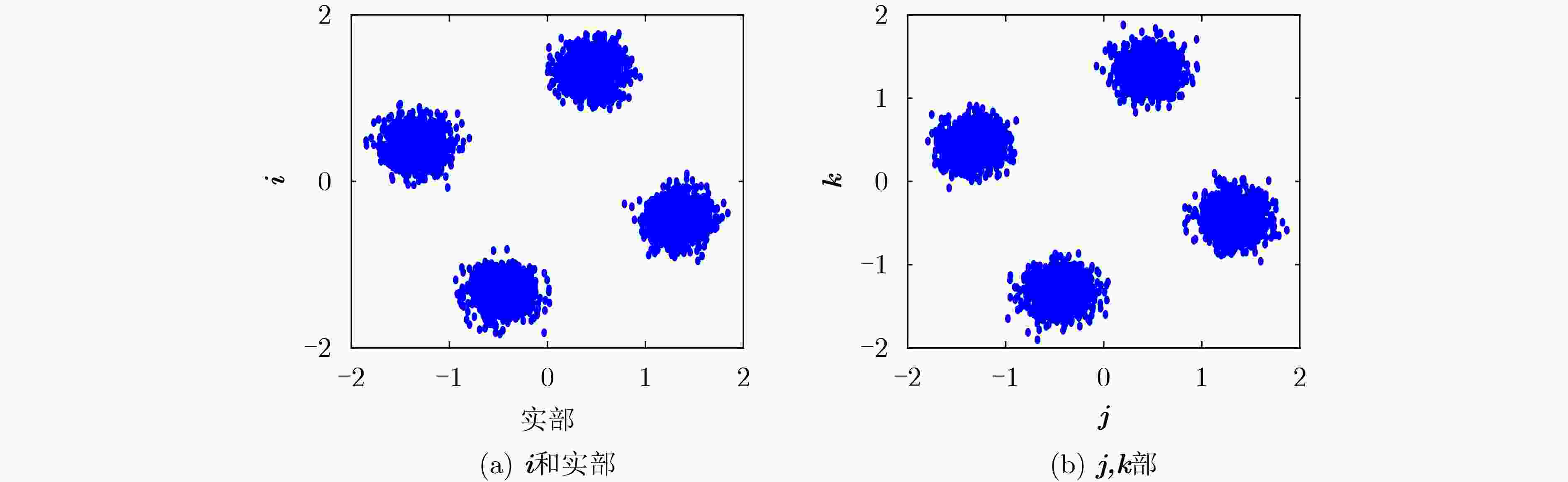
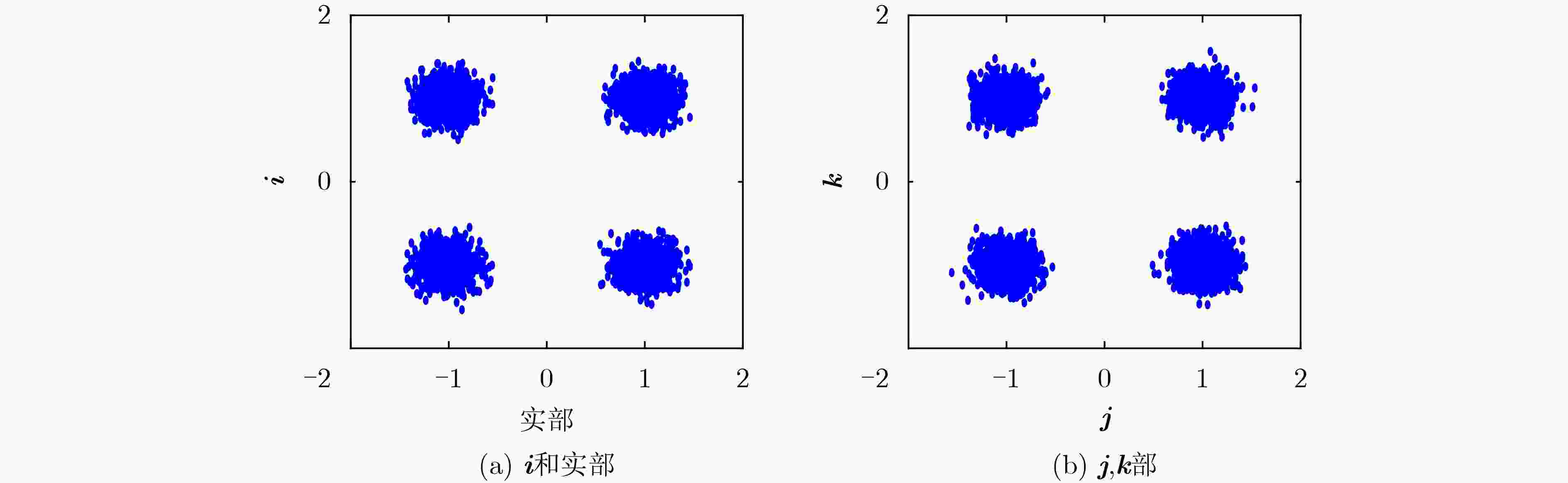
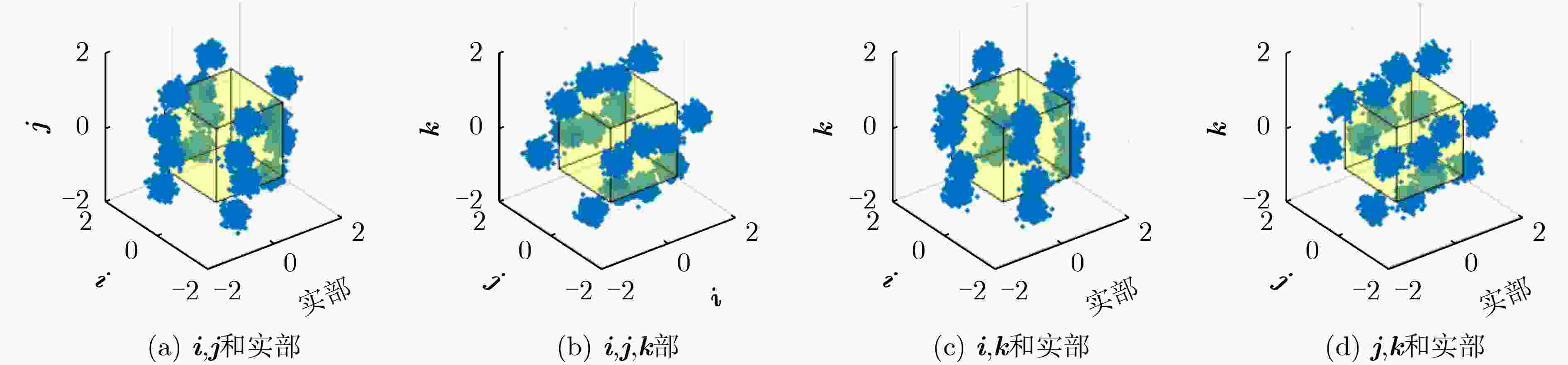
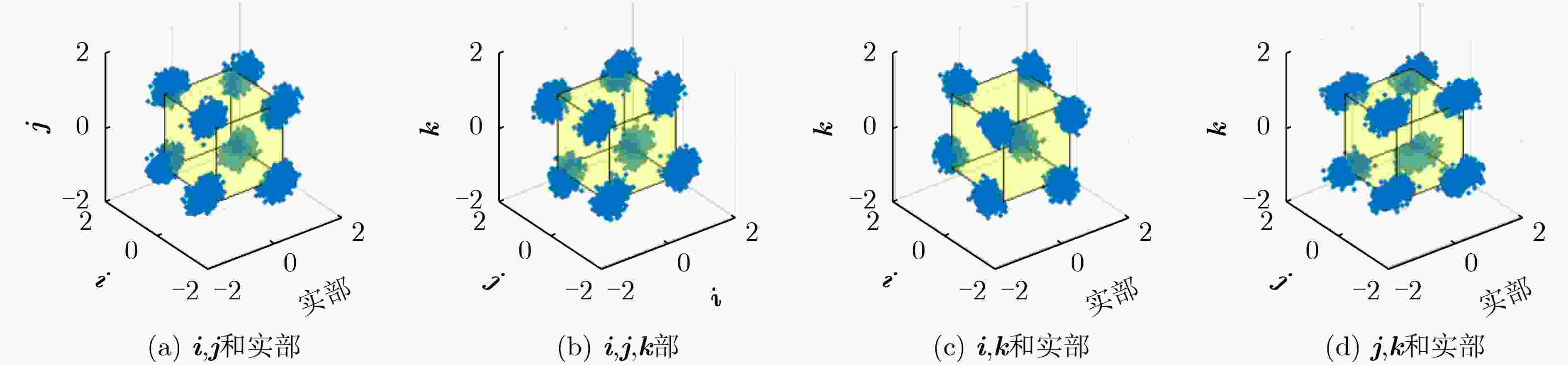
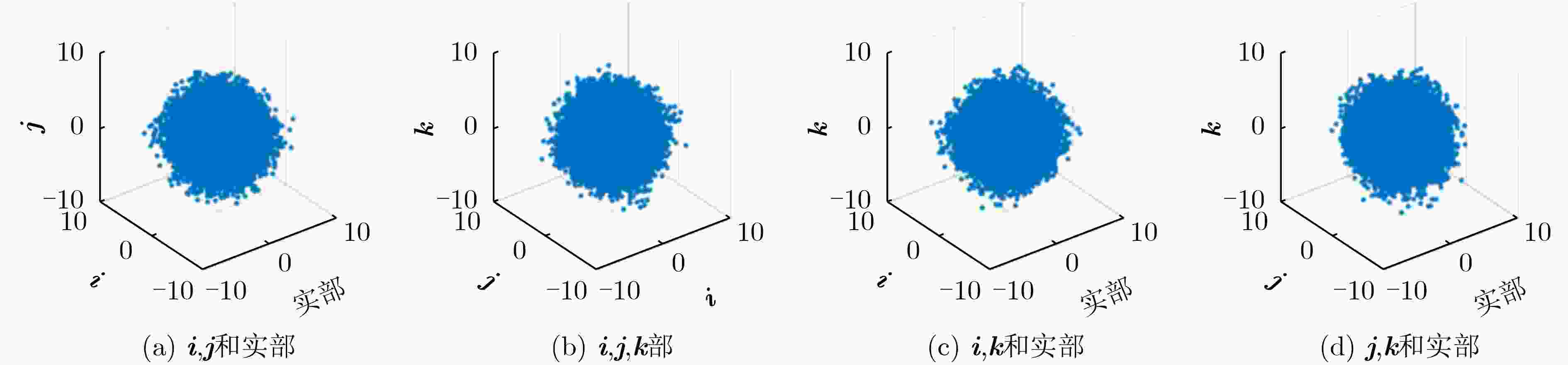
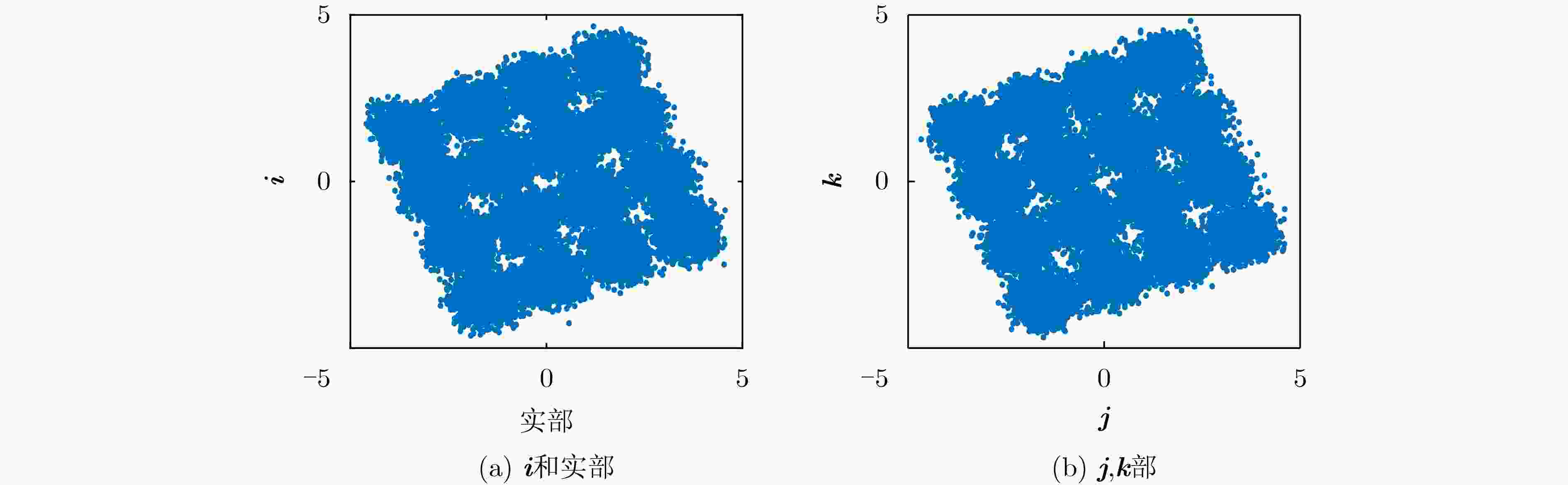
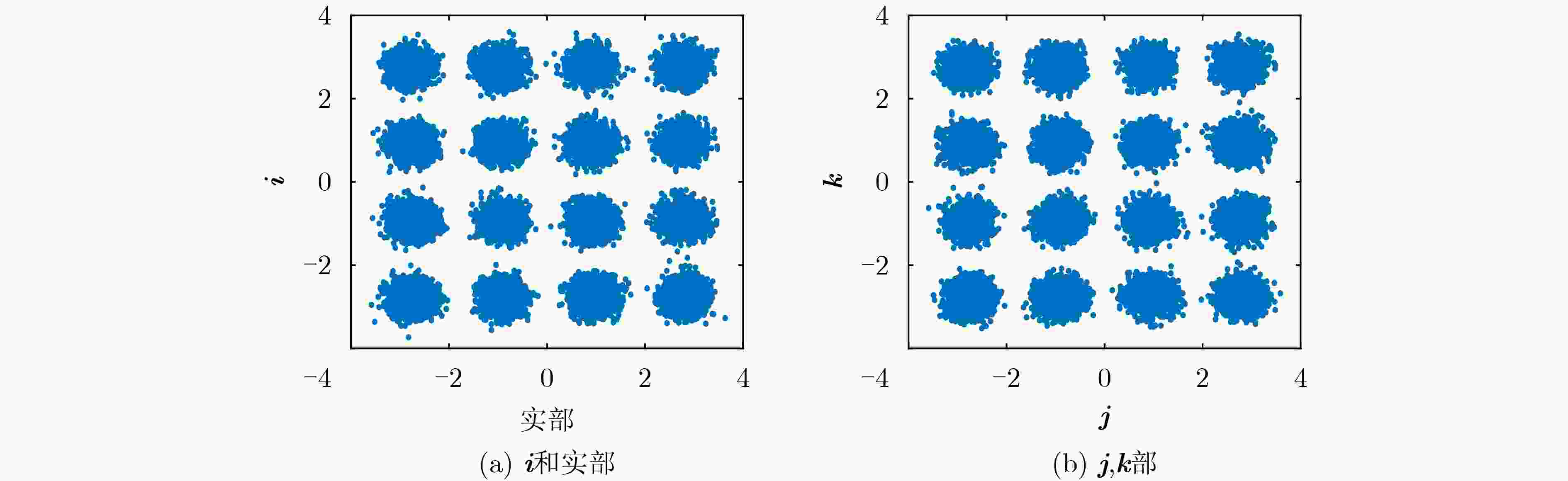
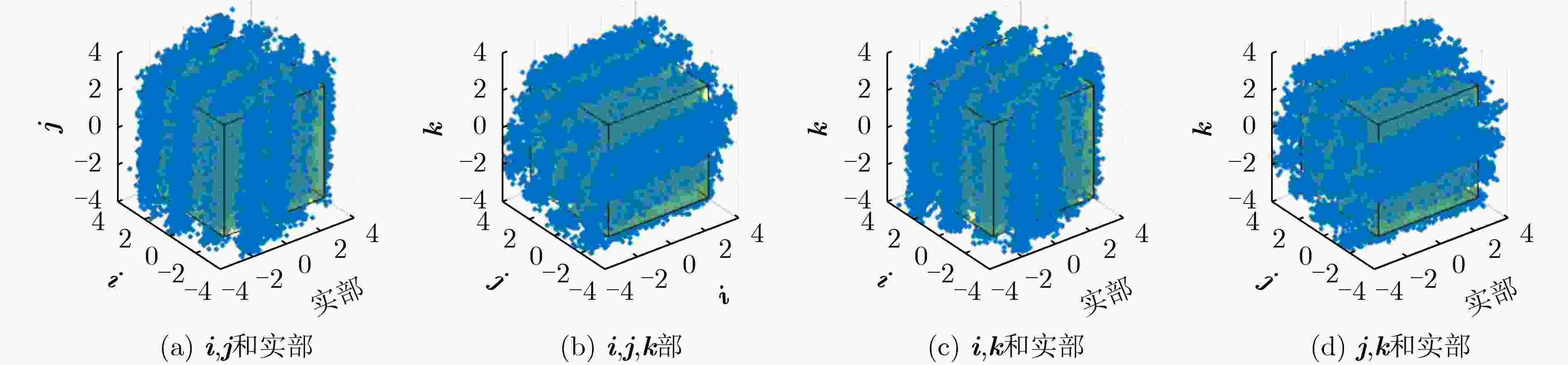
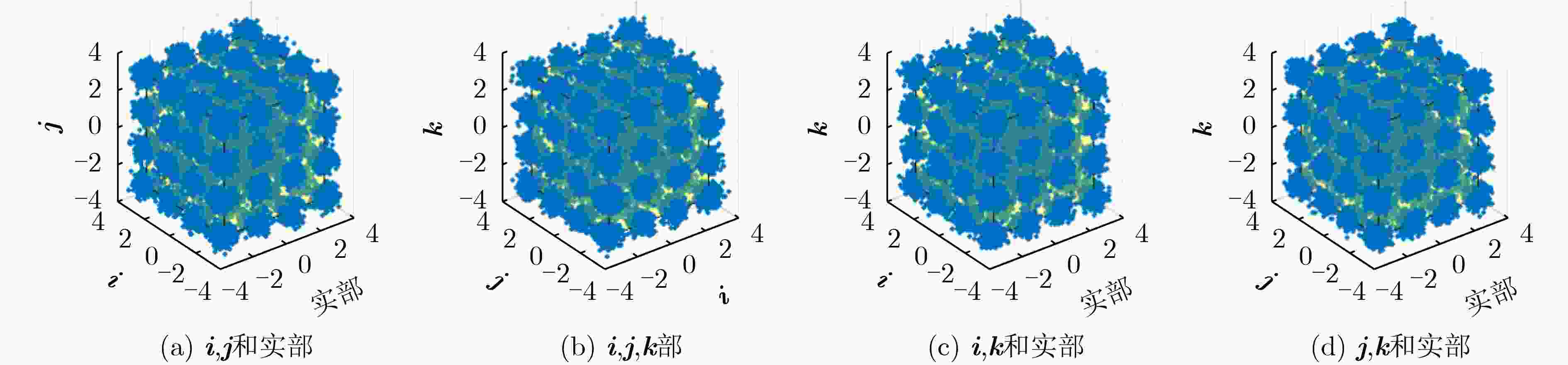


 下载:
下载:
