Multiview Scene Reconstruction Based on Edge Assisted Epipolar Transformer
-
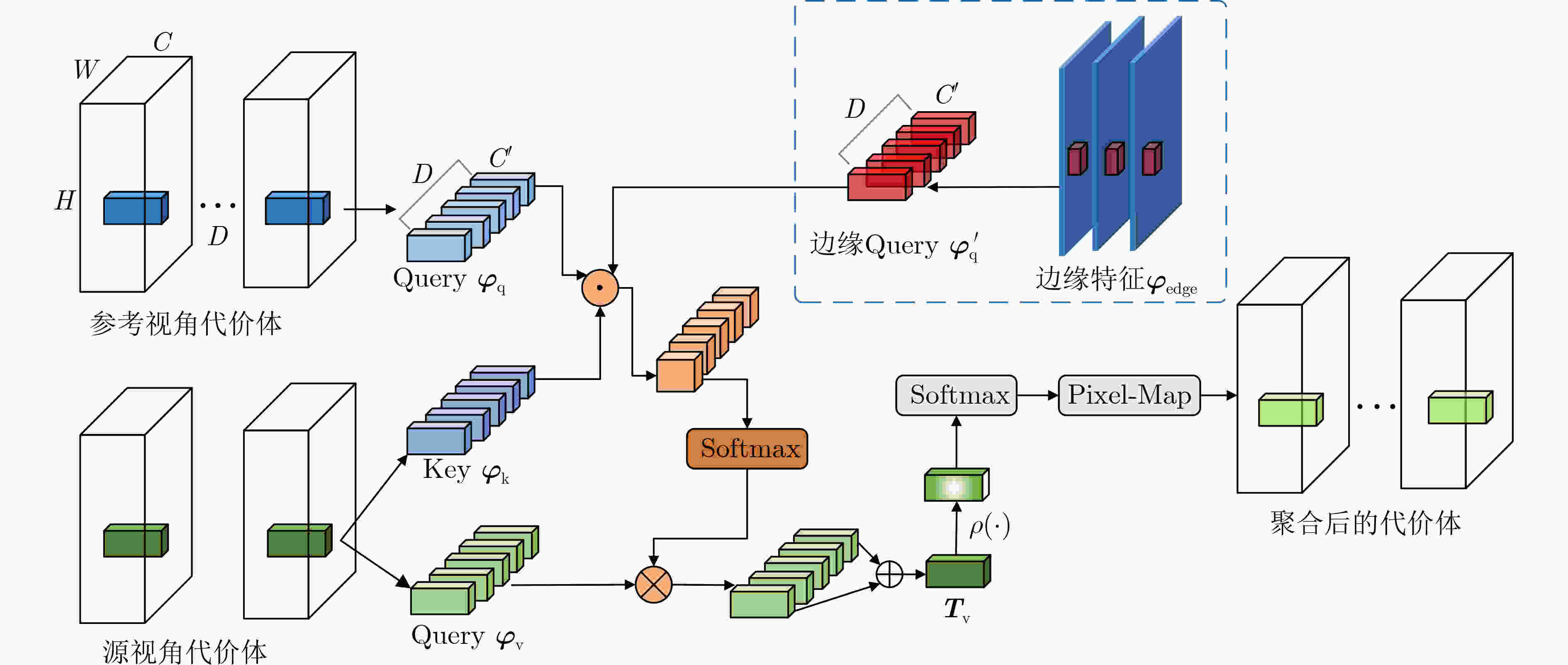
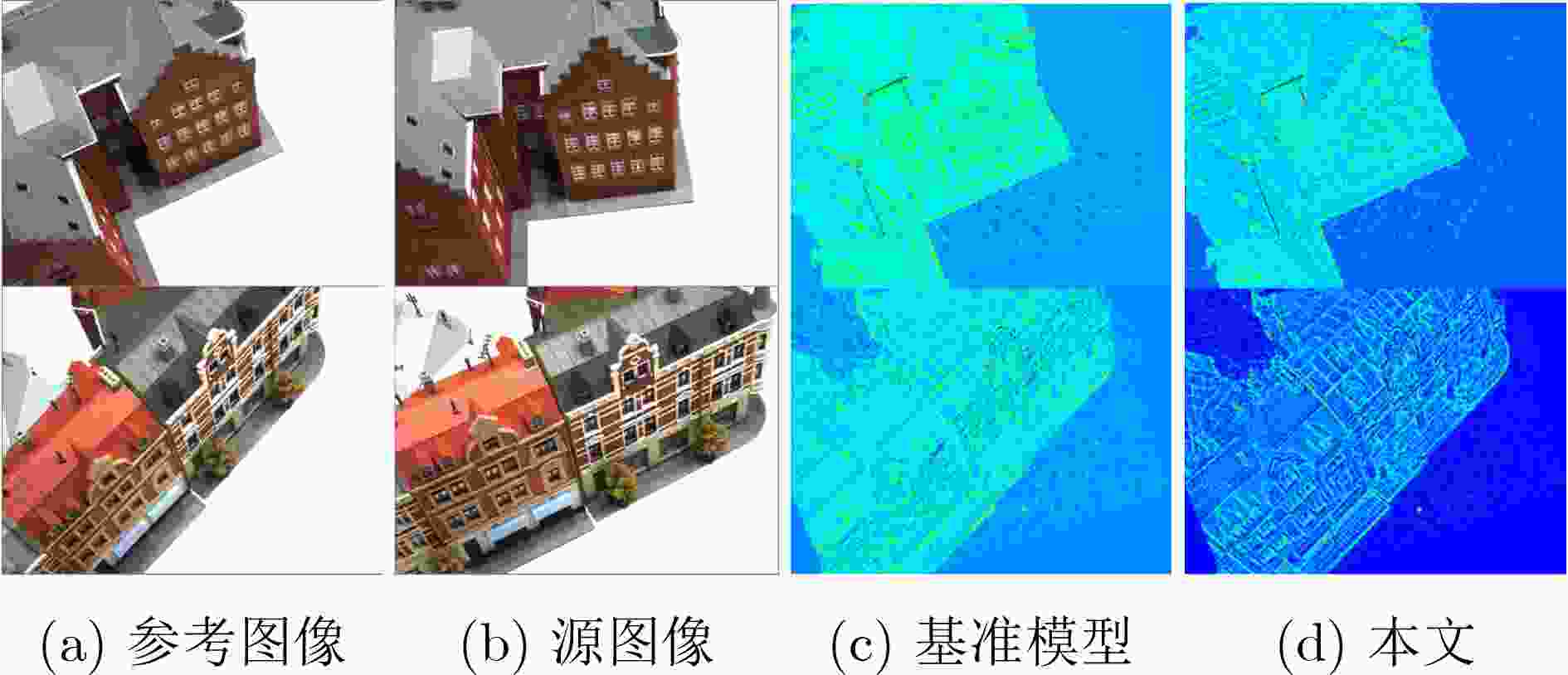
摘要: 基于深度学习的多视角立体几何(MVS)旨在通过多个视图重建出稠密的3维场景。然而现有的方法通常设计复杂的2D网络模块来学习代价体聚合的跨视角可见性,忽略了跨视角2维上下文特征在3D深度方向的一致性假设。此外,基于多阶段的深度推断方法仍需要较高的深度采样率,并且在静态或预先设定的范围内采样深度值,容易在物体边界以及光照遮挡等区域产生错误的深度推断。为了缓解这些问题,该文提出一种基于边缘辅助极线Transformer的密集深度推断模型。与现有工作相比,具体改进如下:将深度回归转换为多深度值分类进行求解,在有限的深度采样率和GPU占用下保证了推断精度;设计一种极线Transformer模块提高跨视角代价体聚合的可靠性,并引入边缘检测分支约束边缘特征在极线方向的一致性;为了提高弱纹理区域的精度,设计了基于概率成本体积的动态深度范围采样机制。与主流的方法在公开的数据集上进行了综合对比,实验结果表明所提模型能够在有限的显存占用下重建出稠密准确的3D场景。特别地,相比于Cas-MVSNet,所提模型的显存占用降低了35%,深度采样率降低约50%,DTU数据集的综合误差从0.355降低至0.325。
-
关键词:
- 多视角场景重建 /
- 多视角立体几何 /
- 深度估计 /
- 极线几何 /
- Transformer
Abstract: Learning-based Multiple-View Stereo (MVS) aims to reconstruct dense 3D scene representation. However, previous methods utilize additional 2D network modules to learn the cross view visibility for cost aggregation, ignoring the consistency assumption of 2D contextual features in the 3D depth direction. In addition, the current multi-stage depth inference model still requires a high depth sampling rate, and depth hypothesis is sampled within static and preset depth range, which is prone to generate errorneous depth inference in the object boundary and occluded area. To alleviate these problems, a multi-view stereo network based on edge assisted epipolar Transformer is proposed. The improvements of this work over the state of the art are as: Depth regression is replaced by the multi-depth hypotheses classification to ensure the accuracy with limited depth sampling rate and GPU consumption. Epipolar Transformer block is developed for reliable cross view cost aggregation, and edge detection branch is designed to constrain the consistency of edge features in the epipolar direction. A dynamic depth range sampling mechanism based on probabilistic cost volume is applied to improve the accuracy of uncertain areas. Comprehensive comparisons with the state of the art are conducted on public benchmarks, which indicate that the proposed method can reconstruct dense scene representations with limited memory bottleblock. Specifically, compared with Cas-MVSNet, the memory consumption is reducted by 35%, the depth sampling rate is reduced by about 50%, and the overall error on DTU datasets is reduced from 0.355 to 0.325. -
表 1 DTU测试集上不同方法的重建结果定量比较
方法 准确性 完整性 综合性 Gipuma
Colmap0.283
0.4000.873
0.6440.578
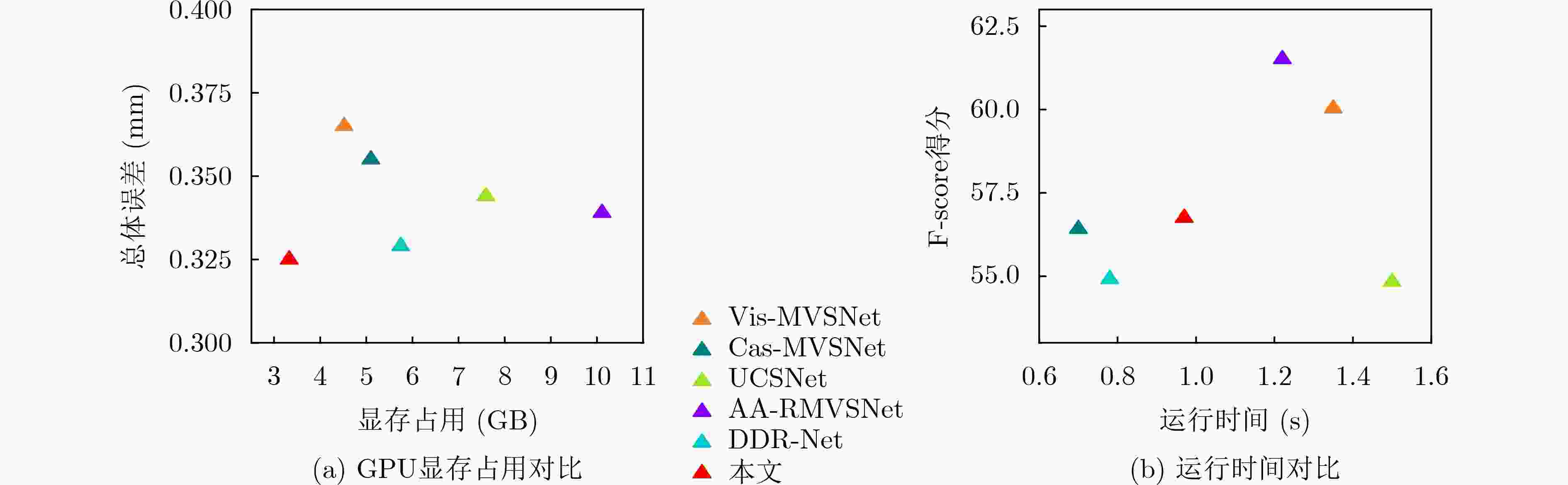
0.532MVSNet 0.456 0.646 0.551 MVSCRF 0.371 0.426 0.398 Fast-MVSNet 0.336 0.403 0.370 R-MVSNet 0.383 0.452 0.417 Cas-MVSNet 0.325 0.385 0.355 PatchmatchNet 0.427 0.277 0.352 AA-RMVSNet 0.376 0.339 0.357 本文 0.364 0.286 0.325 表 2 不同方法在Tanks & Temples数据集的定量比较
方法 Mean M60 Train Horse Lighthouse Family Panther Playground Francis MVSNet 43.48 55.99 28.55 25.07 50.09 53.96 50.86 47.90 34.69 DDR-Net 54.91 55.57 47.17 43.43 55.20 76.18 52.28 56.04 53.36 UCSNet 54.83 55.60 47.89 43.03 54.00 76.09 51.49 57.38 53.16 AA-RMVSNet 61.51 64.05 46.65 51.53 64.02 77.77 59.47 60.85 54.90 Cas-MVSNet 56.42 53.96 46.56 46.20 55.33 76.36 54.02 58.17 58.45 本文 56.75 57.33 50.49 51.12 56.09 75.59 54.26 56.10 53.03 表 3 DTU测试集上消融实验定量比较
方法 平均绝对值误差 固定阈值的预测精度(%) < 2 mm < 4 mm < 8 mm 基准 8.42 77.17 83.03 89.86 基准+分类损失 8.30 79.07 86.70 90.10 本文 7.69 80.25 86.81 90.52 表 4 DTU测试集上不同模块的定量比较(mm)
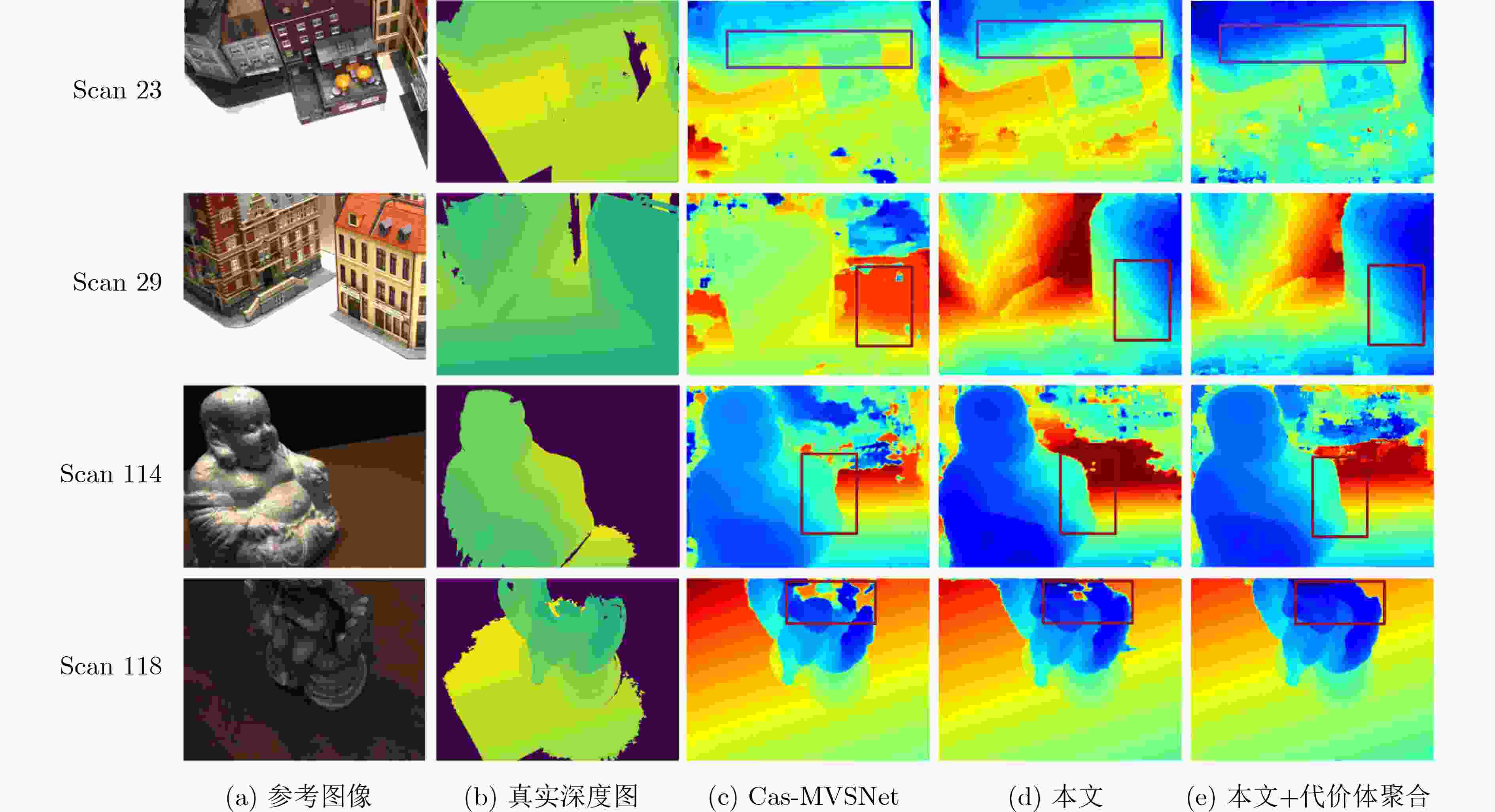
模型 分类损失 极线Transformer 边缘辅助模块 动态采样模块 准确性 完整性 综合性 基准 0.346 0.398 0.372 本文-A √ 0.380 0.334 0.357 本文-B √ √ 0.360 0.302 0.331 本文-C √ √ √ 0.351 0.303 0.327 本文 √ √ √ √ 0.364 0.286 0.325 表 5 DTU测试集上动态采样模块消融实验定量比较
方法 1st范围(mm) 2nd范围(mm) 2nd覆盖占比(%) 3rd范围(mm) 3rd覆盖占比(%) 深度采样数 Cas-MVSNet 508.8 169.72 0.9532 21.09 0.8441 48,32,8 UCSNet 508.8 29.46 0.8507 10.10 0.7310 64,32,8 DDR-Net 508.8 139.46 0.9317 19.24 0.8435 48,32,8 本文 508.8 54.42 0.8891 9.16 0.8381 16,8,4 本文+动态采样 508.8 78.12 0.9003 9.16 0.8412 16,8,4 -
[1] GALLIANI S, LASINGER K, and SCHINDLER K. Massively parallel multiview stereopsis by surface normal diffusion[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 873–881. [2] GU Xiaodong, FAN Zhiwen, ZHU Siyu, et al. Cascade cost volume for high-resolution multi-view stereo and stereo matching[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 2492–2501. [3] LUO Keyang, GUAN Tao, JU Lili, et al. Attention-aware multi-view stereo[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1587–1596. [4] YAO Yao, LUO Zixin, LI Shiwei, et al. MVSNet: Depth inference for unstructured multi-view stereo[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 785–801. [5] YAO Yao, LUO Zixin, LI Shiwei, et al. Recurrent MVSNet for high-resolution multi-view stereo depth inference[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, California, USA, 2019: 5520–5529. [6] XU Haofei and ZHANG Juyong. AANET: Adaptive aggregation network for efficient stereo matching[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1956–1965. [7] CHENG Shuo, XU Zexiang, ZHU Shilin, et al. Deep stereo using adaptive thin volume representation with uncertainty awareness[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 2521–2531. [8] YI Hongwei, WEI Zizhuang, DING Mingyu, et al. Pyramid multi-view stereo net with self-adaptive view aggregation[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 766–782. [9] HE Chenhang, ZENG Hui, HUANG Jianqiang, et al. Structure aware single-stage 3D object detection from point cloud[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 11870–11879. [10] MILDENHALL B, SRINIVASAN P P, TANCIK M, et al. NeRF: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 405–421. [11] LUO Shitong and HU Wei. Diffusion probabilistic models for 3D point cloud generation[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 2836–2844. [12] ZHANG Jingyang, YAO Yao, LI Shiwei, et al. Visibility-aware multi-view stereo network[C/OL]. Proceedings of the 31st British Machine Vision Conference, 2020. [13] XI Junhua, SHI Yifei, WANG Yijie, et al. RayMVSNet: Learning ray-based 1D implicit fields for accurate multi-view stereo[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 8585–8595. [14] YU Zehao and GAO Shenghua. Fast-MVSNet: Sparse-to-dense multi-view stereo with learned propagation and Gauss–Newton refinement[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1946–1955. [15] WANG Fangjinhua, GALLIANI S, VOGEL C, et al. PatchmatchNet: Learned multi-view patchmatch stereo[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minnepolis, USA, 2021: 14189–14198. [16] DEVLIN J, CHANG Mingwei, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[C]. 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minnepolis, USA, 2019: 4171–4186. [17] LI Zhaoshuo, LIU Xingtong, DRENKOW N, et al. Revisiting stereo depth estimation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 6177–6186. [18] SUN Jiaming, SHEN Zehong, WANG Yuang, et al. LoFTR: Detector-free local feature matching with transformers[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 8918–8927. [19] WANG Xiaofeng, ZHU Zheng, QIN Fangbo, et al. MVSTER: Epipolar transformer for efficient multi-view stereo[J]. arXiv: 2204.07346, 2022. [20] DING Yikang, YUAN Wentao, ZHU Qingtian, et al. TransMVSNet: Global context-aware multi-view stereo network with transformers[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 8575–8584. [21] ZHU Jie, PENG Bo, LI Wanqing, et al. Multi-view stereo with transformer[J]. arXiv: 2112.00336, 2021. [22] WEI Zizhuang, ZHU Qingtian, MIN Chen, et al. AA-RMVSNet: Adaptive aggregation recurrent multi-view stereo network[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 6167–6176. [23] YI Puyuan, TANG Shengkun, and YAO Jian. DDR-Net: Learning multi-stage multi-view stereo with dynamic depth range[J]. arXiv: 2103.14275, 2021. -






 下载:
下载:
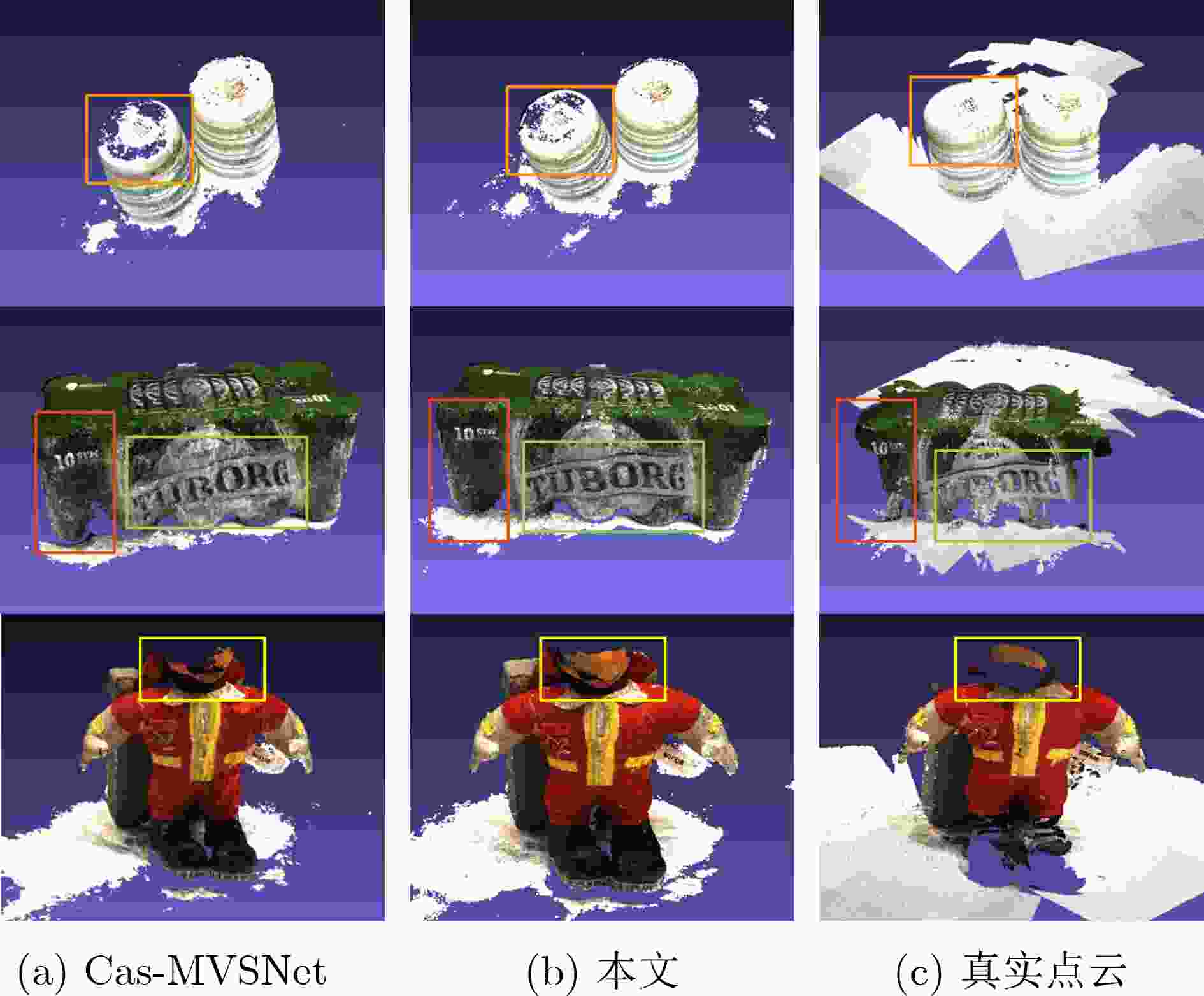
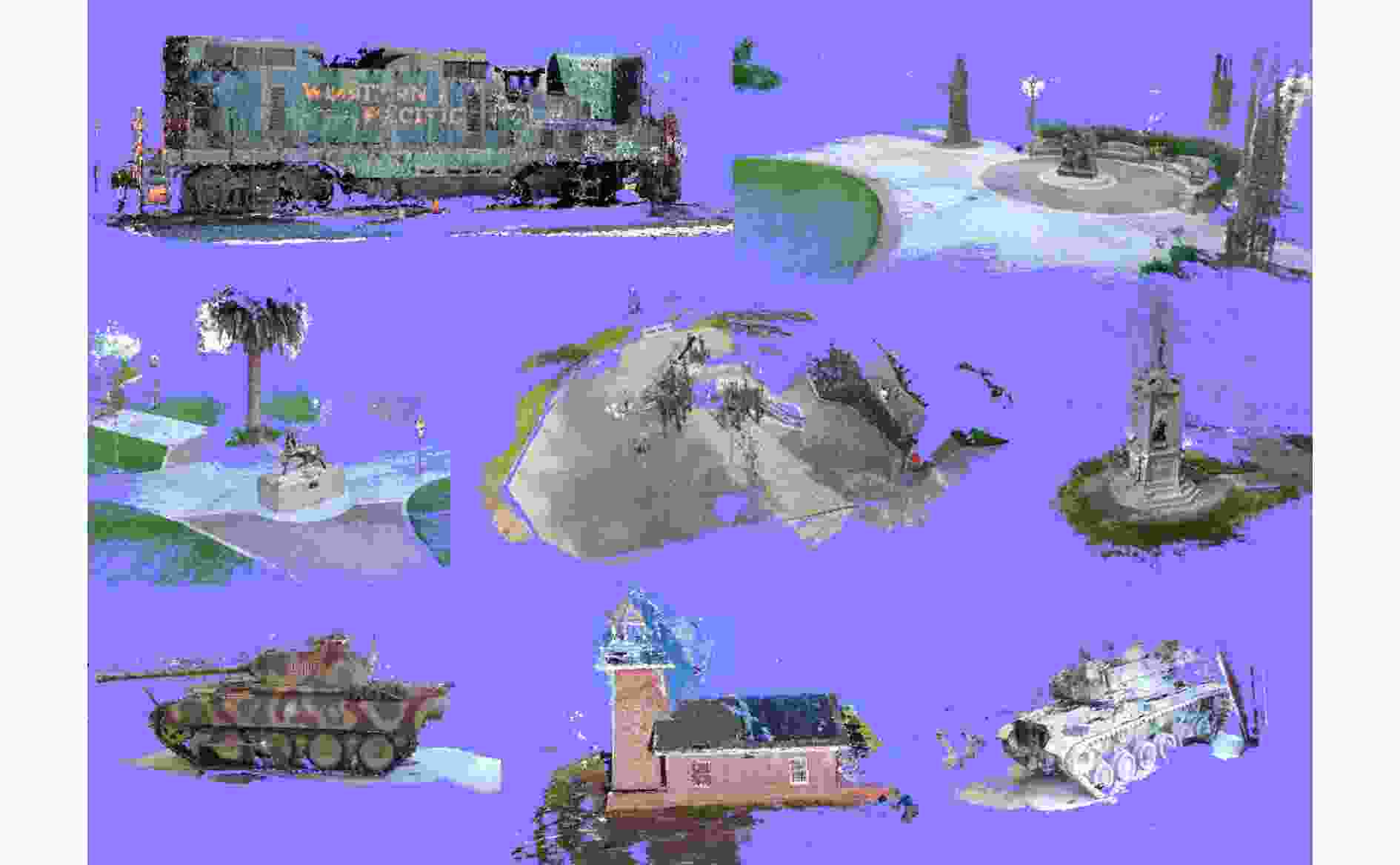




 下载:
下载:
