Secondary Control Methods Based on Distributed Event-triggered Control in Microgrids under Directed Communication Network
-
摘要: 为实现微电网的灵活运行,分布式协同控制技术以其良好的灵活性、可靠性和可扩展性常被用于管控分布式可再生能源。然而,传统基于时间触发的分布式控制策略极大地浪费了分布式电源本地控制器的通信资源,降低了系统运行效率。基于此,该文提出了有向通信拓扑下基于分布式触发控制的微电网2次控制方法。通过为有功功率分配控制设计有向通信拓扑下的分布式触发机制以及为频率恢复设计本地控制器,在实现微电网2次控制目标的同时降低了系统对通信资源的需求。理论证明表明了所设计控制方法不存在芝诺现象。仿真实验结果表明了所提出的频率2次控制方法的有效性和优越性。Abstract: In order to achieve the flexible operation of microgrids, distributed cooperative control is always implemented to manage the distributed renewable energy resources within microgrids due to its better flexibility reliability and scalability. However, the time-triggered traditional distributed control strategies lead to a great waste of the communication resources of distributed generators’ local controller, and hence reduce the efficiency of microgrids’ operation. To this end, a distributed event-triggered control-based frequency secondary control method in microgrids under directed communication network is proposed. By designing an event-triggered mechanism for the active power sharing control under directed communication network and designing a local controller for the frequency restoration control, the secondary control of islanded microgrids can be achieved with greatly reduced communication resources. It is demonstrated by the theoretical analysis that the designed control method does not exist Zeno behavior. The simulation results show the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed control method.
-
Key words:
- Microgrid /
- Secondary control /
- Distributed control /
- Event-triggered control
-
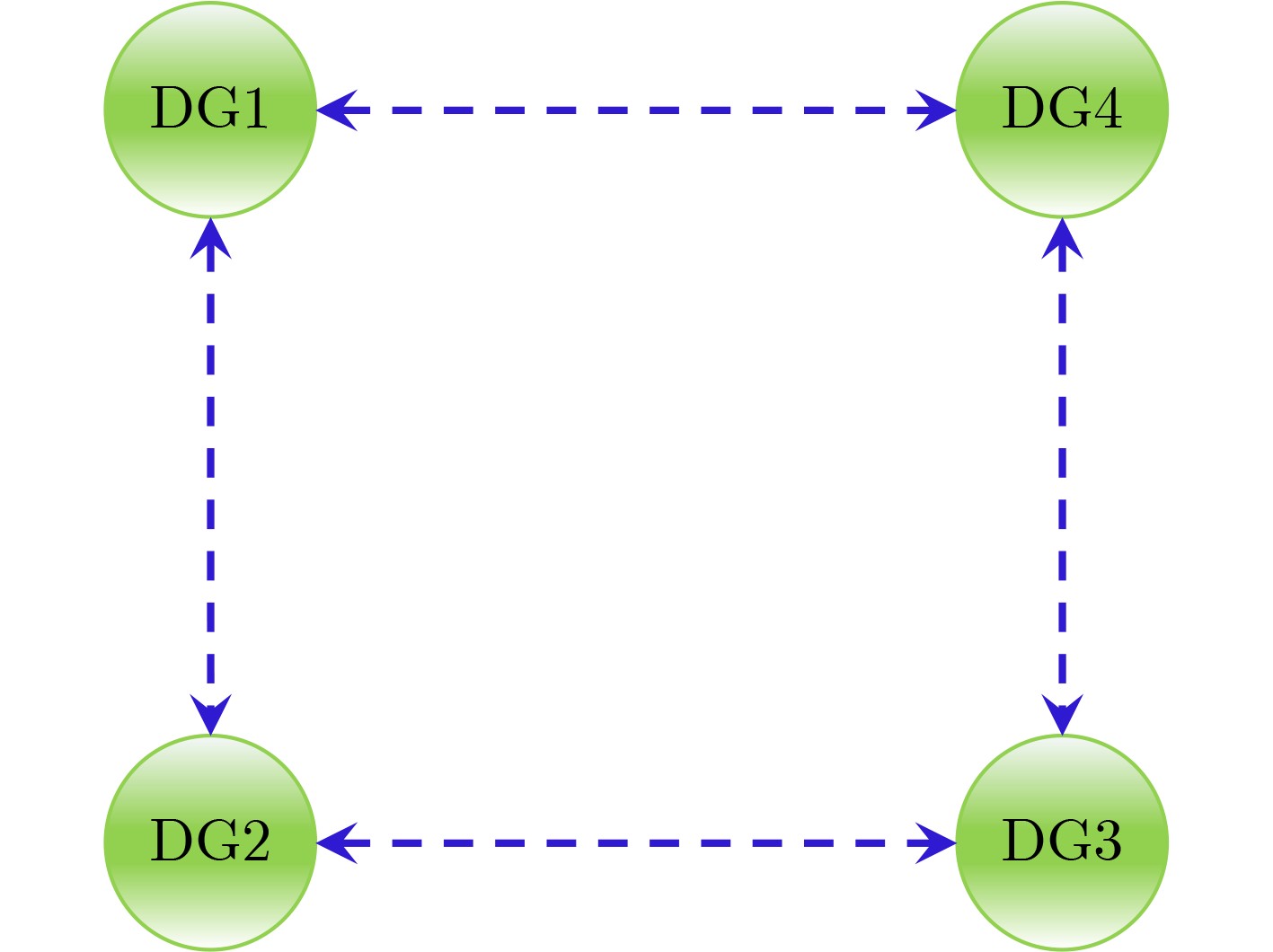
图 4 文献[17]控制策略的通信拓扑
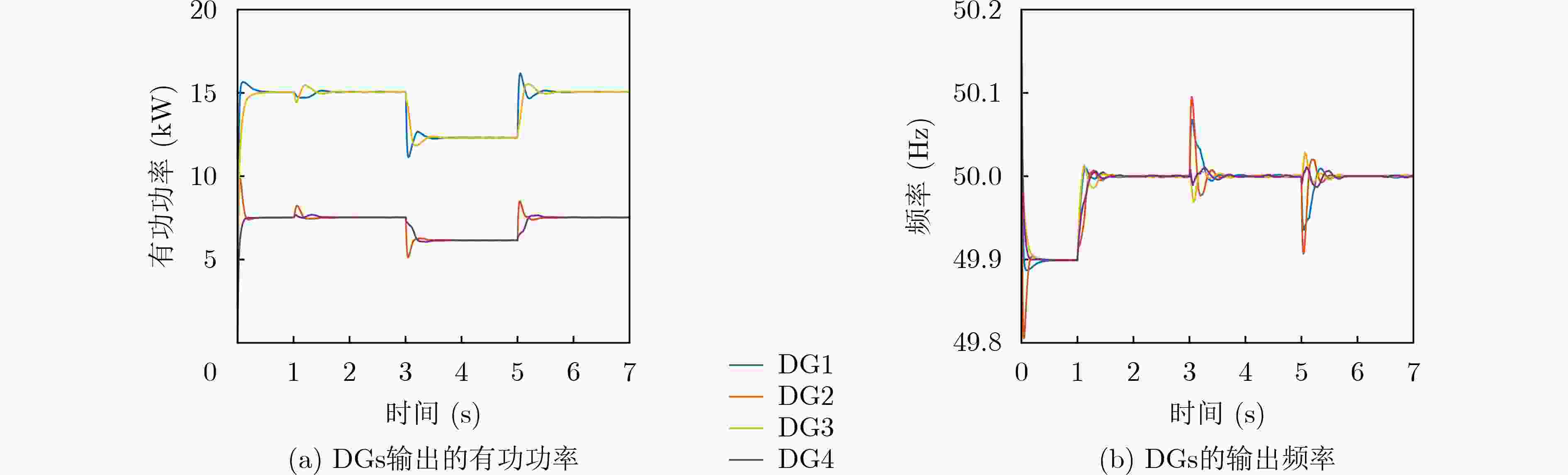
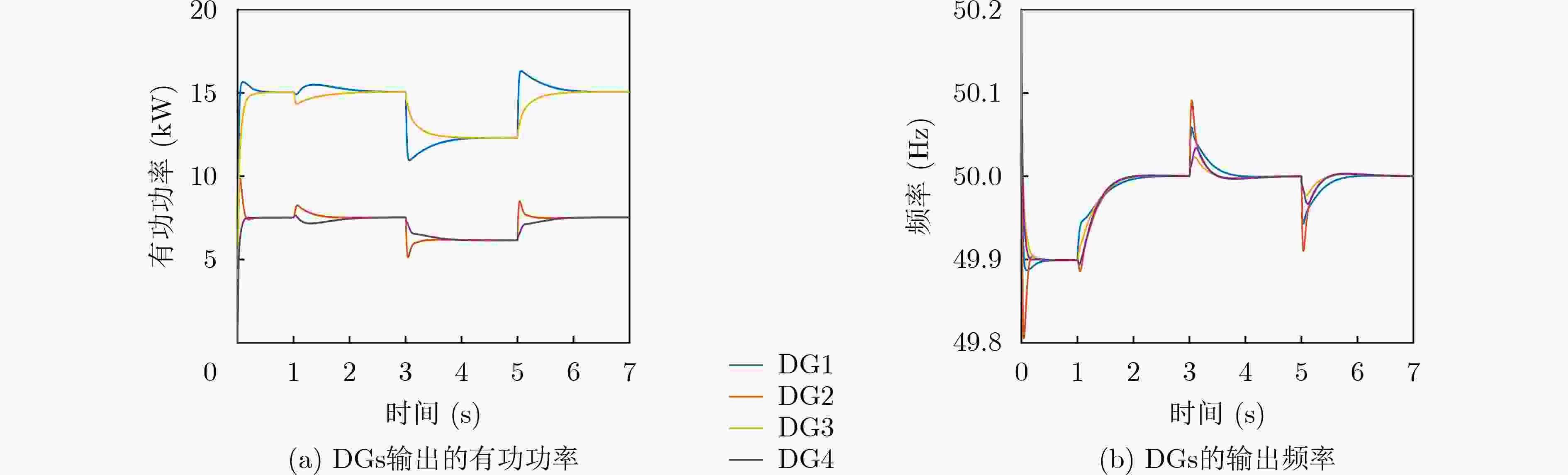
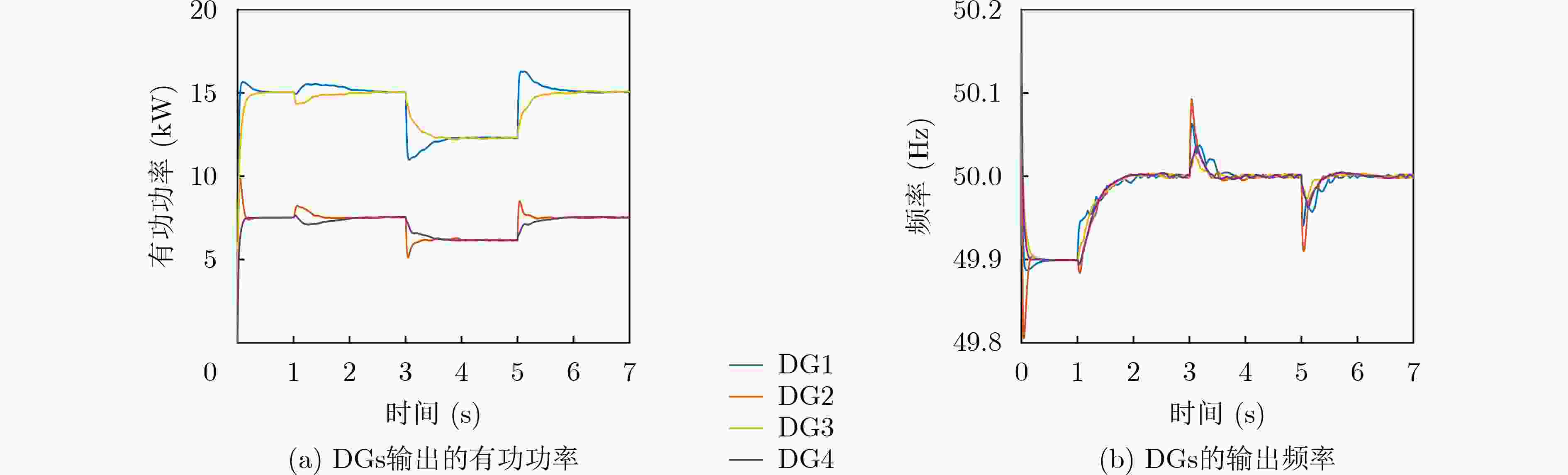
图 7 文献[17]分布式2次控制下微电网DGs输出的有功和频率
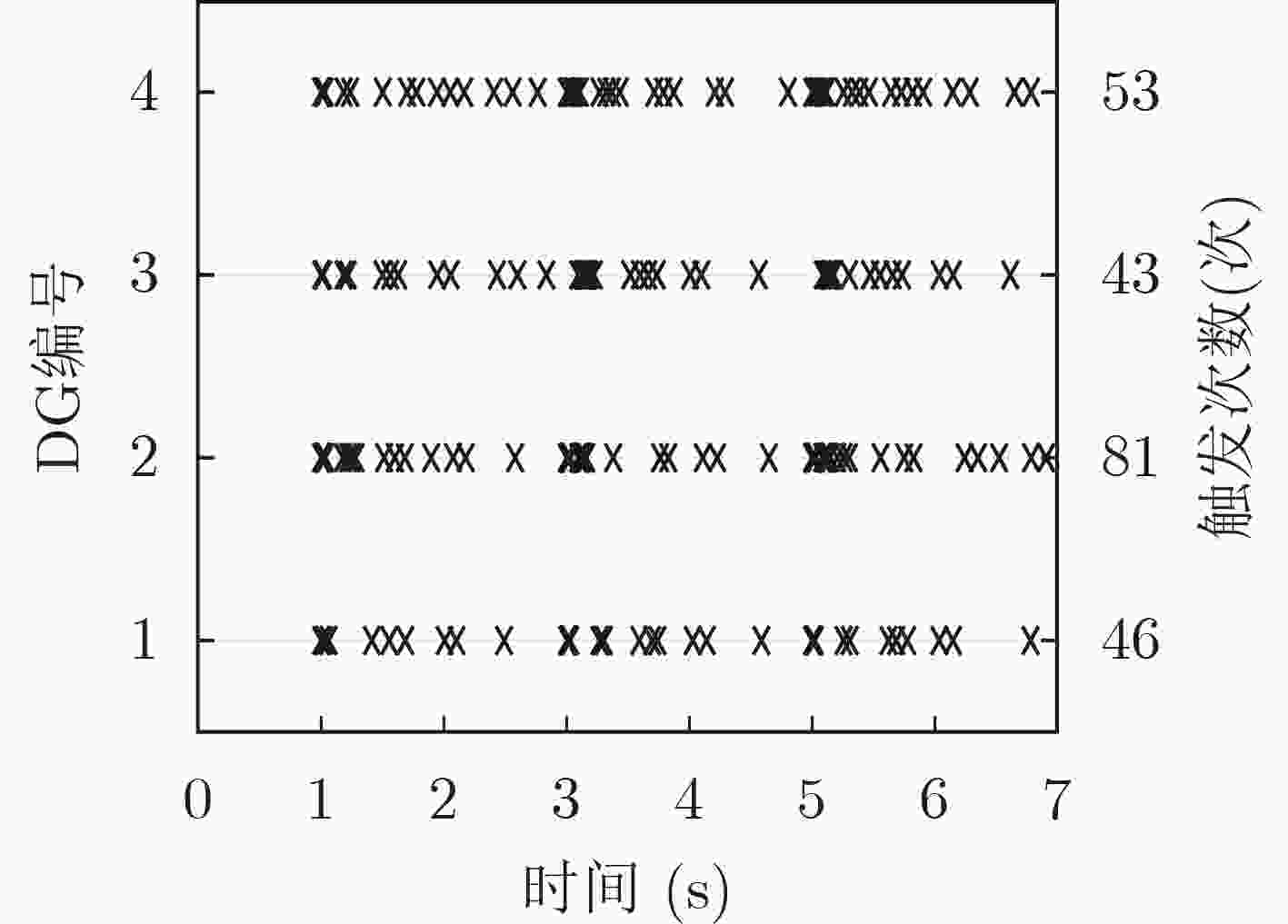
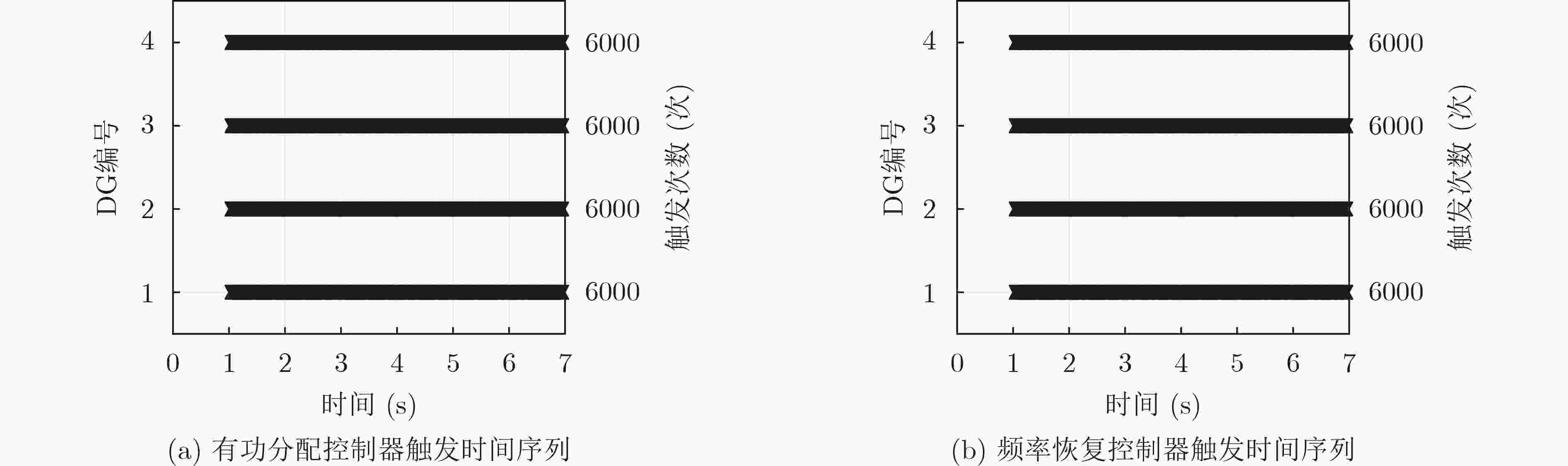
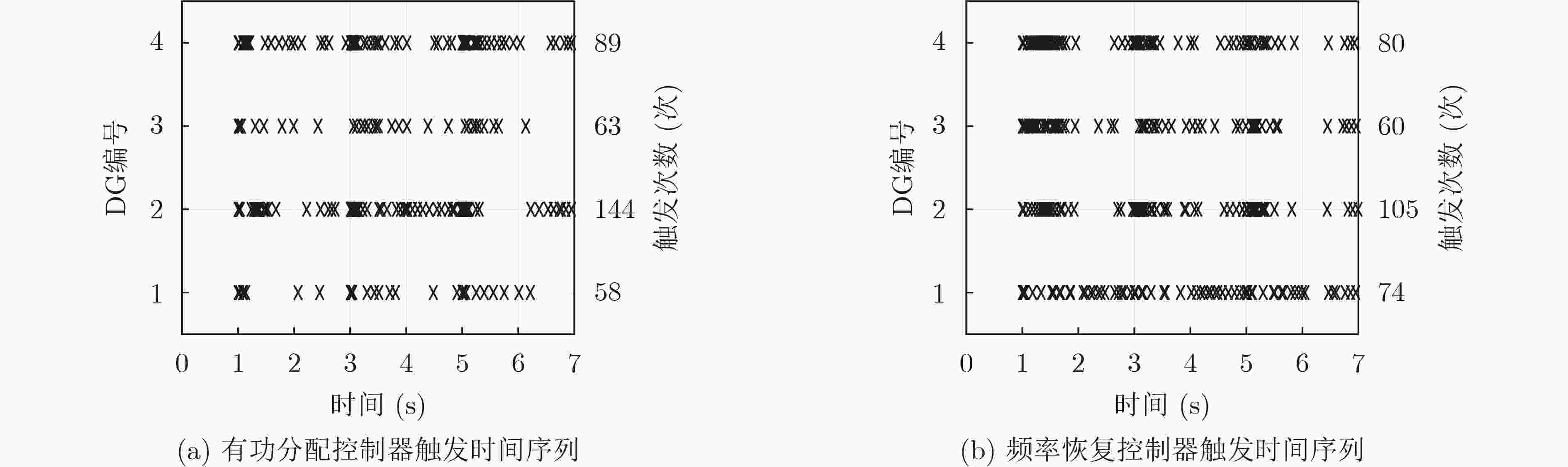
图 8 文献[17]分布式2次控制下有功功率分配和频率恢复控制器的触发时间序列
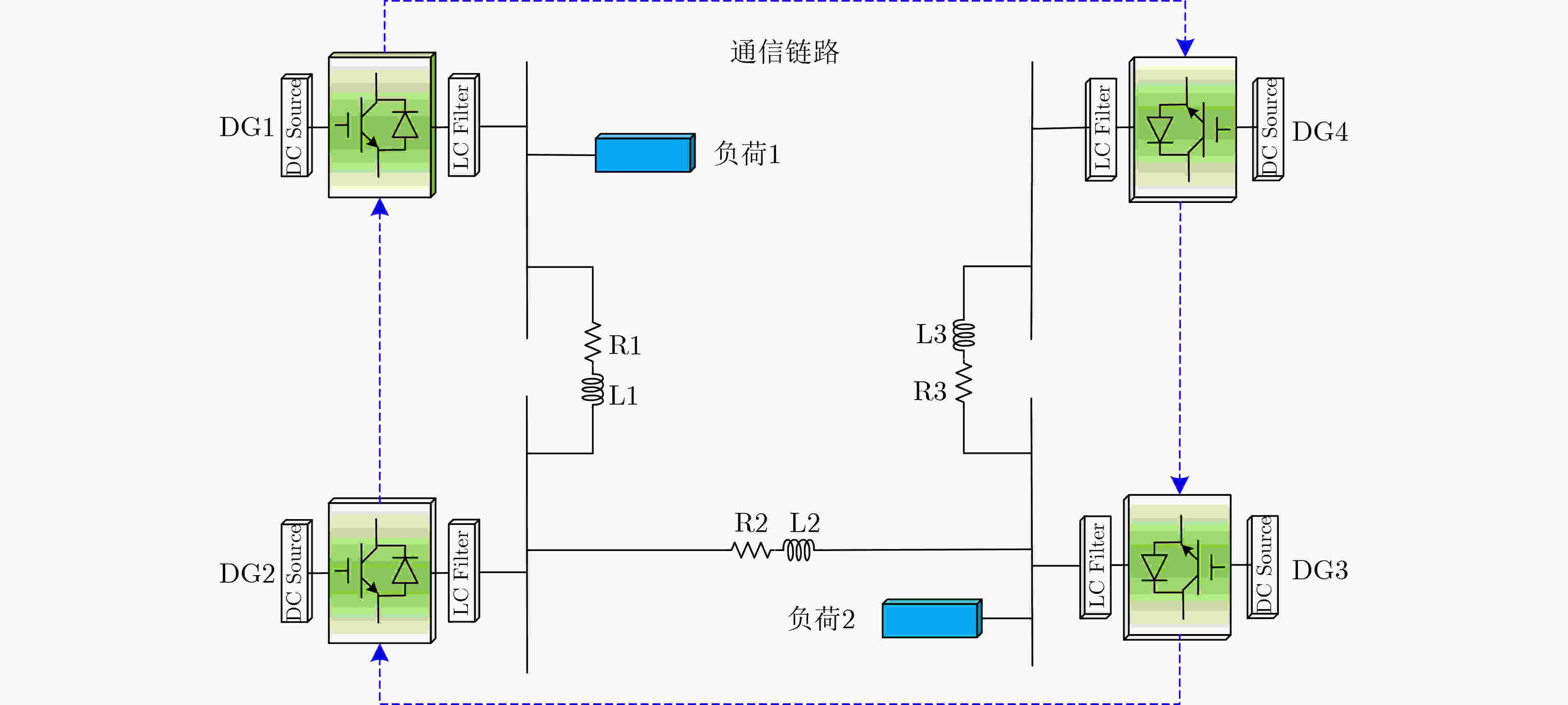
表 1 仿真系统参数
分布式电源 DG1 & DG3 (20 kW) DG2 & DG4 (10 kW) ${m_{1\& 3}}$ $2 \times {10^{ - 5}}$ ${m_{2\& 4}}$ $4 \times {10^{ - 5}}$ ${R_{c(1\& 3)}}$ 0.2 Ω ${R_{c(2\& 4)}}$ 0.2 Ω ${L_{c(1\& 3)}}$ $3 \times {10^{ - 3}}$ H ${L_{c(2\& 4)}}$ $3 \times {10^{ - 3}}$ H 输电线 传输线 1 & 传输线 3 传输线 2 R1 & R3 0.23 Ω R2 0.35 Ω L1 & L3 $0.318 \times {10^{ - 3}}$ H L2 $1.847 \times {10^{ - 3}}$ H 负荷 负荷 1 30 kW 负荷 2 20 kW -
[1] 王成山. 微电网分析与仿真理论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013: 1–11.WANG Chengshan. Analysis and Simulation Theory of Microgrids[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2013: 1–11. [2] GUERRERO J M, VASQUEZ J C, MATAS J, et al. Hierarchical control of droop-controlled AC and DC microgrids—a general approach toward standardization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2011, 58(1): 158–172. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2010.2066534 [3] BIDRAM A and DAVOUDI A. Hierarchical structure of microgrids control system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2012, 3(4): 1963–1976. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2012.2197425 [4] CHEN Yulin, QI Donglian, DONG Hangning, et al. A FDI attack-resilient distributed secondary control strategy for islanded microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12(3): 1929–1938. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2020.3047949 [5] BIDRAM A, LEWIS F L, and DAVOUDI A. Distributed control systems for small-scale power networks: Using multiagent cooperative control theory[J]. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2014, 34(6): 56–77. doi: 10.1109/MCS.2014.2350571 [6] 孙伟, 方昭, 杨建平, 等. 考虑随机时变延时的孤岛微电网分布式二次控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(3): 864–875. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.202489SUN Wei, FANG Zhao, YANG Jianping, et al. Distributed secondary control of islanded microgrid with stochastic time-varying delay[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(3): 864–875. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.202489 [7] XIN Huanhai, QU Zhihua, SEUSS J, et al. A self-organizing strategy for power flow control of photovoltaic generators in a distribution network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2011, 26(3): 1462–1473. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2010.2080292 [8] BIDRAM A, DAVOUDI A, LEWIS F L, et al. Secondary control of microgrids based on distributed cooperative control of multi-agent systems[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2013, 7(8): 822–831. doi: 10.1049/iet-gtd.2012.0576 [9] ZHANG Guoyue, LI Chaoyong, QI Donglian, et al. Distributed estimation and secondary control of autonomous microgrid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2017, 32(2): 989–998. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2016.2590431 [10] 陈郁林, 齐冬莲, 李真鸣, 等. 虚假数据注入攻击下的微电网分布式协同控制[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45(5): 97–103. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20200416002CHEN Yulin, QI Donglian, LI Zhenming, et al. Distributed cooperative control of microgrid under false data injection attacks[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(5): 97–103. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20200416002 [11] NOWZARI C and CORTÉS J. Distributed event-triggered coordination for average consensus on weight-balanced digraphs[J]. Automatica, 2016, 68: 237–244. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.01.069 [12] FAN Yuan, HU Guoqiang, and EGERSTEDT M. Distributed reactive power sharing control for microgrids with event-triggered communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2017, 25(1): 118–128. doi: 10.1109/tcst.2016.2552982 [13] CHEN Yulin, QI Donglian, LI Zhenming, et al. Distributed event-triggered control for frequency restoration in islanded microgrids with reduced trigger condition checking[J]. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems, To be published. [14] WENG Shengxuan, YUE Dong, DOU Chunxia et al. Distributed event-triggered cooperative control for frequency and voltage stability and power sharing in isolated inverter-based microgrid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(4): 1427–1439. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2803754 [15] WANG Yu, NGUYEN T L, XU Yan, et al. Cyber-physical design and implementation of distributed event-triggered secondary control in islanded microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2019, 55(6): 5631–5642. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2019.2936179 [16] ABDOLMALEKI B, SHAFIEE Q, SEIFI A R, et al. A Zeno-free event-triggered secondary control for AC microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11(3): 1905–1916. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2019.2945250 [17] CHEN Yulin, LI Chaoyong, QI Donglian, et al. Distributed event-triggered secondary control for islanded microgrids with proper trigger condition checking period[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2022, 13(2): 837–848. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2021.3115180 [18] WANG Yu, DENG Chao, LIU Dan, et al. Unified real power sharing of generator and storage in islanded microgrid via distributed dynamic event-triggered control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2021, 36(3): 1713–1724. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2020.3039530 [19] OLFATI-SABER R, FAX J A, and MURRAY R M. Consensus and cooperation in networked multi-agent systems[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2007, 95(1): 215–233. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2006.887293 [20] HARDY G H, LITTLEWOOD J E, and PÓLYA G. Inequalities[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1952. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
