Linear Superposition Analysis of HP Memristor Circuits
-
摘要: 基于惠普(HP)忆阻器的元件特性,该文分析了惠普忆阻器的数学关系式,惠普忆阻元件的内部状态变量与忆阻阻值之间存在增量线性关系,在外加电压下惠普忆阻器阻值的变化可叠加,得出了惠普忆阻电路具有线性叠加性的结论。通过PSpice电路仿真验证上述结论的有效性和正确性,为叠加定理在含惠普忆阻器及线性元件的线性电路中的使用提供了理论分析支撑。Abstract: Based on the component characteristics of Hewlett Packard(HP) memristor, the mathematical relationship formula of HP memristor is analyzed. There is an incremental linear relationship between the internal state variables of HP memristor components and the value of memristor. The change of the value of HP memristor can be superimposed under applied voltage, and the conclusion is drawn that HP memristor circuit has linear superposition. The validity and correctness of the above conclusions are verified by PSpice circuit simulation, which provides theoretical analysis support for the use of the superposition theorem in linear circuits containing HP memristors and linear components.
-
表 1 直流电压下忆阻电路的输出电压值(V)
时间(ms) Vout1 Vout2 V测量 V计算 0 –0.505 –0.632 –1.136 –1.137 5 –0.516 –0.650 –1.166 –1.166 10 –0.529 –0.671 –1.199 –1.200 15 –0.543 –0.696 –1.239 –1.239 20 –0.560 –0.726 –1.285 –1.286 25 –0.579 –0.762 –1.340 –1.341 30 –0.601 –0.806 –1.406 –1.407 35 –0.627 –0.860 –1.486 –1.487 40 –0.657 –0.930 –1.587 –1.587 45 –0.694 –1.021 –1.715 –1.715 50 –0.739 –1.145 –1.884 –1.884 表 2 方波电压下忆阻电路的输出电压值(V)
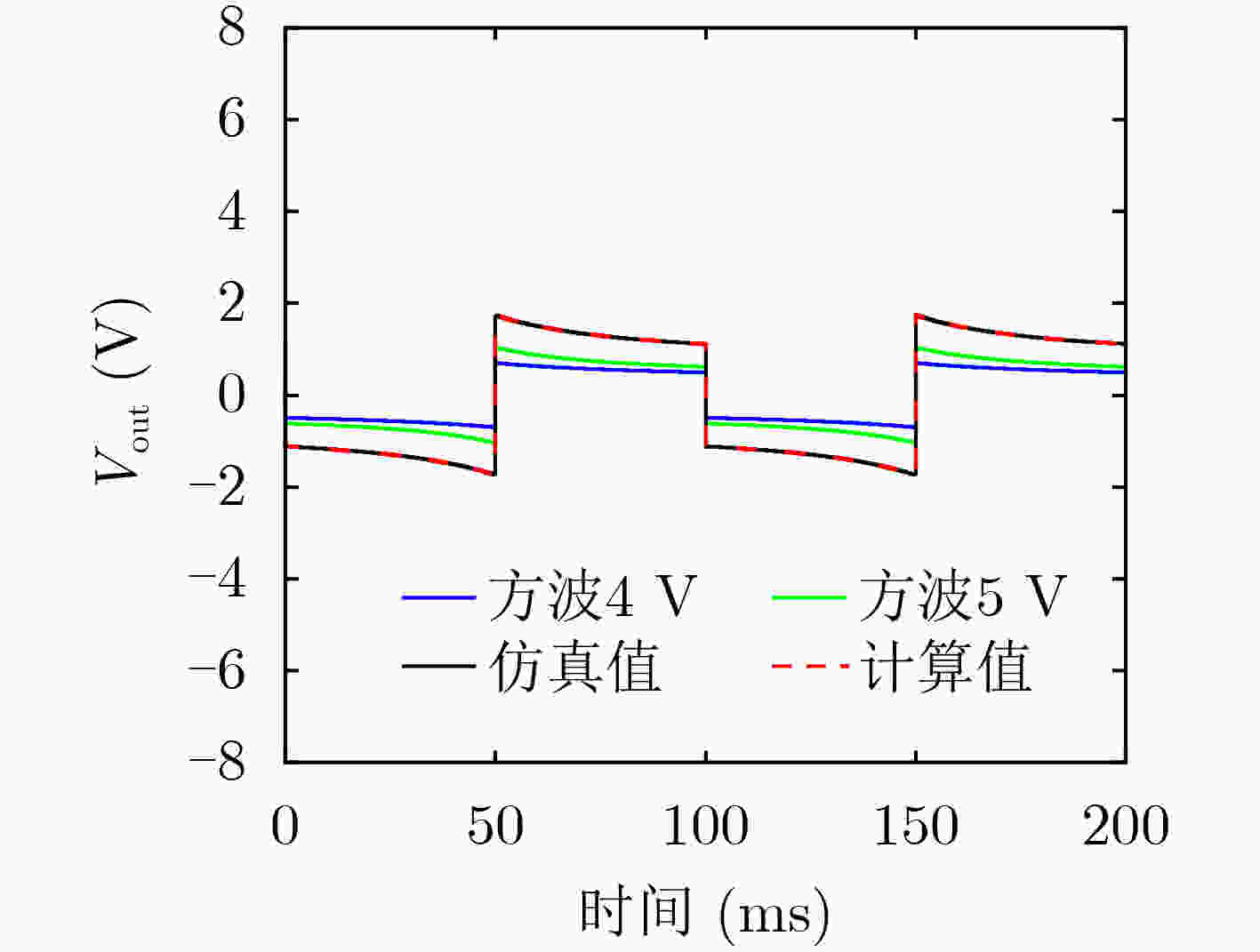
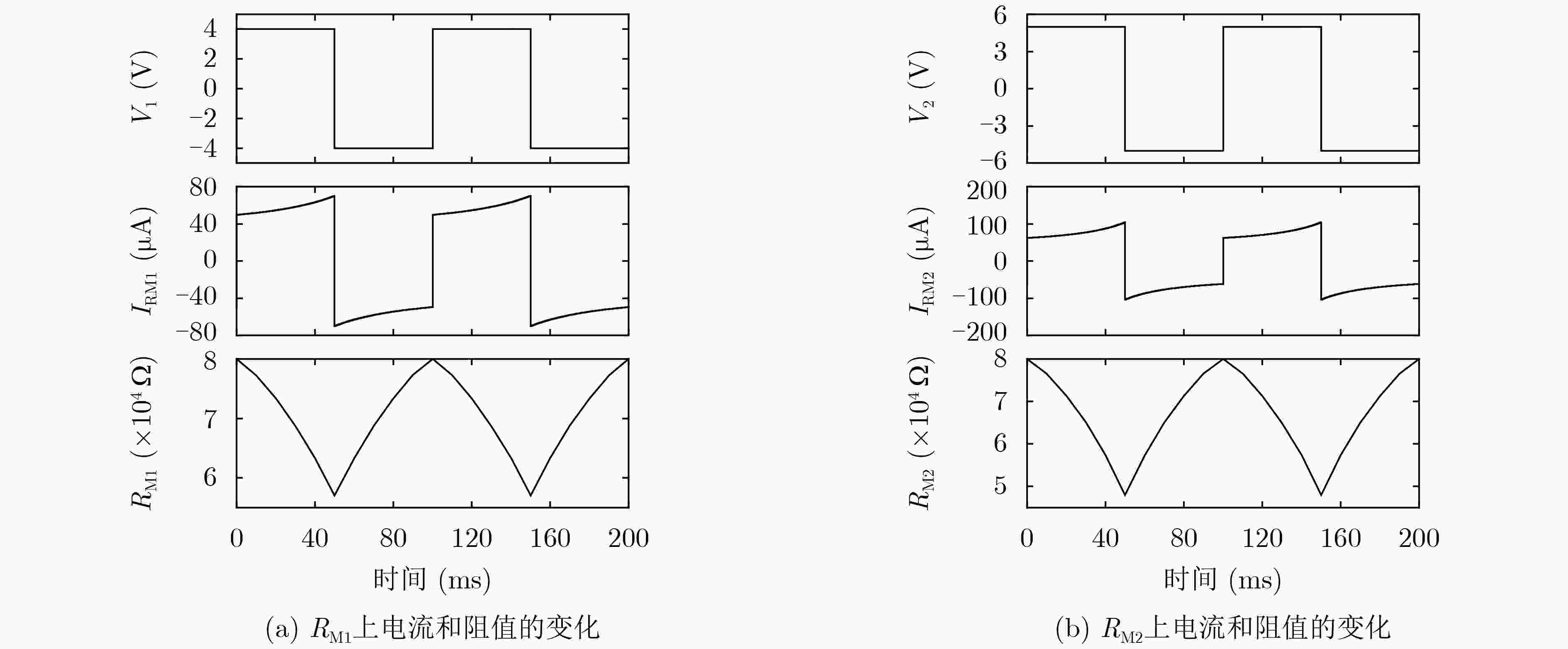
时间(ms) Vout1 Vout2 V测量 V计算 0 0.495 0.618 1.114 1.113 10 –0.518 –0.654 –1.172 –1.172 20 –0.546 –0.701 –1.247 –1.247 30 –0.583 –0.769 –1.351 –1.352 40 –0.632 –0.873 –1.504 –1.505 50 –0.702 –1.042 –1.744 –1.744 60 0.631 0.871 1.503 1.502 70 0.581 0.768 1.350 1.349 80 0.545 0.700 1.246 1.245 90 0.517 0.653 1.170 1.170 100 0.496 0.618 1.115 1.114 表 3 正弦波电压下忆阻电路的输出电压值(V)
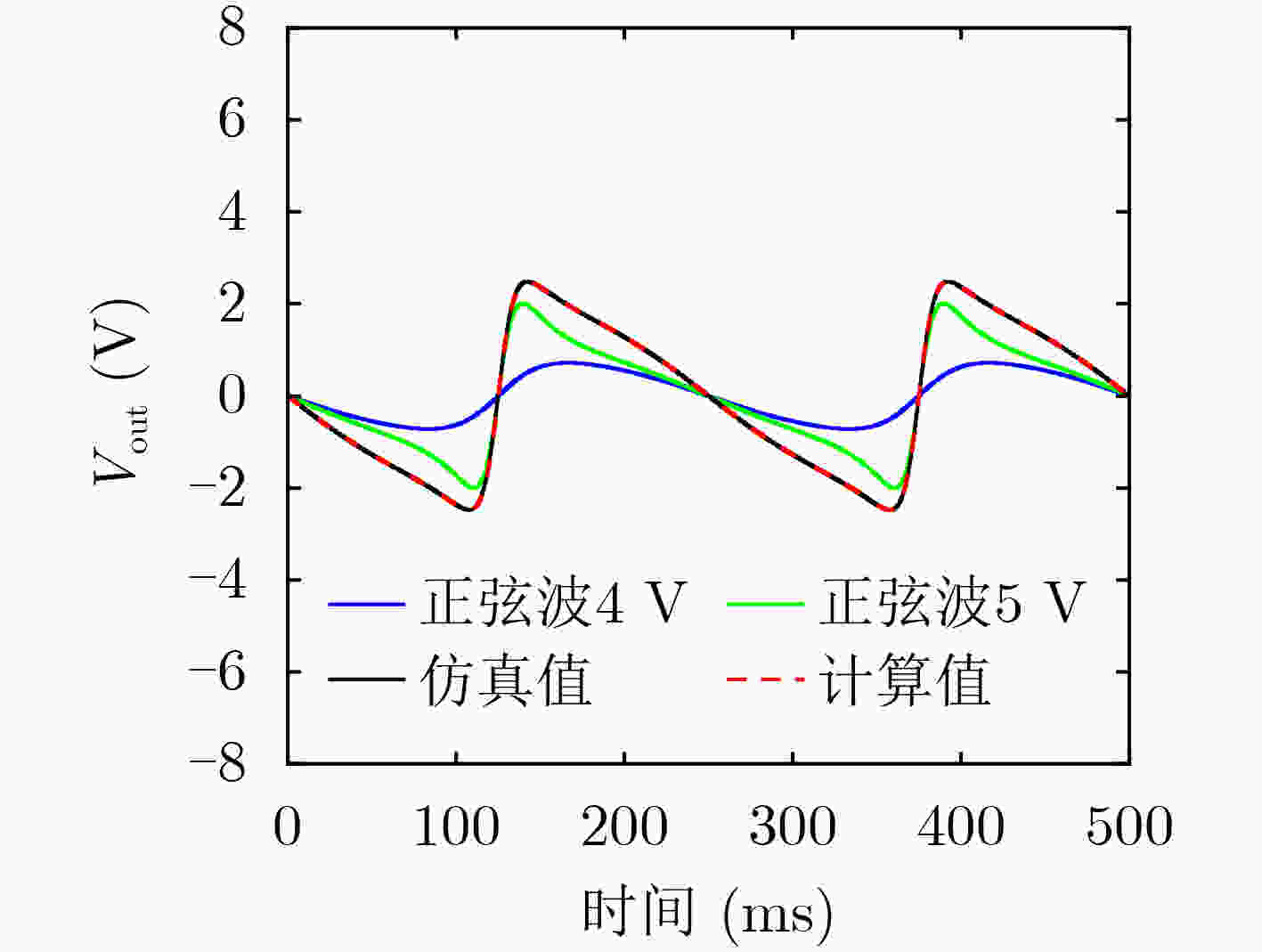
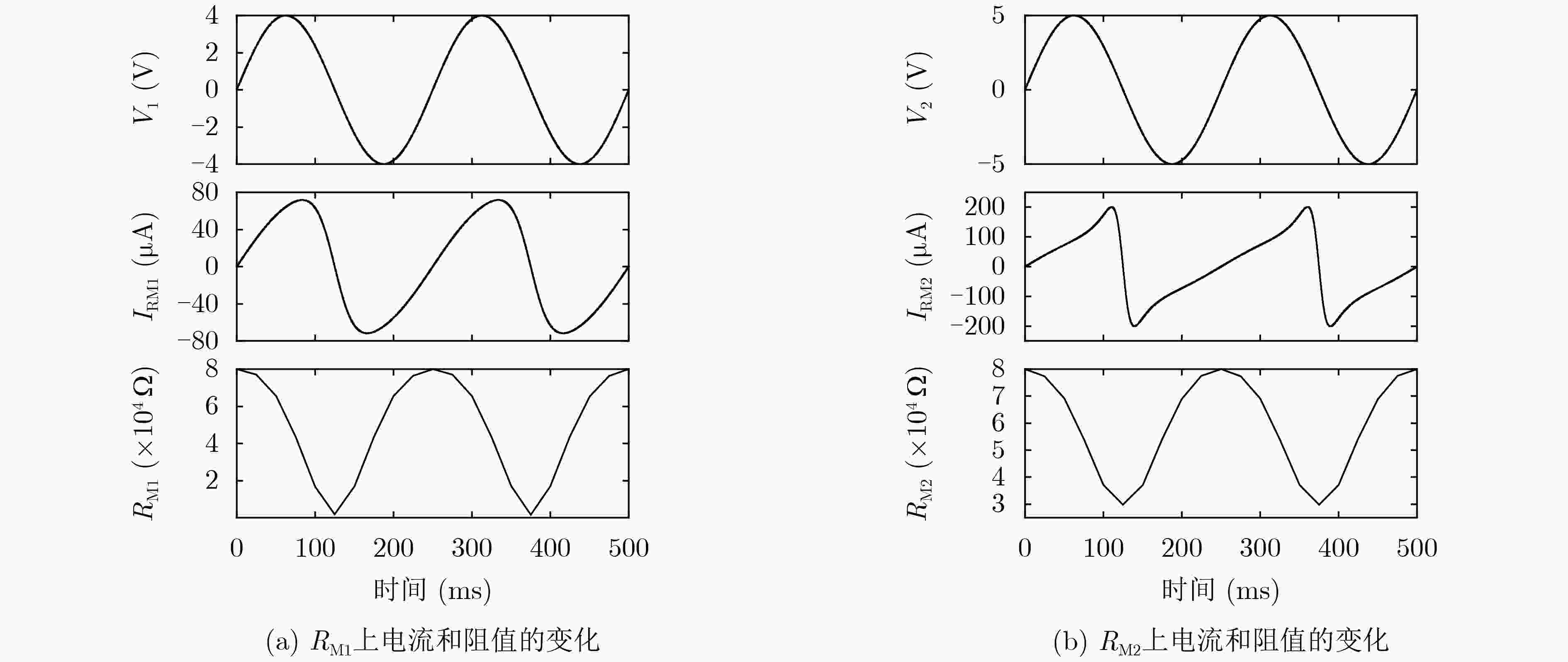
时间(ms) Vout1 Vout2 V测量 V计算 0 0 0 0 0 25 –0.305 –0.384 –0.688 –0.689 50 –0.552 –0.728 –1.280 –1.280 75 –0.703 –1.090 –1.793 –1.793 100 –0.632 –1.735 –2.366 –2.367 125 0 0 0 0 150 0.631 1.732 2.364 2.363 175 0.702 1.088 1.790 1.790 200 0.551 0.726 1.277 1.277 225 0.303 0.382 0.685 0.685 250 0 0 0 0 -
[1] CHUA L O. Memristor-the missing circuit element[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuit Theory, 1971, 18(5): 507–519. doi: 10.1109/TCT.1971.1083337 [2] STRUKOV D B, SNIDER G S, STEWART D R, et al. The missing memristor found[J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7191): 80–83. doi: 10.1038/nature06932 [3] TOUR J M and HE Tao. Electronics: The fourth element[J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7191): 42–43. doi: 10.1038/453042a [4] 王小平, 沈轶, 吴计生, 等. 忆阻及其应用研究综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(8): 1170–1184. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01170WANG Xiaoping, SHEN Yi, WU Jisheng, et al. Review on memristor and its applications[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(8): 1170–1184. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01170 [5] YANG J J, PICKETT M D, LI Xuema, et al. Memristive switching mechanism for metal/oxide/metal nanodevices[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2008, 3(7): 429–433. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2008.160 [6] SHIMA H and TAMAI Y. Oxide nanolayer improving RRAM operational performance[J]. Microelectronics Journal, 2009, 40(3): 628–632. doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2008.06.096 [7] LI Can, GRAVES C E, SHENG Xia, et al. Analog content-addressable memories with memristors[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1638. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15254-4 [8] 孙晶茹, 李梦圆, 康可欣, 等. 基于异构忆阻器的1T2M多值存储交叉阵列设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(6): 1533–1540. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201108SUN Jingru, LI Mengyuan, KANG Kexin, et al. Design of heterogeneous memristor based 1T2M multi-value memory crossbar array[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(6): 1533–1540. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201108 [9] ALI K A, RIZK M, BAGHDADI A, et al. Crossbar memory architecture performing memristor overwrite logic[C]. 2019 26th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), Genoa, Italy, 2019: 723–726. [10] LUO Li, DONG Zhekang, DUAN Shukai, et al. Memristor-based stateful logic gates for multi-functional logic circuit[J]. IET Circuits, Devices & Systems, 2020, 14(6): 811–818. doi: 10.1049/iet-cds.2019.0422 [11] 闵富红, 王珠林, 王恩荣, 等. 新型忆阻器混沌电路及其在图像加密中的应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(10): 2681–2688. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160178MIN Fuhong, WANG Zhulin, WANG Enrong, et al. New Memristor chaotic circuit and its application to image encryption[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(10): 2681–2688. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160178 [12] 马铭磷, 刘颖, 李志军. 忆阻开关混沌电路及其吸引子共存现象研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(12): 3758–3765. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200689MA Minglin, LIU Ying, and LI Zhijun. Study on coexistence of Multipe attractors in memristor-based switching chaotic circuits[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(12): 3758–3765. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200689 [13] 瞿少成, 陈尧, 罗静, 等. 一种单输入控制器下的忆阻混沌同步电路设计与实现[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 400–407. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200947QU Shaocheng, CHEN Yao, LUO Jing, et al. Design and implementation of Memristor-based chaotic synchronization under a single input controller[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 400–407. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200947 [14] 王春华, 蔺海荣, 孙晶如, 等. 基于忆阻器的混沌、存储器及神经网络电路研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 795–810. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190821WANG Chunhua, LIN Hairong, SUN Jingru, et al. Research progress on chaos, memory and neural network circuits based on memristor[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 795–810. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190821 [15] ZHOU Chao, WANG Chunhua, SUN Yichuang, et al. Weighted sum synchronization of memristive coupled neural networks[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 403: 211–233. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.04.087 [16] LIN Hairong, WANG Chunhua, HONG Qinghui, et al. A multi-stable memristor and its application in a neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2020, 67(12): 3472–3476. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2020.3000492 [17] YANG Le, ZENG Zhigang, HUANG Yi, et al. Memristor-based circuit implementations of recognition network and recall network with forgetting stages[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2018, 10(4): 1133–1142. doi: 10.1109/TCDS.2018.2859303 [18] YANG Le, ZENG Zhigang, and WEN Shiping. A full-function Pavlov associative memory implementation with memristance changing circuit[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 272: 513–519. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.07.020 [19] HONG Qinghui, YAN Renao, WANG Chunhua, et al. Memristive circuit implementation of biological nonassociative learning mechanism and its applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 2020, 14(5): 1036–1050. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2020.3018777 [20] ZHANG Yutong and ZENG Zhigang. A Multi-functional memristive Pavlov associative memory circuit based on neural mechanisms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 2021, 15(5): 978–993. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2021.3108354 [21] ADHIKARI S P, YANG Changju, KIM H, et al. Memristor bridge synapse-based neural network and its learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2012, 23(9): 1426–1435. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2204770 [22] WILLIAMS R S. How we found the missing memristor[J]. IEEE Spectrum, 2008, 45(12): 28–35. doi: 10.1109/MSPEC.2008.4687366 [23] 龙际磊. 线性电路的分析方法[J]. 电脑知识与技术, 2014, 10(23): 5543–5545. doi: 10.14004/j.cnki.ckt.2014.0214LONG Jilei. Analysis of linear circuits[J]. Computer Knowledge and Technology, 2014, 10(23): 5543–5545. doi: 10.14004/j.cnki.ckt.2014.0214 [24] 彭军. “纯电阻元件”与“线性元件”概念讨论[J]. 物理通报, 2017(8): 101–103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0509-4038.2017.08.033PENG Jun. Discussion on the concepts of pure resistance elements and linear elements[J]. Physics Bulletin, 2017(8): 101–103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0509-4038.2017.08.033 -





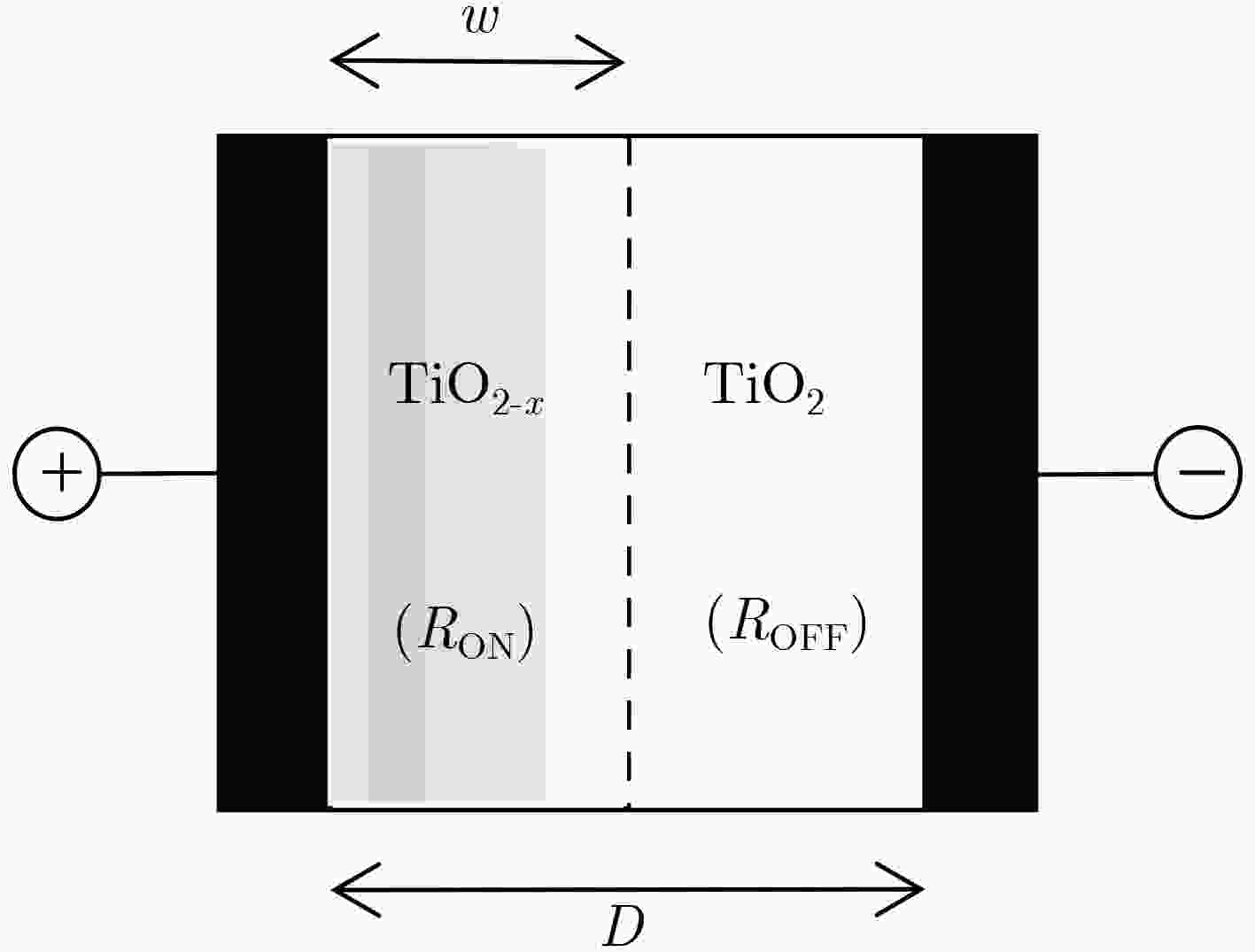
 下载:
下载:
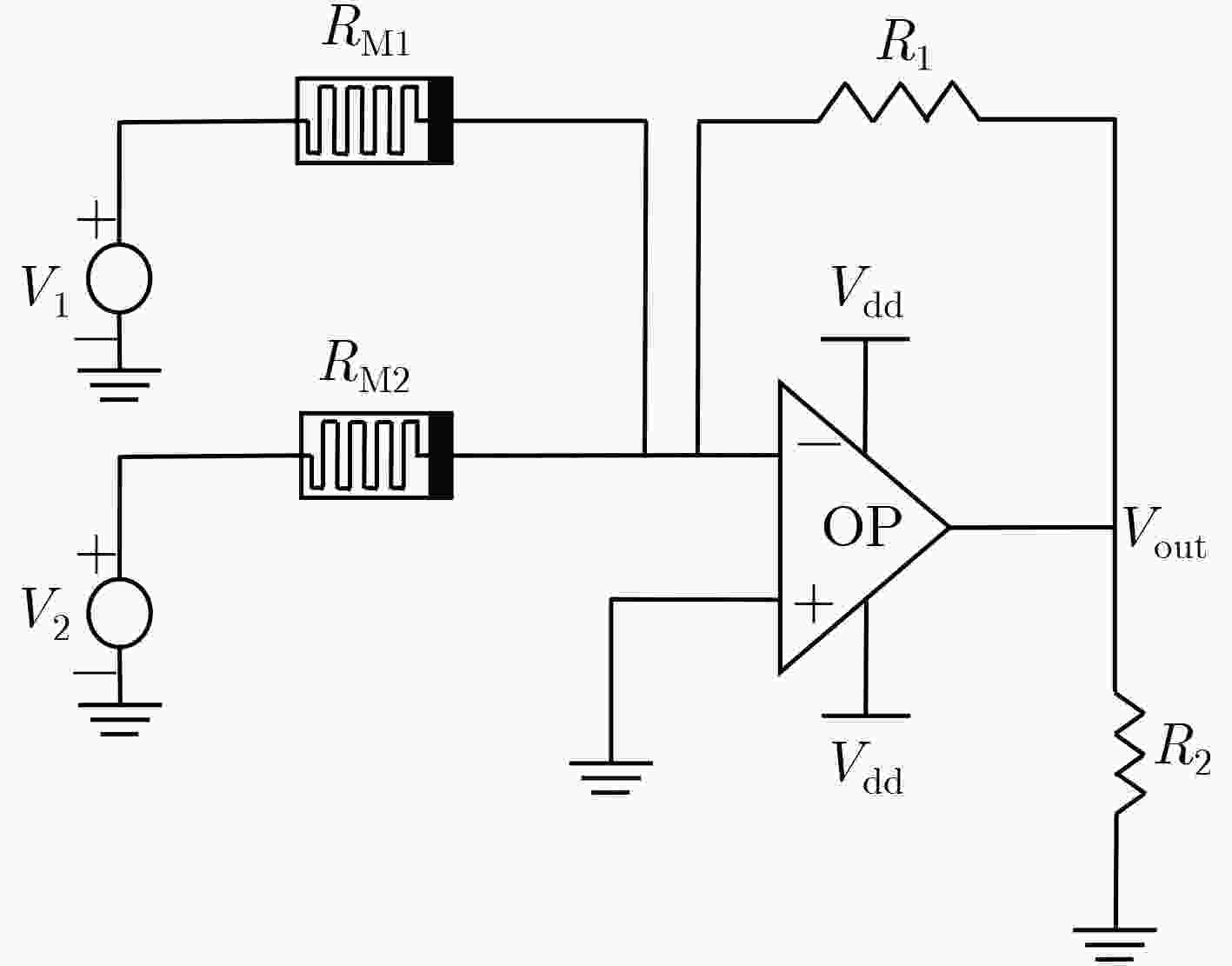
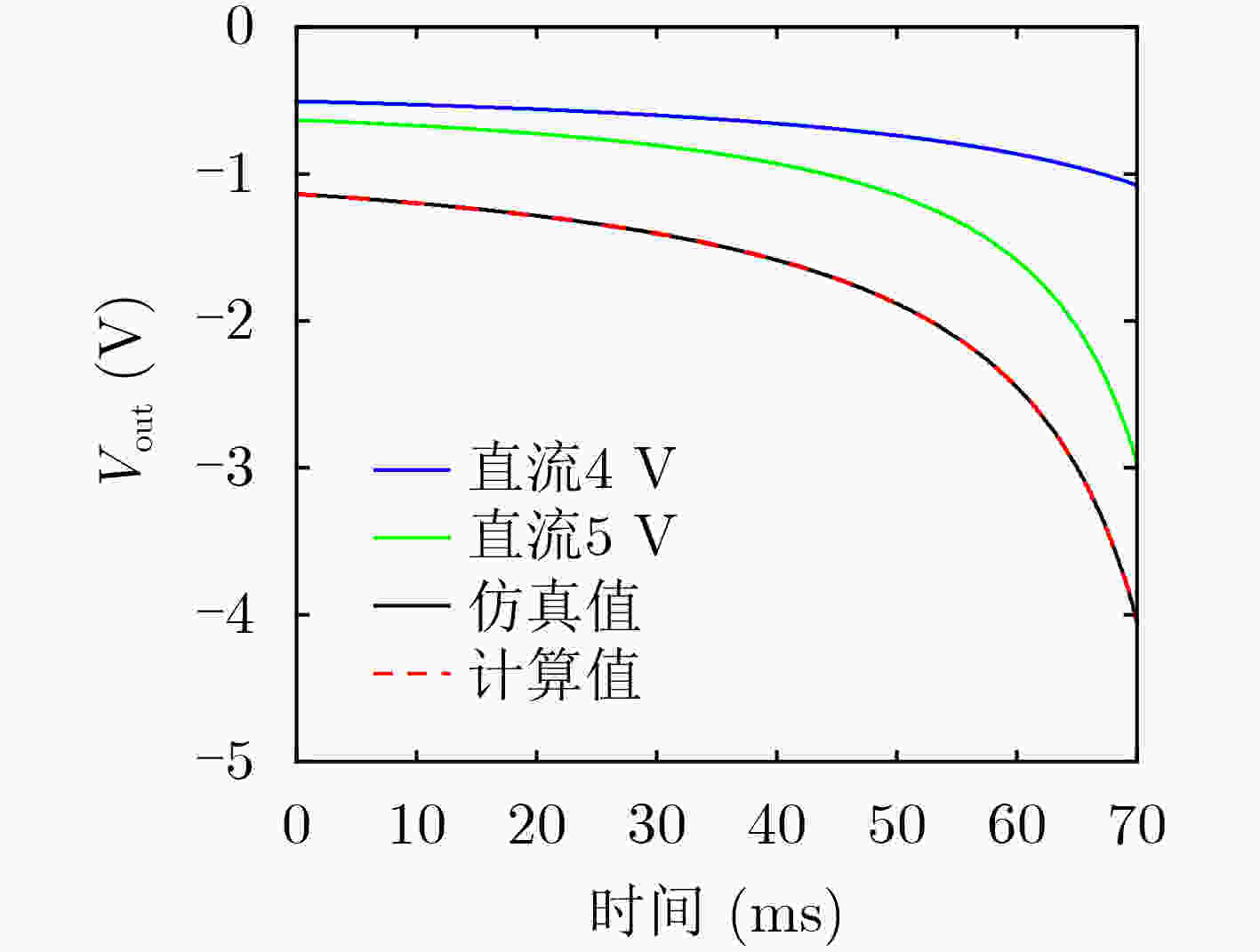
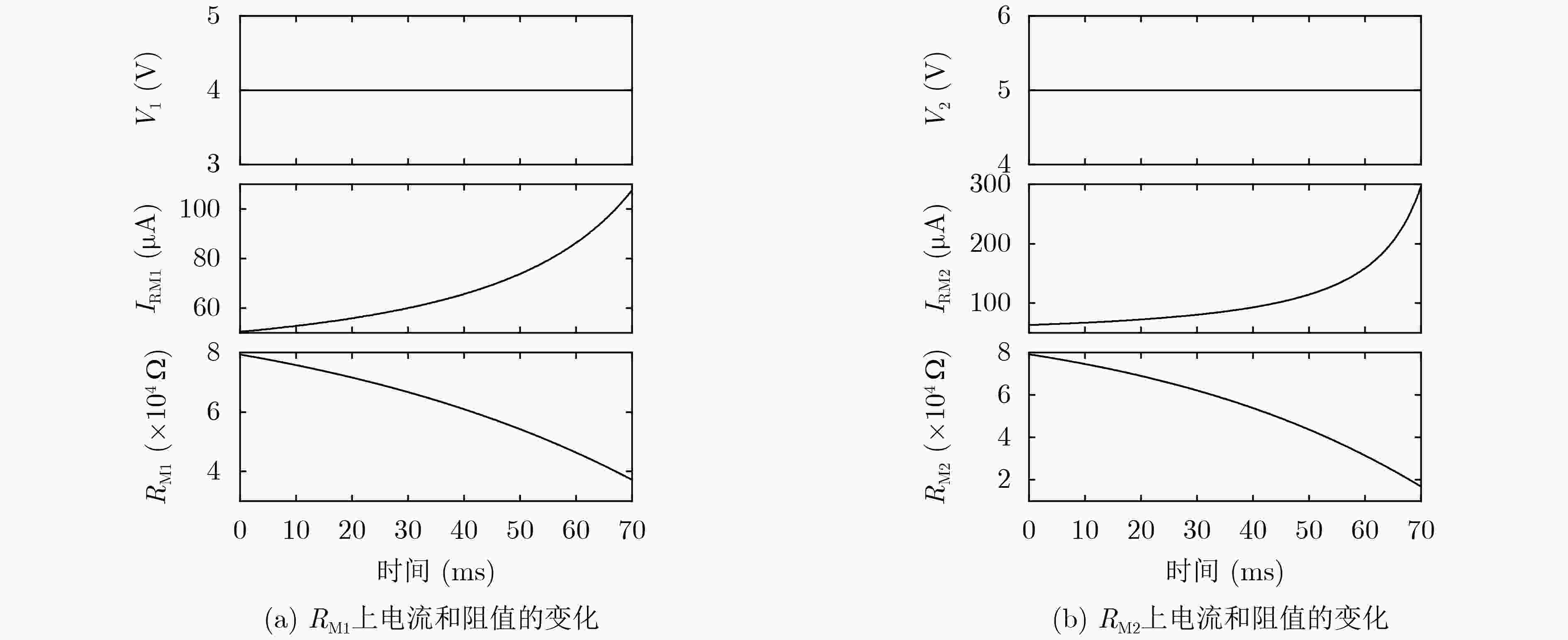


 下载:
下载:
