Differential Analysis of the Initialization of MORUS Based on Mixed-Integer Linear Programming
-
摘要: 认证加密算法 MORUS是凯撒 (CAESAR)竞赛的优胜算法,抗差分分析性能是衡量认证加密算法安全性的重要指标之一。该文研究了MORUS算法初始化阶段的差分性质,首先给出了一个差分推导规则,可以快速获得一条概率较大的差分链。在此基础上利用混合整数线性规划(MILP)自动搜索技术求解更优的差分链。为了提高搜索速度,结合MORUS初始化阶段的结构特点给出了分而治之策略。根据$ \Delta {\text{IV}} $的重量、取值将MILP模型划分为多个子模型并证明了部分子模型的等价性,大大缩减了模型的求解时间,得到了MORUS初始化阶段1~6步状态更新的最优差分链。最后给出了简化版MORUS的差分-区分攻击,该文的结果较之前的工作有较大的提升。
-
关键词:
- 认证加密算法 /
- MORUS /
- 混合整数线性规划自动搜索 /
- 差分分析
Abstract: The authenticated encryption algorithm MORUS is one of the finalists of Competition on Authenticated Encryption: Security, Apllicability, and Robustness (CAESAR). The ability to resist differential analysis is one of the important indicators to evaluate the security of authenticated encryption algorithm. The differential property of the initialization of MORUS is researched in this paper. Firstly, a differential deduction rule is proposed to give fast a differential characteristic with a relatively high probability. Based on this, a better differential characteristic is given by using Mixed-Integer Linear Programming (MILP). To improve the efficiency of solving the MILP model, a Divide-and-Conquer approach is showed. According to the weight and value of $ \Delta {\text{IV}} $, the MILP model is divided to many sub-models. The most sub-models are proved to be equivalent, and this reduces dramatically the time to solve the model. The best differential characteristics are given with 1 to 6 state update functions in the initialization of MORUS. Finally, the differential-distinguish attack on the simplified versions of MORUS is showed. This paper improves the result of the previous related work. -
表 1 MORUS的参数设置(bit)
参数 MORUS-640-128 MORUS-1280-128 MORUS-1280-256 密钥长度 128 128 256 IV长度 128 128 128 状态大小 640 1280 1280 认证码长度 128 128 128 表 2 符号说明
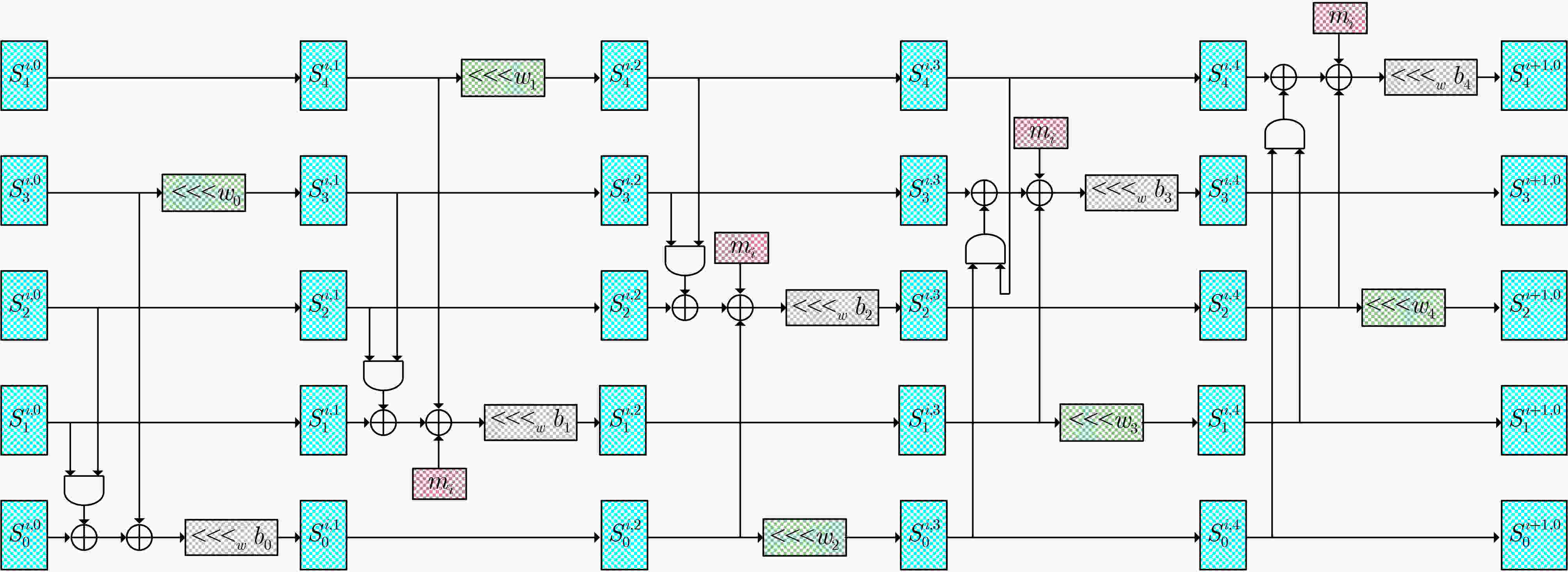
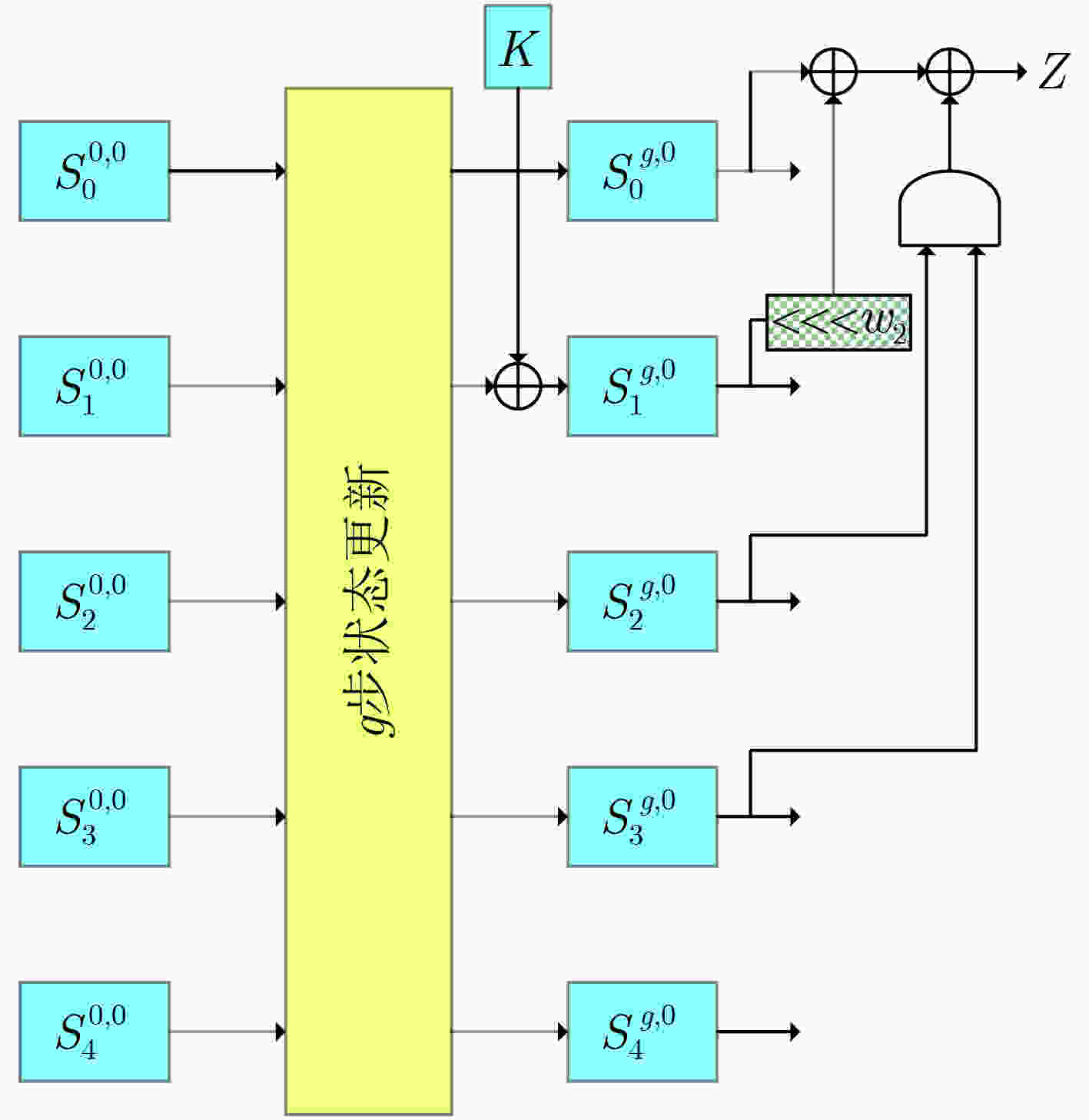
符号 说明 $ \oplus $ 逐比特异或; $ \& $ 逐比特与; <<< 循环左移; $ {0^l} $ $ l $ bit 0; $ {1^l} $ $ l $ bit 1; $ {\text{cons}}{{\text{t}}_{\text{0}}} $ $ 00||01||01||02||03||05||08||0d||15||22||37||59||90||e9||79||62 $; $ {\text{cons}}{{\text{t}}_{\text{1}}} $ $ db||3d||18||55||6d||c2||2f||f1||20||11||31||42||73||b5||28||dd $; $ {S^i} $ 第$ i $步输入状态; $ {S^{i,j}} $ 第$ i $步第$ j $轮输入状态; $ S_k^{i,j} $ $ {S^{i,j}} $第$ k $个bit块,对于MORUS-640,每个状态包含5个128 bit块,对于MORUS-1280,每个状态包含5个256 bit块; $ S_{k,l}^{i,j} $ $ S_k^{i,j} $的第$ l $ bit。 表 3 循环常数
MORUS-640 MORUS-1280 MORUS-640 MORUS-1280 $ {b_0} $ 5 13 $ {w_0} $ 32 64 $ {b_1} $ 31 46 $ {w_1} $ 64 128 $ {b_2} $ 7 38 $ {w_2} $ 96 192 $ {b_3} $ 22 7 $ {w_3} $ 64 128 $ {b_4} $ 13 4 $ {w_4} $ 32 64 表 4 MORUS初始化阶段差分转移概率
状态更新步数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 MORUS-640 $ {2^{ - 1}} $ $ {2^{ - 8}} $ $ {2^{ - 29}} $ $ {2^{ - 82}} $ $ {2^{ - 180}} $ $ {2^{ - 301}} $ $ {2^{ - 453}} $ MORUS-1280 $ {2^{ - 1}} $ $ {2^{ - 8}} $ $ {2^{ - 29}} $ $ {2^{ - 86}} $ $ {2^{ - 201}} $ $ {2^{ - 399}} $ $ {2^{ - 681}} $ 表 5 MORUS初始化阶段的初始状态差分$ \Delta {S^{0,0}} $
MORUS-640 MORUS-1280 $ \Delta S_0^{0,0} $ ${{\Delta {\rm{IV}}} }$ ${{\Delta {\rm{IV}}} }||{0^{128} }$ $ \Delta S_1^{0,0} $ $ {0^{128}} $ $ {0^{256}} $ $ \Delta S_2^{0,0} $ $ {0^{128}} $ $ {0^{256}} $ $ \Delta S_3^{0,0} $ $ {0^{128}} $ $ {0^{256}} $ $ \Delta S_4^{0,0} $ $ {0^{128}} $ $ {0^{256}} $ 表 6 MORUS初始化阶段第5轮状态更新的输入差分$ \Delta {S^{0,4}} $
MORUS-640 MORUS-1280 $ \Delta S_0^{0,4} $ ${\text{Rot\_128\_32(} }\Delta {\rm{IV}},{b_0}) < << {w_2}$ ${\text{Rot\_256\_64(} }\Delta {\rm{IV}}||{0^{128} },{b_0}) < << {w_2}$ $ \Delta S_1^{0,4} $ $ {0^{128}} $ $ {0^{256}} $ $ \Delta S_2^{0,4} $ ${\text{Rot\_128\_32(} }\Delta {\rm{IV}},{b_0} + {b_2})$ ${\text{Rot\_256\_64(} }\Delta {\rm{IV}}||{0^{128} },{b_0} + {b_2})$ $ \Delta S_3^{0,4} $ $ {\text{Rot\_128\_32}}(\Delta S_0^{0,4}\& (S_4^{0,0} < < < {w_1}),{b_3}) $ $ {\text{Rot\_256\_64}}(\Delta S_0^{0,4}\& (S_4^{0,0} < < < {w_1}),{b_3}) $ $ \Delta S_4^{0,4} $ $ {0^{128}} $ $ {0^{256}} $ 表 7 MORUS子轮函数两种刻画方式的比较
刻画方式 (2)+(3) (4) 变量个数 $ 3Rn $ $ Rn $ 不等式个数 $ 2Rn $ $ 4Rn $ 表 8 ${\varOmega _1}$, ${\varOmega _2}$的分类个数
MORUS-640 MORUS-1280 ${\varOmega _1}$ 2 2 ${\varOmega _2}$ 257 382 算法1 基于MILP分而治之策略搜索MORUS初始化阶段差分链 输入:$ R $ 输出:$ {\text{Sol}}({\mathcal{M}_R}) $ 步骤1 根据第3节的差分推导规则,计算$ {\text{U}}{{\text{B}}_R} $的初始值,令
$ i = 0 $;步骤2 令$ i = i + 1 $; 步骤3 计算$ {\text{LB}}(\mathcal{M}\left( i \right)) $,如果${\text{LB} }(\mathcal{M}\left( i \right)) \ge {\text{U} }{ {\text{B} }_R}$,返回步骤2,
否则,执行步骤4;步骤4 求解$ {\text{Sol}}(\mathcal{M}\left( i \right)) $,如果$ {\text{Sol}}(\mathcal{M}\left( i \right)) < {\text{U}}{{\text{B}}_R} $,令
$ {\text{U}}{{\text{B}}_R} = {\text{Sol}}(\mathcal{M}\left( i \right)) $;步骤5 如果$ i = |{\text{Set}}| $,输出$ {\text{U}}{{\text{B}}_R} $,否则,返回步骤2。 表 9 MILP模型中MORUS初始化阶段的最优差分转移概率
状态更新步数 1 2 3 4 5 6 MORUS-640 $ {2^{ - 1}} $ $ {2^{ - 8}} $ $ {2^{ - 29}} $ $ {2^{ - 82}} $ $ {2^{ - 179}} $ $ {2^{ - 279}} $ MORUS-1280 $ {2^{ - 1}} $ $ {2^{ - 8}} $ $ {2^{ - 29}} $ $ {2^{ - 86}} $ $ {2^{{\text{ - 201}}}} $ $ {2^{ - 379}} $ 表 10 简化版MORUS差分-区分攻击的差分转移概率
表 11 简化版MORUS的差分-区分攻击
算法 状态更新步数 差分转移概率 数据量 区分优势 MORUS-640 3 $ {2^{ - 32}} $ $ {2^{35}} $ 0.999665 4 $ {2^{ - 89}} $ $ {2^{92}} $ 0.999665 MORUS-1280 4 $ {2^{ - 91}} $ $ {2^{94}} $ 0.999665 5 $ {2^{ - 207}} $ $ {2^{210}} $ 0.999665 -
[1] BELLARE M and NAMPREMPRE C. Authenticated encryption: Relations among notions and analysis of the generic composition paradigm[J]. Journal of Cryptology, 2008, 21(4): 469–491. doi: 10.1007/s00145-008-9026-x [2] BERNSTEIN DJ. CAESAR call for submissions[EB/OL]. http://competitions:cr:yp:to/caesar-call.html, 2014. [3] LAWRENCE B. Submission requirements and evaluation criteria for the lightweight cryptography standardization process[EB/OL].https://csrc.nist.gov/projects/lightweight-cryptography, 2018. [4] SAHA D, SADAKI Y, SHI Danping, et al. On the security margin of TinyJAMBU with refined differential and linear cryptanalysis[J]. IACR Transactions on Symmetric Cryptology, 2020, 2020(3): 152–174. doi: 10.13154/tosc.v2020.i3.152-174 [5] SONG Ling, TU Yi, SHI Danping, et al. Security analysis of Subterranean 2.0[J]. Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 2021, 89(8): 1875–1905. doi: 10.1007/s10623-021-00892-6 [6] ZHOU Haibo, LI Zheng, DONG Xiaoyang, et al. Practical key-recovery attacks on round-reduced Ketje Jr, Xoodoo-AE and Xoodyak[J]. The Computer Journal, 2020, 63(8): 1231–1246. doi: 10.1093/comjnl/bxz152 [7] LIU Shuai, GUAN Jie, and HU Bin. Fault attacks on authenticated encryption modes for GIFT[J]. IET Information Security, 2022, 16(1): 51–63. doi: 10.1049/ise2.12041 [8] MATSUI M. On correlation between the order of S-boxes and the strength of DES[C]. The Workshop on the Theory and Application of of Cryptographic Techniques, Perugia, Italy, 1995: 366–375. [9] 叶涛, 韦永壮, 李灵琛. ACE密码算法的积分分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(4): 908–914. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200234YE Tao, WEI Yongzhuang, and LI Lingchen. Integral cryptanalysis of ACE encryption algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(4): 908–914. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200234 [10] SHI Danping, SUN Siwen, DERBEZ P, et al. Programming the Demirci-Selcuk meet-in-the-middle attack with constraints[C]. The 24th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Brisbane, Australia, 2018: 3–34. [11] HU Kai, SUN Siwei, TODO Y, et al. Massive superpoly recovery with nested monomial predictions[C]. The 27th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Singapore, 2021: 392–421. [12] SASAKI Y and TODO Y. New algorithm for modeling S-box in MILP based differential and division trail search[C]. The 10th International Conference for Information Technology and Communications, Bucharest, Romania, 2017: 150–165. [13] SUN Siwei, HU Lei, WANG Peng, et al. Automatic security evaluation and (related-key) differential characteristic search: Application to SIMON, PRESENT, LBlock, DES(L) and other bit-oriented block ciphers[C]. The 20th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Kaoshiung, China, 2014: 158–178. [14] ZHOU Chunning, ZHANG Wentao, DING Tianyou, et al. Improving the MILP-based security evaluation algorithm against differential/linear cryptanalysis using a divide-and-conquer approach[J]. IACR Transactions on Symmetric Cryptology, 2019, 2019(4): 438–469. doi: 10.13154/tosc.v2019.i4.438-469 [15] WU Hongjun and HUANG Tao. The authenticated cipher MORUS (v2)[EB/OL]. http://competitions.cr.yp.to/caesar-submissions.html, 2014. [16] 张沛, 关杰, 李俊志, 等. MORUS算法初始化过程的混乱与扩散性质研究[J]. 密码学报, 2015, 2(6): 536–548. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000100ZHANG Pei, GUAN Jie, LI Junzhi, et al. Research on the confusion and diffusion properties of the initialization of MORUS[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2015, 2(6): 536–548. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000100 [17] 施泰荣, 关杰, 李俊志, 等. 故障模型下MORUS算法的差分扩散性质研究[J]. 软件学报, 2018, 29(9): 2861–2873. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005282SHI Tairong, GUAN Jie, LI Junzhi, et al. Research on differential diffusion property of MORUS in fault model[J]. Journal of Software, 2018, 29(9): 2861–2873. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005282 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
