| [1] |
HAENSCH W, GOKMEN T, and PURI R. The next generation of deep learning hardware: Analog computing[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2019, 107(1): 108–122. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2018.2871057
|
| [2] |
MA Yufei, DU Yuan, DU Li, et al. In-memory computing: The next-generation AI computing paradigm[C]. 2020 on Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI, New York, USA, 2020: 265–270.
|
| [3] |
李桂宏, 乔飞. 面向边缘智能设备的持续感知集成电路与系统[J]. 微纳电子与智能制造, 2019, 1(2): 47–61. doi: 10.19816/j.cnki.10-1594/tn.2019.02.007LI Guihong and QIAO Fei. Continuous perception integrated circuits and systems for edge-computing smart devices[J]. Micro/Nano Electronics and Intelligent Manufacturing, 2019, 1(2): 47–61. doi: 10.19816/j.cnki.10-1594/tn.2019.02.007
|
| [4] |
CHOI J. Review of low power image sensors for always-on imaging[C]. 2016 International SoC Design Conference, Jeju, Korea (South), 2016.
|
| [5] |
PAUL S, HONKOTE V, KIM R G, et al. A sub-cm³ energy-harvesting stacked wireless sensor node featuring a near-threshold voltage IA-32 microcontroller in 14-nm tri-gate CMOS for always-on always-sensing applications[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2017, 52(4): 961–971. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2016.2638465
|
| [6] |
CHOI J, SHIN J, KANG Dongwu, et al. Always-on CMOS image sensor for mobile and wearable devices[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2016, 51(1): 130–140. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2015.2470526
|
| [7] |
LUO Yi and MIRABBASI S. Always-on CMOS image sensor pixel design for pixel-wise binary coded exposure[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Baltimore, USA, 2017: 1–4.
|
| [8] |
YOUNG C, OMID-ZOHOOR A, LAJEVARDI P, et al. 5.3 a data-compressive 1.5b/2.75b log-gradient QVGA image sensor with multi-scale readout for always-on object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 98–100.
|
| [9] |
SHI Weisong, CAO Jie, ZHANG Quan, et al. Edge computing: Vision and challenges[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2016, 3(5): 637–646. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2016.2579198
|
| [10] |
CHIANG M and ZHANG Tao. Fog and IoT: An overview of research opportunities[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2016, 3(6): 854–864. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2016.2584538
|
| [11] |
ZHU Bowen, WANG Hong, LIU Yaqing, et al. Skin-inspired haptic memory arrays with an electrically reconfigurable architecture[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(8): 1559–1566. doi: 10.1002/adma.201504754
|
| [12] |
JIANG Chengming, LI Qikun, SUN Nan, et al. A high-performance bionic pressure memory device based on piezo-OLED and piezo-memristor as luminescence-fish neuromorphic tactile system[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 77: 105120. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105120
|
| [13] |
SUN Yihui, ZHENG Xin, YAN Xiaoqin, et al. Bioinspired tribotronic resistive switching memory for self-powered memorizing mechanical stimuli[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(50): 43822–43829. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b15269
|
| [14] |
WAN Changjin, CAI Pingqiang, GUO Xintong, et al. An artificial sensory neuron with visual-haptic fusion[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 4602. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18375-y
|
| [15] |
ZHOU Feichi, ZHOU Zheng, CHEN Jiewei, et al. Optoelectronic resistive random access memory for neuromorphic vision sensors[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2019, 14(8): 776–782. doi: 10.1038/s41565-019-0501-3
|
| [16] |
LORENZI P, SUCRE V, ROMANO G, et al. Memristor based neuromorphic circuit for visual pattern recognition[C]. 2015 International Conference on Memristive Systems, Paphos, Cyprus, 2015: 1–2.
|
| [17] |
HALAWANI Y, MOHAMMAD B, AL-QUTAYRI M, et al. Memristor-based hardware accelerator for image compression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2018, 26(12): 2749–2758. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2018.2835572
|
| [18] |
WANG Wei, PEDRETTI G, MILO V, et al. Learning of spatiotemporal patterns in a spiking neural network with resistive switching synapses[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(9): eaat4752. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aat4752
|
| [19] |
LI Qin, YANG Yuze, LAN Tianxiang, et al. MSP-MFCC: Energy-efficient MFCC feature extraction method with mixed-signal processing architecture for wearable speech recognition applications[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 48720–48730. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2979799
|
| [20] |
CHANG Mengfan, CHEN C F, CHANG Tinghao, et al. 17.3 A 28nm 256kb 6T-SRAM with 280mV improvement in VMIN using a dual-split-control assist scheme[C]. 2015 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference–(ISSCC) Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, USA, 2015: 1–3.
|
| [21] |
KHWA W S, CHEN Jiajing, LI Jiafang, et al. A 65nm 4Kb algorithm-dependent computing-in-memory SRAM unit-macro with 2.3ns and 55.8TOPS/W fully parallel product-sum operation for binary DNN edge processors[C]. 2018 IEEE International Solid–State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 496–498.
|
| [22] |
SI Xin, KHWA W S, CHEN Jiajing, et al. A dual-split 6T SRAM-based computing-in-memory unit-macro with fully parallel product-sum operation for binarized DNN edge processors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2019, 66(11): 4172–4185. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2019.2928043
|
| [23] |
DONG Qing, JELOKA S, SALIGANE M, et al. A 0.3V VDDmin 4+2T SRAM for searching and in-memory computing using 55nm DDC technology[C]. 2017 Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Kyoto, Japan, 2017: C160–C161.
|
| [24] |
NAJAFI D and EBRAHIMI B. A low-leakage 6T SRAM cell for in-memory computing with high stability[C]. The 2021 29th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering, Tehran, Iran, 2021: 98–102.
|
| [25] |
YU Chengshuo, YOO T, CHAI K T C, et al. A 65-nm 8T SRAM compute-in-memory macro with column ADCs for processing neural networks[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2022, 57(11): 3466–3476. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2022.3162602
|
| [26] |
YU Chengshuo, CHAI K T C, KIM T T H, et al. A zero-skipping reconfigurable SRAM in-memory computing macro with binary-searching ADC[C]. The IEEE 47th European Solid State Circuits Conference, Grenoble, France, 2021: 131–134.
|
| [27] |
GUPTA A K and ACHARYA A. Exploration of 9T SRAM cell for in memory computing application[C]. 2021 Devices for Integrated Circuit, Kalyani, India, 2021: 461–465.
|
| [28] |
DONG Qing, SINANGIL M E, ERBAGCI B, et al. 15.3 A 351TOPS/W and 372.4GOPS compute-in-memory SRAM macro in 7nm FinFET CMOS for machine-learning applications[C]. 2020 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2020: 242–244.
|
| [29] |
JIA Hongyang, OZATAY M, TANG Yinqi, et al. 15.1 A programmable neural-network inference accelerator based on scalable in-memory computing[C]. 2021 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2021: 236–238.
|
| [30] |
KIM J and PARK J. A charge-domain 10T SRAM based in-memory-computing macro for low energy and highly accurate DNN inference[C]. The 2021 18th International SoC Design Conference, Jeju Island, Korea (South), 2021: 89–90.
|
| [31] |
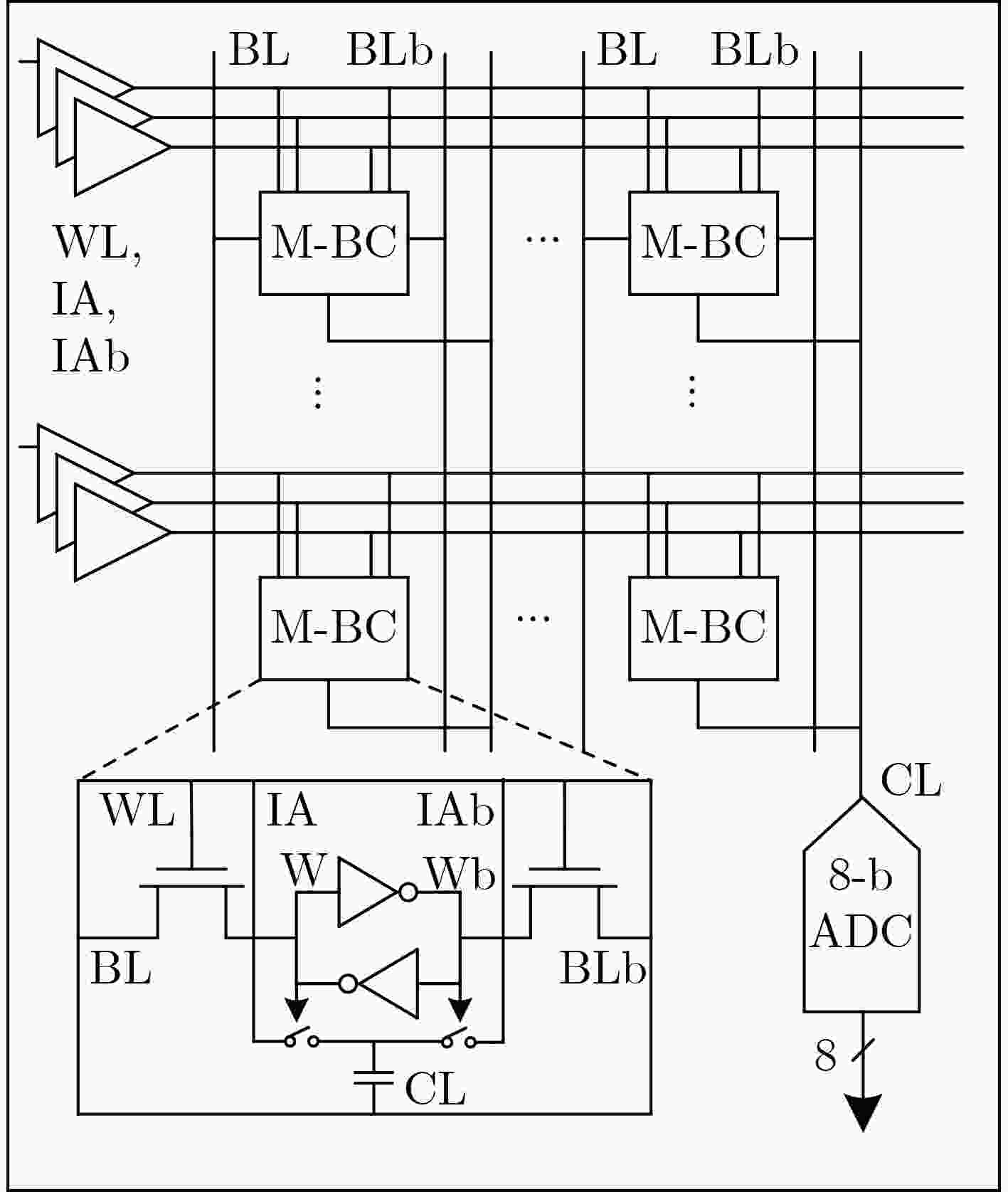
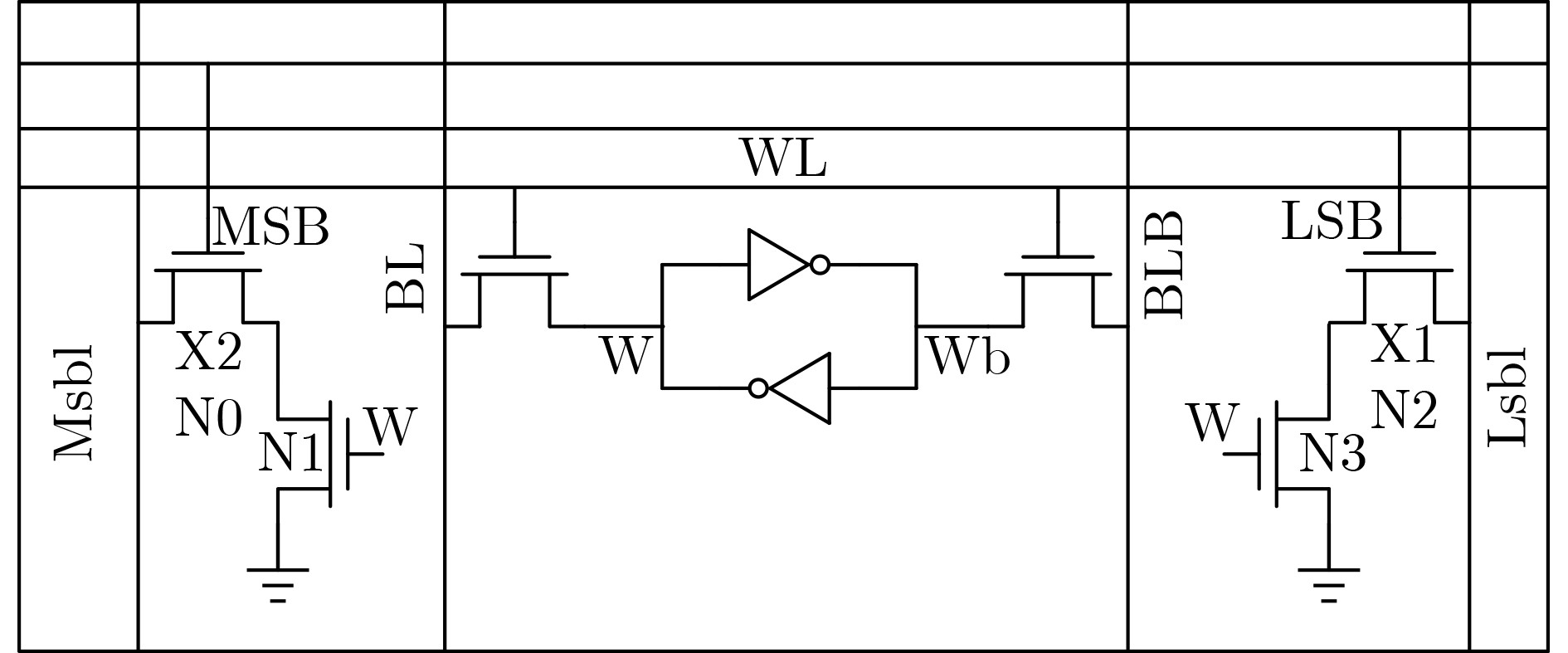
OH H, KIM H, AHN D, et al. Energy-efficient in-memory binary neural network accelerator design based on 8T2C SRAM cell[J]. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Letters, 2022, 2,5: 70–73. doi: 10.1109/LSSC.2022.3161592
|
| [32] |
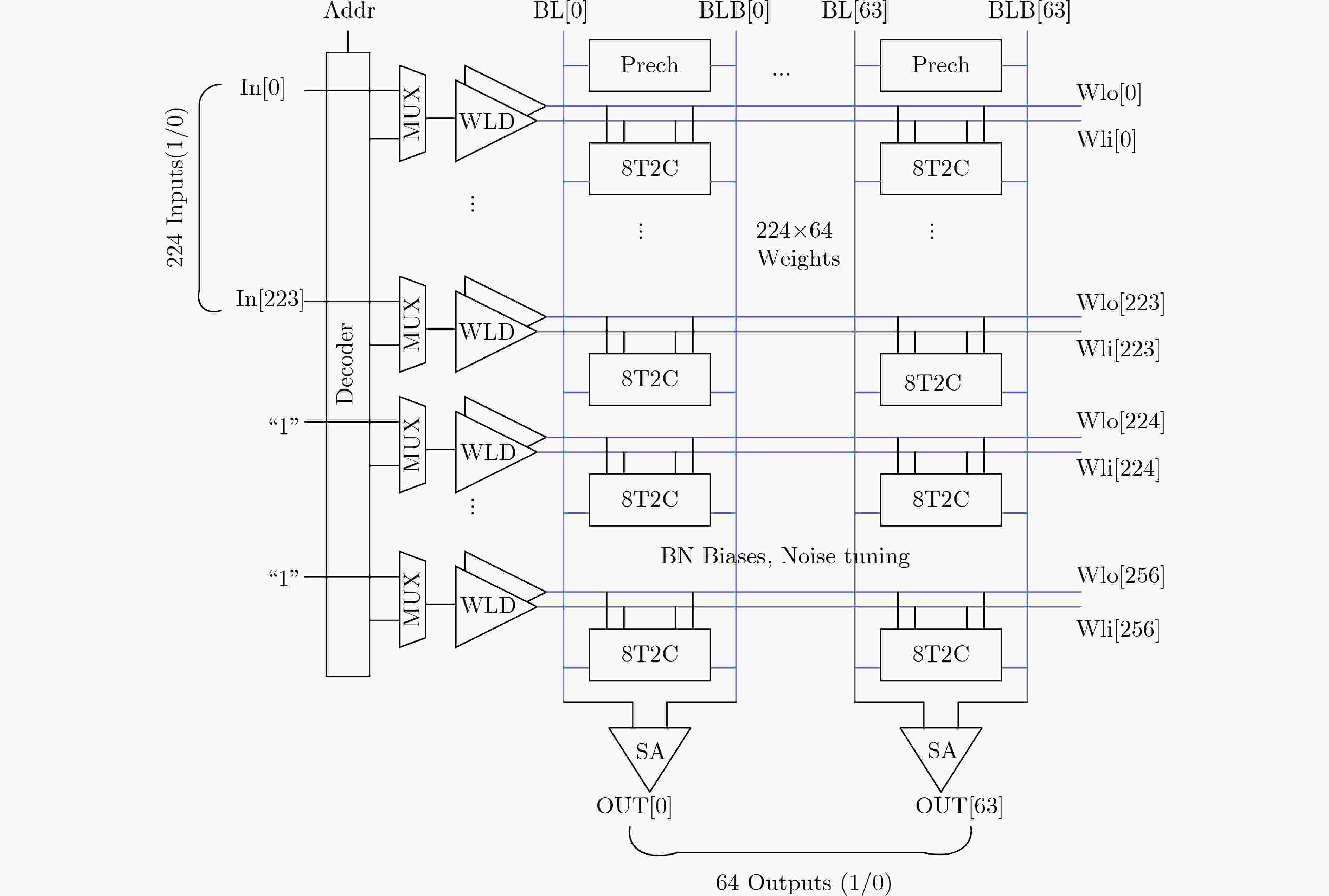
KIM H, CHEN Qian, YOO T, et al. A 1–16b precision reconfigurable digital in-memory computing macro featuring column-MAC architecture and bit-serial computation[C]. The IEEE 45th European Solid State Circuits Conference, Cracow, Poland, 2019: 345–348.
|
| [33] |
CHIH Y D, LEE P H, FUJIWARA H, et al. 16.4 An 89TOPS/W and 16.3TOPS/mm2 all-digital SRAM-based full-precision compute-in memory macro in 22nm for machine-learning edge applications[C]. 2021 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2021: 252–254.
|
| [34] |
KIM H, YOO T, KIM T T H, et al. Colonnade: A reconfigurable SRAM-based digital bit-serial compute-in-memory macro for processing neural networks[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2021, 56(7): 2221–2233. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2021.3061508
|
| [35] |
LIN Zhiting, ZHU Zhiyong, ZHAN Honglan, et al. Two-direction in-memory computing based on 10T SRAM with horizontal and vertical decoupled read ports[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2021, 56(9): 2832–2844. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2021.3061260
|
| [36] |
FUJIWARA H, MORI H, ZHAO Weichang, et al. A 5-nm 254-TOPS/W 221-TOPS/mm2 fully-digital computing-in-memory macro supporting wide-range dynamic-voltage-frequency scaling and simultaneous MAC and write operations[C]. 2022 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2022: 1–3.
|
| [37] |
YAN Bonan, HSU J L, YU Pangcheng, et al. A 1.041-Mb/mm2 27.38-TOPS/W signed-INT8 dynamic-logic-based ADC-less SRAM compute-in-memory macro in 28nm with reconfigurable bitwise operation for AI and embedded applications[C]. 2022 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2022: 188–190.
|
| [38] |
龚龙庆, 徐伟栋, 娄冕. SRAM存内计算技术综述[J]. 微电子学与计算机, 2021, 38(9): 1–7. doi: 10.19304/j.cnki.issn1000-7180.2021.09.001GONG Longqing, XU Weidong, and LOU Mian. An overview of SRAM in-memory computing[J]. Microelectronics &Computer, 2021, 38(9): 1–7. doi: 10.19304/j.cnki.issn1000-7180.2021.09.001
|
| [39] |
周正, 丛瑛瑛. 存内计算技术发展趋势分析[J]. 信息通信技术与政策, 2019(9): 65–68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9217.2019.09.016ZHOU Zheng and CONG Yingying. Analysis on the development trend of Computing in-memory[J]. Information and Communications Technology and Policy, 2019(9): 65–68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9217.2019.09.016
|
| [40] |
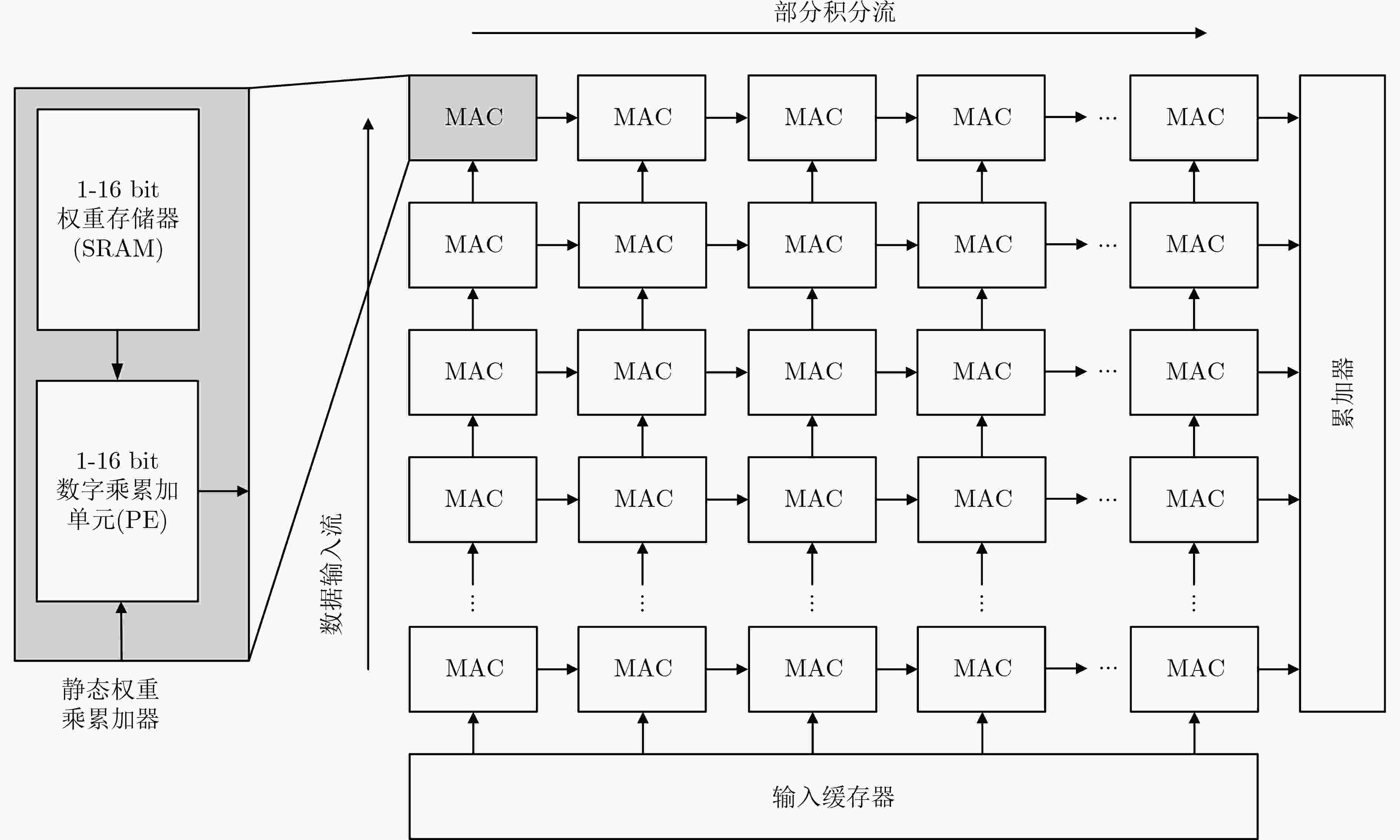
张章, 李超, 韩婷婷, 等. 基于忆阻器的感存算一体技术综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(6): 1498–1509. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201102ZHANG Zhang, LI Chao, HAN Tingting, et al. Review of the fused technology of sensing, storage and computing based on memristor[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(6): 1498–1509. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201102
|





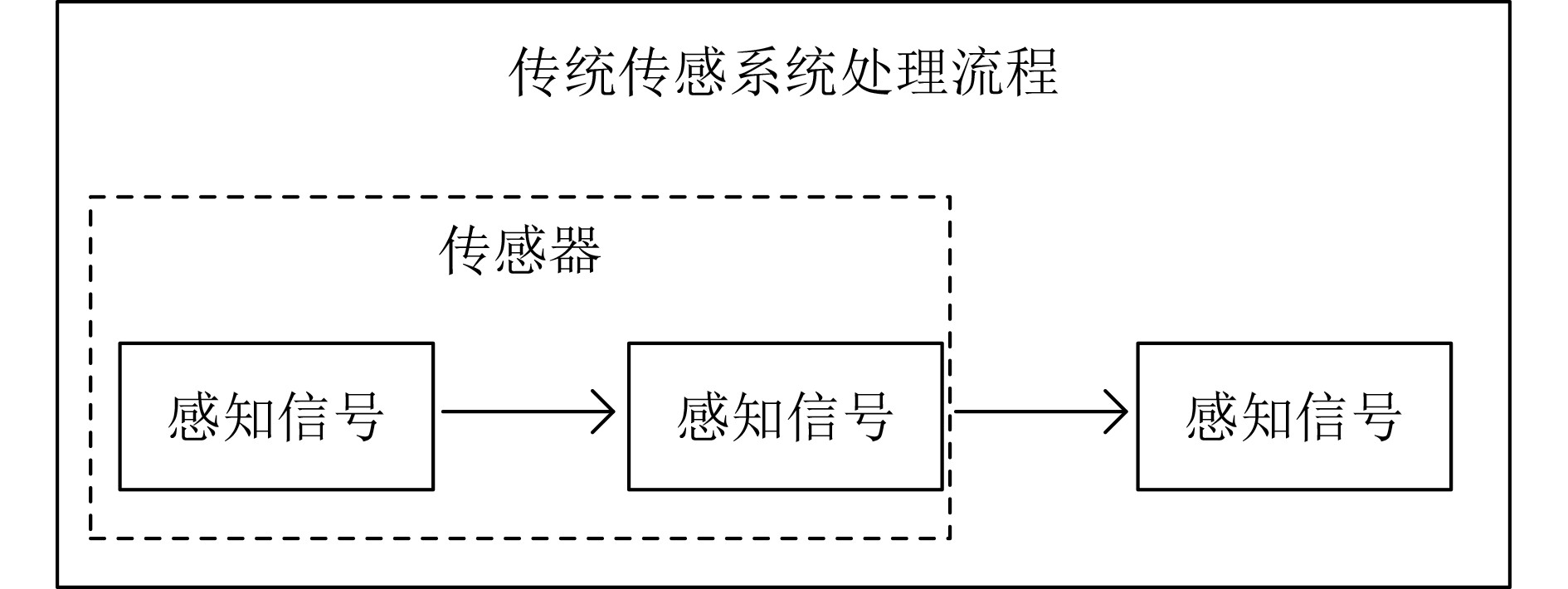
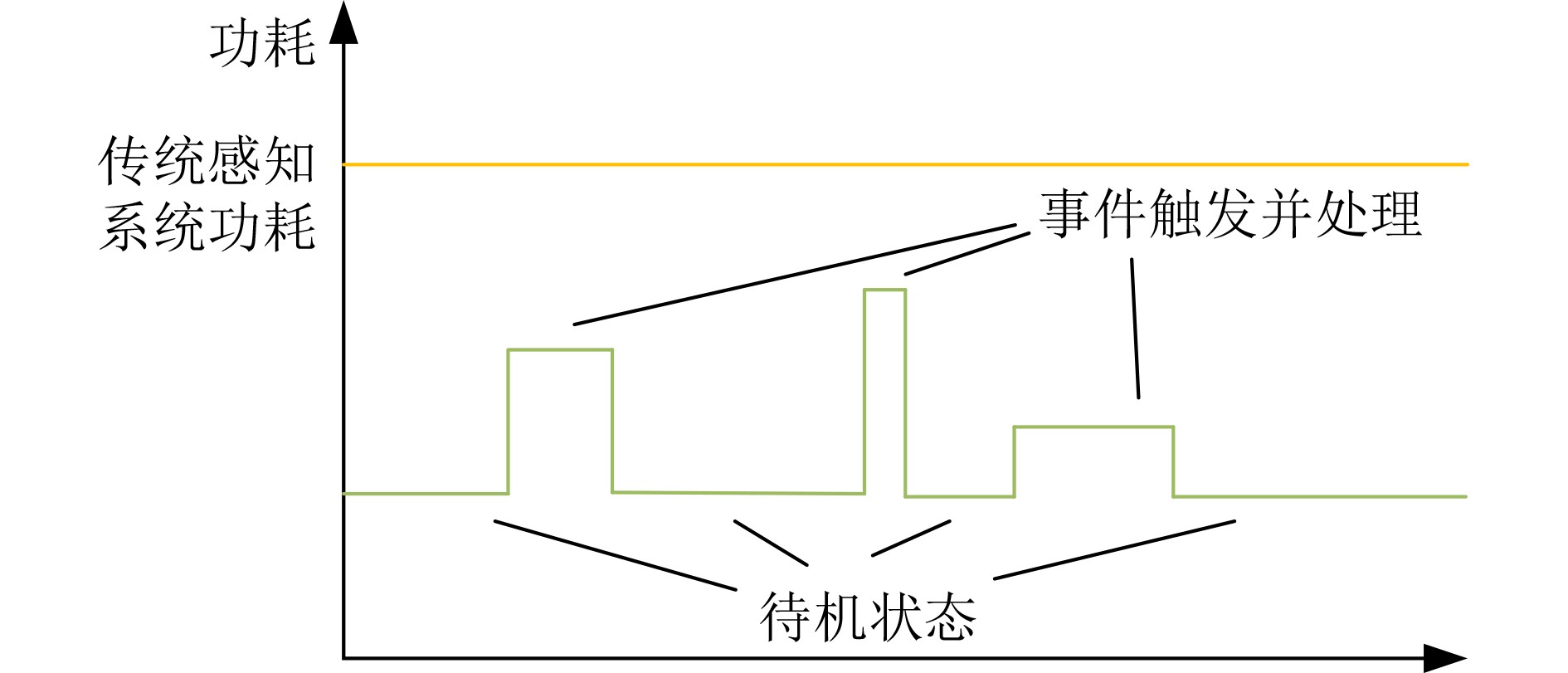
 下载:
下载:
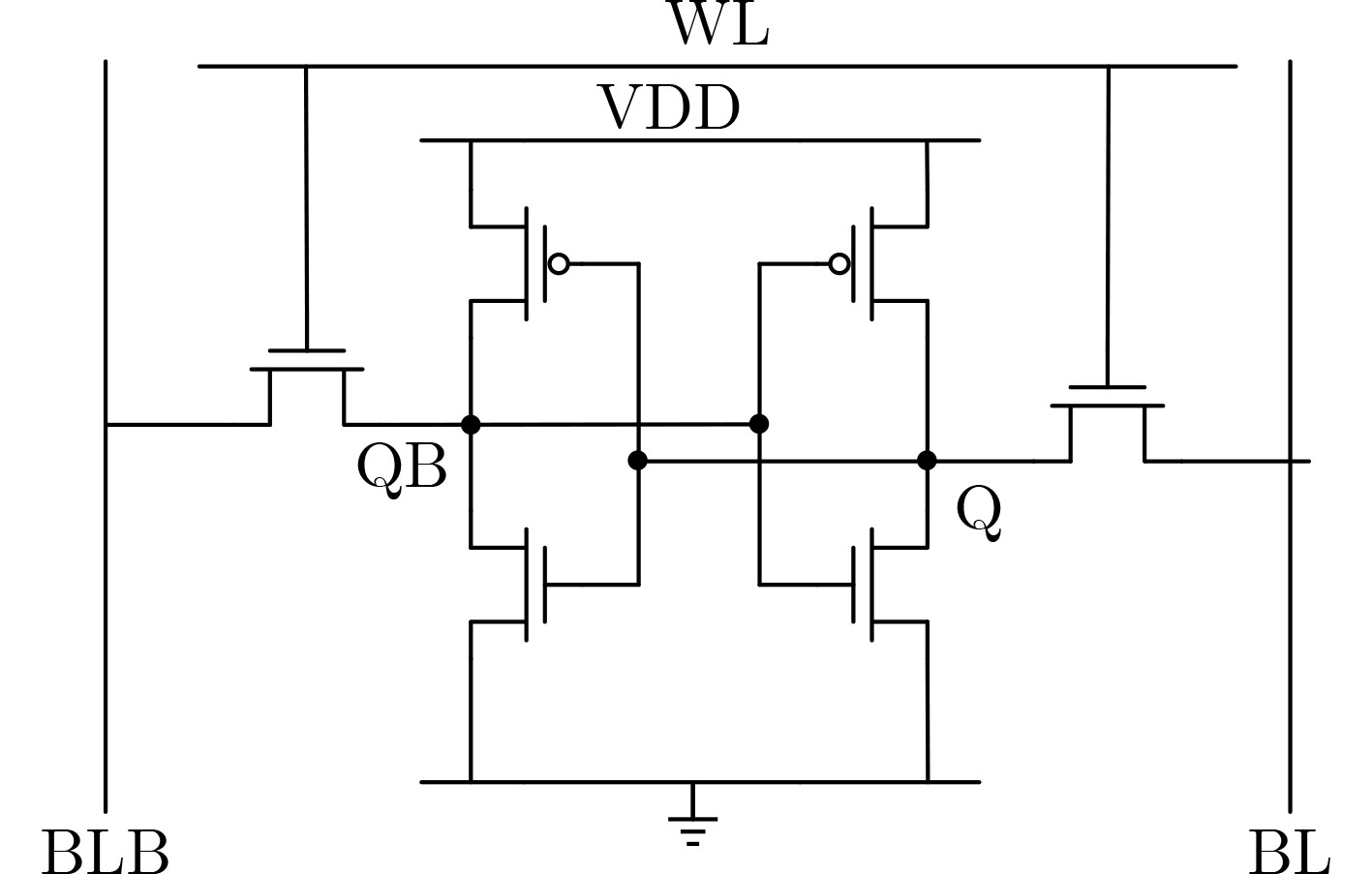
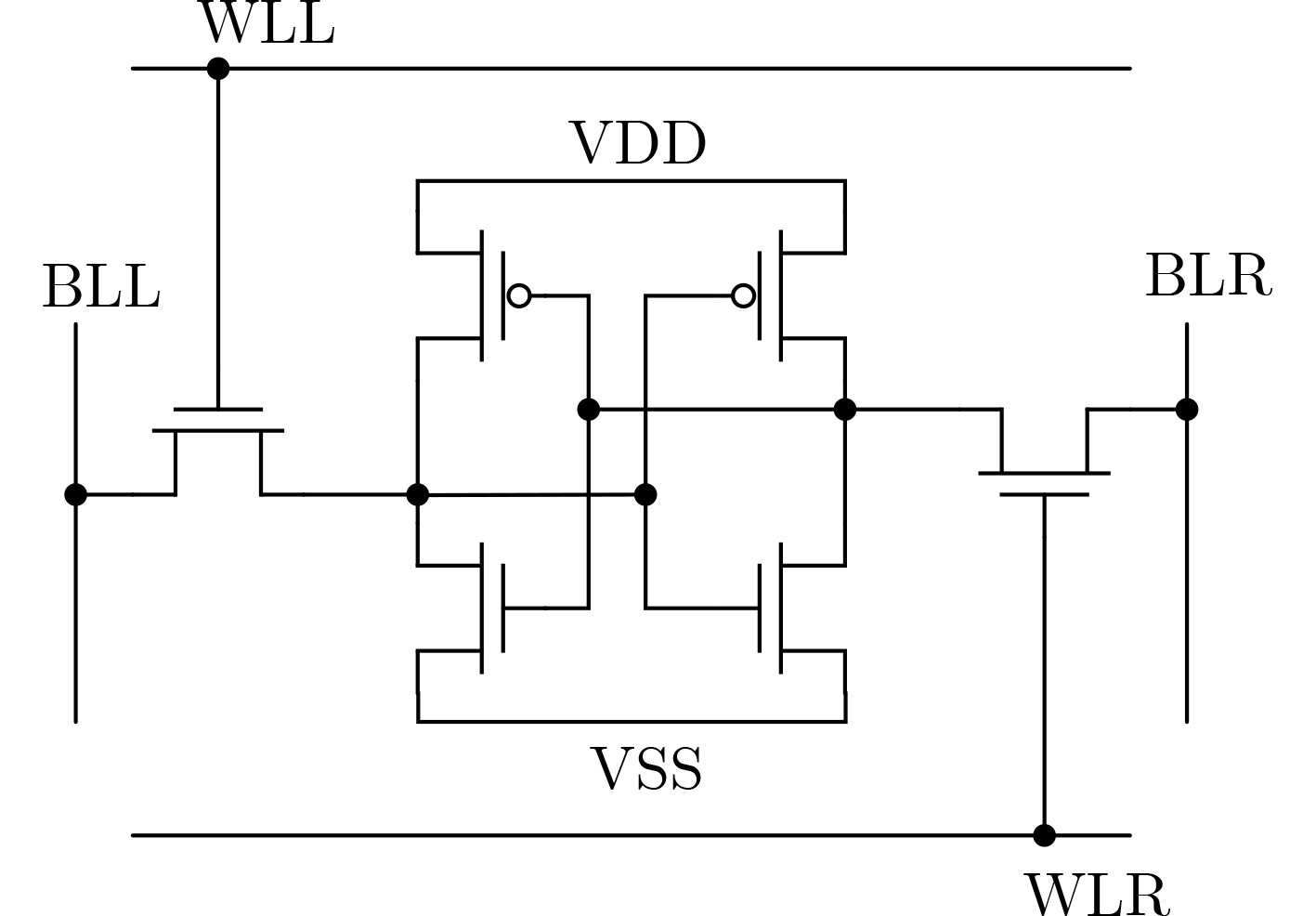


 下载:
下载:
