Auto-extraction of Building Outline with Multi-band Polarimetric SAR
-
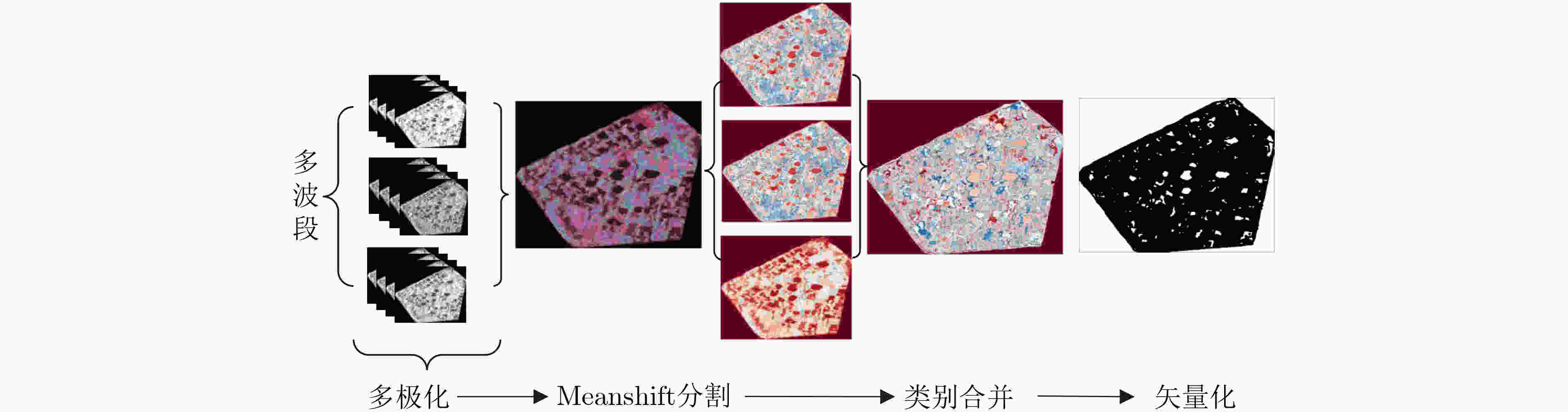
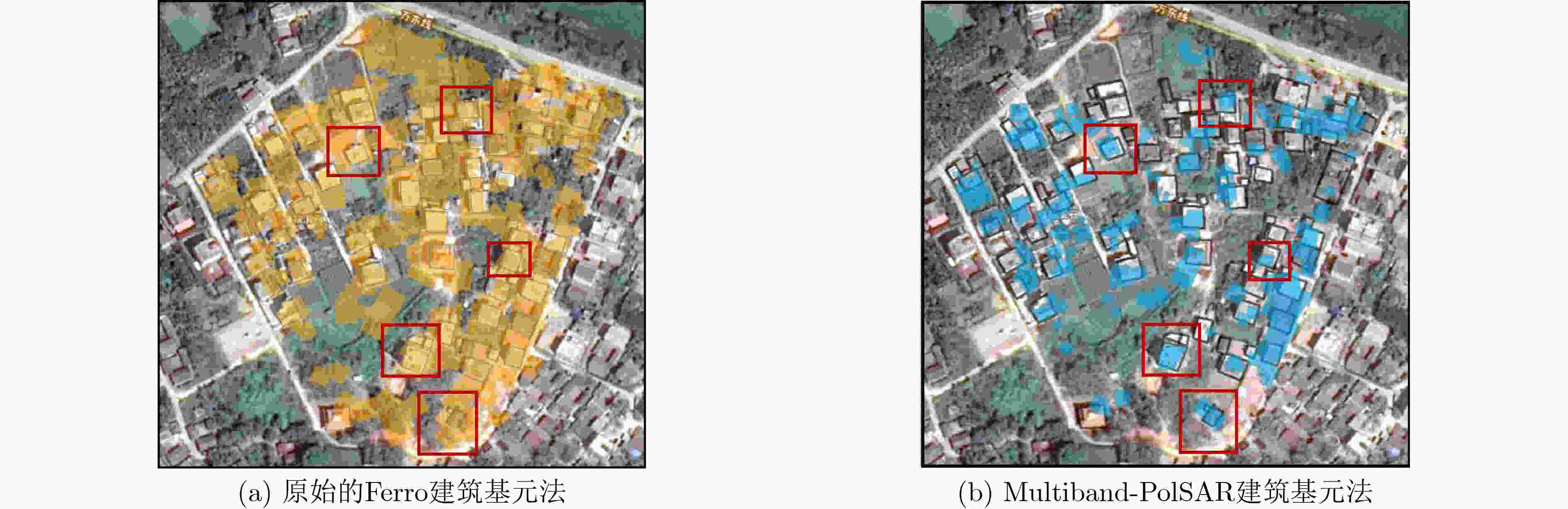
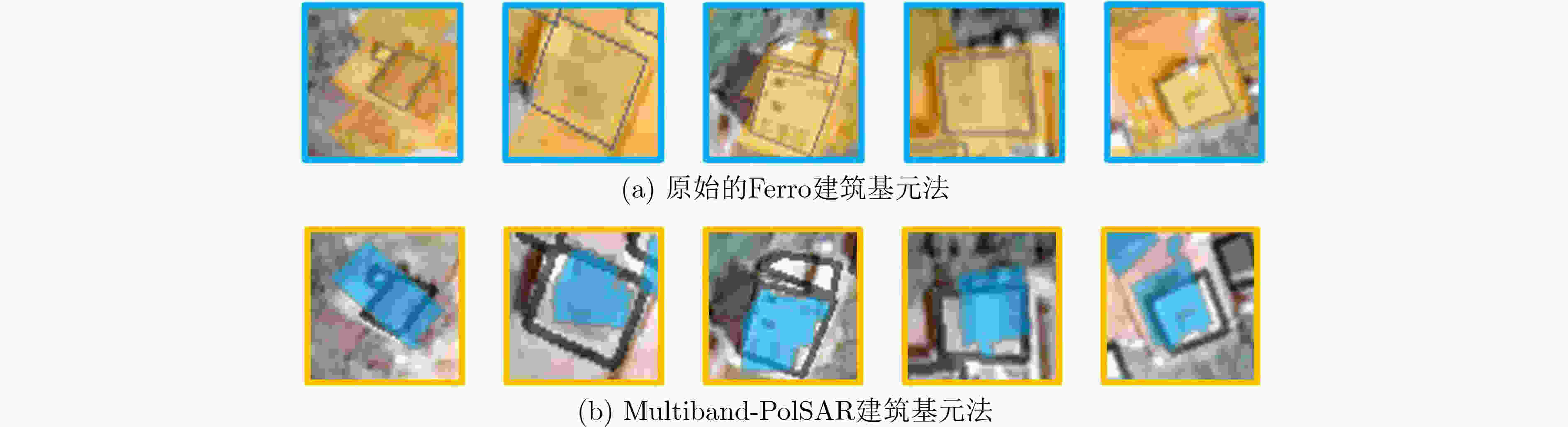
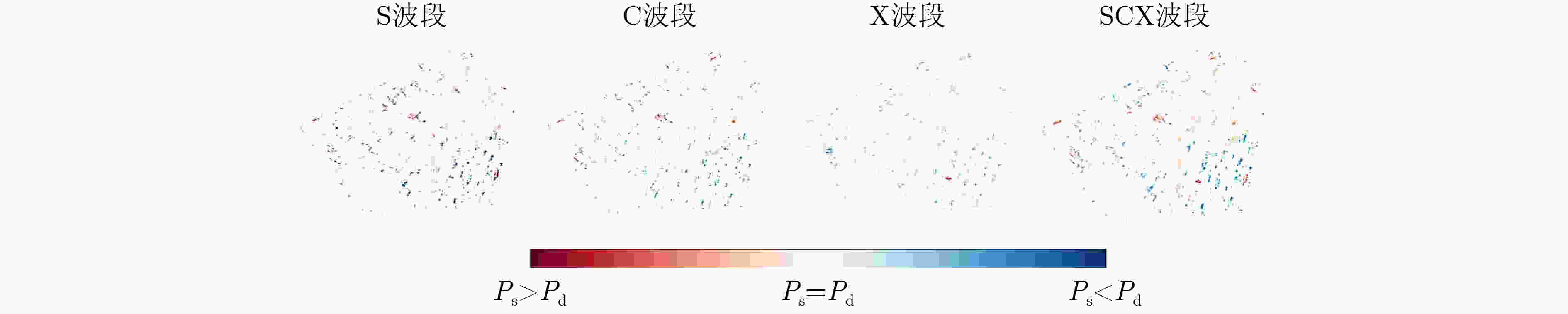
摘要: 多波段全极化合成孔径雷达(Multiband-PolSAR)可以获得地物目标在频率、极化两个维度上的多个观测量,在地物信息提取方面具有良好的应用潜力。然而数据维度增加,其数据处理和应用难度也随之增加,相较于处理单波段单极化SAR数据,处理Multiband-PolSAR数据需要额外考虑多维数据配准和融合的问题。该文选择以建筑轮廓自动提取应用为目标,依托中国科学院空天信息创新研究院在国家高分辨率观测系统重大专项支持下牵头研制的一部机载多维度SAR系统获得的数据,引入SAR-SIFT方法解决了多维数据配准的问题。其次,该文提出一种基于目标散射机制的多维信息融合方法,改进了Ferro 等人(doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2205156)提出的全自动非监督建筑轮廓提取方法,证明了多波段多极化信息融合方法的作用。多波段多极化信息融合前后的实验结果表明,融合后的特征图像对比度增高,像素的空间连续性变好,且对单体建筑轮廓的识别更精准,自动提取的多边形矢量与真实建筑轮廓的吻合度更高。该文是连接多维SAR技术与建筑提取应用的重要一环,并且为基于多维SAR的3维建筑结构重建研究创造了条件。Abstract: Multi-band Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (Multiband-PolSAR) has the capability to obtain multiple observations of ground objects in the two dimensions of frequency and polarization with potential applications in ground information extraction. However, SAR data dimension increase will result in more complex work for data processing and application. Compared with processing single-band single-polarization SAR data, multiband-PolSAR data requires additional consideration of Multiband-PolSAR data registration and fusion. The aim of this study is auto-extraction of building outline with the data obtained by an airborne Multiband-PolSAR system led by Chinese Academy of Sciences and supported by the National High-resolution Observation System Major Project. This study involves the SAR-SIFT method for registration, and proposes a fusion method based on scattering mechanism, to improve the automatic unsupervised building outline extraction method proposed by Ferro et al. (doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2205156), and then forms a new automatic building outline extraction method using Multiband-PolSAR images. The experimental results show that the fusion of multi-band and multi-polarization information will give rise to the contrast of feature image, the continuity of the adjacent pixels, and the accuracy of building extraction. This paper makes a bridge between Multiband-PolSAR technology and building extraction application. Moreover, this article creates conditions for the research on 3D building structure reconstruction by using Multiband-PolSAR data.
-
Key words:
- Polarimetric SAR (PolSAR) /
- Building outline /
- Auto-extraction /
- Multi-band
-
表 1 多维度SAR各个波段系统参数
参数 S C X 带宽Br(MHz) 300 560 500 采样率Fsr(MHz) 400 750 600 方位采样间隔Xbin(m) 0.221 0.443 0.443 距离采样间隔Rbin(m) 0.374 0.199 0.249 脉冲重复频率PRF 500 250 250 表 2 与验证数据对比,Multiband-PolSAR建筑基元法对提取建筑轮廓的精度提升
总数 >50%建筑
(数量/虚警率(%)/识别率(%))60%~90%建筑
(数量/虚警率(%)/识别率(%))Ferro建筑基元法 72 58/19.4/70.7 57/20.8/69.5 多维信息融合+建筑基元法 85 70/16.5/85.3 63/25.9/76.8 多维度聚类+建筑基元法 75 62/17.4/75.6 60/20.0/73.2 Multiband-PolSAR建筑基元法 81 72/11.1/87.8 68/16.7/80.9 -
[1] BRUNNER D, LEMOINE G, GREIDANUS H, et al. Radar imaging simulation for urban structures[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(1): 68–72. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2051214 [2] SUN Yao, MOU Lichao, WANG Yuanyuan, et al. Large-scale building height retrieval from single SAR imagery based on bounding box regression networks[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2022, 184: 79–95. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2021.11.024 [3] FERRO A, BRUNNER D, BRUZZONE L, et al. On the relationship between double bounce and the orientation of buildings in VHR SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(4): 612–616. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2097580 [4] WANG Ke, CHEN Jingyi, KIAGHADI A, et al. A new algorithm for land-cover classification using PolSAR and InSAR data and its application to surface roughness mapping along the gulf coast[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 4502915. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3083492 [5] FERRO A, BRUNNER D, and BRUZZONE L. Automatic detection and reconstruction of building radar footprints from single VHR SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(2): 935–952. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2205156 [6] WEGNER J D, ZIEHN J R, and SOERGEL U. Combining high-resolution optical and InSAR features for height estimation of buildings with flat roofs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(9): 5840–5854. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2293513 [7] MARIN C, BOVOLO F, and BRUZZONE L. Building change detection in multitemporal very high resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(5): 2664–2682. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2363548 [8] TAO Junyi and AUER S. Simulation-based building change detection from multiangle SAR images and digital surface models[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(8): 3777–3791. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2502762 [9] PIRRONE D, BOVOLO F, and BRUZZONE L. An approach to unsupervised detection of fully and partially destroyed buildings in multitemporal VHR SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 5938–5953. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3026838 [10] 仇晓兰, 程遥, 高铭, 等. 机载多维度SAR误差分析与成像自配准处理方法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2021, 19(5): 571–582. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2021.05.014QIU Xiaolan, CHENG Yao, GAO Ming, et al. Error analysis and auto-registration imaging method for airborne multidimensional space joint-observation SAR[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2021, 19(5): 571–582. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2021.05.014 [11] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 吴一戎. 全息合成孔径雷达的概念、体制和方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 399–408. doi: 10.12000/JR20063DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, and WU Yirong. Concept, system, and method of holographic synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 399–408. doi: 10.12000/JR20063 [12] GE Pinglan, GOKON H, and MEGURO K. A review on synthetic aperture radar-based building damage assessment in disasters[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020, 240: 111693. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.111693 [13] TURKAR V, DEO R, RAO Y S, et al. Classification accuracy of multi-frequency and multi-polarization SAR images for various land covers[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2012, 5(3): 936–941. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2012.2192915 [14] DELLINGER F, DELON J, GOUSSEAU Y, et al. SAR-SIFT: A SIFT-like algorithm for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(1): 453–466. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2323552 [15] LIU Chenguang, ABERGEL R, GOUSSEAU Y, et al. LSDSAR, a Markovian a contrario framework for line segment detection in SAR images[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 98: 107034. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.107034 [16] WANG Zezhong, ZENG Qiming, and JIAO Jian. An adaptive decomposition approach with dipole aggregation model for polarimetric SAR data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(13): 2583. doi: 10.3390/rs13132583 -





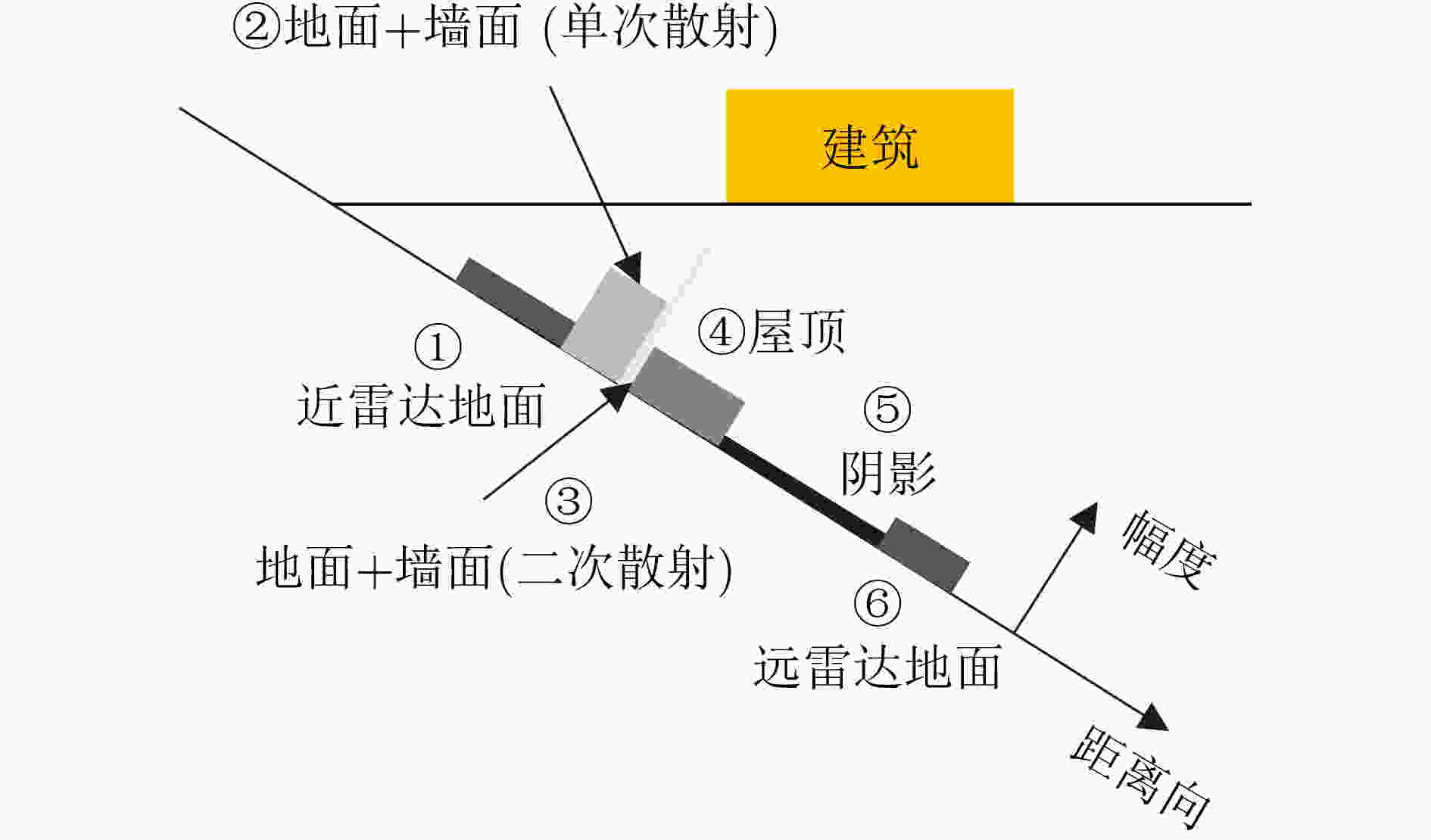
 下载:
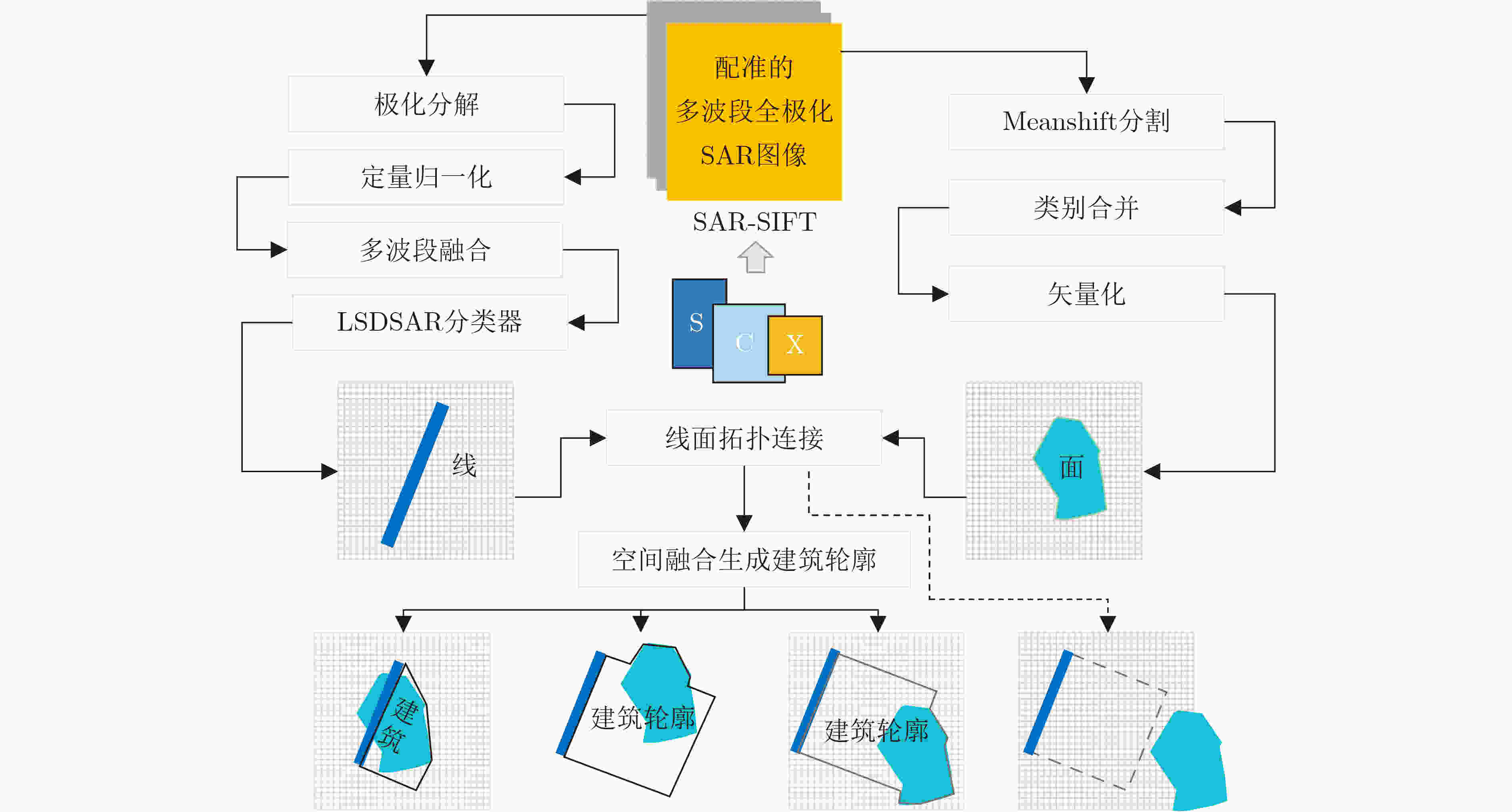
下载:
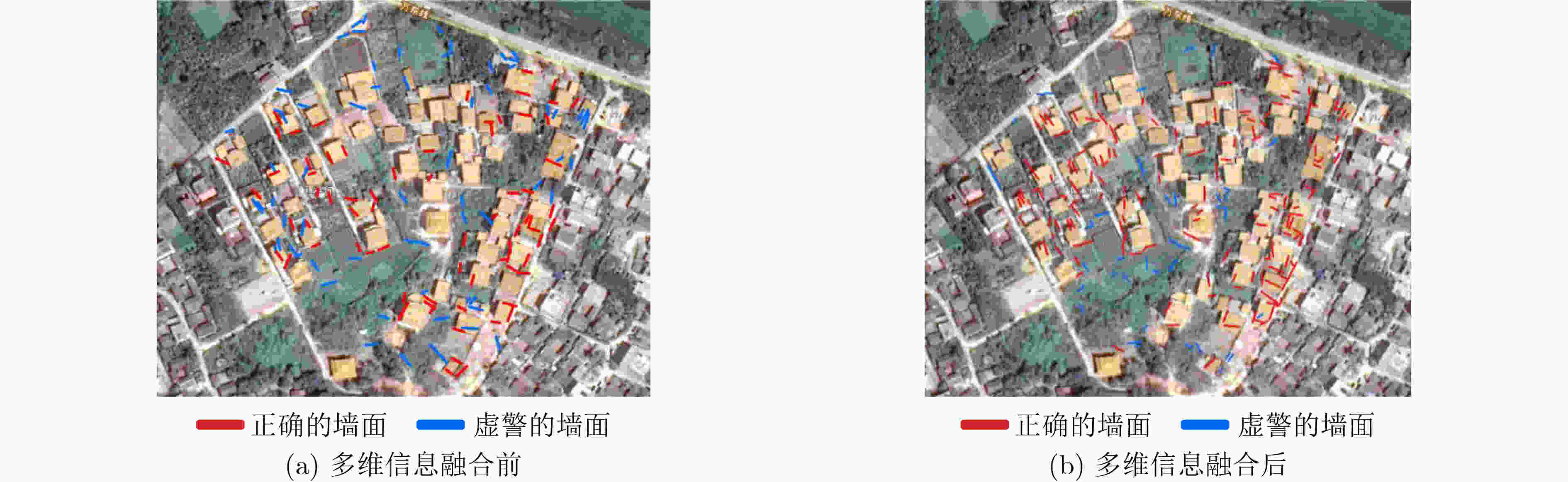
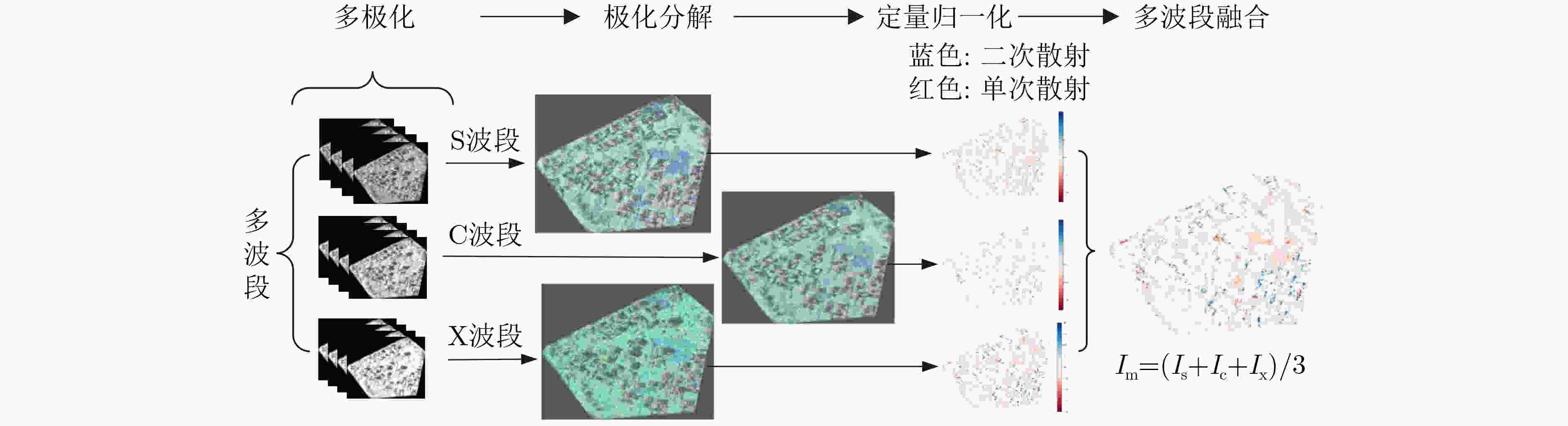

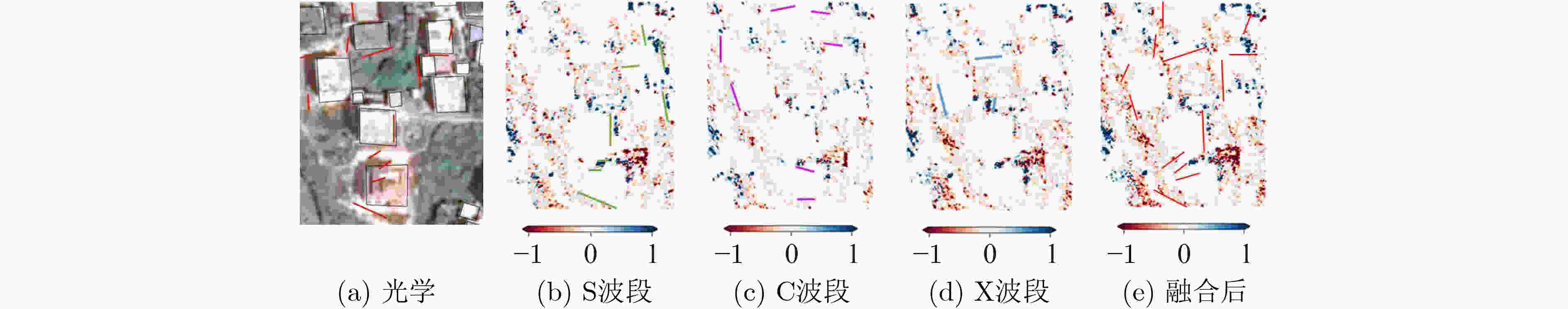
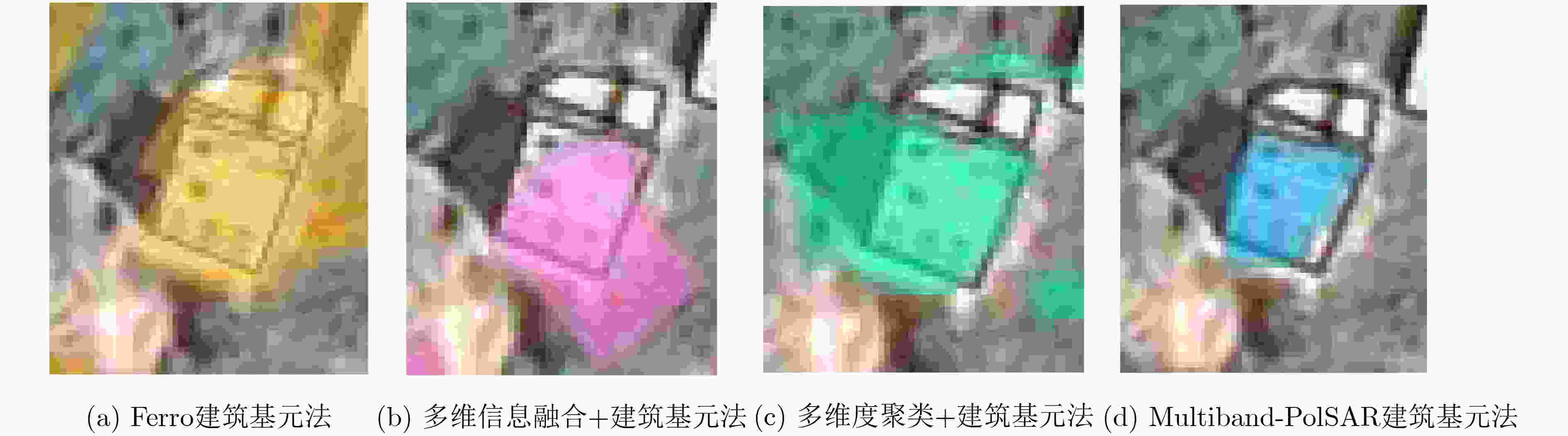


 下载:
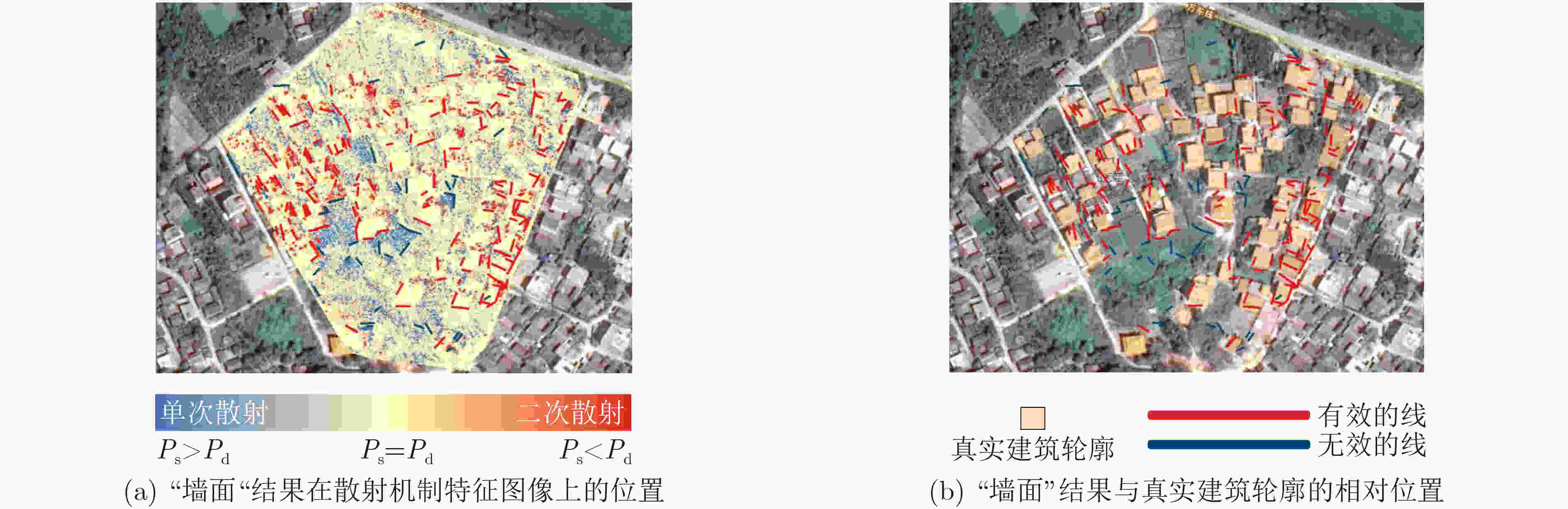
下载:
