1T1M Reconfigurable Array Structure Based on Memristor
-
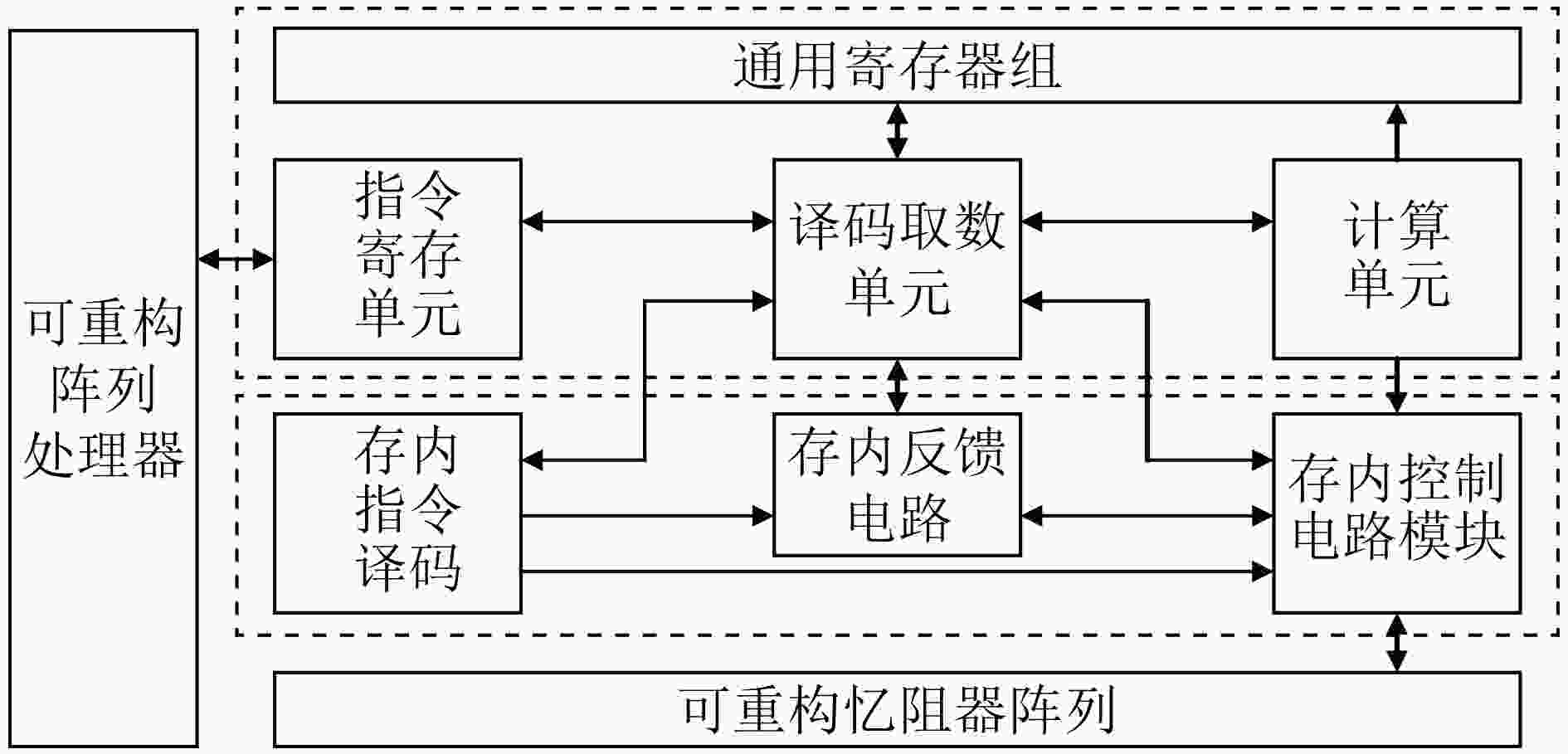
摘要: 忆阻器(Memristor)或者阻变存储器(ReRAM)是一种具有存储和计算功能的新型非易失性存储器(NVM),可以用作存算一体(PIM)的非冯·诺依曼计算机体系架构的基础器件。针对可重构阵列处理器数据计算速度和存储速度不匹配的问题,该文采用电压阈值自适应忆阻器(VTEAM)模型,经过凌力尔特通用模拟电路仿真器(LTSPICE)仿真验证,可以实现布尔逻辑完备集。在此基础上,设计了一种1T1M忆阻器交叉阵列,具有结构简单、可重构性和高并行性的特点,利用蒙特卡罗(MC)法进行容差分析,计算精度达到0.998。该阵列与现有的先进阵列相比,能有效提升芯片的性能,降低处理延迟与能耗,可以与可重构阵列处理器结合以应对“存储墙”问题。Abstract: Memristor or Resistive Random Access Memory (ReRAM) is a novel Non-Volatile Memory (NVM) with storage and computing functions, and it is the basic device of non-Von Neumann computer architecture which is Processing In Memory (PIM). To solve the speed mismatch problem between computing speed and storage of reconfigurable array processor, the model of Voltage ThrEshold Adaptive Memristor (VTEAM) is adopted. And through the simulation of Linear Technology Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis (LTSPICE), the complete set of Boolean logic is realized. On this basis, a 1T1M memristor cross array is designed, which has the characteristics of simple structure, reconfiguration and high parallelism. Monte Carlo (MC) method is used for tolerance analysis, and the calculation accuracy had reached 0.998. Compared with the existing advanced array, the performance of this array is improved effectively, the processing delay and energy consumption are reduced, and this array can be combined with the reconfigurable array processor to deal with the “memory wall” problem.
-
Key words:
- Processing In Memory (PIM) /
- Memristor /
- Array /
- Reconfigurable
-
表 1 忆阻器VTEAM模型参数
参数 β Vth Rinit Ron Roff 数值 e13 ±0.8 V 10 kΩ 160 Ω 11 kΩ 表 2 NMOS具体参数
参数 Vds Rds Qgate 数值 12 V 0.003 Ω 3.6e-8 C 表 3 逻辑运算单元比较
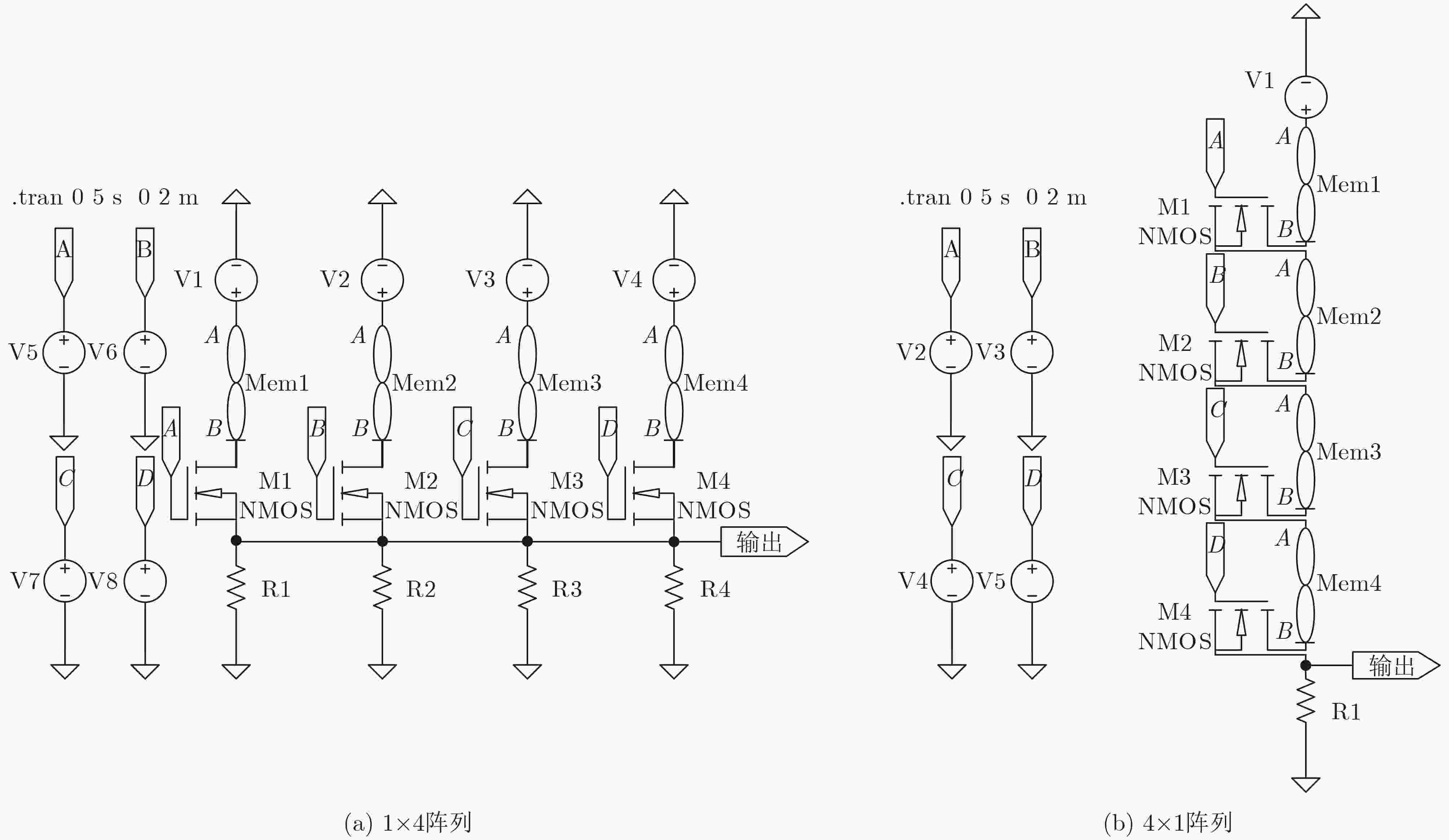
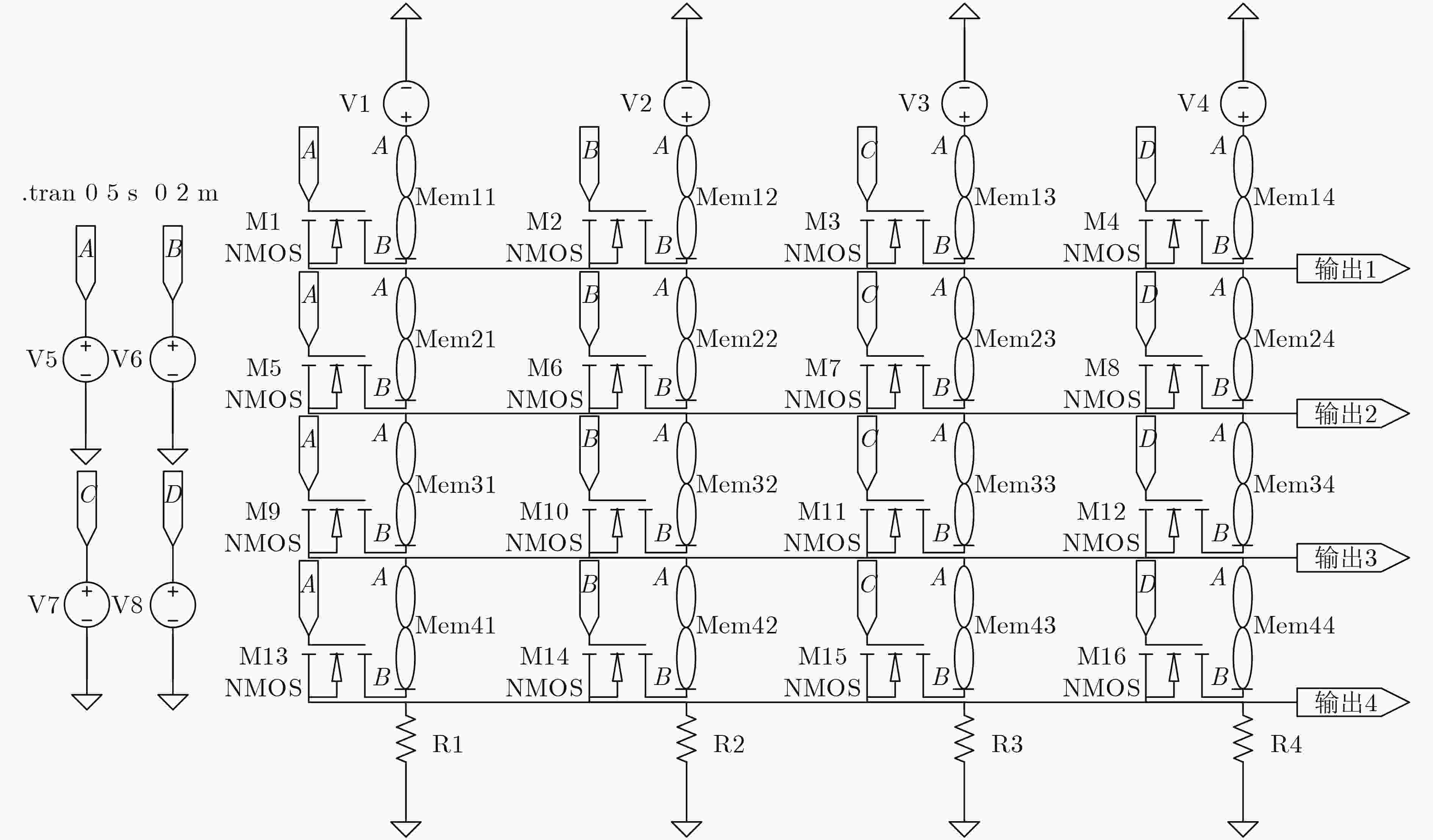
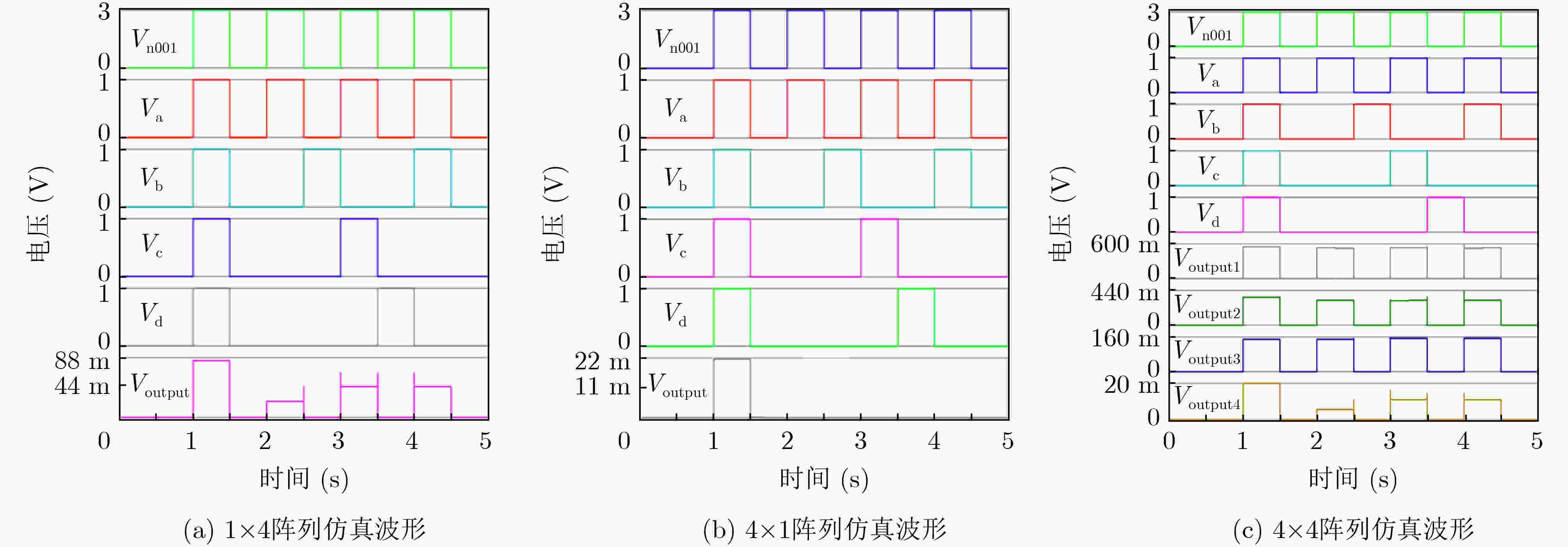
表 4 1×4阵列、4×1阵列电路性能
阵列 输入值 输出值 功能 1×4 4 1 叠加 4×1 4 1 AND -
[1] LI Haitong, GAO Baobin, CHEN Zaoming, et al. A learnable parallel processing architecture towards unity of memory and computing[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 13330. doi: 10.1038/srep13330 [2] SHAFIEE A, NAG A, MURALIMANOHAR N, et al. ISAAC: A convolutional neural network accelerator with in-situ analog arithmetic in crossbars[C]. 2016 ACM/IEEE 43rd Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA), Seoul, Korea, 2016: 14–26. [3] TANG Shibin, YIN Shouyi, ZHENG Shixuan, et al. AEPE: An area and power efficient RRAM crossbar-based accelerator for deep CNNs[C]. 2017 IEEE 6th Non-Volatile Memory Systems and Applications Symposium, Hsinchu, China, 2017: 1–6. [4] ZHANG Xunming, ZHANG Quan, YANG Jianguo, et al. Novel hybrid computing architecture with memristor-based processing-in-memory for data-intensive applications[C]. 2018 14th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology (ICSICT), Qingdao, China, 2018: 1–3. [5] TU Fengbin, WU Weiwei, WANG Yang, et al. Evolver: A deep learning processor with on-device quantization–voltage–frequency tuning[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2021, 56(2): 658–673. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.3021661 [6] LI Ziru, YAN Bonan, and LI Hai. ReSiPE: ReRAM-based single-spiking processing-in-memory engine[C]. 2020 57th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, USA, 2020: 1–6. [7] JIN Hai, LIU Cong, LIU Haikun, et al. ReHy: A ReRAM-based digital/analog hybrid PIM architecture for accelerating CNN training[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2022, 33(11): 2872–2884. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2021.3138087 [8] LALCHHANDAMA F, DATTA K, CHAKRABORTY S, et al. CoMIC: Complementary Memristor based in-memory computing in 3D architecture[J]. Journal of Systems Architecture, 2022, 126: 102480. doi: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2022.102480 [9] TU Fengbin, WANG Yiqi, WU Zihan, et al. A 28nm 29.2TFLOPS/W BF16 and 36.5TOPS/W INT8 reconfigurable digital CIM processor with unified FP/INT pipeline and bitwise in-memory booth multiplication for cloud deep learning acceleration[C]. 2022 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisc, USA, 2022: 1–3. [10] WANG Xiaoping, LI Shuai, LIU Hui, et al. A compact scheme of reading and writing for memristor-based multivalued memory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2018, 37(7): 1505–1509. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2017.2753199 [11] 孙晶茹, 李梦圆, 康可欣, 等. 基于异构忆阻器的1T2M多值存储交叉阵列设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(6): 1533–1540. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201108SUN Jingru, LI Mengyuan, KANG Kexin, et al. Design of heterogeneous memristor based 1T2M multi-value memory crossbar array[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(6): 1533–1540. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201108 [12] YU Shengqi, SHAFIK R, BUNNAM T, et al. Optimized multi-memristor model based low energy and resilient current-mode multiplier design[C]. 2021 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 2021: 1230–1233. [13] WILLIAMS R S. How we found the missing memristor[J]. IEEE Spectrum, 2008, 45(12): 28–35. doi: 10.1109/MSPEC.2008.4687366 [14] PERSHIN Y V and DI VENTRA M. SPICE model of memristive devices with threshold[J]. Radioengineering, 2013, 22(2): 485–489. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1204.2600 [15] KVATINSKY S, FRIEDMAN E G, KOLODNY A, et al. TEAM: ThrEshold adaptive memristor model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2013, 60(1): 211–221. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2012.2215714 [16] BIOLEK D, DI VENTRA M, and PERSHIN Y V. Reliable SPICE simulations of memristors, memcapacitors and meminductors[J]. Radioengineering, 2013, 22(4): 945–968. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1307.2717 [17] 缪向水, 李祎, 孙华军, 等. 忆阻器导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018.MIU Xiangshui, LI Yi, SUN Huajun, et al. Introduction to Memristor[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018. [18] CHUA L. Memristor-the missing circuit element[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuit Theory, 1971, 18(5): 507–519. doi: 10.1109/TCT.1971.1083337 [19] LEHTONEN E and LAIHO M. Stateful implication logic with memristors[C]. 2009 IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Nanoscale Architectures, San Francisco, USA, 2009: 33–36. [20] KVATINSKY S, WALD N, SATAT G, et al. MRL — memristor ratioed logic[C]. 2012 13th International Workshop on Cellular Nanoscale Networks and their Applications, Turin, Italy, 2012: 1–6. [21] KVATINSKY S, BELOUSOV D, LIMAN S, et al. MAGIC—Memristor-aided logic[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2014, 61(11): 895–899. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2014.2357292 [22] WANG Xiaoyuan, JIN Chenxi, ESHRAGHIAN J K, et al. A behavioral SPICE model of a binarized memristor for digital logic implementation[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2021, 40(6): 2682–2693. doi: 10.1007/s00034-020-01611-7 [23] GUPTA S, IMANI M, and ROSING T. FELIX: Fast and energy-efficient logic in memory[C]. 2018 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), San Diego, USA, 2018: 1–7. [24] 毛海宇, 舒继武. 基于3D忆阻器阵列的神经网络内存计算架构[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2019, 56(6): 1149–1160. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2019.20190099MAO Haiyu and SHU Jiwu. 3D memristor array based neural network processing in memory architecture[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2019, 56(6): 1149–1160. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2019.20190099 -





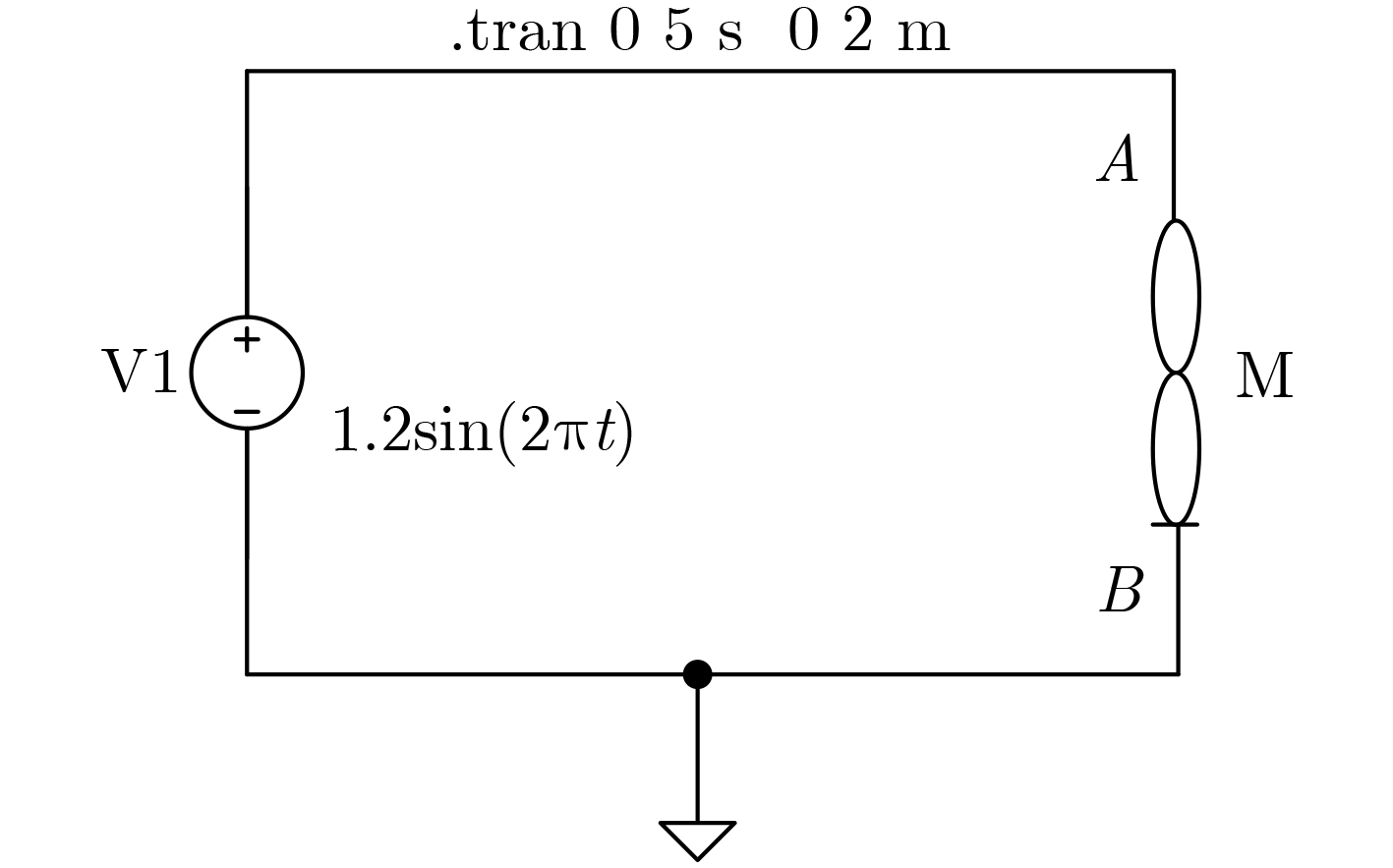
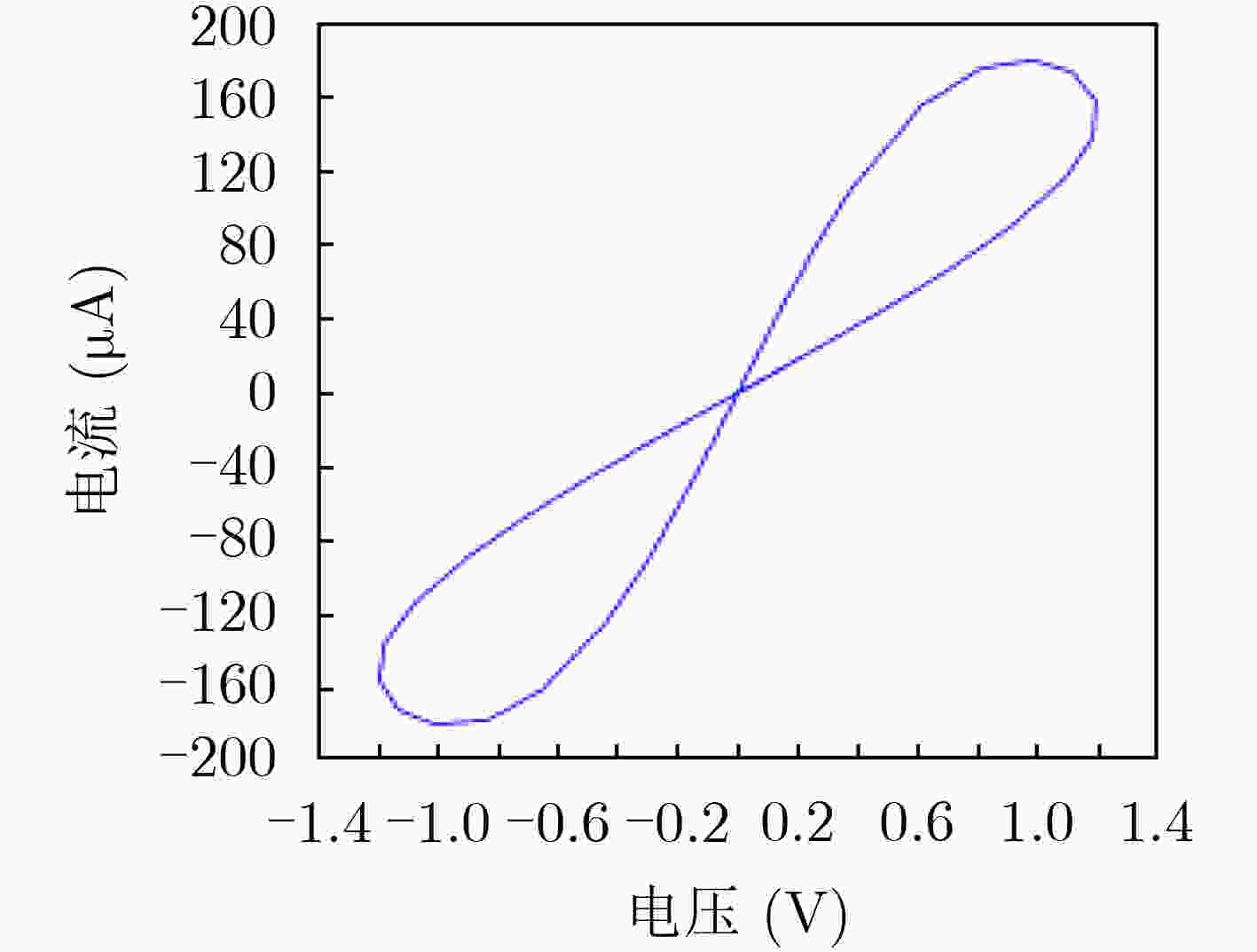
 下载:
下载:
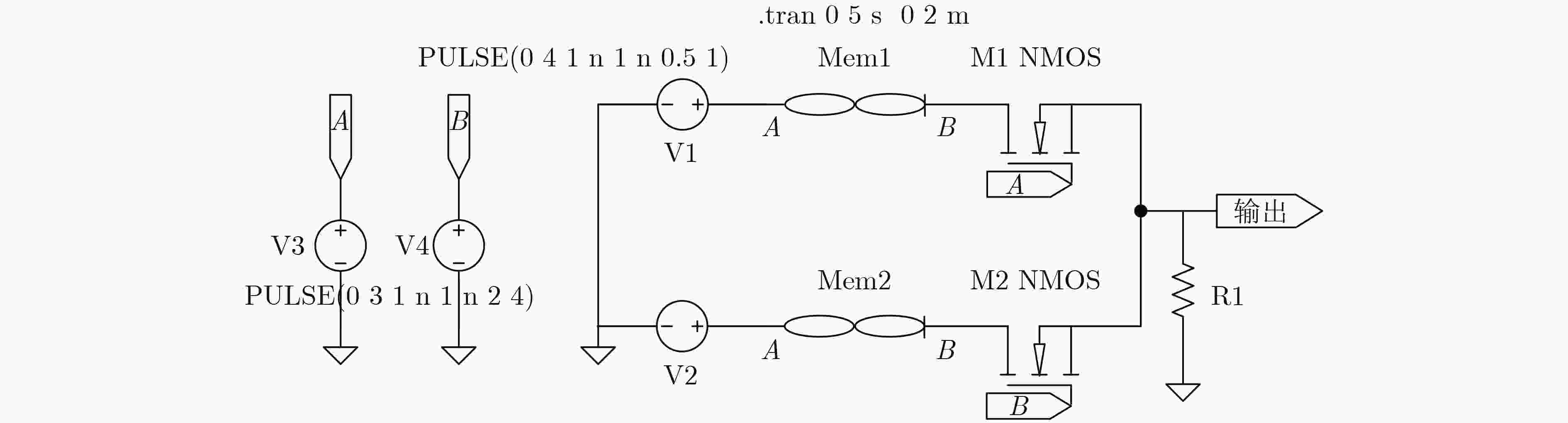
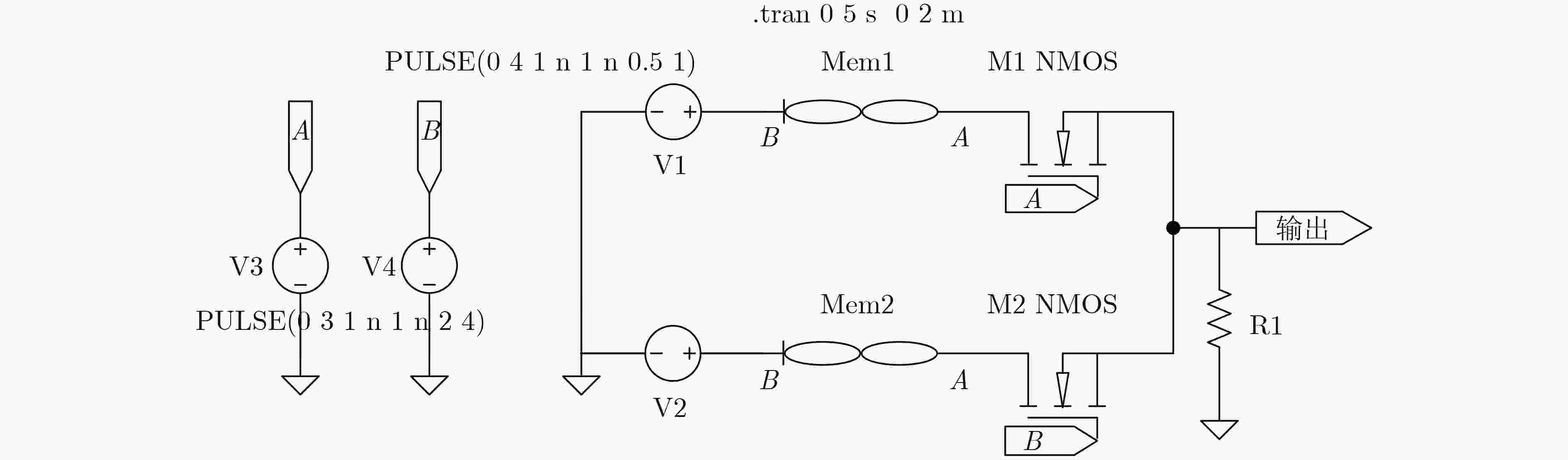
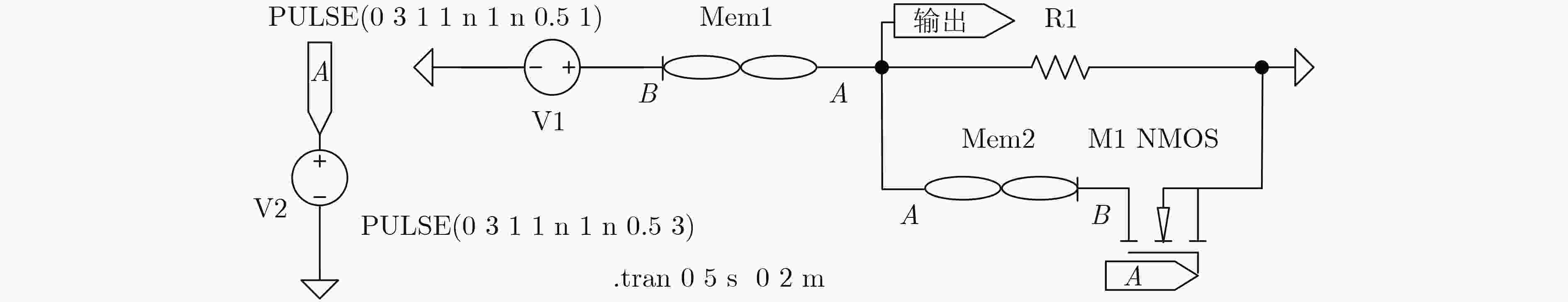
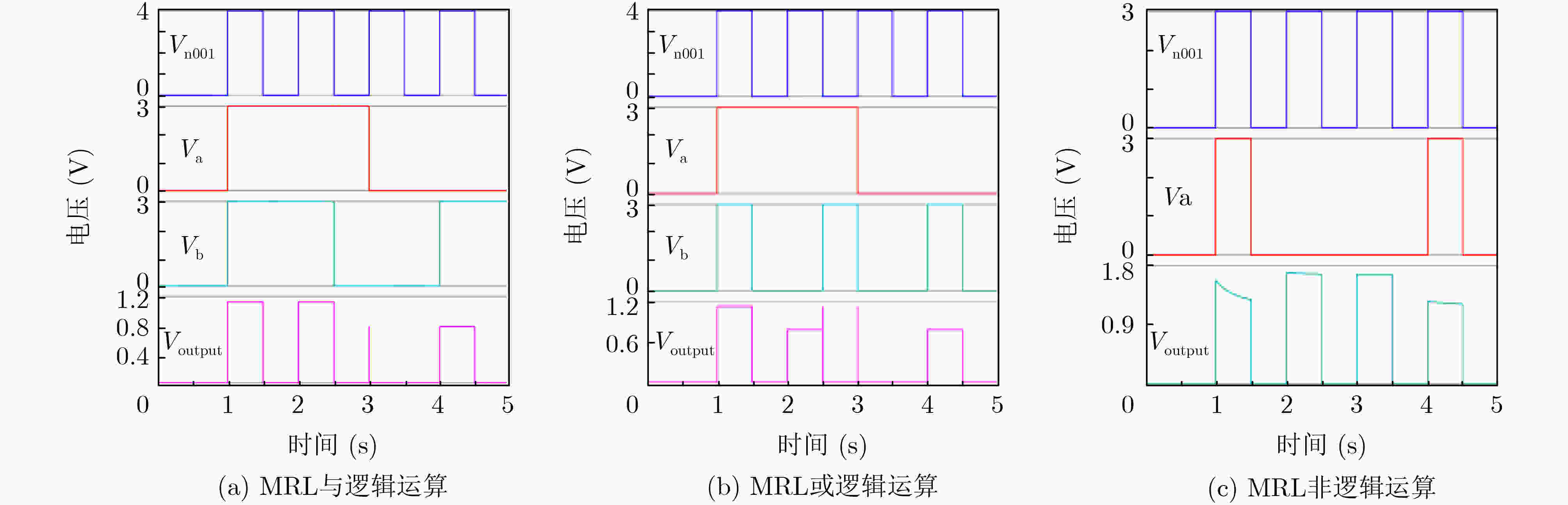



 下载:
下载:
