Dense Heavy Parameter Lightweight Transformer Model for CT Image Recognition of COVID-19
-
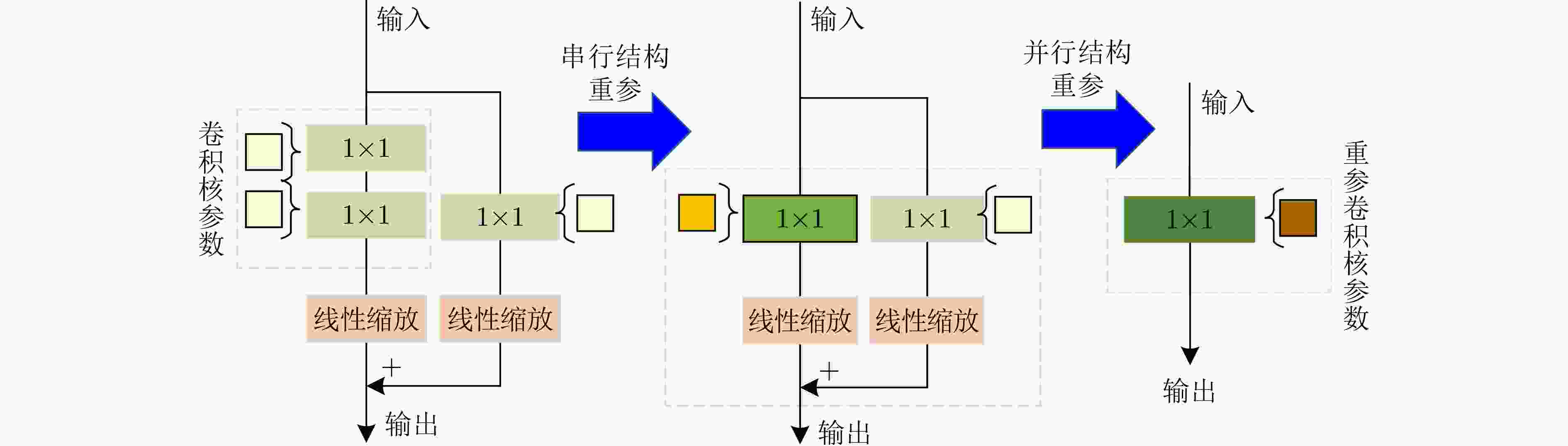
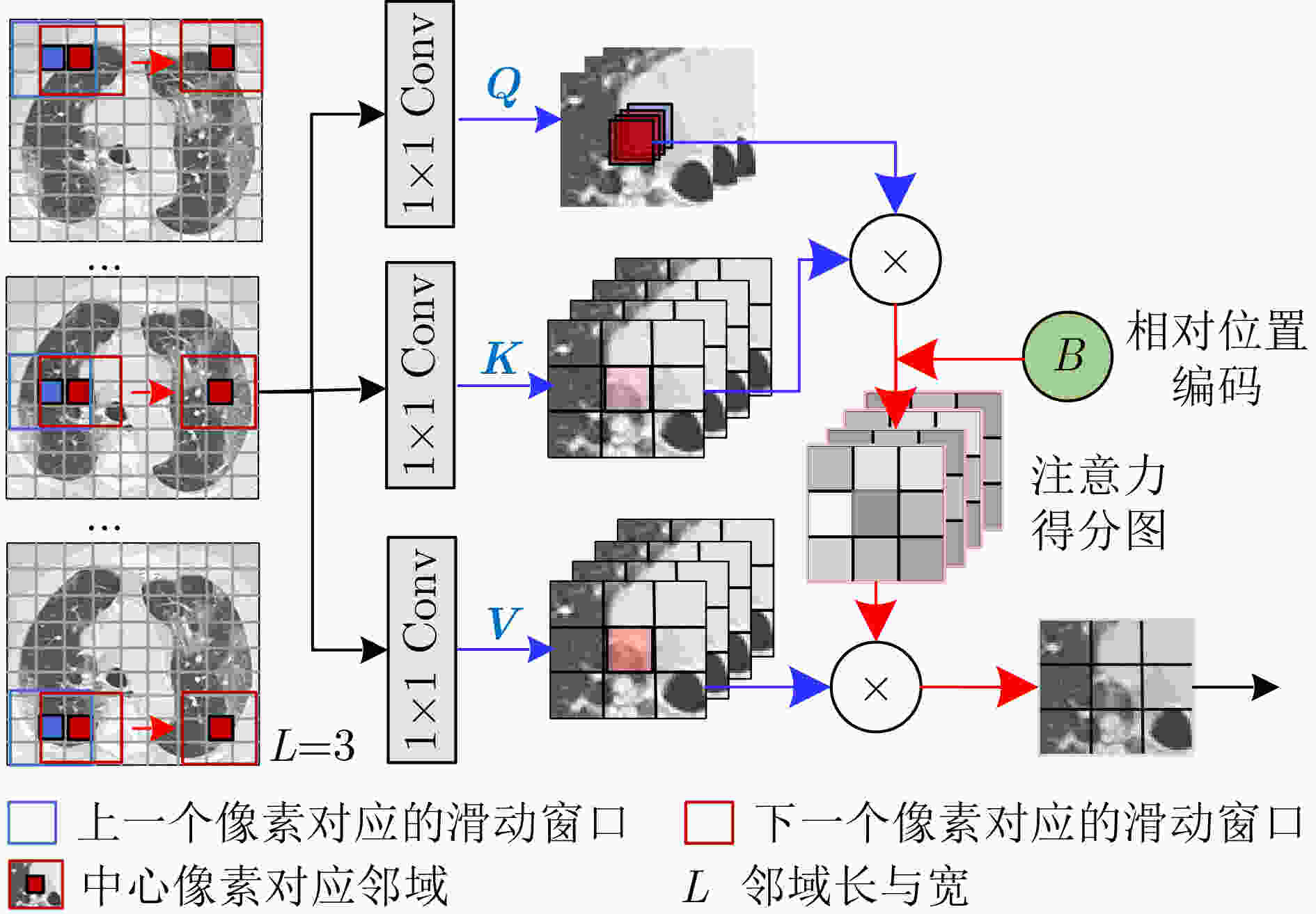
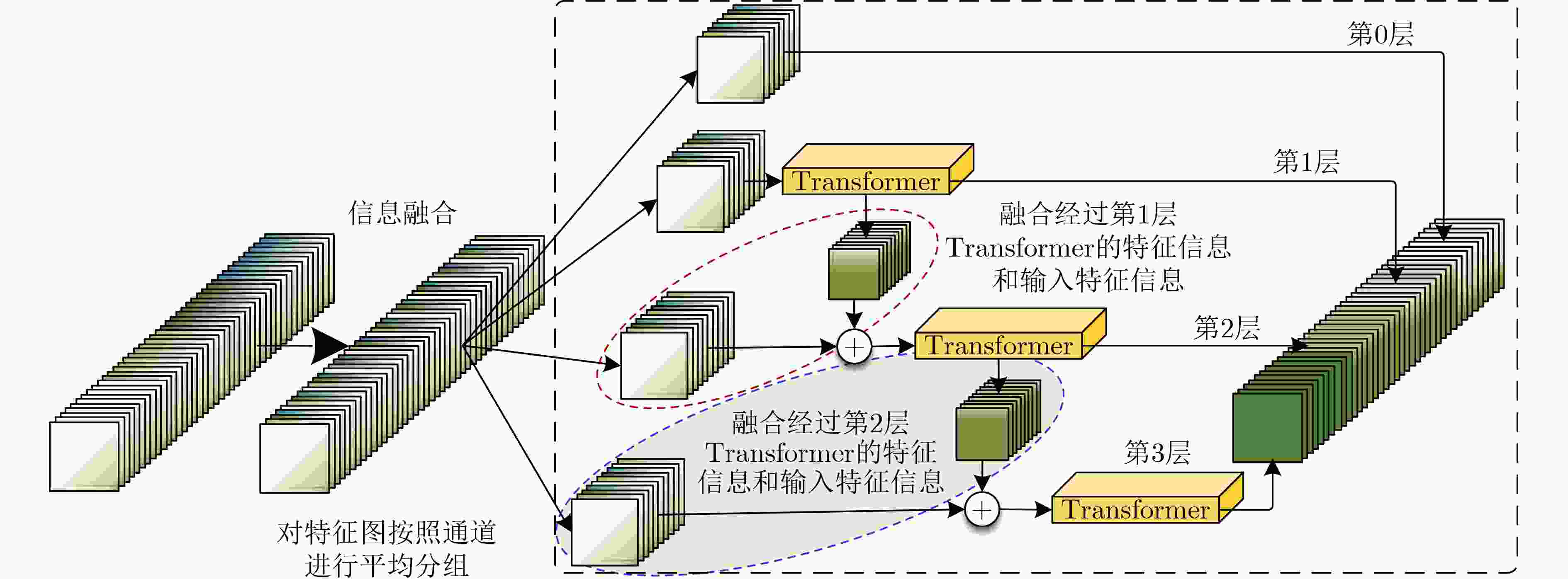
摘要: 新冠(COVID-19)肺炎严重威胁人类健康,基于深度学习的计算机辅助诊断方法能有效提高新冠肺炎的诊断效率。但是深度学习模型结构复杂、参数量和计算量大,在保持模型性能的前提下提高网络轻量化的程度具有重要研究意义,因此,该文提出一种面向CT图像新冠肺炎识别的密集重参轻量化Transformer模型(DRLTransformer)。首先,为提高模型的轻量化程度,构造了重参密集块和层次化Transformer,在保持模型精度的同时提高计算速度,降低模型参数量;然后,为充分提取新冠肺炎病灶的全局与局部信息,设计层次化Transformer增强全局注意力对局部特征相关性的关注程度,其中采用分组提取全局特征,在不同组之间进行融合获得多层次信息,并且进行信息融合,进一步提高组内和组间特征的交互能力,此外对所有全局特征进行聚合,实现深浅层特征深度融合。最后,在新冠肺炎CT数据集中进行对比实验,结果表明该模型参数量和计算量分别为1.47 M和81.232 M,相比密集网络(DenseNet)参数量降低29倍、计算量降低23倍,该模型对新冠肺炎计算机辅助诊断具有积极的意义,为深度学习模型轻量化提供了新思路。
-
关键词:
- 新冠肺炎 /
- 密集网络 /
- 重参密集块 /
- 层次化Transformer /
- 轻量化
Abstract: COrona VIrus Disease 2019(COVID-19) is a serious threat to human health, deep learning computer aided diagnosis method can effectively improve the diagnosis efficiency. But deep learning models have usually complex structure which have large number of parameters and computations, therefore, a Dense Reparameter Lightweight Transformer(DRLTransformer) for COVID-19 CT recognition is proposed. Firstly, reparameter dense block and hierarchical Transformer are proposed to improve lightweight degree of model, which can improve computation speed and reduce parameters without losing model performance. Secondly, in order to fully extract global and local information of lesions, using hierarchical Transformer enhance global attention on local feature relevance, which use grouping to extract global features and fused between different groups to obtain multi-level information, and then information fusion is used to further improve interaction of intra group and inter group features. In addition, all global features are aggregated to achieve deep fusion of deep and shallow features. Finally, comparative experiments in COVID-19 CT dataset, the results show that the parameters and computations of DRLTransformer are 1.47 M and 81.232 M. Compared to Dense Convolutional Network(DenseNet), parameters are reduced by 29 times and computations are reduced by 23 times. The model proposed in this paper has positive implications for computer aided diagnosis of COVID-19 and provides a new idea for lightweight deep learning model. -
表 1 在新冠肺炎CT数据集上的消融实验结果对比
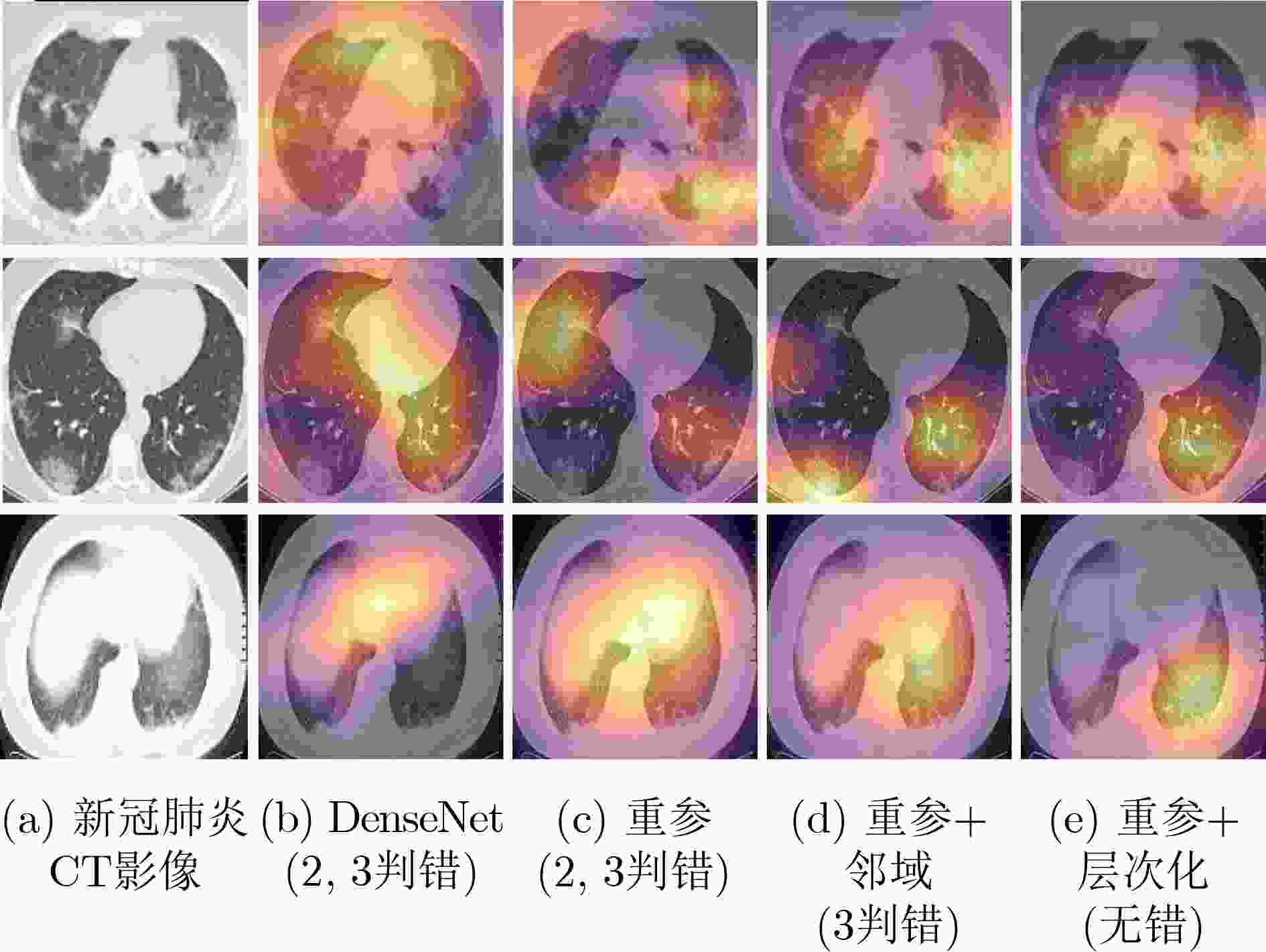
模型 实验 替换添加 参数量(M) 计算量 训练显存(G) 测试显存(G) 训练时间(s) 准确率 精确率 召回率 F1分数 AUC值 DenseNet – DenseNet121 42.62 1.816G 7.09 8.15 11 733 0.945 7 0.944 7 0.947 7 0.946 2 0.945 7 重参 1 重参密集块 1.07 70.381 6.75 3.28 7 398 0.959 7 0.954 4 0.966 2 0.960 2 0.959 6 重参+邻域 2 邻域 13.43 643.195 6.67 3.35 8 991 0.968 9 0.963 5 0.975 4 0.969 4 0.968 9 重参
+层次化
Transfomer3 512层次化 4.55 225.731 6.34 3.16 8 345 0.972 1 0.966 6 0.978 5 0.972 5 0.972 0 4 256层次化 1.28M 76.263M 5.97G 3.14G 8 287 0.967 4 0.963 4 0.972 3 0.967 8 0.967 4 5 512信息融合 4.55 225.731 6.37 3.19 8 385 0.978 3 0.975 5 0.981 5 0.978 5 0.978 3 6 256信息融合 1.28 76.263 5.97 3.17 8 312 0.976 7 0.975 5 0.978 5 0.976 9 0.976 7 7 256聚合 1.47 81.232 6.08 3.17 7 558 0.981 4 0.978 6 0.984 6 0.981 6 0.981 4 表 2 不同模型在新冠肺炎CT数据集上的具体结果
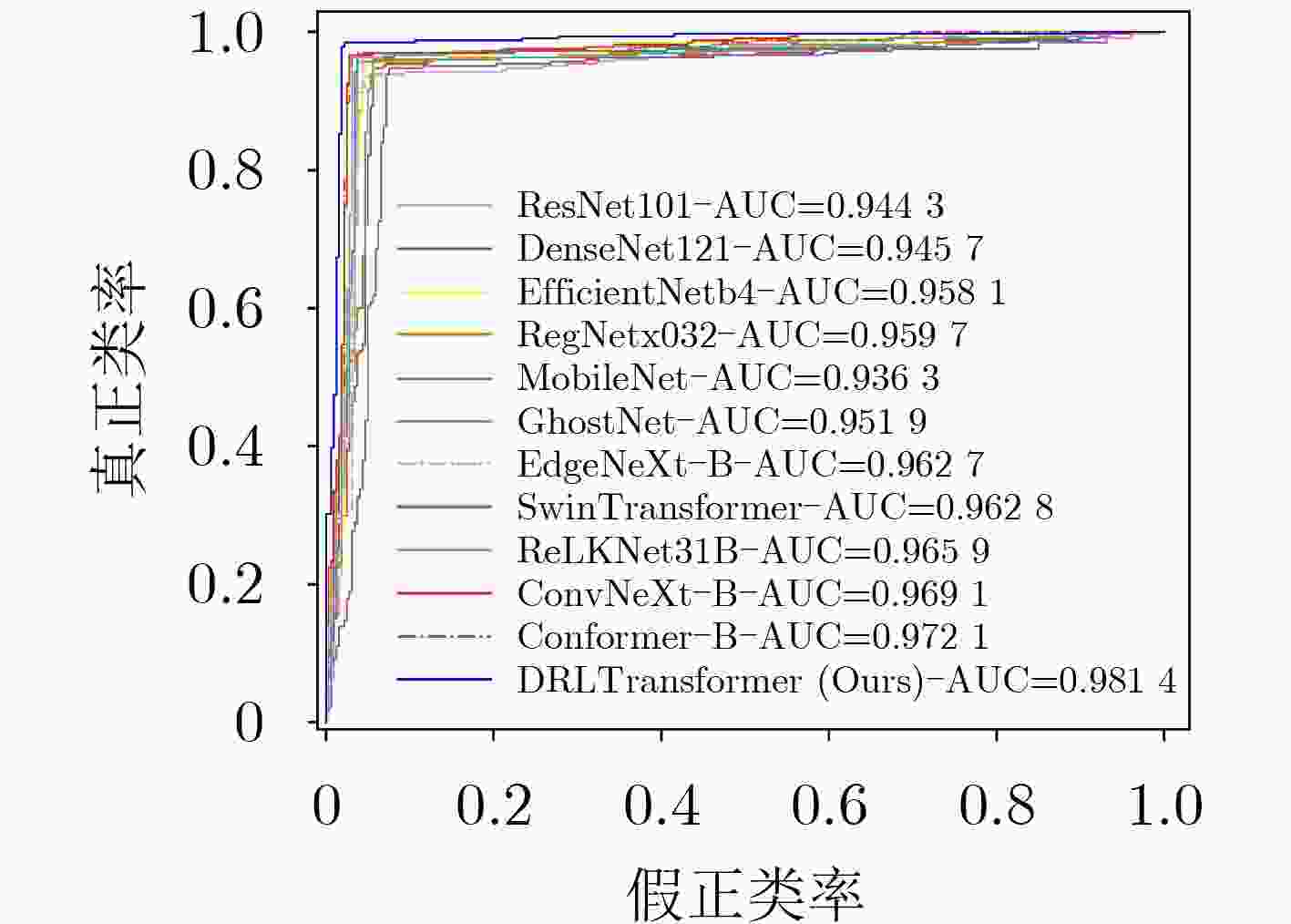
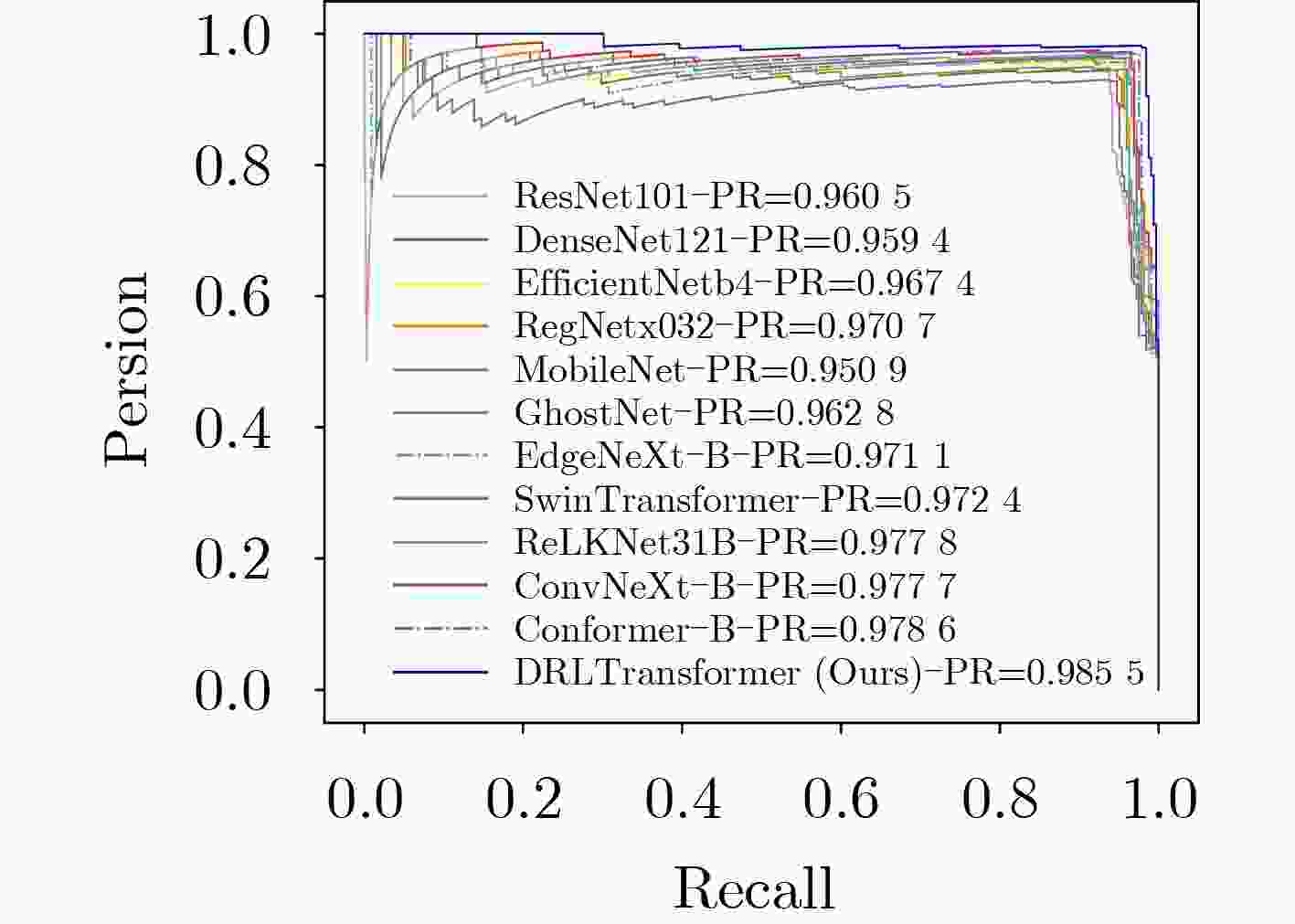
对比模型 模型参数量(M) 模型计算量 训练时间(s) 准确率 精确率 召回率 F1分数 AUC值 ResNet101[3] 162.14 7.832G 12 984 0.944 1 0.952 9 0.935 4 0.944 1 0.944 3 DenseNet121[15] 42.62 1.816G 11 733 0.945 7 0.944 7 0.947 7 0.946 2 0.945 7 EfficientNetb4[5] 66.96 34.125M 11 647 0.958 1 0.951 5 0.966 2 0.958 8 0.958 1 RegNetx032[16] 58.35 3.176G 11 389 0.959 6 0.962 8 0.956 9 0.959 9 0.959 7 MobileNet[9] 12.26 2.322G 10 533 0.936 4 0.927 7 0.947 7 0.937 6 0.936 3 GhostNet[2] 14.89 147.511 7 846 0.951 9 0.945 4 0.960 0 0.952 7 0.951 9 EdgeNeXt-B[11] 113.29 1.851G 12 114 0.962 8 0.957 4 0.969 2 0.963 3 0.962 7 SwinTransformer[17] 330.66 15.126G 17 936 0.962 8 0.963 1 0.963 1 0.963 1 0.962 8 ReLKNet31B[18] 300.76 15.513G 19 346 0.965 9 0.969 0 0.963 1 0.966 0 0.965 9 ConvNeXt-B[16] 333.98 15.359G 16 705 0.968 9 0.972 1 0.966 2 0.969 1 0.969 1 Conformer-B[17] 510.06 14.486G 17 428 0.972 1 0.969 4 0.975 4 0.972 4 0.972 1 DRLTransformer 1.47M 81.232M 7 558 0.981 4 0.978 6 0.984 6 0.981 6 0.981 4 表 3 公开对比实验结果
表 4 公开对比实验结果
-
[1] KAYA A T and AKMAN B. Mediastinal lymph node enlargement in COVID-19: Relationships with mortality and CT findings[J]. Heart & Lung, 2022, 54: 19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2022.03.006 [2] 周涛, 刘赟璨, 陆惠玲, 等. ResNet及其在医学图像处理领域的应用: 研究进展与挑战[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 149–167. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210914ZHOU Tao, LIU Yuncan, LU Huiling, et al. ResNet and its application to medical image processing: Research progress and challenges[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 149–167. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210914 [3] SONG Ying, ZHENG Shuangjia, LI Liang, et al. Deep learning enables accurate diagnosis of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) with CT images[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2021, 18(6): 2775–2780. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2021.3065361 [4] YE Qinghao, GAO Yuan, DING Weiping, et al. Robust weakly supervised learning for COVID-19 recognition using multi-center CT images[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2022, 116: 108291. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2021.108291 [5] RAHHAL M, BAZI Y, JOMAA R M, et al. Deep learning approach for COVID-19 detection in computed tomography images[J]. Computers, Materials & Continua, 2021, 67(2): 2093–2110. doi: 10.32604/CMC.2021.014956 [6] KONG Lingzhi and CHENG Jinyong. Classification and detection of COVID-19 X-Ray images based on DenseNet and VGG16 feature fusion[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 77: 103772. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2022.103772 [7] GARG A, SALEHI S, LA ROCCA M, et al. Efficient and visualizable convolutional neural networks for COVID-19 classification using Chest CT[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 195: 116540. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.116540 [8] MONTALBO F J P. Diagnosing Covid-19 chest x-rays with a lightweight truncated DenseNet with partial layer freezing and feature fusion[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021, 68: 102583. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102583 [9] ASIF S, ZHAO Ming, TANG Fengxiao, et al. A deep learning-based framework for detecting COVID-19 patients using chest X-rays[J]. Multimedia Systems, 2022, 28(4): 1495–1513. doi: 10.1007/s00530-022-00917-7 [10] CHAKRABORTY M, DHAVALE S V, and INGOLE J. Corona-Nidaan: Lightweight deep convolutional neural network for chest X-Ray based COVID-19 infection detection[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2021, 51(5): 3026–3043. doi: 10.1007/s10489-020-01978-9 [11] DEHKORDI H A, KASHIANI H, IMANI A A H, et al. Lightweight local transformer for COVID-19 detection using chest CT scans[C]. The 2021 11th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Knowledge (ICCKE), Tehran, Iran, 2021: 328–333. [12] PARK S, KIM G, OH Y, et al. Multi-task vision Transformer using low-level chest X-ray feature corpus for COVID-19 diagnosis and severity quantification[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2022, 75: 102299. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2021.102299 [13] SOARES E, ANGELOV P, BIASO S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 CT-scan dataset: A large dataset of real patients CT scans for SARS-CoV-2 identification[EB/OL]. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.04.24.20078584, 2020. [14] ZHAO Jinyu, ZHANG Yichen, HE Xuehai, et al. COVID-CT-dataset: A CT scan dataset about COVID-19[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.13865v1, 2020. [15] ZHOU Tao, YE Xinyu, LU Huiling, et al. Dense convolutional network and its application in medical image analysis[J]. BioMed Research International, 2022, 2022: 2384830. doi: 10.1155/2022/2384830 [16] RADOSAVOVIC I, KOSARAJU R P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Designing network design spaces[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10425–10433. [17] PENG Zhiliang, HUANG Wei, GU Shanzhi, et al. Conformer: Local features coupling global representations for visual recognition[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, Canada, 2021: 357–366, [18] DING Xiaohan, ZHANG Xiangyu, ZHOU Yizhuang, et al. Scaling up your kernels to 31x31: Revisiting large kernel design in CNNs[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2203.06717, 2022. [19] RAVI V, NARASIMHAN H, CHAKRABORTY C, et al. Deep learning-based meta-classifier approach for COVID-19 classification using CT scan and chest X-ray images[J]. Multimedia Systems, 2022, 28(4): 1401–1415. doi: 10.1007/s00530-021-00826-1 [20] JAVADIMOGHADDAM S and GHOLAMALINEJAD H. A novel deep learning based method for COVID-19 detection from CT image[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021, 70: 102987. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102987 [21] ARDAKANI A A, KANAFI A R, ACHARYA U R, et al. Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID-19 in routine clinical practice using CT images: Results of 10 convolutional neural networks[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2020, 121: 103795. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103795 -






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
