Spoofing Attack Detection Scheme Based on Channel Fingerprint for Millimeter Wave MIMO System
-
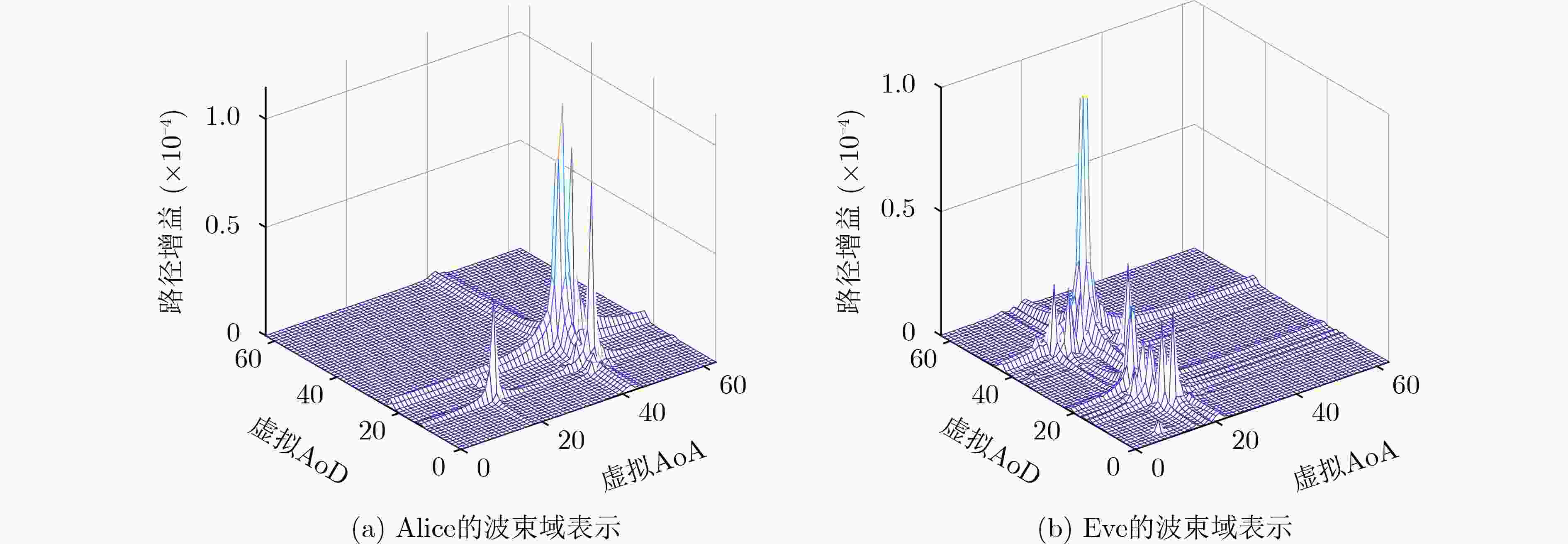
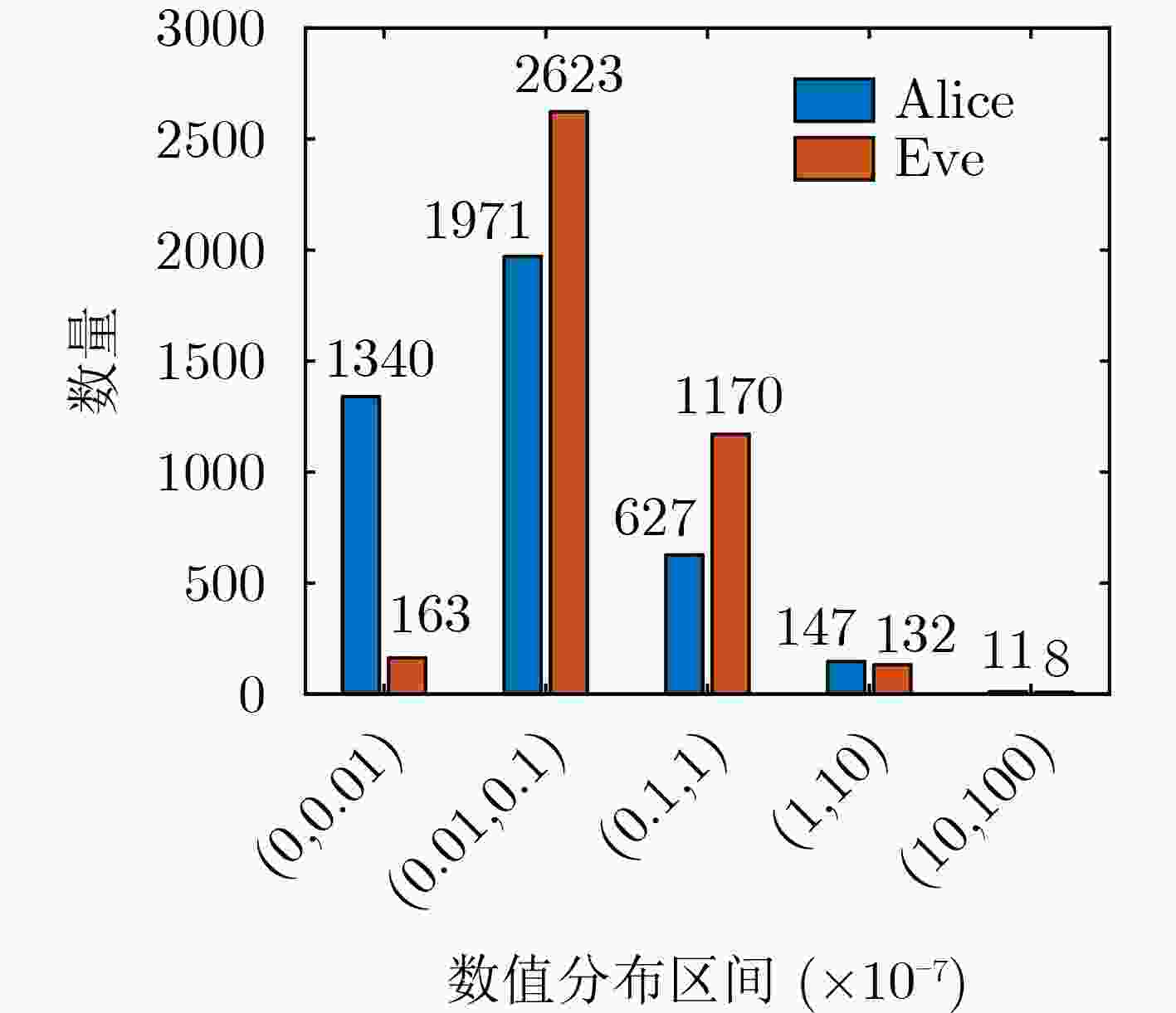
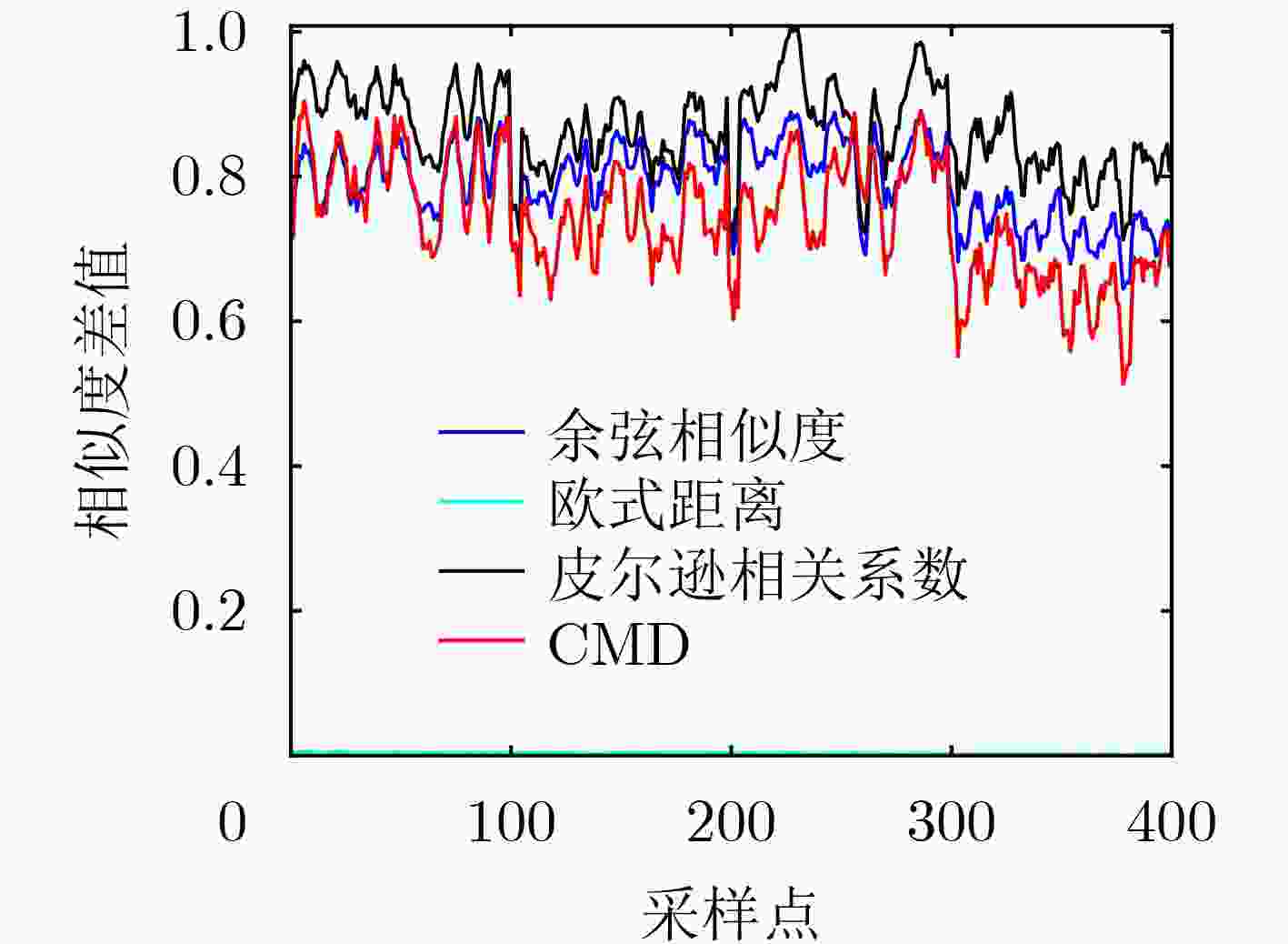
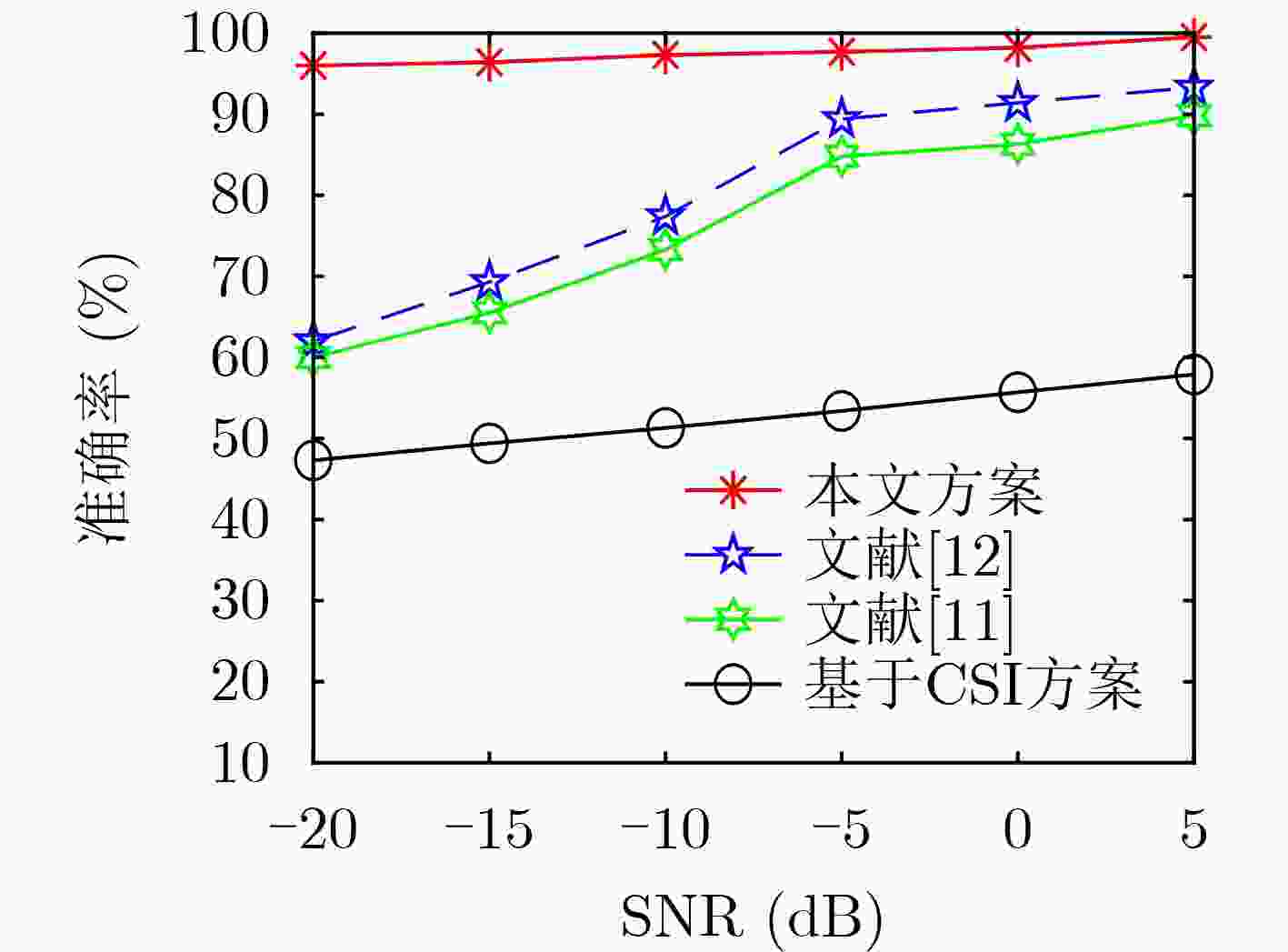
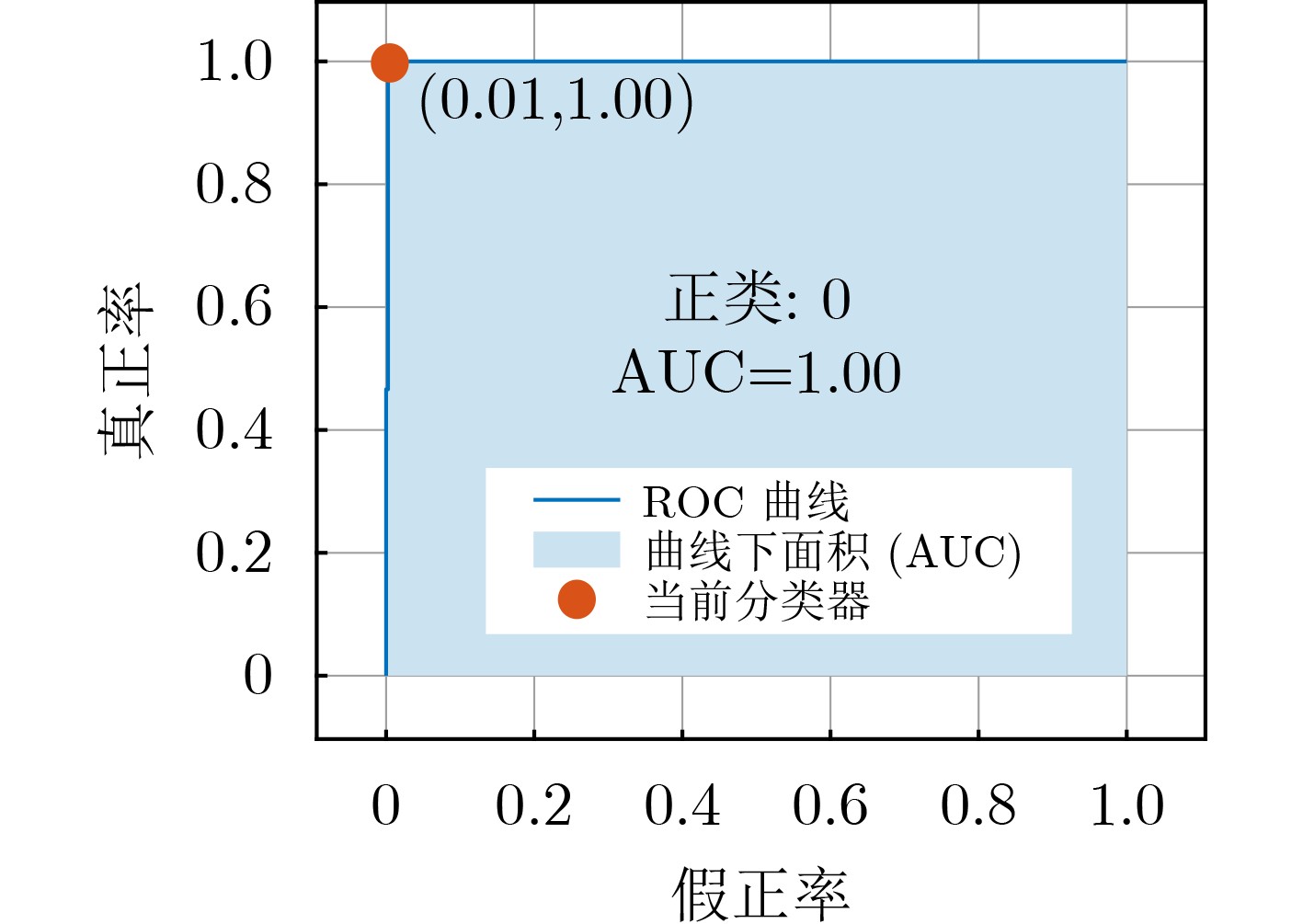
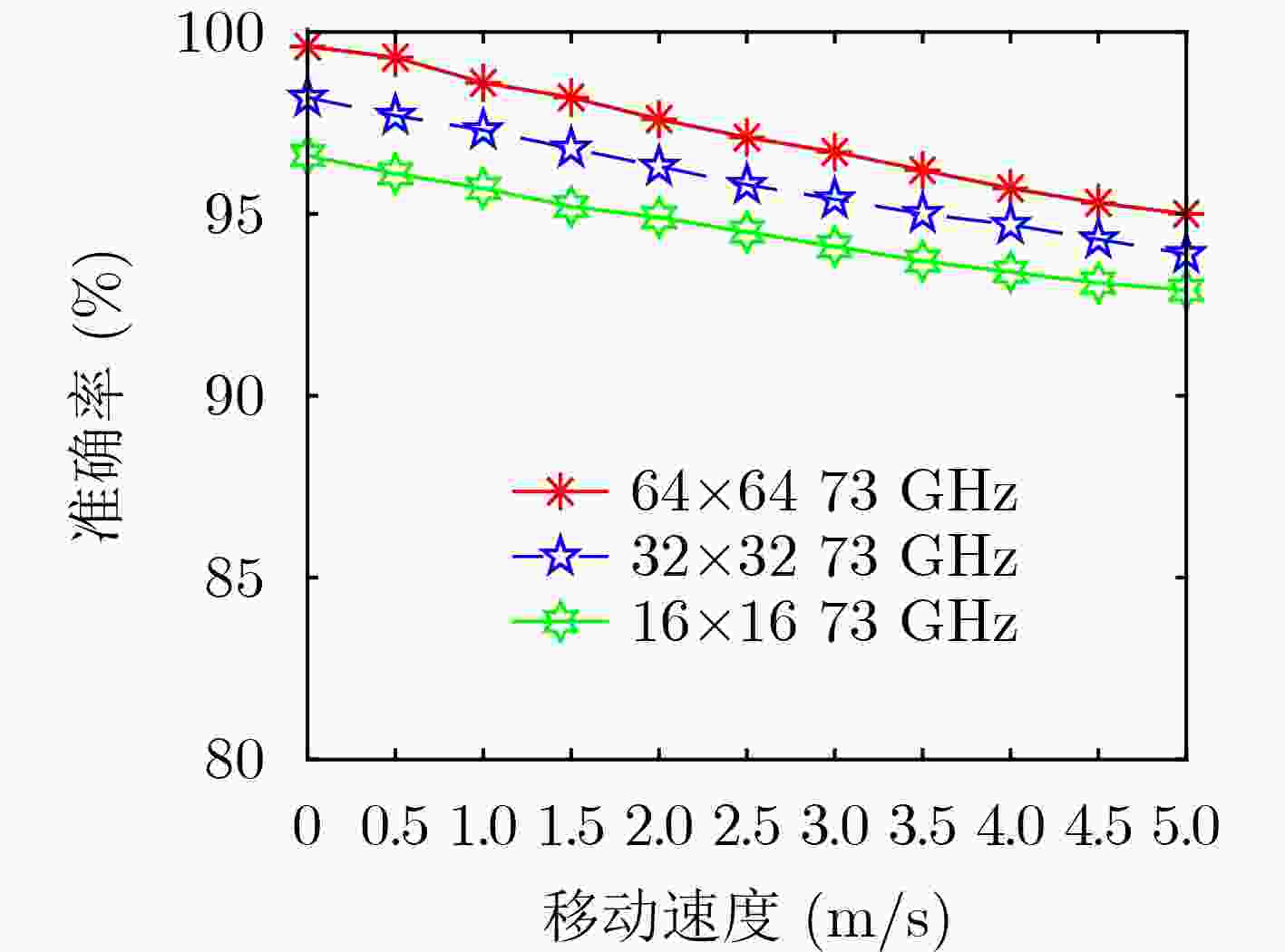
摘要: 针对毫米波多输入输出系统(MIMO)中的身份欺骗攻击问题,该文提出一种基于信道指纹的攻击检测方案。在波束域中,毫米波信道图样呈现波束的稀疏性和高方向特性,且这种波束域特性与终端位置有极高的相关性。该文将该波束域信道图样作为一种信道指纹,提出了一种基于信道指纹的身份欺骗攻击检测方案,将欺骗攻击中的终端身份认证问题建模成对其信道指纹的二分类问题,并使用基于监督学习的支持向量机算法求解该分类问题。为获得好的分类效果,基于对信道指纹的数值分析,比较了皮尔逊相关系数、余弦相似度、相关矩阵距离、欧氏距离等相似度指标。根据比较结果,选择最优的指标作为分类特征训练分类模型。仿真结果表明,即使在低信噪比条件下,该方案仍具有高认证准确性和鲁棒性。与现有相关机制相比,攻击检测精度显著提高。Abstract: Millimeter wave Multiple Input and Multiple Output (MIMO) channel exhibits beam sparsity and high directivity in the beam domain, and the beam domain channel pattern is highly correlated with the terminal position. In this paper, the beam domain channel pattern is regarded as a channel fingerprint. A channel fingerprint-based identity spoofing attacks detection scheme is proposed for millimeter-wave MIMO systems. The identity authentication problem is modeled as a binary classification problem of the corresponding channel fingerprint. Then, the supervised learning Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithm is employed to solve the classification problem. In order to achieve good classification effect, different similarity indexes on channel fingerprint are compared based on the numerical analysis of the beam domain, and the one with the best classification effect is selected as the final classification feature to train the classifier model. The simulation results show that the proposed scheme has good authentication performance even under low signal-to-noise ratio conditions. Compared with the existing relative schemes, the detection accuracy is significantly improved.
-
表 1 信号仿真参数设置
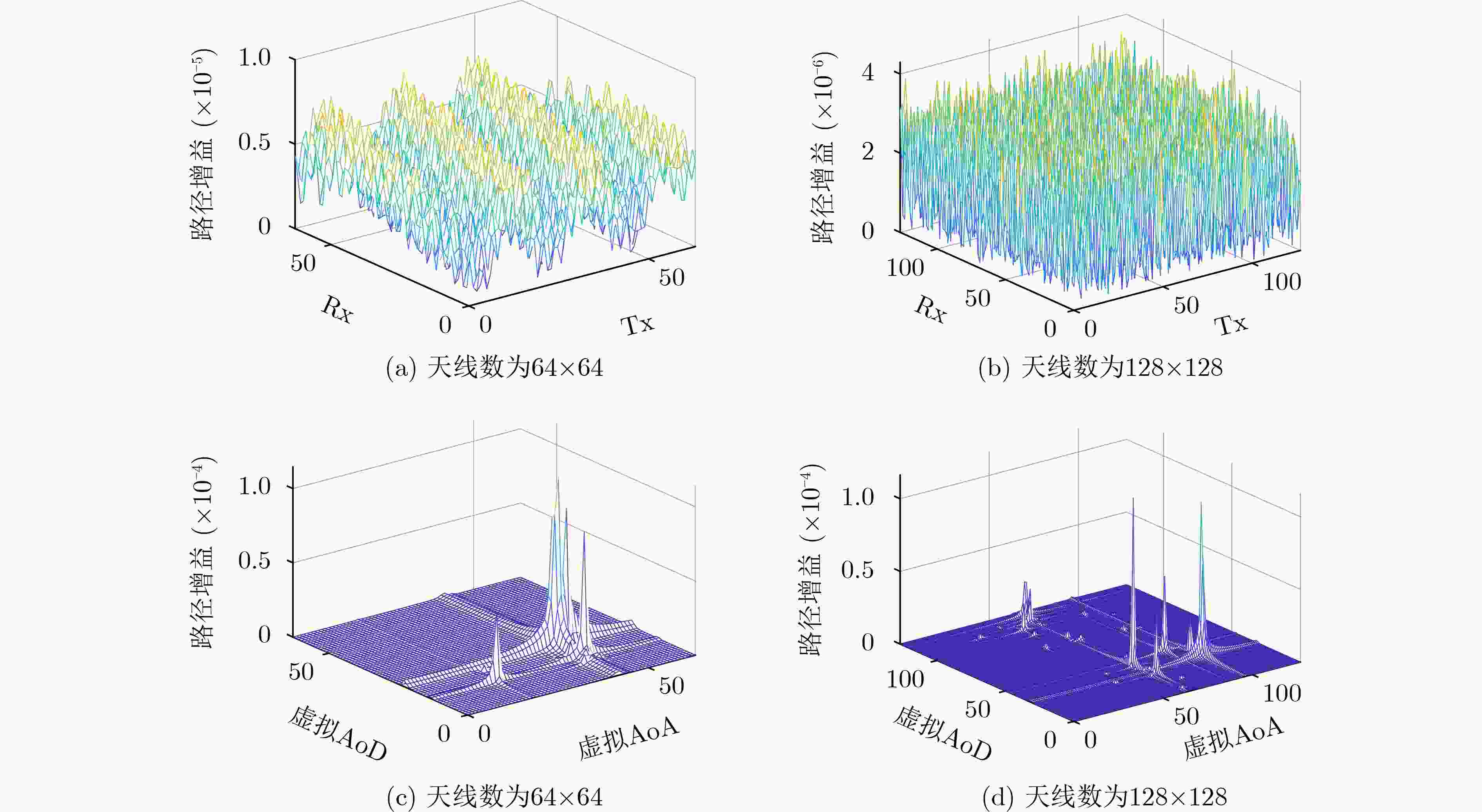
信号参数 频率 带宽 天线类型 天线数目 数值 73 GHz 800 MHz ULA 64×64 表 2 用户仿真参数设置
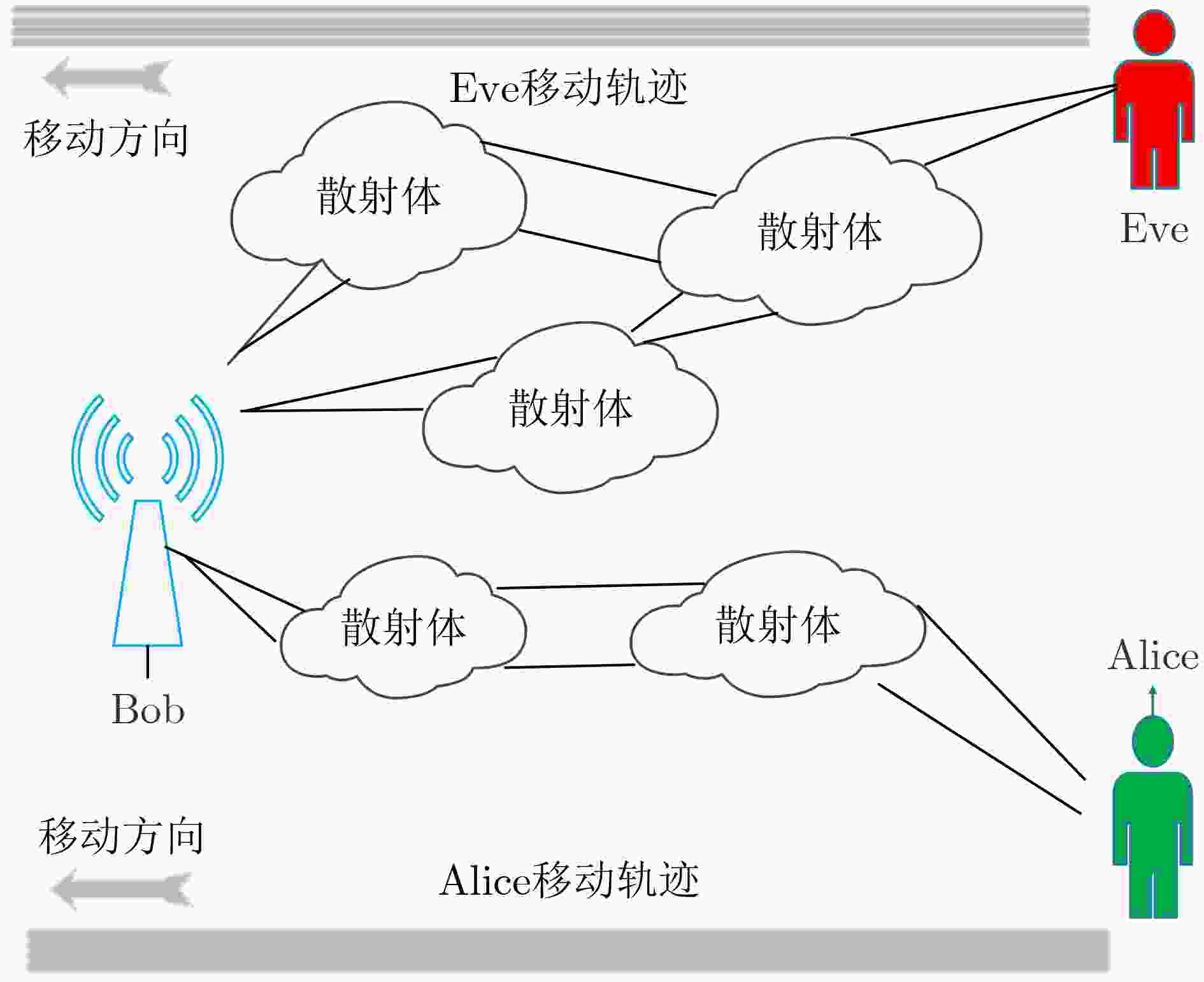
用户参数 移动距离 速度 轨迹 采样间隔 数值 40 m 1 m/s 图1 0.1 次/s -
[1] SEKER C, GÜNESER M T, and OZTURK T. A review of millimeter wave communication for 5G[C]. The 2nd International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT), Ankara, Turkey, 2018: 1–5. [2] HEATH R W, GONZÁLEZ-PRELCIC N, RANGAN S, et al. An overview of signal processing techniques for millimeter wave MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2016, 10(3): 436–453. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2016.2523924 [3] WANG Ning, LI Weiwei, WANG Pu, et al. Physical layer authentication for 5G communications: Opportunities and road ahead[J]. IEEE Network, 2020, 34(6): 198–204. doi: 10.1109/MNET.011.2000122 [4] YILMAZ M H and ARSLAN H. A survey: Spoofing attacks in physical layer security[C]. The IEEE 40th Local Computer Networks Conference Workshops (LCN Workshops), Clearwater Beach, USA, 2015: 812–817. [5] MENEZES A J, VAN OORSCHOT P C, and VANSTONE S A. Handbook of Applied Cryptography[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1996. [6] PAN Fei, WEN Hong, LIAO Runfa, et al. Physical layer authentication based on channel information and machine learning[C]. The 2017 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS), Las Vegas, USA, 2017: 364–365. [7] AHMADPOUR D and KABIRI P. Detecting forged management frames with spoofed addresses in IEEE 802.11 networks using received signal strength indicator[J]. Iran Journal of Computer Science, 2020, 3(3): 137–143. doi: 10.1007/s42044-020-00053-3 [8] GALTIER F, CAYRE R, AURIOL G, et al. A PSD-based fingerprinting approach to detect IoT device spoofing[C]. The IEEE 25th Pacific Rim International Symposium on Dependable Computing (PRDC), Perth, Australia, 2020: 40–49. [9] ALAM J and KENNY P. Spoofing detection employing infinite impulse response—constant Q transform-based feature representations[C]. The 25th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Kos, Greece, 2017: 101–105. [10] SAYEED A M. Deconstructing multiantenna fading channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(10): 2563–2579. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2002.803324 [11] TANG Jie, XU Aidong, JIANG Yixin, et al. MmWave MIMO physical layer authentication by using channel sparsity[C]. The 2020 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Information Systems (ICAIIS), Dalian, China, 2020: 221–224. [12] LI Weiwei, WANG Ning, JIAO Long, et al. Physical layer spoofing attack detection in MmWave massive MIMO 5G networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 60419–60432. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3073115 [13] WANG Ning, JIAO Long, WANG Pu, et al. Exploiting beam features for spoofing attack detection in mmWave 60-GHz IEEE 802.11ad networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(5): 3321–3335. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3049160 [14] BALAKRISHNAN S, GUPTA S, BHUYAN A, et al. Physical layer identification based on spatial–temporal beam features for millimeter-wave wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 1831–1845. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2019.2948283 [15] HEMADEH I A, SATYANARAYANA K, EL-HAJJAR M, et al. Millimeter-wave communications: Physical channel models, design considerations, antenna constructions, and link-budget[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(2): 870–913. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2783541 [16] JU Shihao and RAPPAPORT T S. Millimeter-wave extended NYUSIM channel model for spatial consistency[C]. The 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2018: 1–6. [17] LIM Y G, CHO Y J, SIM M S, et al. Map-based millimeter-wave channel models: An overview, guidelines, and data[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1711.09052, 2017. [18] GOWER J C and LEGENDRE P. Metric and Euclidean properties of dissimilarity coefficients[J]. Journal of Classification, 1986, 3(1): 5–48. doi: 10.1007/BF01896809 [19] 卜凡鹏, 陈俊艺, 张琪祁, 等. 一种基于双层迭代聚类分析的负荷模式可控精细化识别方法[J]. 电网技术, 2018, 42(3): 903–910. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2017.1397BU Fanpeng, CHEN Junyi, ZHANG Qiqi, et al. A controllable refined recognition method of electrical load pattern based on bilayer iterative clustering analysis[J]. Power System Technology, 2018, 42(3): 903–910. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2017.1397 [20] YOU Yang, DEMMEL J, CZECHOWSKI K, et al. CA-SVM: Communication-avoiding support vector machines on distributed systems[C]. The 2015 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium, Hyderabad, India, 2015: 847–859. [21] SINHASHTHITA W and JEARANAITANAKIJ K. Improving KNN algorithm based on weighted attributes by Pearson correlation coefficient and PSO fine tuning[C]. The 5th International Conference on Information Technology (InCIT), Chonburi, Thailand, 2020: 27–32. [22] XIAO L, GREENSTEIN L, MANDAYAM N, et al. Fingerprints in the ether: Using the physical layer for wireless authentication[C]. The 2007 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Glasgow, UK, 2007: 4646–4651. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
