Multisource Track Association Dataset Based on the Global AIS
-
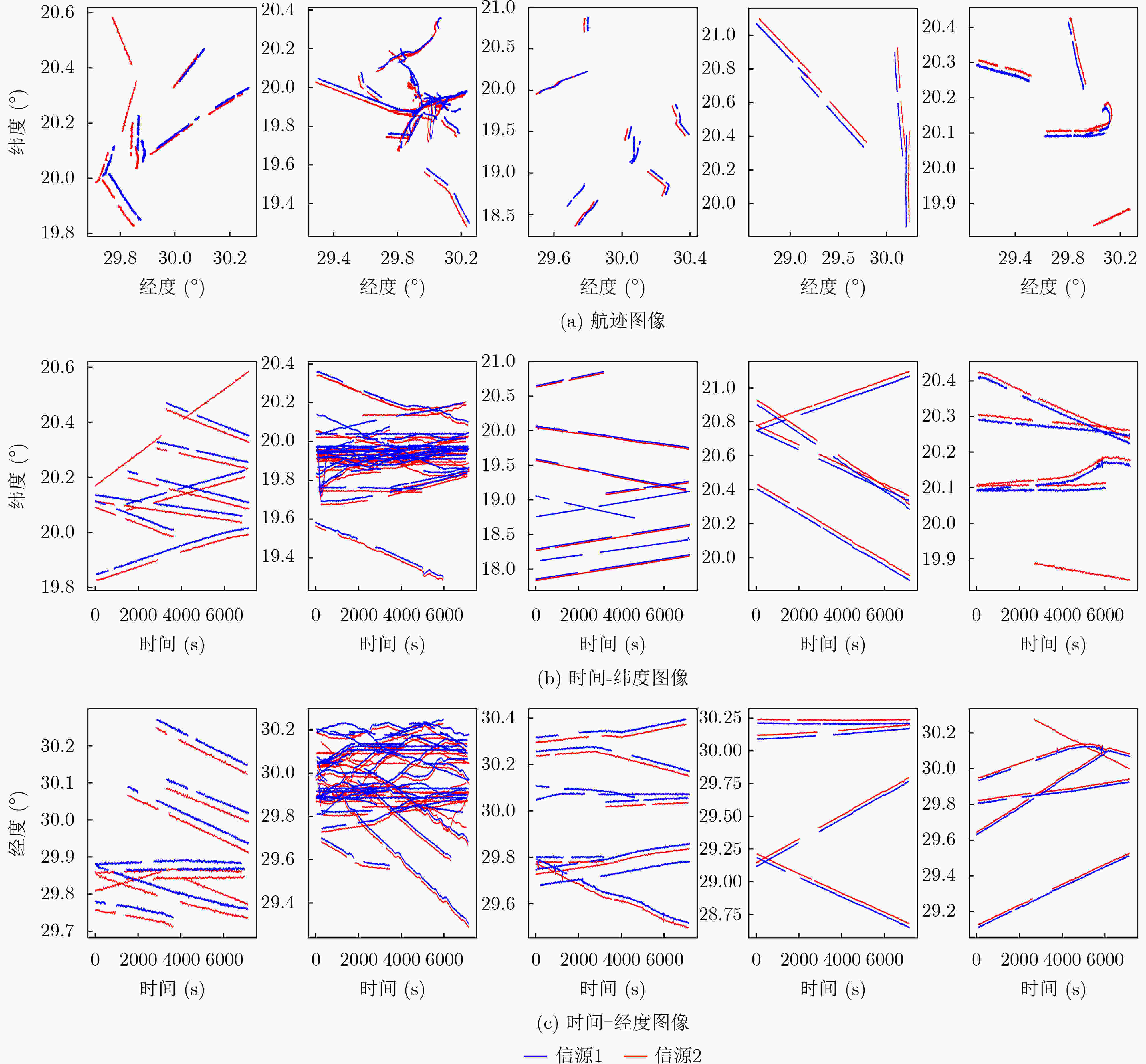
摘要: 数据、算法和算力是当前人工智能技术发展的3大推力,考虑到智能关联算法研究的迫切需求和多雷达协同观测航迹数据获取困难,针对航迹关联数据集缺失问题,该文公开了多源航迹关联数据集(MTAD),其由全球AIS航迹数据经栅格划分、自动中断和噪声添加处理步骤构建。该数据集包括训练集和测试集两大部分,共有航迹百万余条,其中训练集包含5000个场景样本,测试集包含1000个场景样本,每一个场景样本由几个到几百个数量不等的航迹构成,涵盖多种运动模式、多种目标类型和长度不等的持续时间。同时,进一步对构造的MTAD数据集进行可视化分析,详细研究了各个栅格内航迹的特点,证明了该数据集的丰富性、合理性和有效性。最后,作为参考,给出了关联评价指标和关联基线结果。该数据集目前已被用作海军“金海豚”杯竞赛科目专用数据集。
-
关键词:
- 航迹关联 /
- 自动识别系统 (AIS) /
- 人工智能 /
- 深度学习
Abstract: Data, algorithms, and hash rates are the three thrust forces for developing artificial intelligence. Considering the urgent demand for research on the intelligent association algorithm and the difficulty of obtaining track data from multi-radar collaborative observation and addressing the problem of missing track association dataset, a Multi-source Track Association Dataset (MTAD) is constructed in this study. MTAD is based on automatic identification system trajectory data after processing grid division, automatic interruption, and error adding. The dataset includes two parts, namely, the training dataset and the test dataset, with more than 1 million tracks. The train and test datasets contain 5000 and 1000 scene samples, respectively. Each scene sample consists of several to hundreds of tracks, covering various movement patterns, target types, and duration times. In addition, the constructed MTAD is further visualized and analyzed, and the characteristics of tracks in each grid are studied in detail, demonstrating the richness, rationality, and effectiveness of the MTAD. The indicators and baseline results of the association are obtained. This dataset has already been used as a dedicated dataset for the Navy’s “Golden Dolphin” Cup competition. -
表 1 生成信源航迹时所需的参数表
参数 数值 Ts1 20 s Ts2 10 s W0 (20°, 30°) Pd 0.8 Q 10 表 2 多源关联基线结果(%)
关联正确率 关联错误率 训练集 80.83 28.09 测试集 80.98 28.15 表 3 中断关联基线结果(%)
信源1 信源2 关联正确率 关联错误率 关联正确率 关联错误率 训练集 28.12 20.50 28.20 20.26 测试集 27.62 19.41 27.50 19.63 -
[1] BAR-SHALOM Y. Multitarget-Multisensor Tracking: Advanced Applications[M]. Norwood: Artech House, 1990. [2] ENDSLEY M R. Situation awareness global assessment technique (SAGAT)[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE 1988 National Aerospace and Electronics Conference, Dayton, USA, 1988: 789–795. [3] HALL D L and LLINAS J. An introduction to multisensor data fusion[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1997, 85(1): 6–23. doi: 10.1109/5.554205 [4] MUCCI R, ARNOLD J, and BAR-SHALOM Y. Track segment association with a distributed field of sensors[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1985, 78(4): 1317–1324. doi: 10.1121/1.392901 [5] YEOM S W, KIRUBARAJAN T, and BAR-SHALOM Y. Improving track continuity using track segment association[C]. 2003 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings, Big Sky, USA, 2003, 4: 1925–1941. [6] LIN L, BAR-SHALOM Y, and KIRUBARAJAN T. New assignment-based data association for tracking move-stop-move targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2004, 40(2): 714–725. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2004.1310016 [7] ZHANG Shuo and BAR-SHALOM Y. Track segment association for GMTI tracks of evasive move-stop-move maneuvering targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(3): 1899–1914. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5937272 [8] 齐林, 王海鹏, 熊伟, 等. 基于先验信息的多假设模型中断航迹关联算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2015, 37(4): 732–739. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.04.02QI Lin, WANG Haipeng, XIONG Wei, et al. Track segment association algorithm based on multiple-hypothesis models with priori information[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(4): 732–739. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.04.02 [9] XIONG Wei, XU Pingliang, CUI Yaqi, et al. Track segment association with dual contrast neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(1): 247–261. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3098175 [10] XIONG Wei, XU Pingliang, CUI Yaqi, et al. Track segment association via track graph representation learning[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2021, 15(11): 1458–1471. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12138 [11] 徐平亮, 崔亚奇, 熊伟, 等. 生成式中断航迹接续关联方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(5): 1543–1552. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.05.15XU Pingliang, CUI Yaqi, XIONG Wei, et al. Generative track segment consecutive association method[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(5): 1543–1552. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.05.15 [12] DENG Jia, DONG Wei, SOCHER R, et al. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 248–255. [13] EVERINGHAM M, ESLAMI S M A, VAN GOOL L, et al. The PASCAL visual object classes challenge: A retrospective[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 111(1): 98–136. doi: 10.1007/s11263-014-0733-5 [14] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]. Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 740–755. [15] XIA Guisong, HU Jingwen, HU Fan, et al. AID: A benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(7): 3965–3981. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2685945 [16] LU Xiaoqiang, WANG Binqiang, ZHENG Xiangtao, et al. Exploring models and data for remote sensing image caption generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 56(4): 2183–2195. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2776321 [17] GEIGER A, LENZ P, STILLER C, et al. Vision meets robotics: The KITTI dataset[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2013, 32(11): 1231–1237. doi: 10.1177/0278364913491297 [18] BILIC P, CHRIST P F, VORONTSOV E, et al. The liver tumor segmentation benchmark (LiTS)[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1901.04056, 2019. [19] IRVIN J, RAJPURKAR P, KO M, et al. CheXpert: A large chest radiograph dataset with uncertainty labels and expert comparison[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(1): 590–597. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.3301590 [20] DESAI S, BAGHAL A, WONGSURAWAT T, et al. Chest imaging representing a COVID-19 positive rural U. S. population[J]. Scientific Data, 2020, 7(1): 414. doi: 10.6084/m9.figshare.12980795 [21] TETREAULT B J. Use of the automatic identification system (AIS) for maritime domain awareness (MDA)[C]. Proceedings of Oceans 2005 MTS/IEEE, Washington, USA, 2005: 1590–1594. [22] CHEN Zhijun, XUE Jie, WU Chaozhong, et al. Classification of vessel motion pattern in inland waterways based on automatic identification system[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 161: 69–76. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.04.072 [23] KONG Zhan, CUI Yaqi, XIONG Wei, et al. Ship target identification via Bayesian-transformer neural network[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2022, 10(5): 577. doi: 10.3390/jmse10050577 [24] PAPI F, TARCHI D, VESPE M, et al. Radiolocation and tracking of automatic identification system signals for maritime situational awareness[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2015, 9(5): 568–580. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0292 [25] LIU Yong, YAO Libo, XIONG Wei, et al. GF-4 satellite and automatic identification system data fusion for ship tracking[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(2): 281–285. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2869561 [26] SCHWEHR K D and MCGILLIVARY P A. Marine ship automatic identification system (AIS) for enhanced coastal security capabilities: An oil spill tracking application[C]. OCEANS 2007, Vancouver, Canada, 2007: 1–9. [27] CHEN M Y and WU H T. An automatic-identification-system-based vessel security system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 19(1): 870–879. -





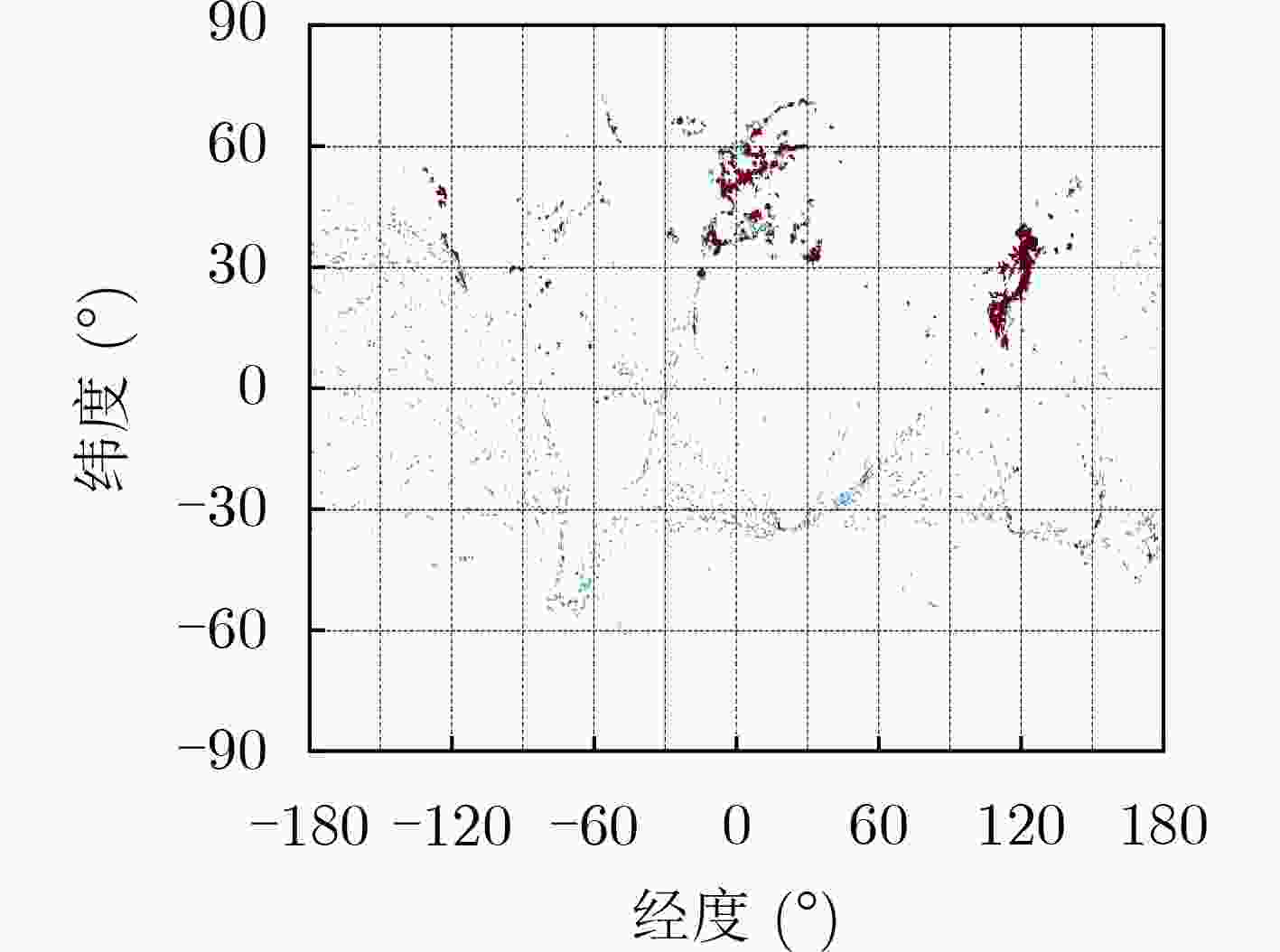
 下载:
下载:
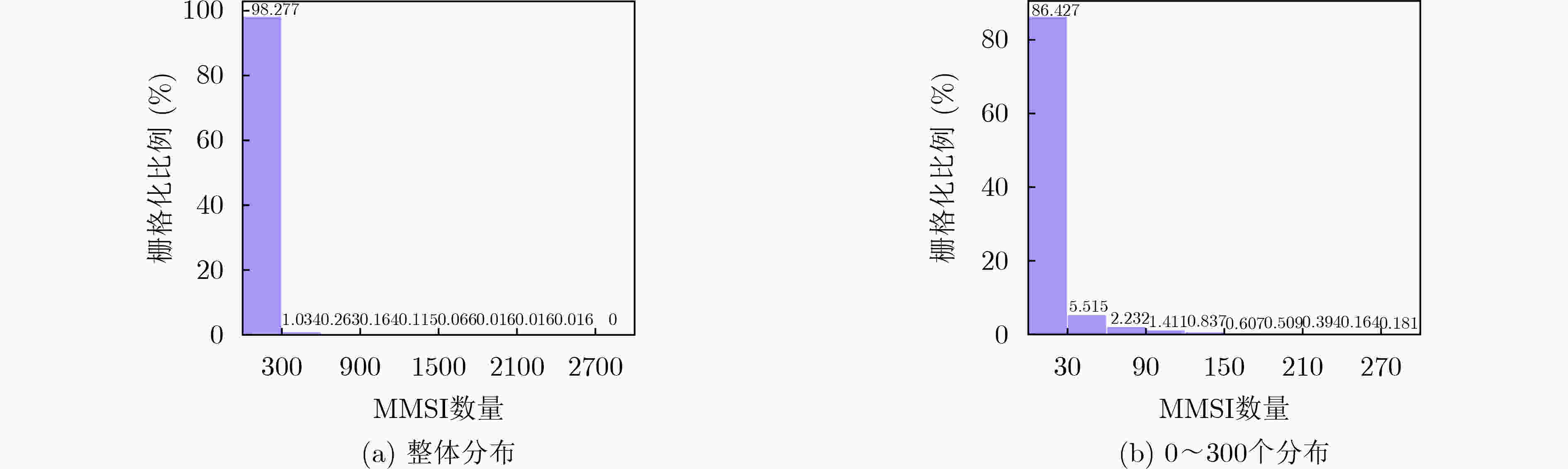
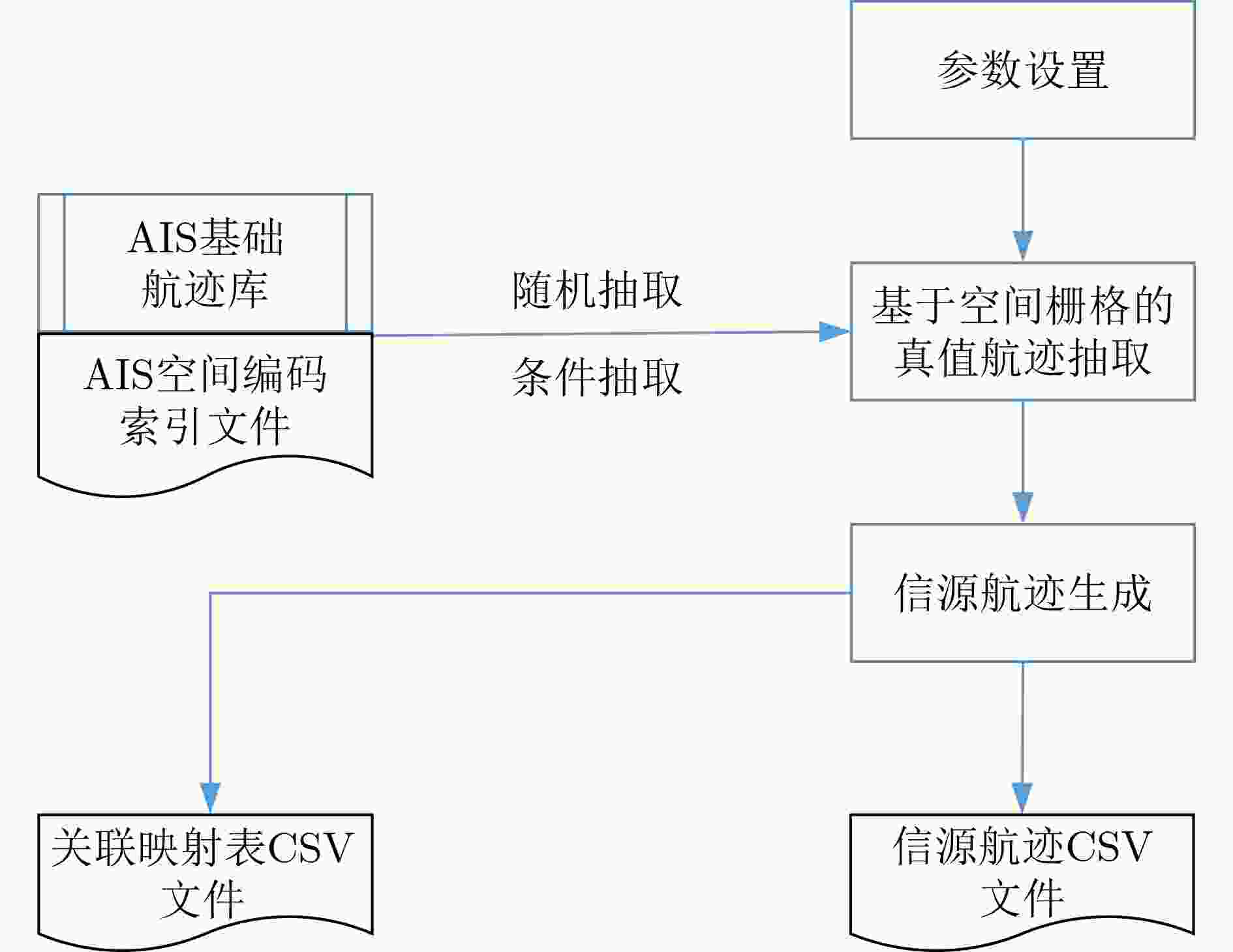
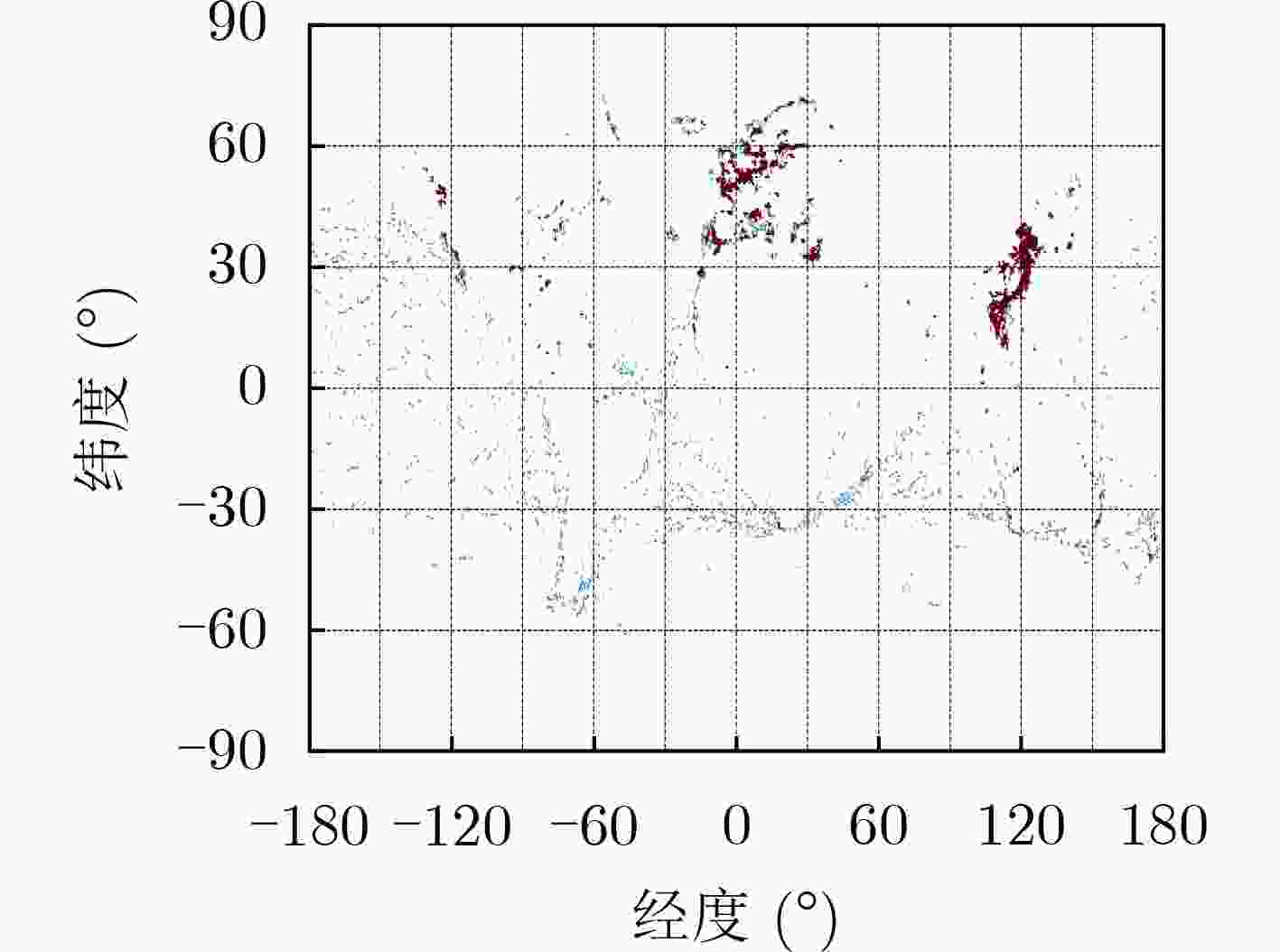
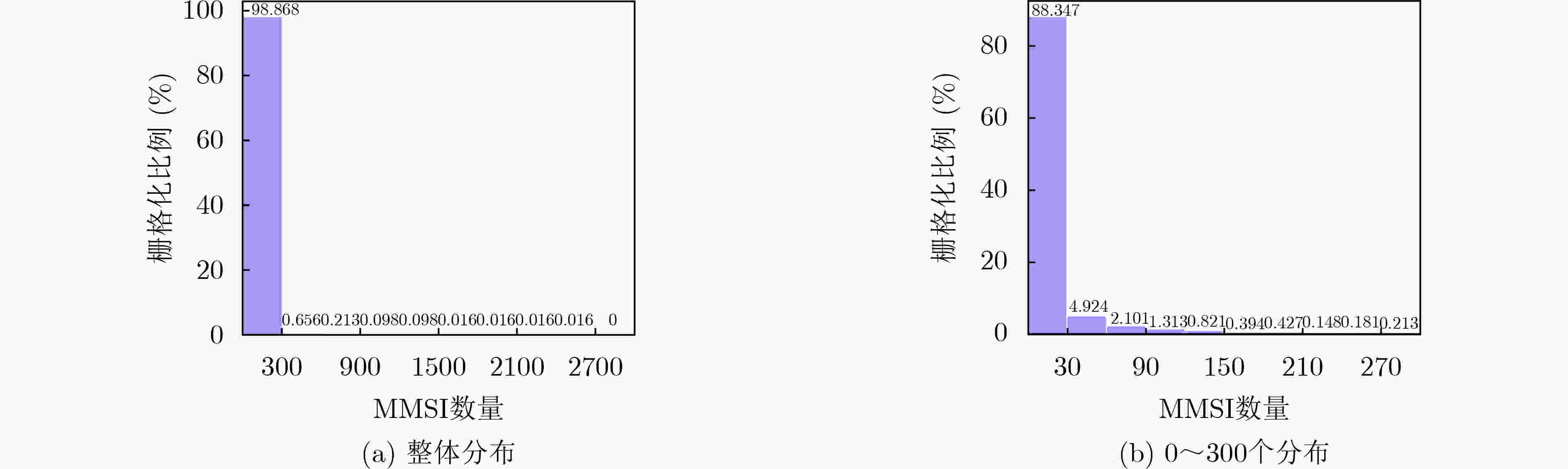
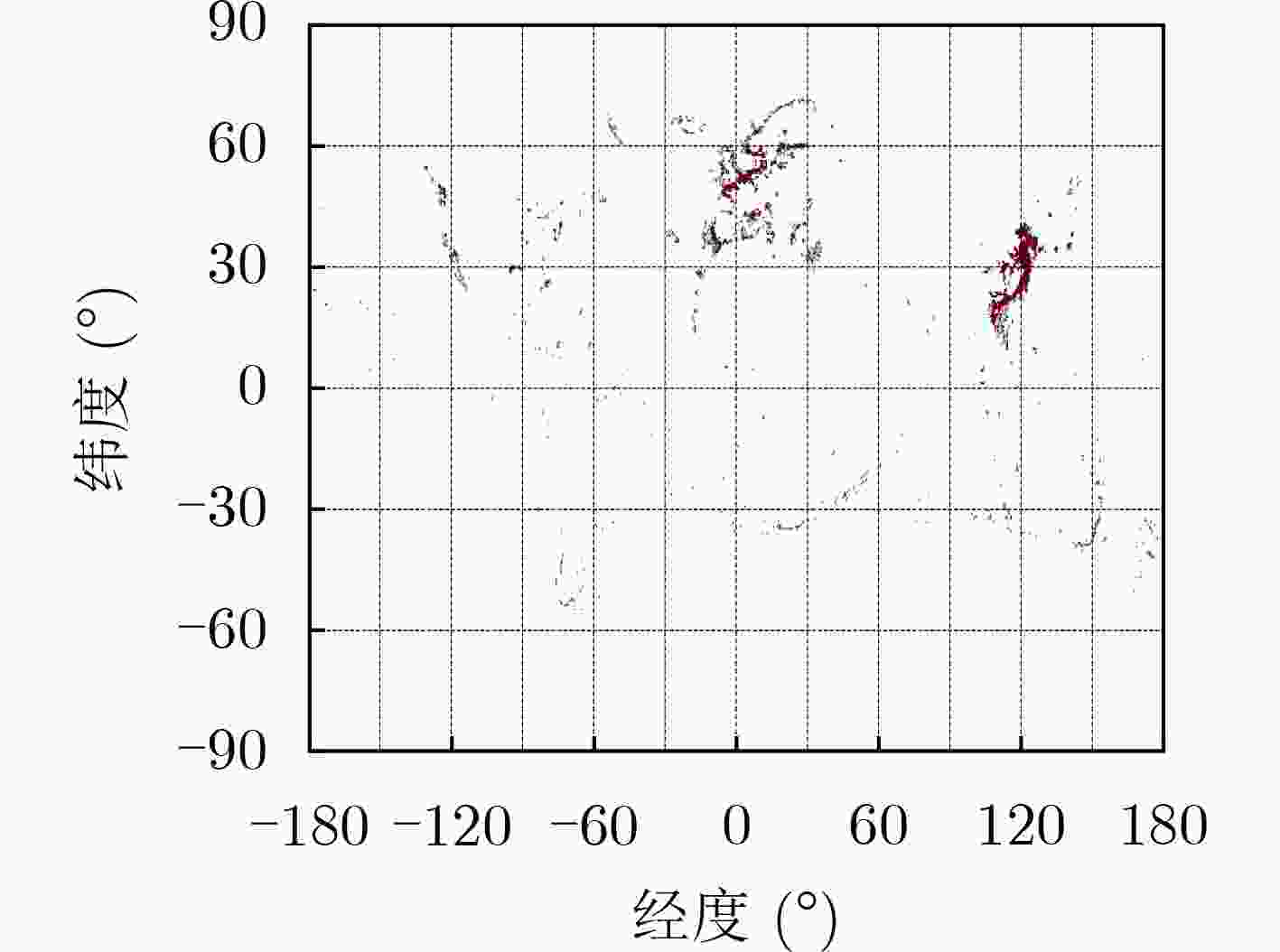
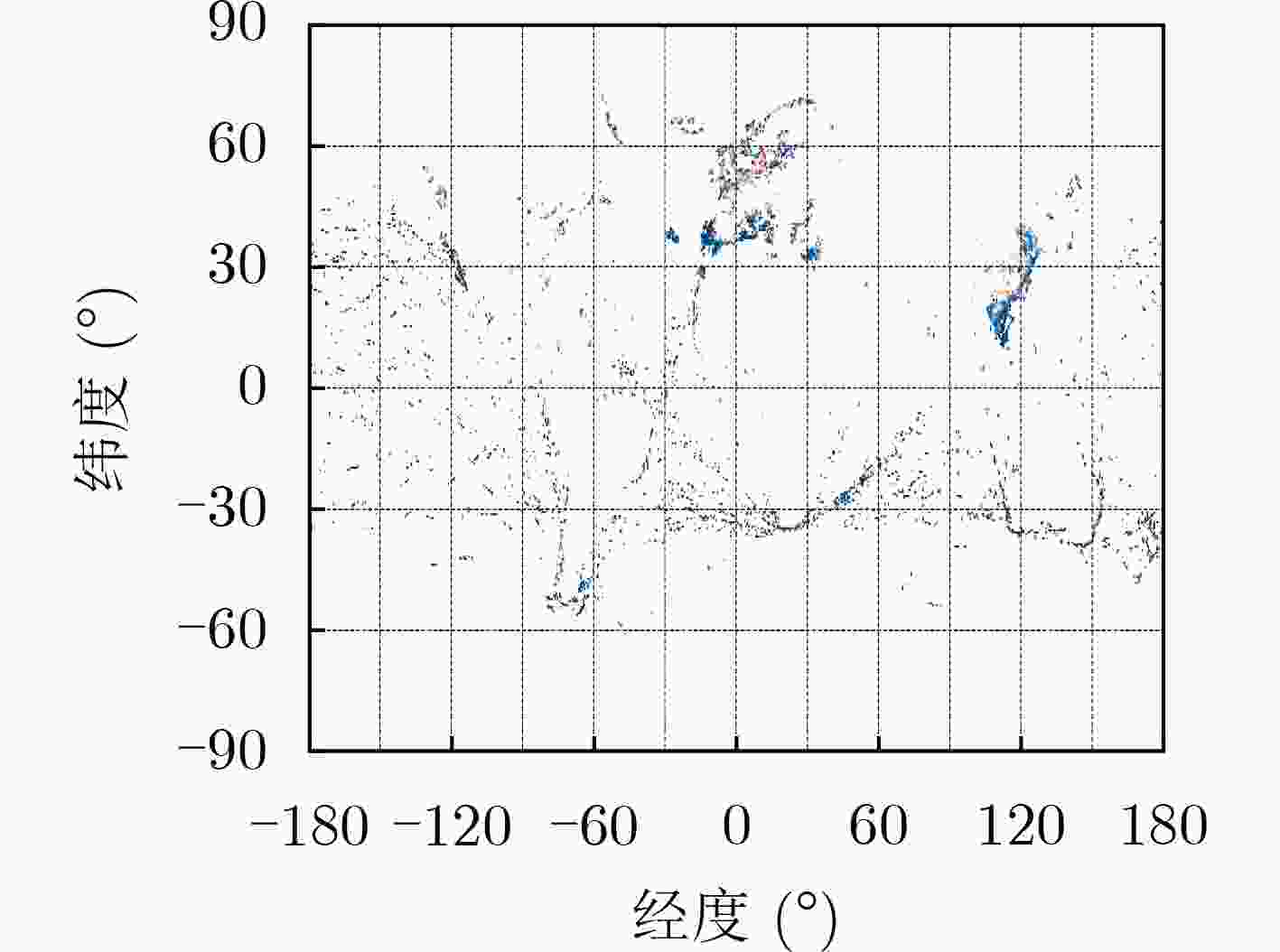
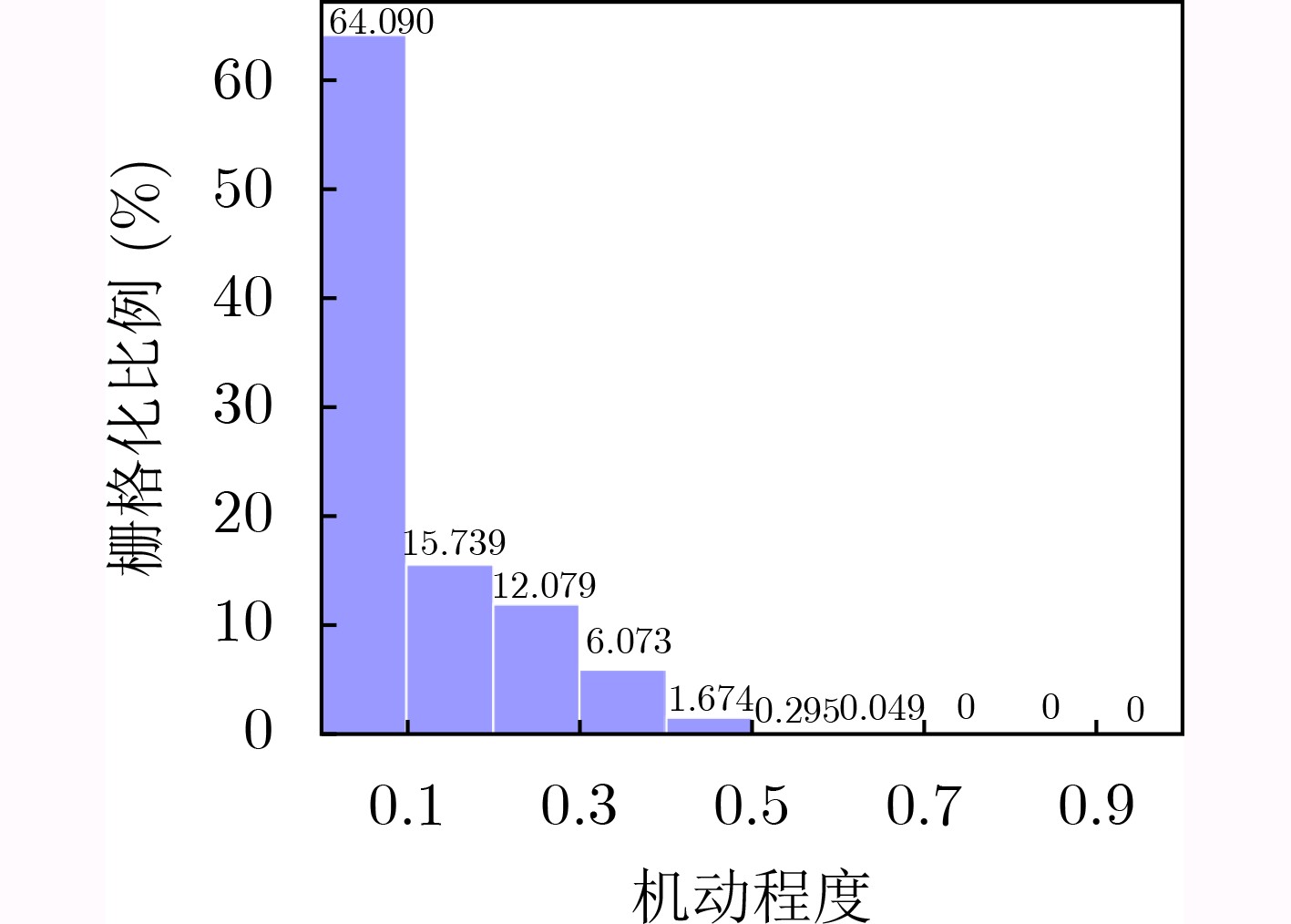


 下载:
下载:
