A Routing Algorithm on Low Earth Orbit Mega-constellation Network with Iincremental Deployment of Terahertz Links
-
摘要: 太赫兹通信作为6G研究的关键技术之一,将在下一代巨型近地轨道(LEO)星座网络中与其他频段链路共存,在这样增量部署太赫兹的巨型LEO星座网络中,星间链路扭曲窗口期的路径次优问题将变得更加明显,现有的路由算法仅依赖于最短时延路径难以解决这个问题。为此该文提出一种增量部署太赫兹链路的时空图建模,以及考虑弯管转发和星间链路相结合的自适应选择路由算法(ATLS)。在Hypatia网络模拟器中的测试表明,与已有的路由方式相比,ATLS路由能够将任务完成时间降低了17.14%,端到端时延降低16.67%。
-
关键词:
- 巨型近地轨道星座网络 /
- 太赫兹通信 /
- 增量部署 /
- 时空图 /
- 路由算法
Abstract: Terahertz communication, as one of the key technologies of 6G research, will coexist with other frequency band links in the next generation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) mega-constellation network. In such LEO mega-constellation network with incremental deployment of terahertz, the path suboptimization problem when the inter-satellite links are distorted will become more obvious, and the existing routing algorithm only based on the shortest delay path can not solve this problem. The modeling of space-time graph for incremental deployment of terahertz links is proposed and the routing algorithm for Adaptive Transmission Link Selection (ATLS) with combination of bent-pipe and inter-satellite link is considered. Simulation result of the proposed ATLS routing algorithm in the Hypatia network simulator show that compared with the existing methods, ATLS routing algorithm reduces task completion time and end-to-end latency by 17.14% and by 16.67%, respectively. -
表 1 实验参数设置
参数名称 值 参数名称 值 时间间隔$ \tau $ 100 ms 太赫兹天线发射功率 1 W 卫星轨道数 72 太赫兹天线等效噪声温度 0.01 K 每轨卫星数 22 Ka天线频率 27.0 GHz 轨道倾斜角 53.7° Ka天线发射功率 1 W 每星固定天线数 4 存储/转发的单元能耗$ {\mathit{\delta }}_{\mathit{s}} $ $ {10}^{-6} $ kJ 每星机动天线数 4 地面站发送/接收节点数 100 每星GSL数 1 地面中继节点数 196 单星存储容量 200 MB 流量平均大小 100 MB 单星电池容量 50 kW·h 每节点对流数量 100 太赫兹天线频率 0.145 THz 拥塞控制算法 TCP Cubic -
[1] 张更新, 王运峰, 丁晓进, 等. 卫星互联网若干关键技术研究[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(8): 1–14. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021156ZHANG Gengxin, WANG Yunfeng, DING Xiaojin, et al. Research on several key technologies of satellite Internet[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(8): 1–14. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021156 [2] 倪少杰, 岳洋, 左勇, 等. 卫星网络路由技术现状及展望[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(2): 383–395. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211393NI Shaojie, YUE Yang, ZUO Yong, et al. The status quo and prospect of satellite network routing technology[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2023, 45(2): 383–395. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211393 [3] 王宁远, 陈东, 刘亮, 等. 未来低轨信息网络发展与架构展望[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(2): 396–406. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211400WANG Ningyuan, CHEN Dong, LIU Liang, et al. Development trend and architecture prospect of future low-earth-orbit information networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2023, 45(2): 396–406. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211400 [4] BHATTACHERJEE D, KASSING S, LICCIARDELLO M, et al. In-orbit computing: An outlandish thought experiment?[C]. The 19th ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks (HotNets’19), Virtual Event, USA, 2020: 197–204. [5] 孙喆. “长征”十一号火箭成功发射“虹云”工程首颗卫星[J]. 中国航天, 2019(1): 42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7742.2019.01.014SUN Zhe. A LM-11 carrier rocket successfully sends the first satellite in Hongyun project[J]. Aerospace China, 2019(1): 42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7742.2019.01.014 [6] HWU S U, DESILVA K B, and JIH C T. Terahertz (THz) wireless systems for space applications[C]. 2013 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium Proceedings, Galveston, USA, 2013: 171–175. [7] KHALATPOUR A, PAULSEN A K, DEIMERT C, et al. High-power portable terahertz laser systems[J]. Nature Photonics, 2021, 15(1): 16–20. doi: 10.1038/s41566-020-00707-5 [8] LI Jian, LU Hancheng, XUE Kaiping, et al. Temporal netgrid model-based dynamic routing in large-scale small satellite networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(6): 6009–6021. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2910570 [9] SONG Guanghua, CHAO Mengyuan, YANG Bowei, et al. TLR: A traffic-light-based intelligent routing strategy for NGEO satellite IP networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2014, 13(6): 3380–3393. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.041014.130040 [10] 陈全, 杨磊, 郭剑鸣, 等. 低轨巨型星座网络: 组网技术与研究现状[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(5): 177–189. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022075CHEN Quan, YANG Lei, GUO Jianming, et al. LEO mega-constellation network: Networking technologies and state of the art[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(5): 177–189. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022075 [11] BAO Jinzhen, ZHAO Baokang, YU Wanrong, et al. OpenSAN: A software-defined satellite network architecture[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2014, 44(4): 347–348. doi: 10.1145/2740070.2631454 [12] PAPA A, DE COLA T, VIZARRETA P, et al. Dynamic SDN controller placement in a LEO constellation satellite network[C]. 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2018: 206–212. [13] LI Taixin, ZHOU Huachun, LUO Hongbin, et al. SERvICE: A software defined framework for integrated space-terrestrial satellite communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2018, 17(3): 703–716. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2017.2732343 [14] TANG Feilong. Dynamically adaptive cooperation transmission among satellite-ground integrated networks[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2020-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Toronto, Canada, 2020: 1559–1568. [15] CHEN Quan, GIAMBENE G, YANG Lei, et al. Analysis of inter-satellite link paths for LEO mega-constellation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(3): 2743–2755. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3058126 [16] HANDLEY M. Using ground relays for low-latency wide-area routing in megaconstellations[C]. The 18th ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks, Princeton, USA, 2019: 125–132. [17] KASSING S, BHATTACHERJEE D, ÁGUAS A B, et al. Exploring the "Internet from space" with Hypatia[C]. The ACM Internet Measurement Conference, Virtual Event, USA, 2020: 214–229. [18] BHATTACHERJEE D and SINGLA A. Network topology design at 27, 000 km/hour[C]. The 15th International Conference on Emerging Networking Experiments and Technologies, Orlando, USA, 2019: 341–354. [19] HANDLEY M. Delay is not an option: Low latency routing in space[C]. The 17th ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks, Redmond, USA, 2018: 85–91. [20] SpaceX. SpaceX non-geostationary satellite system[EB/OL]. https://fcc.report/IBFS/SAT-MOD-20190830-00087/1877671. 2022. [21] CHEN Quan, CHEN Xiaoqian, YANG Lei, et al. A distributed congestion avoidance routing algorithm in mega-constellation network with multi-gateway[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2019, 162: 376–387. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2019.05.051 [22] COMELLAS F, DALFÓ C, FIOL M A, et al. The spectra of Manhattan street networks[J]. Linear Algebra and its Applications, 2008, 429(7): 1823–1839. doi: 10.1016/j.laa.2008.05.018 [23] KARAPANTAZIS S, PAPAPETROU E, and PAVLIDOU F N. Multiservice on-demand routing in LEO satellite networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2009, 8(1): 107–112. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2009.080334 [24] JORNET J M and AKYILDIZ I F. Channel modeling and capacity analysis for electromagnetic wireless nanonetworks in the terahertz band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2011, 10(10): 3211–3221. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2011.081011.100545 [25] AGI. Systems Tool Kit (STK)[EB/OL]. https://ww2.mathworks.cn/en/products/connections/product_detail/systems-tool-kit.html, 2022. -





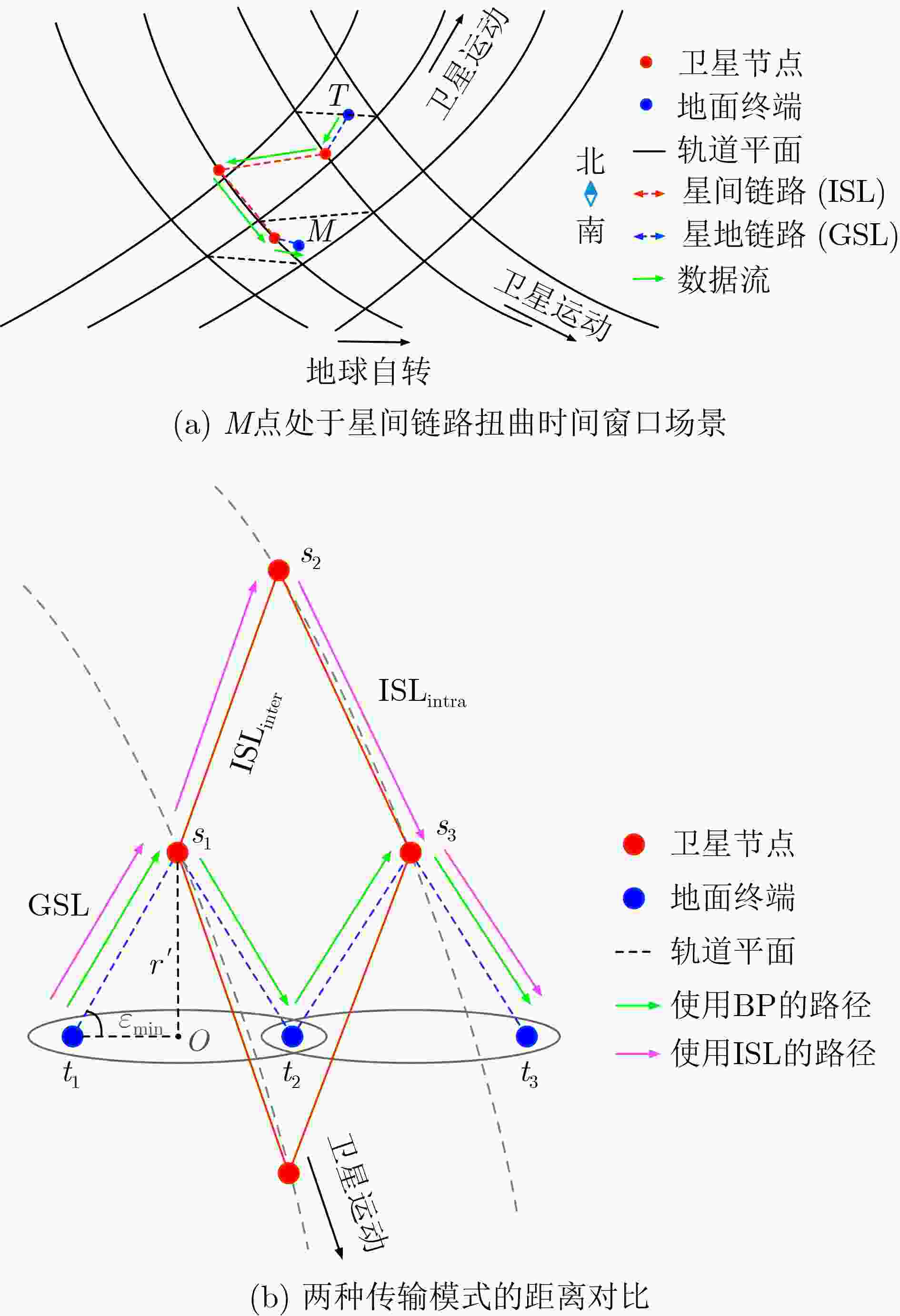
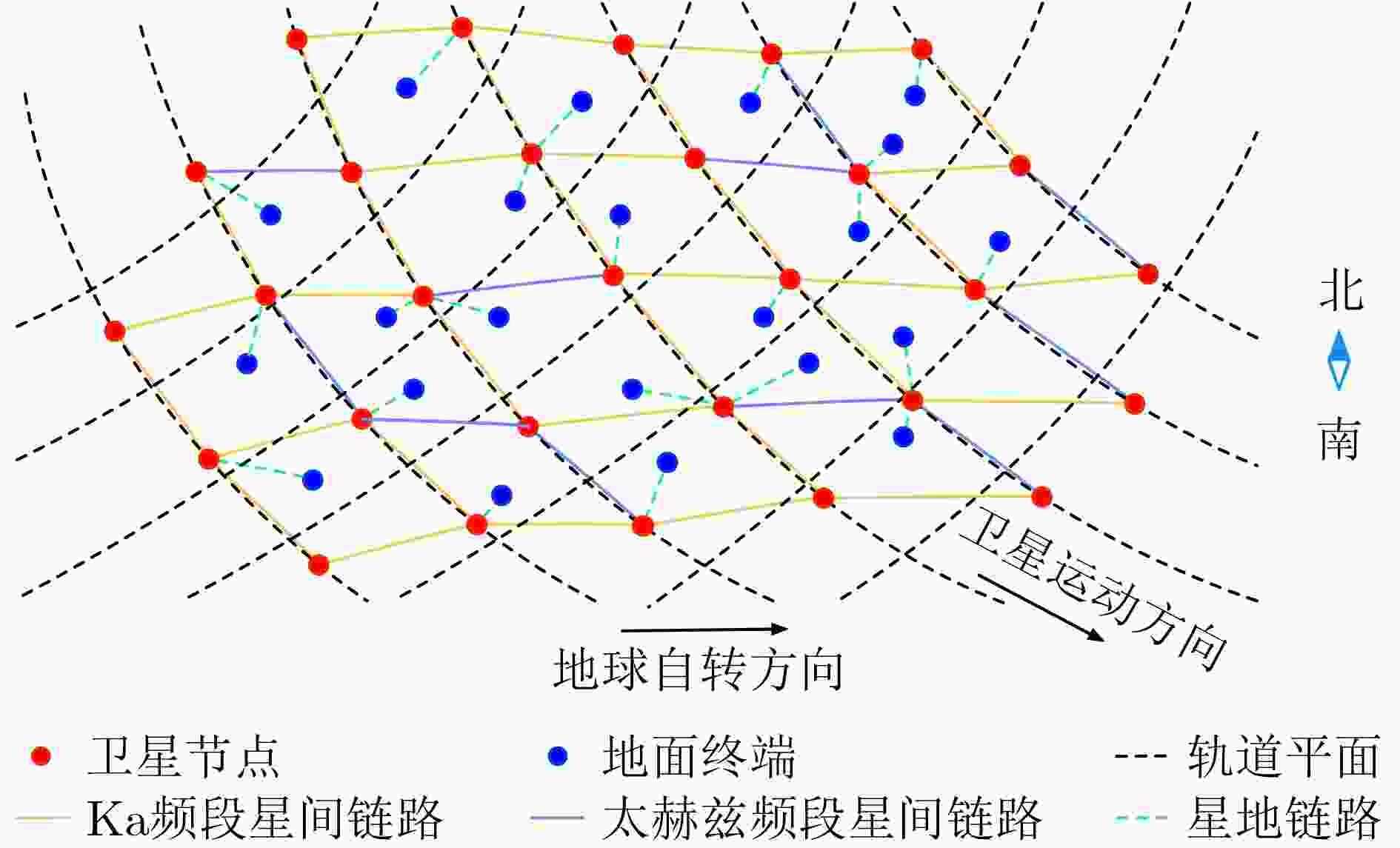
 下载:
下载:
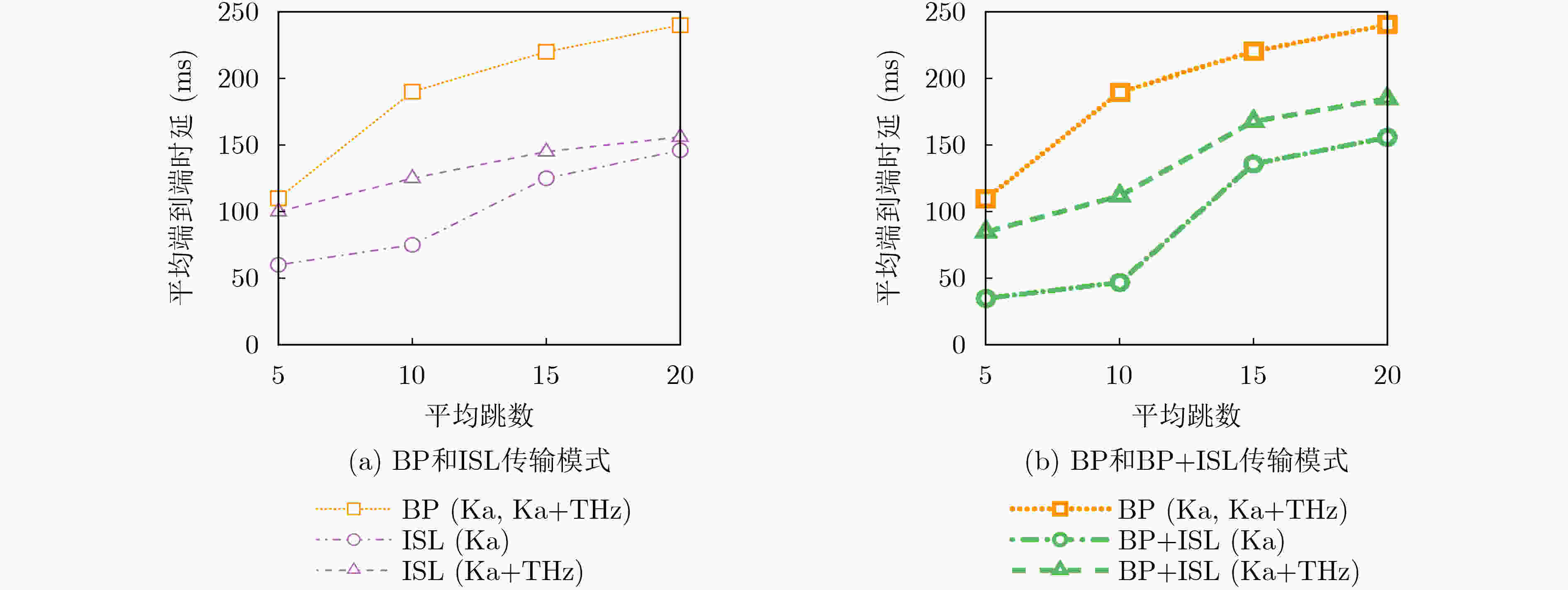
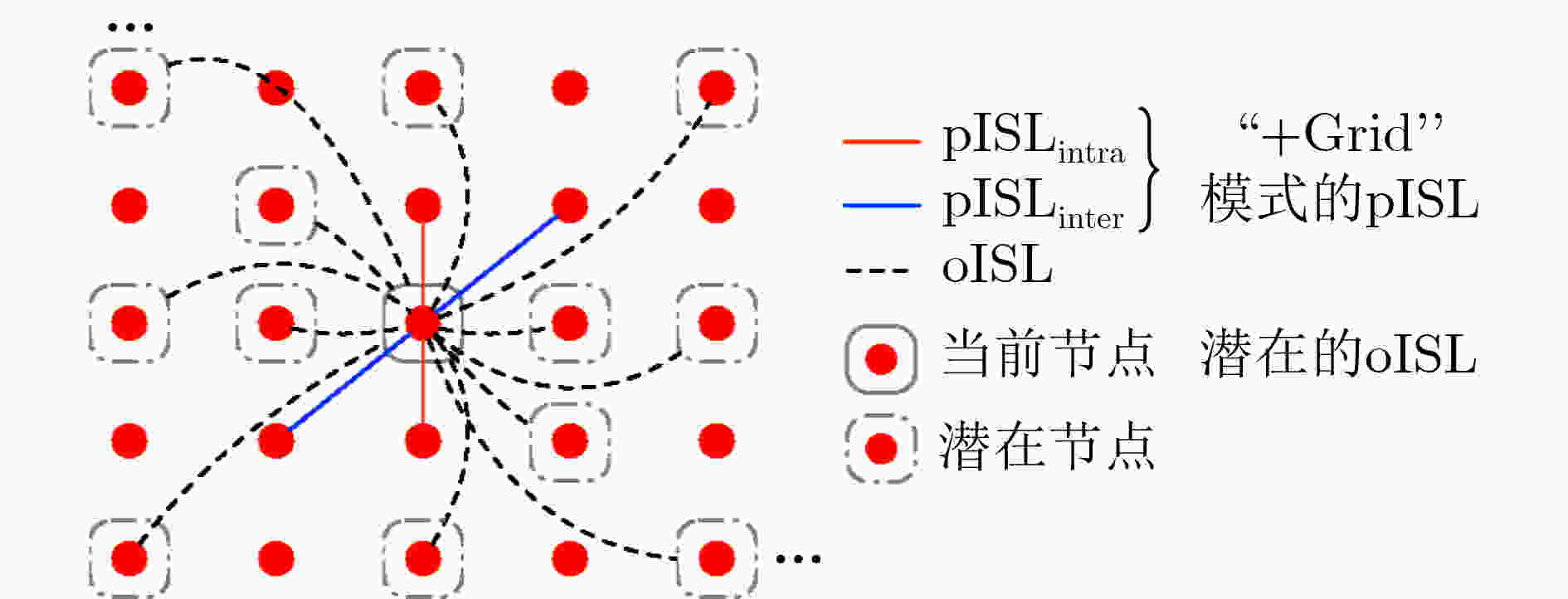
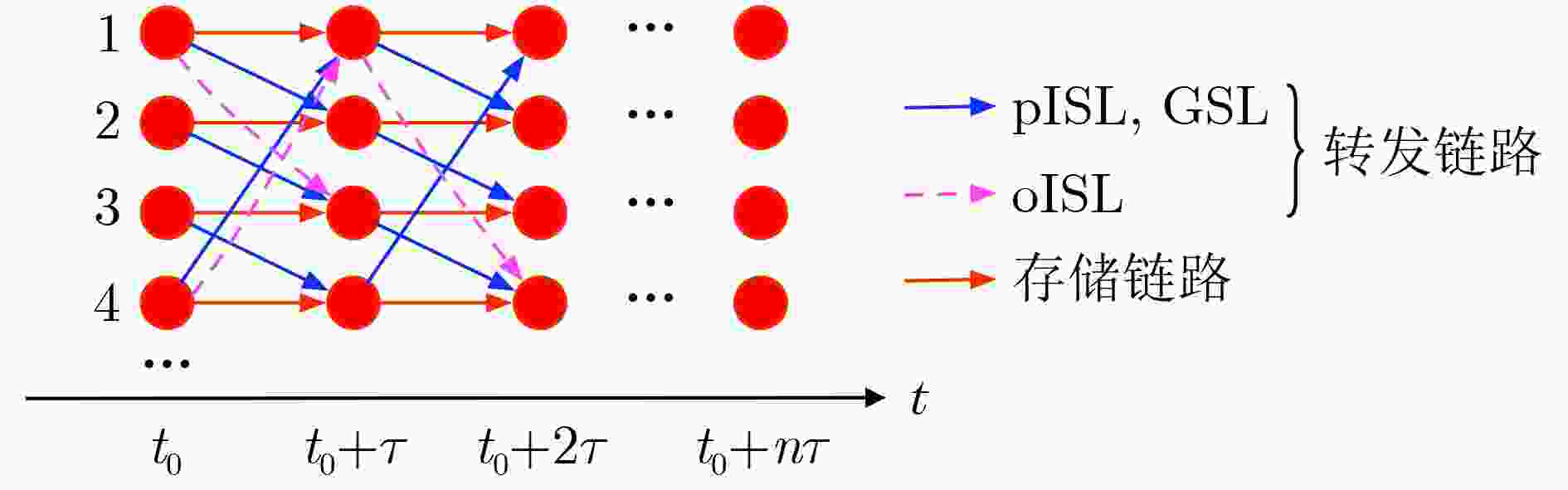
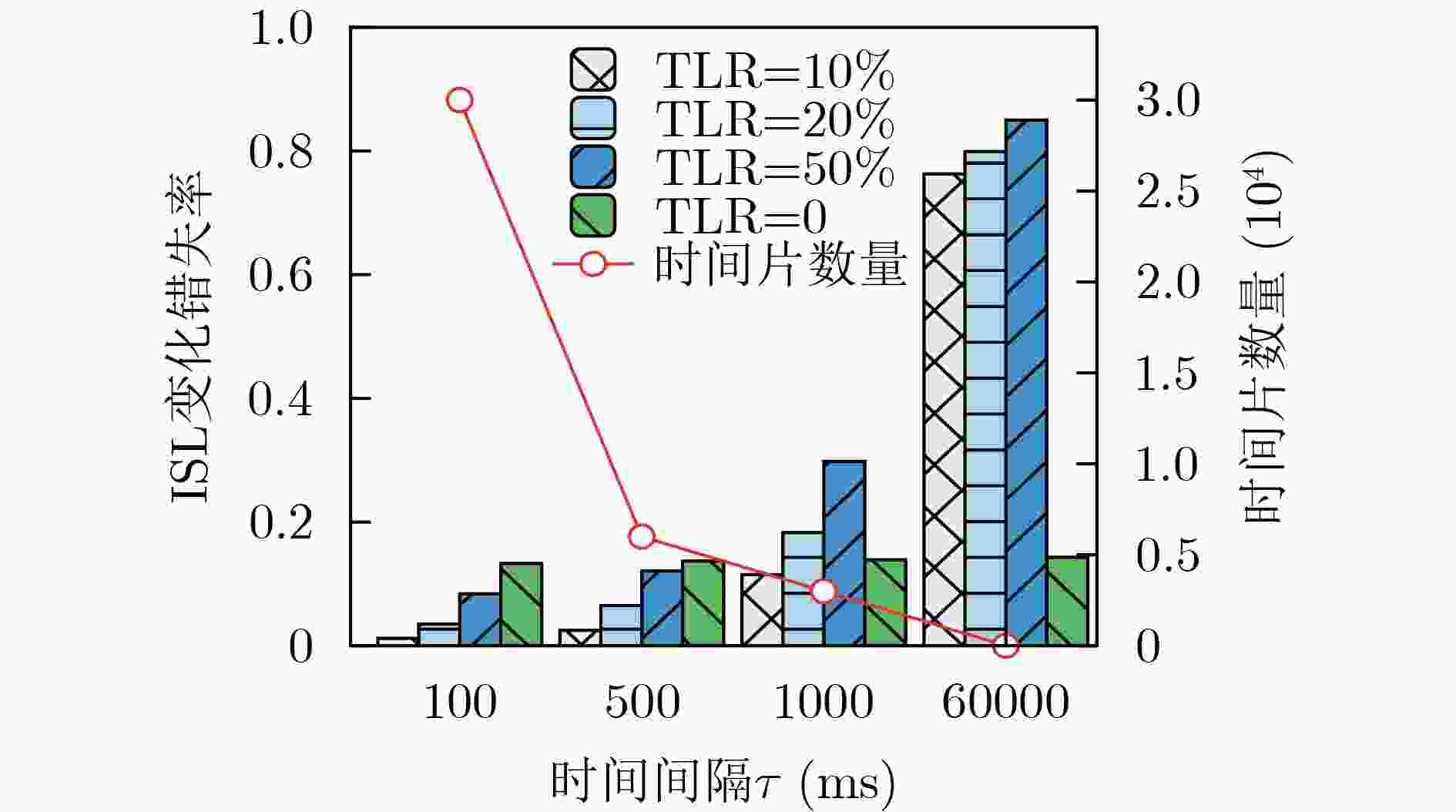
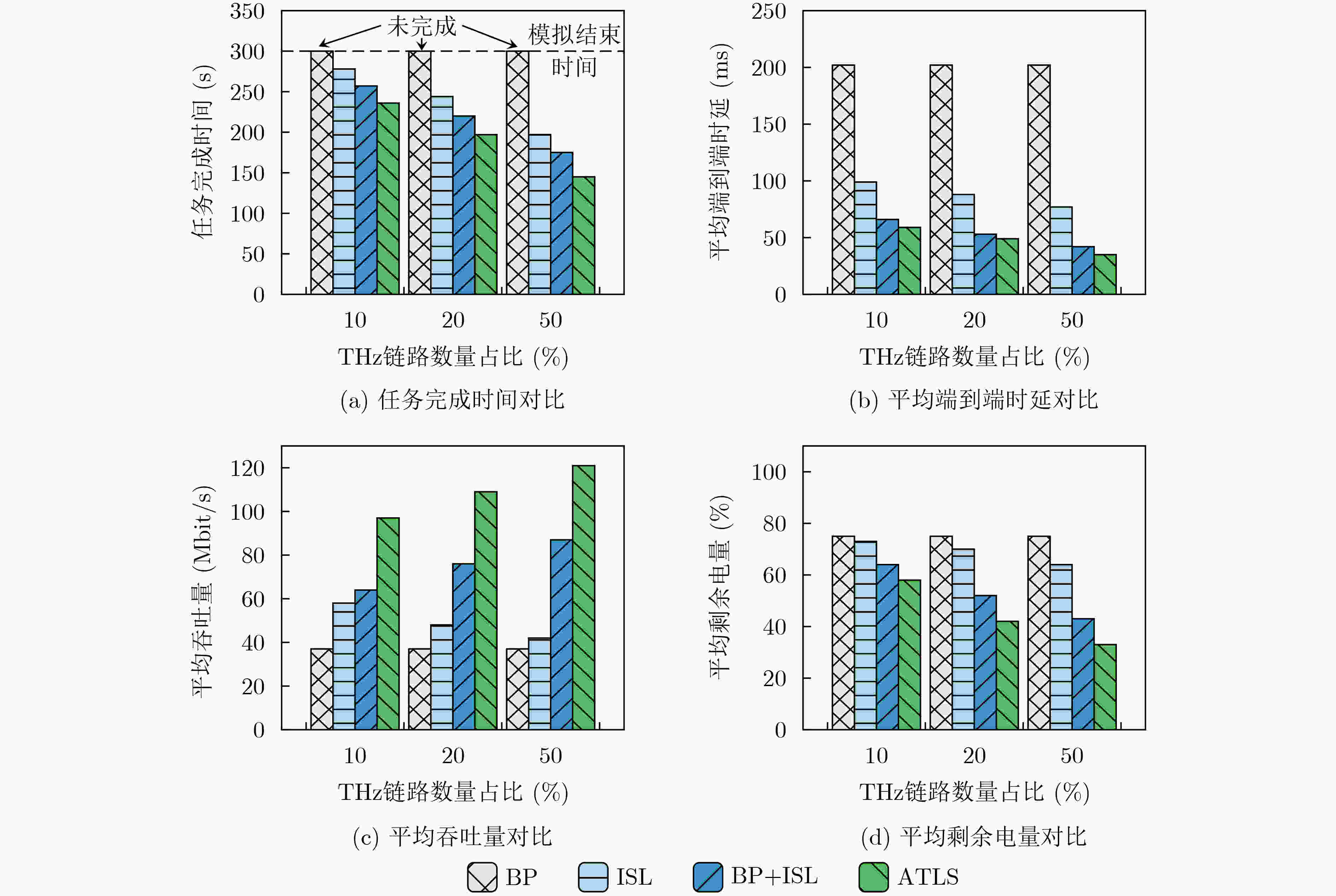


 下载:
下载:
