Passive WiFi Internet of Things Backscatter Communication Based on Electromagnetic Energy Harvesting
-
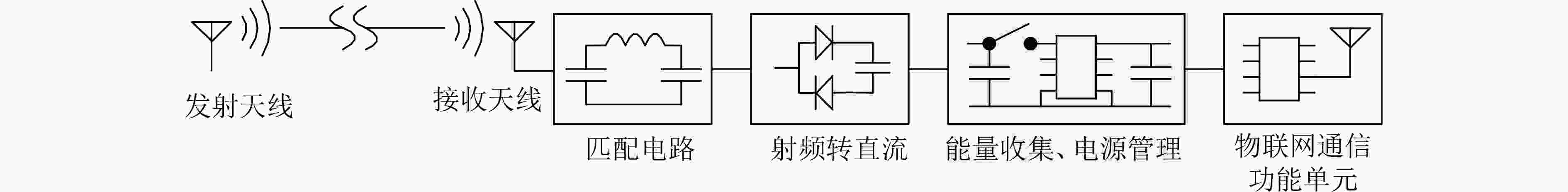
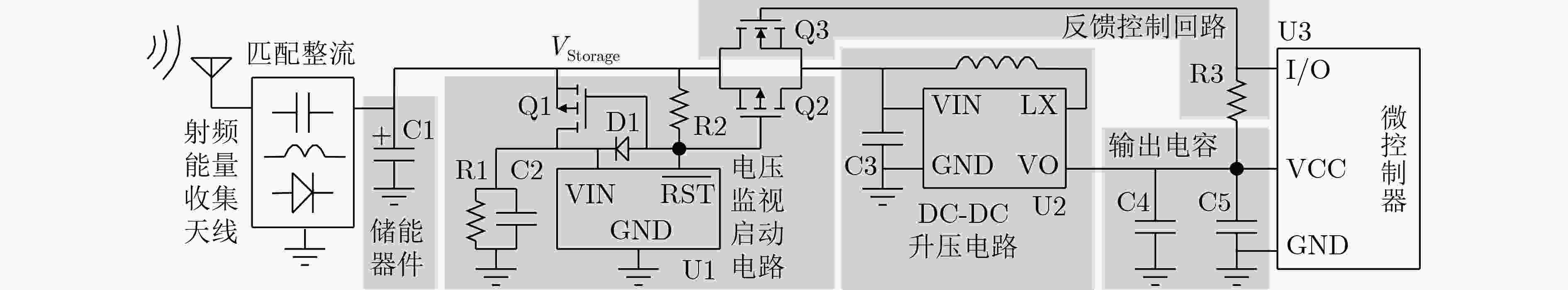
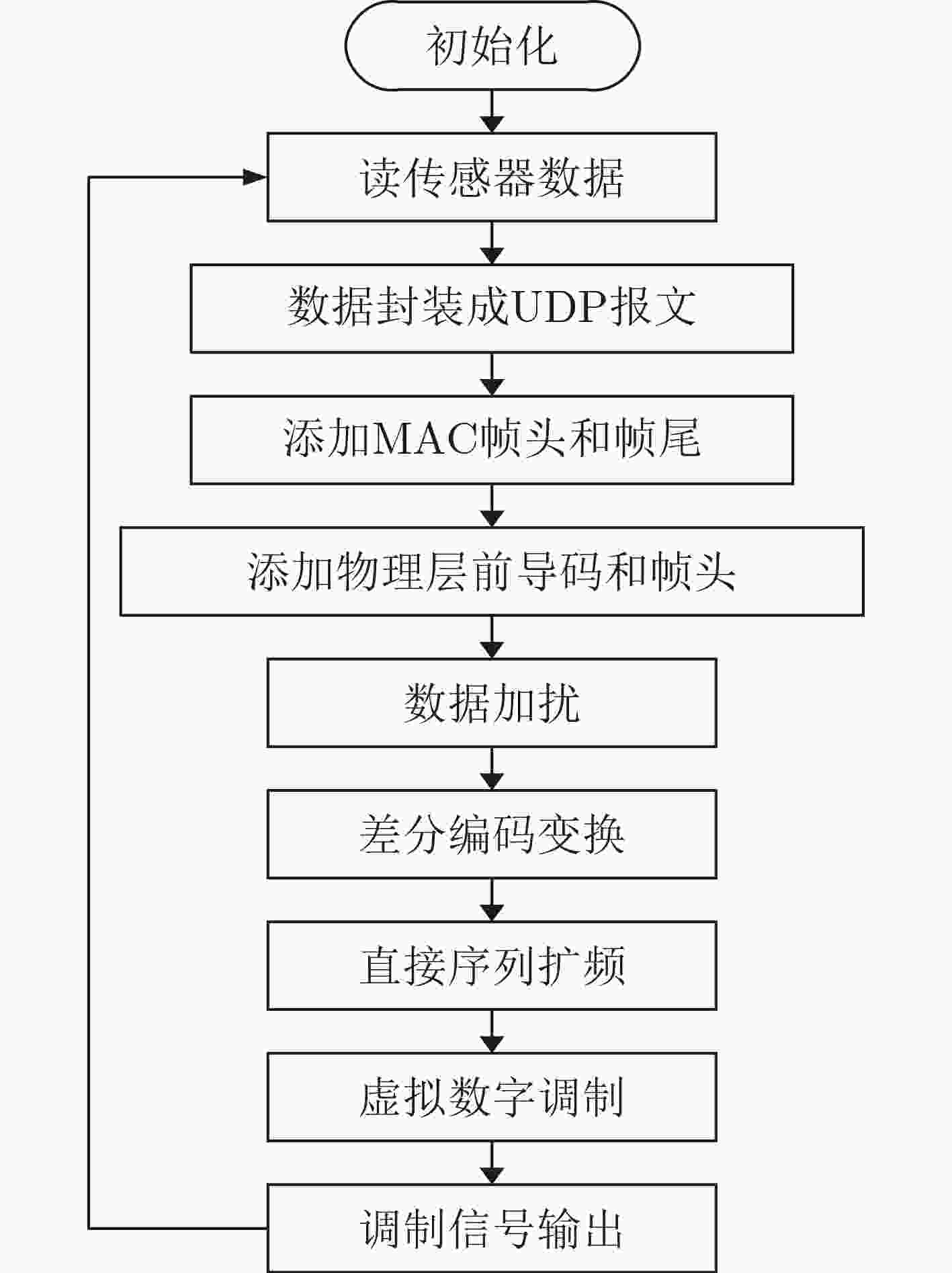
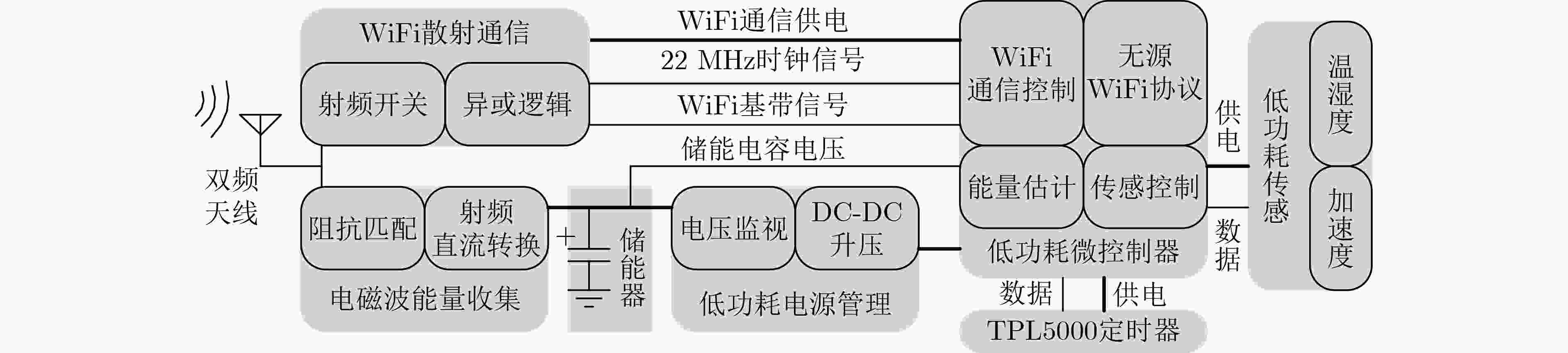
摘要: 为解决传统的物联网(IoT)通信设备功耗大、需要人工定期维护、频繁更换电池等问题,该文提出一种基于电磁波能量收集的无源WiFi物联网散射通信方法。该方法基于低功耗微处理器实现WiFi反向散射通信,同时利用自身收集的电磁波能量实现系统自供电,具有功耗低、无需电池、体积小、成本低、免人工维护、容易大量部署等诸多优势,可广泛用于物联网领域。Abstract: To solve the problems of high power consumption, requiring manual maintenance and frequent battery replacement of traditional Internet of Things (IoT) communication device, a passive WiFi IoT backscattering communication method based on electromagnetic wave energy harvesting is proposed. The device is implemented based on a low-power microprocessor platform. It can use the electromagnetic wave energy collected by itself to achieve ultra-low-power WiFi scattering communication, having advantages of low power consumption, no batteries, small size, low production cost, and no manual maintenance. It can be widely used in IoT applications.
-
表 1 散射通信技术性能对比
散射通信技术 样机供电 样机处理器 通信功耗 通信速率 通信距离(m) 2016 Passive WiFi [10] 市电 ASIC/FPGA 15~59 μW(仿真) 1~11 Mbit/s 9~30 2017 BLE Backscatter[15] 纽扣电池 MCU 623 μA(样机) 1 Mbit/s 13~30 2020 PV-RFID[21] 无源 EM4325 10~45 μW(样机) 64~320 kbit/s 4 2021 RBLE[16] 市电 ASIC/FPGA 37 μW(仿真) 17.4 kbit/s 56 2022 TD FM[22] 纽扣电池 MCU 150 μW(样机) 1 kbit/s 20 本文 无源 MCU 700 μA(样机) 1 Mbit/s 15 -
[1] SHAFIQUE K, KHAWAJA B A, SABIR F, et al. Internet of things (IoT) for next-generation smart systems: A review of current challenges, future trends and prospects for emerging 5G-IoT scenarios[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 23022–23040. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2970118 [2] 郭海潮, 张献, 杨庆新, 等. 空间全向无线电能传输技术研究与应用综述[J/OL]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(2): 1–18. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2107.TM.20220124.1515.004.html, 2022.GUO Haichao, ZHANG Xian, YANG Qingxin, et al. Review of research and application of spatial omnidirectional wireless power transmission technology[J/OL]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(2): 1–18. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2107.TM.20220124.1515.004.html, 2022. [3] 李阳, 石少博, 刘雪莉, 等. 磁场耦合式无线电能传输耦合机构综述[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(S2): 389–403. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.L90276LI Yang, SHI Shaobo, LIU Xueli, et al. Overview of magnetic coupling mechanism for wireless power transfer[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Societ, 2021, 36(S2): 389–403. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.L90276 [4] LITVIŅENKO A, ĀBOLTIŅŠ A, TJUKOVS S, et al. The impact of waveform on the efficiency of RF to DC conversion using prefabricated energy harvesting device[C]. 2017 Advances in Wireless and Optical Communications (RTUWO), Riga, Latvia, 2017: 61–66. [5] BITO J, BAHR R, HESTER J G, et al. A novel solar and electromagnetic energy harvesting system with a 3-D printed package for energy efficient internet-of-things wireless sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2017, 65(5): 1831–1842. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2017.2660487 [6] LIU Ye, LI Dong, DU Bangsong, et al. Rethinking sustainable sensing in agricultural internet of things: From power supply perspective[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2022, 29(4): 102–109. [7] FRITH J. A Billion Little Pieces: RFID and Infrastructures of Identification[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2019: 93–142. [8] 苏健, 杨晓娇, 韩雨. 一种时间高效的易于实现的多标签射频识别技术[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(4): 903–910. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.04.019SU Jian, YANG Xiaojiao, and HAN Yu. A time-efficient and easy-to-implement RFID technology for multiple tags[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(4): 903–910. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.04.019 [9] WANT R. An introduction to RFID technology[J]. IEEE Pervasive Computing, 2006, 5(1): 25–33. doi: 10.1109/MPRV.2006.2 [10] KELLOGG B, TALLA V, SMITH J R, et al. Passive Wi-Fi: Bringing low power to Wi-Fi transmissions[J]. GetMobile:Mobile Computing and Communications, 2016, 20(3): 38–41. doi: 10.1145/3036699.3036711 [11] 唐晓庆, 谢桂辉, 佘亚军, 等. 基于MCU的无源Wi-Fi散射通信方法[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(10): 2069–2075. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.10.007TANG Xiaoqing, XIE Guihui, SHE Yajun, et al. Passive Wi-Fi scattering communication method based on MCU[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(10): 2069–2075. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.10.007 [12] MIT Technology Review. 10 breakthrough technologies 2016[EB/OL]. https://www.technologyreview.com/lists/technologies/2016/, 2022. [13] TALLA V, HESSAR M, KELLOGG B, et al. LoRa backscatter: Enabling the vision of ubiquitous connectivity[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2017, 1(3): 105. doi: 10.1145/3130970 [14] TALLA V, KELLOGG B, GOLLAKOTA S, et al. Battery-free cellphone[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2017, 1(2): 25. doi: 10.1145/3090090 [15] ENSWORTH J F and REYNOLDS M S. BLE-backscatter: Ultralow-power IoT nodes compatible with Bluetooth 4.0 low energy (BLE) smartphones and tablets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2017, 65(9): 3360–3368. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2017.2687866 [16] CHEN Si, ZHANG Maolin, ZHAO Jia, et al. Reliable and practical Bluetooth backscatter with commodity devices[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2021, 29(4): 1717–1729. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2021.3068865 [17] IYER V, TALLA V, KELLOGG B, et al. Inter-technology backscatter: Towards internet connectivity for implanted devices[C]. The 2016 ACM SIGCOMM Conference, Florianopolis, Brazil, 2016: 356–369. [18] LI Dong. Hybrid active and passive antenna selection for backscatter-assisted MISO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(11): 7258–7269. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3014917 [19] IEEE. IEEE 802.11–2007 IEEE standard for information technology - telecommunications and information exchange between systems - local and metropolitan area networks - specific requirements - Part 11: Wireless LAN medium access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) specifications[S]. New York: IEEE, 2012. [20] ZHANG Pengyu, BHARADIA D, JOSHI K, et al. HitchHike: Practical backscatter using commodity WiFi[C]. The 14th ACM Conference on Embedded Network Sensor Systems CD-ROM, Stanford, USA, 2016: 259–271. [21] KANTAREDDY S N R, MATHEWS I, SUN Shijing, et al. Perovskite PV-powered RFID: Enabling low-cost self-powered IoT sensors[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(1): 471–478. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2939293 [22] HU Jia, ZHONG Linling, MA Tao, et al. Long-range FM backscatter tag with tunnel diode[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2022, 32(1): 92–95. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2021.3117033 -





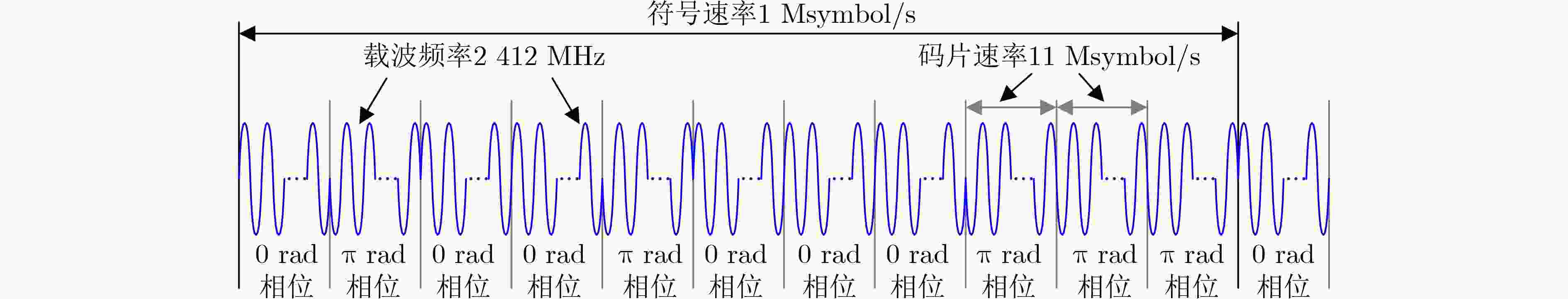
 下载:
下载:
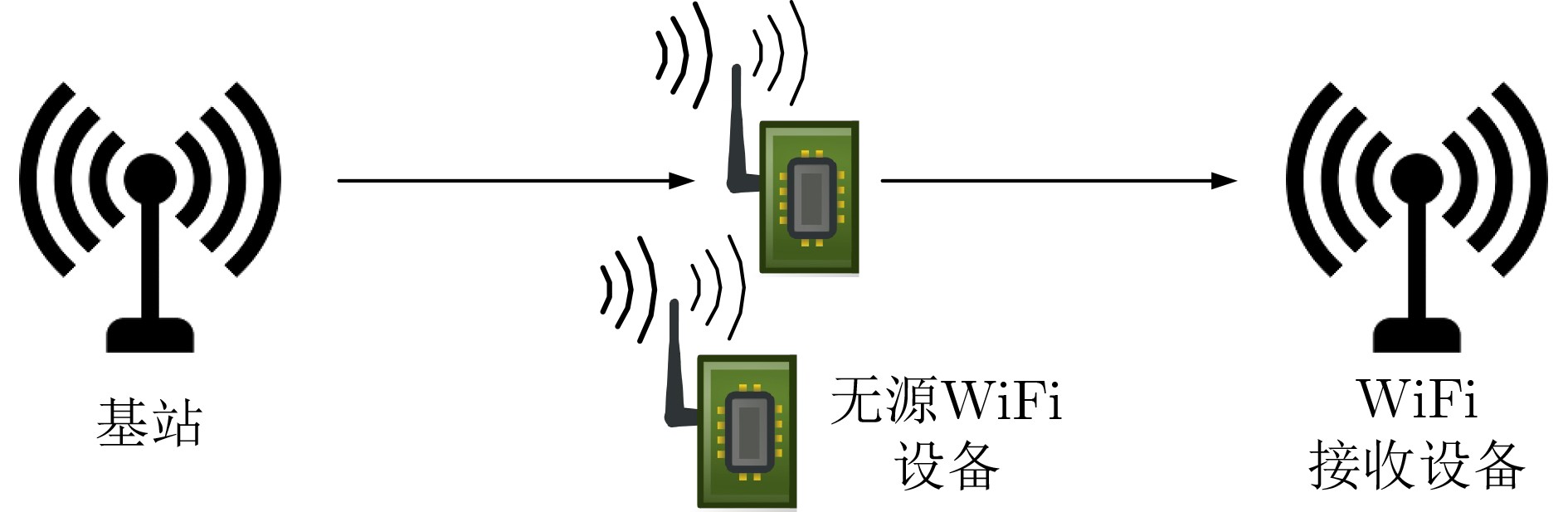
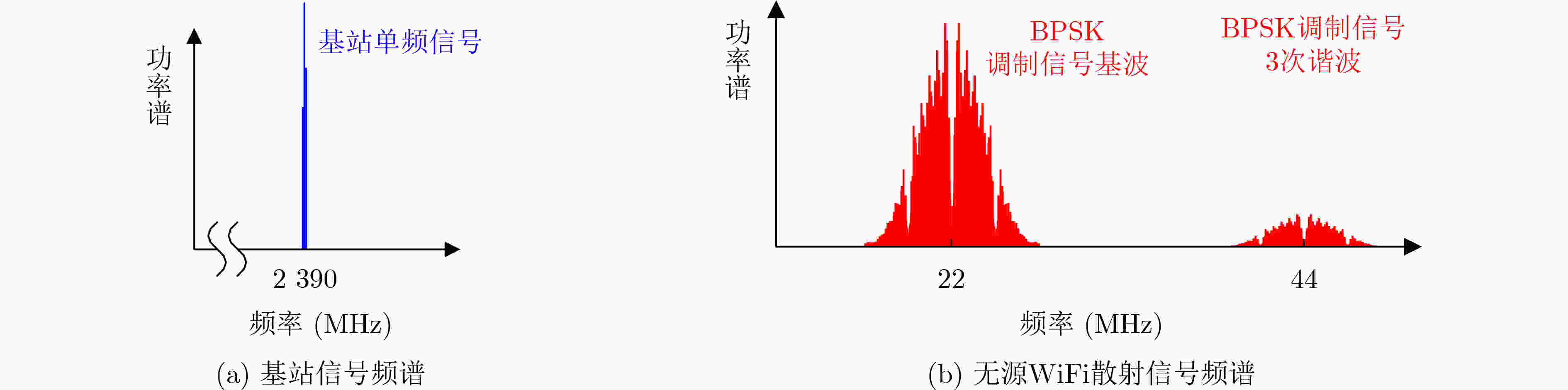
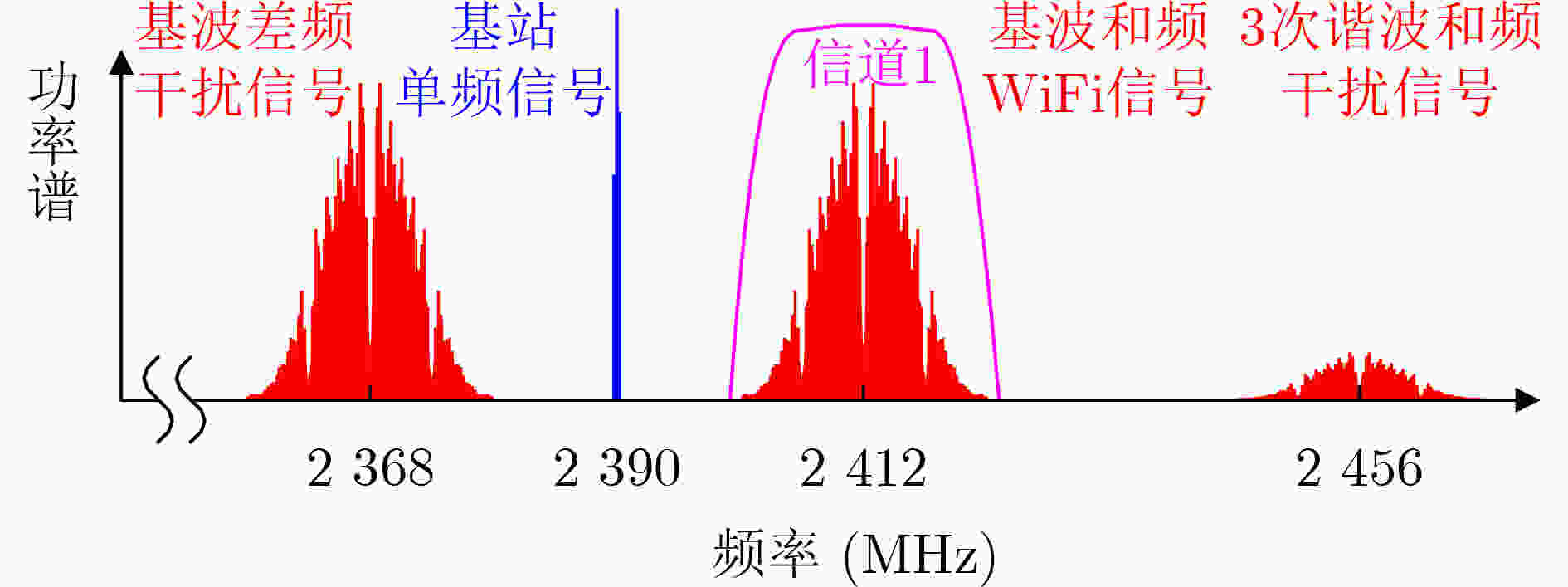

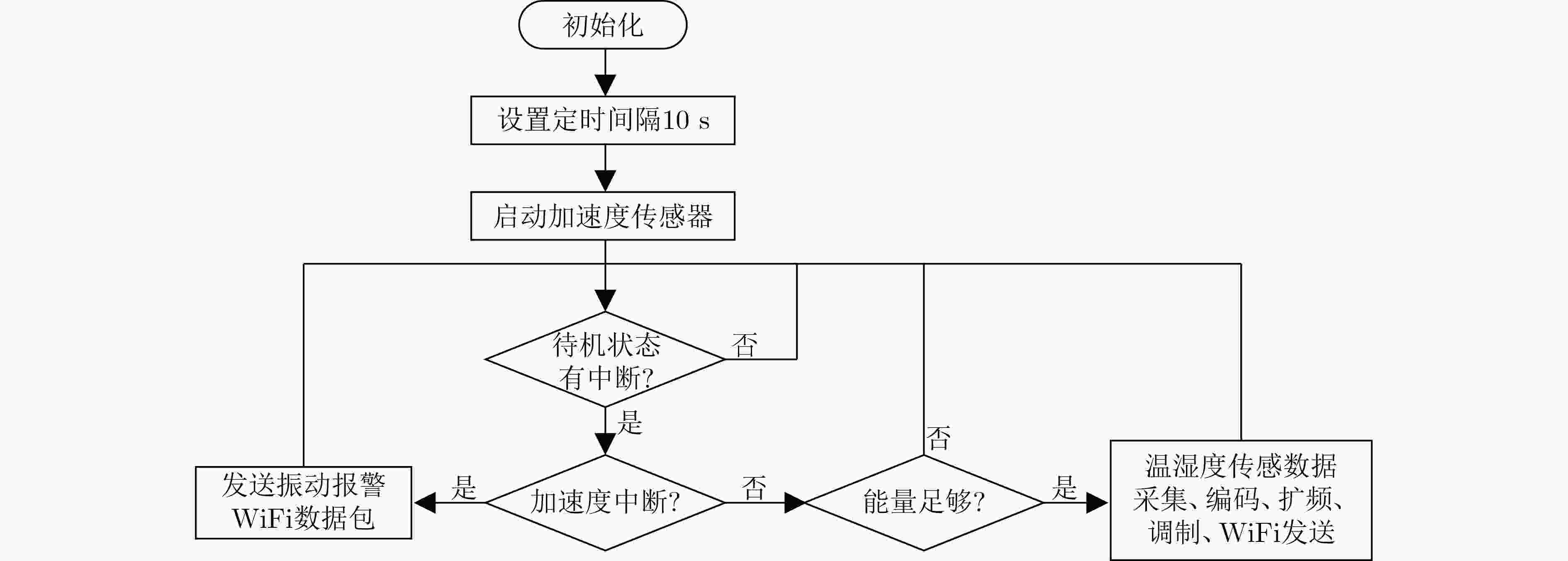
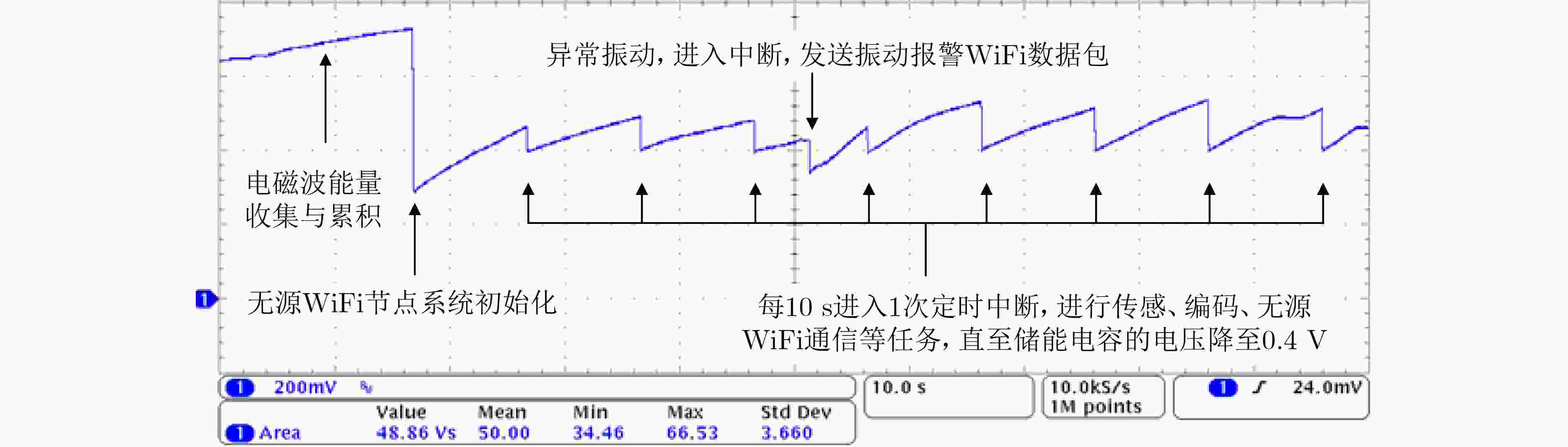
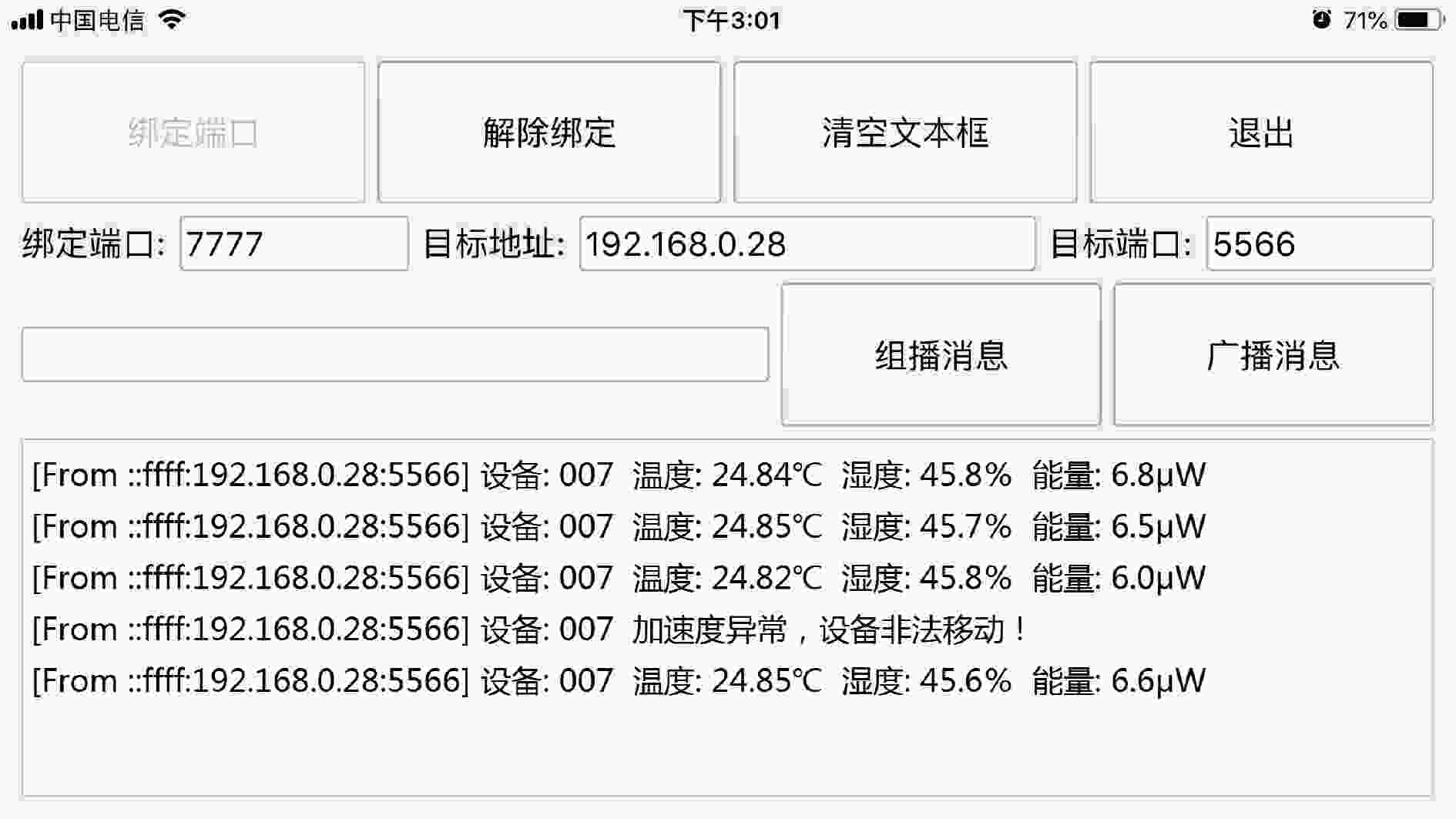
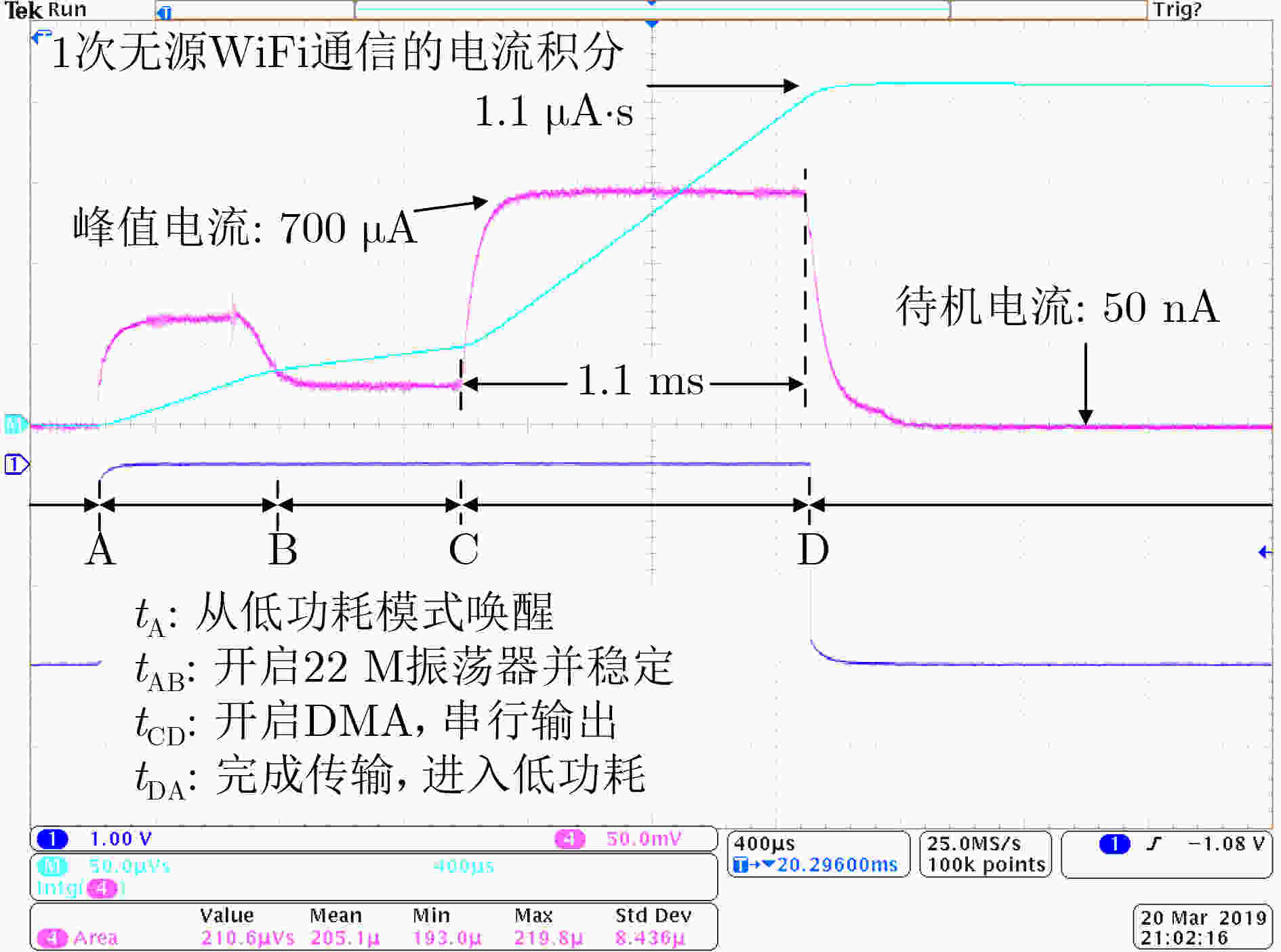
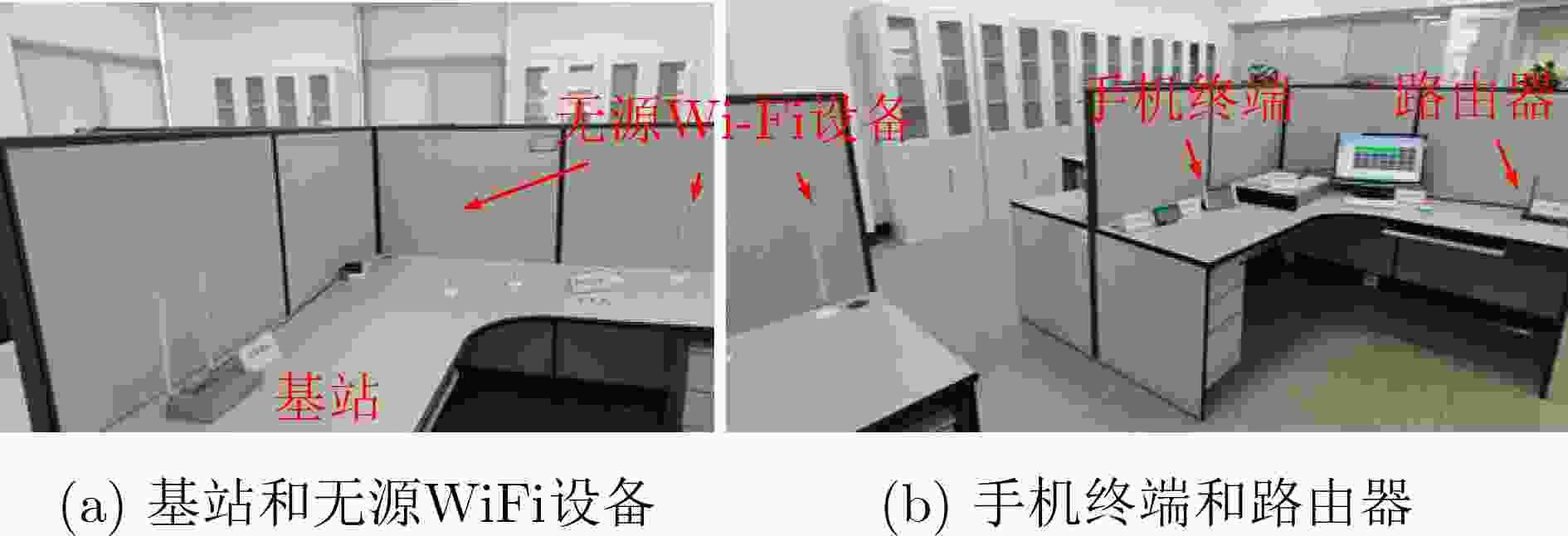
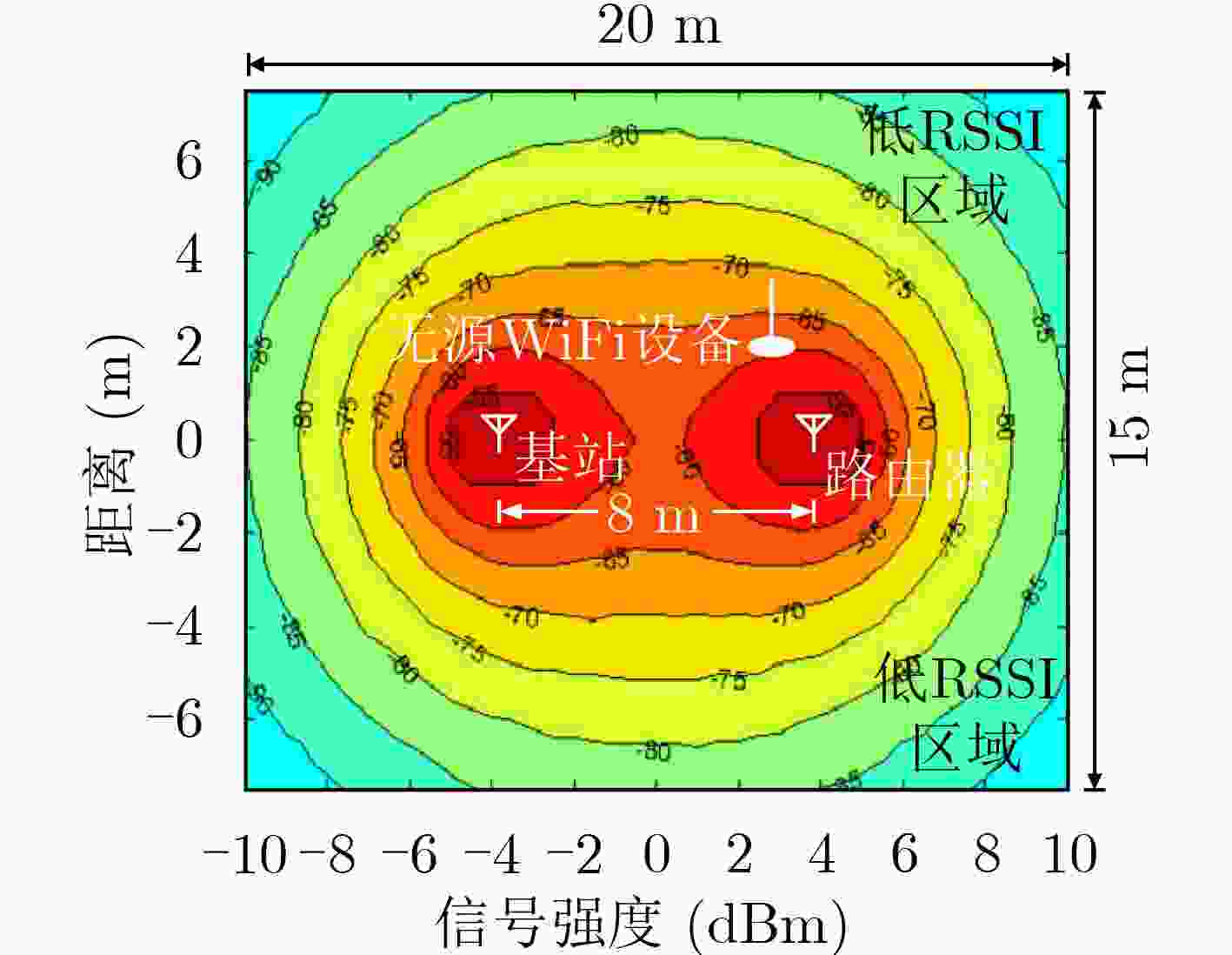


 下载:
下载:
