Magnetic Induction Tomography of IntraCerebral Hemorrhage Based on Improved Newton-Raphson Algorithm
-
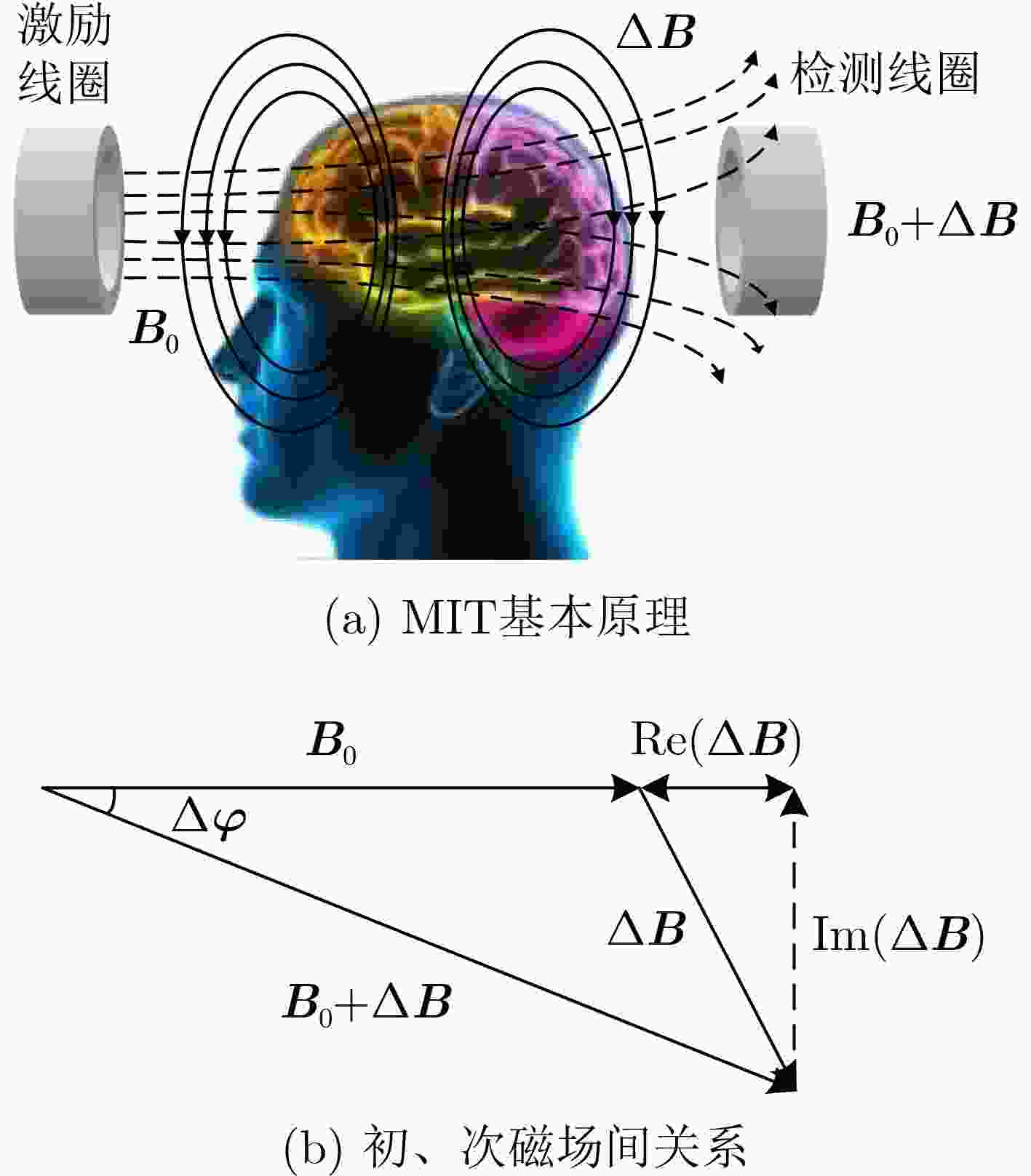
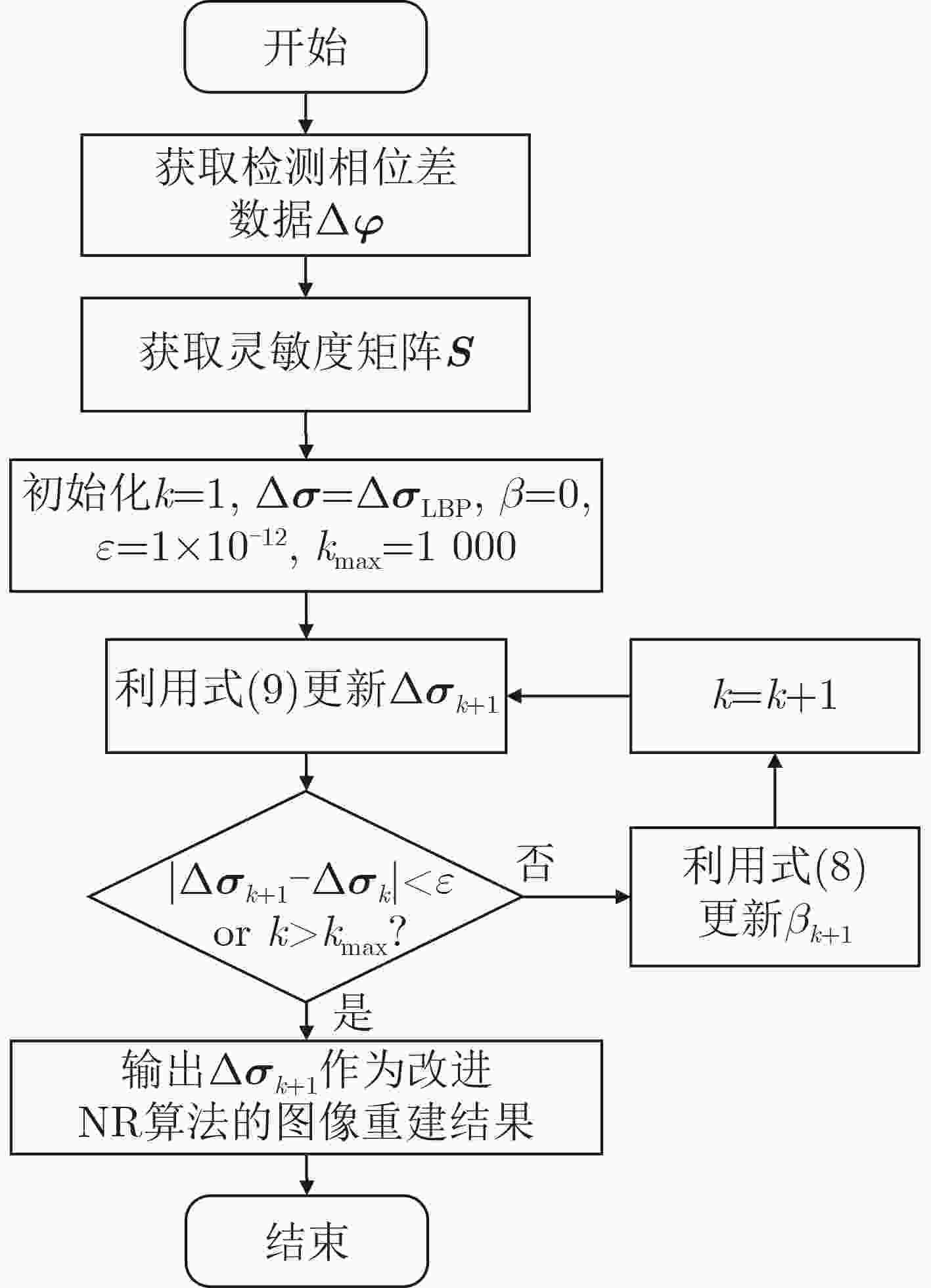
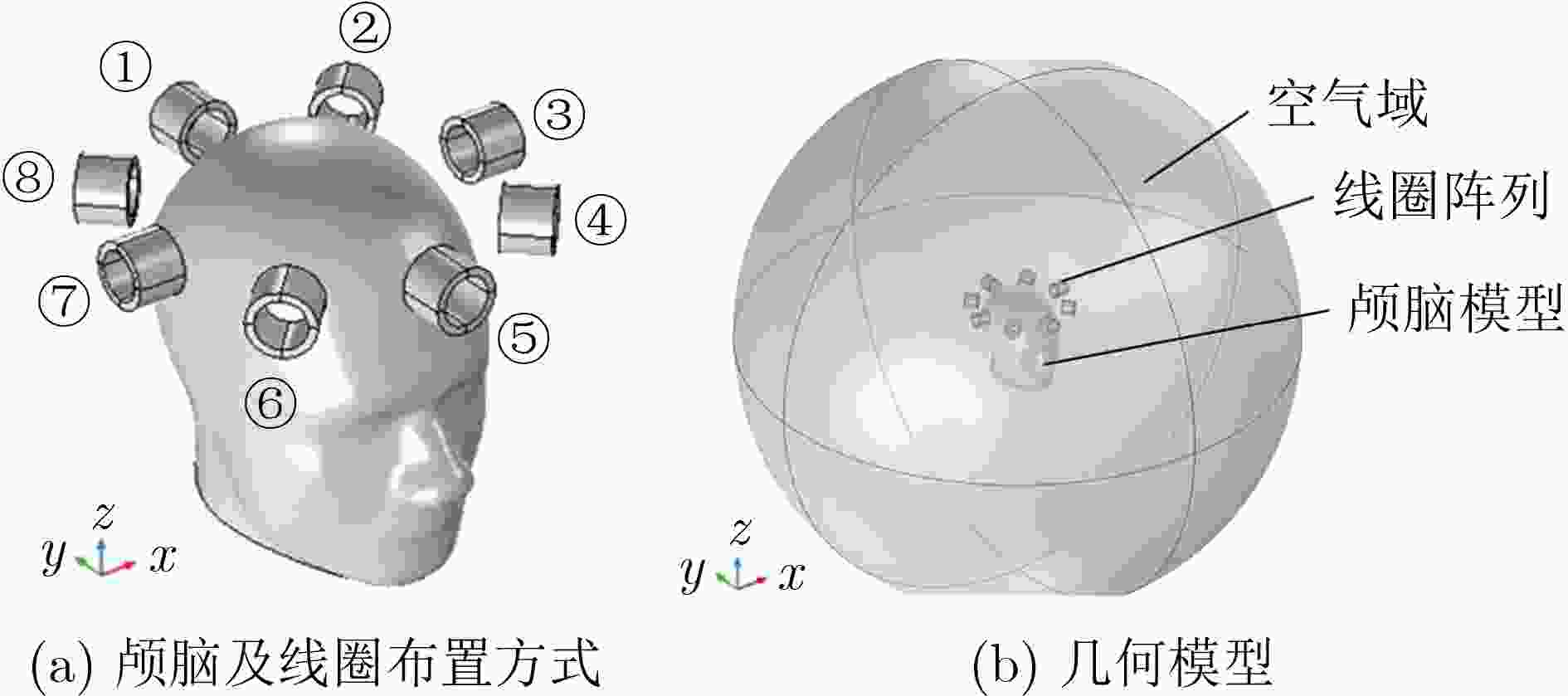
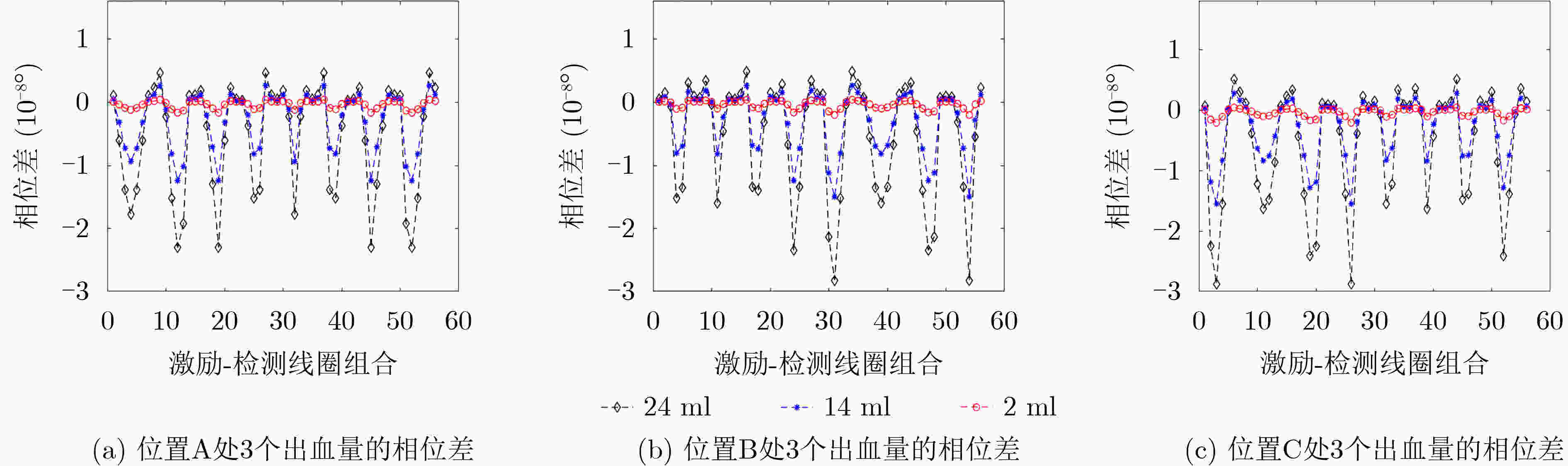
摘要: 针对脑出血磁感应断层成像(MIT)中正问题模型过于简化、图像重建质量较低、算法收敛效率低、病变与背景间伪影较大、耗时较长等问题,该文提出一种用于脑出血MIT的改进牛顿-拉夫逊(NR)算法。将线性反投影(LBP)算法计算结果作为改进NR算法的迭代初值,在目标函数中加入自适应加速惩罚项和L2范数惩罚项,提高算法每一步迭代的效率,减少重建图像的伪影。引入投影算子P施加物理意义上的约束,提高收敛速度并改善成像质量。利用Comsol Multiphysics构建了包含头皮、颅骨、脑脊液和脑实质的真实3维颅脑模型。仿真计算了相位差检测值和灵敏度矩阵用于后续的图像重建。利用所提改进NR算法与5种图像重建算法分别对3个位置出血量分别为24 ml, 14 ml, 2 ml的脑出血进行磁感应断层成像。实验结果表明,所提算法相比其他5种算法重建图像的质量更高,成像时间平均只需NR算法的1/3。使用更少的迭代次数重建出更高质量的图像,并且能实现2 ml脑出血的图像重建,为脑出血的MIT检测提供一种新的有效算法。Abstract: To solve the problems of over-simplified positive problem model, low image reconstruction quality, low algorithm convergence efficiency, large artifacts between lesion and background, and long time consuming in IntraCerebral Hemorrhage (ICH) Magnetic Induction Tomography (MIT), an improved Newton-Raphson (NR) algorithm for MIT of intracerebral hemorrhage is proposed. The calculation results of Linear Back Projection (LBP) algorithm are used as the iterative initial values of the improved NR algorithm, the adaptive acceleration penalty term and the L2 norm penalty term are added to the objective function to improve the efficiency of each iteration of the algorithm and reduce the artifacts of the reconstructed image. A real three-dimensional brain model including scalp, skull, cerebrospinal fluid and brain parenchyma is constructed by Comsol Multiphysics. The phase difference detection value and sensitivity matrix are simulated and calculated for subsequent image reconstruction. The proposed improved NR algorithm and five image reconstruction algorithms are used to perform magnetic induction tomography on intracerebral hemorrhage with blood loss of 24 ml, 14 ml and 2 ml at three locations, respectively. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has higher quality of reconstructed images than the other five algorithms. The average imaging time is only 1/3 of the NR algorithm. The higher quality image is reconstructed with fewer iterations, the image reconstruction of 2 ml intracerebral hemorrhage can be realized, which provides a new and effective algorithm for MIT detection of intracerebral hemorrhage.
-
表 1 1 MHz下的脑组织电磁特性
脑组织 头皮 颅骨 脑脊液 脑实质 脑出血 电导率(S/m) 0.044 0.024 2.000 0.102 0.822 介电常数(F/m) 50.8 145 109 480 3030 表 2 相关系数
脑出血分布 Tikhonov Landweber CGLS NR NR (优化迭代策略) 改进NR (无投影算子) 改进NR 位置A:24 ml 0.505 0.355 0.490 0.483 0.512 0.513 0.676 位置A:14 ml 0.437 0.306 0.422 0.416 0.443 0.441 0.595 位置A: 2 ml 0.269 0.209 0.255 0.253 0.275 0.267 0.377 位置B:24 ml 0.455 0.311 0.449 0.416 0.468 0.448 0.590 位置B:14 ml 0.378 0.282 0.380 0.342 0.388 0.367 0.401 位置B: 2 ml 0.207 0.171 0.199 0.189 0.213 0.202 0.286 位置C:24 ml 0.481 0.364 0.476 0.446 0.491 0.474 0.619 位置C:14 ml 0.407 0.308 0.404 0.375 0.417 0.397 0.528 位置C: 2 ml 0.244 0.180 0.243 0.227 0.250 0.240 0.333 表 3 图像误差/归一化均方距离
脑出血分布 Tikhonov Landweber CGLS NR NR (优化迭代策略) 改进NR (无投影算子) 改进NR 位置A:24 ml 0.962/1.182 0.993/1.005 0.956/0.968 0.957/0.969 0.961/0.975 0.959/0.970 0.910/0.949 位置A:14 ml 1.022/1.030 1.510/1.527 1.163/1.174 1.184/0.987 0.991/0.977 0.975/0.983 0.947/0.876 位置A: 2 ml 1.867/1.872 2.709/2.610 2.505/2.514 2.517/2.525 1.662/1.666 1.860/1.865 1.544/1.550 位置B:24 ml 0.970/0.983 0.994/1.007 0.967/0.980 0.969/0.983 0.970/0.984 0.971/0.984 0.938/0.967 位置B:14 ml 1.013/1.022 1.525/1.540 1.043/1.052 1.135/1.145 0.997/0.993 1.144/1.153 0.968/0.920 位置B: 2 ml 1.825/1.779 2.226/2.247 2.098/2.111 2.256/2.262 1.716/1.675 1.887/1.891 1.501/1.505 位置C:24 ml 0.965/0.978 0.993/1.006 0.961/0.974 0.964/0.977 0.966/0.980 0.965/0.978 0.933/0.961 位置C:14 ml 0.990/0.989 1.540/1.567 1.038/1.046 1.101/1.111 0.981/0.967 1.107/1.117 0.962/0.910 位置C: 2 ml 1.663/1.622 1.877/1.765 1.855/1.860 2.026/2.038 1.575/1.510 1.705/1.710 1.354/1.358 表 4 图像重建时间(s)/迭代次数
脑出血分布 Tikhonov Landweber CGLS NR NR (优化迭代策略) 改进NR (无投影算子) 改进NR 位置A:24 ml 0.064/1 0.027/300 0.002/40 0.750/12 1.949/33 0.411/8 0.223/5 位置A:14 ml 0.078/1 0.029/303 0.002/45 0.801/13 1.841/30 0.406/8 0.217/5 位置A: 2 ml 0.071/1 0.041/460 0.002/52 1.134/17 2.133/35 0.410/8 0.287/6 位置B:24 ml 0.061/1 0.026/300 0.001/38 0.706/11 1.534/25 0.405/8 0.285/6 位置B:14 ml 0.068/1 0.032/332 0.002/40 0775/12 1.797/30 0.391/8 0.235/5 位置B: 2 ml 0.063/1 0.042/510 0.002/46 0.983/15 1.910/32 0.393/8 0.293/6 位置C:24 ml 0.061/1 0.026/302 0.002/39 0.765/12 1.527/26 0.414/8 0.253/5 位置C:14 ml 0.070/1 0.030/303 0.002/40 0.770/12 1.678/28 0.413/8 0.297/6 位置C: 2 ml 0.064/1 0.030/310 0.002/44 1.053/15 1.873/31 0.396/8 0.295/6 -
[1] XUE Mengzhou and YONG V W. Neuroinflammation in intracerebral haemorrhage: Immunotherapies with potential for translation[J]. The Lancet Neurology, 2020, 19(12): 1023–1032. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30364-1 [2] LI Xiangyu, LUO Gongning, WANG Wei, et al. Hematoma expansion context guided intracranial hemorrhage segmentation and uncertainty estimation[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2022, 26(3): 1140–1151. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2021.3103850 [3] ALQADAMI A S M, TRAKIC A, STANCOMBE A E, et al. Flexible electromagnetic cap for head imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 2020, 14(5): 1097–1107. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2020.3025341 [4] 刘敬璇, 樊金宇, 汪权, 等. SS-OCTA对黑色素瘤皮肤结构和血管的成像实验[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(2): 190239. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190239LIU Jingxuan, FAN Jinyu, WANG Quan, et al. Imaging of skin structure and vessels in melanoma by swept source optical coherence tomography angiography[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2020, 47(2): 190239. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190239 [5] 尹海涛, 岳勇赢. 基于半监督学习和生成对抗网络的医学图像融合算法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(22): 2215005. doi: 10.3788/LOP202259.2215005YIN Haitao and YUE Yongying. Medical image fusion based on semisupervised learning and generative adversarial network[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(22): 2215005. doi: 10.3788/LOP202259.2215005 [6] 杨珊珊, 姚霖, 刘开元, 等. 光学相干层析功能成像及脑中风研究进展[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47(2): 0207015. doi: 10.3788/CjL202047.0207015YANG Shanshan, YAO Lin, LIU Kaiyuan, et al. Advances in functional optical coherence tomography and neuroimaging of stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(2): 0207015. doi: 10.3788/CjL202047.0207015 [7] ROSA B M G and YANG G Z. Urinary bladder volume monitoring using magnetic induction tomography: A rotational simulation model for anatomical slices within the pelvic region[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2022, 69(2): 547–557. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2021.3100804 [8] CHEN Yixuan, TAN Chao, ZHAO Shu, et al. Intracranial hemorrhage detection by open MIT sensor array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 4500611. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2022.3141146 [9] 宣杨, 王旭, 刘承安, 等. 不完全乔列斯基分解共轭梯度法在磁感应成像三维有限元正问题中的应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(1): 187–194. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150437XUAN Yang, WANG Xu, LIU Cheng’an, et al. Incomplete cholesky conjugate gradient method for the three-dimensional forward problem in magnetic induction tomography using finite element method[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(1): 187–194. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150437 [10] YANG Dan, LIU Jiahua, WANG Yuchen, et al. Application of a generative adversarial network in image reconstruction of magnetic induction tomography[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(11): 3869. doi: 10.3390/s21113869 [11] 罗海军, 廖勇, 潘海涛, 等. 导数法峰值锐化算法提高磁感应成像图像分辨率[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(8): 1847–1852. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171102LUO Haijun, LIAO Yong, PAN Haitao, et al. Derivative method peak sharpening algorithm improves image resolution of magnetic induction tomography[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(8): 1847–1852. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171102 [12] HAN Min, CHENG Xiaolin, and XUE Yuyan. Comparison with reconstruction algorithms in magnetic induction tomography[J]. Physiological Measurement, 2016, 37(5): 683–697. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/37/5/683 [13] KE Li, ZU Wanni, DU Qiang, et al. A bio-impedance quantitative method based on magnetic induction tomography for intracranial hematoma[J]. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 2020, 58(4): 857–869. doi: 10.1007/s11517-019-02114-7 [14] 柯丽, 刘欢, 杜强, 等. 基于滤波反投影的脑磁感应迭代重建算法研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2016, 37(11): 2445–2451. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2016.11.005KE Li, LIU Huan, DU Qiang, et al. Study on iterative reconstruction algorithm for brain magnetic induction based on filtered back-projection[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2016, 37(11): 2445–2451. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2016.11.005 [15] CHEN Yixuan, TAN Chao, and DONG Feng. Combined planar magnetic induction tomography for local detection of intracranial hemorrhage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 4500111. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.3011621 [16] CHEN Yixuan, TAN Chao, and DONG Feng. Multifrequency weighted difference magnetic induction tomography for intracranial hemorrhage detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 4501209. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2021.3137539 [17] ZHANG Tao, LIU Xuechao, ZHANG Weirui, et al. Adaptive threshold split bregman algorithm based on magnetic induction tomography for brain injury monitoring imaging[J]. Physiological Measurement, 2021, 42(6): 065004. doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/ac05d4 [18] CHEN Yixuan, DONG Feng, and TAN Chao. Space-constrained optimized Tikhonov regularization method for 3D hemorrhage reconstruction by open magnetic induction tomography[J]. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2022, 67(22): 225012. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ac9e42 [19] 周曦, 柴晓宇, 王彬, 等. 一种改进牛顿-拉夫逊ERT算法[J]. 计算机仿真, 2022, 39(9): 252–256.ZHOU Xi, CHAI Xiaoyu, WANG Bin, et al. An improved newton-raphson ERT algorithm[J]. Computer Simulation, 2022, 39(9): 252–256. [20] 周涛, 刘赟璨, 陆惠玲, 等. ResNet及其在医学图像处理领域的应用: 研究进展与挑战[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 149–167. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210914ZHOU Tao, LIU Yuncan, LU Huiling, et al. ResNet and its application to medical image processing: Research progress and challenges[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 149–167. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210914 [21] ZHANG Tao, ZHANG Weirui, LIU Xuechao, et al. Multifrequency magnetic induction tomography for hemorrhagic stroke detection using an adaptive threshold split bregman algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 4005713. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2022.3180406 [22] ZHANG Yuyan, SUN Yurong, and WEN Yintang. An imaging algorithm of planar array capacitance sensor for defect detection[J]. Measurement, 2021, 168: 108466. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108466 [23] ENGL H W and RAMLAU R. Regularization of inverse problems[M]. ENGQUIST B. Encyclopedia of Applied and Computational Mathematics. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 1233–1241. [24] HASGALL P A, NEUFELD E, GOSSELIN M C, et al. IT’IS database for thermal and electromagnetic parameters of biological tissues version 4.0[DB/OL]. https//: www. itis. ethz. ch/database, 2019. [25] YANG Jinzhu, TAN Wenjun, MA Shuang, et al. Automatic MRI brain tissue extraction algorithm based on three-dimensional gray-scale transformation model[J]. Journal of Medical Imaging and Health Informatics, 2014, 4(6): 907–911. doi: 10.1166/jmihi.2014.1340 [26] TAN R H and ROSSA C. Electrical impedance tomography using differential evolution integrated with a modified newton raphson algorithm[C]. IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Toronto, Canada, 2020: 2528–2534. [27] BABAIE-KAFAKI S and GHANBARI R. A hybridization of the hestenes-stiefel and Dai-Yuan conjugate gradient methods based on a least-squares approach[J]. Optimization Methods and Software, 2015, 30(4): 673–681. doi: 10.1080/10556788.2014.966825 [28] 马敏, 郭鑫, 于洁. 改进正则化半阈值算法的ECT图像重建[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2022, 43(5): 110–119. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2209154MA Min, GUO Xin, and YU Jie. ECT image reconstruction based on improved regularized half threshold algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2022, 43(5): 110–119. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2209154 [29] 张立峰, 周雷. 基于小波融合的电容层析成像图像重建[J]. 计量学报, 2019, 40(2): 285–288. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1158ZHANG Lifeng and ZHOU Lei. Image reconstruction for electrical capacitance tomography based on wavelet fusion[J]. Acta Metrologica Sinica, 2019, 40(2): 285–288. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1158 [30] LI Feng, DONG Feng, and TAN Chao. Landweber iterative image reconstruction method incorporated deep learning for electrical resistance tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 4501811. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.3038014 -





 下载:
下载:

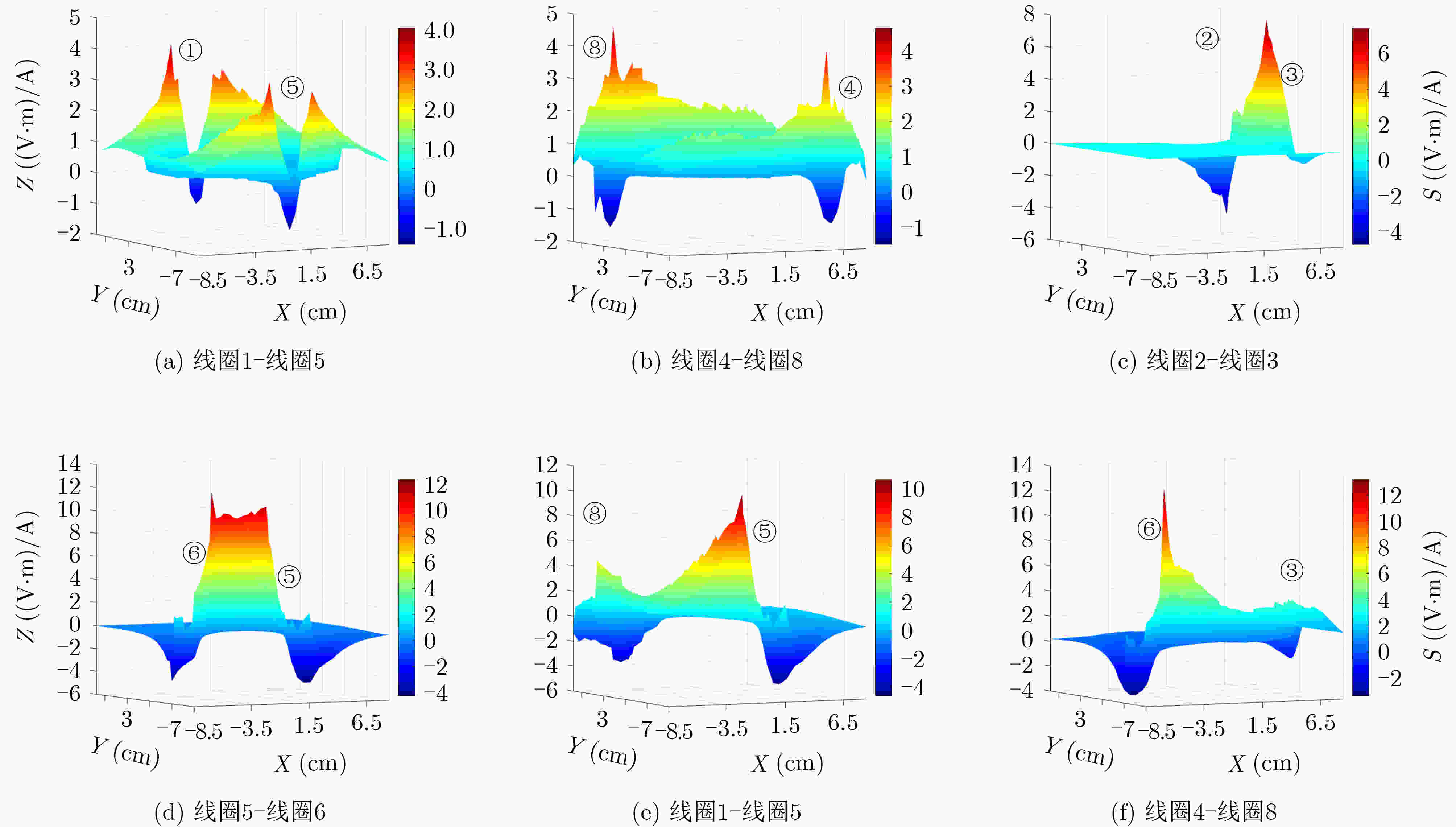
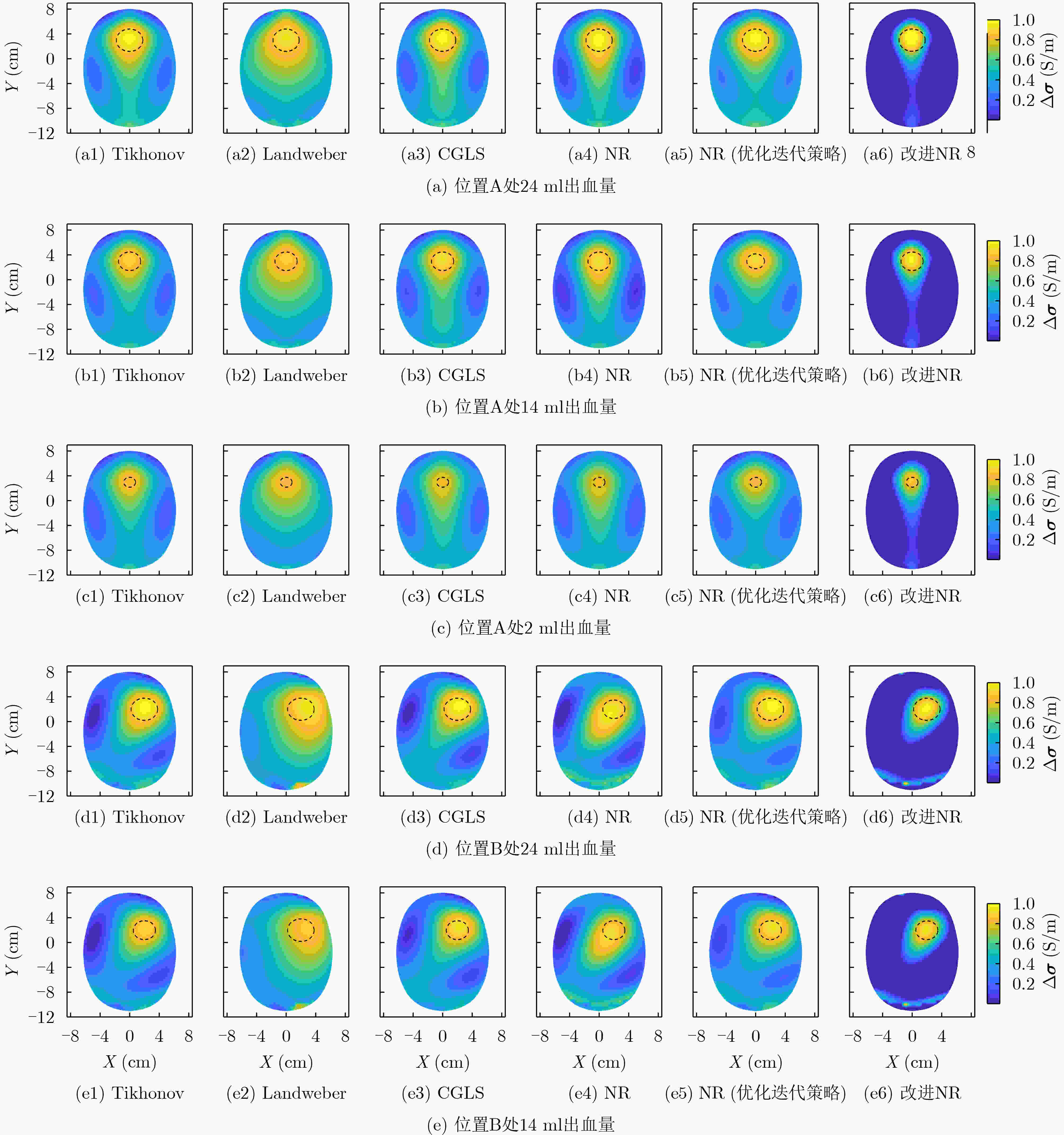
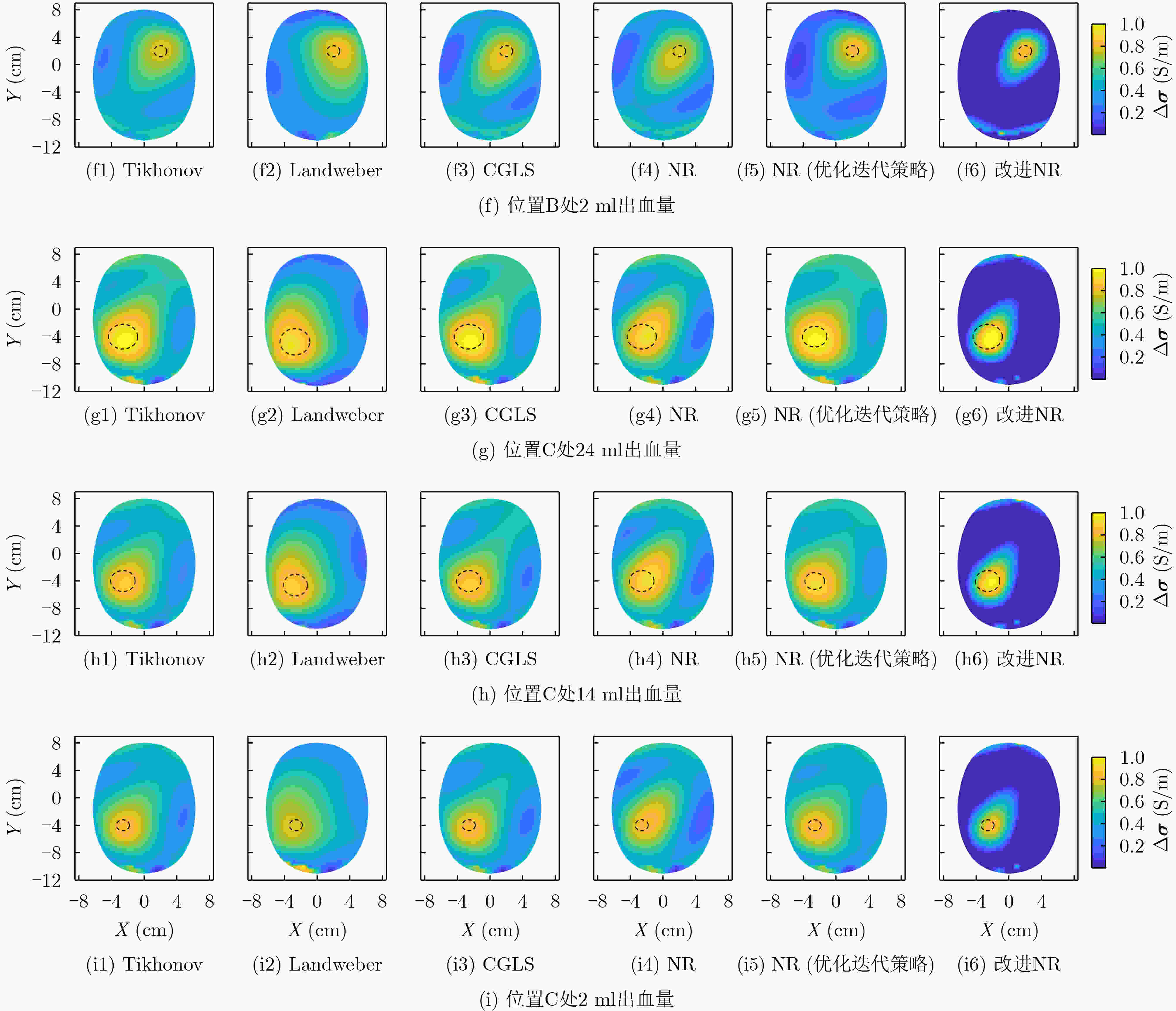


 下载:
下载:
