Intrinsic Mode Decomposition and Combined Deep Learning Prediction of Urban Rail Transit Passenger Flow at Variable Time Scales
-
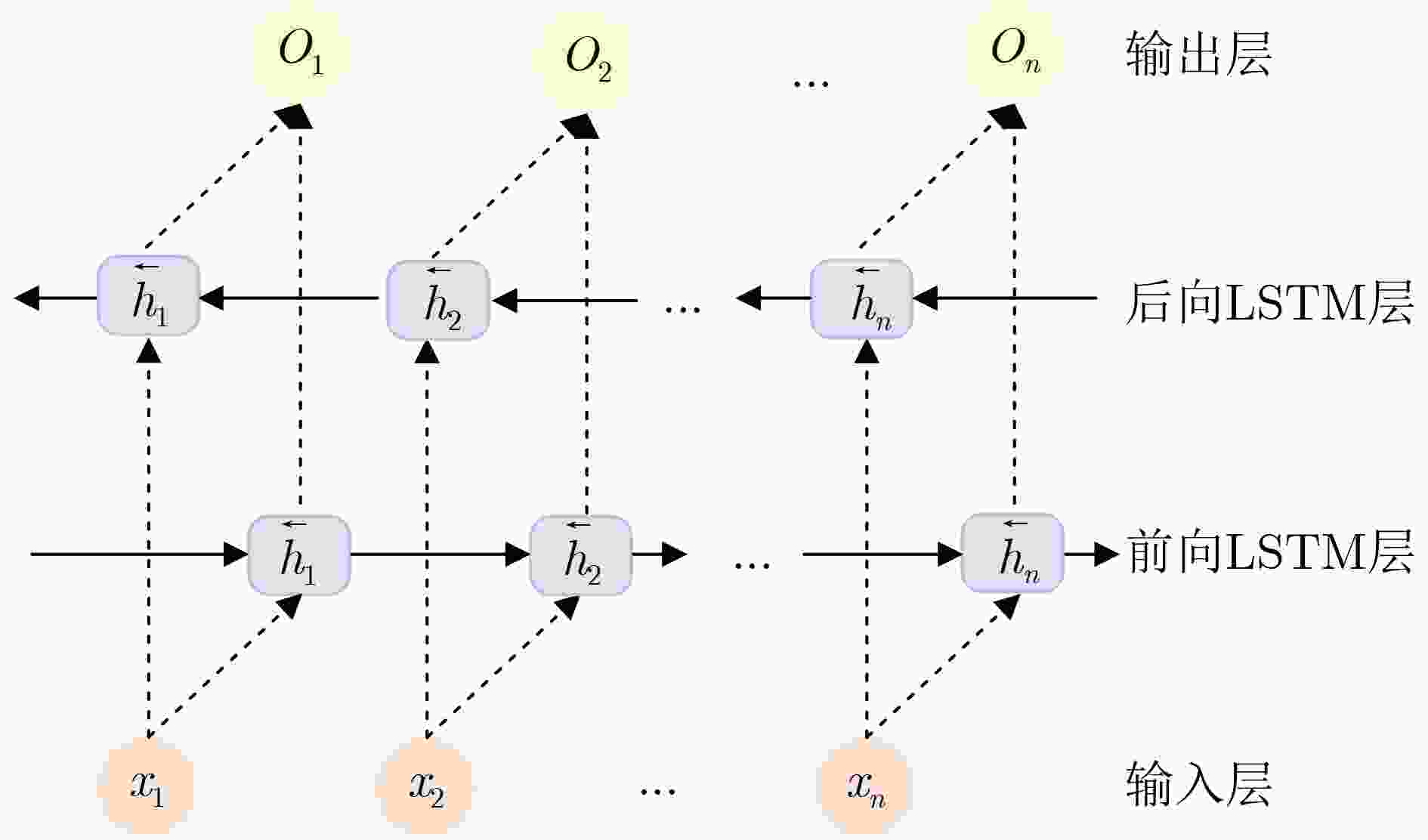
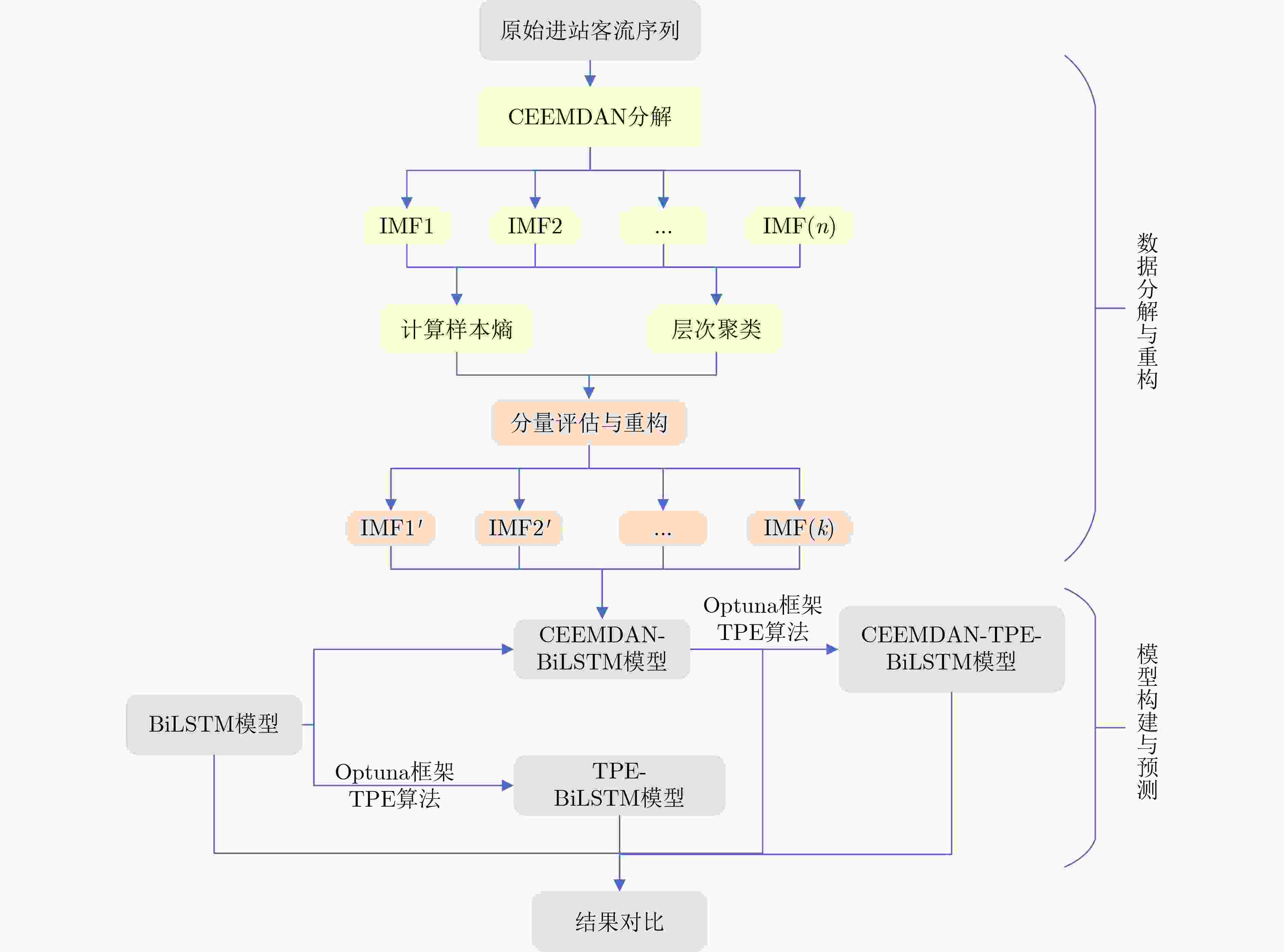
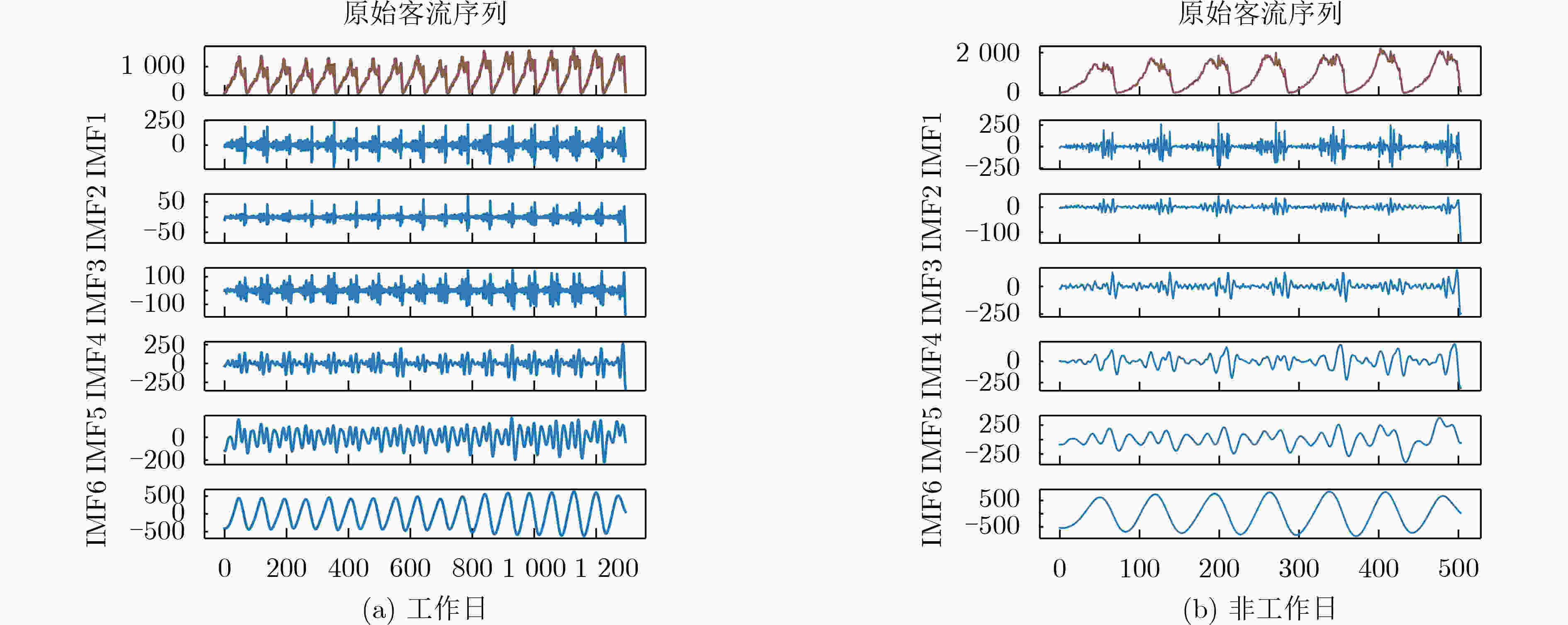
摘要: 城市轨道交通的不同运营状态,通常对应着客流时间序列中不同的本征模态分量(IMF)及时间尺度特征。基于自适应噪声的完全总体经验模态分解(CEEMDAN)算法和双向长短期记忆(BiLSTM)网络,该文构建了地铁短时客流时间序列的组合深度学习预测模型。具体包括:基于CEEMDAN算法实现了客流时间序列的模态分解。分别使用样本熵和层次聚类对IMF分量进行复杂性和相似度分析,并在此基础上完成IMF分量的分类合并与重构;使用Optuna框架中的树形Parzen优化器(TPE)对模型的超参数进行优化,构建CEEMDAN-TPE-BiLSTM组合预测模型。采用实际数据对该文模型进行验证,结果表明,对于特定特征的客流时间序列数据,该文模型的精确性、有效性指标均达到最优。
-
关键词:
- 城市轨道交通 /
- 短时客流时间序列 /
- 自适应噪声的完全总体经验模态分解 /
- 双向长短期记忆 /
- 组合预测
Abstract: Different operational states of urban rail transit usually correspond to different Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs) and time-scale characteristics in passenger flow time series. A combined deep learning prediction model for short-term passenger flow time series of subway is proposed based on the Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise (CEEMDAN) and Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory network (BiLSTM), including: mode decomposition of passenger flow time series based on the CEEMDAN algorithm. The sample entropy and hierarchical clustering are used respectively to analyze the complexity and similarity of IMFs. The IMFs are then classified, merged and reconstructed on this basis. The hyper-parameters of the model are optimized using the Tree-structured Parzen Estimator (TPE) in the Optuna framework, and the combined prediction model CEEMDAN-TPE-BiLSTM is established. Actual data are used to validate the model. The results show that the accuracy and validity indicators of the model all reach the optimum for passenger flow time series data with specific characteristics. -
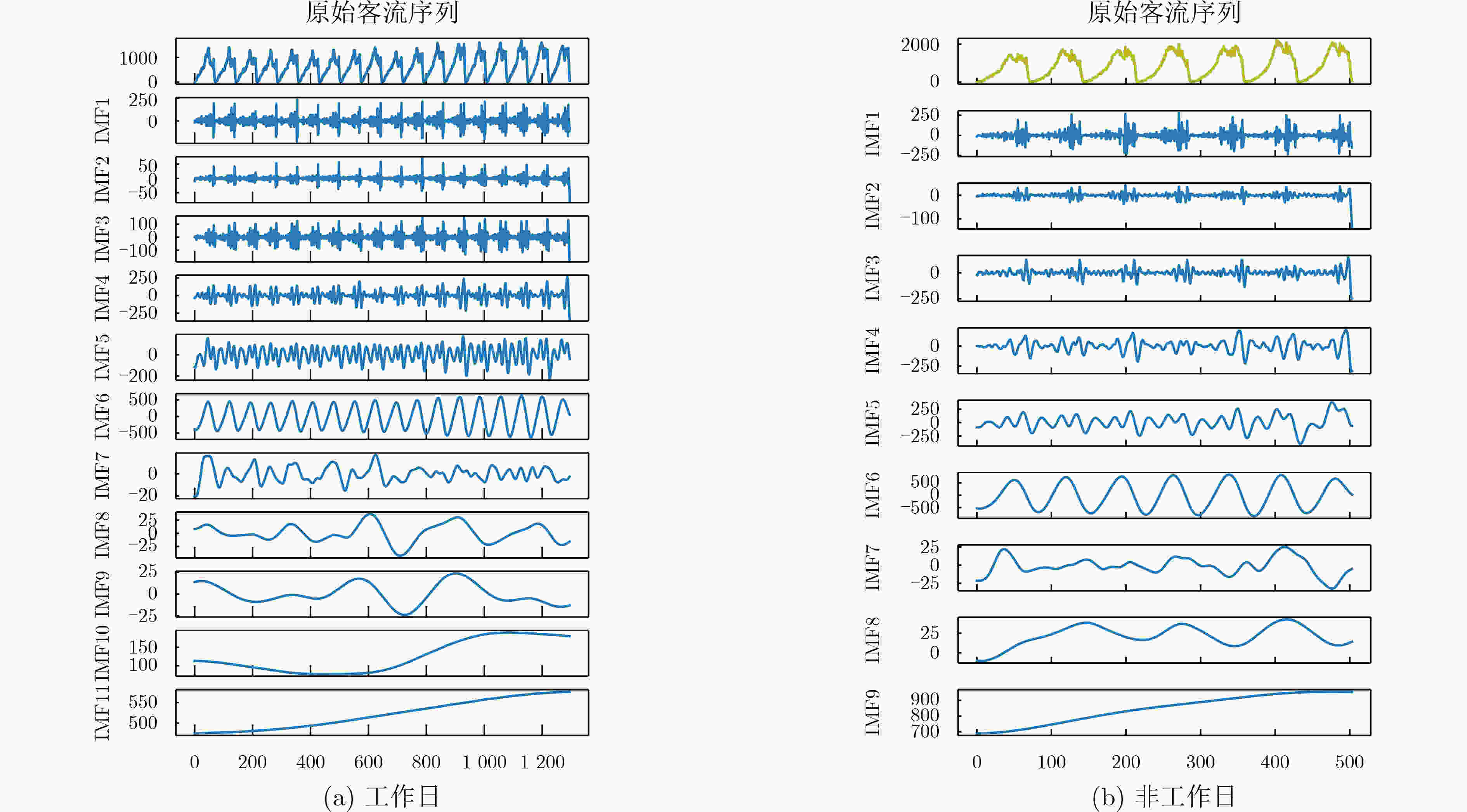
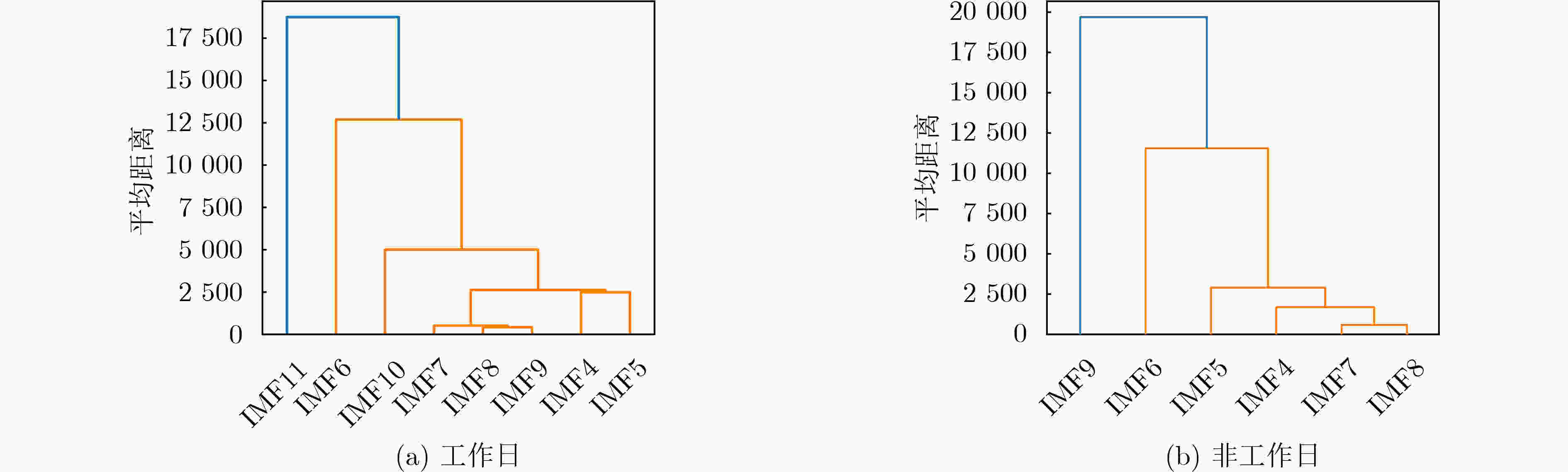
表 1 IMF分量样本熵计算结果
IMF1 IMF2 IMF3 IMF4 IMF5 IMF6 IMF7 IMF8 IMF9 IMF10 IMF11 工作日 0.954 0.894 0.789 0.483 0.524 0.300 0.296 0.076 0.038 0.005 0.001 非工作日 0.812 0.983 1.178 0.544 0.514 0.282 0.240 0.102 0.002 — — 表 2 待优化超参数搜索空间范围
神经元个数 批大小 迭代次数 学习率 搜索空间范围 (16, 64) (16, 64) (30, 70) (0.0001, 0.01) 步长 2 4 5 0.0001 表 3 优化后各模型的超参数
模型 IMF 隐藏层神经元个数 批大小 迭代次数 学习率 工作日 BiLSTM模型 — 26 40 65 0.0072 CEEMDAN-BiLSTM
模型IMF1 60 24 65 0.0084 IMF2 60 36 65 0.0034 IMF3 42 16 60 0.0090 IMF4 60 28 65 0.0066 IMF5 50 20 55 0.0041 IMF6 62 20 60 0.0054 非工作日 BiLSTM模型 — 38 52 65 0.0078 CEEMDAN-BiLSTM
模型IMF1 62 20 70 0.0080 IMF2 36 16 60 0.0023 IMF3 42 24 50 0.0062 IMF4 54 24 70 0.0082 IMF5 58 16 40 0.0092 IMF6 40 16 50 0.0065 表 4 模型预测性能评价指标
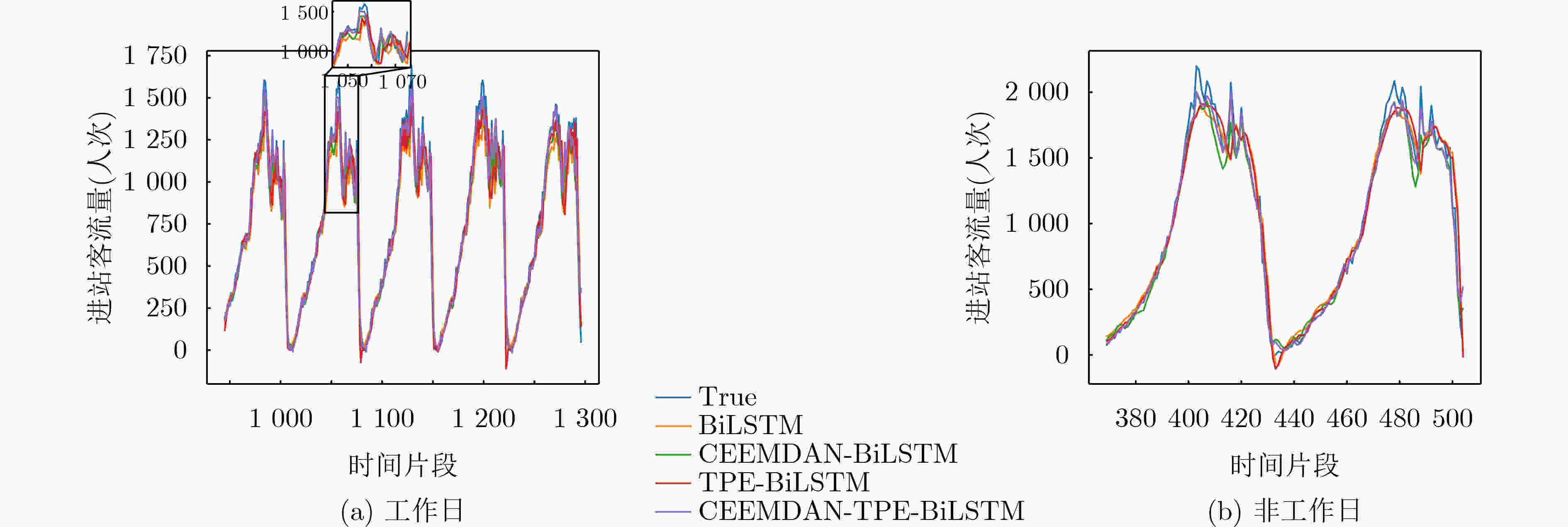
模型 工作日 非工作日 RMSE MAE MAPE(%) R2 RMSE MAE MAPE(%) R2 BiLSTM 137.467 92.486 21.094 0.914 147.001 94.828 22.838 0.956 TPE-BiLSTM 121.868 77.680 19.004 0.933 140.193 90.248 19.352 0.960 CEEMDAN-BiLSTM 70.945 51.258 14.627 0.977 104.186 75.919 22.573 0.978 CEEMDAN-TPE-BiLSTM 57.730 36.981 12.071 0.985 80.575 52.587 16.300 0.987 表 5 高峰状态下模型预测性能评价指标
模型 工作日 非工作日 RMSE MAE MAPE(%) R2 RMSE MAE MAPE(%) R2 BiLSTM 194.380 170.480 11.823 –1.601 229.810 175.016 8.749 –2.047 TPE-BiLSTM 138.215 106.626 7.296 –0.315 222.178 167.007 8.411 –1.848 CEEMDAN-BiLSTM 115.999 107.435 7.561 0.074 171.194 154.437 7.916 –0.691 CEEMDAN-TPE-BiLSTM 73.466 57.771 4.019 0.628 117.462 108.406 5.539 0.204 -
[1] CHEN Enhui, YE Zhirui, WANG Chao, et al. Subway passenger flow prediction for special events using smart card data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(3): 1109–1120. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2902405 [2] RYU U, WANG Jian, KIM T, et al. Construction of traffic state vector using mutual information for short-term traffic flow prediction[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2018, 96: 55–71. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2018.09.015 [3] LIANG Shidong, MA Minghui, HE Shengxue, et al. Short-term passenger flow prediction in urban public transport: Kalman filtering combined k-Nearest Neighbor approach[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 120937–120949. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2937114 [4] WANG Xuemei, ZHANG Ning, ZHANG Yunlong, et al. Forecasting of short-term metro ridership with Support Vector Machine online model[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2018, 2018: 3189238. doi: 10.1155/2018/3189238 [5] 陈忠辉, 凌献尧, 冯心欣, 等. 基于模糊C均值聚类和随机森林的短时交通状态预测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(8): 1879–1886. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171090CHEN Zhonghui, LING Xianyao, FENG Xinxin, et al. Short-term traffic state prediction approach based on FCM and random forest[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(8): 1879–1886. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171090 [6] SUN Bo, SUN Tuo, and JIAO Pengpeng. Spatio-temporal segmented traffic flow prediction with ANPRS data based on improved XGBoost[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2021, 2021: 5559562. doi: 10.1155/2021/5559562 [7] YANG Dan, CHEN Kairun, YANG Mengning, et al. Urban rail transit passenger flow forecast based on LSTM with enhanced long-term features[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2019, 13(10): 1475–1482. doi: 10.1049/iet-its.2018.5511 [8] 代亮, 梅洋, 钱超, 等. 基于生成对抗网络的大规模路网交通流预测算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(12): 2937–2945. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.0333DAI Liang, MEI Yang, QIAN Chao, et al. Traffic flow forecasting algorithm for large-scale road network based on GAN[J]. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(12): 2937–2945. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.0333 [9] 秦超, 高晓光, 万开方. 深度卷积记忆网络时空数据模型[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(3): 451–462. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180788QIN Chao, GAO Xiaoguang, and WAN Kaifang. Deep spatio-temporal convolutional long-short memory network[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(3): 451–462. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180788 [10] 曾诚, 吴佳媛, 罗霞. 城市轨道交通短时客流预测文献综述[J]. 铁道运输与经济, 2021, 43(8): 105–111,125. doi: 10.16668/j.cnki.issn.1003-1421.2021.08.17ZENG Cheng, WU Jiayuan, and LUO Xia. Literature review of short-term passenger flow forecast for urban rail transit[J]. Railway Transport and Economy, 2021, 43(8): 105–111,125. doi: 10.16668/j.cnki.issn.1003-1421.2021.08.17 [11] 殷礼胜, 唐圣期, 李胜, 等. 基于整合移动平均自回归和遗传粒子群优化小波神经网络组合模型的交通流预测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(9): 2273–2279. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181073YIN Lisheng, TANG Shengqi, LI Sheng, et al. Traffic flow prediction based on hybrid model of auto-regressive integrated moving average and genetic particle swarm optimization wavelet neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(9): 2273–2279. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181073 [12] ZHANG Lizong, ALHARBE N R, LUO Guangchun, et al. A hybrid forecasting framework based on support vector regression with a modified genetic algorithm and a random forest for traffic flow prediction[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2018, 23(4): 479–492. doi: 10.26599/tst.2018.9010045 [13] 寇唯. 基于数据稳定化处理的城市轨道交通短时客流预测研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北京交通大学, 2020.KOU Wei. Research on short-term passenger flow prediction of urban rail transit based on data stability processing[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing Jiaotong University, 2020. [14] ZHANG Shuaichao, ZHOU Lingxiao, CHEN Xiqun, et al. Network-wide traffic speed forecasting: 3D convolutional neural network with ensemble empirical mode decomposition[J]. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2020, 35(10): 1132–1147. doi: 10.1111/mice.12575 [15] WANG Jiaxuan, WANG Rui, and ZENG Xin. Short-term passenger flow forecasting using CEEMDAN meshed CNN-LSTM-attention model under wireless sensor network[J]. IET Communications, 2022, 16(10): 1253–1263. doi: 10.1049/cmu2.12350 [16] 沈琼. 城市轨道交通进站客流短时预测方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北京交通大学, 2019.SHEN Qiong. Study on short-term forecasting method for boarding passenger flows in urban rail transit[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019. [17] AKIBA T, SANO S, YANASE T, et al. Optuna: A next-generation hyperparameter optimization framework[C]. The 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, USA, 2019: 2623–2631. [18] LACERDA P, BARROS B, ALBUQUERQUE C, et al. Hyperparameter optimization for COVID-19 pneumonia diagnosis based on chest CT[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(6): 2174. doi: 10.3390/S21062174 [19] 黄宇, 高珊, 李其贤, 等. SCR脱硝系统的分数阶 ${\text{P}}{{\text{I}}^\lambda }{{\text{D}}^\mu }$参数优化控制[J]. 动力工程学报, 2022, 42(2): 122–128. doi: 10.19805/j.cnki.jcspe.2022.02.004HUANG Yu, GAO Shan, LI Qixian, et al. Optimal control of fractional ${\text{P}}{{\text{I}}^\lambda }{{\text{D}}^\mu }$ parameters of SCR denitration system[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2022, 42(2): 122–128. doi: 10.19805/j.cnki.jcspe.2022.02.004 [20] 石庄彬, 张宁, 邵星杰. 城市轨道交通客流高峰持续时间预测方法[J]. 城市轨道交通研究, 2016, 19(7): 35–39. doi: 10.16037/j.1007-869x.2016.07.008SHI Zhuangbin, ZHANG Ning, and SHAO Xingjie. Prediction of passenger flow duration in urban rail transit peak hours[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2016, 19(7): 35–39. doi: 10.16037/j.1007-869x.2016.07.008 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
