Application of Improved Memristor in Character Associative Memory
-
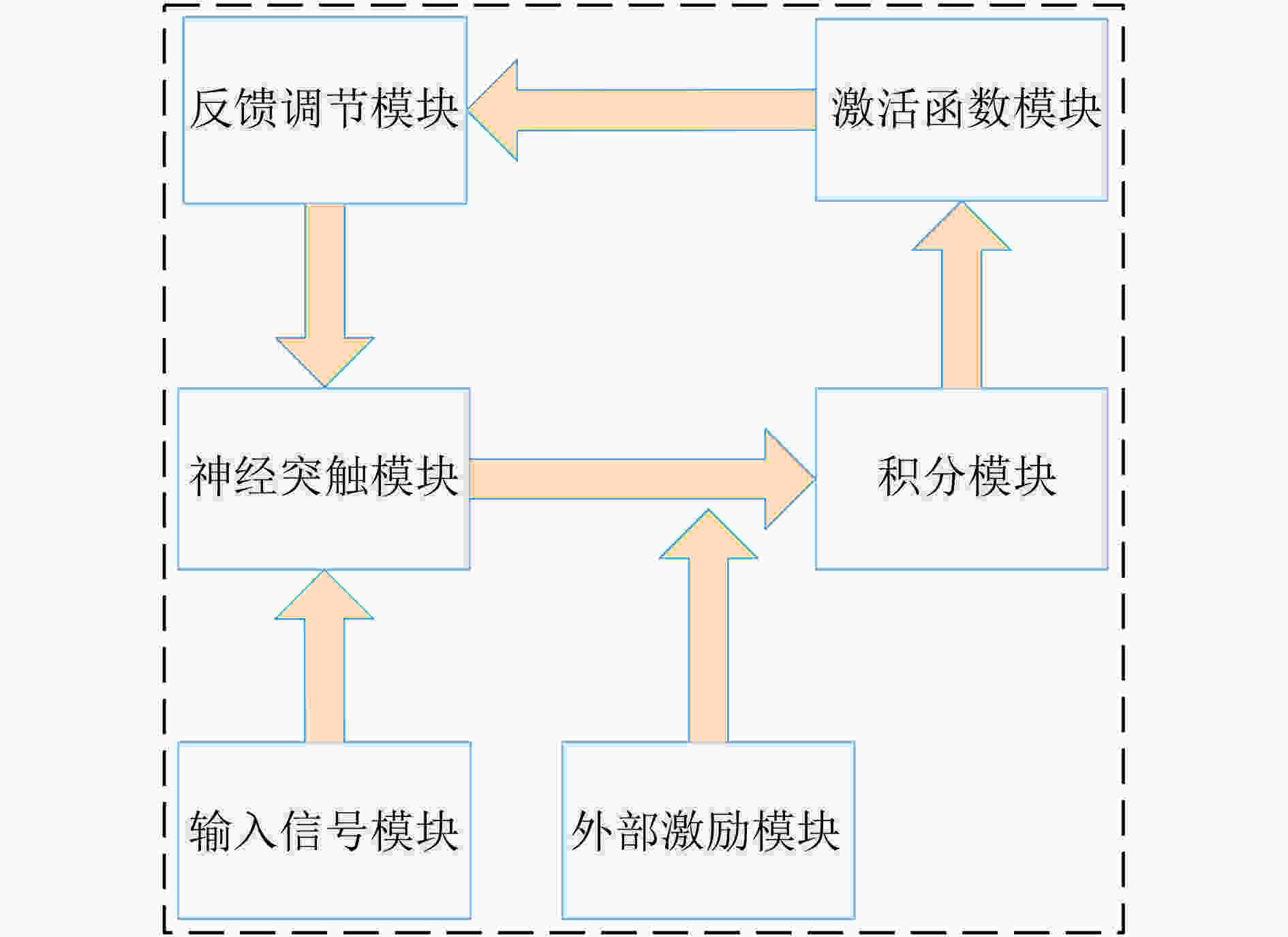
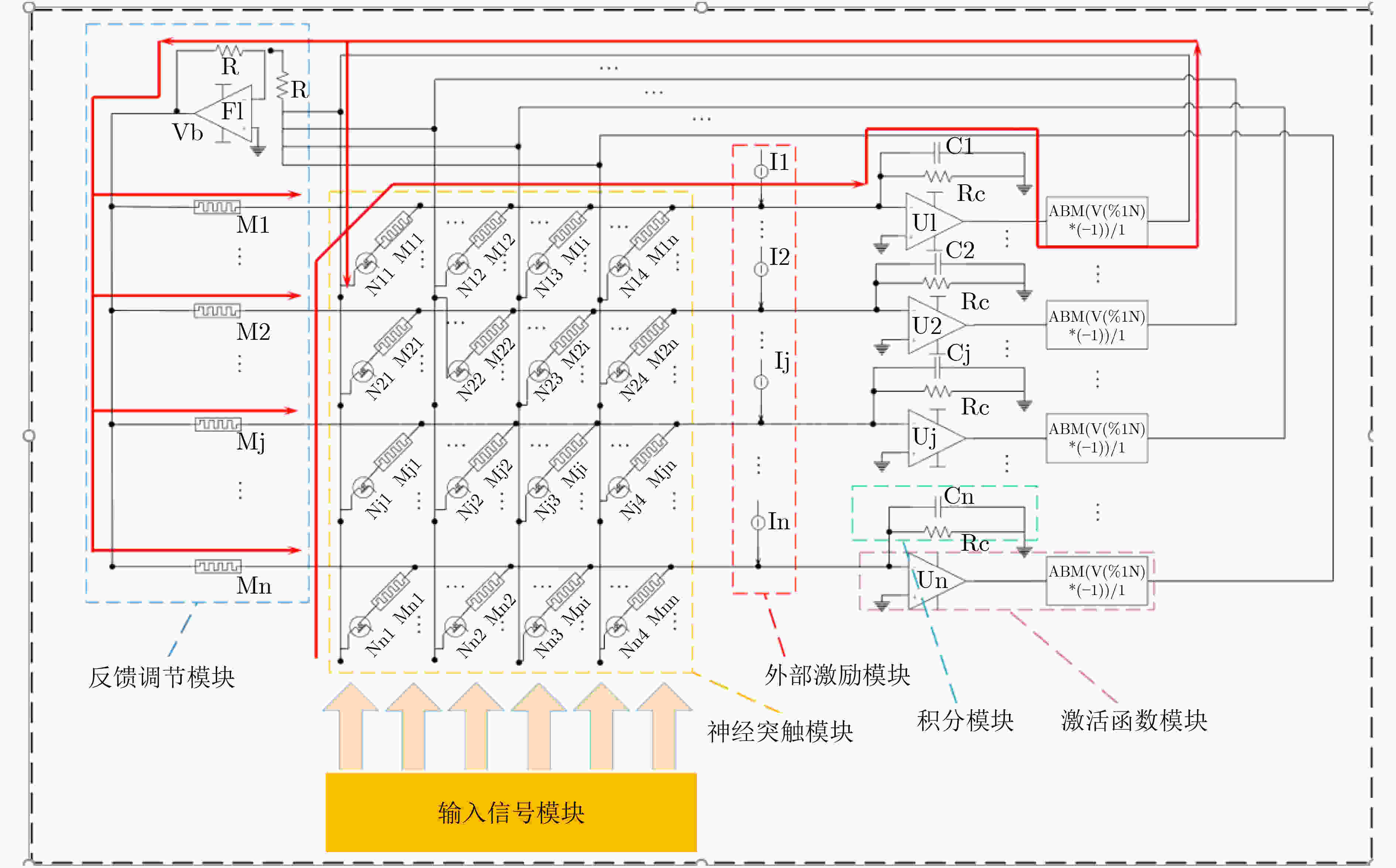
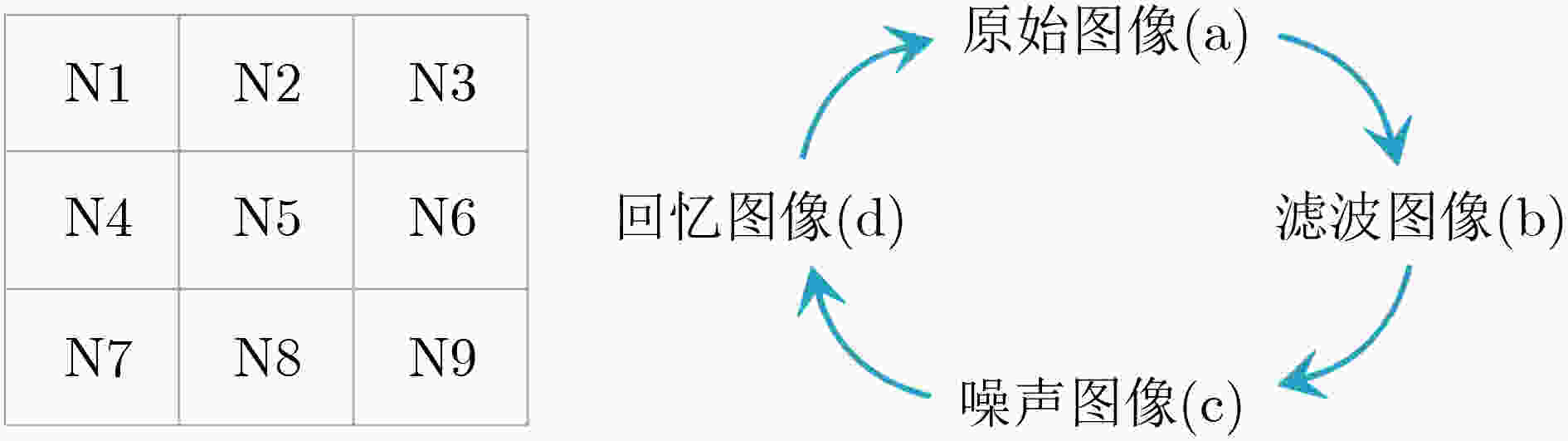
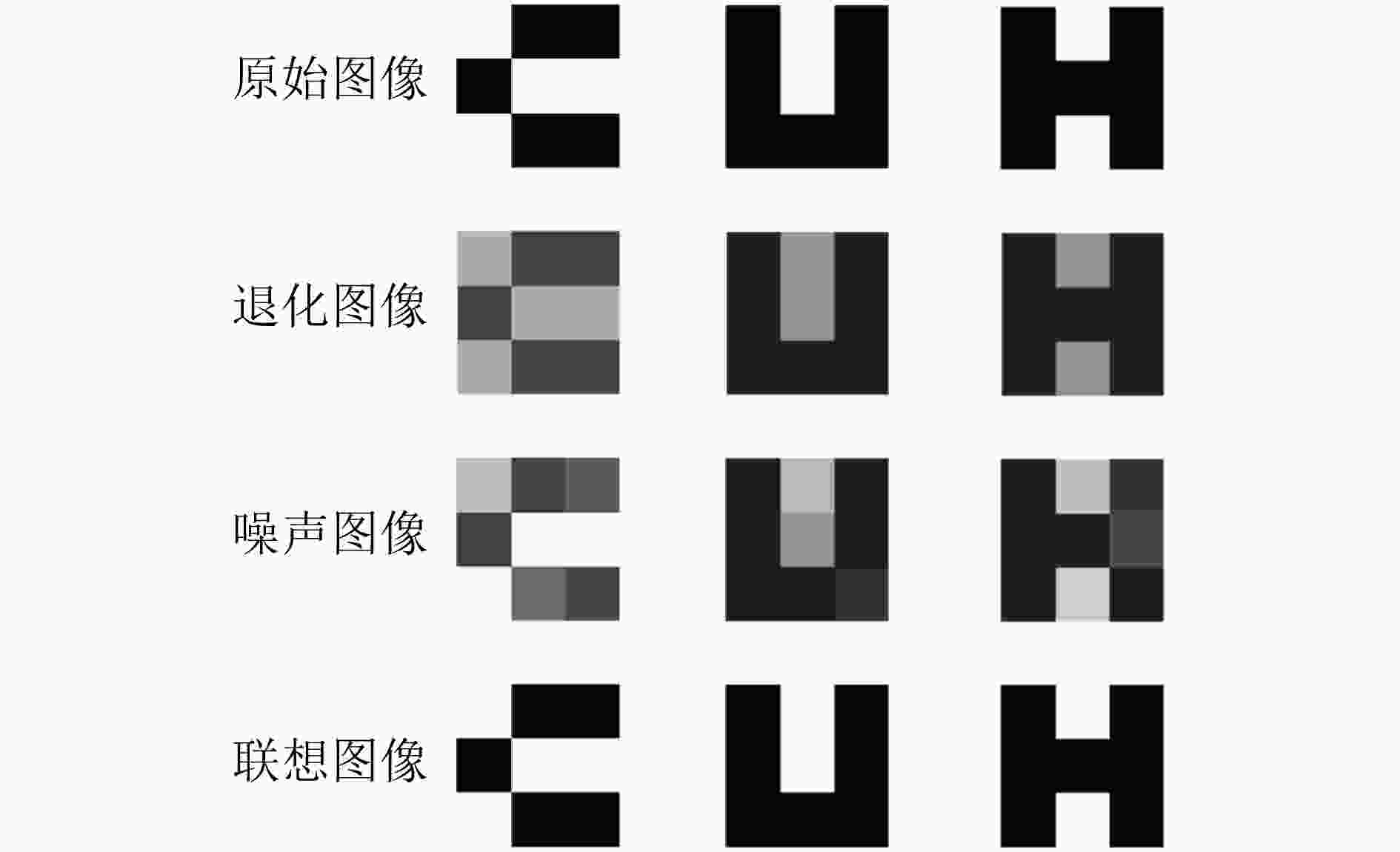
摘要: 忆阻因具有阻值可调、记忆特性以及纳米尺寸等特点,非常适合作为实现神经网络突触的电子元器件。为构建出更加符合真实物理忆阻器特性的忆阻器模型,该文在现有忆阻器模型的基础之上,克服了边界锁定、正负电压调整速率问题以及电路结构通用性问题,提出一种改进忆阻器模型。然后结合Pavlov联想记忆实验和Hopfield神经网络理论设计出了该文的字符联想记忆电路。电路结构主要有输入信号模块、突触阵列模块、激活函数模块以及反馈控制模块。该电路可以解决因传统阵列模块使用电阻作为突触模块的灵活性问题,而且还可以实现对3阶字符模糊图像的自联想功能。此外,该电路与深度学习相关的卷积计算模块原理类似,为实现基于忆阻的智能硬件奠定了理论基础。Abstract: Memristor is a very suitable electronic component for synapse of neural network because of its adjustable resistance, memory property and nano size. In order to build a memristor model more consistent with the characteristics of real physical memristors, an improved memristor model is proposed based on existing ones to overcome the problems of boundary locking, positive and negative voltage rate adjustment and the universality of circuit structure. Then combining Pavlov associative memory experiment and Hopfield neural network theory, the character associative memory circuit is designed in this paper. The circuit structure includes mainly input signal module, synaptic array module, activation function module and feedback control module. This circuit can solve the flexibility problem of using resistors as synaptic modules in traditional array modules, and can also realize the self-association function of third-order character blurred images. In addition, the circuit is similar to the convolutional computation module related to deep learning, and provides a theoretical basis for realizing memristor-based intelligent hardware.
-
Key words:
- Memristor /
- Neural network /
- Circuit design /
- Associative memory
-
表 1 本文模型与现有的部分代表性忆阻模型的比较
-
[1] CHUA L. Memristor-the missing circuit element[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuit Theory, 1971, 18(5): 507–519. doi: 10.1109/TCT.1971.1083337 [2] STRUKOV D B, SNIDER G S, STEWART D R, et al. The missing memristor found[J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7191): 80–83. doi: 10.1038/nature06932 [3] WANG Leimin, ZENG Zhigang, and GE Mingfeng. A disturbance rejection framework for finite-time and fixed-time stabilization of delayed memristive neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics:Systems, 2021, 51(2): 905–915. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2018.2888867 [4] GUO Mei, ZHU Yongliang, LIU Renyuan, et al. An associative memory circuit based on physical memristors[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 472: 12–23. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.11.034 [5] LAI Qiang, WAN Zhiqiang, ZHANG Hui, et al. Design and analysis of multiscroll memristive Hopfield neural network with adjustable memductance and application to image encryption[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, To be published. [6] ZHANG Yang, WANG Xiaoping, LI Yi, et al. Memristive model for synaptic circuits[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2017, 64(7): 767–771. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2016.2605069 [7] CHANG Ting, JO S H, and LU Wei. Short-term memory to long-term memory transition in a nanoscale memristor[J]. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(9): 7669–7676. doi: 10.1021/nn202983n [8] 王春华, 蔺海荣, 孙晶如, 等. 基于忆阻器的混沌、存储器及神经网络电路研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 795–810. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190821WANG Chunhua, LIN Hairong, SUN Jingru, et al. Research progress on chaos, memory and neural network circuits based on memristor[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 795–810. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190821 [9] 李志军, 谭茂林, 王梦蛟, 等. 具有艾宾浩斯遗忘规则的忆阻联想记忆电路[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3657–3665. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210677LI Zhijun, TAN Maolin, WANG Mengjiao, et al. Associative memory circuit based on memristor with the ebbinghaus forgetting rule[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3657–3665. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210677 [10] HU S G, LIU Y, LIU Z, et al. Associative memory realized by a reconfigurable memristive hopfield neural network[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 7522. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8522 [11] LI Haoyu, WANG Leimin, and LAI Qiang. Synchronization of a memristor chaotic system and image encryption[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2021, 31(16): 2150251. doi: 10.1142/S0218127421502515 [12] 董哲康, 钱智凯, 周广东, 等. 基于忆阻的全功能巴甫洛夫联想记忆电路的设计、实现与分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(6): 2080–2092. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210376DONG Zhekang, QIAN Zhikai, ZHOU Guangdong, et al. Memory circuit design, implementation and analysis based on memristor full-function Pavlov associative[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(6): 2080–2092. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210376 [13] HOPFIELD J J. Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of Sciences of the United States of America, 1982, 79(8): 2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2554 [14] HOPFIELD J J. Neurons with graded response have collective computational properties like those of two-state neurons[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1984, 81(10): 3088–3092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3088 [15] GUO Tengteng, WANG Lidan, ZHOU Mengzhe, et al. A recurrent neural network based on memristive activation function and its associative memory[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2017, 47(9): 1226–1241. doi: 10.1360/N112016-00266 [16] TARKOV M S. Hopfield network with interneuronal connections based on memristor bridges[C]. The 13th International Symposium on Neural Networks. St. Petersburg, Russia: Springer, 2016: 196–203. [17] YANG Jiu, WANG Lidan, WANG Yan, et al. A novel memristive Hopfield neural network with application in associative memory[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 227: 142–148. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.07.065 [18] HONG Qinghui, YAN Renao, WANG Chunhua, et al. Memristive circuit implementation of biological nonassociative learning mechanism and its applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 2020, 14(5): 1036–1050. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2020.3018777 [19] CHEN Chengjie, CHEN Jingqi, BAO Han, et al. Coexisting multi-stable patterns in memristor synapse-coupled Hopfield neural network with two neurons[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2019, 95(4): 3385–3399. doi: 10.1007/s11071-019-04762-8 [20] SUN Junwei, XIAO Xiao, YANG Qinfei, et al. Memristor-based Hopfield network circuit for recognition and sequencing application[J]. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2021, 134: 153698. doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2021.153698 [21] WANG Leimin and ZOU Huayu. A new emotion model of associative memory neural network based on memristor[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 410: 83–92. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.05.002 [22] HONG Qinghui, CHEN Hegan, SUN Jingru, et al. Memristive circuit implementation of a self-repairing network based on biological astrocytes in robot application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(5): 2106–2120. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3041624 [23] HONG Qinghui, SHI Zirui, SUN Jingru, et al. Memristive self-learning logic circuit with application to encoder and decoder[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2021, 33(10): 4901–4913. doi: 10.1007/s00521-020-05281-z [24] YAN Renao, HONG Qinghui, WANG Chunhua, et al. Multilayer memristive neural network circuit based on online learning for license plate detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2022, 41(9): 3000–3011. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2021.3121347 [25] JOGLEKAR Y N and WOLF S J. The elusive memristor: Properties of basic electrical circuits[J]. European Journal of Physics, 2009, 30(4): 661–675. doi: 10.1088/0143-0807/30/4/001 [26] BIOLEK Z, BIOLEK D, and BIOLKOVÁ V. SPICE model of memristor with nonlinear dopant drift[J]. Radioengineering, 2009, 18(2): 210–214. [27] KVATINSKY S, FRIEDMAN E G, KOLODNY A, et al. TEAM: Threshold adaptive memristor model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2013, 60(1): 211–221. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2012.2215714 [28] KVATINSKY S, RAMADAN M, FRIEDMAN E G, et al. VTEAM: A general model for voltage-controlled memristors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2015, 62(8): 786–790. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2015.2433536 -





 下载:
下载:
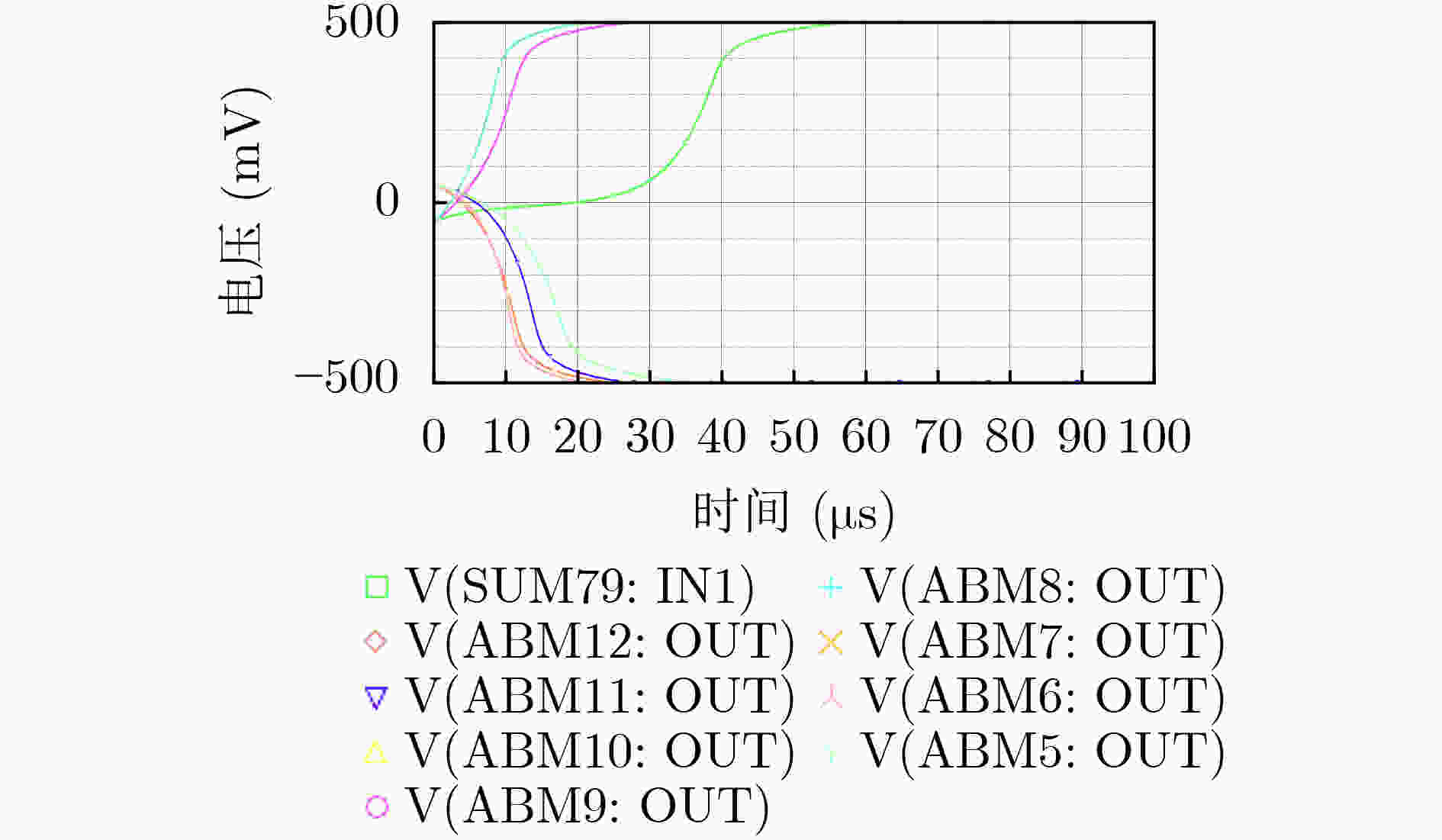
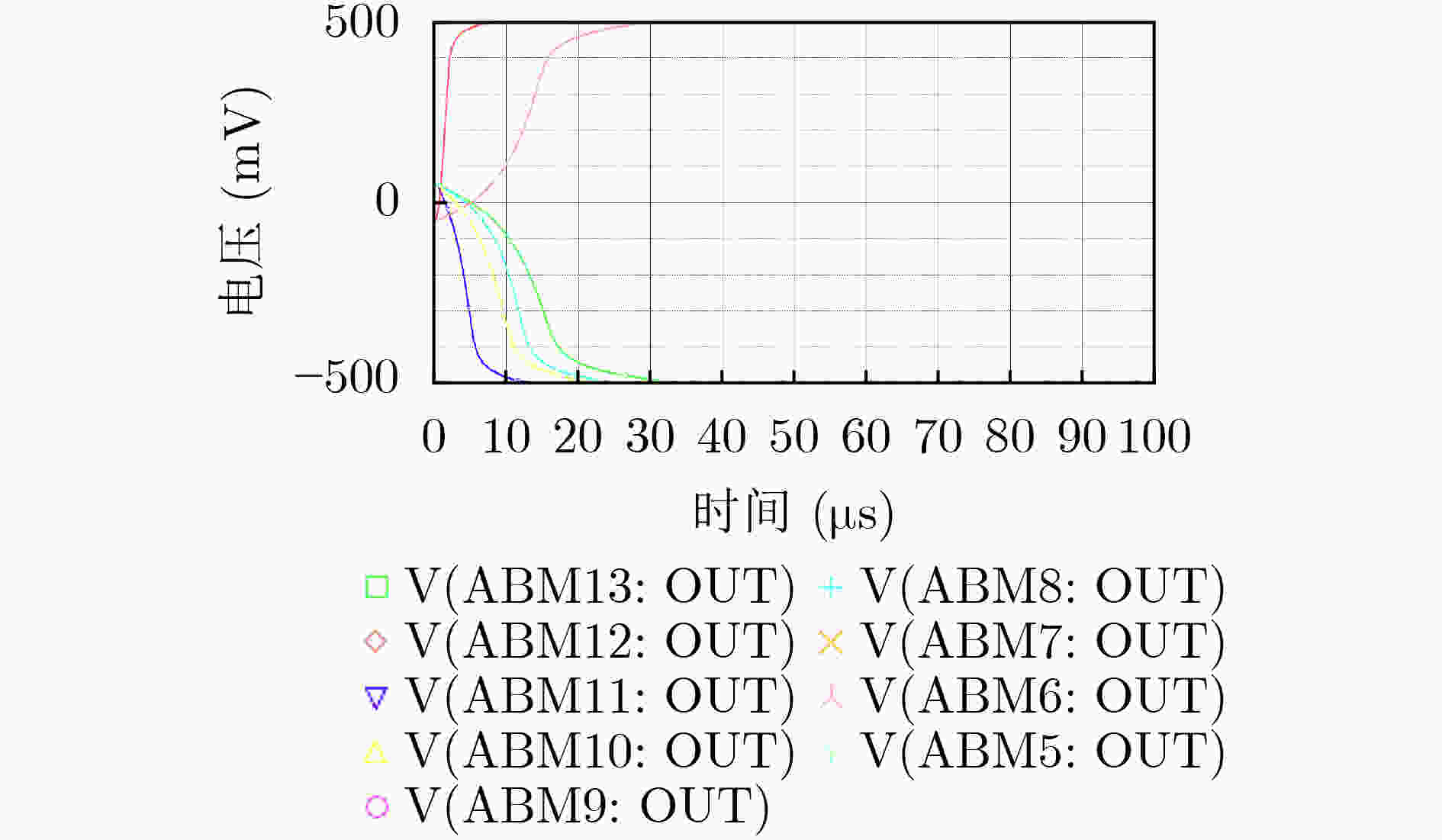
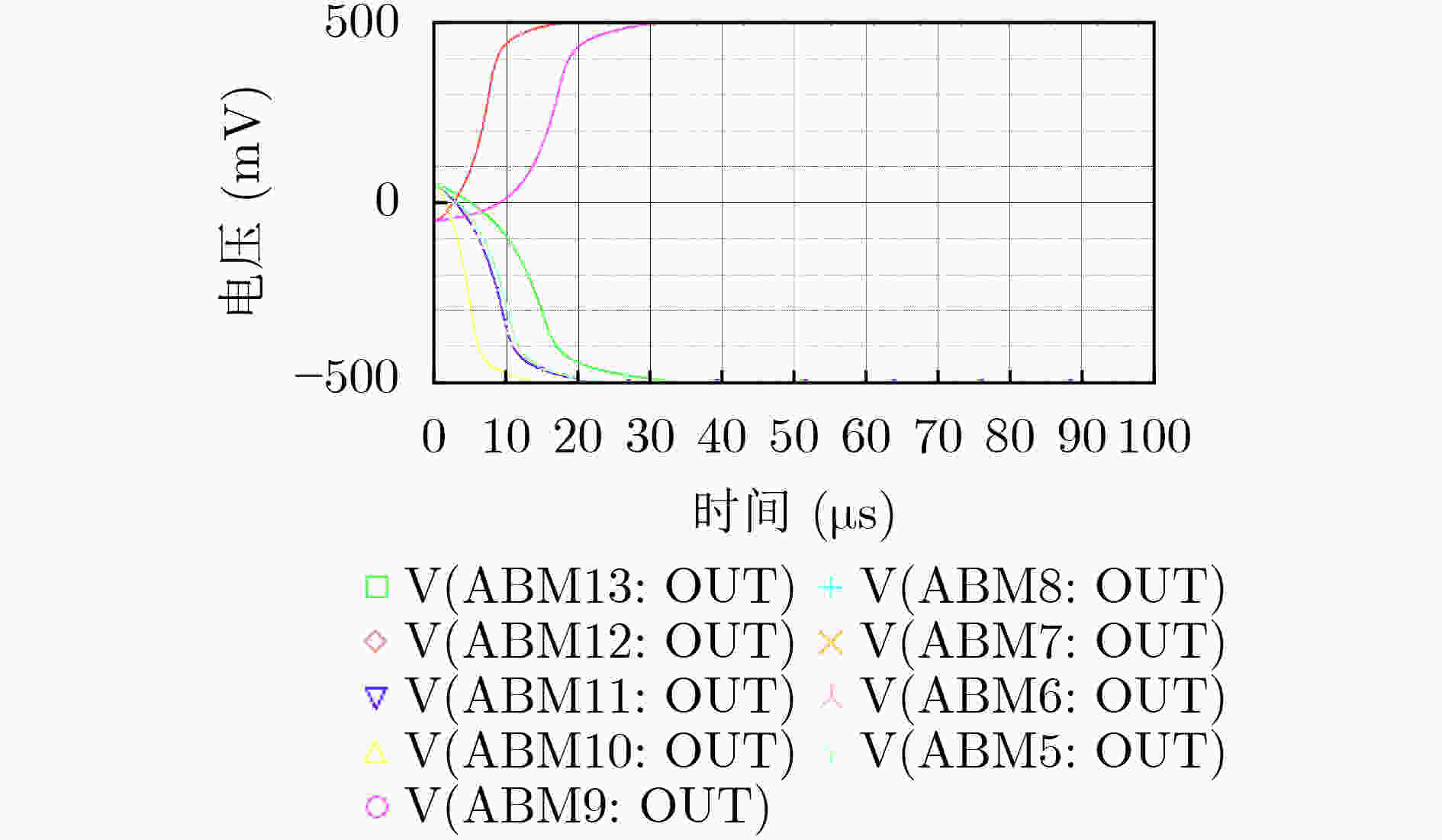


 下载:
下载:
