A Novel Target Localization Method for Frequency Diverse Array Based on Graph Signal Processing
-
摘要: 针对现代雷达应用对目标高精度测角和测距的需求,该文将图信号处理(GSP)应用于频控阵(FDA)雷达目标定位中,提出一种基于图信号处理的频控阵雷达目标定位新方法。首先,基于频控阵雷达几何模型及回波数据间的信号关联性构建回波数据的图信号模型,进而利用图傅里叶变换对上述图信号作图谱分解,构建2维谱峰搜索优化函数,最终有效获得目标的方位角-距离联合估计。仿真实验结果表明,该算法能够正确估计出目标的方位角和距离信息;在相同仿真条件下,算法的估计精度优于同类算法且提升了对弱目标的定位性能。
-
关键词:
- 雷达目标定位 /
- 阵列信号处理 /
- 频控阵 /
- 图傅里叶变换 /
- 方位角-距离联合估计
Abstract: In most target localization applications, achieving high spatial resolution on angle and range is requested. Addressing this demand, a novel Graph Signal Processing (GSP) based target localization method for monostatic Frequency Diverse Array (FDA) is proposed in this paper. Firstly, a directed graph model applicable to the FDA is established based on the array geometry and the signal correlations among array elements, in which echoes received in the array are mapped to a graph signal. By leveraging the concept of the graph Fourier transform, the obtained graph signal is decomposed into a set of spectrums, and then the joint angle and range estimation can be solved successfully using a well-designed two-dimensional spectral peak search. The simulation results illustrate the validity and effectiveness of the proposed method, and it is shown that the proposed method outperforms the existing methods in estimation accuracy and is capable to achieve performance improvement for the weak target in a low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) environment. -
表 1 实验仿真参数列表
载频 频率增量 最大无模糊探测距离 阵元数 阵元间距 快拍数 目标位置 扫描精度 信噪比 参数值 5 GHz 10 kHz 15 km 11 0.015 m 128 (45°, 10 km) 角度维0.1°距离维0.5 m 10 dB 表 2 各算法仿真平均耗时比较(s)
2维MUSIC DPGSP RFGSP 仿真平均耗时 2.1902 8.1986 3.6768 -
[1] 丁鹭飞, 耿富录, 陈建春. 雷达原理[M]. 4版. 北京: 电子工业出版, 2009: 8–13.DING Lufei, GENG Fulu, and CHEN Jianchun. Principle of Radar[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2009: 8–13. [2] VAN TREES H L. Optimum Array Processing: Part IV of Detection, Estimation and Modulation Theory[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2002: 204–207. [3] ANTONIK P, WICKS M C, GRIFFITHS H D, et al. Frequency diverse array radars[C]. 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, USA, 2006: 215–217. [4] 王文钦, 邵怀宗, 陈慧. 频控阵雷达: 概念、原理与应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(4): 1000–1011. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151235WANG Wenqin, SHAO Huaizong, and CHEN Hui. Frequency diverse array radar: Concept, principle and application[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(4): 1000–1011. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151235 [5] WANG Wenqin, SO H C, and SHAO Huaizong. Nonuniform frequency diverse array for range-angle imaging of targets[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2014, 14(8): 2469–2476. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2014.2304720 [6] LIU Yimin, RUAN Hang, WANG Lei, et al. The random frequency diverse array: A new antenna structure for uncoupled direction-range indication in active sensing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2017, 11(2): 295–308. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2016.2627183 [7] WANG Wenqin and SHAO Huaizong. Range-angle localization of targets by a double-pulse frequency diverse array radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2014, 8(1): 106–114. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2013.2285528 [8] ORTEGA A, FROSSARD P, KOVAČEVIĆ J, et al. Graph signal processing: Overview, challenges, and applications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2018, 106(5): 808–828. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2018.2820126 [9] SANDRYHAILA A and MOURA J M F. Discrete signal processing on graphs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(7): 1644–1656. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2238935 [10] MOREIRA L A S, RAMOS A L L, DE CAMPOS M L R, et al. A graph signal processing approach to direction of arrival estimation[C]. 2019 27th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), A Coruna, Spain, 2019: 1–5. [11] PROUDLER I K, STANKOVIC V, and WEISS S. Narrowband angle of arrival estimation exploiting graph topology and graph signals[C]. 2020 Sensor Signal Processing for Defence Conference (SSPD), Edinburgh, UK, 2020: 1–5. [12] ALCANTARA E, ATLAS L, and ABADI S. Direction-of-arrival estimation using signal processing on graphs[C]. 2021 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop (SSP), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2021: 1–5. [13] XIAO Peng and YANG Jianmin. A graph-based narrowband matched-field source localization method[J]. JASA Express Letters, 2021, 1(12): 124803. doi: 10.1121/10.0009060 [14] WANG Junxiong and PAN Xiang. The signal feature extraction of graph Fourier transform on the constructed graph[C]. 2021 6th International Conference on Communication, Image and Signal Processing (CCISP), Chengdu, China, 2021: 379–383. [15] LIAO Kefei, YU Zerui, XIE Ningbo, et al. Joint estimation of azimuth and distance for far-field multi targets based on graph signal processing[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(5): 1110. doi: 10.3390/rs14051110 [16] JONES A M and RIGLING B D. Planar frequency diverse array receiver architecture[C]. 2012 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, USA, 2012: 145–150. [17] KRIM H and VIBERG M. Two decades of array signal processing research: The parametric approach[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 1996, 13(4): 67–94. doi: 10.1109/79.526899 [18] CUI Can, XU Jian, GUI Ronghua, et al. Search-free DOD, DOA and range estimation for bistatic FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 15431–15445. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2816780 -





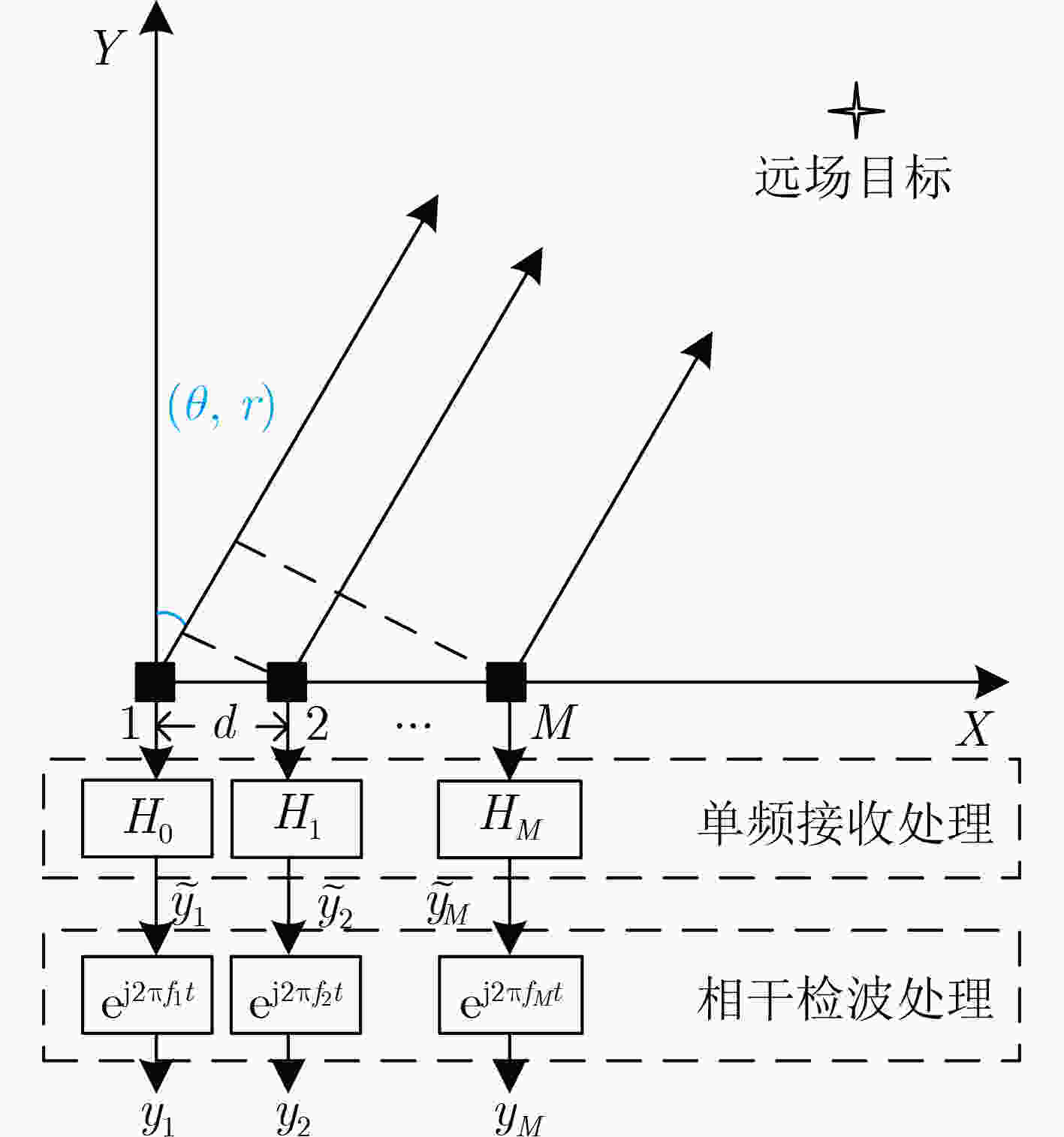
 下载:
下载:
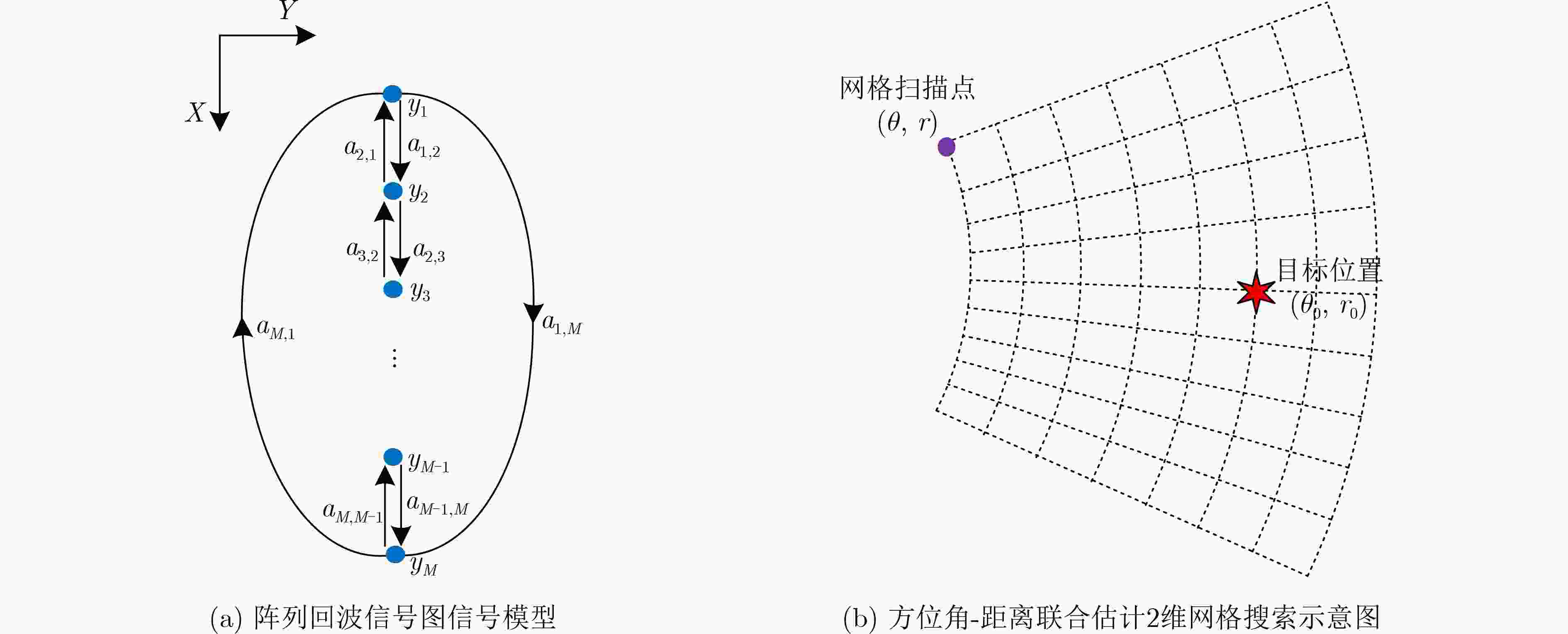
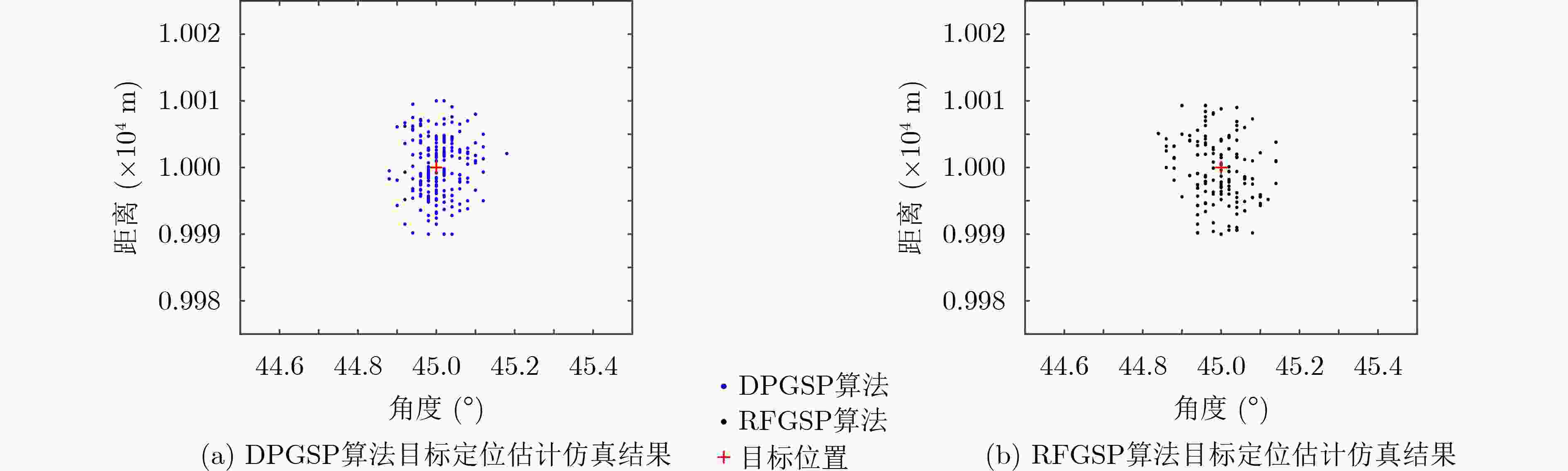
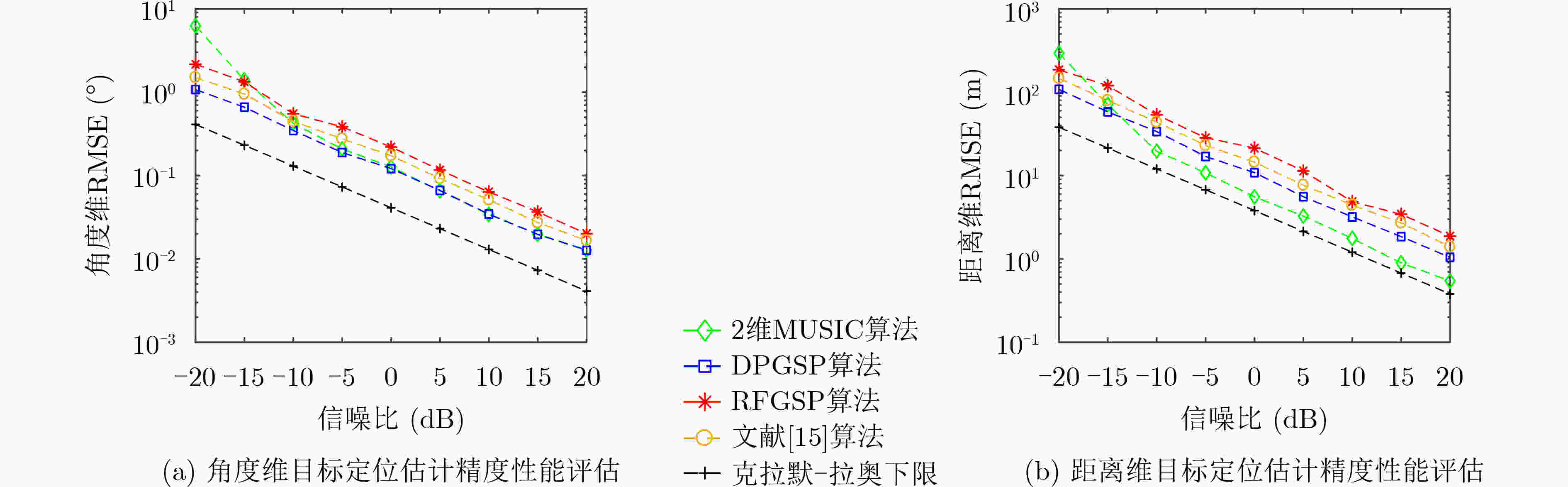


 下载:
下载:
